Heterogeneity in Signaling Pathway Activity within Primary and between Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
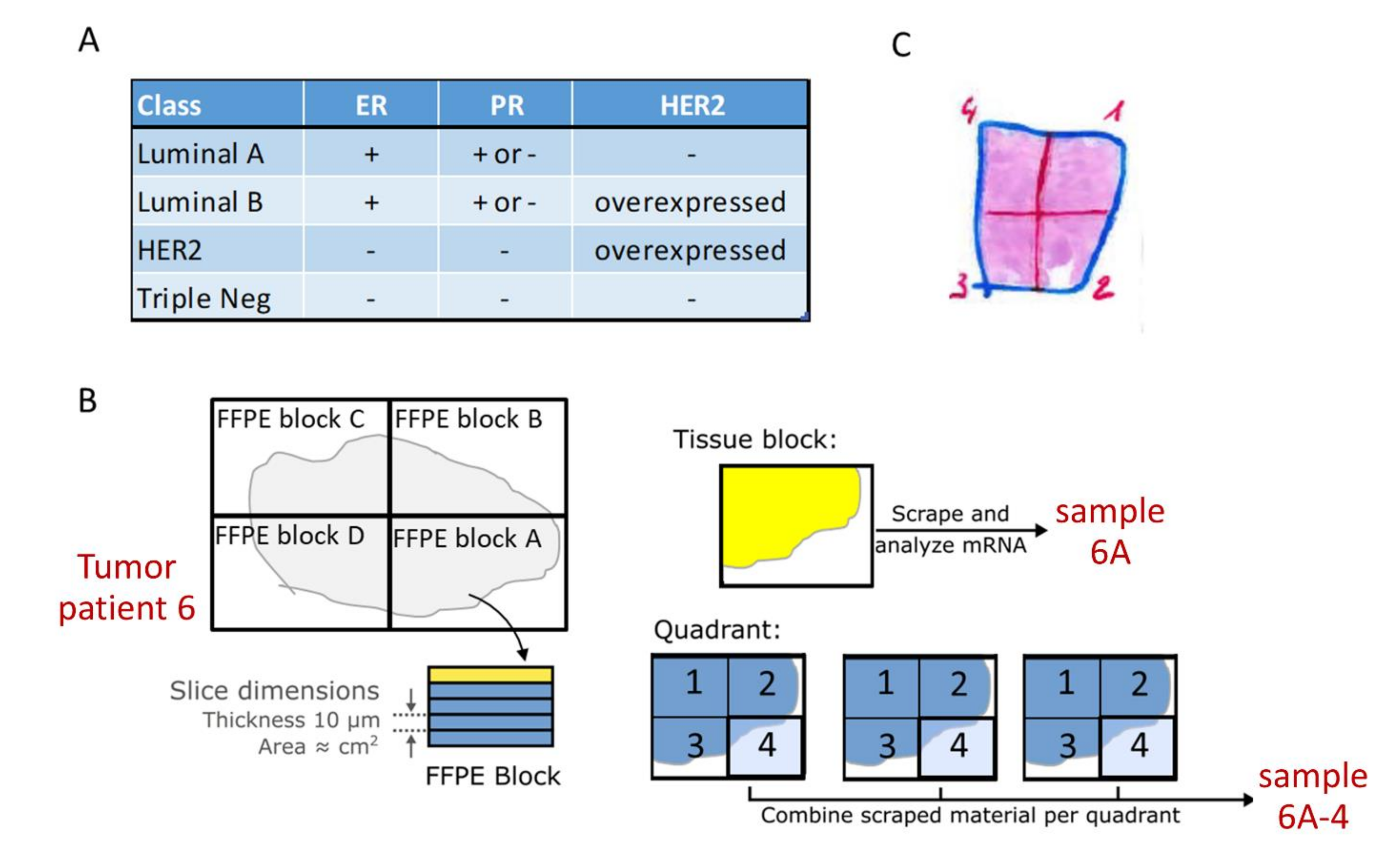
2.2. Tissue Sample Sets
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Measuring Pathway Activity
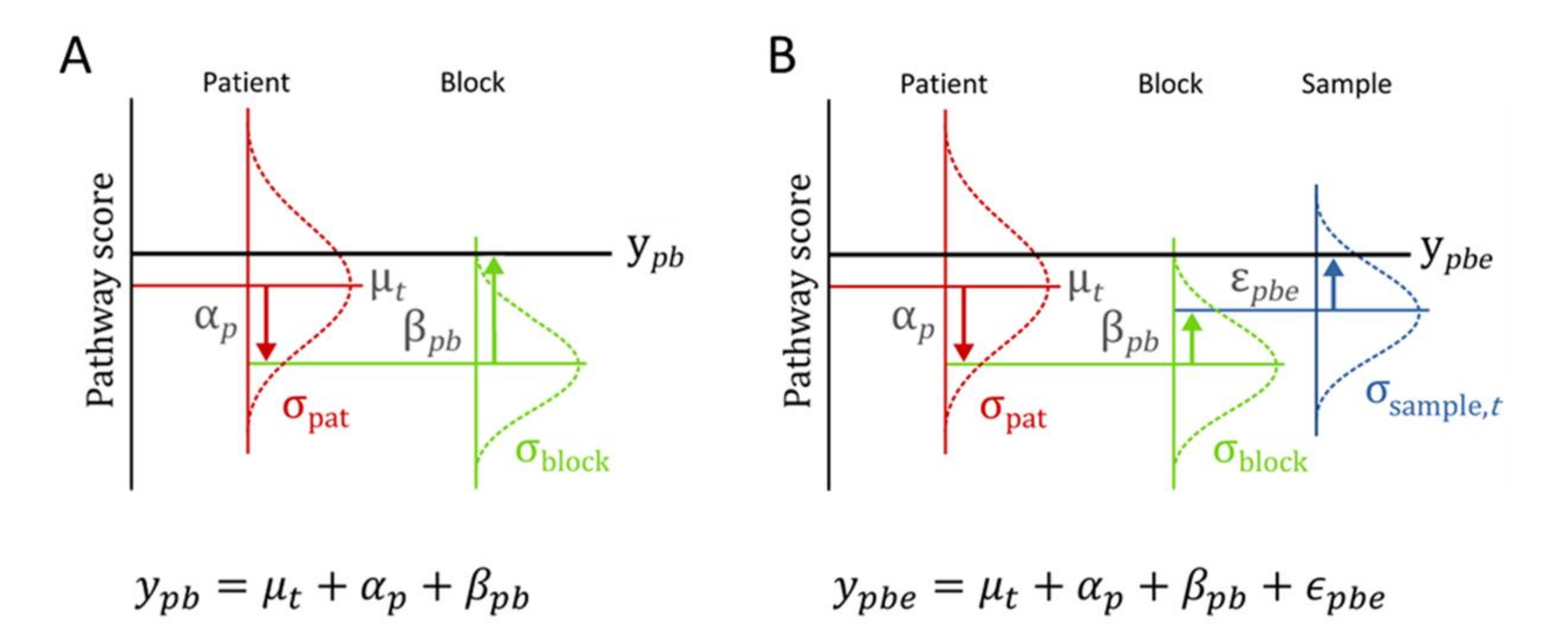
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
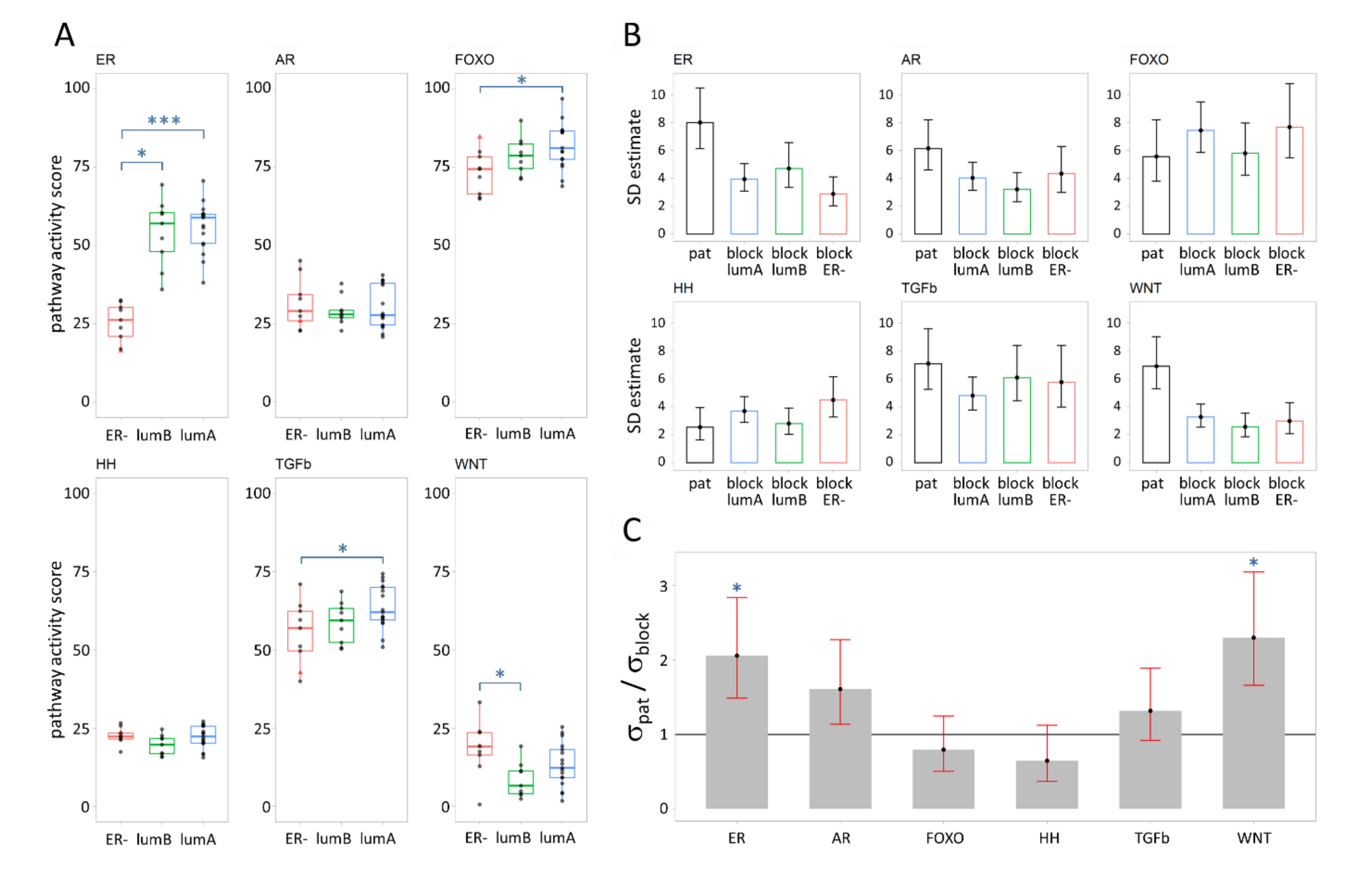
3.1. Signal Transduction Pathway Activity in Primary Breast Cancer Subtypes
3.2. Variance Explained per Model Parameter
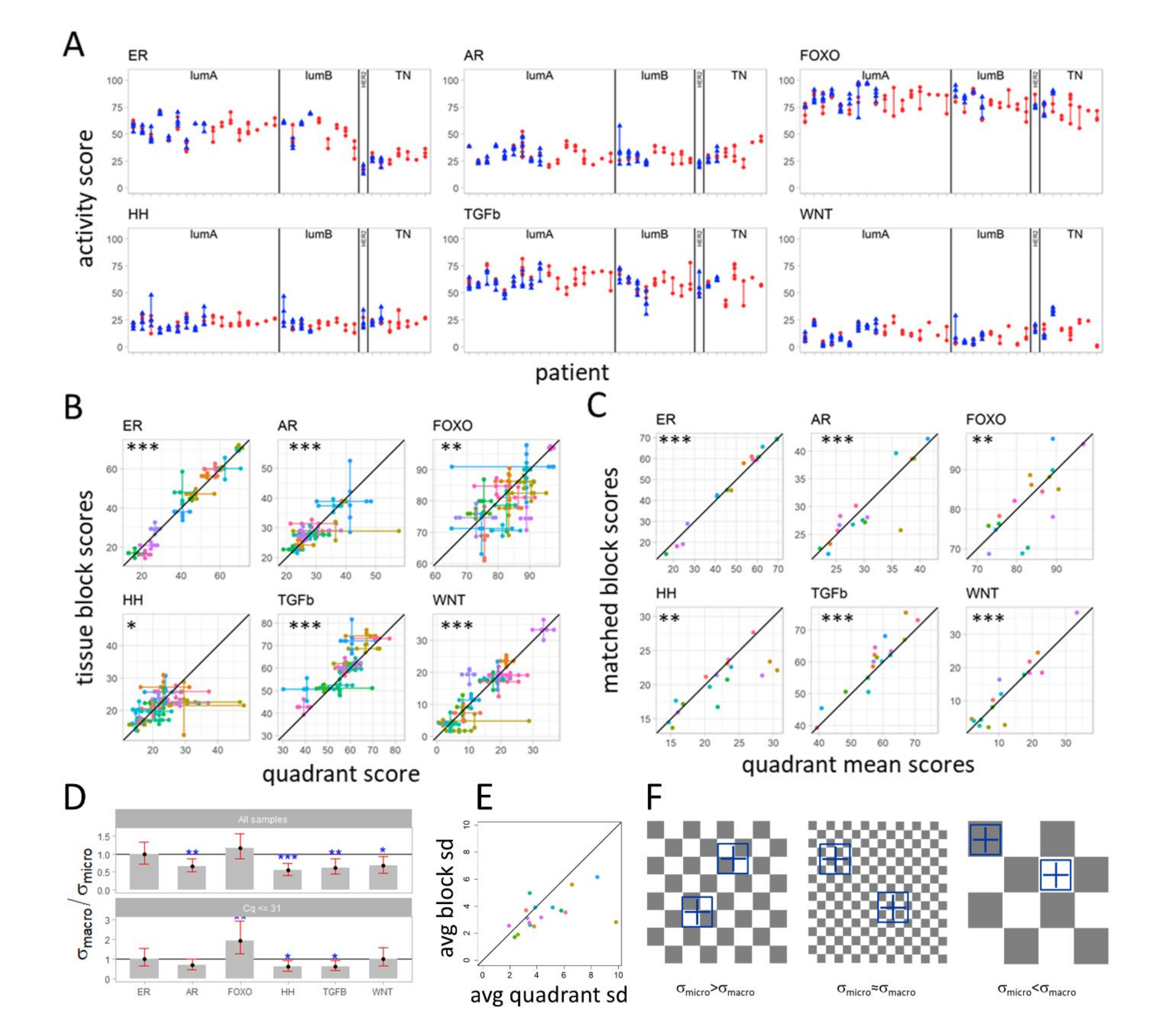
3.3. Variation in Pathway Activity within a Single Tumor in Primary Breast Cancer
3.4. Variation in Signaling Pathway Activity at Micro-Scale versus Macro-Scale
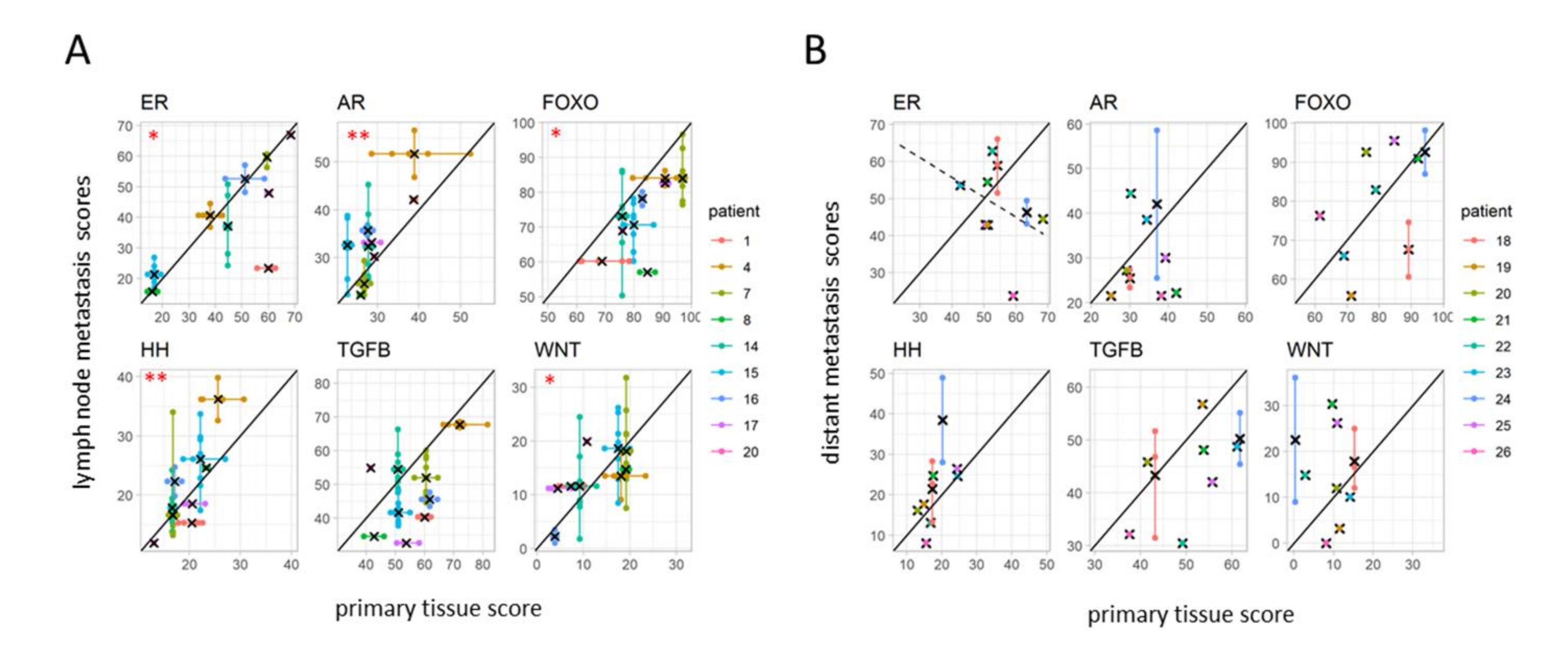
3.5. Differences in Pathway Activity between Primary Tumors and Matched Lymph Node Metastases
3.6. Differences in Pathway Activity between Primary Tumors and Matched Distant Metastases
3.7. Comparing Pathway Activity between Lymph Node and Distant Metastases
3.8. Pathway Activity Related to Metastatic Organ Site
3.9. PI3K-FOXO Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Pathway Activity between Breast Cancer Subtypes
4.2. Within Tumor Heterogeneity of Signaling Pathway Activity
4.3. A “Checkerboard” Clone-Size Cancer Model and “Big Bang” Type of Cancer Evolution
4.4. Variation in Pathway Activity between Primary and Lymph Node Metastases
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Stolpe, A. On the origin and destination of cancer stem cells: A conceptual evaluation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schütz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, R.; Glass, C.K. Signaling by Nuclear Receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Frasor, J. Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31 (Suppl. 3), 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, J.; Beachy, P.A. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, L.; Beachy, P.A. The Hedgehog response network: Sensors, switches, and routers. Science 2004, 304, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Katoh, M. Hedgehog target genes: Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffer, P.J.; Burgering, B.M.T. Forkhead-box transcription factors and their role in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgering, B.M.T. A brief introduction to FOXOlogy. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2258–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancey, J.E.; Bedard, P.L.; Onetto, N.; Hudson, T.J. The genetic basis for cancer treatment decisions. Cell 2012, 148, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, C.; Michiels, S.; Ferté, C.; Le Deley, M.-C.; Lacroix, L.; Hollebecque, A.; Verlingue, L.; Ileana, E.; Rosellini, S.; Ammari, S.; et al. High-Throughput Genomics and Clinical Outcome in Hard-to-Treat Advanced Cancers: Results of the MOSCATO 01 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquart, J.; Chen, E.Y.; Prasad, V. Estimation of the Percentage of US Patients with Cancer Who Benefit From Genome-Driven Oncology. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, W.A.M.E.; Selenica, P.; Lee, J.Y.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Burke, K.A.; Piscuoglio, S.; Berman, S.H.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Weigelt, B.; van Diest, P.J.; et al. Mutation Profiling of Key Cancer Genes in Primary Breast Cancers and Their Distant Metastases. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3112–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrijver, W.A.M.E.; Suijkerbuijk, K.P.M.; van Gils, C.H.; van der Wall, E.; Moelans, C.B.; van Diest, P.J. Receptor Conversion in Distant Breast Cancer Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sottoriva, A.; Kang, H.; Ma, Z.; Graham, T.A.; Salomon, M.P.; Zhao, J.; Marjoram, P.; Siegmund, K.D.; Press, M.F.; Shibata, D.; et al. A Big Bang model of human colorectal tumor growth. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Hu, Z.; Curtis, C. Big Bang Tumor Growth and Clonal Evolution. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegh, W.; van Ooijen, H.; Inda, M.A.; Hatzis, P.; Versteeg, R.; Smid, M.; Martens, J.; Foekens, J.; Van De Wiel, P.; Clevers, H.; et al. Selection of Personalized Patient Therapy through the Use of Knowledge-Based Computational Models That Identify Tumor-Driving Signal Transduction Pathways. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooijen, H.; Hornsveld, M.; Dam-de Veen, C.; Velter, R.; Dou, M.; Verhaegh, W.; Burgering, B.; van de Stolpe, A. Assessment of Functional Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway Activity in Cancer Tissue Using Forkhead Box-O Target Gene Expression in a Knowledge-Based Computational Model. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1956–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Stolpe, A.; Holtzer, L.; van Ooijen, H.; de Inda, M.A.; Verhaegh, W. Enabling precision medicine by unravelling disease pathophysiology: Quantifying signal transduction pathway activity across cell and tissue types. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaegh, W.; van de Stolpe, A. Knowledge-based computational models. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5196–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inda, M.A.; Blok, E.J.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Charehbili, A.; den Biezen-Timmermans, E.C.; van Brussel, A.; Fruytier, S.E.; Kranenbarg, E.M.-K.; Kloet, S.; van der Burg, B.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Pathway Activity Score to Predict Clinical Response or Resistance to Neoadjuvant Endocrine Therapy in Primary Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brussel, A.; Inda, M.A.; Den Biezen, E.; van Strijp, D.; Wrobel, J.; van Ooijen, H.; Hoffmann, R.; Verhaegh, W.; van de Stolpe, A. Assessing functional Androgen Receptor (AR) pathway activity using a computational model. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. 5), 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Stolpe, A.; Verhaegh, W.; Blay, J.-Y.; Ma, C.X.; Pauwels, P.; Pegram, M.; Prenen, H.; Ruysscher, D.D.; Saba, N.F.; Slovin, S.F.; et al. RNA based approaches to profile oncogenic pathways from low quantity samples to drive precision oncology strategies. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 598118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Winer, E.P.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.-J.; Albain, K.S.; André, F.; Bergh, J.; et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Stolpe, A. Quantitative Measurement of Functional Activity of the PI3K Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp, L.L.C. Command mixed (Multilevel mixed-effects linear regression). In Multilevel Mixed-Effects Reference Manual Release 15; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 513–568. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-PLUS; Statistics and Computing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Lenth, R.V. Least-Squares Means: The R Package lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, B.; Valenta, T.; Dimitrieva, S.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. GLI1-expressing mesenchymal cells form the essential Wnt-secreting niche for colon stem cells. Nature 2018, 558, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Stolpe, A.; van Brussel, A.; Moelans, C.; Inda, M.A.; Verhaegh, W.; den Biezen, E.; van Diest, P. Measuring functional signal transduction pathway activity on breast cancer tissue samples to determine intra-tumor heterogeneity and heterogeneity between primary and metastatic tumors. Cancer Res. 2018, 78 (Suppl. 13), 3690. [Google Scholar]
- Heldring, N.; Pike, A.; Andersson, S.; Matthews, J.; Cheng, G.; Hartman, J.; Tujague, M.; Ström, A.; Treuter, E.; Warner, M.; et al. Estrogen receptors: How do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 905–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-R.; Van De Stolpe, A.; Van Brussel, A.; Van Ooijen, H.; Galimzianova, A.; Cohn, D.; Beca, F.; Rubin, D.; Allison, K. Abstract P5-11-06: Does hormone expression by IHC predict ER pathway activity? An analysis in a metastatic breast cancer patient cohort. Poster Sess. Abstr. 2019, 79, P5-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.W.; Zava, D.T.; Locher, G.W.; Goldhirsch, A.; Hartmann, W.H. Receptor heterogeneity of human breast cancer as measured by multiple intratumoral assays of estrogen and progesterone receptor. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1984, 20, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaratone, L.; Simonetti, M.; Wernersson, E.; Marchiò, C.; Garnerone, S.; Scalzo, M.S.; Bienko, M.; Chiarle, R.; Sapino, A.; Crosetto, N. Quantification of HER2 and estrogen receptor heterogeneity in breast cancer by single-molecule RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18680–18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertschuk, L.P.; Axiotis, C.A.; Feldman, J.G.; Kim, Y.-D.; Karavattayhayyil, S.J.; Braithwaite, L. Marked Intratumoral Heterogeneity of the Proto-Oncogene Her-2/neu Determined by Three Different Detection Systems. Breast J. 1999, 5, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, J. Breast cancer stem cells: Features, key drivers and treatment options. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.J.; Lui, P.P.; Obajdin, J.; Riccio, F.; Stroukov, W.; Willis, T.L.; Spagnoli, F.; Watt, F.M. Mechanisms, Hallmarks, and Implications of Stem Cell Quiescence. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachy, P.; Cai, S.; Ma, Y.; Hatakeyama, J.; Zhao, C.; Stoffels, M.; Verhaegh, W.; van de Stolpe, A.; Pegram, M. Targeted disruption of transcriptional effector GLI2 attenuates breast tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78 (Suppl. 4), P5-03-11. [Google Scholar]
- Cantley, L.C.; Hunter, T.; Sever, R.; Thorner, J.W. (Eds.) Signal Transduction: Principles, Pathways, and Processes; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Mayne, C.G.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Greene, G.L.; Chandarlapaty, S. Structural underpinnings of oestrogen receptor mutations in endocrine therapy resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. Metastatic colonization: Settlement, adaptation and propagation of tumor cells in a foreign tissue environment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, J.P. The lymph node pre-metastatic niche. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkandera, J.; Kiesslich, T.; Haybaeck, J.; Gerger, A.; Pichler, M. Hedgehog signaling pathway in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1179–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Meng, E.; Reed, E.; Shevde, L.A.; Rocconi, R.P. Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates the growth of ovarian cancer spheroid forming cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nienhuis, H.H.; van Kruchten, M.; Elias, S.G.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Bongaerts, A.H.H.; Schröder, C.P.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Hospers, G.A.P. 18F-Fluoroestradiol Tumor Uptake Is Heterogeneous and Influenced by Site of Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Morales-Vasquez, F.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 608, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Sample Set | Description | Total | Per Breast Cancer Subtype | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LumA | LumB | HER2 | TN | |||
| I | 1 to 5 block (b) samples from primary tumors | 18 (49 b) | 8 (20 b) | 5 (15 b) | - | 5 (14 b) |
| II | 2 to 5 block samples from primary tumors with 4 matched quadrant samples (per patient) | 17 (50 b) | 9 (28 b) | 4 (12 b) | 1 (2 b) | 3 (8 b) |
| III | Primary tumors (PT) and 1 to 3 matched distant metastasis samples | 10 (9 PT/13 DS) | Subtyping not available | |||
| IV | 1 to 10 lymph node metastasis from 9 patients from sample sets II and III | 9 (33 LN) * | 4 (20 LN) | 2 (3 LN) | 1 (1 LN) | 1 (8 LN) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inda, M.A.; van Swinderen, P.; van Brussel, A.; Moelans, C.B.; Verhaegh, W.; van Zon, H.; den Biezen, E.; Bikker, J.W.; van Diest, P.J.; van de Stolpe, A. Heterogeneity in Signaling Pathway Activity within Primary and between Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061345
Inda MA, van Swinderen P, van Brussel A, Moelans CB, Verhaegh W, van Zon H, den Biezen E, Bikker JW, van Diest PJ, van de Stolpe A. Heterogeneity in Signaling Pathway Activity within Primary and between Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061345
Chicago/Turabian StyleInda, Márcia A., Paul van Swinderen, Anne van Brussel, Cathy B. Moelans, Wim Verhaegh, Hans van Zon, Eveline den Biezen, Jan Willem Bikker, Paul J. van Diest, and Anja van de Stolpe. 2021. "Heterogeneity in Signaling Pathway Activity within Primary and between Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061345
APA StyleInda, M. A., van Swinderen, P., van Brussel, A., Moelans, C. B., Verhaegh, W., van Zon, H., den Biezen, E., Bikker, J. W., van Diest, P. J., & van de Stolpe, A. (2021). Heterogeneity in Signaling Pathway Activity within Primary and between Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers, 13(6), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061345






