Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
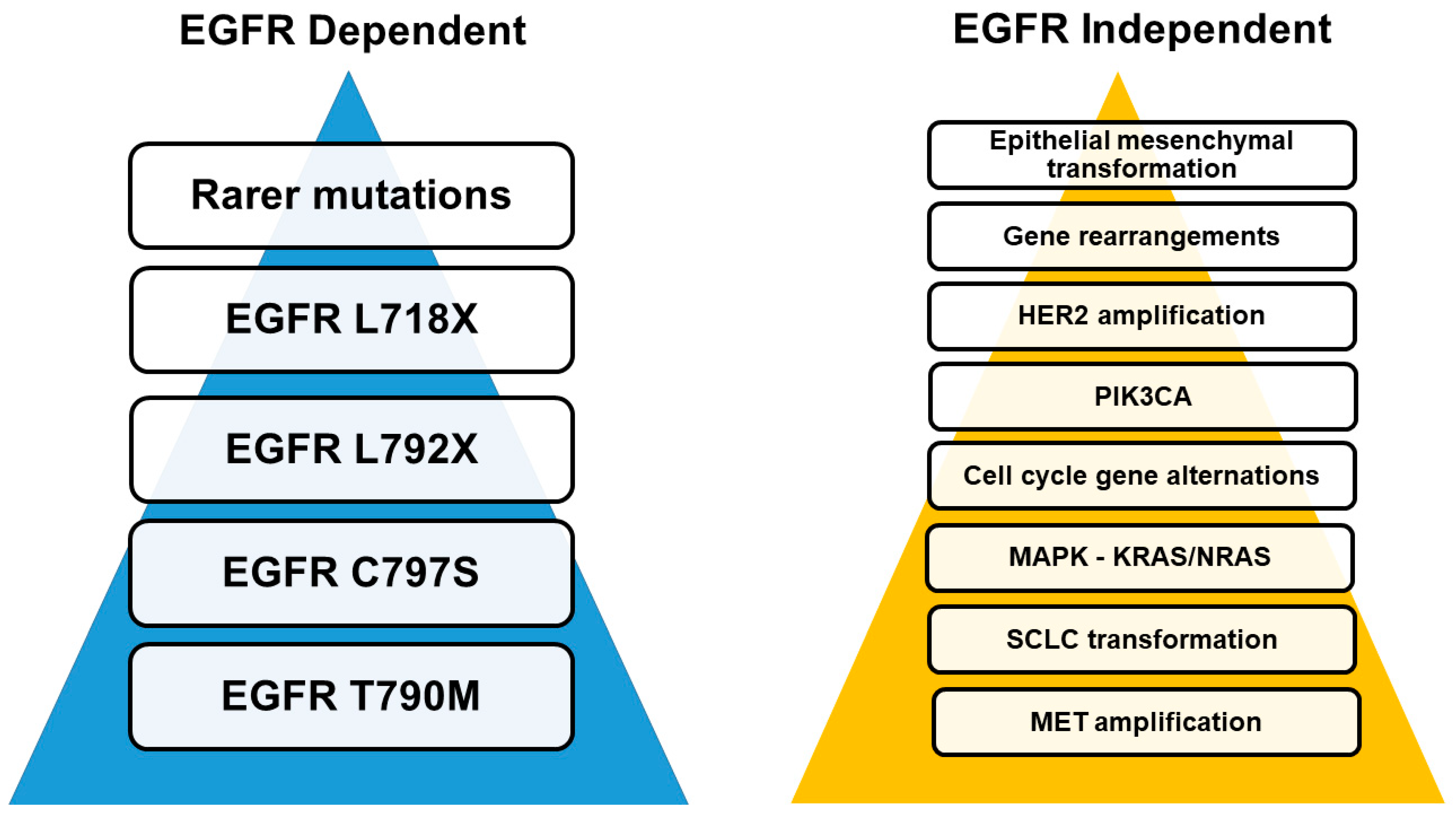
3.1. Mechanisms of Resistance
3.2. EGFR Target-Dependent Mutations
3.2.1. T790M Mutations
3.2.2. C797S Mutation
3.2.3. Rare EGFR-Dependent Mutations
3.2.4. EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
3.3. EGFR Independent Pathways
3.3.1. MET Amplification
3.3.2. HER2 Amplification and Point Mutations
3.4. MAPK–KRAS/NRAS
3.4.1. PIK3Cam
3.4.2. Gene Rearrangements
3.4.3. Genetic Aberrations in the Cell-Cycle Related Genes
3.4.4. NSCLC to SCLC Transformation
3.4.5. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
| Resistance Mechanism(s) | Study Design | Outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amplification of MET, HER2, and PIK3CA | Analysis of plasma samples of 83 patients with PD on first-line osimertinib | MET: 14 samples—19%, HER2: 4 samples—5%, PIK3CA: 3 samples—4% | Papadimitrakopoulou et al., 2018 [103] |
| Mutations in AKT1, BRAF, ERBB2, KRAS, MEK1, NRAS and PIK3CA, MET and HER2 | Molecular analysis of tumor samples from 155 patients with lung adenocarcinomas and acquired resistance to erlotinib or gefitinib | MET amplification in 4 samples, HER2 amplification in 3 samples | Yu et al., 2013 [119] |
| MET, EGFR, PIK3CA, ERRB2, KRAS, RB1 | CAPP-Seq ctDNA analysis of 115 plasma samples from 43 patients to identify resistance-inducing mutations in 43 NSCLC patients treated with rociletinib | An increased copy number in MET or ERBB2 was detected in 14 patients (34%) in combination to EGFR mutations, single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in EGFR, PIK3CA or RB1 in 3 patients (7%) and an increased copy number in MET in combination with SNVs in PIK3CA or RB1 in 2 patients (5%) | Chabon et al., 2016 [120] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | Amplicon-seq analysis on tissue samples of 20 NSCLC patients at PD or baseline treated with TKIs | MET amplification in 1 patient with brain metastasis after prolonged treatment with osimertinib | Martinez-Marti et al., 2017 [64] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | Tumor biopsy analysis of 7 patients treated with TKIs (AZD9291 or rociletinib) | Recurrent MET or ERBB2 amplification in 5 patients with resistance to third-generation TKIs, KRASG12S mutation in one tumor resistant to AZD9291 | Ortiz-Cuaran et al., 2016 [66] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | Molecular profiling analysis at the time of PD in blood and tissue samples of 118 patients treated with TKIs | MET amplification in 14% of the patients, recurrent alterations detected in PIK3CA, EGFR, and RET of >3.3% of patients | Le et al., 2018 [121] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | NGS on tumor tissue or blood samples of 117 patients with stage IIIb-IV EGFR-T790M NSCLC | MET amplification in 3 (33.33%) patients, BCL2L11 loss (BIM deletion polymorphism) in 1 (11.11%) patient, ERBB2 amplification in 1 (11.11%) patient, PTEN mutation in 1 (11.11%) patient, EZH2 mutation in 1 (11.11%) patient | T.S.K. Mok et al., 2019 [26] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | NGS plasma samples’ analysis from 559 patients with previously untreated EGFRm advanced NSCLC treated with TKIs; osimertinib (n = 279), gefitinib or erlotinib (n = 277) | MET amplification in 14 patients treated with osimertinib and in 5 patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib, HER2 amplification, PIK3CA and RAS mutations in 6 patients treated with osimertinib and 3 patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib | Ramalingam et al., 2018 [22] |
| EGFR dependent and independent mutations | Molecular analysis of tumor tissue and plasma samples from 12 EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients before and after osimertinib treatment | KRAS G12D mutation in 1 patient, PIK3CA E545K mutations in 2 patients, pre-existing KRAS G12D mutation and PTEN loss in 2 patients with primary resistance to osimertinib | Hong et al., 2018 [122] |
3.5. CNS Disease
3.5.1. Immunotherapy and EGFR TKIs Resistance
3.5.2. Clinical Trials of Immunotherapy in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC
3.5.3. Detection of EGFR TKIs Resistance by Means of Liquid Biopsy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlsen, E.A.; Kahler, S.; Tefay, J.; Joseph, S.R.; Simpson, F. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression and Resistance Patterns to Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Janne, P.A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, M.S.; Sakurada, A.; Cutz, J.C.; Zhu, C.Q.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Squire, J.; Lorimer, I.; Zhang, T.; Liu, N.; Daneshmand, M.; et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer—Molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Rodrigues Pereira, J.; Ciuleanu, T.; Tan, E.H.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Campos, D.; Maoleekoonpiroj, S.; Smylie, M.; Martins, R.; et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Janne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar]
- Janne, P.A.; Engelman, J.A.; Johnson, B.E. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: Implications for treatment and tumor biology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.D.; Pei, D.Q. Identification of EGFR kinase domain mutations among lung cancer patients in China: Implication for targeted cancer therapy. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F.; Tu, H.Y.; Laktionov, K.K.; Feng, J.; Poltoratskiy, A.; Zhao, J.; Tan, E.H.; Gottfried, M.; Lee, V.; et al. Afatinib in EGFR TKI-Naive Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Three Phase IIIb Studies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 709877. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; O’Byrne, K.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Janne, P.A.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Taylor, I.; Sbar, E.I.; Paz-Ares, L. Dacomitinib versus erlotinib in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Pooled subset analyses from two randomized trials. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, D.; Wu, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 2b, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 829–839. [Google Scholar]
- Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Melchior, L.C.; Urbanska, E.M.; Jakobsen, J.N.; Stricker, K.; Grauslund, M.; Sorensen, J.B. Intrinsic resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 923. [Google Scholar]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cortot, A.B.; Janne, P.A. Molecular mechanisms of resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Huebner, A.; McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. LBA11 Defining the lethal subclone in metastatic lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii702. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.T.; Chen, J.S.; Liao, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Hsu, C.L.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, Z.Z.; Shih, J.Y.; et al. Clinical outcomes and secondary epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation among first-line gefitinib, erlotinib and afatinib-treated non-small cell lung cancer patients with activating EGFR mutations. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2887–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients With EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, T.; Jia, Y.; Shi, J.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Gao, G.; et al. Loss of T790M mutation is associated with early progression to osimertinib in Chinese patients with advanced NSCLC who are harboring EGFR T790M. Lung Cancer 2019, 128, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Hao, X.; Xing, P.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. Acquired resistance to osimertinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and clinical outcomes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib As First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating Novel Resistance Mechanisms to Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar]
- Bordi, P.; Del Re, M.; Minari, R.; Rofi, E.; Buti, S.; Restante, G.; Squadrilli, A.; Crucitta, S.; Casartelli, C.; Gnetti, L.; et al. From the beginning to resistance: Study of plasma monitoring and resistance mechanisms in a cohort of patients treated with osimertinib for advanced T790M-positive NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2019, 131, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, E.; Nguyen, M.; Karlovich, C.A.; Despain, D.; Choquette, A.K.; Spira, A.I.; Yu, H.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Harding, T.C.; Lanman, R.B.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Next-Generation Sequencing Prediction of Response and Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2018, 19, 518–530 e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, H.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Chuai, S.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of AC0010, a Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Safety, Efficacy, and Potential Mechanism of Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, C.; Geng, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lan, K.; Ji, Y. Mutational Profiling of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Resistant to Osimertinib Using Next-Generation Sequencing in Chinese Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9010353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Facchinetti, F.; Olaussen, K.A.; Besse, B.; Friboulet, L. Making the first move in EGFR-driven or ALK-driven NSCLC: First-generation or next-generation TKI? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Tu, H.Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.L. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S Responds to Combination Therapy of First- and Third-Generation EGFR TKIs and Shifts Allelic Configuration at Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, T.; Tong, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. LS-106, a novel EGFR inhibitor targeting C797S, exhibits antitumor activities both in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalm, S.S.; Dineen, T.; Lim, S.M.; Park, C.W.; Hsieh, J.; Woessner, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wilson, K.; Eno, M.; Wilson, D.; et al. 384P—BLU-945, a highly potent and selective 4th generation EGFR TKI for the treatment of EGFR T790M/C797S resistant NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1386–S1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.I.; Cui, J.; Schrock, A.B.; Goldberg, M.E.; Zhu, V.W.; Albacker, L.; Stephens, P.J.; Miller, V.A.; Ali, S.M. Emergence of novel and dominant acquired EGFR solvent-front mutations at Gly796 (G796S/R) together with C797S/R and L792F/H mutations in one EGFR (L858R/T790M) NSCLC patient who progressed on osimertinib. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishino, M.; Suda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohara, S.; Fujino, T.; Koga, T.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; et al. Effects of secondary EGFR mutations on resistance against upfront osimertinib in cells with EGFR-activating mutations in vitro. Lung Cancer 2018, 126, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Yang, G.J.; Wang, Y. Case Report: Dacomitinib May Not Benefit Patients Who Develop Rare Compound Mutations After Later-Line Osimertinib Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 649843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, D.; Choi, H.G.; Yun, C.H.; Capelletti, M.; Xie, T.; Eck, M.J.; Gray, N.S.; Janne, P.A. EGFR Mutations and Resistance to Irreversible Pyrimidine-Based EGFR Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3913–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Hu, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ni, J.; et al. EGFR G796D mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49671–49679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, B.P.; Zhang, Y.K.; Westover, D.; Yan, Y.; Qiao, H.; Huang, V.; Du, Z.; Smith, J.A.; Ross, J.S.; Miller, V.A.; et al. On-target Resistance to the Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor Osimertinib Can Develop in an Allele-Specific Manner Dependent on the Original EGFR-Activating Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fassunke, J.; Muller, F.; Keul, M.; Michels, S.; Dammert, M.A.; Schmitt, A.; Plenker, D.; Lategahn, J.; Heydt, C.; Bragelmann, J.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(G724S)-mediated osimertinib resistance through unique binding characteristics of second-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Yang, J.J.; Yang, Z.F.; Bai, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. EGFR L792H and G796R: Two Novel Mutations Mediating Resistance to the Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.M.; Song, A.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Keam, B.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to AZD9291: A Mutation-Selective, Irreversible EGFR Inhibitor. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Lo, P.C.; Nishino, M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Butaney, M.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Janne, P.A. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riess, J.W.; Gandara, D.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Madison, R.; Peled, N.; Bufill, J.A.; Dy, G.K.; Ou, S.I.; Stephens, P.J.; McPherson, J.D.; et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, I.B.; Joe, A. Oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3077–3080; discussion 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedlaender, A.; Subbiah, V.; Russo, A.; Banna, G.L.; Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C.; Addeo, A. EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions in solid tumours: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Eck, M.J.; Yun, C.H. Structural and mechanistic underpinnings of the differential drug sensitivity of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Targeting EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, C.; Yoshida, T.; Shirasawa, M.; Masuda, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shinno, Y.; Yagishita, S.; Okuma, Y.; Goto, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; et al. Clinical characteristics of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR exon 20 insertions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Amivantamab for the treatment of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2022, 22, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1/2 Open-label Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riely, G.J.; Neal, J.W.; Camidge, D.R.; Spira, A.I.; Piotrowska, Z.; Costa, D.B.; Tsao, A.S.; Patel, J.D.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Bazhenova, L.; et al. Activity and Safety of Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in Previously Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations from a Phase I/II Trial. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Wang, M.; Mitchell, P.; Fang, J.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.C.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Preliminary safety and efficacy results from phase 1 studies of DZD9008 in NSCLC patients with EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Goldman, J.W.G.; Clarke, J.M.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Piotrowska, Z.; Chu, D.; Bhat, G.; Lebel, F.M.; Socinski, M.A. Poziotinib shows activity and durability of responses in subgroups of previously treated EGFR exon 20 NSCLC patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Redman, M.W.; Lilenbaum, R.; Politi, K.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Horn, L.; Chen, E.H.; Mashru, S.H.; Gettinger, S.N.; Melnick, M.A.; et al. Randomized Trial of Afatinib Plus Cetuximab Versus Afatinib Alone for First-Line Treatment of EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Final Results from SWOG S1403. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4076–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veggel, B.; de Langen, A.J.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Monkhorst, K.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Thunnissen, E.; Smit, E.F. Afatinib and Cetuximab in Four Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gan, J.; Hong, S.; Zhang, L. A Patient with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Responded to Osimertinib plus Cetuximab Combination Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e201–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Yasuda, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Masuzawa, K.; Tani, T.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Manabe, T.; Terai, H.; et al. Efficacy of afatinib or osimertinib plus cetuximab combination therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gan, J.; Shao, Y.W.; Zhang, L. Durable Response of Low-Dose Afatinib plus Cetuximab in an Adenocarcinoma Patient with a Novel EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e220–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Hayashi, H.; Thomas, M.; Lu, S.; Besse, B.; Sun, T.; Martinez, M.; Sethi, S.N.; Shreeve, S.M.; et al. MARIPOSA: Phase 3 study of first-line amivantamab + lazertinib versus osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, T.; Artis, E.; Xie, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Haddish-Berhane, N.; Gopen, T.; Curtin, J.C.; Karkera, J.; Roshak, A.; Knoblauch, R.E.; et al. P76.74 PAPILLON: Randomized Phase 3 Study of Amivantamab Plus Chemotherapy vs Chemotherapy Alone in EGFR Exon20ins NSCLC. in P76 Targeted Therapy—Clinically Focused—EGFR. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Marti, A.; Felip, E.; Matito, J.; Mereu, E.; Navarro, A.; Cedres, S.; Pardo, N.; Martinez de Castro, A.; Remon, J.; Miquel, J.M.; et al. Dual MET and ERBB inhibition overcomes intratumor plasticity in osimertinib-resistant-advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kane, G.M.; Barnes, T.A.; Leighl, N.B. Resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, T790M, and clinical trials. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S28–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Scheffler, M.; Plenker, D.; Dahmen, L.; Scheel, A.H.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Persigehl, T.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; et al. Heterogeneous Mechanisms of Primary and Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4837–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Zhang, G.; Yao, W.; Yue, P.; Li, Y.; Kanteti, R.; Riehm, J.; Salgia, R.; Owonikoko, T.K.; et al. Met gene amplification and protein hyperactivation is a mechanism of resistance to both first and third generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzawa, K.; Offin, M.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Odintsov, I.; Lu, D.; Lockwood, W.W.; Arcila, M.E.; Rudin, C.M.; Drilon, A.; et al. Acquired MET Exon 14 Alteration Drives Secondary Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.19.00011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinquie, F.; Cortot, A.B.; Chevalier, L.M.; Morel, A.; Sandrini, J.; Guguen, C.; Morvan, B.; Molinier, O. A Case Report of Successful Treatment With Crizotinib to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in an EGFR Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient Harboring an Acquired MET Exon 14 Mutation. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e131–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, A.S.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Bunn, P.A.; Carbone, D.P., Jr.; Warren, G.W.; Bai, C.; de Koning, H.J.; Yousaf-Khan, A.U.; McWilliams, A.; Tsao, M.S.; et al. Scientific Advances in Lung Cancer 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 613–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib in MET Exon 14-Mutated or MET-Amplified Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Cantarini, M.; Frewer, P.; Hawkins, G.; Peters, J.; Howarth, P.; Ahmed, G.F.; Sahota, T.; Hartmaier, R.; Li-Sucholeiki, X.; et al. SAVANNAH: A Phase II trial of osimertinib plus savolitinib for patients (pts) with EGFR-mutant, MET-driven (MET+), locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), following disease progression on osimertinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, TPS9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, J.S.; Su, W.C.; Kowalski, D.; et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Fang, J.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Guo, Q.; Liang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, N.; et al. Once-daily savolitinib in Chinese patients with pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas and other non-small-cell lung cancers harbouring MET exon 14 skipping alterations: A multicentre, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Berardi, R.; Lim, W.T.; de Jonge, M.; Bauer, T.M.; Azaro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Wollner, M.; et al. Molecular correlates of response to capmatinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Clinical and biomarker results from a phase I trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Otterson, G.A.; Clark, J.W.; Ignatius Ou, S.H.; Weiss, J.; Ades, S.; Shapiro, G.I.; Socinski, M.A.; Murphy, D.A.; Conte, U.; et al. Crizotinib in Patients With MET-Amplified NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Baik, C.; Su, W.C.; Johnson, M.L.; Hayashi, H.; Nishio, M.; Kim, D.W.; Koczywas, M.; Gold, K.A.; Steuer, C.E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR Inhibitor-Resistant, EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonesaka, K. HER2-/HER3-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Treating Lung and Colorectal Cancers Resistant to EGFR Inhibitors. Cancers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Nagasaka, M.; Felip, E.; Pacheco, J.; Baik, C.; Goto, Y.; Saltos, A.; Li, B.; Udagawa, H.; Gadgeel, S.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-overexpressing metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Interim results of DESTINY-Lung01. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S109–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Saura, C.; Yamashita, T.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Tamura, K.; Andre, F.; Iwata, H.; Ito, Y.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazieres, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Bang, Y.J.; Iwasa, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Ryu, M.H.; Sakai, D.; Chung, H.C.; Kawakami, H.; Yabusaki, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Ross, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Chaft, J.E.; Hsu, M.; Kako, S.L.; Kris, M.G.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Arcila, M.E. HER2 Amplification and HER2 Mutation Are Distinct Molecular Targets in Lung Cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.T.; Shen, R.; Buonocore, D.; Olah, Z.T.; Ni, A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Ulaner, G.A.; Offin, M.; Feldman, D.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine for Patients With HER2-Mutant Lung Cancers: Results From a Phase II Basket Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Peters, S.; Lepage, B.; Cortot, A.B.; Barlesi, F.; Beau-Faller, M.; Besse, B.; Blons, H.; Mansuet-Lupo, A.; Urban, T.; et al. Lung cancer that harbors an HER2 mutation: Epidemiologic characteristics and therapeutic perspectives. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazieres, J.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Besse, B.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Peters, S.; Dansin, E.; Fruh, M.; Pless, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: Results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Lafitte, C.; Ricordel, C.; Greillier, L.; Negre, E.; Zalcman, G.; Domblides, C.; Madelaine, J.; Bennouna, J.; Mascaux, C.; et al. Combination of Trastuzumab, Pertuzumab, and Docetaxel in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring HER2 Mutations: Results From the IFCT-1703 R2D2 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Cornelissen, R.; Garassino, M.; Clarke, J.M.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Goldman, J.W.; Leu, S.Y.; Bhat, G.; Lebel, F.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Poziotinib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring HER2 Exon 20 Insertion Mutations After Prior Therapies: ZENITH20-2 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Rivard, C.; Gao, G.; Ng, T.L.; Tu, M.M.; et al. HER2 exon 20 insertions in non-small-cell lung cancer are sensitive to the irreversible pan-HER receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor pyrotinib. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, J.; et al. Pyrotinib in HER2-Mutant Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma After Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Suda, K.; Nishino, M.; Fujino, T.; Ohara, S.; Hamada, A.; Soh, J.; Tirunagaru, V.; Vellanki, A.; Doebele, R.C.; et al. Activity and mechanism of acquired resistance to tarloxotinib in HER2 mutant lung cancer: An in vitro study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3659–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, J.; Ying, J.; Mitsudomi, T.; Lee, D.H.; Wang, Z.; Chu, Q.; Mack, P.C.; Cheng, Y.; Duan, J.; et al. Consensus for HER2 alterations testing in non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, C.A.; Stetson, D.; Markovets, A.A.; Al-Kadhimi, K.J.; Lai, Z.; Fisher, P.R.; Meador, C.B.; Spitzler, P.; Ichihara, E.; Ross, S.J.; et al. Acquired Resistance to the Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor AZD9291 Is Associated with Increased Dependence on RAS Signaling in Preclinical Models. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, T.M.; Quoix, E.; Souquet, P.J.; Barlesi, F.; Baik, C.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With BRAF V600E-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC: Updated 5-Year Survival Rates and Genomic Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Plodkowski, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M.; Drilon, A. Impact of Concurrent PIK3CA Mutations on Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers and on Prognosis in Oncogene-Driven Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, A.C. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gu, W.; Gan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway alterations in advanced NSCLC patients after progression on EGFR-TKI and clinical response to EGFR-TKI plus everolimus combination therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, M.P. The ever-changing world of gene fusions in cancer: A secondary gene fusion and progression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 7197–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Wu, Y.-L.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Bu-lusu, K.C.; Laus, G.; et al. Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, C.M.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Wu, W.; Gini, B.; Chabon, J.J.; McCoach, C.E.; McGranahan, N.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Olivas, V.R.; et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Monica, S.; Fumarola, C.; Cretella, D.; Bonelli, M.; Minari, R.; Cavazzoni, A.; Digiacomo, G.; Galetti, M.; Volta, F.; Mancini, M.; et al. Efficacy of the CDK4/6 Dual Inhibitor Abemaciclib in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Cell Lines with Different Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib. Cancers 2020, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Zeng, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Zhong, D. CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib overcomes acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2389–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Youk, J.; Park, S.; An, Y.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S.; Kim, Y.T.; et al. Clonal History and Genetic Predictors of Transformation Into Small-Cell Carcinomas From Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Sun, C.; Zhou, C. Third-Generation TKI Resistance Due to SCLC Transformation: A Case Report and Brief Review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 11305–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K.; Byeon, S.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Han, J.; et al. Two Cases of Small Cell Lung Cancer Transformation from EGFR Mutant Adenocarcinoma During AZD9291 Treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonetti, A.; Minari, R.; Mazzaschi, G.; Gnetti, L.; La Monica, S.; Alfieri, R.; Campanini, N.; Verze, M.; Olivani, A.; Ventura, L.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Transformation as a Resistance Mechanism to Osimertinib in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yan, X. Transformation to small-cell carcinoma as an acquired resistance mechanism to AZD9291: A case report. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18609–18614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Del Re, M.; Facchinetti, F.; Mazzoni, F.; Barbieri, F.; Camerini, A.; Comin, C.E.; Gnetti, L.; Azzoni, C.; et al. Primary resistance to osimertinib due to SCLC transformation: Issue of T790M determination on liquid re-biopsy. Lung Cancer 2018, 115, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Morikawa, T.; Usui, K. Small-Cell Carcinoma Transformation of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma after Osimertinib Treatment: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2018, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Tseng, R.Y.; Chiu, A.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.T.; Fang, J.M.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI. Oncogene 2019, 38, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castosa, R.; Martinez-Iglesias, O.; Roca-Lema, D.; Casas-Pais, A.; Diaz-Diaz, A.; Iglesias, P.; Santamarina, I.; Grana, B.; Calvo, L.; Valladares-Ayerbes, M.; et al. Hakai overexpression effectively induces tumour progression and metastasis in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Q.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Zeng, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Zhong, D. Targeting the EMT transcription factor Snail overcomes resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Deng, T.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, P.; Wei, D.; Ling, N.; Li, L.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Deubiquitinase DUB3 Regulates Cell Cycle Progression via Stabilizing Cyclin A for Proliferation of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yochum, Z.A.; Cades, J.; Wang, H.; Chatterjee, S.; Simons, B.W.; O’Brien, J.P.; Khetarpal, S.K.; Lemtiri-Chlieh, G.; Myers, K.V.; Huang, E.H.; et al. Targeting the EMT transcription factor TWIST1 overcomes resistance to EGFR inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chabon, J.J.; Simmons, A.D.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Esfahani, M.S.; Newman, A.M.; Haringsma, H.J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Stehr, H.; Scherer, F.; Karlovich, C.A.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.; Boyle, T.; Hicks, J.K.; Lovinger, K.L.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; et al. Landscape of EGFR-Dependent and -Independent Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib and Continuation Therapy Beyond Progression in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, M.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Heo, S.G.; Kang, H.-N.; Park, C.-W.; Barrett, J.C.; Stetson, D.; Chmielecki, J.; Marko-vets, A.; et al. Molecular landscape of osimertinib resistance revealed by targeted panel sequencing and patient-derived cancer models in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Ravera, E.; Cheng, H.; Halmos, B. Response to Dual Crizotinib and Osimertinib Treatment in a Lung Cancer Patient with MET Amplification Detected by Liquid Biopsy Who Acquired Secondary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, e169–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Planchard, D.; Loriot, Y.; Andre, F.; Gobert, A.; Auger, N.; Lacroix, L.; Soria, J.C. EGFR-independent mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC patients. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Kubota, D.; Sato, H.; Rizvi, H.; Daneshbod, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Paik, P.K.; Offin, M.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Tumor Analyses Reveal Squamous Transformation and Off-Target Alterations As Early Resistance Mechanisms to First-line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoenmaekers, J.; Paats, M.S.; Dingemans, A.C.; Hendriks, L.E.L. Central nervous system metastases and oligoprogression during treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer: How to treat and when? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2599–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heon, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Britt, G.J.; Costa, D.B.; Rabin, M.S.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E. Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5873–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, W.J.; Shah, N.J.; Subramaniam, D.S. Management of Brain Metastases in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, T.A.; Popat, S. Toward precision medicine with next-generation EGFR inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, B.; Wilner, K.D.; Shaw, A.T. Current status of targeted therapy for anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, R.; Liang, X.; Zhan, Q. High probability and frequency of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 135, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, L.; Cassoni, P.; Bacillo, E.; Cappia, S.; Righi, L.; Volante, M.; Tondat, F.; Inghirami, G.; Sapino, A.; Scagliotti, G.V.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary tumor and metastatic sites from non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gow, C.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tsai, M.F.; Wu, C.T.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, P.C.; Shih, J.Y. Comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations between primary and corresponding metastatic tumors in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuchi, T.; Shingyoji, M.; Itakura, M.; Yokoi, S.; Moriya, Y.; Tamura, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Ashinuma, H.; Kawasaki, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Frequency of brain metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer, and their association with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 20, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Takahashi, K.; Iwakawa, R.; Matsuno, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kohno, T.; Shimizu, E.; Yokota, J. Frequent EGFR mutations in brain metastases of lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Behrens, C.; Feng, L.; Ozburn, N.; Tang, X.; Yin, G.; Komaki, R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Hong, W.K.; Aldape, K.D.; et al. HER family receptor abnormalities in lung cancer brain metastases and corresponding primary tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4829–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, A.; Katakami, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Takeshita, J.; Tanaka, K.; Nanjo, S.; Fujita, S.; Kaji, R.; Imai, Y.; Monden, K.; et al. Rebiopsy of non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Comparison between T790M mutation-positive and mutation-negative populations. Cancer 2013, 119, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Campelo, R.; Arrieta, O.; Massuti, B.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Granados, A.L.O.; Majem, M.; Vicente, D.; Lianes, P.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Insa, A.; et al. Combination of gefitinib and olaparib versus gefitinib alone in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A multicenter, randomized phase II study (GOAL). Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, V.; Joshi, A.; Gokarn, A.; Sharma, V.; Patil, V.; Janu, A.; Purandare, N.; Chougule, A.; Jambhekar, N.; Prabhash, K. The Importance of Brain Metastasis in EGFR Mutation Positive NSCLC Patients. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 856156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.K.; Hahn, S.; Kim, D.W.; Suh, K.J.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Heo, D.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors vs conventional chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harboring wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 311, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gong, L.; Fang, L.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Han, N.; Xie, F.; Qiu, G.; Huang, Z. Effects of icotinib with and without radiation therapy on patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy of brain radiotherapy plus EGFR-TKI for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients who develop brain metastasis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, F.; Ren, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J. EGFR TKIs plus WBRT Demonstrated No Survival Benefit Other Than That of TKIs Alone in Patients with NSCLC and EGFR Mutation and Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, G.Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Yan, H.H.; Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Erlotinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases: A phase II study (CTONG-0803). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.W.; Yang, J.C.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of Osimertinib with Other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastases Models, and Early Evidence of Clinical Brain Metastases Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbour, K.C.; Kris, M.G.; Riely, G.J.; Ni, A.; Beal, K.; Daras, M.; Hayes, S.A.; Young, R.J.; Rodriguez, C.R.; Ahn, L.; et al. Twice weekly pulse and daily continuous-dose erlotinib as initial treatment for patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancers and brain metastases. Cancer 2018, 124, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Han, J.Y.; Katakami, N.; Kim, H.R.; Hodge, R.; Kaur, P.; Brown, A.P.; Ghiorghiu, D.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib in Patients With T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Data From a Randomized Phase III Trial (AURA3). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, B.C.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, T.M.; Goldman, J.W.; Natale, R.B.; et al. Osimertinib in Patients With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Leptomeningeal Metastases: The BLOOM Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, M.H.; Seong, M.; Kim, S.T.; Kang, J.H.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, E.K.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; et al. multicenter, two cohort study of 160 mg osimertinib in EGFR T790M-positive non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease who progressed on prior EGFR TKI therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper-Vallillo, A.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Piotrowska, Z. Emerging Treatment Paradigms for EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers Progressing on Osimertinib: A Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xing, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Ma, Z. The efficacy and clinical survival outcome of different first-line treatments in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, E.A.; Koyama, S.; Carretero, J.; Altabef, A.; Tchaicha, J.H.; Christensen, C.L.; Mikse, O.R.; Cherniack, A.D.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C. Checkpoint Inhibitors in Metastatic EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-A Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Ning, Z.; Zhao, W.; Shi, H.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. PD-1/PD-L1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer and its correlation with EGFR/KRAS mutations. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting: Integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Liu, S.Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Tu, H.Y.; Xu, C.R.; Yan, L.X.; et al. EGFR mutation correlates with uninflamed phenotype and weak immunogenicity, causing impaired response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1356145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Fu, X.; Azzoli, C.G.; Piotrowska, Z.; Huynh, T.G.; Zhao, L.; Fulton, L.; Schultz, K.R.; et al. EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements Are Associated with Low Response Rates to PD-1 Pathway Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4585–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Qiao, M.; Luo, J.; et al. EGFR-targeted therapy alters the tumor microenvironment in EGFR-driven lung tumors: Implications for combination therapies. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, M.; Hu, T.; Pai, C.C.; Chu, B.; Belair, C.D.; Chang, A.; Montabana, E.; Lang, U.E.; Fu, Q.; Fong, L.; et al. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell 2019, 177, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Chen, K.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Hsu, C.L.; Su, K.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Wu, C.T.; Hsu, C.C.; et al. Association between programmed death-ligand 1 expression, immune microenvironments, and clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 124, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, K. PD-L1 expression in uncommon EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer and its response to immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Wei, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, S.C. PD-L1 Expression and Outcome in Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR Mutations Receiving EGFR-TKI as Frontline Treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhou, K.; Deng, S.; Mei, J. Predictive value of pretreatment PD-L1 expression in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, K.; Hao, Y.; Yang, C.; Zha, R.; Yi, C.; Qian, Z. Advances in nanotechnology-based delivery systems for EGFR tyrosine kinases inhibitors in cancer therapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiantian, Y.; Wenji, Z.; Mingshuang, S.; Rui, Y.; Shuangshuang, S.; Yuling, M.; Jianhua, Y.; Xinggang, Y.; Shujun, W.; Weisan, P. Study on intralymphatic-targeted hyaluronic acid-modified nanoliposome: Influence of formulation factors on the lymphatic targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Mittal, N.K.; Balabathula, P.; Thoma, L.A.; Wood, G.C. Development and in vitro evaluation of core-shell type lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for the delivery of erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 81, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markman, J.L.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. The Application of Inorganic Nanoparticles in Molecular Targeted Cancer Therapy: EGFR Targeting. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 702445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.C.; Tsang, K.C.; Choi, H.C.; Lee, V.H.; Lam, K.O.; Chiang, C.L.; So, T.H.; Chan, W.W.; Nyaw, S.F.; Lim, F.; et al. Combination atezolizumab, bevacizumab, pemetrexed and carboplatin for metastatic EGFR mutated NSCLC after TKI failure. Lung Cancer 2021, 159, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; et al. IMpower150 Final Overall Survival Analyses for Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Jian, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sun, M.; Han, L.; et al. VP9-2021: ORIENT-31: Phase III study of sintilimab with or without IBI305 plus chemotherapy in patients with EGFR mutated nonsquamous NSCLC who progressed after EGFR-TKI therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metro, G.; Baglivo, S.; Siggillino, A.; Ludovini, V.; Chiari, R.; Rebonato, A.; Bellezza, G. Successful Response to Osimertinib Rechallenge after Intervening Chemotherapy in an EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer Patient. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.G.; Yang, H.R.; Yoon, A.; Lee, S. Bispecific Antibody-Based Immune-Cell Engagers and Their Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, R.; van den Borne, B.; Youssef-El Soud, M.; Belderbos, H.; Brunsveld, L.; Scharnhorst, V.; Deiman, B. Therapy Monitoring of EGFR-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Using ddPCR Multiplex Assays. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B. Update on the types and usage of liquid biopsies in the clinical setting: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Liquid biopsy: From discovery to clinical implementation. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Siravegna, G. How to use liquid biopsies to treat patients with cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Re, M.; Crucitta, S.; Gianfilippo, G.; Passaro, A.; Petrini, I.; Restante, G.; Michelucci, A.; Fogli, S.; de Marinis, F.; Porta, C.; et al. Understanding the Mechanisms of Resistance in EGFR-Positive NSCLC: From Tissue to Liquid Biopsy to Guide Treatment Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisapia, P.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G. Liquid Biopsy and Lung Cancer. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jori, B.; Schatz, S.; Kaller, L.; Kah, B.; Roeper, J.; Ramdani, H.O.; Diehl, L.; Hoffknecht, P.; Grohe, C.; Griesinger, F.; et al. Comparison of Resistance Spectra after First and Second Line Osimertinib Treatment Detected by Liquid Biopsy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, V.; Roisman, L.; Kian, W.; Daniel, L.; Dudnik, J.; Nechushtan, H.; Goldstein, I.; Dvir, A.; Soussan-Gutman, L.; Grinberg, R.; et al. The impact of osimertinib’ line on clonal evolution in EGFRm NSCLC through NGS-based liquid biopsy and overcoming strategies for resistance. Lung Cancer 2021, 153, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Sun, B.; Yin, W.; Deng, S.; Wan, Y.; Lu, W. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Liquid Biopsy in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 40 Studies. SLAS Technol. 2021, 26, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bironzo, P.; Di Maio, M. A review of guidelines for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1556–S1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients With Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Halmos, B. VEGF inhibitors in EGFR-mutated lung cancer: A never-ending story? Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.I.; Chao, H.S.; Shiao, T.H.; Chiang, C.L.; Huang, H.C.; Luo, Y.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, Y.M. Comparison of the outcome between immunotherapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Arbour, K.C.; Rizvi, H.; Iqbal, A.N.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Girshman, J.; Kris, M.G.; Riely, G.J.; Yu, H.A.; Hellmann, M.D. Severe immune-related adverse events are common with sequential PD-(L)1 blockade and osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Makhnin, A.; Kim, R.; Rizvi, H.; Tsui, D.; Falcon, C.; Houck-Loomis, B.; Meng, F.; Yang, J.L.; et al. Effect of Osimertinib and Bevacizumab on Progression-Free Survival for Patients With Metastatic EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers: A Phase 1/2 Single-Group Open-Label Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, E.; Tsoulos, N.; Tsantikidi, K.; Metaxa-Mariatou, V.; Stamou, P.E.; Kladi-Skandali, A.; Kapeni, E.; Tsaousis, G.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Petrakis, D.; et al. Clinical feasibility of NGS liquid biopsy analysis in NSCLC patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beyett, T.S.; To, C.; Heppner, D.E.; Rana, J.K.; Schmoker, A.M.; Jang, J.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Gomez, G.; Scott, D.A.; Gray, N.S.; et al. Molecular basis for cooperative binding and synergy of ATP-site and allosteric EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, C.; Jang, J.; Chen, T.; Park, E.; Mushajiang, M.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Cameron, M.D.; Heppner, D.E.; et al. Single and Dual Targeting of Mutant EGFR with an Allosteric Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- To, C.; Beyett, T.S.; Jang, J.; Feng, W.W.; Bahcall, M.; Haikala, H.M.; Shin, B.H.; Heppner, D.E.; Rana, J.K.; Leeper, B.A.; et al. An allosteric inhibitor against the therapy-resistant mutant forms of EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, A.; Garcia-Mayea, Y.; Jubierre, L.; Mir, C.; Hummel, M.; Castellvi, J.; Hernandez-Losa, J.; Paciucci, R.; Sansano, I.; Sun, Y.; et al. miR-99a reveals two novel oncogenic proteins E2F2 and EMR2 and represses stemness in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, W.; Ping, W.; Deng, Y.; Fu, X. miR-138-5p reverses gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via negatively regulating G protein-coupled receptor 124. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Chiang, A.C.; Zhang, X.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. WNT/TCF signaling through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Cell 2009, 138, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Lee, K.H.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Zhou, C.; Prabhash, K.; Seto, T.; Voon, P.J.; Tan, D.S.W.; Yang, J.C.H.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with locally-advanced unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: A KSMO-ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, ISMPO, JSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Reference | TKIs | Study Design | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y.L. Wu et al., 2013 [144] | Erlotinib | Phase II Clinical Trial including 48 patients with EGFR mutant and non-EGFR mutant NSCLC BMs previously treated with first-line platinum-doublet chemotherapy | Median PFS: 10.1 months; EGFRmut median PFS: 15.2 months; EGFR wt median PFS: 4.4 months |
| Schuler et al., 2016 [77] | Afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed | Clinical trial recruiting patients with metastatic EGFR mutant NSCLC; subgroup analysis of patients with brain metastases | Median PFS with afatinib: 8.2 months; Median PFS with chemotherapy: 5.4 months |
| Ballard et al., 2016 [145] | Osimertinib | Preclinical assessment of Osimertinib CNS penetration in animal models | Osimertinib was superior to gefitinib, rociletinib (CO-1686), or afatinib in terms of penetration of the mouse BBB, Osimertinib induced sustained tumor regression in an EGFRmut PC9 mouse brain metastases model, where rociletinib failed |
| J.C.-H. Yang et al., 2017 [146] | Osimertinib | AURA—Phase I/II Clinical trial involving 201 patients with asymptomatic, stable T970M+ brain metastases that did not require corticosteroids | ORR: 62%; DRR: 90%; Median PFS: 12.3 months |
| Arbour et al., 2018 [147] | Erlotinib (pulse/continuous-dose erlotinib) | Phase 1 clinical trial with 19 patients with EGFR mutant NSCLC brain metastases | RR in brain metastases: 74%; overall median PFS: 10 months |
| Y.-L. Wu et al., 2018 [148] | Osimertinib | Randomized Phase III Trial (AURA3)—analysis reporting the CNS effectiveness of osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed chemotherapy in patients with EGFR T790M+ advanced NSCLC who experience disease progression with prior EGFR-TKI treatment | CNS ORR in patients with ≥1 measurable CNS lesions: 70% with osimertinib and 31% with chemotherapy; median CNS PFS: 11.7 months with osimertinib and 5.6 months with chemotherapy |
| J.C.H. Yang et al., 2020 [149] | Osimertinib 160 mg | Phase I clinical trial BLOOM; 41 patients with leptomeningeal metastases from EGFRmut advanced NSCLC with a history of disease progression on previous EGFR-TKI therapy | ORR: 41%; median DoR: 8.3 months; median PFS: 8.6 months; median OS: 11.0 months; safety and toxicity consistent with previous knowledge |
| Park et al., 2020 [150] | Osimertinib | Phase II, multicentre, two cohort study of 160 mg osimertinib in EGFR T790M+ NSCLC patients with brain or leptomeningeal metastases and a history of progression on previous EGFR TKI therapy | Median PFS: 7.6 months; Median OS: 16.9 months, Previous radiotherapy favored increased PFS (HR: 0.42) |
| Piper-Vallillo et al., 2020 [151] | Osimertinib | Retrospective real-world cohort of EGFRmut NSCLC patients with brain or leptomeningeal metastases on osimertinib 80 mg, dose escalation to 160 mg | Dose escalation increased PFS by 3.6 months and improved CNS disease control |
| H. Wang et al., 2021 [152] | 1st generation EGFR TKIs alone or combined with chemotherapy or bevacizumab | Retrospective analysis of 584 EGFRmut advanced NSCLC patients | 1st generation EGFR TKIs plus bevacizumab achieved the highest intracranial PFS (27.2 months), 1st generation EGFR TKIs alone achieved the highest OS (27.8 months)—no available data for the same on 1st generation TKIs plus bevacizumab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koulouris, A.; Tsagkaris, C.; Corriero, A.C.; Metro, G.; Mountzios, G. Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143337
Koulouris A, Tsagkaris C, Corriero AC, Metro G, Mountzios G. Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143337
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoulouris, Andreas, Christos Tsagkaris, Anna Chiara Corriero, Giulio Metro, and Giannis Mountzios. 2022. "Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143337
APA StyleKoulouris, A., Tsagkaris, C., Corriero, A. C., Metro, G., & Mountzios, G. (2022). Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers, 14(14), 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143337










