Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—A Novel View on Inflammation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Findings
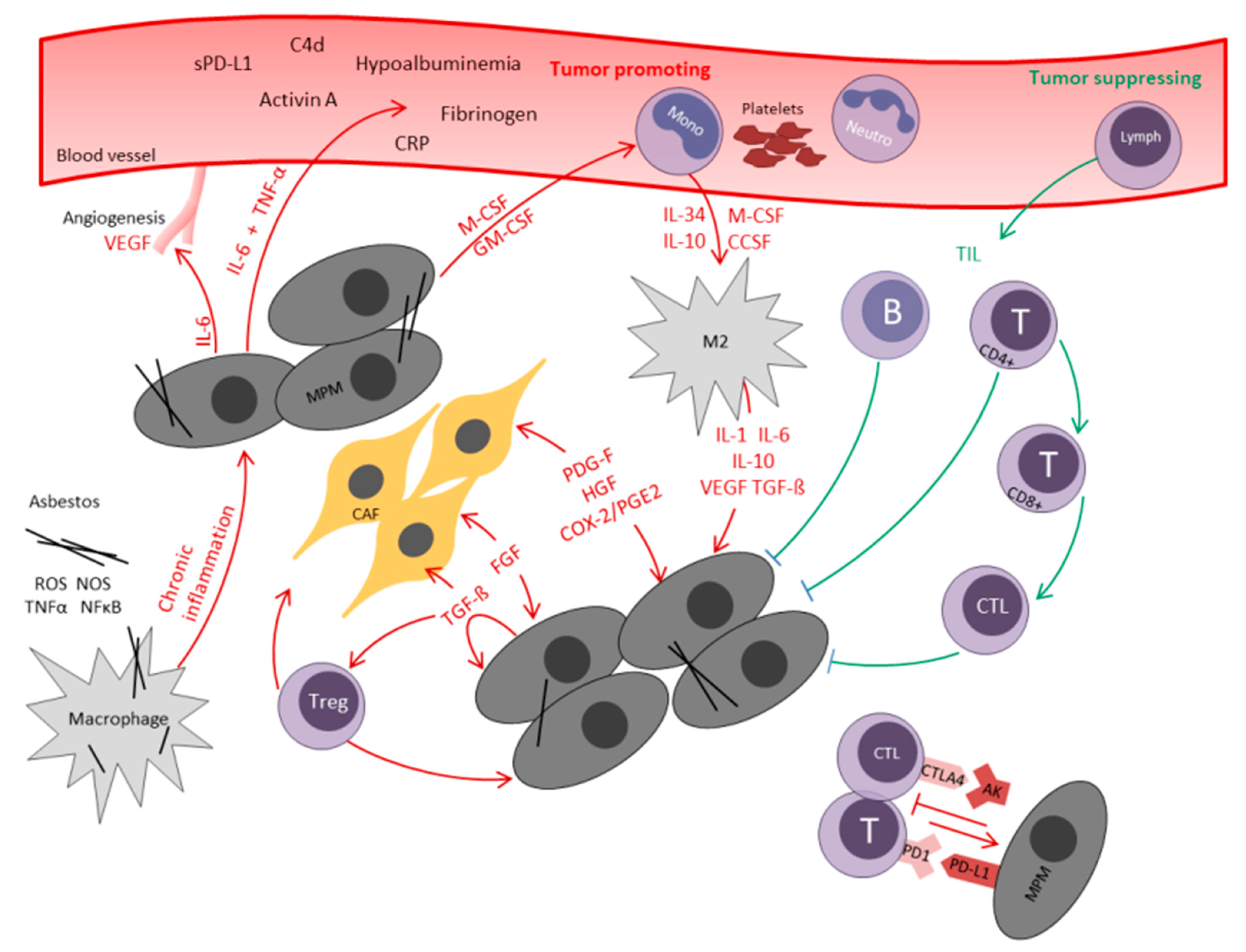
2.1. The Role of Local Inflammation in MPM
2.2. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TIL)
2.3. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAF)
2.4. Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β)
2.5. COX-2
2.6. M2 Macrophages
2.7. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs)
2.8. Natural Killer Cells and Dendritic Cells (DC)
2.9. Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) and Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4 (CTLA-4)
2.10. The Role of Systemic Inflammatory Response in MPM
2.11. Acute-Phase Proteins
2.12. Interleukin 6
2.13. C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
2.14. Fibrinogen
2.15. Albumin—A Negative Acute Phase Protein
2.16. Ferritin
2.17. The Complement System
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, B.W.; Musk, A.W.; Lake, R.A. Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2005, 366, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, S.; Cardillo, G.; Zirafa, C.C.; Carleo, F.; Facciolo, F.; Fontanini, G.; Mutti, L.; Melfi, F. Surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma: An international guidelines review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S285–S292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiki, Y.; Goto, H.; Fukuyama, T.; Nakanishi, K. Should Lung-Sparing Surgery Be the Standard Procedure for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Scherpereel, A.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bölükbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2020, 58, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.C.; Sleggs, C.A.; Marchand, P. Diffuse pleural mesothelioma and asbestos exposure in the North Western Cape Province. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1960, 17, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bononi, A.; Napolitano, A.; Pass, H.I.; Yang, H.; Carbone, M. Latest developments in our understanding of the pathogenesis of mesothelioma and the design of targeted therapies. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2015, 9, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekido, Y. Molecular pathogenesis of malignant mesothelioma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klikovits, T.; Stockhammer, P.; Laszlo, V.; Dong, Y.; Hoda, M.A.; Ghanim, B.; Opitz, I.; Frauenfelder, T.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.L.; Weder, W.; et al. Circulating complement component 4d (C4d) correlates with tumor volume, chemotherapeutic response and survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Klikovits, T.; Hoda, M.A.; Lang, G.; Szirtes, I.; Setinek, U.; Rozsas, A.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Laszlo, V.; Grusch, M.; et al. Ki67 index is an independent prognostic factor in epithelioid but not in non-epithelioid malignant pleural mesothelioma: A multicenter study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Winter, M.P.; Alimohammadi, A.; Grusch, M.; Dome, B.; Arns, M.; Schenk, P.; Jakopovic, M.; et al. Circulating fibrinogen is a prognostic and predictive biomarker in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Winter, M.P.; Klikovits, T.; Alimohammadi, A.; Hegedus, B.; Dome, B.; Grusch, M.; Arns, M.; Schenk, P.; et al. Pretreatment serum C-reactive protein levels predict benefit from multimodality treatment including radical surgery in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective multicenter analysis. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, A.; van Zandwijk, N.; Reid, G.; Clarke, S.; Cao, C.; Kao, S. Inflammation in malignant mesothelioma—friend or foe? Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Friess, M.; Kestenholz, P.; Schneiter, D.; Frauenfelder, T.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.; Seifert, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Klepetko, W.; Stahel, R.A.; et al. A New Prognostic Score Supporting Treatment Allocation for Multimodality Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Review of 12 Years’ Experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarucci, C.; Cannito, S.; Daffinà, M.G.; Amato, G.; Giacobini, G.; Cutaia, O.; Lofiego, M.F.; Fazio, C.; Giannarelli, D.; Danielli, R.; et al. Circulating Levels of PD-L1 in Mesothelioma Patients from the NIBIT-MESO-1 Study: Correlation with Survival. Cancers 2020, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, E.W.; Lopez, J.; Santoro, A.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; van Brummelen, E. Clinical safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): Preliminary results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispel-Janssen, J.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Zimmerman, M.; Lalezari, F.; Thunnissen, E.; Monkhorst, K.; Schouten, R.; Schunselaar, L.; Disselhorst, M.; et al. Programmed Death 1 Blockade With Nivolumab in Patients With Recurrent Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Thomas, A.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Patel, M.R.; Bennouna, J.; Chen, F.L.; Delord, J.P.; Dowlati, A.; Kochuparambil, S.T.; Taylor, M.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Avelumab Treatment in Patients With Advanced Unresectable Mesothelioma: Phase 1b Results From the JAVELIN Solid Tumor Trial. Jama Oncol. 2019, 5, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K. FDA Approves Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab for Previously Untreated Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Oncology (Williston Park) 2020, 34, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Furrer, K. Preoperative Identification of Benefit from Surgery for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2020, 30, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Thangue, N.B.; Kerr, D.J. Predictive biomarkers: A paradigm shift towards personalized cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Opitz, I.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bolukbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur Respir J. 2020, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalamenti, G.; Fanale, D.; Incorvaia, L.; Barraco, N.; Listì, A.; Maragliano, R.; Vincenzi, B.; Calò, V.; Iovanna, J.L.; Bazan, V.; et al. Role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with solid tumors: Can a drop dig a stone? Cell. Immunol. 2019, 343, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, S.; Salgado, R.; Gevaert, T.; Russell, P.A.; John, T.; Thapa, B.; Christie, M.; van de Vijver, K.; Estrada, M.V.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. Assessing Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Solid Tumors: A Practical Review for Pathologists and Proposal for a Standardized Method from the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 2: TILs in Melanoma, Gastrointestinal Tract Carcinomas, Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Mesothelioma, Endometrial and Ovarian Carcinomas, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Genitourinary Carcinomas, and Primary Brain Tumors. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, R.A.; Webster, I. Lymphocytic infiltration of pleural mesothelioma and its significance for survival. South. Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afrik. Tydskr. Vir Geneeskd. 1982, 61, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Koebel, C.M.; Vermi, W.; Swann, J.B.; Zerafa, N.; Rodig, S.J.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature 2007, 450, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnema-Luiting, J.; Vroman, H.; Aerts, J.; Cornelissen, R. Heterogeneity in Immune Cell Content in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcq, E.; Siozopoulou, V.; De Waele, J.; van Audenaerde, J.; Zwaenepoel, K.; Santermans, E.; Hens, N.; Pauwels, P.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Smits, E.L. Prognostic and predictive aspects of the tumor immune microenvironment and immune checkpoints in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1261241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M.; Cunningham, K.S.; Yun, Z.; Tsao, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Keshavjee, S.; Johnston, M.R.; de Perrot, M. Impact of tumor-infiltrating T cells on survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 135, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Oizumi, S.; Kikuchi, E.; Shinagawa, N.; Konishi-Sakakibara, J.; Ishimine, A.; Aoe, K.; Gemba, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Torigoe, T.; et al. CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes predict favorable prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma after resection. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. Cii 2010, 59, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Jones, R.E.; Liu, H.; Lizotte, P.H.; Ivanova, E.V.; Kulkarni, M.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; Liao, X.; Santos, A.A.; Bittinger, M.A.; et al. Cytotoxic T Cells in PD-L1-Positive Malignant Pleural Mesotheliomas Are Counterbalanced by Distinct Immunosuppressive Factors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, G.J.; van Zandwijk, N.; Rasko, J.E.J. The Immune Microenvironment in Mesothelioma: Mechanisms of Resistance to Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.A.; Aerts, J.G.; Popat, S.; Fennell, D.A. Novel insights into mesothelioma biology and implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltman, J.D.; Lambers, M.E.; van Nimwegen, M.; Hendriks, R.W.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Aerts, J.G.; Hegmans, J.P. COX-2 inhibition improves immunotherapy and is associated with decreased numbers of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mesothelioma. Celecoxib influences MDSC function. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Kadota, K.; Nitadori, J.I.; Aerts, J.G.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Travis, W.D.; Jones, D.R.; Krug, L.M.; Adusumilli, P.S. The tumoral and stromal immune microenvironment in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A comprehensive analysis reveals prognostic immune markers. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1009285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasello, G.; Zago, G.; Lunardi, F.; Urso, L.; Kern, I.; Vlacic, G.; Grosso, F.; Mencoboni, M.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Schiavon, M.; et al. Malignant pleural mesothelioma immune microenvironment and checkpoint expression: Correlation with clinical-pathological features and intratumor heterogeneity over time. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, A.; Santini, D.; Vasaturo, F.; Santini, M.; Vicidomini, G.; Di Marino, M.P.; Esposito, V.; Groeger, A.M.; Liuzzi, G.; Vincenzi, B.; et al. Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and expression of cell cycle inhibitors p21 and p27 in human pleural malignant mesothelioma. Thorax 2004, 59, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mineo, T.C.; Ambrogi, V.; Cufari, M.E.; Pompeo, E. May cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), p21 and p27 expression affect prognosis and therapeutic strategy of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2010, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.G.; Faux, S.P.; Plummer, S.M.; Abrams, K.R.; Walker, R.A.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a novel prognostic factor in malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar]
- O’Kane, S.L.; Cawkwell, L.; Campbell, A.; Lind, M.J. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression predicts survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxf. Engl. 1990) 2005, 41, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedrés, S.; Ponce-Aix, S.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Sansano, I.; Enguita, A.; Navarro-Mendivil, A.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Martinez, P.; Felip, E. Analysis of expression of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, R.; Lievense, L.A.; Maat, A.P.; Hendriks, R.W.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Bogers, A.J.; Hegmans, J.P.; Aerts, J.G. Ratio of intratumoral macrophage phenotypes is a prognostic factor in epithelioid malignant pleural mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondy, T.; d’Almeida, S.M.; Briolay, T.; Tabiasco, J.; Meiller, C.; Chéné, A.L.; Cellerin, L.; Deshayes, S.; Delneste, Y.; Fonteneau, J.F.; et al. Involvement of the M-CSF/IL-34/CSF-1R pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaguma, S.; Lasota, J.; Wang, Z.; Czapiewski, P.; Langfort, R.; Rys, J.; Szpor, J.; Waloszczyk, P.; Okoń, K.; Biernat, W.; et al. Expression of ALCAM (CD166) and PD-L1 (CD274) independently predicts shorter survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, A.S.; Roden, A.C.; Peikert, T.; Sheinin, Y.M.; Harrington, S.M.; Krco, C.J.; Dong, H.; Kwon, E.D. B7-H1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma is associated with sarcomatoid histology and poor prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2014, 9, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, B.; Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K. CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: A review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8509–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, R.; Lievense, L.A.; Robertus, J.L.; Hendriks, R.W.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Hegmans, J.P.; Aerts, J.G. Intratumoral macrophage phenotype and CD8+ T lymphocytes as potential tools to predict local tumor outgrowth at the intervention site in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer (Amst. Neth.) 2015, 88, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Contribution of regulatory T cells to cancer: A review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7983–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegmans, J.P.; Hemmes, A.; Hammad, H.; Boon, L.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N. Mesothelioma environment comprises cytokines and T-regulatory cells that suppress immune responses. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, D.R.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Himbeck, R.P.; Jarnicki, A.G.; Marzo, A.L.; Robinson, B.W. Transforming growth factor-beta: Antisense RNA-mediated inhibition affects anchorage-independent growth, tumorigenicity and tumor-infiltrating T-cells in malignant mesothelioma. Growth Factors (ChurSwitz.) 1994, 11, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, M.A.; Münzker, J.; Ghanim, B.; Schelch, K.; Klikovits, T.; Laszlo, V.; Sahin, E.; Bedeir, A.; Lackner, A.; Dome, B.; et al. Suppression of activin A signals inhibits growth of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, M.A.; Dong, Y.; Rozsas, A.; Klikovits, T.; Laszlo, V.; Ghanim, B.; Stockhammer, P.; Ozsvar, J.; Jakopovic, M.; Samarzija, M.; et al. Circulating activin A is a novel prognostic biomarker in malignant pleural mesothelioma—A multi-institutional study. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxf. Engl. 1990) 2016, 63, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvoli, B.; Galati, R. Cyclooxygenase-2, epidermal growth factor receptor, and aromatase signaling in inflammation and mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrogi, A.; Pass, H.I.; Khan, M.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Harris, C.C.; Gerwin, B.I. Human mesothelioma samples overexpress both cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2): In vitro antiproliferative effects of a COX-2 inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Sakai, K.; Bando, Y.; Uehara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S.; Iwakiri, S.; et al. Pleural mesothelioma instigates tumor-associated fibroblasts to promote progression via a malignant cytokine network. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelch, K.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Münzker, J.; Ghanim, B.; Wagner, C.; Garay, T.; Laszlo, V.; Setinek, U.; Dome, B.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibition is active against mesothelioma and synergizes with radio- and chemotherapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelch, K.; Wagner, C.; Hager, S.; Pirker, C.; Siess, K.; Lang, E.; Lin, R.; Kirschner, M.B.; Mohr, T.; Brcic, L.; et al. FGF2 and EGF induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells via a MAPKinase/MMP1 signal. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlacic, G.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Sinn, K.; Gschwandtner, E.; Mohorcic, K.; Schelch, K.; Pirker, C.; Peter-Vorosmarty, B.; Brankovic, J.; et al. Expression of FGFR1-4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cells 2019, 8, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahremanifard, P.; Chanda, A.; Bonni, S.; Bose, P. TGF-beta Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer-Spotlight on Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers 2020, 12, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Goradel, N.; Najafi, M.; Salehi, E.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: A review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5683–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tołoczko-Iwaniuk, N.; Dziemiańczyk-Pakieła, D.; Nowaszewska, B.K.; Celińska-Janowicz, K.; Miltyk, W. Celecoxib in Cancer Therapy and Prevention—Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yi, C. The role of celecoxib for colorectal cancer treatment: A systematic review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Blanke, C.D.; Haller, D.G.; Benson, A.B.; Dragovich, T.; Lenz, H.J.; Robles, C.; Li, H.; Mori, M.; Mattek, N.; et al. A Phase II Study of Celecoxib with Irinotecan, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in Patients With Previously Untreated Advanced or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yi, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J. Comparison of the benefits of celecoxib combined with anticancer therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Shen, J.; Zou, J.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the benefit of celecoxib in treating advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Alfonso, H.; Woo, S.; Olsen, N.; Bill Musk, A.W.; Robinson, B.W.; Nowak, A.K.; Lake, R.A. Effect of NSAIDS and COX-2 inhibitors on the incidence and severity of asbestos-induced malignant mesothelioma: Evidence from an animal model and a human cohort. Lung Cancer (Amst. Neth.) 2014, 86, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Janeiro, Á.; Padilla-Ansala, C.; de Andrea, C.E.; Hardisson, D.; Melero, I. Prognostic value of macrophage polarization markers in epithelial neoplasms and melanoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. United States Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc. 2020, 33, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Graciotti, L.; Rinaldi, L.; Raffaelli, G.; Rodilossi, S.; Betta, P.; Gianni, W.; Amoroso, S.; Procopio, A. Preclinical evaluation of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent celecoxib on malignant mesothelioma chemoprevention. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; Zenzie, B.W.; Rheinwald, J.G.; Griffin, J.D. Expression of colony-stimulating factor genes by normal human mesothelial cells and human malignant mesothelioma cells lines in vitro. Blood 1989, 74, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, B.M.; Rodig, S.J.; Tilleman, T.R.; Elbardissi, A.W.; Bueno, R.; Sugarbaker, D.J. Circulating and tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells predict survival in human pleural mesothelioma. Cancer 2011, 117, 5234–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chéné, A.L.; d’Almeida, S.; Blondy, T.; Tabiasco, J.; Deshayes, S.; Fonteneau, J.F.; Cellerin, L.; Delneste, Y.; Grégoire, M.; Blanquart, C. Pleural Effusions from Patients with Mesothelioma Induce Recruitment of Monocytes and Their Differentiation into M2 Macrophages. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitter, D.; Lauber, B.; Fagg, B.; Stahel, R.A. Hematopoietic growth factors secreted by seven human pleural mesothelioma cell lines: Interleukin-6 production as a common feature. Int. J. Cancer 1992, 51, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueugnon, F.; Leclercq, S.; Blanquart, C.; Sagan, C.; Cellerin, L.; Padieu, M.; Perigaud, C.; Scherpereel, A.; Gregoire, M. Identification of novel markers for the diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanquart, C.; Gueugnon, F.; Nguyen, J.M.; Roulois, D.; Cellerin, L.; Sagan, C.; Perigaud, C.; Scherpereel, A.; Gregoire, M. CCL2, galectin-3, and SMRP combination improves the diagnosis of mesothelioma in pleural effusions. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2012, 7, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, A.Z.; Pang, H.; Kratzke, R.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Hodgson, L.; Vokes, E.E.; Kindler, H.L. Phase II study of dasatinib in patients with previously treated malignant mesothelioma (cancer and leukemia group B 30601): A brief report. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2012, 7, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.; Fujimoto, N.; Ebara, T.; Omori, T.; Oguri, T.; Niimi, A.; Yokoyama, T.; Kato, M.; Usami, I.; Nishio, M.; et al. Serum levels of the chemokine CCL2 are elevated in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients. Bmc Cancer 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, C.; Knapp, S.; Mascaux, C.; Hirsch, F. Rationale for targeting the immune system through checkpoint molecule blockade in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol 2013, 24, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Yu, P.C.; Long, D.; Liao, X.L.; Zhang, S.; You, X.M.; Zhong, J.H.; Li, L.Q. Prognostic value of PD -L1 expression in patients with primary solid tumors. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5058–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Rosenmayr, A.; Stockhammer, P.; Vogl, M.; Celik, A.; Bas, A.; Kurul, I.C.; Akyurek, N.; Varga, A.; Plönes, T.; et al. Tumour cell PD-L1 expression is prognostic in patients with malignant pleural effusion: The impact of C-reactive protein and immune-checkpoint inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aggarwal, C.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 1.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.L.; Walsh, R.J.; Ang, Y.; Chan, G.; Soo, R.A. The evolving immuno-oncology landscape in advanced lung cancer: First-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919870360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Gu, W.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. PD-L1 and prognosis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics study. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920962362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosseau, S.; Danel, C.; Scherpereel, A.; Mazières, J.; Lantuejoul, S.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Gounant, V.; Antoine, M.; et al. Shorter Survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Patients With High PD-L1 Expression Associated With Sarcomatoid or Biphasic Histology Subtype: A Series of 214 Cases From the Bio-MAPS Cohort. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e564–e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.G.; Schulte, J.J.; Xue, L.; Berger, Y.; Schuitevoerder, D.; Vining, C.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Husain, A.; Turaga, K.K.; Eng, O.S. Heterogeneity in PD-L1 expression in malignant peritoneal mesothelioma with systemic or intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gooijer, C.J.; Borm, F.J.; Scherpereel, A.; Baas, P. Immunotherapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carosio, R.; Fontana, V.; Mastracci, L.; Ferro, P.; Grillo, F.; Banelli, B.; Canessa, P.A.; Dessanti, P.; Vigani, A.; Morabito, A.; et al. Characterization of soluble PD-L1 in pleural effusions of mesothelioma patients: Potential implications in the immune response and prognosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hall, S.R.R.; Sun, B.; Yao, F. Comment on “Heterogeneity in PD-L1 expression in malignant peritoneal mesothelioma with systemic or intraperitoneal chemotherapy”. Br. J. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyotani, K.; Park, J.H.; Inoue, H.; Husain, A.; Olugbile, S.; Zewde, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Vigneswaran, W.T. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and immune microenvironment in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1278330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Yang, Z.; Yao, F.; Zhao, H.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.W. Systematic Analysis of Aberrant Biochemical Networks and Potential Drug Vulnerabilities Induced by Tumor Suppressor Loss in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.W. Biomarker-guided targeted and immunotherapies in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920971421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk-Wojtaś, A.; Lubas, A.; Stec, R.; Syryło, T.; Niemczyk, S.; Szczylik, C. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio, and C-reactive Protein as New and Simple Prognostic Factors in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2018, 16, e685–e693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, C.; McRae, L.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Kirk, A.; Milroy, R. Elevated preoperative C-reactive protein predicts poor cancer specific survival in patients undergoing resection for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2010, 5, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, C.; Ding, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Xie, M.; Zhou, J. The prognostic value of the preoperative c-reactive protein/albumin ratio in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Chu, L.; Fang, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Xu, Q. Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Liang, R.; Chen, G.; Qin, G.; Li, Y.; Zou, D. Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen in digestive cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, L. Prognostic role of pre-treatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrikulu, A.C.; Abakay, A.; Komek, H.; Abakay, O. Prognostic value of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio and other inflammatory markers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2016, 21, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Mauri, F.A.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Wahab, L.; Lloyd, T.; Sharma, R. Inflammation-based prognostic indices in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2012, 7, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoshi, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Kaku, S.; Iki, R.; Hirabayashi, M. Prognostic Impact of Inflammation-related Biomarkers on Overall Survival of Patients with Inoperable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Vivo (Athens Greece) 2018, 32, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D.; Sahmoud, T.; Therasse, P.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Postmus, P.E.; Giaccone, G. Prognostic factors in patients with pleural mesothelioma: The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer experience. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, J.E.; Green, M.R.; Chahinian, A.P.; Corson, J.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Vogelzang, N.J. Factors predictive of survival among 337 patients with mesothelioma treated between 1984 and 1994 by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. Chest 1998, 113, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.A.; Parmar, A.; Shamash, J.; Evans, M.T.; Sheaff, M.T.; Sylvester, R.; Dhaliwal, K.; Gower, N.; Steele, J.; Rudd, R. Statistical validation of the EORTC prognostic model for malignant pleural mesothelioma based on three consecutive phase II trials. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meniawy, T.M.; Creaney, J.; Lake, R.A.; Nowak, A.K. Existing models, but not neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, are prognostic in malignant mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.G.; Abrams, K.R.; Leverment, J.N.; Spyt, T.J.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J. Prognostic factors for malignant mesothelioma in 142 patients: Validation of CALGB and EORTC prognostic scoring systems. Thorax 2000, 55, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, A.; Guerrera, F.; Roffinella, M.; Olivetti, S.; Costardi, L.; Oliaro, A.; Filosso, P.L.; Lausi, P.O.; Ruffini, E. Validation of EORTC and CALGB prognostic models in surgical patients submitted to diagnostic, palliative or curative surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billé, A.; Krug, L.M.; Woo, K.M.; Rusch, V.W.; Zauderer, M.G. Contemporary Analysis of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cao, S.; Jin, S.; Cao, J.; Shen, J.; Pan, B.; Zhu, R.; Yu, Y. Elevated aspartate aminotransferase and monocyte counts predict unfavorable prognosis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffie, P.; Feld, R.; Minkin, S.; Cormier, Y.; Boutan-Laroze, A.; Ginsberg, R.; Ayoub, J.; Shepherd, F.A.; Evans, W.K.; Figueredo, A.; et al. Diffuse malignant mesothelioma of the pleura in Ontario and Quebec: A retrospective study of 332 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, M.; Strano, S.; Dechartres, A.; Jouni, R.; Triponez, F.; Chouaid, C.; Forgez, P.; Damotte, D.; Roche, N.; Régnard, J.F.; et al. Outcome and prognostic factors of pleural mesothelioma after surgical diagnosis and/or pleurodesis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bowen, R.C.; Little, N.A.B.; Harmer, J.R.; Ma, J.; Mirabelli, L.G.; Roller, K.D.; Breivik, A.M.; Signor, E.; Miller, A.B.; Khong, H.T. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic indicator in gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32171–32189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, S.; Raunegger, T.; Hacker, P.; Ghanim, B.; Einwallner, E.; Müllauer, L.; Schiefer, A.I.; Moser, J.; Klepetko, W.; Ankersmit, H.J.; et al. Prognostic and diagnostic impact of fibrinogen, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio on thymic epithelial tumors outcome. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21861–21875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethier, J.L.; Desautels, D.; Templeton, A.; Shah, P.S.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Bcr 2017, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haram, A.; Boland, M.R.; Kelly, M.E.; Bolger, J.C.; Waldron, R.M.; Kerin, M.J. The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: A systematic review. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, S.; Schmid, S.; Krapf, M.; Flatz, L.; Born, D.; Jochum, W.; Templeton, A.J.; Früh, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer (Amst. Neth.) 2017, 111, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriu, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagano, T.; Hazama, D.; Sekiya, R.; Katsurada, M.; Tamura, D.; Tachihara, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. The time-series behavior of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is useful as a predictive marker in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodying, H.; Matsuda, A.; Miyashita, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sakurazawa, N.; Yamada, M.; Uchida, E. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Oncologic Outcomes of Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Schweiger, T.; Jedamzik, J.; Glueck, O.; Glogner, C.; Lang, G.; Klepetko, W.; Hoetzenecker, K. Elevated inflammatory parameters and inflammation scores are associated with poor prognosis in patients undergoing pulmonary metastasectomy for colorectal cancer. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Pavlakis, N.; Harvie, R.; Vardy, J.L.; Boyer, M.J.; van Zandwijk, N.; Clarke, S.J. High blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an indicator of poor prognosis in malignant mesothelioma patients undergoing systemic therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5805–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Klebe, S.; Henderson, D.W.; Reid, G.; Chatfield, M.; Armstrong, N.J.; Yan, T.D.; Vardy, J.; Clarke, S.; van Zandwijk, N.; et al. Low calretinin expression and high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are poor prognostic factors in patients with malignant mesothelioma undergoing extrapleural pneumonectomy. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2011, 6, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X. Prognostic role of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio for patients with cancer: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31926–31942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zheng, G.; Su, S.; Liang, Y. The Value of COX-2, NF-κB, and Blood Routine Indexes in the Prognosis of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2019, 42, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, T.; Xiao, J. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in advanced Cancer: Review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2018, 483, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Li, W.; Huang, K.; Yang, W.; Huang, L.; Cong, T.; Li, Q.; Qiu, M. Increased platelet-lymphocyte ratio closely relates to inferior clinical features and worse long-term survival in both resected and metastatic colorectal cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 24 studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32356–32369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Fathy, A.H.; Qian, H.; Zhao, Y. Prognostic value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: A comprehensive meta-analysis of 17 cohort studies. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Prognostic value of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Chahinian, A.P.; Shinjo, M.; Tonomura, A.; Miyake, M.; Togawa, N.; Ninomiya, K.; Higashino, K. Interleukin 6 and its relationship to clinical parameters in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Jaurand, M.C.; Monnet, I.; Chretien, P.; Saint-Etienne, L.; Zeng, L.; Portier, A.; Devillier, P.; Galanaud, P.; Bignon, J.; et al. Intrapleural production of interleukin 6 during mesothelioma and its modulation by gamma-interferon treatment. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 4419–4423. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Rahim, S.N.; Ho, G.Y.; Coward, J.I. The role of interleukin-6 in malignant mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scambia, G.; Testa, U.; Benedetti Panici, P.; Foti, E.; Martucci, R.; Gadducci, A.; Perillo, A.; Facchini, V.; Peschle, C.; Mancuso, S. Prognostic significance of interleukin 6 serum levels in patients with ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 71, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelot, T.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Menetrier-Caux, C.; Rastkha, M.; Duc, A.; Blay, J.Y. Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainer, N.; Dehlendorff, C.; Johansen, J.S. Systematic literature review of IL-6 as a biomarker or treatment target in patients with gastric, bile duct, pancreatic and colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29820–29841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, H. Prognostic value of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in laryngeal squamous cell cancer. Med. Oncol. (Northwood Lond. Engl.) 2013, 30, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Hsiao, C.F.; Yeh, Y.M.; Chang, G.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Huang, M.S.; Chen, H.L.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, P.C.; et al. Circulating interleukin-6 level is a prognostic marker for survival in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Tomida, M.; Akiyama, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Okada, D.; Yoshino, N.; Takiguchi, Y.; Tanzawa, H. Serum hepatocyte growth factor and interleukin-6 are effective prognostic markers for non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3251–3258. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Qiao, M.; Luo, J.; et al. Impact of serum vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 on treatment response to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amst. Neth.) 2018, 125, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Luukkaala, T.; Moilanen, E.; Tammela, T.L.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.L. Resistin and interleukin 6 as predictive factors for recurrence and long-term prognosis in renal cell cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 544.e525–544.e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, D.H.; Park, C.K.; Chung, C.; Oh, I.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, D.; Kim, J.; Kwon, G.C.; Kwon, I.; Sun, P.; et al. Baseline Serum Interleukin-6 Levels Predict the Response of Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilskog, M.; Nilsen, G.H.; Beisland, C.; Straume, O. Elevated plasma interleukin 6 predicts poor response in patients treated with sunitinib for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2019, 19, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Chen, P.T.; Lu, M.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Lee, K.D. IL-6 expression predicts treatment response and outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Harvie, R.; Paturi, F.; Taylor, R.; Davey, R.; Abraham, R.; Clarke, S.; Marx, G.; Cullen, M.; Kerestes, Z.; et al. The predictive role of serum VEGF in an advanced malignant mesothelioma patient cohort treated with thalidomide alone or combined with cisplatin/gemcitabine. Lung Cancer (Amst. Neth.) 2012, 75, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.G.; Cox, G.; Andi, A.; Jones, J.L.; Walker, R.A.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J. Angiogenesis is an independent prognostic factor in malignant mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizzi, L.; Catalano, A.; Vianale, G.; Orecchia, S.; Casalini, A.; Tassi, G.; Puntoni, R.; Mutti, L.; Procopio, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human malignant mesothelioma. J. Pathol. 2001, 193, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Aoki, C.; Yoshio-Hoshino, N.; Takayama, K.; Curiel, D.T.; Nishimoto, N. Interleukin-6 induces both cell growth and VEGF production in malignant mesotheliomas. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Yoshio-Hoshino, N.; Aoki, C.; Nishimoto, N. VEGF targeting in mesotheliomas using an interleukin-6 signal inhibitor based on adenovirus gene delivery. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.K.; Brosseau, S.; Cook, A.; Zalcman, G. Antiangiogeneic Strategies in Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounant, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillett, W.S.; Francis, T. Serological Reactions in Pneumonia with a Non-Protein Somatic Fraction of Pneumococcus. J. Exp. Med. 1930, 52, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibuki, Y.; Hamai, Y.; Hihara, J.; Emi, M.; Taomoto, J.; Furukawa, T.; Yamakita, I.; Kurokawa, T.; Okada, M. Role of Postoperative C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Prognosis After Surgical Treatment of Esophageal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yu, X.F.; Zhang, S.D.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Teng, L.S. Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2013, 14, 5735–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, S.; Bekos, C.; Hacker, P.; Raunegger, T.; Ghanim, B.; Einwallner, E.; Beer, L.; Klepetko, W.; Müllauer, L.; Ankersmit, H.J.; et al. Elevated CRP levels predict poor outcome and tumor recurrence in patients with thymic epithelial tumors: A pro- and retrospective analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47090–47102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Gemba, K.; Aoe, K.; Kato, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sato, T.; Kubota, K.; Kishimoto, T. Survival and prognostic factors in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective study of 314 patients in the west part of Japan. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 41, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Vardy, J.; Harvie, R.; Chatfield, M.; van Zandwijk, N.; Clarke, S.; Pavlakis, N. Health-related quality of life and inflammatory markers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Supportive Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Supportive Care Cancer 2013, 21, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvoix, A.; Dickens, J.; Haq, I.; Mannino, D.; Miller, B.; Tal-Singer, R.; Lomas, D.A. Blood fibrinogen as a biomarker of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 2013, 68, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Koenig, W. Utility of inflammatory markers in the management of coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 10i–18i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Deng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Lin, G.; Dong, M.; Huang, Z. Pretreatment plasma fibrinogen level as a prognostic biomarker for patients with lung cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo Braz.) 2020, 75, e993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y. Prognostic value of pretreatment plasma fibrinogen in patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Y. Clinicopathological and prognostic value of preoperative plasma fibrinogen in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e17310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisanidis, C.; Psyrri, A.; Cohen, E.E.; Engelmann, J.; Heinze, G.; Perisanidis, B.; Stift, A.; Filipits, M.; Kornek, G.; Nkenke, E. Prognostic role of pretreatment plasma fibrinogen in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebacher, V.; Polterauer, S.; Grimm, C.; Husslein, H.; Leipold, H.; Hefler-Frischmuth, K.; Tempfer, C.; Reinthaller, A.; Hefler, L. The prognostic value of plasma fibrinogen levels in patients with endometrial cancer: A multi-centre trial. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Hess, S.; Bertoglio, P.; Celik, A.; Bas, A.; Oberndorfer, F.; Melfi, F.; Mussi, A.; Klepetko, W.; Pirker, C.; et al. In-trathoracic solitary fibrous tumor—An international multicenter study on clinical outcome and novel circulating biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.B.; Yi, P.H.; Thomas, C.F.; Garcia, J.; Della Valle, C.J. Evaluation of malnutrition in orthopaedic surgery. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.C.; Aboud, A.; Henry, B.M.; Omara, M.; Lindner, J.; Pirk, J. Serum albumin in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A meta-analysis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 20, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, P.L.; Goh, S.L.; Dhital, K. Is low serum albumin associated with postoperative complications in patients undergoing cardiac surgery? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvetti, D.J.; Tempel, Z.J.; Goldschmidt, E.; Colwell, N.A.; Angriman, F.; Panczykowski, D.M.; Agarwal, N.; Kanter, A.S.; Okonkwo, D.O. Low preoperative serum prealbumin levels and the postoperative surgical site infection risk in elective spine surgery: A consecutive series. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 29, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, T.J.; Brown, M.P.; Slish, J.H.; Rosenthal, M.D. Serum Levels of Prealbumin and Albumin for Preoperative Risk Stratification. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 34, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.H.; Tian, G.Y.; Yang, S.X.; Wan, Y.Y.; Kang, Y.M.; Liu, Q.H.; Yao, F.; Lin, D.J. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 6839–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.J.A.; Kao, S.; McCaughan, B.; Nakano, T.; Kondo, N.; Hyland, R.; Nowak, A.K.; de Klerk, N.H.; Brims, F.J.H. Prediction modelling using routine clinical parameters to stratify survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brims, F.J.; Meniawy, T.M.; Duffus, I.; de Fonseka, D.; Segal, A.; Creaney, J.; Maskell, N.; Lake, R.A.; de Klerk, N.; Nowak, A.K. A Novel Clinical Prediction Model for Prognosis in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Using Decision Tree Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score: A decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, E.; Cairns, E.; Hamilton, J.; Kelly, C. Evaluation of a modified early warning system for acute medical admissions and comparison with C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of patient outcome. Clin. Med. (Lond. Engl.) 2009, 9, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranzani, O.T.; Zampieri, F.G.; Forte, D.N.; Azevedo, L.C.; Park, M. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts 90-day mortality of septic patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudou, K.; Saeki, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Kamori, T.; Kawazoe, T.; Haruta, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Sasaki, S.; Jogo, T.; et al. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio is a poor prognostic factor of esophagogastric junction and upper gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, S. Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Dose-Response A Publ. Int. Hormesis Soc. 2020, 18, 1559325820931290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Li, W.M. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with lung cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, P.; Li, F.S. Prognostic role of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in colorectal cancer: A meta analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamori, S.; Toyokawa, G.; Shimokawa, M.; Kinoshita, F.; Kozuma, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Haratake, N.; Akamine, T.; Hirai, F.; Seto, T.; et al. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio is a Novel Significant Prognostic Factor in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Retrospective Multi-institutional Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thachil, J. The beneficial effect of acute phase increase in serum ferritin. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 35, e16–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernan, K.F.; Carcillo, J.A. Hyperferritinemia and inflammation. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.Y.; Mina, E.; Roetto, A.; Porporato, P.E. Iron: An Essential Element of Cancer Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, S. Iron addiction with ferroptosis-resistance in asbestos-induced mesothelial carcinogenesis: Toward the era of mesothelioma prevention. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döngel, İ.; Akbaş, A.; Benli, İ.; Bayram, M. Comparison of serum biochemical markers in patients with mesothelioma and pleural plaques versus healthy individuals exposed to environmental asbestos. Turk. Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2019, 27, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgi, C.; Taylan, M.; Sen, H.S.; Evliyaoğlu, O.; Kaya, H.; Abakay, O.; Abakay, A.; Tanrıkulu, A.C.; Senyiğit, A. Oxidative status and acute phase reactants in patients with environmental asbestos exposure and mesothelioma. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 902748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Akatsuka, S.; Nagai, H.; Chew, S.H.; Ohara, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Yasui, H.; Ikuta, K.; et al. Iron overload signature in chrysotile-induced malignant mesothelioma. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, Y.; Chew, S.H.; Shibata, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Toyokuni, S. Phlebotomy as a preventive measure for crocidolite-induced mesothelioma in male rats. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinis, C.; Vidergar, R.; Belmonte, B.; Mangogna, A.; Amadio, L.; Geri, P.; Borelli, V.; Zanconati, F.; Tedesco; Confalonieri, M.; et al. Complement Protein C1q Binds to Hyaluronic Acid in the Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Microenvironment and Promotes Tumor Growth. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker | Unfavorable | Univariate Value | Multivariate Value | Impact | Design | Number of Patients/Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-TIL | Low | HR: N.R. | HR: 0.7 | Prog | R | 217 | [37] |
| CD8+ TIL | Low | HR: N.S.-N.R. | HR: N.S.-0.4 | All prog | All R | 16–32 | [30,31,38,39] |
| CD8+ TIL | High | HR: N.R. | HR: N.R. | Prog | R | 93 | [38] |
| M2/CD8+ TIL | high | HR: N.R. | HR: 1.6 | Prog | R | 210 | [37] |
| M2/B-TIL | Low | HR: N.R. | HR: 1.6 | Prog | R | 210 | [37] |
| CD4+ TIL | Low | HR: N.S.-N.R. | HR: N.S.-N.R. | All prog | All R | 27–218 | [30,31,32,37,38] |
| COX-2 | High | HR: N.R.-2.9 | HR: N.S.-4.6 | All prog | R/R/P | 29–77 | [39,40,41] |
| COX-2 | Low | HR: N.R. | HR: N.R. | Prog | R | 86 | [42] |
| M2 | High | HR: N.S.-1.7 | HR: N.S. | All prog | All R | 4–210 | [38,39,43] |
| M2/TAM | High | HR: N.R. | HR: N.S. | Prog | R | 8 | [44] |
| IL-34 | High | HR: N.R. | HR: N.R. | Prog | R | 74 | [45] * |
| M-CSF | High | HR: N.R. | HR: N.S. | Prog | R | 74 | [45] * |
| PD-L1 | High | HR: N.S.-N.R | HR: N.S.-2.3 | All prog | All R | 33–106 | [17,30,43,46,47] |
| Biomarker | Unfavorable | Univariate Value | Multivariate Value | Impact | Design | Number of Patients/Range | Cut-Off Value | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC count | High | HR: N.S.-1.9 | HR: N.S.-2.3 | All prog | All R | 84–363 | 8.1–15.6 109/L/8.3 109/L * | [102,103,107,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117] | |
| Lymphocytes | Low | N.S.-N.R. | N.S. | All prog | All R | 105–285 | 1.27–2.0 109/L | [102,114,117] | |
| Monocyte count | High | HR: N.R.-4.0 | HR: N.S.-2.7 | All prog | All R | 105–667 | 0.55 109/L | [43,102,114] | |
| M-CSF | High | HR: 1.6 | HR: N.S | Prog | R | 36 | 1120 | [79] | |
| Neutrophil count | High | HR: N.S.-N.R. | HR: N.S. | All prog | All R | 105–285 | 5.3–5.89 109/L | [102,114,117] | |
| Platelet count | High | HR: N.S-2.1 | HR: N.S.-2.1 | All prog | All R | 84–363 | 300–450 g/L, 400 109/L * | [102,103,107,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118] | |
| NLR | High | HR: N.S.-2.3 | HR: N.S.-2.7 | All prog | All R | 30–285 | 3 and 5/5 * | [102,103,104,109,110,111,112,113,119,120,121] | |
| NLR normalization after treatment | No | HR: N.R.-2.2 | All prog | All R | 66–69 | Decline to 5 | [109,111] | ||
| LMR | Low | HR: N.R. | HR: N.S.-1.8 | All prog | All R | 105–283 | 2.36–2.74 | [102,114,122] | |
| PLR | High | HR: N.R.-1.5 | HR: N.S. | All prog | All R | 105–285 | 144–300 | [102,103,114] | |
| CRP | High | HR: N.S-2.8 | HR: N.S.-2.7 | All prog and [11] pred | All R | 115–363 | 10–50 mg/L/10 mg/L* | [11,102,103,115,116,123] | |
| CAR | High | HR: N.S.-2.6 | HR: N.S.-2.1 | All prog | All R | 100–201 | 0.58 and 7.5, 0.58 * | [102,104,124] | |
| mGPS | High | HR: N.R. | HR: 2.6 | Prog | R | 132 | 1 | [103] | |
| Fibrinogen | High | HR: 2.1 | HR: 1.8 | Prog and pred | R | 176 | 750 mg/dL | [10] | |
| Albumin | Low | HR: N.R.-1.5 | HR: N.S.-1.8 | All prog | All R | 97–278 | 35–40 g/L, 35 g/L * | [102,103,114,125] | |
| C4d | High | HR: 7.3 high vs. low | HR: 0.3 low vs. high | Prog | R | 30 | 1.5 µg/mL | [8] | |
| Activin A | High | HR: 0.4 | HR: 0.4 | Prog | R | 119 | 574.0 pg/mL | [55] | |
| sPD-L1 | High | HR: N.R. | H.R.: N.S. | Prog | P | 40 | 0.07–1.83 ng/mL measured at 4 timepoints during therapy | [15] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogl, M.; Rosenmayr, A.; Bohanes, T.; Scheed, A.; Brndiar, M.; Stubenberger, E.; Ghanim, B. Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—A Novel View on Inflammation. Cancers 2021, 13, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040658
Vogl M, Rosenmayr A, Bohanes T, Scheed A, Brndiar M, Stubenberger E, Ghanim B. Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—A Novel View on Inflammation. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040658
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogl, Melanie, Anna Rosenmayr, Tomas Bohanes, Axel Scheed, Milos Brndiar, Elisabeth Stubenberger, and Bahil Ghanim. 2021. "Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—A Novel View on Inflammation" Cancers 13, no. 4: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040658
APA StyleVogl, M., Rosenmayr, A., Bohanes, T., Scheed, A., Brndiar, M., Stubenberger, E., & Ghanim, B. (2021). Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—A Novel View on Inflammation. Cancers, 13(4), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040658








