3D Model Characterization by 2D and 3D Imaging in t(14;18)-Positive B-NHL: Perspectives for In Vitro Drug Screens in Follicular Lymphoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
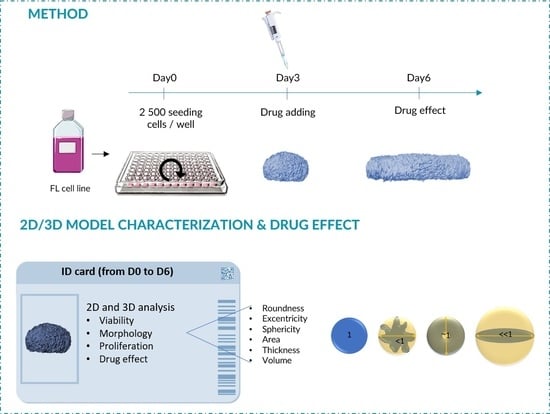
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Drugs
2.2. ULA-MALC Generation
2.3. ULA-MALC Characterization by 2D Imaging
- Volume was calculated as described [23] according to the formula:
- Sphericity index (SI): the spherical geometry shape was calculated according to Equations (3) and (4):ULA-MALC were considered spherical when SI = 1.
- Roundness index (RI) corresponded to the circularity of the ULA-MALC where a perfect circle = 1.
- Solidity is an indicator of the roughness of the spheroidal surface. This index was determined to assess its regularity.
2.4. ULA-MALC Characterization by 3D Imaging
- Volume.
- Eccentricity:with a: longest ellipsoid axis, b: second longest ellipsoid axis, c: shortest ellipsoid axis. Eccentricity = 0 for a perfect sphere and increases following ellipsoid deformation with a maximum of 1.
- Sphericity:
- A sphere is considered perfect when S = 1 and decreases with the rugosity or deformation of the shape.
- Roundness:
- Roundness = 1 for a perfect sphere and decreases with deformation.
2.5. Visualization of Proliferative Cells in Whole ULA-MALC
2.6. Determination of Cell Death by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Determination of Cell Viability by Trypan Blue Assay
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
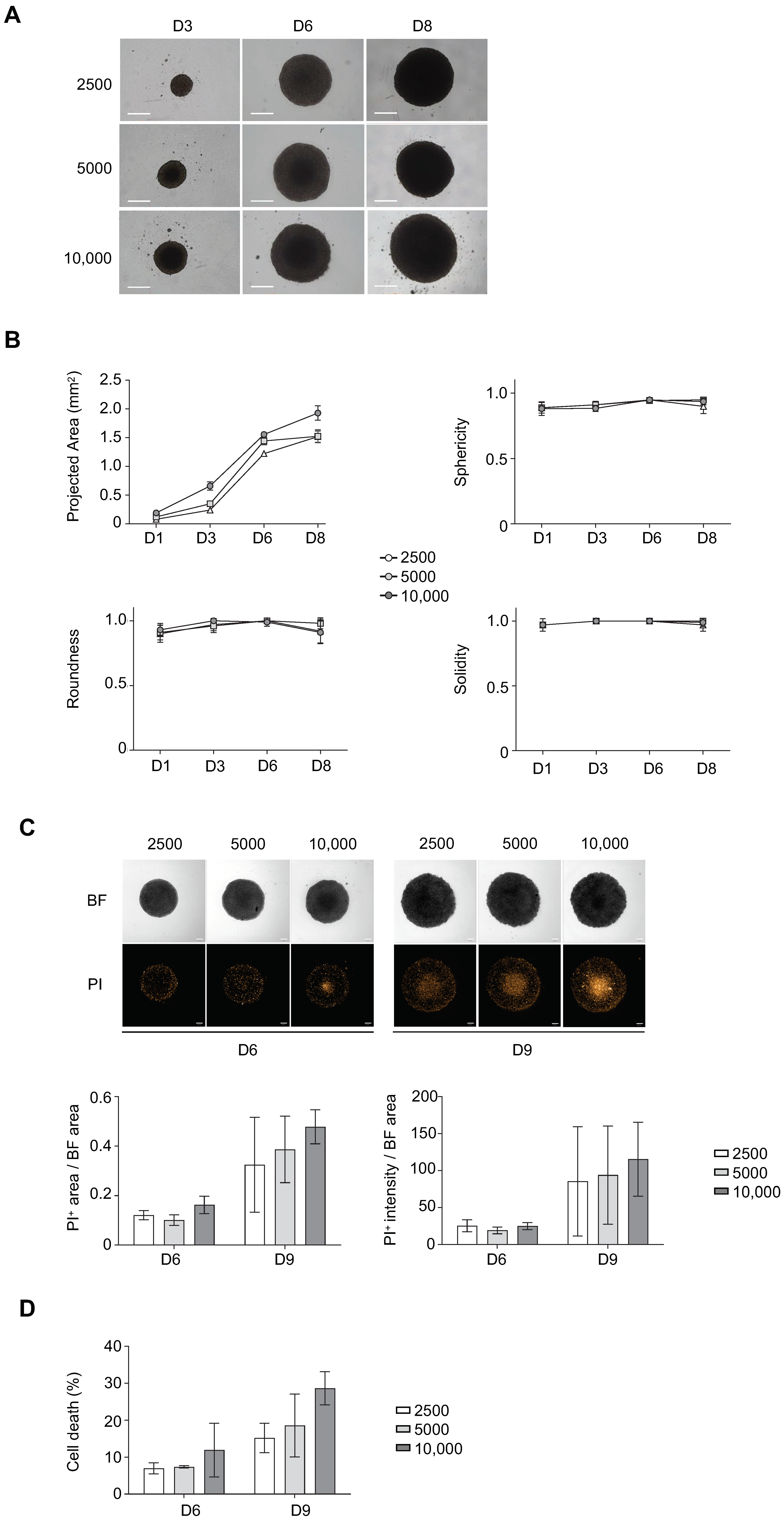
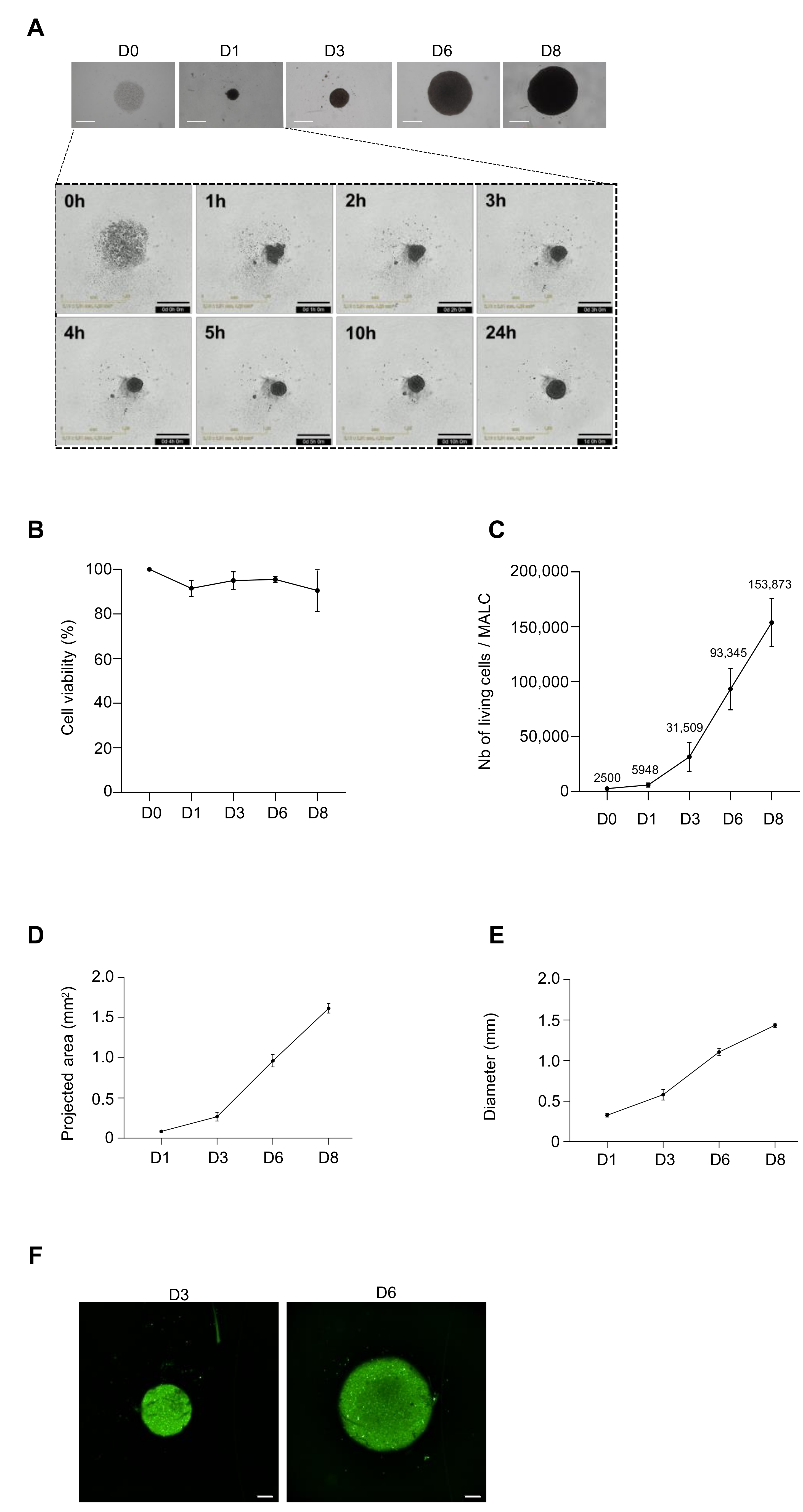
3.1. Determination of Optimal Cell Seeding Density for ULA-MALC Formation
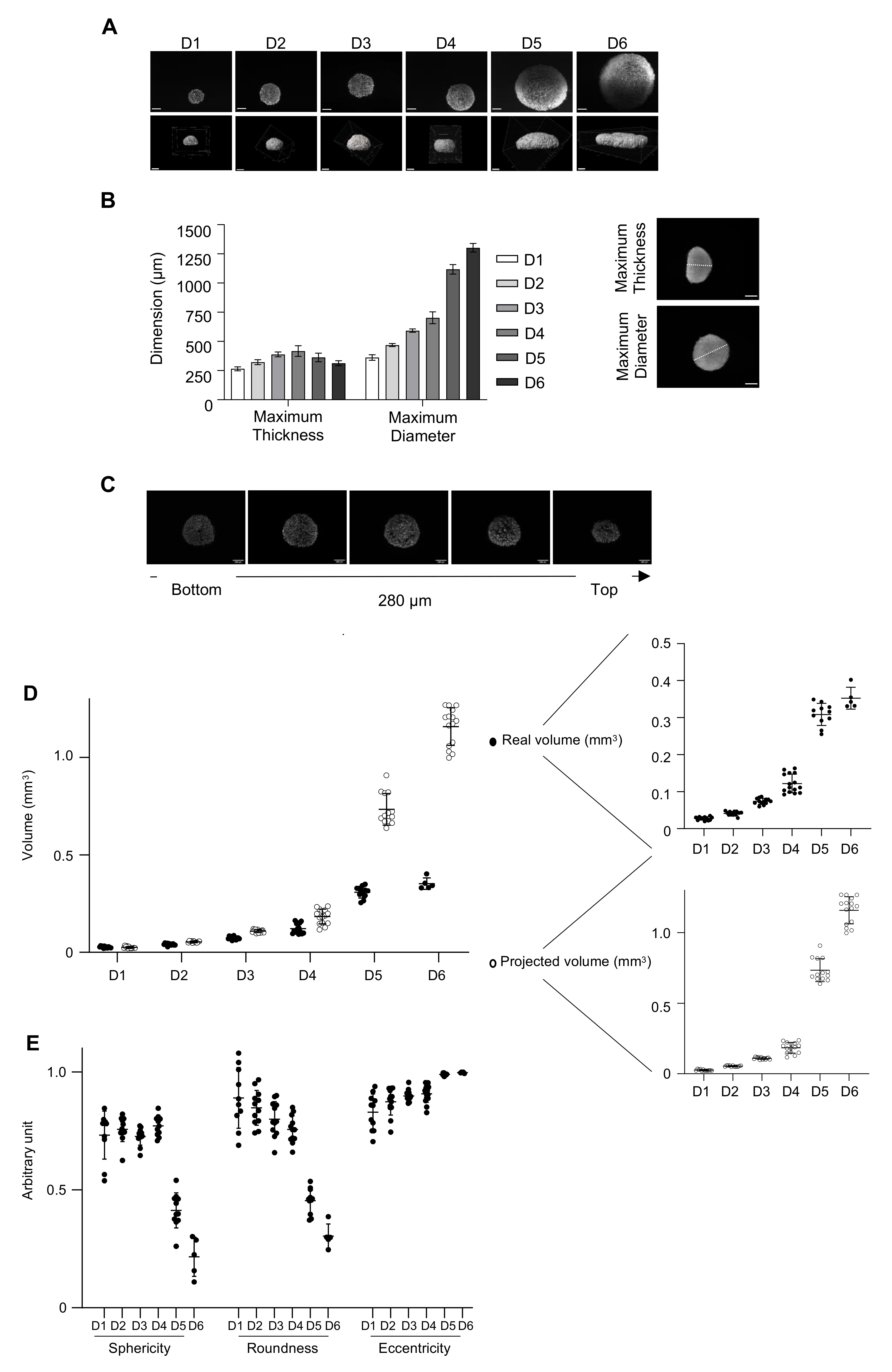
3.2. Biological Characterization of ULA-MALC
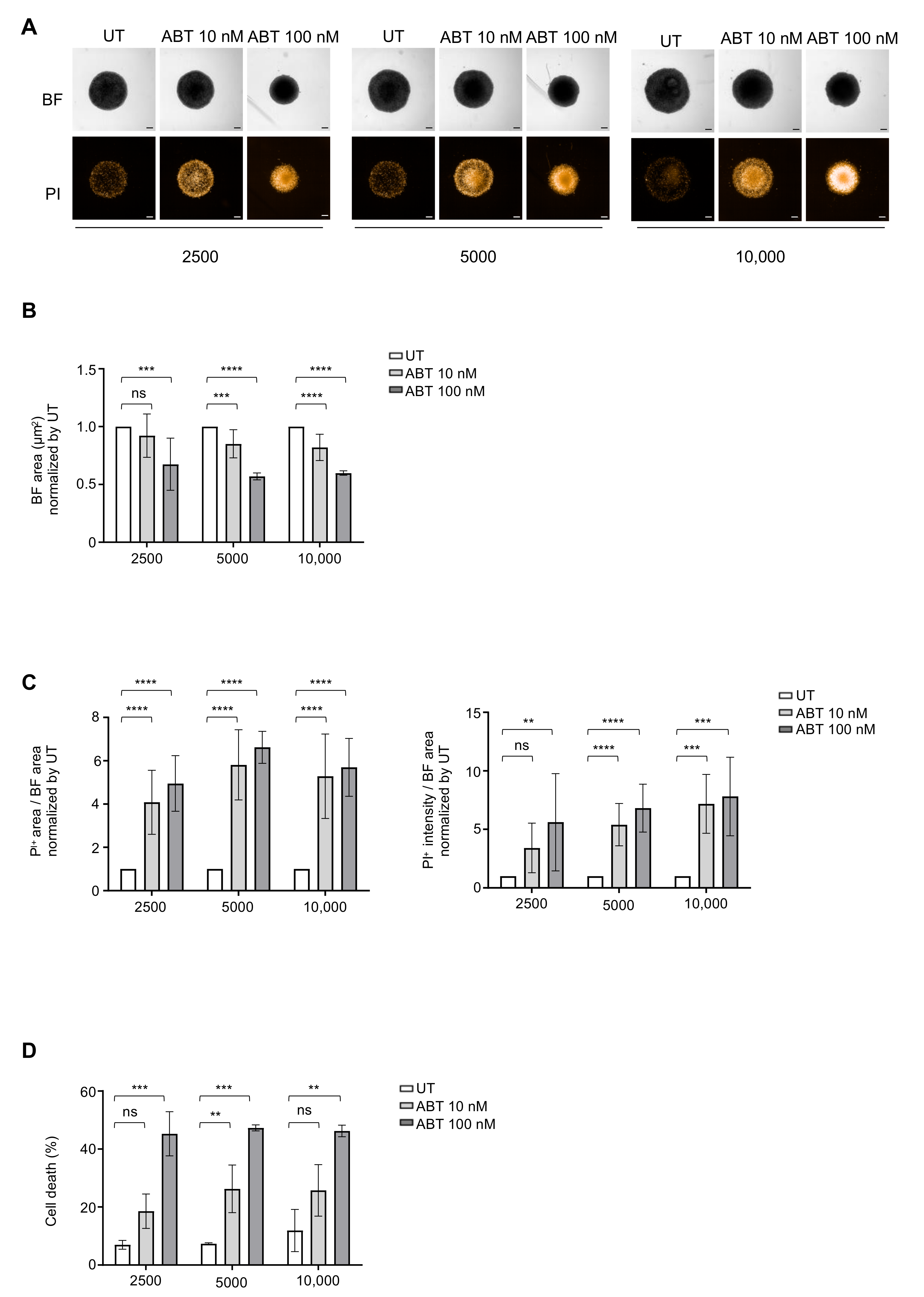
3.3. Determination of Optimal Cell Density for Drug Testing
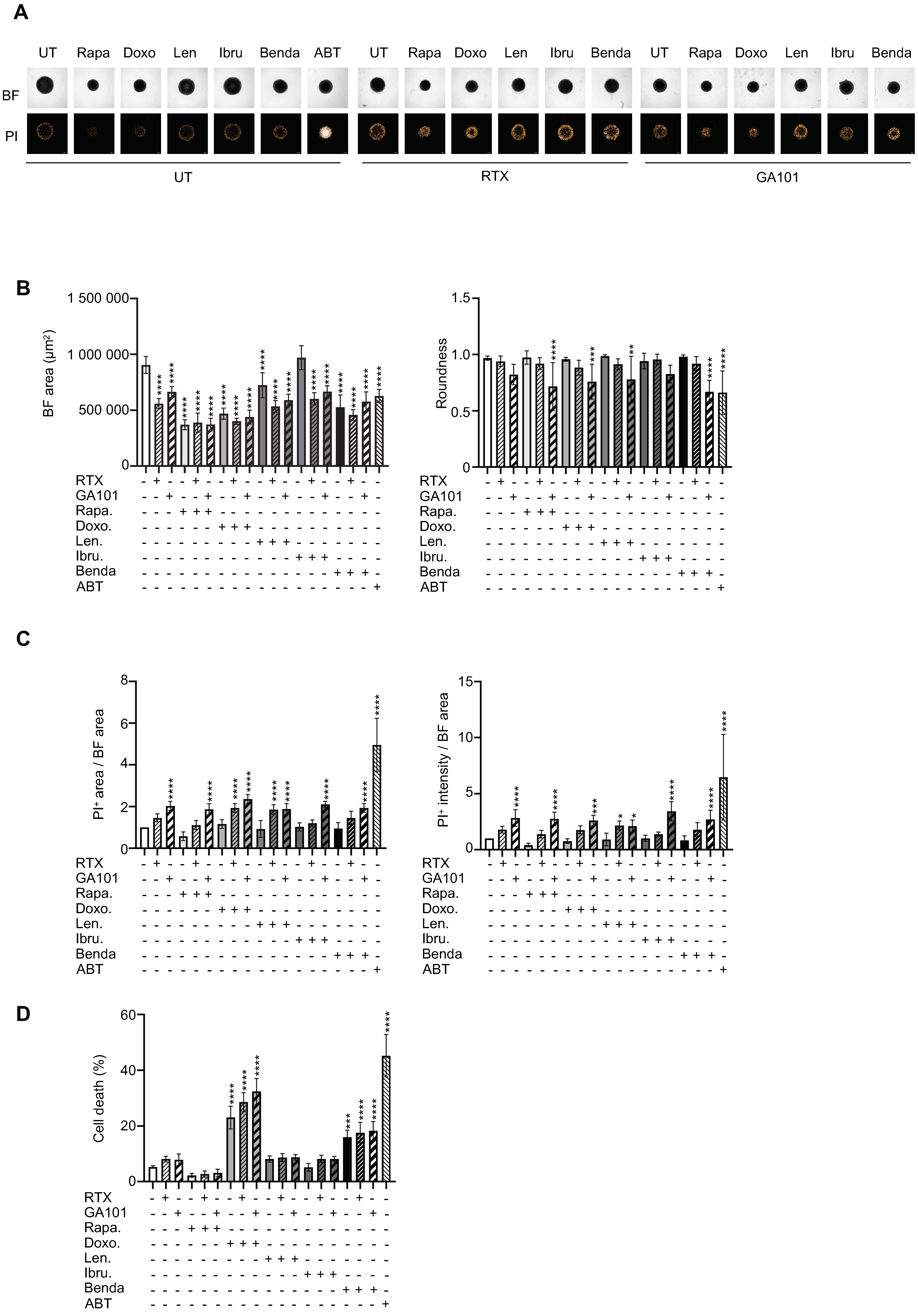
3.4. Drug Sensitivity Testing
3.5. Three-Dimensional Imaging to Characterize the 3D Model
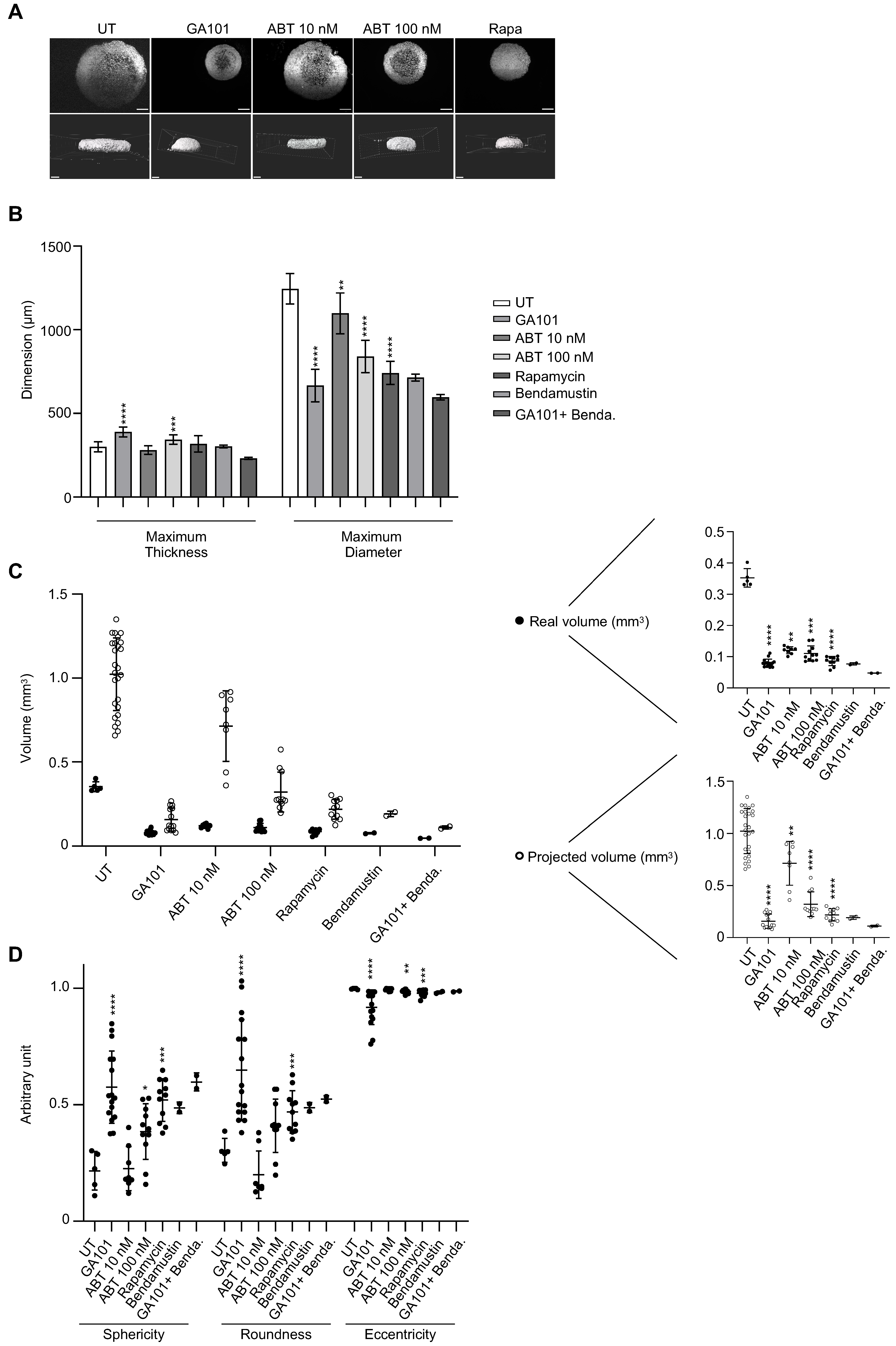
3.6. Three-Dimensional Imaging to Evaluate Drug Sensitivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carbone, A.; Roulland, S.; Gloghini, A.; Younes, A.; von Keudell, G.; López-Guillermo, A.; Fitzgibbon, J. Follicular Lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dada, R. Diagnosis and Management of Follicular Lymphoma: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 103, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampaloni, F.; Reynaud, E.G.; Stelzer, E.H.K. The Third Dimension Bridges the Gap between Cell Culture and Live Tissue. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.M.; McCredie, J.A.; Inch, W.R. Growth of Multicell Spheroids in Tissue Culture as a Model of Nodular Carcinomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1971, 46, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simian, M.; Bissell, M.J. Organoids: A Historical Perspective of Thinking in Three Dimensions. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, P.; Aulner, N.; Bickle, M.; Davies, A.M.; Nery, E.D.; Ebner, D.; Montoya, M.C.; Östling, P.; Pietiäinen, V.; Price, L.S.; et al. Screening out Irrelevant Cell-Based Models of Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 751–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissell, M.J. Goodbye Flat Biology—Time for the 3rd and the 4th Dimensions. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Freyer, J.P.; Hofstaedter, F.; Ebner, R. The Use of 3-D Cultures for High-Throughput Screening: The Multicellular Spheroid Model. J. Biomol. Screen 2004, 9, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Seidel, C.; Ebner, R.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Spheroid-Based Drug Screen: Considerations and Practical Approach. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampaloni, F.; Stelzer, E. Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures in Toxicology. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2010, 26, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirenko, O.; Mitlo, T.; Hesley, J.; Luke, S.; Owens, W.; Cromwell, E.F. High-Content Assays for Characterizing the Viability and Morphology of 3D Cancer Spheroid Cultures. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2015, 13, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Piccinini, F.; Arienti, C.; Zamagni, A.; Santi, S.; Polico, R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tesei, A. 3D Tumor Spheroid Models for in Vitro Therapeutic Screening: A Systematic Approach to Enhance the Biological Relevance of Data Obtained. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, P.; Jean, C.; Familiades, J.; Decaup, E.; Blanc, A.; Bezombes-Cagnac, C.; Laurent, C.; Savina, A.; Fournié, J.-J.; Laurent, G. Cell Growth in Aggregates Determines Gene Expression, Proliferation, Survival, Chemoresistance, and Sensitivity to Immune Effectors in Follicular Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaup, E.; Jean, C.; Laurent, C.; Gravelle, P.; Fruchon, S.; Capilla, F.; Marrot, A.; Al Saati, T.; Frenois, F.-X.; Laurent, G.; et al. Anti-Tumor Activity of Obinutuzumab and Rituximab in a Follicular Lymphoma 3D Model. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravelle, P.; Jean, C.; Valleron, W.; Laurent, G.; Fournié, J.-J. Innate Predisposition to Immune Escape in Follicular Lymphoma Cells. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rossi, C.; Gravelle, P.; Decaup, E.; Bordenave, J.; Poupot, M.; Tosolini, M.; Franchini, D.-M.; Laurent, C.; Morin, R.; Lagarde, J.-M.; et al. Boosting Γδ T Cell-Mediated Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity by PD-1 Blockade in Follicular Lymphoma. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1554175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaup, E.; Rossi, C.; Gravelle, P.; Laurent, C.; Bordenave, J.; Tosolini, M.; Tourette, A.; Perrial, E.; Dumontet, C.; Poupot, M.; et al. A Tridimensional Model for NK Cell-Mediated ADCC of Follicular Lymphoma. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, S.; Roumier, C.; Bertrand, E.; Renneville, A.; Caillault-Venet, A.; Doye, E.; Geffroy, S.; Sebda, S.; Nibourel, O.; Nudel, M.; et al. TP53 Mutation and Its Prognostic Significance in Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6325–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.P.; Grabowska, A.M. Spheroid Arrays for High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis of Spatial Patterns and Biomarker Expression in 3D. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.C.; Chang, F.J.; Chang, S. A New Criterion for Automatic Multilevel Thresholding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, R.L.F.; Miranda, M.; Marcato, P.D.; Swiech, K. Comparative Analysis of 3D Bladder Tumor Spheroids Obtained by Forced Floating and Hanging Drop Methods for Drug Screening. Front. Physiol 2017, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, C.P. Volume Doubling Measurement of Spherical and Ellipsoidal Tumors. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1984, 12, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, J.A.; Polson, A.G.; Klymkowsky, M.W. A Whole-Mount Immunocytochemical Analysis of the Expression of the Intermediate Filament Protein Vimentin in Xenopus. Development 1989, 105, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodt, H.-U.; Leischner, U.; Schierloh, A.; Jährling, N.; Mauch, C.P.; Deininger, K.; Deussing, J.M.; Eder, M.; Zieglgänsberger, W.; Becker, K. Ultramicroscopy: Three-Dimensional Visualization of Neuronal Networks in the Whole Mouse Brain. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisken, J.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy Techniques in Developmental Biology. Development 2009, 136, 1963–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.; Frongia, C.; Jorand, R.; Fehrenbach, J.; Weiss, P.; Maandhui, A.; Gay, G.; Ducommun, B.; Lobjois, V. Live Cell Division Dynamics Monitoring in 3D Large Spheroid Tumor Models Using Light Sheet Microscopy. Cell Div. 2011, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombelli, J.; Lorenzo, C. Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy Applications for Multicellular Systems. In Fluorescence Microscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 109–120. ISBN 978-0-12-409513-7. [Google Scholar]
- Abadie, S.; Jardet, C.; Colombelli, J.; Chaput, B.; David, A.; Grolleau, J.-L.; Bedos, P.; Lobjois, V.; Descargues, P.; Rouquette, J. 3D Imaging of Cleared Human Skin Biopsies Using Light-Sheet Microscopy: A New Way to Visualize in-Depth Skin Structure. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Alieva, M.; Wellens, L.M.; Ariese, H.C.R.; Jamieson, P.R.; Vonk, A.M.; Amatngalim, G.D.; Hu, H.; Oost, K.C.; Snippert, H.J.G.; et al. High-Resolution 3D Imaging of Fixed and Cleared Organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, C.R.; Zimmermann, M.; Agarkova, I.; Kelm, J.M.; Krek, W. 3D Cell Culture Systems Modeling Tumor Growth Determinants in Cancer Target Discovery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69–70, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiswald, L.-B.; Bellet, D.; Dangles-Marie, V. Spherical Cancer Models in Tumor Biology. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.M. Cell and Environment Interactions in Tumor Microregions: The Multicell Spheroid Model. Science 1988, 240, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Menne, H.; Dittfeld, C.; West, J.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Multicellular Tumor Spheroids: An Underestimated Tool Is Catching up Again. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, J.; Frongia, C.; Cazales, M.; Mondesert, O.; Ducommun, B.; Lobjois, V. Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models to Explore Cell Cycle Checkpoints in 3D. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffle, S.; Pandey, R.N.; Albert, M.; Hegde, R.S. Linking Hypoxia, DNA Damage and Proliferation in Multicellular Tumor Spheroids. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeber, F.; Ooft, S.N.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Voest, E.E. Tumor Organoids as a Pre-Clinical Cancer Model for Drug Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglen, R.M.; Randle, D.H. Drug Discovery Goes Three-Dimensional: Goodbye to Flat High-Throughput Screening? Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2015, 13, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Systems and Their Applications in Drug Discovery and Cell-Based Biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D. New Agents in Follicular Lymphoma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2011, 24, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, B.S.; Yang, D.T. Follicular Lymphoma: Evolving Therapeutic Strategies. Blood 2016, 127, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, T.-M.; Meyer, J.; Morgan, J.R. Advances in the Formation, Use and Understanding of Multi-Cellular Spheroids. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.C.; Silva, D.N.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. Optical Clearing Methods: An Overview of the Techniques Used for the Imaging of 3D Spheroids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 2742–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduaij, W.; Ivanov, A.; Honeychurch, J.; Cheadle, E.J.; Potluri, S.; Lim, S.H.; Shimada, K.; Chan, C.H.T.; Tutt, A.; Beers, S.A.; et al. Novel Type II Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody (GA101) Evokes Homotypic Adhesion and Actin-Dependent, Lysosome-Mediated Cell Death in B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2011, 117, 4519–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W. Biomaterials Offer Cancer Research the Third Dimension. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, D.; Brodaczewska, K.K.; Lipiec, M.; Szymanski, Ł.; Szczylik, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Colony, Hanging Drop, and Methylcellulose Three Dimensional Hypoxic Growth Optimization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, V.E.; Estrada, M.F.; Rebelo, S.P.; Abreu, S.; Silva, I.; Pinto, C.; Veloso, S.C.; Serra, A.T.; Boghaert, E.; Alves, P.M.; et al. Adaptable Stirred-Tank Culture Strategies for Large Scale Production of Multicellular Spheroid-Based Tumor Cell Models. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 221, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Lin, C.; Cheng, J.; Su, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Wen, X.; Zhao, P. Generation of Multicellular Tumor Spheroids with Microwell-Based Agarose Scaffolds for Drug Testing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daydé, D.; Ternant, D.; Ohresser, M.; Lerondel, S.; Pesnel, S.; Watier, H.; Le Pape, A.; Bardos, P.; Paintaud, G.; Cartron, G. Tumor Burden Influences Exposure and Response to Rituximab: Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling Using a Syngeneic Bioluminescent Murine Model Expressing Human CD20. Blood 2009, 113, 3765–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottereau, A.S.; Versari, A.; Luminari, S.; Dupuis, J.; Chartier, L.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Berriolo-Riedinger, A.; Menga, M.; Haioun, C.; Tilly, H.; et al. Prognostic Model for High-Tumor-Burden Follicular Lymphoma Integrating Baseline and End-Induction PET: A LYSA/FIL Study. Blood 2018, 131, 2449–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meignan, M.; Cottereau, A.S.; Versari, A.; Chartier, L.; Dupuis, J.; Boussetta, S.; Grassi, I.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Haioun, C.; Tilly, H.; et al. Baseline Metabolic Tumor Volume Predicts Outcome in High-Tumor-Burden Follicular Lymphoma: A Pooled Analysis of Three Multicenter Studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3618–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.S.; Lichtman, J.W. Clarifying Tissue Clearing. Cell 2015, 162, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntifering, M.; Castranova, D.; Gibson, G.A.; Meyer, E.; Kofron, M.; Watson, A.M. Clearing for Deep Tissue Imaging. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2018, 86, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Germain, R.N.; Gerner, M.Y. Multiplex, Quantitative Cellular Analysis in Large Tissue Volumes with Clearing-Enhanced 3D Microscopy (Ce3D). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7321–E7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, A.C.; Capaldo, B.D.; Vaillant, F.; Pal, B.; van Ineveld, R.; Dawson, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Nolan, E.; Fu, N.Y.; 3DTCLSM Group; et al. Intraclonal Plasticity in Mammary Tumors Revealed through Large-Scale Single-Cell Resolution 3D Imaging. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 618–632.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampaloni, F.; Stelzer, E.H.K.; Masotti, A. Three-Dimensional Tissue Models for Drug Discovery and Toxicology. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualda, E.J.; Pereira, H.; Vale, T.; Estrada, M.F.; Brito, C.; Moreno, N. SPIM-Fluid: Open Source Light-Sheet Based Platform for High-Throughput Imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eismann, B.; Krieger, T.G.; Beneke, J.; Bulkescher, R.; Adam, L.; Erfle, H.; Herrmann, C.; Eils, R.; Conrad, C. Automated 3D Light-Sheet Screening with High Spatiotemporal Resolution Reveals Mitotic Phenotypes. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gava, F.; Faria, C.; Gravelle, P.; Valero, J.G.; Dobaño-López, C.; Morin, R.; Norlund, M.; Gomes, A.; Lagarde, J.-M.; Rossi, C.; et al. 3D Model Characterization by 2D and 3D Imaging in t(14;18)-Positive B-NHL: Perspectives for In Vitro Drug Screens in Follicular Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071490
Gava F, Faria C, Gravelle P, Valero JG, Dobaño-López C, Morin R, Norlund M, Gomes A, Lagarde J-M, Rossi C, et al. 3D Model Characterization by 2D and 3D Imaging in t(14;18)-Positive B-NHL: Perspectives for In Vitro Drug Screens in Follicular Lymphoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(7):1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071490
Chicago/Turabian StyleGava, Fabien, Carla Faria, Pauline Gravelle, Juan G. Valero, Cèlia Dobaño-López, Renaud Morin, Marine Norlund, Aurélie Gomes, Jean-Michel Lagarde, Cédric Rossi, and et al. 2021. "3D Model Characterization by 2D and 3D Imaging in t(14;18)-Positive B-NHL: Perspectives for In Vitro Drug Screens in Follicular Lymphoma" Cancers 13, no. 7: 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071490
APA StyleGava, F., Faria, C., Gravelle, P., Valero, J. G., Dobaño-López, C., Morin, R., Norlund, M., Gomes, A., Lagarde, J.-M., Rossi, C., Bordenave, J., Pieruccioni, L., Rouquette, J., Matas-Céspedes, A., Fournié, J.-J., Ysebaert, L., Laurent, C., Pérez-Galán, P., & Bezombes, C. (2021). 3D Model Characterization by 2D and 3D Imaging in t(14;18)-Positive B-NHL: Perspectives for In Vitro Drug Screens in Follicular Lymphoma. Cancers, 13(7), 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071490