A New Functional Screening Platform Identifies Colistin Sulfate as an Enhancer of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Reagents and Drugs
2.3. Generation of Cell Lines
2.4. Luciferase Release-Based Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Screening of the Prestwick Chemical Library and Plate Configuration
2.6. Z′ Factor, Fold-Change, and Normalization Analysis
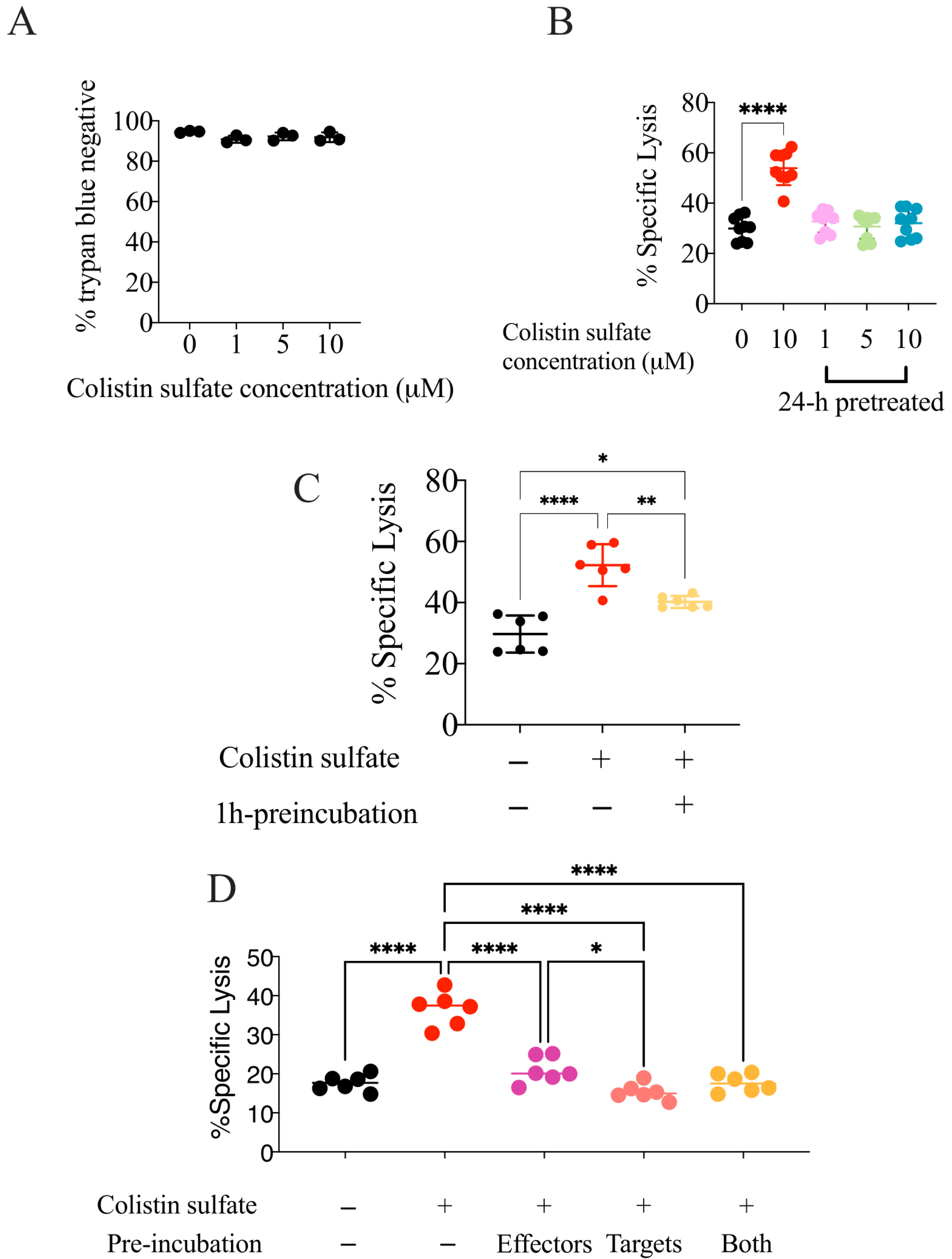
2.7. Dose–Response Experiments
2.8. Colistin Sulfate Pre-Treatment
2.9. Human PBMC Isolation
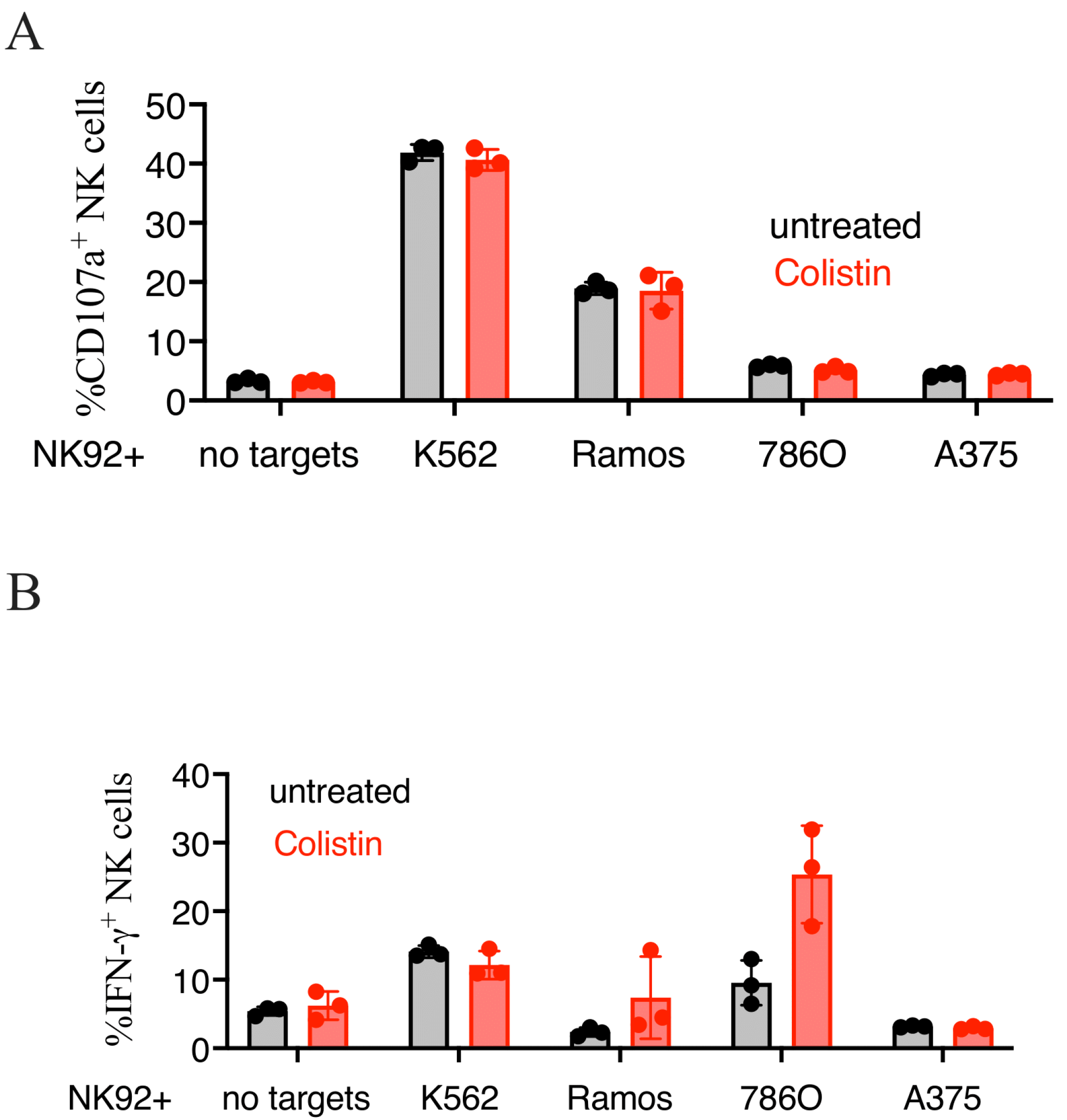
2.10. Flow Cytometry-Based Functional Assays
2.11. Human NK Cell Cytotoxicity Assays with Colistin Treatment
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of K562-NL and Validation of a Luciferase Release-Based Killing Assay
3.2. Optimization of the Conditions for a High-Throughput Luciferase Release-Based Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3. Screening of the Prestwick Chemical Library to Identify Enhancers of NK Cell Cytotoxicity
3.4. Validation of Candidate Drugs
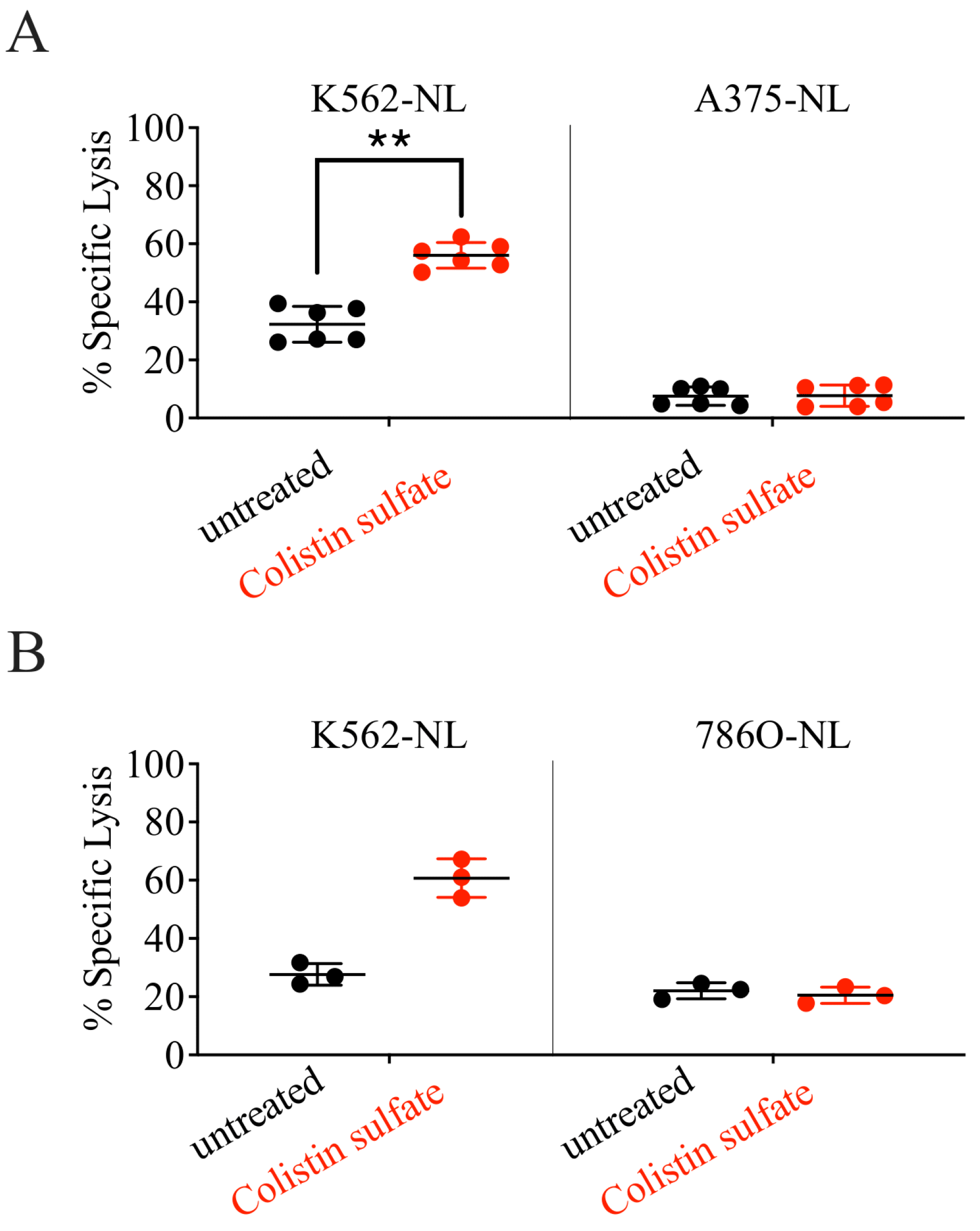
3.5. The Effect of Colistin Sulfate on NK Cells Is Short Lived
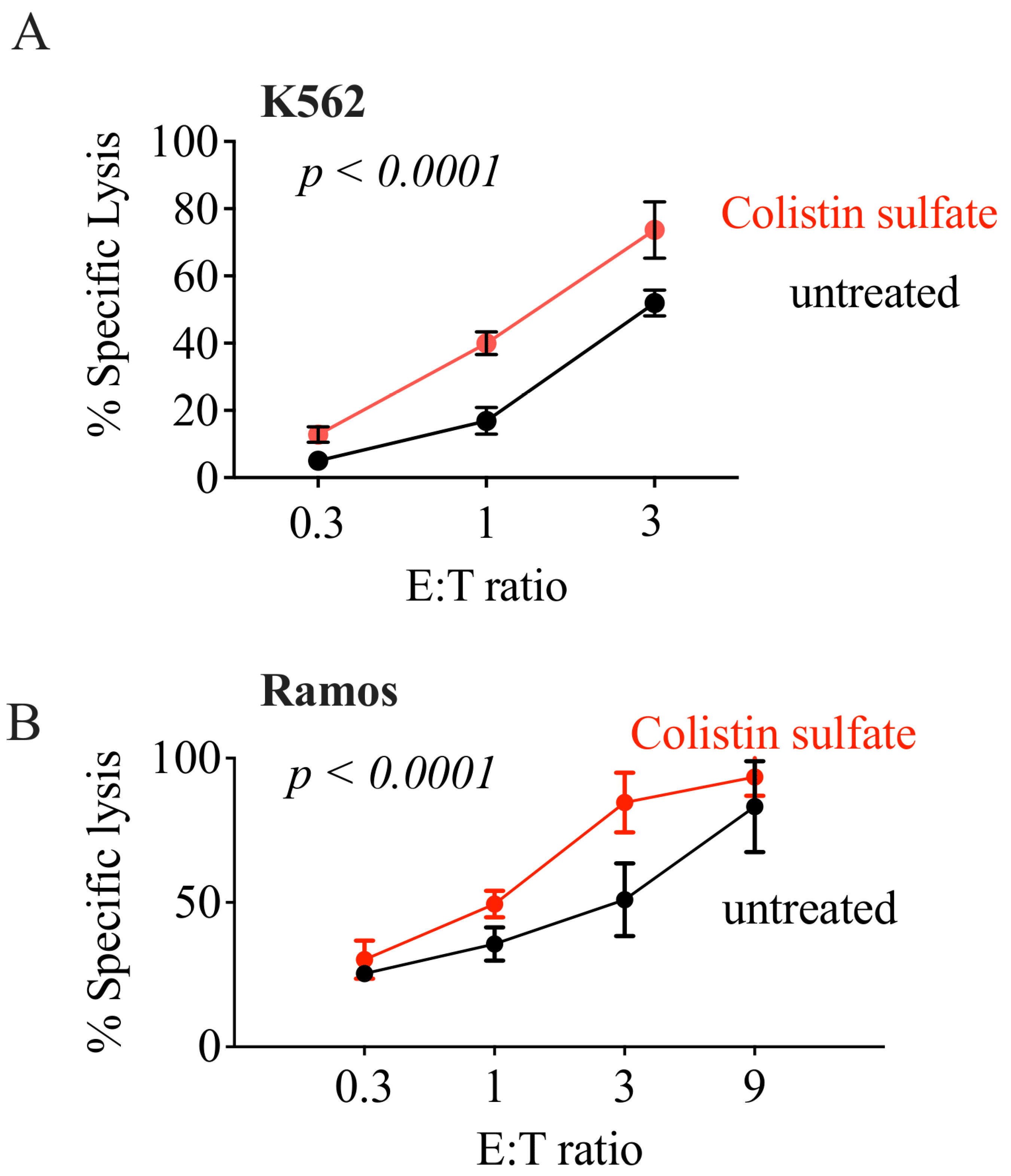
3.6. Colistin Sulfate Increases Cytotoxicity of Primary Human NK Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vesely, M.D.; Kershaw, M.H.; Schreiber, R.D.; Smyth, M.J. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelker, R. Immunotherapy Is Now First-line Therapy for Some Colorectal Cancers. JAMA 2020, 324, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, P.; Peters, S.; Stammers, T.; Soria, J.C. Immunotherapy for the First-Line Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgins, J.J.; Khan, S.T.; Park, M.M.; Auer, R.C.; Ardolino, M. Killers 2.0: NK cell therapies at the forefront of cancer control. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3499–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Iizuka, K.; Aguila, H.L.; Weissman, I.L.; Yokoyama, W.M. In Vivo natural killer cell activities revealed by natural killer cell-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2731–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Thia, K.Y.; Cretney, E.; Kelly, J.M.; Snook, M.B.; Forbes, C.A.; Scalzo, A.A. Perforin is a major contributor to NK cell control of tumor metastasis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6658–6662. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, W.Y.; Powis, S.J. Does Natural Killer Cell Deficiency (NKD) Increase the Risk of Cancer? NKD May Increase the Risk of Some Virus Induced Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, J.S. Natural killer cell deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesian, S.; Schwartz, S.L.; Grantham, S.R.; MacLean, L.K.; Lee, S.N.; Pugh-Toole, M.; Boudreau, J.E. NK cell infiltration is associated with improved overall survival in solid cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Zhu, H.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Xia, Y.; Wu, J.Z.; Wu, W.; Liang, J.-H.; Wang, L.; Fen, L.; Li, J.-Y.; et al. Elevated absolute NK cell counts in peripheral blood predict good prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.A.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kwon, J.; Kim, T.J.; Im, K.; Han, Y.; Kwon, W.; Kim, S.-W.; et al. Defective Localization with Impaired Tumor Cytotoxicity Contributes to the Immune Escape of NK Cells in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, E.; Song, A.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ko, D.H.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Bryceson, Y.; Kim, S.C.; et al. Progressive Impairment of NK Cell Cytotoxic Degranulation Is Associated With TGF-β1 Deregulation and Disease Progression in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Li, C.; Peng, J.; Gao, L.; Liang, X.; Ma, C. Increased expression of programmed cell death protein 1 on NK cells inhibits NK-cell-mediated anti-tumor function and indicates poor prognosis in digestive cancers. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, W.G.; Chisholm, J.D. The Next Generation of Immunotherapy for Cancer: Small Molecules Could Make Big Waves. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, C.J.; Wolf, N.; Chang, I.C.; Kirn, G.; Marcus, A.; Ndubaku, C.O.; McWhirter, S.W.; Raulet, D.H. NK cells mediate clearance of CD8+ T cell-resistant tumors in response to STING agonists. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaaz273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.F.; Li, Y. Small-Molecule Targets in Tumor Immunotherapy. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2018, 8, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, S.; Bekaddour, N.; Besson, L.; Alves de Sousa, R.; Pietrancosta, N.; Viel, S.; Smith, N.; Jacob, Y.; Nisole, S.; Mandal, R.; et al. Identification of Primary Natural Killer Cell Modulators by Chemical Library Screening with a Luciferase-Based Functional Assay. SLAS Discov. 2019, 24, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Choi, J.W.; Park, H.R.; Kim, I.; Kim, H.S. Amphotericin B, an Anti-Fungal Medication, Directly Increases the Cytotoxicity of NK Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theorell, J.; Gustavsson, A.L.; Tesi, B.; Sigmundsson, K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Lundbäck, T.; Bryceson, Y.T. Immunomodulatory activity of commonly used drugs on Fc-receptor-mediated human natural killer cell activation. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ni, Z.; Yao, C.; Zhu, X.; Ni, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S. A High-Throughput Assay for Screening of Natural Products that Enhanced Tumoricidal Activity of NK Cells. Biol. Proced. Online 2015, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Su, L.; Zou, C.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Gong, C.; Ng, W.; Ni, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. A high-throughput assay for screening natural products that boost NK cell-mediated killing of cancer cells. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardolino, M.; Azimi, C.S.; Iannello, A.; Trevino, T.N.; Horan, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W.; Ring, A.M.; Fischer, S.; Garcia, K.C.; et al. Cytokine therapy reverses NK cell anergy in MHC-deficient tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, H.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Choi, S.; Prakash, R.; Natarajan, V.; Prins, R.; Gong, S.; Chitnis, S.D.; Kahn, M.; Chaudhary, V.; et al. Development and characterization of a novel luciferase based cytotoxicity assay. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, C.G.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Cai, W. NanoLuc: A Small Luciferase Is Brightening Up the Field of Bioluminescence. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachanova, V.; McKenna, D.H., Jr.; Luo, X.; Defor, T.E.; Cooley, S.; Warlick, E.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Brachya, G.; Peled, T.; Miller, J.S. First-in-Human Phase I Study of Nicotinamide-Expanded Related Donor Natural Killer Cells for the Treatment of Re-lapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, S175–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conly, J.; Johnston, B. Colistin: The phoenix arises. The phoenix arises. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 17, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Kadota, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Gohda, E. Induction of cytolytic activity and interferon-gamma production in murine natural killer cells by polymyxins B and E. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cirioni, O.; Simonetti, O.; Pierpaoli, E.; Barucca, A.; Ghiselli, R.; Orlando, F.; Pelloni, M.; Cappelletti Trombettoni, M.M.; Guerrieri, M.; Offidani, A.; et al. Colistin enhances therapeutic efficacy of daptomycin or teicoplanin in a murine model of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii sepsis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Cao, X.; Aballay, A. Whole-animal chemical screen identifies colistin as a new immunomodulator that targets conserved pathways. mBio 2014, 5, e01235-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroval, M.Y.; Boyd, A.C.; Young, J.R.; Smith, A.L. A critical role for MAPK signalling pathways in the transcriptional regulation of toll like receptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Niu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Immunomodulatory Effects of Colistin on Macrophages in Rats by Activating the p38/MAPK Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Churov, A.; Fu, R. Research Progress on NK Cell Receptors and Their Signaling Pathways. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 6437057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

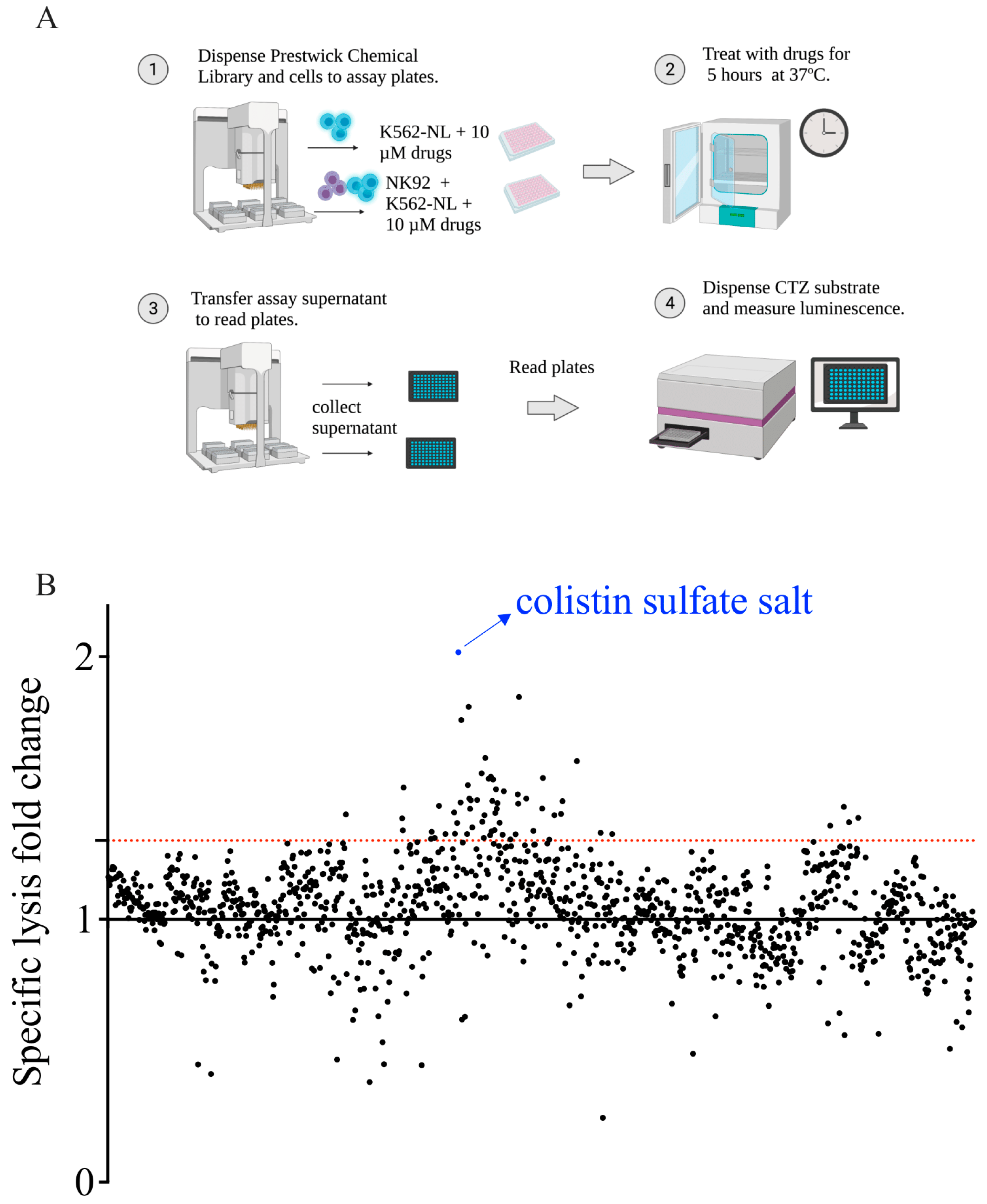
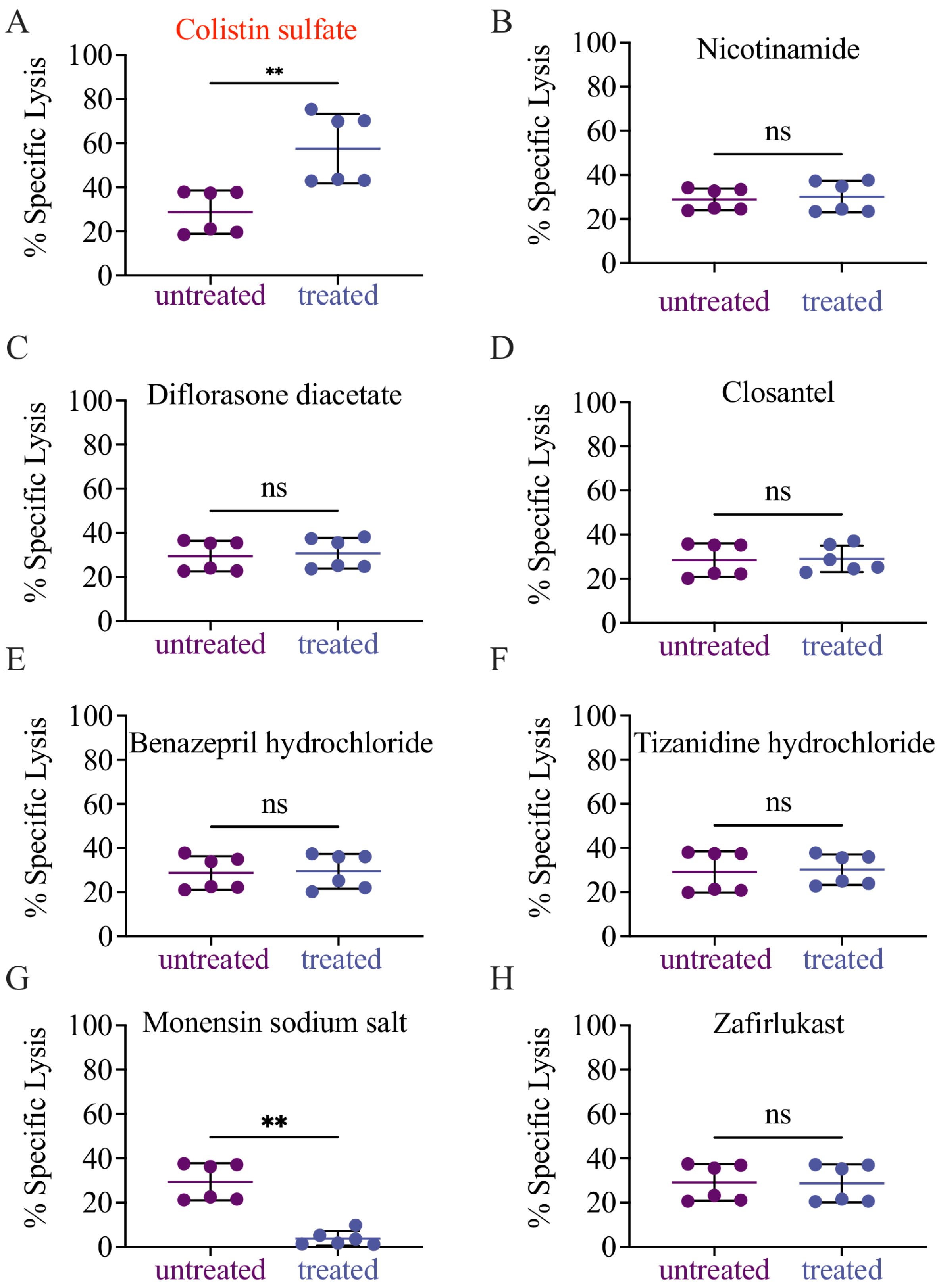


| Drug | Fold-Change | Drug Class | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Colistin sulfate salt a.b | 2.02 | antibiotic |
| 2 | Nicotinamide a | 1.85 | vitamin B3 |
| 3 | Monensin sodium salt a | 1.62 | antibiotic |
| 4 | Butirosin disulfate salt | 1.60 | aminoglycoside antibiotic |
| 5 | Zafirlukast a | 1.54 | anti-asthmatic |
| 6 | Amphotericin B | 1.50 | antifungal |
| 7 | Argatroban | 1.46 | anti-coagulant |
| 8 | Dimethisoquin hydrochloride | 1.45 | anesthetic |
| 9 | Tizanidine hydrochloride a | 1.42 | adrenergic agonist |
| 10 | Closantel a | 1.41 | anti-parasitic |
| 11 | Benazepril hydrochloride a | 1.40 | ACE inhibitor |
| 12 | Diflorasone diacetate a | 1.40 | topical steroid |
| 13 | Butoconazole nitrate | 1.38 | anti-fungal |
| 14 | Etretinate | 1.34 | retinoid |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés-Kaplan, S.; Kurdieh, R.; Hasim, M.S.; Kaczmarek, S.; Taha, Z.; Maznyi, G.; McComb, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Diallo, J.-S.; Ardolino, M. A New Functional Screening Platform Identifies Colistin Sulfate as an Enhancer of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity. Cancers 2022, 14, 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122832
Cortés-Kaplan S, Kurdieh R, Hasim MS, Kaczmarek S, Taha Z, Maznyi G, McComb S, Lee S-H, Diallo J-S, Ardolino M. A New Functional Screening Platform Identifies Colistin Sulfate as an Enhancer of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity. Cancers. 2022; 14(12):2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122832
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés-Kaplan, Serena, Reem Kurdieh, Mohamed S. Hasim, Shelby Kaczmarek, Zaid Taha, Glib Maznyi, Scott McComb, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jean-Simon Diallo, and Michele Ardolino. 2022. "A New Functional Screening Platform Identifies Colistin Sulfate as an Enhancer of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity" Cancers 14, no. 12: 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122832
APA StyleCortés-Kaplan, S., Kurdieh, R., Hasim, M. S., Kaczmarek, S., Taha, Z., Maznyi, G., McComb, S., Lee, S.-H., Diallo, J.-S., & Ardolino, M. (2022). A New Functional Screening Platform Identifies Colistin Sulfate as an Enhancer of Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity. Cancers, 14(12), 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122832








