Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
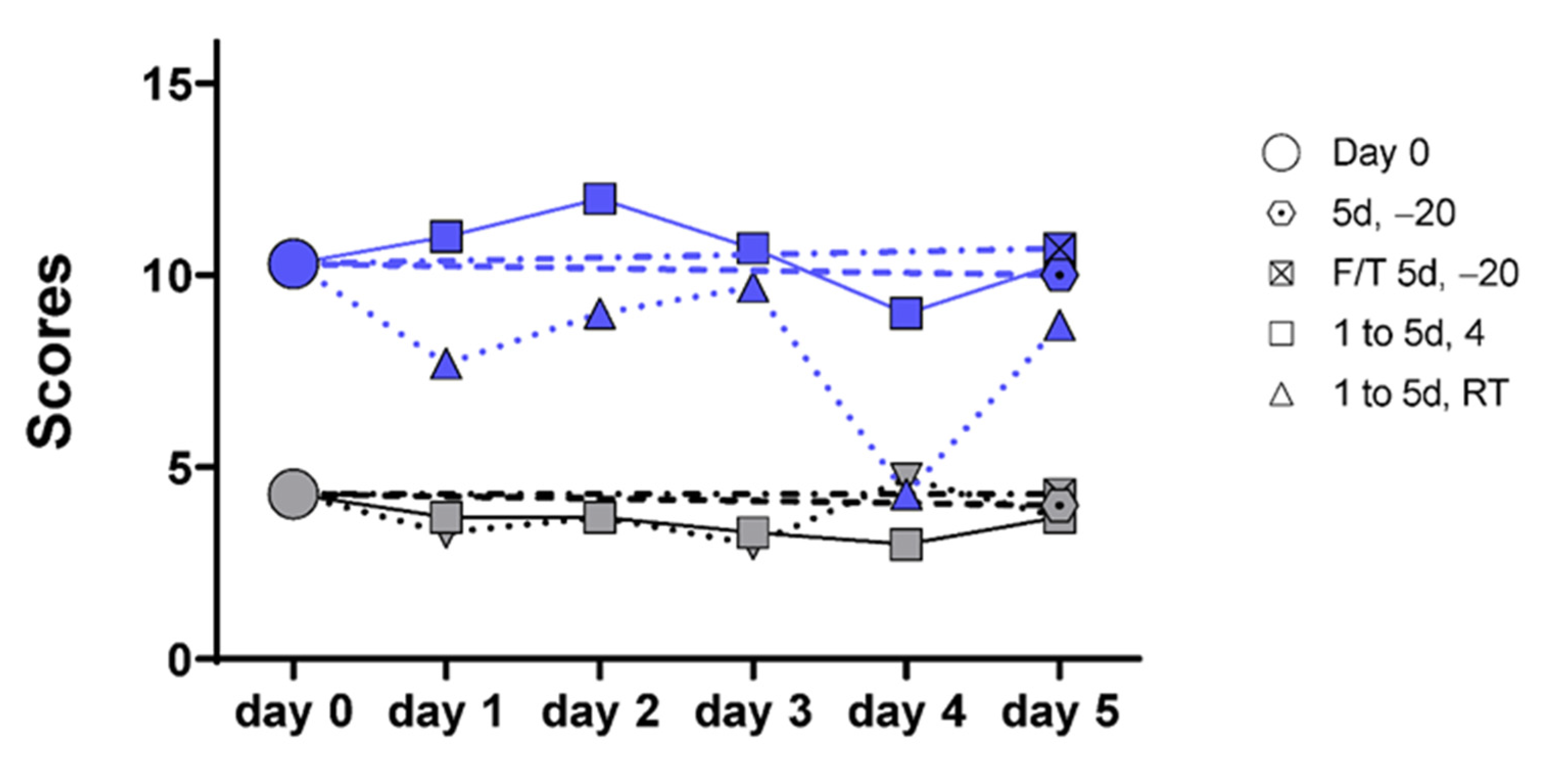
2.2. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, Preamplification, and PCR Amplification
2.3. Data Presentation and Statistical Analysis
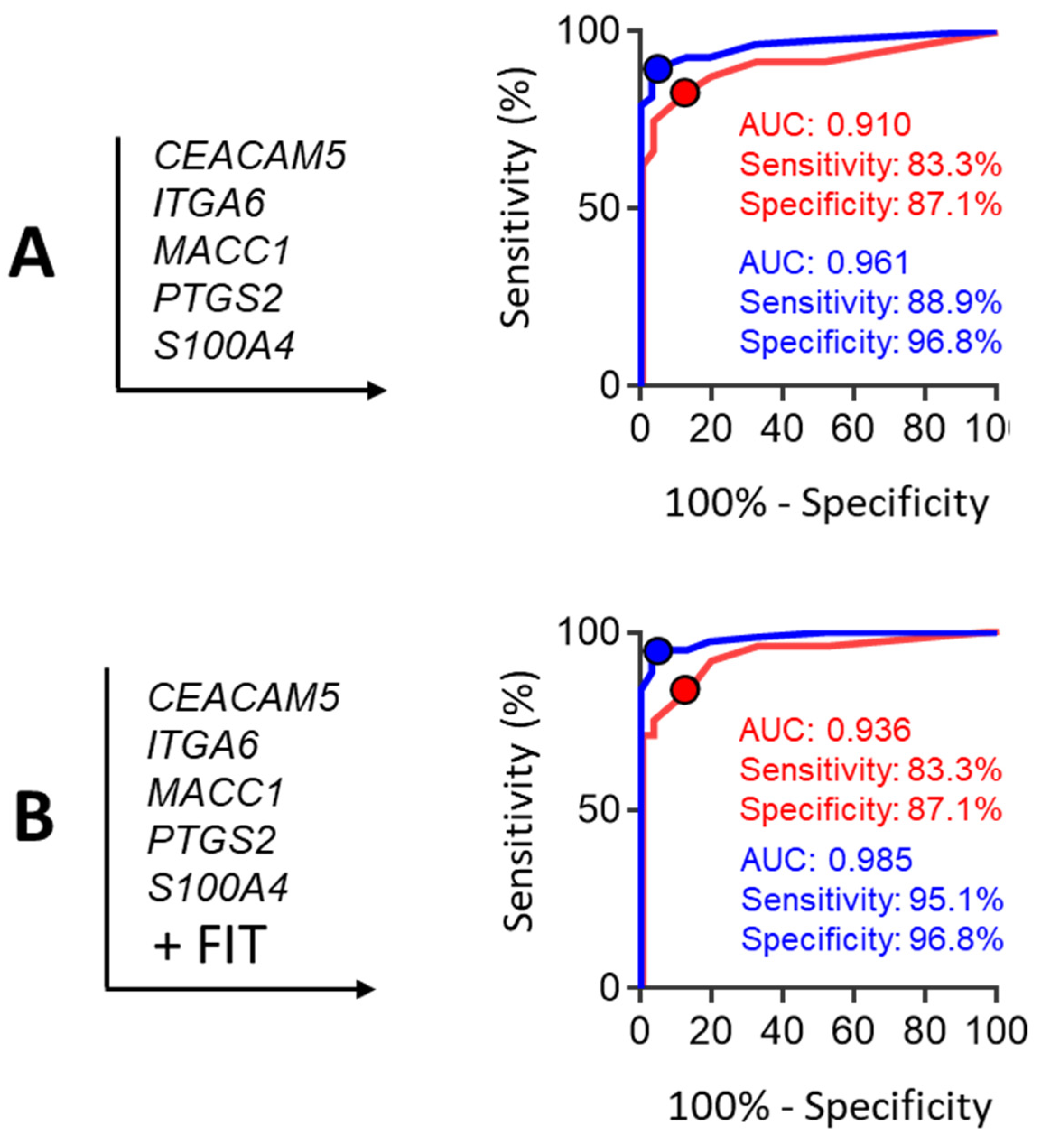
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladabaum, U.; Dominitz, J.A.; Kahi, C.; Schoen, R.E. Strategies for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, S.; Bouvier, A.M.; Lepage, C.; Hatem, C.; Dancourt, V.; Faivre, J. Incidence and patterns of recurrence after resection for cure of colonic cancer in a well defined population. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Imperiale, T.F. Stool testing for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willyard, C. Screening: Early alert. Nature 2015, 521, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, H.; Hoffmeister, M.; Stegmaier, C.; Brenner, G.; Altenhofen, L.; Haug, U. Risk of progression of advanced adenomas to colorectal cancer by age and sex: Estimates based on 840,149 screening colonoscopies. Gut 2007, 56, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Click, B.; Pinsky, P.F.; Hickey, T.; Doroudi, M.; Schoen, R.E. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA 2018, 319, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroy, P.C., 3rd; Lal, S.; Glick, J.T.; Robinson, P.A.; Zamor, P.; Heeren, T.C. Patient preferences for colorectal cancer screening: How does stool DNA testing fare? Am. J. Manag. Care 2007, 13, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.S.; Piper, M.A.; Perdue, L.A.; Rutter, C.M.; Webber, E.M.; O’Connor, E.; Smith, N.; Whitlock, E.P. Screening for colorectal cancer: Updated evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA 2016, 315, 2576–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.E.; Fraser, C.G.; Halloran, S.P.; Young, G.P. Population screening for colorectal cancer means getting FIT: The past, present, and future of colorectal cancer screening using the fecal immunochemical test for hemoglobin (FIT). Gut Liver 2014, 8, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundt, S.; Haug, U.; Brenner, H. Comparative evaluation of immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for colorectal adenoma detection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Liles, E.G.; Bent, S.; Levin, T.R.; Corley, D.A. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laanani, M.; Coste, J.; Blotiere, P.O.; Carbonnel, F.; Weill, A. Patient, procedure, and endoscopist risk factors for perforation, bleeding, and splenic injury after colonoscopies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 719–727.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Ladabaum, U. Opportunities and challenges in moving from current guidelines to personalized colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.J.; Majumdar, A.P.; Nechvatal, J.M.; Ram, J.L.; Basson, M.D.; Heilbrun, L.K.; Kato, I. Exfoliated cells in stool: A source for reverse transcription-PCR-based analysis of biomarkers of gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.S.; Baker, M.S.; Nice, E.C. Mass spectrometry-based analysis for the discovery and validation of potential colorectal cancer stool biomarkers. Methods Enzymol. 2017, 586, 247–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, B.M.; Ahlquist, D.A. Stool DNA screening for colorectal neoplasia: Biological and technical basis for high detection rates. Pathology 2012, 44, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Katayose, S.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Baba, H.; Matsumura, Y. Improved recovery of exfoliated colonocytes from feces using newly developed immunomagnetic beads. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2008, 2008, 605273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperiale, T.F.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Itzkowitz, S.H.; Levin, T.R.; Lavin, P.; Lidgard, G.P.; Ahlquist, D.A.; Berger, B.M. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, D.F.; Sox, H.C. Clinical practice guidelines for colorectal cancer screening: New recommendations and new challenges. JAMA 2016, 315, 2529–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; van Ballegooijen, M.; Zauber, A.G.; Habbema, J.D.; Kuipers, E.J. Effect of rising chemotherapy costs on the cost savings of colorectal cancer screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.J.; Cohen, J.T.; Weinstein, M.C. Updating cost-effectiveness—The curious resilience of the $50,000-per-QALY threshold. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperiale, T.F.; Kahi, C.J. Cost-effectiveness of future biomarkers for colorectal cancer screening: Quantified futility or call for innovation? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, U.; Knudsen, A.B.; Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; Kuntz, K.M. Development of new non-invasive tests for colorectal cancer screening: The relevance of information on adenoma detection. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Kozu, T.; Baba, H.; Matsumura, Y. Detection of colorectal cancer cells from feces using quantitative real-time RT-PCR for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, S.; Yoshida, K.; Miura, N.; Sugimura, H.; Kajimura, M. Potential usefulness of detecting cyclooxygenase 2 messenger RNA in feces for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, T.; Kanaoka, S.; Yoshida, K.; Hamaya, Y.; Ikuma, M.; Miura, N.; Sugimura, H.; Kajimura, M.; Hishida, A. Fecal cyclooxygenase 2 plus matrix metalloproteinase 7 mRNA assays as a marker for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaya, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Takai, T.; Ikuma, M.; Hishida, A.; Kanaoka, S. Factors that contribute to faecal cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA expression in subjects with colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydensborg, A.B.; Teller, I.C.; Groulx, J.F.; Basora, N.; Pare, F.; Herring, E.; Gauthier, R.; Jean, D.; Beaulieu, J.F. Integrin alpha6Bbeta4 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and c-Myc activity. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groulx, J.F.; Giroux, V.; Beausejour, M.; Boudjadi, S.; Basora, N.; Carrier, J.C.; Beaulieu, J.F. Integrin alpha6A splice variant regulates proliferation and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.N.; Rustin, R.B.; Sullivan, J.D. Oncotype DX((R)) colon cancer assay for prediction of recurrence risk in patients with stage II and III colon cancer: A review of the evidence. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 24, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, E.; Kanaoka, S.; Tremblay, E.; Beaulieu, J.F. A stool multitarget mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal neoplasms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1765, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.F.; Herring, E.; Kanaoka, S.; Tremblay, E. Use of integrin alpha 6 transcripts in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers at curable stages. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14684–14692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, E.; Kanaoka, S.; Tremblay, E.; Beaulieu, J.F. Droplet digital PCR for quantification of ITGA6 in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Tomasch, J.; Deng, Z.; Jarek, M.; Husemann, P.; Wagner-Dobler, I.; Consortium, C. Stool metatranscriptomics: A technical guideline for mRNA stabilisation and isolation. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, J.; Shaikh, N.; Ordiz, M.I.; Tarr, P.I.; Manary, M.J. Droplet digital PCR quantifies host inflammatory transcripts in feces reliably and reproducibly. Cell. Immunol. 2016, 303, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydensborg, A.B.; Herring, E.; Auclair, J.; Tremblay, E.; Beaulieu, J.-F. Normalizing genes for quantitative RT-PCR in differentiating human intestinal epithelial cells and adenocarcinomas of the colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G1067–G1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, L.; Dorigo-Zetsma, J.W.; de Groot, C.J.; Bouter, S.; Plotz, F.B.; van Ewijk, B.E. Detection of intestinal protozoa in paediatric patients with gastrointestinal symptoms by multiplex real-time PCR. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.L.; Chatigre, J.K.; Gohou, J.P.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Leuppi, R.; Polman, K.; Chappuis, F.; Mertens, P.; Herrmann, M.; N’Goran, E.K.; et al. Combined stool-based multiplex PCR and microscopy for enhanced pathogen detection in patients with persistent diarrhoea and asymptomatic controls from Cote d’Ivoire. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 591.e1–591.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnell, E.K.; Kang, Y.; Wurtzler, E.M.; Griffith, M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Griffith, O.L.; Geneoscopy, S. Noninvasive detection of high-risk adenomas using stool-derived eukaryotic RNA sequences as biomarkers. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 884–887.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengucci, C.; De Maio, G.; Menghi, M.; Benzi, F.; Calistri, D. Evaluation of colorectal cancer risk and prevalence by stool DNA integrity detection. J. Vis. Exp. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Ahmed, N.C.; Gouda, M.M.; Vos, P.W.; Bonnerup, C. RT-qPCR for fecal mature MicroRNA quantification and validation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1765, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Chaver, P.; Otero-Estevez, O.; Paez de la Cadena, M.; Rodriguez-Berrocal, F.J.; Martinez-Zorzano, V.S. Proteomics for discovery of candidate colorectal cancer biomarkers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3804–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
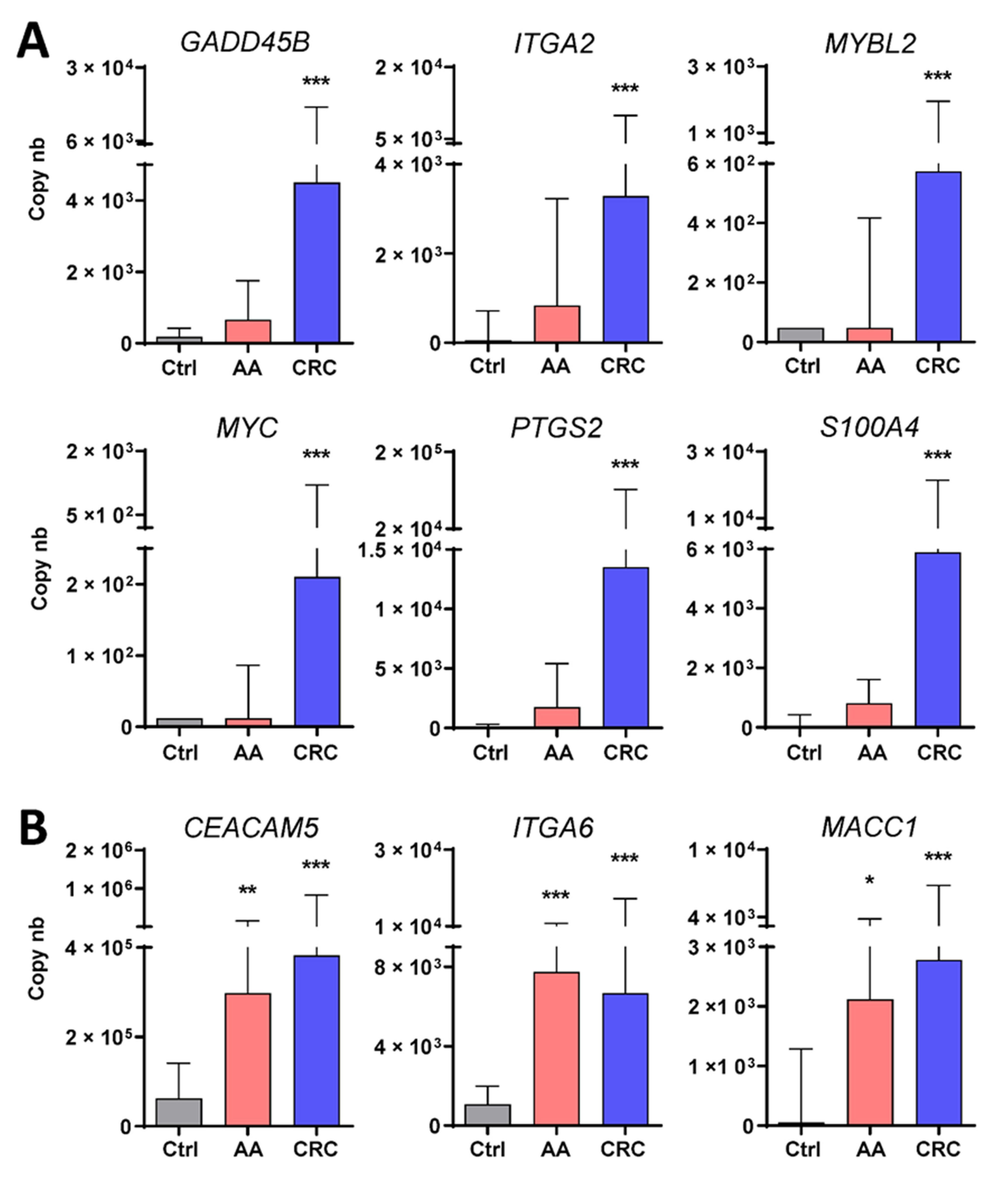
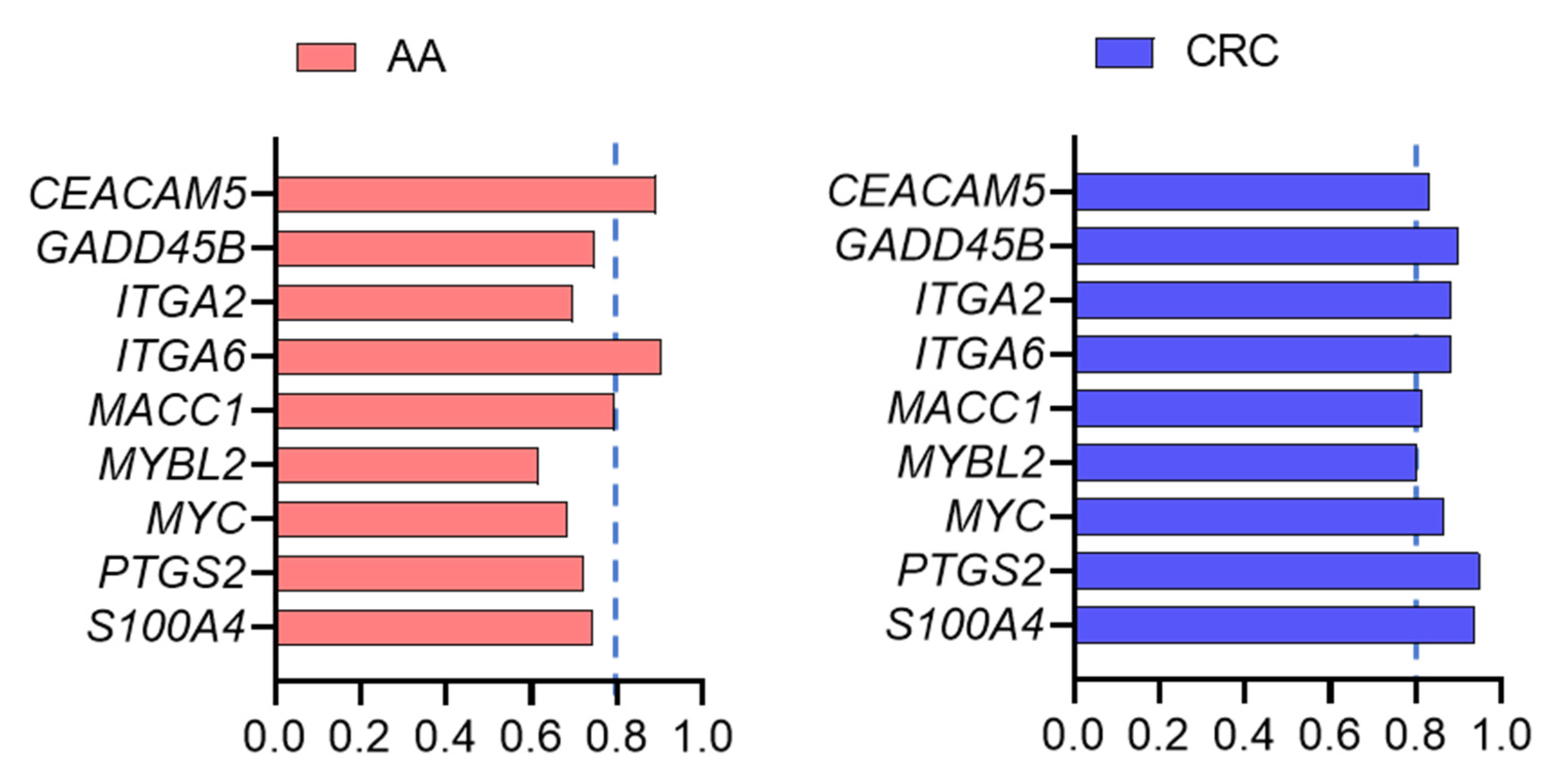
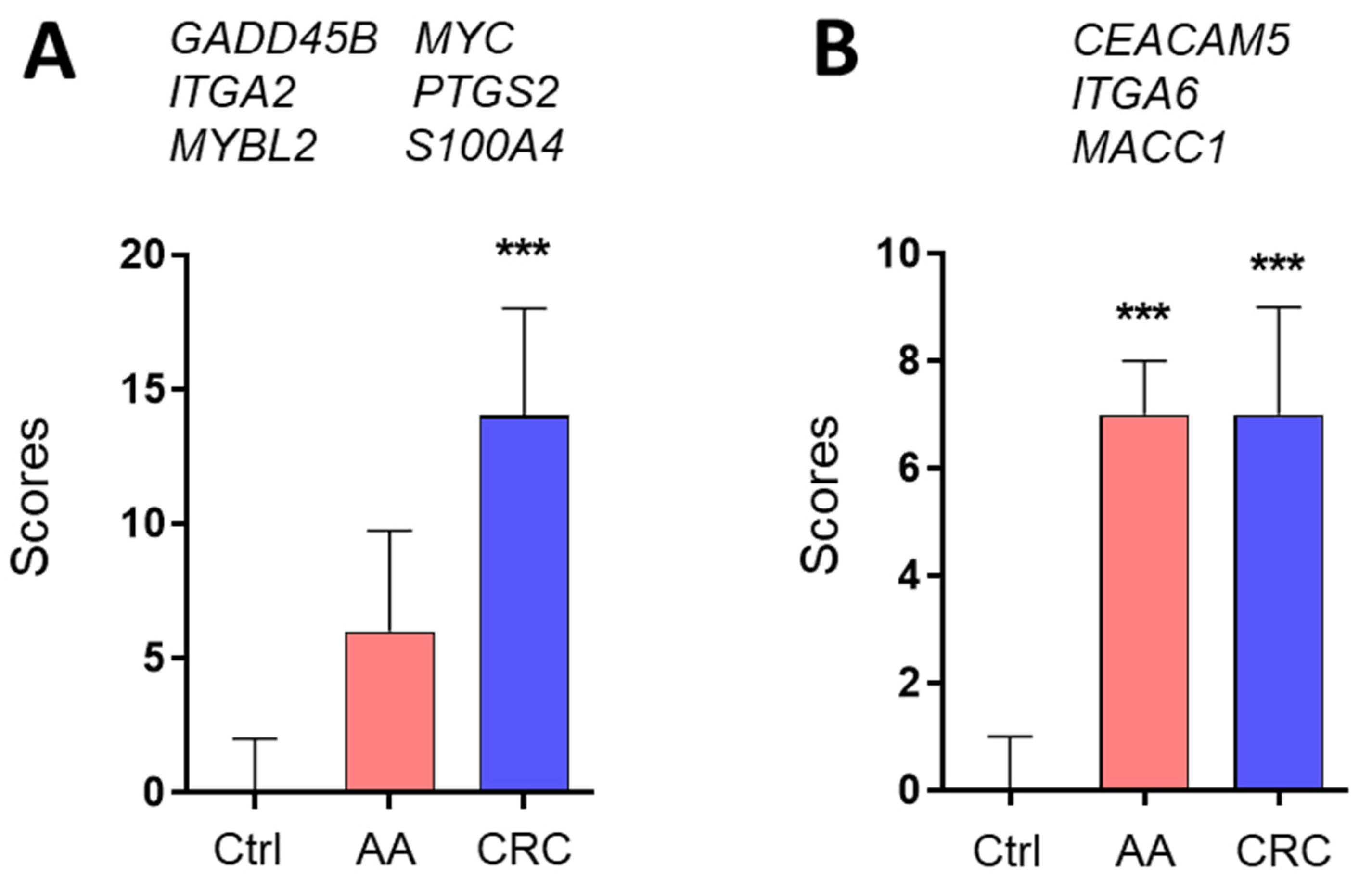
| Gene Name | TaqMan Assay I.D. | Consistently | Over-Represented | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected in Stools | CRC Only | AA and CRC | ||
| BGN | Hs00156076_m1 | |||
| CEACAM5 | Hs00944025_m1 | Y | Y | |
| CTNNB1 | Hs00355049_m1 | |||
| DYNC2H1 | Hs00941787_m1 | |||
| FAP | Hs00990806_m1 | |||
| GADD45B | Hs00169587_m1 | Y | Y | |
| GLI1 | Hs00171790_m1 | |||
| HMAN1B1 | Hs01032463_m1 | |||
| HNRNPA2B1 | Hs00955384_m1 | |||
| INHBA | Hs04187260_m1 | |||
| ITGA1 | Hs00235006_m1 | Y | ||
| ITGA2 | Hs01673848_m1 | Y | ||
| ITGA6A | Hs01041013_m1 | Y | Y | |
| ITGA6 | Hs01041011_m1 | Y | Y | |
| KI67 | Hs01032434_m1 | |||
| KIF3A | Hs01126351_m1 | |||
| KIF7 | Hs00419527_m1 | |||
| MACC1 | Hs00766186_m1 | Y | Y | |
| MLH1 | Hs00179866_m1 | Y | ||
| MSH1 | Hs00954125_m1 | Y | ||
| MTR | Hs01090031_m1 | |||
| MYBL2 | Hs00942543_m1 | Y | Y | |
| MYC | Hs00153408_m1 | Y | Y | |
| PTGS2 | Hs00153133_m1 | Y | Y | |
| S100A4 | Hs00243202_m1 | Y | Y | |
| VDAC2 | Hs01075603_m1 | |||
| AA | CRC | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Sen 1 | Spe 1 | YI 2 | Sen 3 Spe ≥95% | Spe 4 Sen ≥80% | AUC | Sen 1 | Spe 1 | YI 2 | Sen 3 Spe ≥95% | Spe 4 Sen ≥80% | ||
| Gr. A | 0.819 | 79.1 | 87.10 | 0.66 | 45.30 | 51.61 | 0.969 | 85.19 | 96.97 | 0.86 | 85.19 | 100.0 | |
| Gr. B | 0.917 | 91.67 | 83.87 | 0.76 | 75.00 | 83.87 | 0.914 | 79.01 | 96.97 | 0.76 | 79.01 | 83.87 | |
| Gr. B | + GADD45B | 0.900 | 75.00 | 87.88 | 0.63 | 70.83 | 72.73 | 0.923 | 79.01 | 96.97 | 0.76 | 79.01 | 87.88 |
| Gr. B | + ITGA2 | 0.900 | 79.17 | 90.91 | 0.70 | 70.83 | 66.67 | 0.929 | 83.95 | 96.97 | 0.81 | 83.95 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + MYBL2 | 0.915 | 79.17 | 93.94 | 0.73 | 75.00 | 78.79 | 0.924 | 85.19 | 93.94 | 0.79 | 80.25 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + MYC | 0.918 | 83.33 | 93.94 | 0.77 | 66.67 | 93.94 | 0.939 | 85.19 | 94.94 | 0.79 | 80.25 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + PTGS2 | 0.905 | 79.17 | 90.32 | 0.70 | 66.67 | 70.97 | 0.944 | 86.42 | 93.55 | 0.80 | 81.48 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + S100A4 | 0.910 | 79.17 | 93.94 | 0.73 | 75.00 | 87.88 | 0.952 | 86.42 | 93.94 | 0.80 | 81.48 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + ITGA2 + S100A4 | 0.897 | 79.17 | 90.91 | 0.69 | 70.83 | 84.85 | 0.958 | 86.42 | 93.94 | 0.80 | 82.72 | 96.97 |
| Gr. B | + ITGA2 + S100A4 | 0.890 | 75.00 | 93.55 | 0.69 | 66.67 | 80.65 | 0.952 | 87.65 | 93.55 | 0.81 | 83.95 | 100.0 |
| Gr. B | + PTGS2 + S100A4 | 0.910 | 83.33 | 87.10 | 0.70 | 75.00 | 87.10 | 0.961 | 88.89 | 96.77 | 0.86 | 88.89 | 96.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herring, E.; Tremblay, É.; McFadden, N.; Kanaoka, S.; Beaulieu, J.-F. Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061228
Herring E, Tremblay É, McFadden N, Kanaoka S, Beaulieu J-F. Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061228
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerring, Elizabeth, Éric Tremblay, Nathalie McFadden, Shigeru Kanaoka, and Jean-François Beaulieu. 2021. "Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061228
APA StyleHerring, E., Tremblay, É., McFadden, N., Kanaoka, S., & Beaulieu, J.-F. (2021). Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas. Cancers, 13(6), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061228






