The Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in a Nationwide Cohort of Young Colorectal Cancer Patients Using a Panel of 18 Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients with Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants
2.2. Patients with No Reported Pathogenic Germline Variants
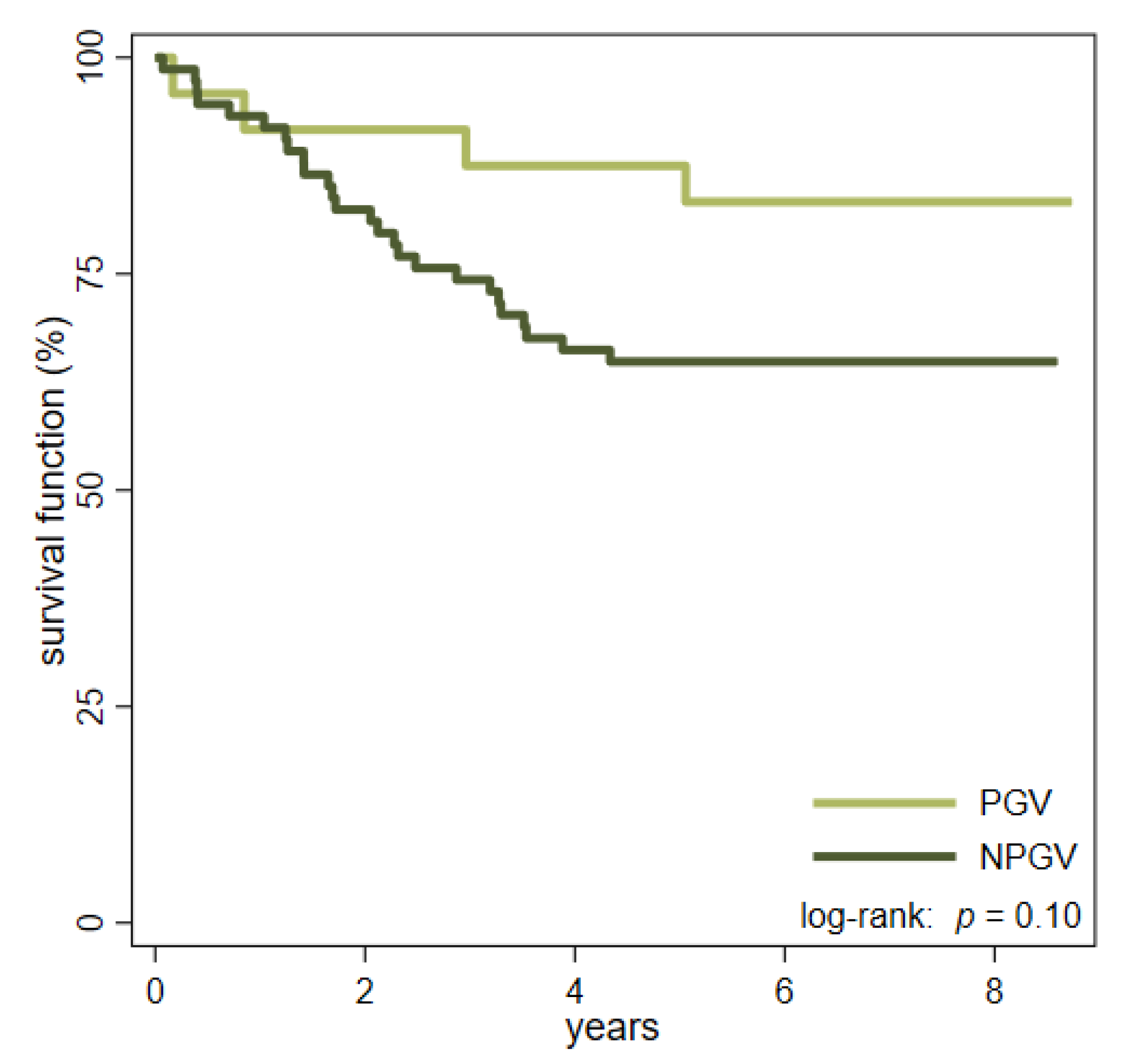
2.3. Differences between PGV Carriers and Non-Carriers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Clinical and Pathological Data
4.3. Molecular Analysis
4.4. Statistical Methods
4.5. Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danish Colorectal Cancer Group (DCCG). Landsdækkende Database for Kræft i Tyk- og Endetarm—Årsrapport 2017 (Annual Report 2017). 2018. Available online: https://dccg.dk/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/DCCG-%C3%85rsrapport-2017.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2019). (In Danish).
- Vuik, F.E.; Nieuwenburg, S.; Bardou, M.; Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Bento, M.J.; Zadnik, V.; Pellisé, M.; Esteban, L.; Kaminski, M.; et al. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in young adults in Europe over the last 25 years. Gut 2019, 68, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, E.M.; Koeppe, E.; Everett, J.; Ulintz, P.; Kiel, M.; Osborne, J.; Williams, L.; Hanson, K.; Gruber, S.B.; Rozek, L.S. Germline Genetic Features of Young Individuals with Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 897–905.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, R.; Frankel, W.L.; Swanson, B.; Zhao, W.; Yilmaz, A.; Miller, K.; Bacher, J.; Bigley, C.; Nelsen, L.; Goodfellow, P.J. Prevalence and Spectrum of Germline Cancer Susceptibility Gene Mutations among Patients with Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.T.; Pai, R.K.; Rybicki, L.A.; Dimaio, M.A.; Limaye, M.; Jayachandran, P.; Koong, A.C.; Kunz, P.A.; Fisher, G.A.; Ford, J.M.; et al. Clinicopathologic and molecular features of sporadic early-onset colorectal adenocarcinoma: An adenocarcinoma with frequent signet ring cell differentiation, rectal and sigmoid involvement, and adverse morphologic features. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.W.; Sundaram, V.; Chew, T.A.; Ladabaum, U. Low Prevalence of Criteria for Early Screening in Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limburg, P.J.; Harmsen, W.S.; Chen, H.H.; Gallinger, S.; Haile, R.W.; Baron, J.A.; Casey, G.; Woods, M.O.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Lindor, N.M. Prevalence of alterations in DNA mismatch repair genes in patients with young-onset colorectal cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giraldez, M.D.; Balaguer, F.; Bujanda, L.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Muñoz, J.; Alonso-Espinaco, V.; Larzabal, M.; Petit, A.; Gonzalo, V.; Ocaña, T.; et al. MSH6 and MUTYH Deficiency Is a Frequent Event in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5402–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yurgelun, M.B.; Masciari, S.; Joshi, V.A.; Mercado, R.C.; Lindor, N.M.; Gallinger, S.; Hopper, J.L.; Jenkins, M.; Buchanan, D.; Newcomb, P.A.; et al. GermlineTP53Mutations in Patients with Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer in the Colon Cancer Family Registry. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perea, J.; Rodríguez, Y.; Rueda, D.; Marín, J.C.; Díaz-Tasende, J.; Álvaro, E.; Alegre, C.; Osorio, I.; Colina, F.; Lomas, M.; et al. Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer is an Easy and Effective Tool to Identify Retrospectively Lynch Syndrome. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Nagasaka, T.; Spiegel, J.; Meyer, R.; Lichliter, W.E.; Boland, C.R. Low Frequency of Lynch Syndrome Among Young Patients with Non-Familial Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 966–971.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mork, M.E.; You, Y.N.; Ying, J.; Bannon, S.A.; Lynch, P.M.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Vilar, E. High Prevalence of Hereditary Cancer Syndromes in Adolescents and Young Adults with Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3544–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeRycke, M.S.; Gunawardena, S.; Balcom, J.R.; Pickart, A.M.; Waltman, L.A.; French, A.J.; McDonnell, S.; Riska, S.M.; Fogarty, Z.C.; Larson, M.C.; et al. Targeted sequencing of 36 known or putative colorectal cancer susceptibility genes. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2017, 5, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thutkawkorapin, J.; Lindblom, A.; Tham, E. Exome sequencing in 51 early onset non-familial CRC cases. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.D.; Quintana, I.; Terradas, M.; Mur, P.; Balaguer, F.; Valle, L. The Inherited and Familial Component of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, L. Recent Discoveries in the Genetics of Familial Colorectal Cancer and Polyposis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dozois, E.J.; Boardman, L.A.; Suwanthanma, W.; Limburg, P.J.; Cima, R.R.; Bakken, J.L.; Vierkant, R.; Aakre, J.A.; Larson, D.W. Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer in Patients with No Known Genetic Predisposition. Medicine 2008, 87, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boardman, L.A.; Johnson, R.A.; Petersen, G.M.; Oberg, A.L.; Kabat, B.F.; Slusser, J.P.; Wang, L.; Morlan, B.W.; French, A.J.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Higher Frequency of Diploidy in Young-Onset Microsatellite-Stable Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearlman, R.; De La Chapelle, A.; Hampel, H. Mutation Frequencies in Patients with Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer-Reply. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.C. Genetic Testing and Early Onset Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 788–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danish Society of Medical Genetics (DSMG). National Recommendations Regarding Screening and Genetic Counseling in Patients with Colorectal Cancer (In Danish: Genetisk Udredning og Mutationsscreening ved Arvelige Disposition til Kolorektal Cancer.) 2017. Available online: http://www.dsmg.dk (accessed on 23 May 2019). (In Danish).
- Nielsen, M.; Morreau, H.; Vasen, H.F.; Hes, F.J. MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP). Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2011, 79, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.; Dowty, J.; Cleary, S.; Kim, H.; Buchanan, D.; Young, J.; Clendenning, M.; Rosty, C.; MacInnis, R.; Giles, G.; et al. Risk of Colorectal Cancer for Carriers of Mutations in MUTYH, with and without a Family History of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1208–1211.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Møller, P.; Seppälä, T.T.; Bernstein, I.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Sala, P.; Evans, D.G.; Lindblom, A.; Macrae, F.; Blanco, I.; Sijmons, R.H.; et al. Cancer risk and survival in path_MMR carriers by gene and gender up to 75 years of age: A report from the Prospective Lynch Syndrome Database. Gut 2018, 67, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasen, H.; Watson, P.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Lynch, H.T. New clinical criteria for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC, Lynch syndrome) proposed by the International Collaborative group on HNPCC. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Boland, C.R.; Terdiman, J.P.; Syngal, S.; de la Chapelle, A.; Ruschoff, J.; Fishel, R.; Lindor, N.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Hamelin, R.; et al. Revised Bethesda Guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, T.; Handorf, E.A.; Meyer, J.E.; Hall, M.J.; Esnaola, N.F. Mismatch Repair Deficiency Testing in Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Nonadherence to Testing Guidelines in Young Adults. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlitz, J.J.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Liu, Y.; Blanton, C.; Schmidt, B.; Jessup, M.J.; Wu, X.-C.; Chen, V.W. Population-Based Lynch Syndrome Screening by Microsatellite Instability in Patients ≤50: Prevalence, Testing Determinants, and Result Availability Prior to Colon Surgery. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noll, A.; Parekh, P.J.; Zhou, M.; Weber, T.K.; Ahnen, D.; Ms, X.-C.W.; Karlitz, J.J. Barriers to Lynch Syndrome Testing and Preoperative Result Availability in Earlyonset Colorectal Cancer: A National Physician Survey Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Colorectal Cancer Group (DCCG). Retningslinier for Diagnostik og Behandling af Kolorektalcancer, 3 udgave, National Recommendations, 3rd ed. 2005. Available online: http://www.dccg.dk (accessed on 23 May 2019). (In Danish).
- Danish Colorectal Cancer Group (DCCG). Retningslinier for Diagnostik og Behandling af Kolorektalcancer. Arvelig Tarmkræft, National Recommendations). 2016. Available online: https://dccg.dk/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/2016_refs_arveligKRC.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2019). (In Danish).
- Syngal, S.; Brand, R.E.; Church, J.M.; Giardiello, F.M.; Hampel, H.L.; Burt, R.W. ACG Clinical Guideline: Genetic Testing and Management of Hereditary Gastrointestinal Cancer Syndromes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frostberg, E.; Rahr, H.B. Clinical characteristics and a rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer in a nationwide cohort of 521 patients aged 18–40 years. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 66, 101704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingeholm, P.; Gögenur, I.; Iversen, L.H. Danish Colorectal Cancer Group Database. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 8, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, I.T.; Bisgaard, M.L.; Myrhoj, T. Registration of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. Ugeskr. Laeger 1999, 161, 6174–6178. [Google Scholar]
- Lugli, A.; Kirsch, R.; Ajioka, Y.; Bosman, F.; Cathomas, G.; Dawson, H.; El Zimaity, H.; Fléjou, J.-F.; Hansen, T.P.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Recommendations for reporting tumor budding in colorectal cancer based on the International Tumor Budding Consensus Conference (ITBCC) 2016. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesker, W.E.; Junggeburt, J.M.C.; Szuhai, K.; de Heer, P.; Morreau, H.; Tanke, H.J.; Tollenaar, R.A.E.M. The Carcinoma–Stromal Ratio of Colon Carcinoma Is an Independent Factor for Survival Compared to Lymph Node Status and Tumor Stage. Cell. Oncol. 2007, 29, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Pristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, D.W.; Garrison, E.K.; Quinlan, A.; Strömberg, M.P.; Marth, G.T. BamTools: A C++ API and toolkit for analyzing and managing BAM files. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1691–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang le, L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; De Pristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Id | Gene | Variant (c.) | Variant (p.) | MLH1 | MSH2 | MSH6 | PMS2 | FDR | Sex | HIS | TL | UICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | MLH1 | c.1276C > T | p.(Gln426Ter) | L | N | N | L | Yes | M | AC | RS | III |
| 1.2 | MLH1 | c.1667 + 2_1667 + 8delinsATTT | L | N | N | L | Yes | F | AC | RS | III | |
| 1.3 | MLH1 | c.2041G > A | p.(Ala681Thr) | L | N | N | L | NA | M | AC | RS | II |
| 1.4 | MLH1 | c.2041G > A | p.(Ala681Thr) | L | N | NA | NA | NA | F | AC | RS | III |
| 1.5 | MLH1 | c.298C > T | p.(Arg100Ter) | N | N | N | N | Yes | M | AC | RS | I |
| 1.6 | MLH1 | c.350C > T | p.(Thr117Met) | L | N | N | L | Yes | F | AC | RS | I |
| 1.7 | MLH1 | c.350C > T | p.(Thr117Met) | L | N | N | L | NA | M | AC | SY | II |
| 1.8 | MLH1 | c.350C > T | p.(Thr117Met) | L | N | N | L | No | F | AC | RS | II |
| 1.9 | MLH1 | c.677 + 3A > T | L | N | N | L | NA | F | AC | LS | II | |
| 1.10 | MLH1 | c.67delG | p.(Glu23Lysfs*13) | L | N | N | L | Yes | F | AC | RS | I |
| 1.11 | MLH1 | c.76C > T | p.(Gln26Ter) | L | N | N | L | Yes | M | MUC | SY | II |
| 1.12 | MSH2 | c.1165C > T | p.(Arg389Ter) | L | L | L | L | Yes | F | AC | RS | II |
| 1.13 | MSH2 | c.1276 + 1G > T | N | L | L | N | Yes | M | AC | SY | II | |
| 1.14 | MSH2 | c.1759 + 2T > G | N | L | L | N | No | M | AC | RE | II | |
| 1.15 | MSH2 | c.1786_1788delAAT | p.(Asn596del) | N | L | L | N | No | F | AC | LS | II |
| 1.16 | MSH2 | c.892C > T | p.(Gln298Ter) | N | L | L | N | Yes | M | SRC | RS | I |
| 1.17 | MSH2 | c.942 + 2dupT | N | L | L | N | No | F | AC | LS | II | |
| 1.18 | MSH2 | c.942 + 6A > T | N | L | L | N | Yes | F | AC | RS | I | |
| 1.19 | MSH6 | c.3261dupC | p.(Phe1088Leufs*5) | N | N | L | N | Yes | M | AC | RS | III |
| 1.20 | PMS2 | c.613C > T | p.(Gln205Ter) | N | N | N | L | No | F | AC | RS | II |
| 1.21 | MUTYH | c.1214C > T | p.(Ala405Val) | N | N | N | N | NA | F | AC | LS | III |
| 1.22 | MUTYH | c.536A > G | p.(Tyr179Cys) | N | N | N | N | Yes | F | AC | LS | IV |
| Multicarrier | ||||||||||||
| 1.23 | APC MUTYH MUTYH | c.1748C > A c.536A > G c.1187G > A | p.(Ser583Ter) p.(Tyr179Cys) p.(Gly396Asp) | N | N | N | N | No | F | AC | LS | III |
| 1.24 | MLH1 MUTYH | c.1667 + 2_1667 + 8delinsATTT c.1187G > A | p.(Gly396Asp) | L | N | N | L | Yes | M | MUC | RS | I |
| Id | MLH1 | MSH2 | MSH6 | PMS2 | HYP | BRAF | Gene | Variant (c.) | Variant (p.) | FDR | Sex | HIS | TL | UICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | L | N | N | L | NEG | NA | MLH1 | c.1996T > C | p.(Tyr721His) | NA | F | AC | RS | II |
| 2.2 | N | N | N | L | NR | NR | RNF43 | c.989G > A | p.(Arg330Gln) | NA | M | MUC | LS | IV |
| 2.3 | N | L | L | N | NR | NR | MSH3 | c.2732T > G | p.(Leu911Trp) | No | F | MUC | LS | I |
| 2.4 | L | N | N | L | NA | NEG | PMS2 | c.857A > G | p.(Asp286Gly) | No | M | MED | LS | II |
| 2.5 | L | N | N | L | NA | NA | NA | M | AC | LS | III | |||
| 2.6 | L | N | NA | NA | NA | NA | MSH2 | c.1275A > G | p.(Glu425=) | No | F | SRC | SY | IV |
| Patient Characteristics | PGV n = 24 | NPGV n = 74 | p | All Patients n = 98 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.802 | |||
| Female | 14 (58.3) | 41 (55.4) | 55 (56.1) | |
| Male | 10 (41.7) | 33 (44.6) | 43 (43.9) | |
| Location | 0.001 | |||
| Right-sided | 14 (58.3) | 22 (29.7) | 36 (36.7) | |
| Left-sided | 6 (25.0) | 25 (33.8) | 31 (31.6) | |
| Rectum | 1 (4.2) | 26 (35.1) | 27 (27.5) | |
| Synchronous | 3 (12.5) | 1 (1.4) | 4 (4.1) | |
| Histology | 0.708 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 21 (87.5) | 56 (75.7) | 77 (78.6) | |
| Mucinous | 2 (8.3) | 11 (14.9) | 13 (13.3) | |
| Signet-ring cell | 1 (4.2) | 6 (8.1) | 7 (7.1) | |
| Medullary carcinoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.3) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Tumor grade (only adenocarcinomas) | 0.056 | |||
| Moderately differentiated | 13 (61.9) | 48 (85.7) | 61 (79.2) | |
| Poorly differentiated | 5 (23.8) | 6 (10.7) | 11 (14.3) | |
| Not assessed | 3 (14.3) | 2 (3.6) | 5 (6.5) | |
| UICC | 0.016 | |||
| I | 6 (25.0) | 14 (18.9) | 20 (20.4) | |
| II | 11 (45.8) | 14 (18.9) | 25 (25.5) | |
| III | 6 (25.0) | 27 (36.5) | 33 (33.7) | |
| IV | 1 (4.2) | 19 (25.7) | 20 (20.4) | |
| MMR | <0.0001 | |||
| pMMR | 4 (16.7) | 68 (91.9) | 72 (73.5) | |
| dMMR | 20 (83.3) | 6 (8.1) | 26 (26.5) | |
| First degree relative with CRC | 0.004 | |||
| Yes | 13 (54.2) | 16 (21.6) | 29 (29.6) | |
| No | 6 (25.0) | 45 (60.8) | 51 (52.0) | |
| Unknown | 5 (20.8) | 13 (17.6) | 18 (18.4) | |
| Tumor–stroma ratio | 0.092 | |||
| High | 19 (79.2) | 44 (59.5) | 63 (64.3) | |
| Low | 5 (20.8) | 30 (40.5) | 35 (35.7) | |
| Venous invasion | 0.112 | |||
| Yes | 3 (12.5) | 22 (29.7) | 73 (74.5) | |
| No | 21 (87.5) | 52 (70.3) | 25 (25.5) | |
| Perineural invasion | 0.347 | |||
| Yes | 2 (8.3) | 13 (17.6) | 15 (15.3) | |
| No | 22 (91.7) | 61 (82.4) | 83 (84.7) | |
| Tumor budding | 0.172 | |||
| Low | 15 (62.5) | 39 (52.7) | 54 (55.1) | |
| Intermediate | 6 (25.0) | 12 (16.2) | 18 (18.4) | |
| High | 3 (12.5) | 23 (31.1) | 26 (26.5) | |
| T-stage | 0.121 | |||
| T1 | 4 (16.7) | 3 (4.0) | 7 (7.1) | |
| T2 | 3 (12.5) | 12 (16.2) | 15 (15.3) | |
| T3 | 14 (58.3) | 39 (52.7) | 53 (54.1) | |
| T4 | 3 (12.5) | 20 (27.0) | 23 (23.5) | |
| N-stage | 0.007 | |||
| N0 | 17 (70.8) | 28 (37.8) | 45 (45.9) | |
| N1 | 4 (16.7) | 13 (17.6) | 17 (17.4) | |
| N2 | 3 (12.5) | 33 (44.6) | 36 (36.7) | |
| Surgical resection | <0.0001 | |||
| Extended surgery | 11 (45.8) | 6 (8.1) | 17 (17.4) | |
| Segmental resection | 13 (54.2) | 68 (91.9) | 81 (82.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frostberg, E.; Petersen, A.H.; Bojesen, A.; Rahr, H.B.; Lindebjerg, J.; Rønlund, K. The Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in a Nationwide Cohort of Young Colorectal Cancer Patients Using a Panel of 18 Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205094
Frostberg E, Petersen AH, Bojesen A, Rahr HB, Lindebjerg J, Rønlund K. The Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in a Nationwide Cohort of Young Colorectal Cancer Patients Using a Panel of 18 Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(20):5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205094
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrostberg, Erik, Annabeth Høgh Petersen, Anders Bojesen, Hans Bjarke Rahr, Jan Lindebjerg, and Karina Rønlund. 2021. "The Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in a Nationwide Cohort of Young Colorectal Cancer Patients Using a Panel of 18 Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 20: 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205094
APA StyleFrostberg, E., Petersen, A. H., Bojesen, A., Rahr, H. B., Lindebjerg, J., & Rønlund, K. (2021). The Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in a Nationwide Cohort of Young Colorectal Cancer Patients Using a Panel of 18 Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 13(20), 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205094






