Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Molecular Targeted Agents for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objective
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Baseline Characteristics of Included Studies
3.2. Network Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes
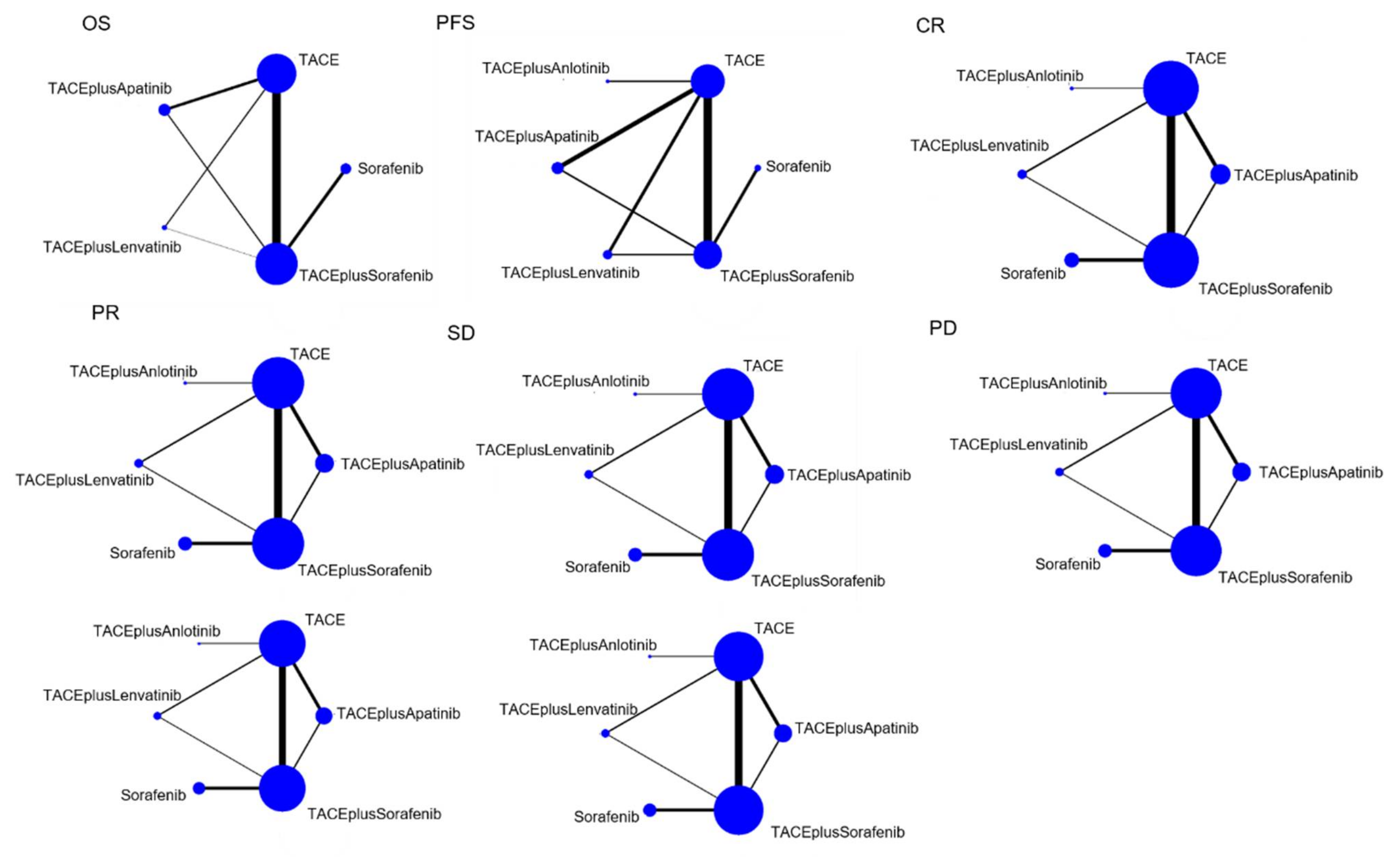
3.2.1. Indirect Comparisons of OS
3.2.2. Indirect Comparisons of PFS
3.2.3. Indirect Comparisons of CR
3.2.4. Indirect Comparisons of PR
3.2.5. Indirect Comparisons of SD
3.2.6. Indirect Comparisons of PD
3.2.7. Indirect Comparisons of ORR
3.2.8. Indirect Comparisons of DCR
3.3. Results of Quality Assessment, Convergence, Publication Bias, Inconsistency, and Heterogeneity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimassa, L.; Danesi, R.; Pressiani, T.; Merle, P. Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Improving outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 77, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Zhu, K.; Yang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, W.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, X.; Song, T.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Apatinib as first-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase II clinical trial. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, T.; Dou, W.; Wang, E.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Du, X.; Liu, L. A comparison of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization used with and without apatinib for intermediate- to advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, W.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y. Trans-catheter arterial chemoembolization plus Sorafenib, an unsuccessful therapy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma? Medicine 2020, 99, e20962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, S.; Geng, J.; Zhao, S.; Tan, K.; Yang, Z.; Feng, D.; Liu, L. Efficacy evaluation of the combination therapy of sorafenib and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable HCC: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Bae, S.-H.; Paik, S.W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Han, S.Y.; Cheong, J.Y.; et al. Sorafenib with or without concurrent transarterial chemoembolization in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The phase III STAH trial. J. Hepatol. 2018, 70, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M.; Han, G.; Tak, W.Y.; Yang, J.; Guglielmi, A.; Paik, S.W.; Reig, M.; Kim, D.Y.; Chau, G.-Y.; et al. Sorafenib or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Fox, R.; Ma, Y.T.; Ross, P.J.; James, M.; Strugess, R.; Stubbs, C.; Wall, L.; Watkinson, A.; Hacking, N.; et al. TACE 2: A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blinded, phase III trial evaluating sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-Background. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Ikeda, M.; Torimura, T.; Aikata, H.; Izumi, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Hino, K.; Kuzuya, T.; Isoda, N.; et al. TACTICS: Final overall survival (OS) data from a randomized, open label, multicenter, phase II trial of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) therapy in combination with sorafenib as compared with TACE alone in patients (pts) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Jin, X.-L.; Yang, C.; Du, P.; Jiang, F.-Q.; Ma, J.-P.; Yang, J.; Xie, P.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of efficacy between TACE combined with apatinib and TACE alone in the treatment of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A single-center randomized controlled trial. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhuang, W.; Yang, J. Efficacy and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Anlotinib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; He, L.; Guo, Y.; Song, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, L. The combination therapy of transarterial chemoembolisation and sorafenib is the preferred palliative treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, M.; Zhao, S.; Long, Y.; Zhang, W. Effectiveness and Safety of Combination Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Apatinib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Chinese Population: A Meta-Analysis. Chemotherapy 2019, 64, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, T.; Guo, X.; Ouyang, T.; Kan, X.; Chen, L.; Liang, B.; Wang, M.; Zheng, C. Sorafenib Versus Apatinib Both Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: A Comparative Retrospective Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Shen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Xu, Z.; Shi, M.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with apatinib versus TACE combined with sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, K.; Ding, N.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, J.; Qu, Z. Lenvatinib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): A retrospective controlled study. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, D.M.; Ades, T.; Higgins, J. Simultaneous comparison of multiple treatments: Combining direct and indirect evidence. BMJ 2005, 331, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Fan, W.; Xue, M.; Li, J. Evaluation of the Benefits of TACE Combined with Sorafenib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Untreatable TACE (unTACEable) Progression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 4013–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Wan, D.; Wan, P.; Wu, D. Efficacy of sorafenib combined with transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization in treating intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. B.U.ON. Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2021, 26, 868–874. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C.; Göller, M.; Schott, E.; Waidmann, O.; Winkel, M.O.D.; Paprottka, P.; Zangos, S.; Vogl, T.; Bechstein, W.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Combination of Sorafenib and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Selected Patients with Advanced-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study at Three German Liver Centers. Cancers 2021, 13, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Sun, W.; Li, W.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Teng, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study. Cancer 2021, 127, 3782–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Kawaoka, T.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kikukawa, C.; Kosaka, Y.; Uchikawa, S.; Morio, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Lenvatinib-Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Sequential Therapy for Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2021, 99, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, E.; Bai, W.; Xia, D.; Ding, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Mu, W.; et al. Exploratory Analysis to Identify Candidates Benefitting from Combination Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib for First-Line Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shen, L.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Z.; Qi, H.; Yuan, H.; Cao, F.; Xie, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, W. Transarterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization alone for hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: A propensity score matching analysis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, Y. Sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization prolongs survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. B.U.ON. Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2020, 25, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.-C.; Hao, Y.-H.; Lv, W.-F.; Jia, W.-D.; Ji, C.-S.; Zhou, C.-Z.; Cheng, D.-L.; Xu, S.-B.; Gao, Z.-G.; Su, M.-X.; et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib in Patients with BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, S.; Duan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, X. Assessment of efficacy and safety of the transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with or without apatinib in the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, T.Y.; Peng, Y.C.; Yang, S.-S.; Yeh, H.Z.; Chang, C.S. The therapeutic benefits of combined sorafenib and transarterial chemoembolization for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Kaneko, R.; Yano, Y.; Kamada, K.; Ikehara, T.; Nagai, H.; Sato, Y.; Igarashi, Y. The Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib in Combination with TACE. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Liang, B.; Zhou, G.; Xiong, B.; Pan, F.; Ren, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Zheng, C. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Apatinib for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, J.; You, N.; Wu, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Peng, X.; Zheng, L. Efficacy and safety of apatinib combined with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in treating patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Q.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yue, Y.X.; Cai, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.X. Survival analysis of sorafenib combined with TACE in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 13, 6823–6828. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Yin, X.; Tang, B.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Xie, X.; Ren, Z. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Combined with Sorafenib in Treatment of HBV Background Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Propensity Score Matching Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2141859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, G.; Su, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Yang, K.; Jin, L. The safety and efficacy of TACE combined with apatinib on patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 20, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Wang, W.; Shen, J.; Li, W.; Ni, C.; Zhu, X. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Combined with Sorafenib versus TACE Alone for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Ikeda, M.; Torimura, T.; Tanabe, N.; Aikata, H.; Izumi, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Nojiri, S.; Hino, K.; et al. Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial. Gut 2019, 69, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, V.C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Su, Y.-C.; Ku, M.-C.; Kuo, J.-T.; Yoshida, G.J. Sorafenib with Transarterial Chemoembolization Achieves Improved Survival vs. Sorafenib Alone in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yuan, G.; Fan, H.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M.; Yang, J.; et al. Apatinib Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct. Sorafenib Monotherapy vs. TACE-sorafenib Sequential Therapy for HCC with Metastasis. 2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03518502 (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- Lei, X.-F.; Ke, Y.; Bao, T.-H.; Tang, H.-R.; Wu, X.-S.; Shi, Z.-T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Gu, H.; Wang, L. Effect and safety of sorafenib in patients with intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma who received transarterial chemoembolization: A retrospective comparative study. World J. Clin. Cases 2018, 6, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, B.; Zheng, C. Combination of sorafenib and TACE inhibits portal vein invasion for intermediate stage HCC: A single center retrospective controlled study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 79012–79022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-X.; Chen, J.; Bai, T.; Zhu, S.-L.; Yang, T.-B.; Qi, L.-N.; Zou, L.; Li, Z.-H.; Ye, J.-Z.; Li, L.-Q. The safety and efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib and sorafenib mono-therapy in patients with BCLC stage B/C hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Fox, R.; Ma, Y.T.; Ross, P.J.; James, M.W.; Sturgess, R.; Stubbs, C.; Stocken, D.D.; Wall, L.; Watkinson, A.; et al. Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (TACE 2): A randomised placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, N.; Dao, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Li, N. Overall survival in response to sorafenib with transarterial chemoembolization for BCLC stage B hepatocellular carcinoma: Propensity score analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 55, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-P.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.-H.; Xu, L.; Jian, P.-E.; Xiao, C.-Z.; Zhong, X.-P.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Y.-F. Transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatic vein tumor thrombus. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4239–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wan, X.; Zhai, X.; Yan, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, K.; Xia, Y.; Shen, F. Retrospective analysis of transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib in Chinese patients with unresectable and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83806–83816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Fu, S.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, W.; Li, J. Sorafenib with and without Transarterial Chemoembolization for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Main Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: A Retrospective Analysis. Oncologist 2015, 20, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, J.; Lai, L.; Meng, X.; Zhou, B.; Huang, W.; Cai, M.; Shan, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: Treatment with Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib—A Retrospective Controlled Study. Radiology 2014, 272, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Duan, Z.; Long, X.; Hertzanu, Y.; Shi, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z. Sorafenib Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization versus Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone for Advanced-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Dhamija, M.; Vidyarthi, G.; Amodeo, D.; Boyd, W.; Miladinovic, B.; Kumar, A. Comparative effectiveness of traditional chemoembolization with or without sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.H.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, M.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Kang, Y.K.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, H.C. Sorafenib alone versus sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of Propensity score analyses1. Radiology 2013, 269, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, X.S.; Yin, Z.X.; He, C.Y.; Li, R.J.; Wu, K.C.; Xia, J.L.; Fan, D.M.; et al. Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization improves the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching study. J. Dig. Dis. 2013, 14, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.-D.; Chen, C.-S.; Wang, J.-H.; Yan, Z.-P.; Chen, J.-M.; Gong, G.-Q.; Liu, Q.-X.; Luo, J.-J.; Liu, L.-X.; Liu, R.; et al. The efficacy of TACE combined sorafenib in advanced stages hepatocellullar carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicho, A.; Hellerbrand, C.; Krüger, K.; Beyer, L.P.; Wohlgemuth, W.; Niessen, C.; Hohenstein, E.; Stroszczynski, C.; Pereira, P.L.; Wiggermann, P. Impact of Different Embolic Agents for Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Procedures on Systemic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Levels. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, A.; Cristofori, C.; Cardin, R.; Pivetta, G.; Ragazzi, R.; Baldan, A.; Girardi, L.; Cillo, U.; Burra, P.; Giacomin, A.; et al. Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): The Role of Angiogenesis and Invasiveness. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, T.; Yamashita, T.; Takata, N.; Toyama, T.; Shimakami, T.; Takatori, H.; Arai, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kitamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Comparative analysis of liver functional reserve during lenvatinib and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Q.-A.; Zha, M.; Nesterova, A.; Cao, H. Apatinib Mesylate in the treatment of advanced progressed lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR-TKI resistance —A Multicenter Randomized Trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.; Carter, C.; Lynch, M.; Lowinger, T.; Dumas, J.; Smith, R.A.; Schwartz, B.; Simantov, R.; Kelley, S. Discovery and development of sorafenib: A multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cao, G.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, D.; Xu, H.; Shi, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Regorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Qin, S.; Kudo, M.; Su, Y.; Hudgens, S.; Yamashita, T.; Yoon, J.-H.; Fartoux, L.; Simon, K.; López, C.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib for first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Patient-reported outcomes from a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. A New Treatment Option for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma with High Tumor Burden: Initial Lenvatinib Therapy with Subsequent Selective TACE. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaruz, L.C.; Socinski, M.A. The Clinical Viewpoint: Definitions, Limitations of RECIST, Practical Considerations of Measurement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, G.; Su, F.; Chu, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, Y. Regorafenib-loaded poly (lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres designed to improve transarterial chemoembolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| OS | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 0.97 (0.66, 1.42) | TACE | ||||
| 2.02 (1.26, 3.31) | 2.09 (1.5, 2.91) | TACE + Apatinib | |||
| 2.63 (1.23, 5.86) | 2.72 (1.37, 5.59) | 1.3 (0.61, 2.85) | TACE + Lenvatinib | ||
| 1.41 (1.01, 1.97) | 1.46 (1.2, 1.75) | 0.7 (0.49, 0.99) | 0.54 (0.26, 1.07) | TACE + Sorafenib | |
| PFS | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 1.05 (0.57, 1.95) | TACE | ||||
| 1.74 (0.64, 4.87) | 1.66 (0.74, 3.74) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 1.74 (0.9, 3.73) | 1.67 (1.12, 2.63) | 1 (0.41, 2.56) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 3.14 (1.45, 7.02) | 2.99 (1.72, 5.28) | 1.8 (0.68, 4.86) | 1.79 (0.88, 3.5) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 1.62 (0.96, 2.84) | 1.54 (1.17, 2.08) | 0.93 (0.4, 2.2) | 0.93 (0.57, 1.44) | 0.52 (0.29, 0.92) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| CR | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 0.17 (0.02, 0.87) | TACE | ||||
| 0.13 (0.01, 1.34) | 0.79 (0.15, 3.96) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 0.09 (0.01, 0.67) | 0.57 (0.18, 1.64) | 0.71 (0.1, 5.04) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 0.09 (0.01, 0.73) | 0.53 (0.13, 1.9) | 0.67 (0.08, 5.32) | 0.94 (0.16, 5.2) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 0.11 (0.01, 0.47) | 0.65 (0.3, 0.99) | 0.81 (0.13, 4.18) | 1.12 (0.33, 3.5) | 1.21 (0.26, 4.92) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| PR | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 0.75 (0.32, 1.78) | TACE | ||||
| 0.25 (0.05, 1.28) | 0.34 (0.08, 1.32) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 0.41 (0.16, 1.08) | 0.55 (0.33, 0.91) | 1.63 (0.38, 7.29) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 0.38 (0.12, 1.18) | 0.51 (0.22, 1.13) | 1.52 (0.31, 7.6) | 0.93 (0.36, 2.37) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 0.43 (0.2, 0.91) | 0.57 (0.38, 0.83) | 1.71 (0.4, 7.2) | 1.05 (0.57, 1.84) | 1.13 (0.48, 2.57) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| SD | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 1.03 (0.73, 1.51) | TACE | ||||
| 3.24 (1.25, 9.86) | 3.13 (1.28, 8.94) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 1.01 (0.67, 1.67) | 0.98 (0.73, 1.38) | 0.31 (0.11, 0.82) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 1.46 (0.82, 2.6) | 1.42 (0.87, 2.26) | 0.45 (0.14, 1.24) | 1.44 (0.79, 2.48) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 0.89 (0.67, 1.22) | 0.87 (0.7, 1.05) | 0.28 (0.09, 0.69) | 0.88 (0.61, 1.2) | 0.61 (0.38, 1) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| PD | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 0.72 (0.45, 1.09) | TACE | ||||
| 2.58 (0.53, 21.46) | 3.6 (0.79, 28.85) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 1.17 (0.69, 1.92) | 1.63 (1.2, 2.24) | 0.45 (0.06, 2.15) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 2.91 (1.08, 8.57) | 4.07 (1.62, 11.39) | 1.12 (0.12, 7.08) | 2.49 (0.95, 7.2) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 1.34 (0.91, 1.91) | 1.86 (1.48, 2.39) | 0.52 (0.06, 2.41) | 1.14 (0.81, 1.63) | 0.46 (0.17, 1.15) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| ORR | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 0.66 (0.29, 1.47) | TACE | ||||
| 0.27 (0.06, 1.24) | 0.41 (0.11, 1.5) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 0.36 (0.14, 0.88) | 0.54 (0.33, 0.89) | 1.32 (0.33, 5.24) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 0.33 (0.11, 0.94) | 0.5 (0.23, 1.06) | 1.21 (0.26, 5.4) | 0.92 (0.37, 2.24) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 0.36 (0.17, 0.72) | 0.55 (0.37, 0.78) | 1.33 (0.34, 5) | 1.01 (0.56, 1.73) | 1.1 (0.49, 2.44) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| DCR | |||||
| Sorafenib | |||||
| 1.05 (0.72, 1.55) | TACE | ||||
| 0.93 (0.43, 2.02) | 0.88 (0.45, 1.73) | TACE + Anlotinib | |||
| 0.71 (0.45, 1.1) | 0.67 (0.51, 0.87) | 0.76 (0.37, 1.57) | TACE + Apatinib | ||
| 0.71 (0.39, 1.23) | 0.68 (0.41, 1.03) | 0.77 (0.33, 1.69) | 1.01 (0.58, 1.65) | TACE + Lenvatinib | |
| 0.74 (0.53, 1.03) | 0.71 (0.58, 0.85) | 0.8 (0.4, 1.61) | 1.05 (0.78, 1.41) | 1.05 (0.67, 1.71) | TACE + Sorafenib |
| Intervention | Rank 1 | Rank 2 | Rank 3 | Rank 4 | Rank 5 | Rank 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.000165 | 0.002785 | 0.02387 | 0.54582 | 0.42736 | |
| TACE | 0 | 0.00002 | 0.00174 | 0.42741 | 0.57083 | |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.24607 | 0.73248 | 0.019875 | 0.00156 | 0.000015 | |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.752815 | 0.20918 | 0.030835 | 0.005385 | 0.001785 | |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.00095 | 0.055535 | 0.92368 | 0.019825 | 0.00001 | |
| PFS | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.001495 | 0.010155 | 0.024575 | 0.098535 | 0.319985 | 0.545255 |
| TACE | 0 | 0.00005 | 0.00137 | 0.05933 | 0.550845 | 0.388405 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.102385 | 0.352125 | 0.164635 | 0.23307 | 0.08498 | 0.062805 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.03351 | 0.35386 | 0.36118 | 0.21973 | 0.02867 | 0.00305 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.859055 | 0.11471 | 0.01953 | 0.00542 | 0.00115 | 0.000135 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.003555 | 0.1691 | 0.42871 | 0.383915 | 0.01437 | 0.00035 |
| CR | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.000045 | 0.000215 | 0.00062 | 0.00209 | 0.016385 | 0.980645 |
| TACE | 0.000085 | 0.00653 | 0.085675 | 0.40477 | 0.500935 | 0.002005 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.189375 | 0.188725 | 0.15837 | 0.14672 | 0.30269 | 0.01412 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.33443 | 0.293095 | 0.17729 | 0.110045 | 0.08378 | 0.00136 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.41794 | 0.24931 | 0.14345 | 0.098015 | 0.08942 | 0.001865 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.058125 | 0.262125 | 0.434595 | 0.23836 | 0.00679 | 0.000005 |
| PR | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.00206 | 0.00715 | 0.016925 | 0.0559 | 0.18513 | 0.732835 |
| TACE | 0 | 0.00014 | 0.004565 | 0.078665 | 0.696835 | 0.219795 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.632085 | 0.128915 | 0.07674 | 0.0959 | 0.038135 | 0.028225 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.105135 | 0.298485 | 0.315525 | 0.25067 | 0.026925 | 0.00326 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.204805 | 0.33027 | 0.190945 | 0.210705 | 0.04741 | 0.015865 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.055915 | 0.23504 | 0.3953 | 0.30816 | 0.005565 | 0.00002 |
| SD | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.17797 | 0.244155 | 0.22778 | 0.28737 | 0.060625 | 0.0021 |
| TACE | 0.03658 | 0.191355 | 0.417 | 0.32856 | 0.026175 | 0.00033 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.002335 | 0.00165 | 0.002725 | 0.005405 | 0.05199 | 0.935895 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.17685 | 0.21434 | 0.243985 | 0.2837 | 0.078615 | 0.00251 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.018445 | 0.02053 | 0.036525 | 0.083655 | 0.781695 | 0.05915 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.58782 | 0.32797 | 0.071985 | 0.01131 | 0.0009 | 0.000015 |
| PD | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.05472 | 0.59534 | 0.252775 | 0.07829 | 0.017455 | 0.00142 |
| TACE | 0.891825 | 0.104465 | 0.00368 | 0.00003 | 0 | 0 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.050625 | 0.06541 | 0.05785 | 0.049785 | 0.32718 | 0.44915 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.001515 | 0.21449 | 0.47315 | 0.24921 | 0.05787 | 0.003765 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.00131 | 0.009085 | 0.016815 | 0.022905 | 0.412635 | 0.53725 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.000005 | 0.01121 | 0.19573 | 0.59978 | 0.18486 | 0.008415 |
| ORR | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.000485 | 0.001855 | 0.00743 | 0.03348 | 0.127235 | 0.829515 |
| TACE | 0.00001 | 0.00011 | 0.00478 | 0.09716 | 0.76965 | 0.12829 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.514745 | 0.14113 | 0.101675 | 0.153605 | 0.05618 | 0.032665 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.129925 | 0.28231 | 0.311385 | 0.26125 | 0.01362 | 0.00151 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.264965 | 0.290715 | 0.192055 | 0.212025 | 0.032225 | 0.008015 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.08987 | 0.28388 | 0.382675 | 0.24248 | 0.00109 | 0.000005 |
| DCR | ||||||
| Sorafenib | 0.009365 | 0.02357 | 0.07199 | 0.27588 | 0.320075 | 0.29912 |
| TACE | 0 | 0.000055 | 0.006505 | 0.14567 | 0.46151 | 0.38626 |
| TACEplusAnlotinib | 0.13843 | 0.092665 | 0.101555 | 0.21938 | 0.15188 | 0.29609 |
| TACEplusApatinib | 0.336555 | 0.32534 | 0.22673 | 0.09481 | 0.01573 | 0.000835 |
| TACEplusLenvatinib | 0.385705 | 0.20037 | 0.21111 | 0.139195 | 0.045935 | 0.017685 |
| TACEplusSorafenib | 0.129945 | 0.358 | 0.38211 | 0.125065 | 0.00487 | 0.00001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Zheng, S.; Xie, X.; Zhang, B. Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Molecular Targeted Agents for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153710
Zhang Z, Wu Y, Zheng T, Chen X, Chen G, Chen H, Guo X, Zheng S, Xie X, Zhang B. Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Molecular Targeted Agents for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2022; 14(15):3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153710
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenzhen, Yanfang Wu, Tanghui Zheng, Xiaochun Chen, Guobin Chen, Hong Chen, Xinkun Guo, Susu Zheng, Xiaoying Xie, and Boheng Zhang. 2022. "Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Molecular Targeted Agents for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis" Cancers 14, no. 15: 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153710
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wu, Y., Zheng, T., Chen, X., Chen, G., Chen, H., Guo, X., Zheng, S., Xie, X., & Zhang, B. (2022). Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Molecular Targeted Agents for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 14(15), 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14153710






