pH-Responsive Lipid Nanocapsules: A Promising Strategy for Improved Resistant Melanoma Cell Internalization
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Formulation and Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.1.1. Blank Formulation of LNC (BLK)
2.1.2. Fluorescent LNC Formulation
2.1.3. Polymer Post-Insertion
2.1.4. Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.1.5. Stability
2.1.6. Endosome Buffering Effect
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Resazurin Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS): Internalization
2.5. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS): Internalization Pathway
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Complement Activation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Polymer Post-Insertion and Switch Charge Capacities of Modified LNC
3.2. Buffering Effect of pH-Responsive LNC
3.3. Stealth Properties of LNC
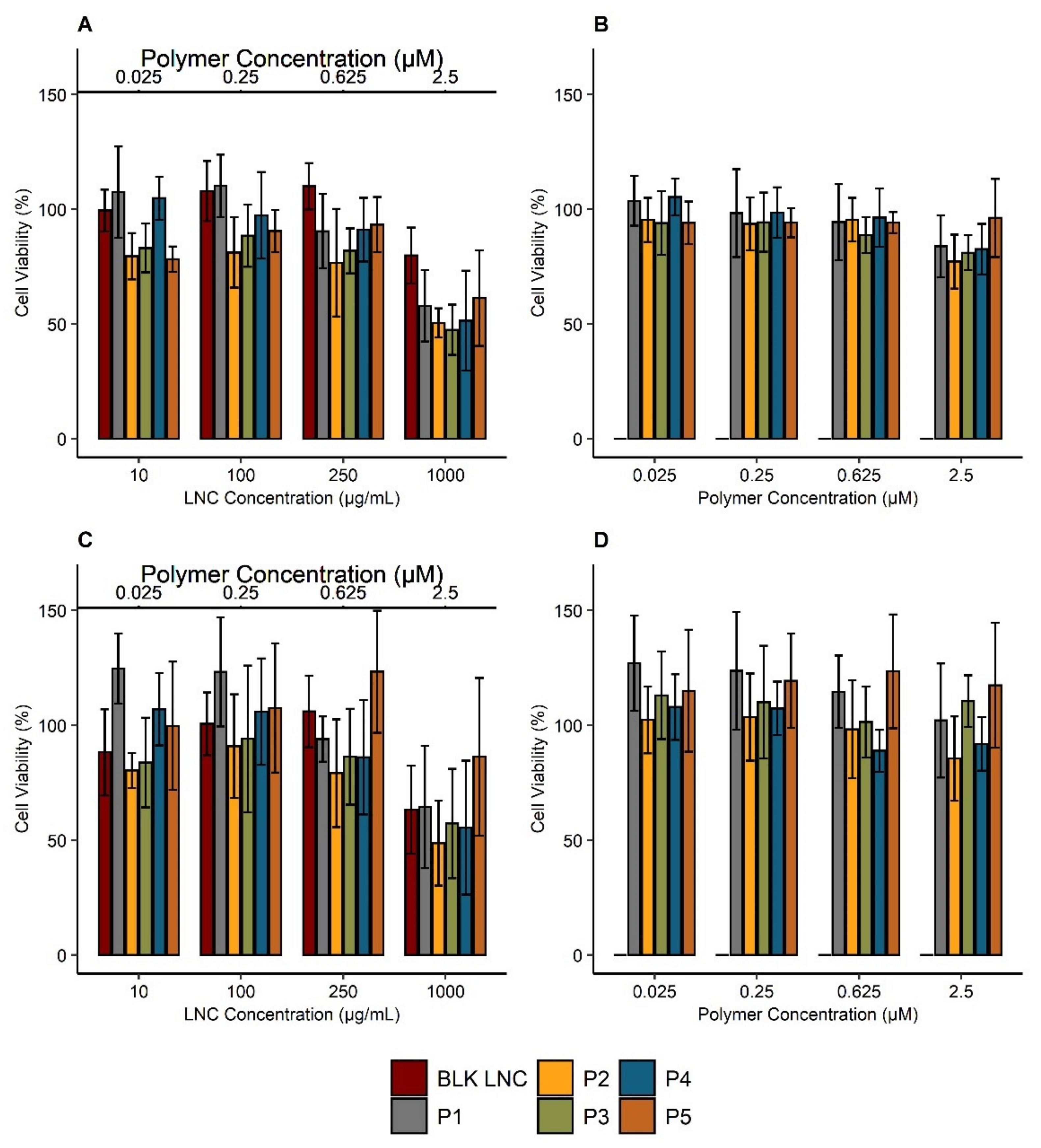
3.4. Impact of Polymers and Modified LNC on Cell Viability
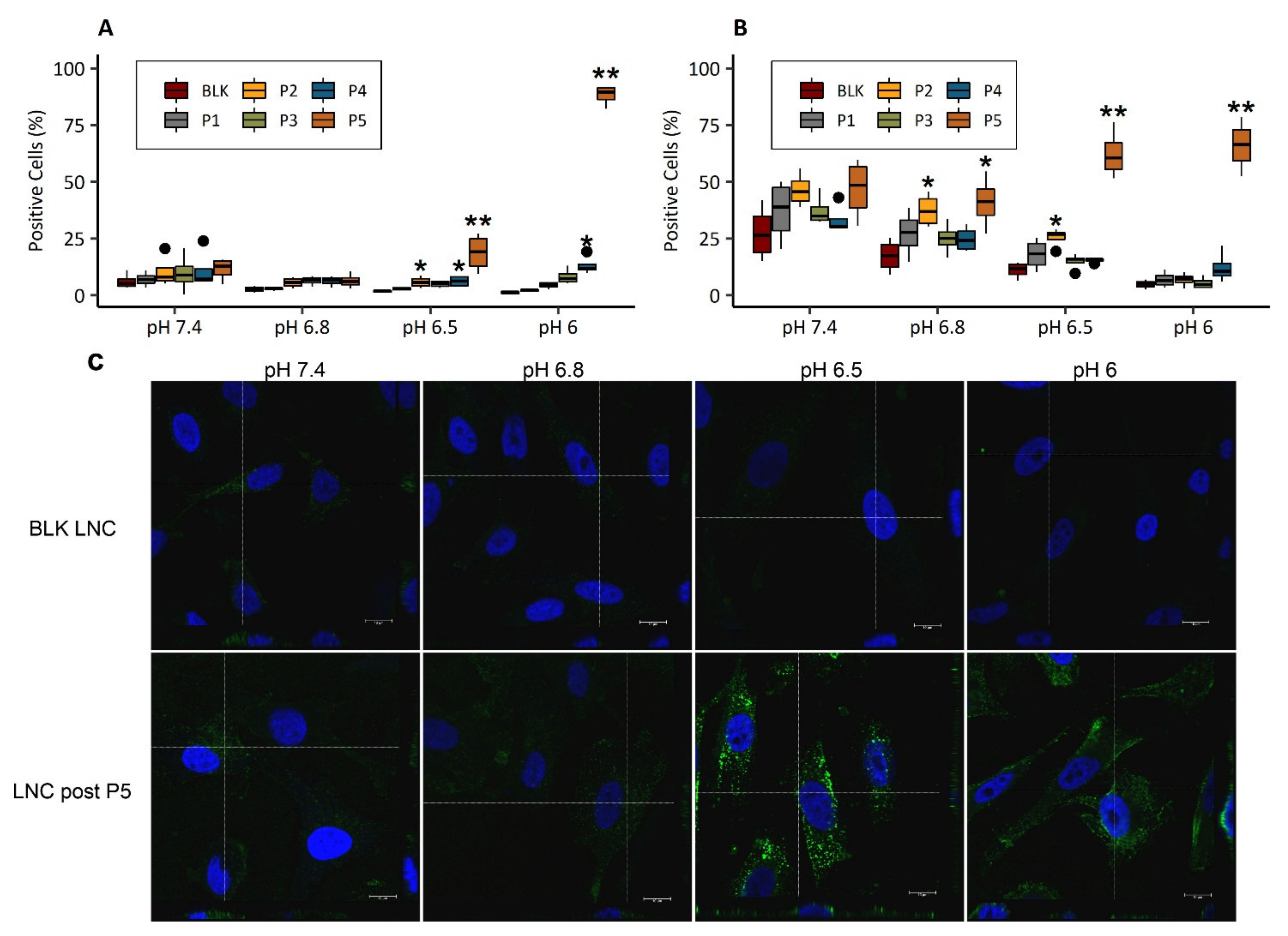
3.5. Cell Uptake of pH-Responsive LNC
3.5.1. pH-Dependent Cellular Uptake
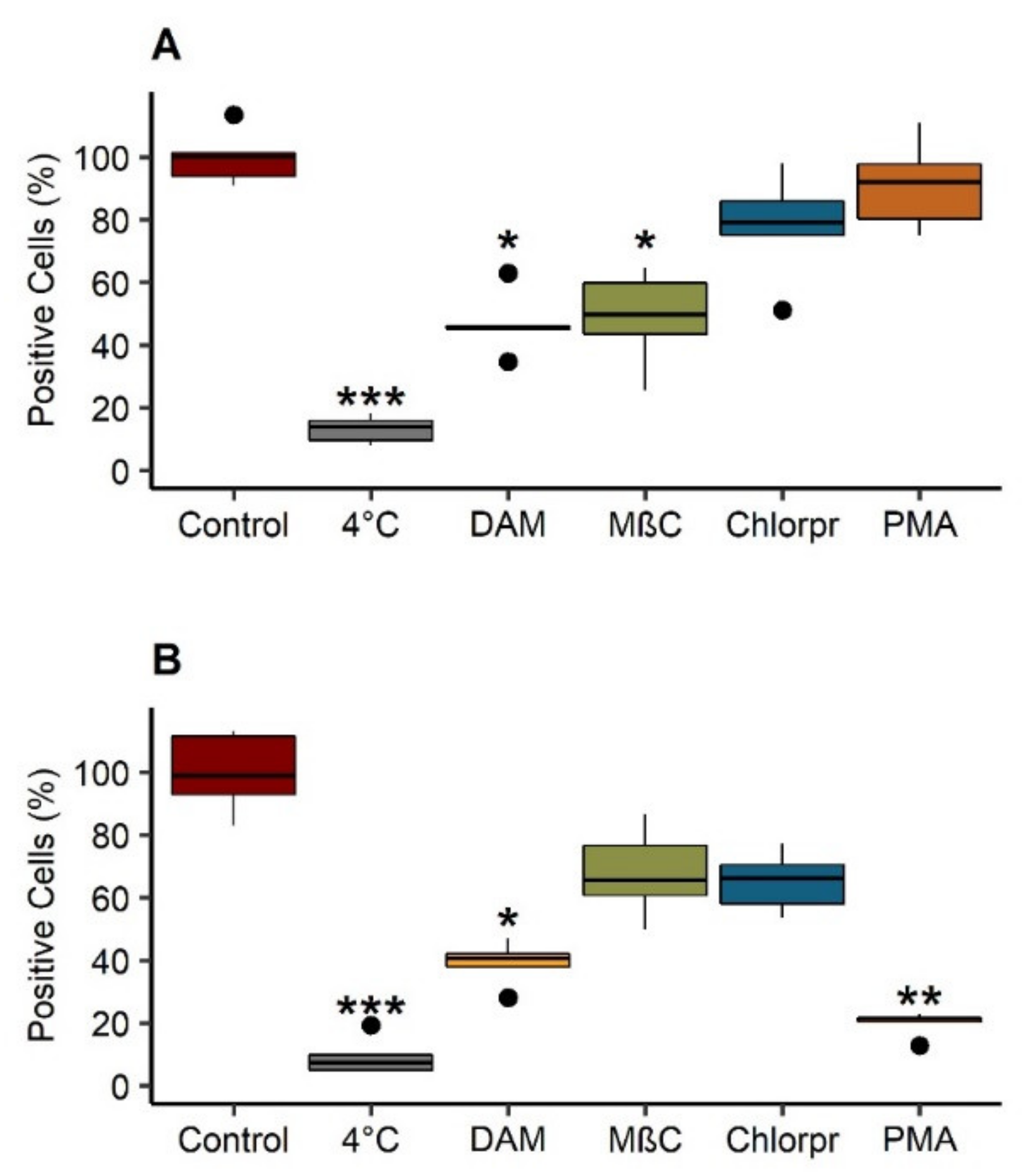
3.5.2. Internalization Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Hodi, F.S.; Wolchok, J.D. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.S.; Tammam, S.N.; Shetab Boushehri, M.A.; Lamprecht, A. MDR in cancer: Addressing the underlying cellular alterations with the use of nanocarriers. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 126, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautu, V.; Mellinger, A.; Resnier, P.; Lepeltier, E.; Martin, L.; Boussemart, L.; Letournel, F.; Passirani, C.; Clere, N. Melanoma tumour vasculature heterogeneity: From mice models to human. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shain, A.H.; Bastian, B.C. From melanocytes to melanomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erin, N.; Grahovac, J.; Brozovic, A.; Efferth, T. Tumor microenvironment and epithelial mesenchymal transition as targets to overcome tumor multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 53, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaraf, Y.G.; Brozovic, A.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Jurkovicova, D.; Linē, A.; Machuqueiro, M.; Saponara, S.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. The multi-factorial nature of clinical multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates 2019, 46, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Boehme, B.; Podda, M.; Henschler, R.; Jager, E.; Tandi, C.; Boehncke, W.-H.; Zollner, T.M.; Kaufmann, R.; Gille, J. Endothelial P-Selectin as a Target of Heparin Action in Experimental Melanoma Lung Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliev, Y.M. Chitosan-based vaccine adjuvants: Incomplete characterization complicates preclinical and clinical evaluation. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.R.; Liu, A.J.; Pudakalakatti, S.; Dutta, P.; Jayaprakash, P.; Bartkowiak, T.; Ager, C.R.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Reuben, A.; Cooper, Z.A.; et al. Melanoma Evolves Complete Immunotherapy Resistance through the Acquisition of a Hypermetabolic Phenotype. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Roy, D.; Schindler, M. Intracellular pH and the control of multidrug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.-Y.; Xu, Y.-M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Recent Progress of Nanocarrier-Based Therapy for Solid Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepeltier, E.; Rijo, P.; Rizzolio, F.; Popovtzer, R.; Petrikaite, V.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Passirani, C. Nanomedicine to target multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 52, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Benoit, J.P. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcion, E.; Lamprecht, A.; Heurtault, B.; Paillard, A.; Aubert-Pouessel, A.; Denizot, B.; Menei, P.; Benoît, J.-P. A new generation of anticancer, drug-loaded, colloidal vectors reverses multidrug resistance in glioma and reduces tumor progression in rats. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, A.; Benoit, J.-P. Etoposide nanocarriers suppress glioma cell growth by intracellular drug delivery and simultaneous P-glycoprotein inhibition. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy Abd-Ellatef, G.-E.; Gazzano, E.; Chirio, D.; Ragab Hamed, A.; Belisario, D.C.; Zuddas, C.; Peira, E.; Rolando, B.; Kopecka, J.; Assem Said Marie, M.; et al. Curcumin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Bypass P-Glycoprotein Mediated Doxorubicin Resistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, L.; Srivastava, S.; Panjeta, A.; Chaudhari, D.; Ghadi, R.; Kuche, K.; Malik, R.; Preet, S.; Jain, S.; Raza, K. Exploration of docetaxel palmitate and its solid lipid nanoparticles as a novel option for alleviating the rising concern of multi-drug resistance. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, E.; Passirani, C.; Garcion, E.; Pigeon, P.; Vessières, A.; Jaouen, G.; Benoit, J.P. Lipid nanocapsules loaded with an organometallic tamoxifen derivative as a novel drug-carrier system for experimental malignant gliomas. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, E.; Huynh, N.T.; Vessières, A.; Pigeon, P.; Jaouen, G.; Benoit, J.P.; Passirani, C. Dose effect activity of ferrocifen-loaded lipid nanocapsules on a 9L-glioma model. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, E.; Jarnet, D.; Vessières, A.; Vinchon-Petit, S.; Jaouen, G.; Benoit, J.P.; Passirani, C. Local delivery of ferrociphenol lipid nanocapsules followed by external radiotherapy as a synergistic treatment against intracranial 9L glioma xenograft. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, N.T.; Morille, M.; Bejaud, J.; Legras, P.; Vessieres, A.; Jaouen, G.; Benoit, J.-P.; Passirani, C. Treatment of 9L Gliosarcoma in Rats by Ferrociphenol-Loaded Lipid Nanocapsules Based on a Passive Targeting Strategy via the EPR Effect. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.T.; Passirani, C.; Allard-Vannier, E.; Lemaire, L.; Roux, J.; Garcion, E.; Vessieres, A.; Benoit, J.P. Administration-dependent efficacy of ferrociphenol lipid nanocapsules for the treatment of intracranial 9L rat gliosarcoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, A.L.; Huynh, N.T.; Clavreul, A.; Balzeau, J.; Béjaud, J.; Vessieres, A.; Benoit, J.P.; Eyer, J.; Passirani, C. Brain tumour targeting strategies via coated ferrociphenol lipid nanocapsules. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainé, A.L.; Adriaenssens, E.; Vessières, A.; Jaouen, G.; Corbet, C.; Desruelles, E.; Pigeon, P.; Toillon, R.A.; Passirani, C. The in vivo performance of ferrocenyl tamoxifen lipid nanocapsules in xenografted triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6949–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainé, A.L.; Clavreul, A.; Rousseau, A.; Tétaud, C.; Vessieres, A.; Garcion, E.; Jaouen, G.; Aubert, L.; Guilbert, M.; Benoit, J.P.; et al. Inhibition of ectopic glioma tumor growth by a potent ferrocenyl drug loaded into stealth lipid nanocapsules. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Guan, S.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Q. Polymeric Micelles with Uniform Surface Properties and Tunable Size and Charge: Positive Charges Improve Tumor Accumulation. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.R.; Bondurant, B.; McLean, S.D.; McGovern, K.A.; O’Brien, D.F. Liposome-cell interactions in vitro: Effect of liposome surface charge on the binding and endocytosis of conventional and sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 12875–12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, C.; Molinaro, R.; Taraballi, F.; Toledano Furman, N.E.; Sherman, M.B.; Parodi, A.; Salvatore, F.; Tasciotti, E. Effects of the protein corona on liposome-liposome and liposome-cell interactions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3049–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya James, H.; John, R.; Alex, A.; Anoop, K.R. Smart polymers for the controlled delivery of drugs-a concise overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fujita, Y.; Onishi, N.; Ogawara, K.-i.; Nakayama, H.; Mukai, T. Preparation and characterization of lipid emulsions containing styrene maleic acid copolymer for the development of pH-responsive drug carriers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2020, 232, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Ou, T.W.; Chen, H.H.; Tsai, H.C.; Wen, C.J.; Lo, C.L.; Wey, S.P.; Lin, K.J.; Yen, T.C.; et al. Multifunctional hollow nanoparticles based on graft-diblock copolymers for doxorubicin delivery. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala-Lagunes, E.; Ruiz, J.C.; Varca, G.H.C.; Bucio, E. Synthesis and characterization of stimuli-responsive polypropylene containing N-vinylcaprolactam and N-vinylimidazole obtained by ionizing radiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 67, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kamada, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kodaira, H.; Tsunoda, S.; Okamoto, T.; Mukai, Y.; Shibata, H.; et al. The use of PVP as a polymeric carrier to improve the plasma half-life of drugs. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.M.; Navale, T.S.; Bates, F.S.; Reineke, T.M. Precise Compositional Control and Systematic Preparation of Multimonomeric Statistical Copolymers. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Feijen, J.; Lok, M.C.; Hennink, W.E.; Christensen, L.V.; Yockman, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.W. Low molecular weight linear polyethylenimine-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-polyethylenimine triblock copolymers: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro gene transfer properties. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3440–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchardt, F.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Schwarz, H.; Fischer, R.; Brock, R. A comprehensive model for the cellular uptake of cationic cell-penetrating peptides. Traffic 2007, 8, 848–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.A.; Chen, Y.; Norkin, L.C. Bound simian virus 40 translocates to caveolin-enriched membrane domains, and its entry is inhibited by drugs that selectively disrupt caveolae. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, T.; Soriano, J.; Barrios, L.; Ibanez, E.; Nogues, C. Surface modification of microparticles causes differential uptake responses in normal and tumoral human breast epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passirani, C.; Barratt, G.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Labarre, D. Interactions of nanoparticles bearing heparin or dextran covalently bound to poly(methyl methacrylate) with the complement system. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. The Pairwise Multiple Comparison of Mean Ranks Package (PMCMR). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=PMCMR (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Vonarbourg, A.; Passirani, C.; Saulnier, P.; Simard, P.; Leroux, J.C.; Benoit, J.P. Evaluation of pegylated lipid nanocapsules versus complement system activation and macrophage uptake. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivusalo, M.; Welch, C.; Hayashi, H.; Scott, C.C.; Kim, M.; Alexander, T.; Touret, N.; Hahn, K.M.; Grinstein, S. Amiloride inhibits macropinocytosis by lowering submembranous pH and preventing Rac1 and Cdc42 signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodal, S.K.; Skretting, G.; Garred, O.; Vilhardt, F.; van Deurs, B.; Sandvig, K. Extraction of cholesterol with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin perturbs formation of clathrin-coated endocytic vesicles. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmer, S.; van Deurs, B.; Sandvig, K. Membrane ruffling and macropinocytosis in A431 cells require cholesterol. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gratton, S.E.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, A.L.; Gravier, J.; Henry, M.; Sancey, L.; Bejaud, J.; Pancani, E.; Wiber, M.; Texier, I.; Coll, J.L.; Benoit, J.P.; et al. Conventional versus stealth lipid nanoparticles: Formulation and in vivo fate prediction through FRET monitoring. J. Control. Release 2014, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, D.; Rethore, G.; Newland, B.; Parra, J.; Elvira, C.; Pandit, A.; Rojo, L.; San Roman, J. Low polydispersity (N-ethyl pyrrolidine methacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) linear oligomers for gene therapy applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarley, C.R.T.; Corazza, M.Z.; Somera, B.F.; Segatelli, M.G. Preparation of new ion-selective cross-linked poly(vinylimidazole-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) using a double-imprinting process for the preconcentration of Pb2+ ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Sheth, V.R.; Pagel, M.D. Imaging in vivo extracellular pH with a single paramagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Mol. Imaging 2012, 11, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussif, O.; Lezoualc’h, F.; Zanta, M.A.; Mergny, M.D.; Scherman, D.; Demeneix, B.; Behr, J.P. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: Polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7297–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asayama, S.; Nishinohara, S.; Kawakami, H. Zinc-chelated poly(1-vinylimidazole) and a carbohydrate ligand polycation form DNA ternary complexes for gene delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakamatani, T.; Asayama, S.; Kawakami, H. Synthesis of alkylated poly(1-vinylimidazole) for a new pH-sensitive DNA carrier. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 2008, 52, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Resnier, P.; Guillot, A.; Pitard, B.; Benoit, J.P.; Passirani, C. siRNA LNCs—A novel platform of lipid nanocapsules for systemic siRNA administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Topin-Ruiz, S.; Mellinger, A.; Lepeltier, E.; Bourreau, C.; Fouillet, J.; Riou, J.; Jaouen, G.; Martin, L.; Passirani, C.; Clere, N. p722 ferrocifen loaded lipid nanocapsules improve survival of murine xenografted-melanoma via a potentiation of apoptosis and an activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierstead, P.H.; Okochi, H.; Venditto, V.J.; Chuong, T.C.; Kivimae, S.; Frechet, J.M.J.; Szoka, F.C. The effect of polymer backbone chemistry on the induction of the accelerated blood clearance in polymer modified liposomes. J. Control. Release 2015, 213, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Maeda, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Takasaki, N.; Shigyo, M.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H.; Mizushima, Y.; Mizushima, T. Evasion of the accelerated blood clearance phenomenon by coating of nanoparticles with various hydrophilic polymers. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.; Vadon, M.; Rinner, B.; Novak, A.; Wintersteiger, R.; Frohlich, E. The role of nanoparticle size in hemocompatibility. Toxicology 2009, 258, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskov, A.N.; Kulikov, P.P.; Shtilman, M.I.; Rakitskii, V.N.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Amphiphilic poly-N-vynilpyrrolidone nanoparticles: Cytotoxicity and acute toxicity study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundel, D.; Allmeroth, M.; Reime, S.; Zentel, R.; Thews, O. Endocytotic uptake of HPMA-based polymers by different cancer cells: Impact of extracellular acidosis and hypoxia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5571–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnier, P.; Galopin, N.; Sibiril, Y.; Clavreul, A.; Cayon, J.; Briganti, A.; Legras, P.; Vessières, A.; Montier, T.; Jaouen, G.; et al. Efficient ferrocifen anticancer drug and Bcl-2 gene therapy using lipid nanocapsules on human melanoma xenograft in mouse. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 126, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Lepeltier, E.; Esnault, L.; Pigeon, P.; Lemaire, L.; Lépinoux-Chambaud, C.; Clere, N.; Jaouen, G.; Eyer, J.; Piel, G.; et al. Enhanced and preferential internalization of lipid nanocapsules into human glioblastoma cells: Effect of a surface-functionalizing NFL peptide. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13485–13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnier, P.; Lepeltier, E.; Emina, A.L.; Galopin, N.; Bejaud, J.; David, S.; Ballet, C.; Benvegnu, T.; Pecorari, F.; Chourpa, I.; et al. Model Affitin and PEG modifications onto siRNA lipid nanocapsules: Cell uptake and in vivo biodistribution improvements. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27264–27278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Jacobs, T.M.; McCallen, J.D.; Moore, D.T.; Huckaby, J.T.; Edelstein, J.N.; Lai, S.K. Analysis of Pre-existing IgG and IgM Antibodies against Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) in the General Population. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11804–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. Tumor delivery of macromolecular drugs based on the EPR effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Zaguilan, R.; Seftor, E.A.; Seftor, R.E.; Chu, Y.W.; Gillies, R.J.; Hendrix, M.J. Acidic pH enhances the invasive behavior of human melanoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1996, 14, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
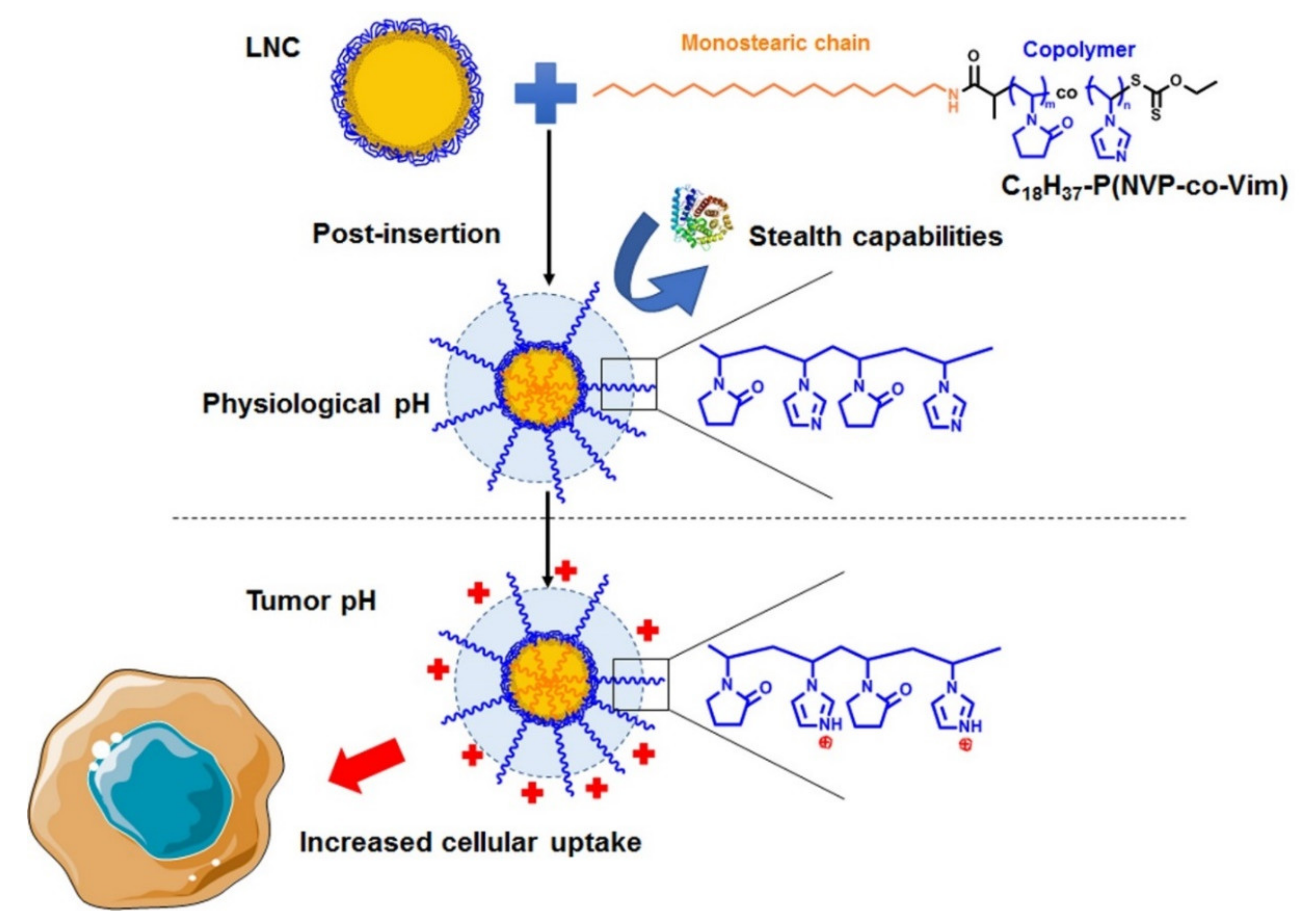
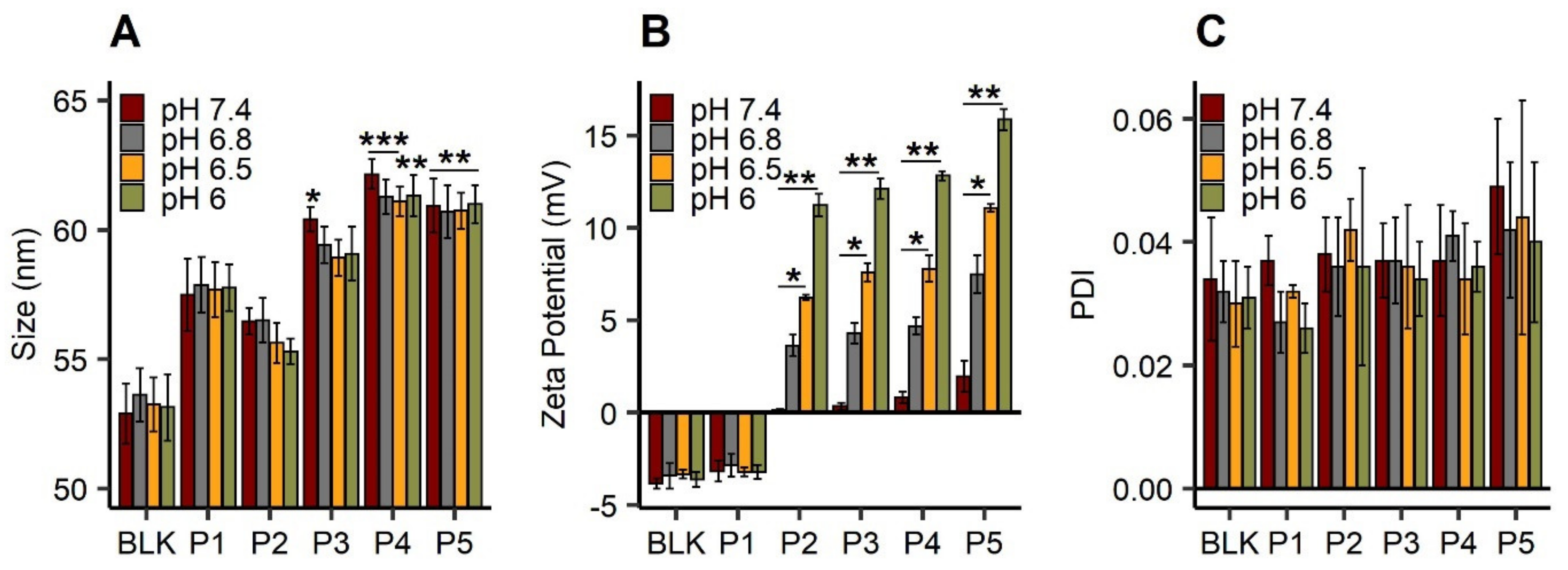
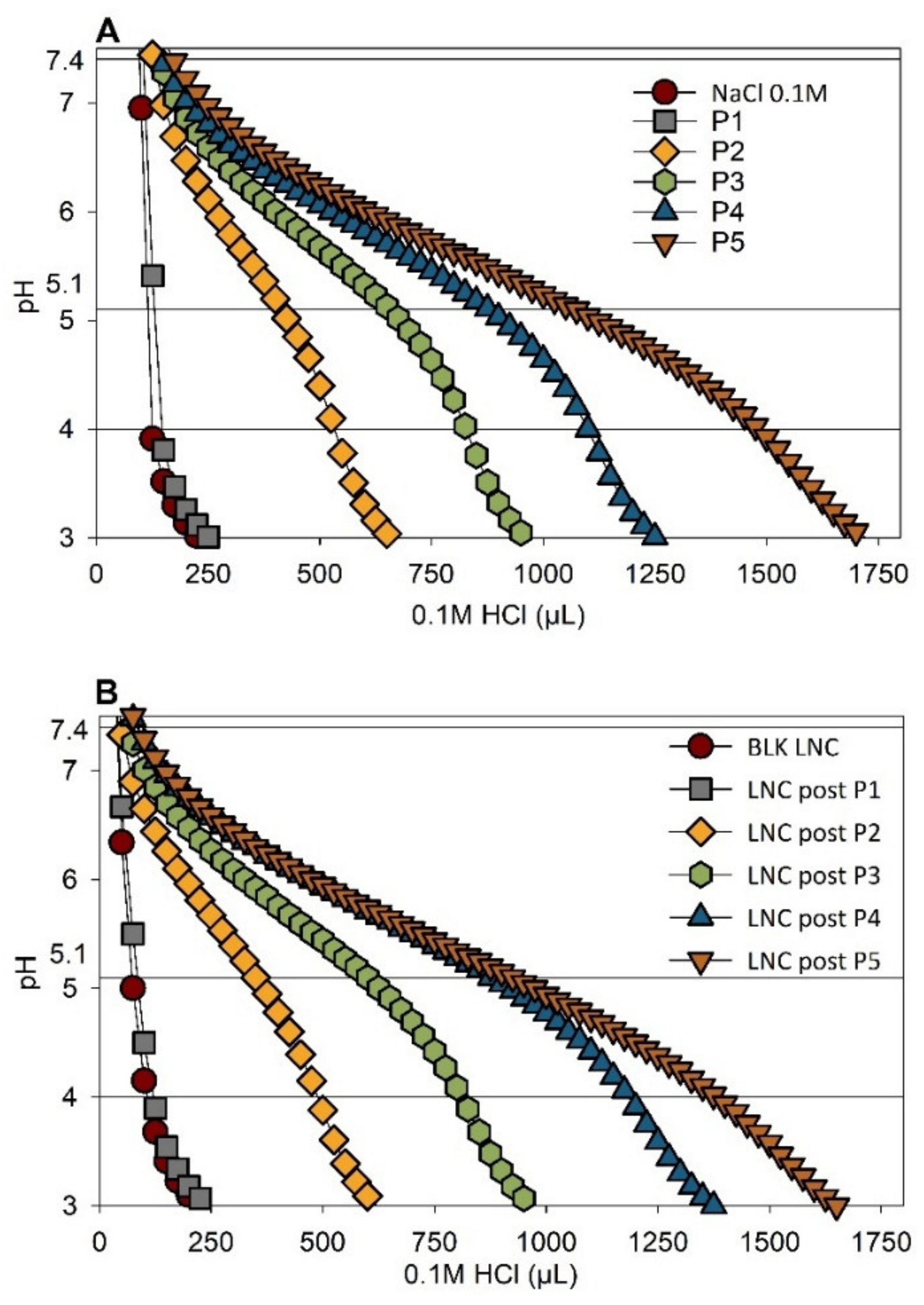
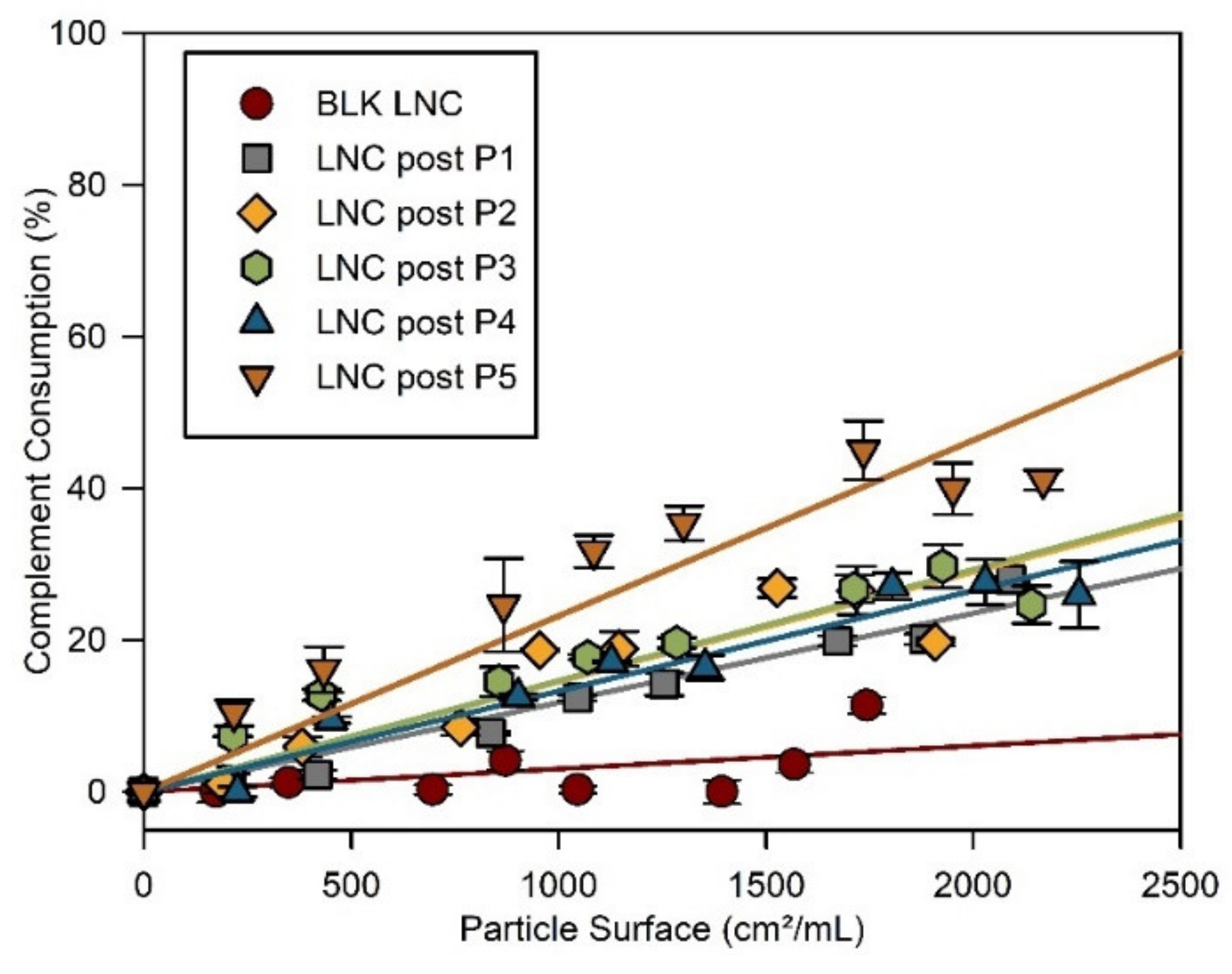
| Entry | Copolymer Composition | DP | Mn (g·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | C18H37-PNVP49 | 49 | 5900 |
| P2 | C18H37-P(NVP15-co-Vim5) | 20 | 2600 |
| P3 | C18H37-P(NVP22-co-Vim8) | 30 | 3600 |
| P4 | C18H37-P(NVP35-co-Vim10) | 45 | 5300 |
| P5 | C18H37-P(NVP21-co-Vim15) | 36 | 4200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pautu, V.; Lepeltier, E.; Mellinger, A.; Riou, J.; Debuigne, A.; Jérôme, C.; Clere, N.; Passirani, C. pH-Responsive Lipid Nanocapsules: A Promising Strategy for Improved Resistant Melanoma Cell Internalization. Cancers 2021, 13, 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092028
Pautu V, Lepeltier E, Mellinger A, Riou J, Debuigne A, Jérôme C, Clere N, Passirani C. pH-Responsive Lipid Nanocapsules: A Promising Strategy for Improved Resistant Melanoma Cell Internalization. Cancers. 2021; 13(9):2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092028
Chicago/Turabian StylePautu, Vincent, Elise Lepeltier, Adélie Mellinger, Jérémie Riou, Antoine Debuigne, Christine Jérôme, Nicolas Clere, and Catherine Passirani. 2021. "pH-Responsive Lipid Nanocapsules: A Promising Strategy for Improved Resistant Melanoma Cell Internalization" Cancers 13, no. 9: 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092028
APA StylePautu, V., Lepeltier, E., Mellinger, A., Riou, J., Debuigne, A., Jérôme, C., Clere, N., & Passirani, C. (2021). pH-Responsive Lipid Nanocapsules: A Promising Strategy for Improved Resistant Melanoma Cell Internalization. Cancers, 13(9), 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092028







