Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
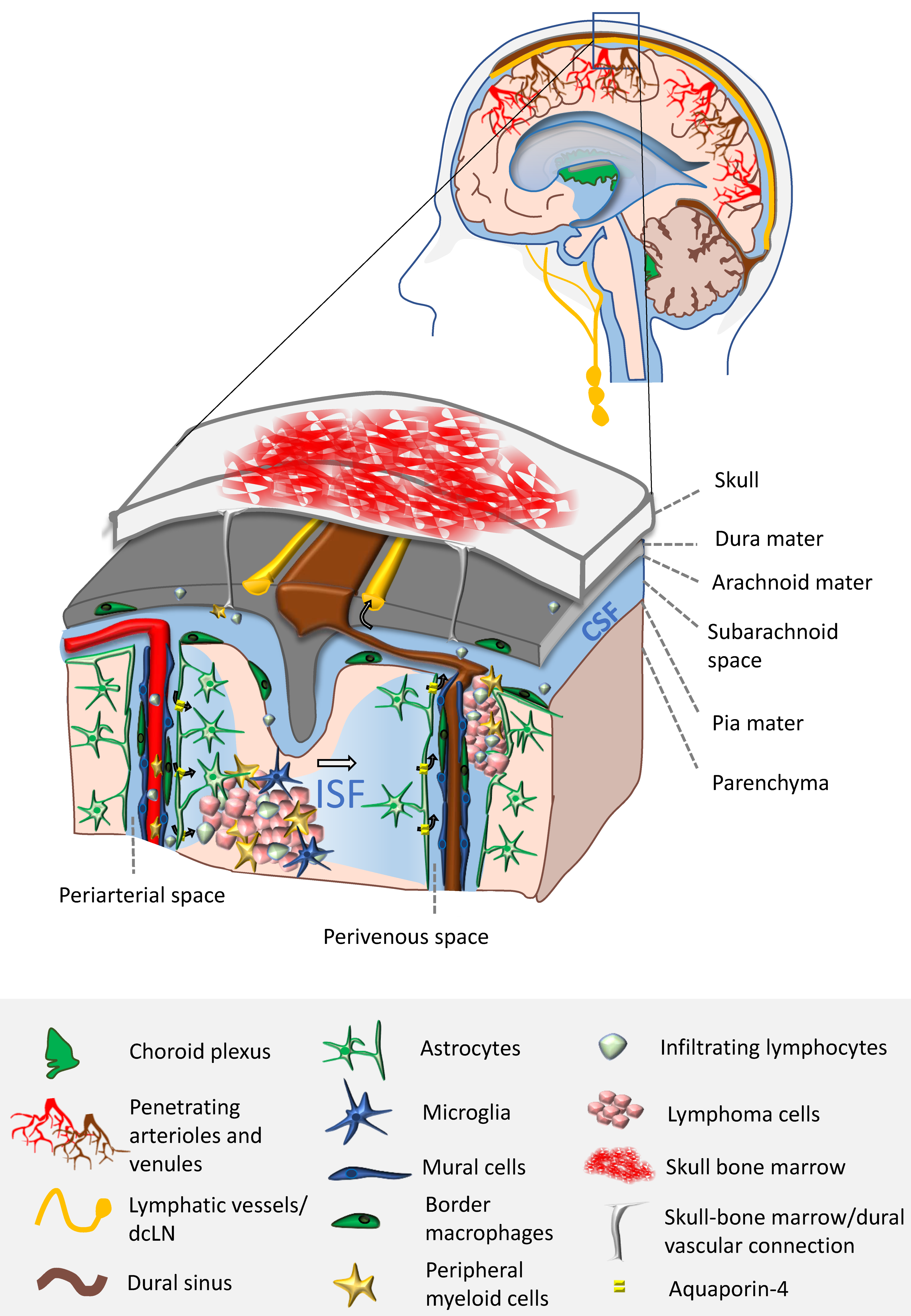
2. Brain Microenvironment
3. Available Clinical Data
3.1. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (alloHSCT)
3.2. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.3. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI)
3.4. CAR-T Cells
3.5. Other Targeted Therapies
| Treatment | N Patients | Median Follow-Up | ORR | CR | Median PFS | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlloHSCT [37] | 6 | 45 months | 4/6 | 4/6 | NR | Retrospective study. Four patients alive in CR at 4 years |
| Rituximab [47] R-MBVP vs. MBVP (1st line) | 199 | 32.9 months | 81% vs. 75% | 68% vs. 66% | NA | 1-year EFS 52% vs. 49% |
| Rituximab [9] HD-MTX plus cytarabine vs. HD-MTX, cytarabine plus rituximab vs. HD-MTX, cytarabine, rituximab plus thiotepa (1st line) | 227 | 30 months | 53% vs. 74% vs. 87% | 23% vs. 30% vs. 49% | NA | Long-term analysis: 7-year OS 37% for HD-MTX plus cytarabine plus rituximab vs. 26% for HD-MTX plus cytarabine independently of the consolidation arm [49] |
| Nivolumab [58] | 5 | 17 months | 5/5 | 4/5 | NA | Results not confirmed in a prospective study (NCT02857426) |
| Nivolumab [59] | 9 | 18 months | 7/9 | 3/9 | 12 months | Results not confirmed in a prospective study (NCT02857426) |
| Pembrolizumab [60] | 50 | 6.7 months | 26% | 16% | 2.6 months | Median DoR 10 months |
| CD19 CAR-T cells [68] | 9 | 6.5 months | 6/9 | 5/9 | 4 months | Median DoR NR |
| Ibrutinib [78] | 44 | 25.7 months | 59% | 23% | 4.8 months | DoR > 12 months in 15 patients |
| Tirabrutinib [79] | 44 | 9.1 months | 64% | 34% | 2.9 months | |
| Lenalidomide [80] | 14 | NA | 9/14 | 3/14 | 6 months | |
| Lenalidomide plus rituximab [81] | 45 | 19.2 months | 36% | 29% | 7.8 months | |
| Pomalidomide plus dexamethasone [82] | 25 | 16.5 months | 48% | 32% | 5.3 months |
| Drug | Cellular Target | Potential Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|
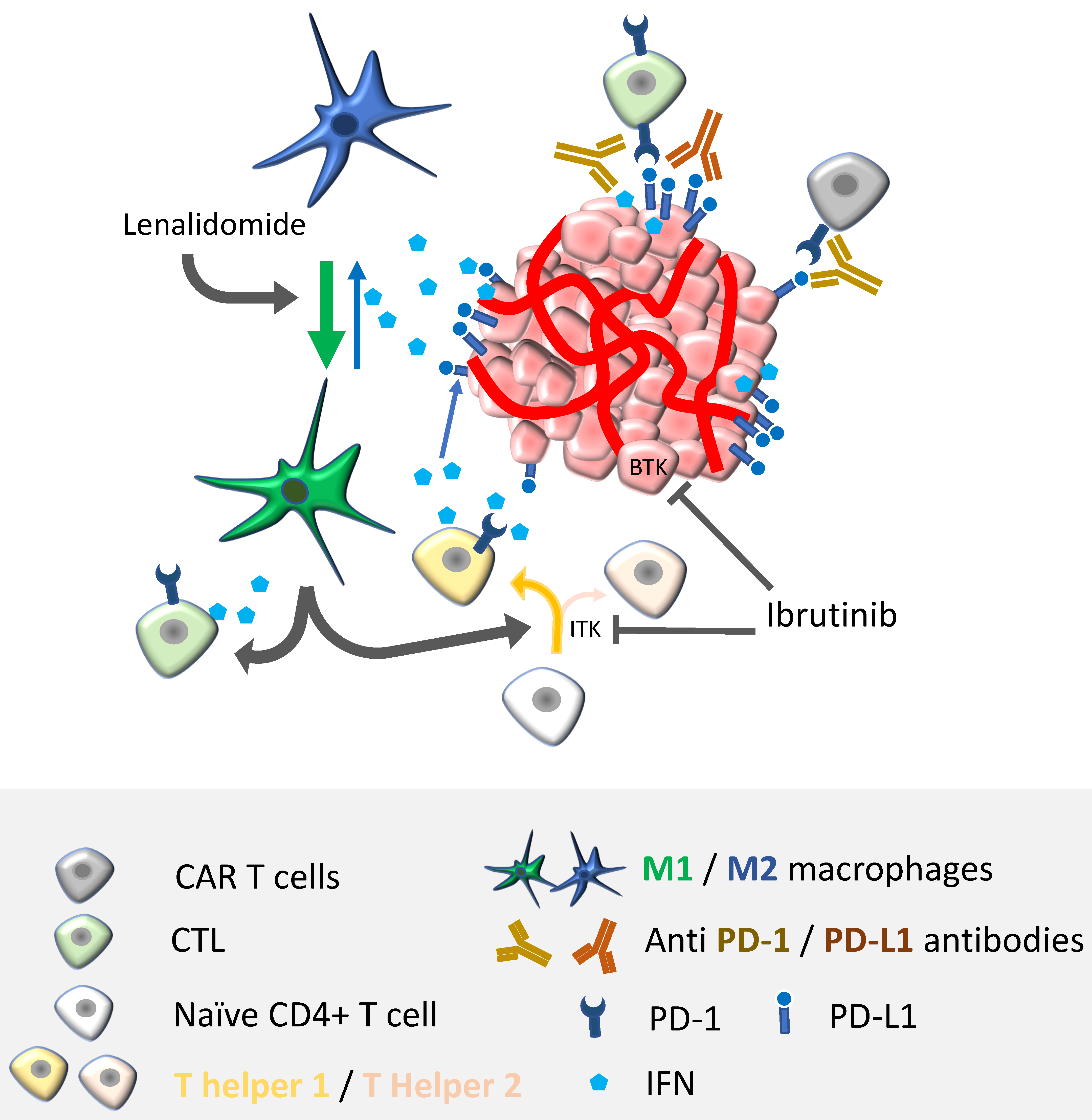
| Ibrutinib | Adaptive immunity | Lymphocytes | ↑ Th1 immunity [83] ↑ Persistence [84] ↓ CD8+ T-cell exhaustion [85] |
| Innate immunity | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells | ↓Migration, depletion [86] | |
| IMIDs (lenalidomide/pomalidomide) | Adaptive immunity | Lymphocytes | ↑ Th1 immunity [87,88] ↑ Effector functions [89] |
| Innate immunity | TAMs NK cells | ↑ M1/M2 phenotype [90] ↑ Effector functions [91] | |
4. Future Perspectives
4.1. Combination Therapies
4.2. Optimizing the Timing of Immunotherapy
4.3. Improving Trafficking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Soubeyran, P.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Lamy, T.; Choquet, S.; Ahle, G.; Damaj, G.; et al. Management and Outcome of Primary CNS Lymphoma in the Modern Era: An LOC Network Study. Neurology 2020, 94, e1027–e1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Broët, S.; Crinière, E.; Broët, P.; Delwail, V.; Mokhtari, K.; Moreau, A.; Kujas, M.; Raphaël, M.; Iraqi, W.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; et al. A Uniform Activated B-Cell-like Immunophenotype Might Explain the Poor Prognosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: Analysis of 83 Cases. Blood 2006, 107, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, J.L.; Koshy, M.; Shaikh, H.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J. Age, Gender, and Racial Differences in Incidence and Survival in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable Genetic Features of Primary Testicular and Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houillier, C.; Taillandier, L.; Dureau, S.; Lamy, T.; Laadhari, M.; Chinot, O.; Moluçon-Chabrot, C.; Soubeyran, P.; Gressin, R.; Choquet, S.; et al. Radiotherapy or Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation for Primary CNS Lymphoma in Patients 60 Years of Age and Younger: Results of the Intergroup ANOCEF-GOELAMS Randomized Phase II PRECIS Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Cwynarski, K.; Pulczynski, E.; Fox, C.P.; Schorb, E.; La Rosée, P.; Binder, M.; Fabbri, A.; Torri, V.; Minacapelli, E.; et al. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy or Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation as Consolidation Strategies after High-Dose Methotrexate-Based Chemoimmunotherapy in Patients with Primary CNS Lymphoma: Results of the Second Randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e510–e523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soussain, C.; Choquet, S.; Fourme, E.; Delgadillo, D.; Bouabdallah, K.; Ghesquières, H.; Damaj, G.; Dupriez, B.; Vargaftig, J.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Intensive Chemotherapy with Thiotepa, Busulfan and Cyclophosphamide and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Rescue in Relapsed or Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and Intraocular Lymphoma: A Retrospective Study of 79 Cases. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner-Lemercier, S.; Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Soubeyran, P.; Lamy, T.; Morschhauser, F.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; et al. Primary CNS Lymphoma at First Relapse/Progression: Characteristics, Management, and Outcome of 256 Patients from the French LOC Network. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Cwynarski, K.; Pulczynski, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Deckert, M.; Politi, L.S.; Torri, V.; Fox, C.P.; Rosée, P.L.; Schorb, E.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with Methotrexate, Cytarabine, Thiotepa, and Rituximab (MATRix Regimen) in Patients with Primary CNS Lymphoma: Results of the First Randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e217–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambady, P.; Holdhoff, M.; Bonekamp, D.; Wong, F.; Grossman, S.A. Late Relapses in Primary CNS Lymphoma after Complete Remissions with High-Dose Methotrexate Monotherapy. CNS Oncol. 2015, 4, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Fridlyand, J.; Shen, A.; Aldape, K.; Ginzinger, D.; Batchelor, T.; Treseler, P.; Berger, M.; McDermott, M.; Prados, M.; et al. Gene Expression and Angiotropism in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Blood 2006, 107, 3716–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tun, H.W.; Personett, D.; Baskerville, K.A.; Menke, D.M.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Kreinest, P.; Edenfield, B.; Zubair, A.C.; O’Neill, B.P.; Lai, W.R.; et al. Pathway Analysis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3200–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, A.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Strack, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Mawrin, C.; Schaller, C.; Deckert, M. Expression Pattern and Cellular Sources of Chemokines in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medawar, P.B. Immunity to Homologous Grafted Skin. III. The Fate of Skin Homographs Transplanted to the Brain, to Subcutaneous Tissue, and to the Anterior Chamber of the Eye. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aspelund, A.; Antila, S.; Proulx, S.T.; Karlsen, T.V.; Karaman, S.; Detmar, M.; Wiig, H.; Alitalo, K. A Dural Lymphatic Vascular System That Drains Brain Interstitial Fluid and Macromolecules. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Kevin, S.L.; et al. Structural and Functional Features of Central Nervous System Lymphatics. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absinta, M.; Ha, S.-K.; Nair, G.; Sati, P.; Luciano, N.J.; Palisoc, M.; Louveau, A.; Zaghloul, K.A.; Pittaluga, S.; Kipnis, J.; et al. Human and Nonhuman Primate Meninges Harbor Lymphatic Vessels That Can Be Visualized Noninvasively by MRI. eLife 2017, 6, e29738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prinz, M.; Masuda, T.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Microglia and Central Nervous System–Associated Macrophages—From Origin to Disease Modulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugurra, A.; Mamuladze, T.; Rustenhoven, J.; Dykstra, T.; Beroshvili, G.; Greenberg, Z.J.; Baker, W.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Drieu, A.; Blackburn, S.; et al. Skull and Vertebral Bone Marrow Are Myeloid Cell Reservoirs for the Meninges and CNS Parenchyma. Science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brioschi, S.; Wang, W.-L.; Peng, V.; Wang, M.; Shchukina, I.; Greenberg, Z.J.; Bando, J.K.; Jaeger, N.; Czepielewski, R.S.; Swain, A.; et al. Heterogeneity of Meningeal B Cells Reveals a Lymphopoietic Niche at the CNS Borders. Science 2021, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herisson, F.; Frodermann, V.; Courties, G.; Rohde, D.; Sun, Y.; Vandoorne, K.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Masson, G.S.; Vinegoni, C.; Kim, J.; et al. Direct Vascular Channels Connect Skull Bone Marrow and the Brain Surface Enabling Myeloid Cell Migration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, M.; Berger, F.; Chassagne-Clement, C.; Tinguely, M.; Jouvet, A.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Dell’Oro, S.; Terreni, M.R.; Doglioni, C.; Weis, J.; et al. Reactive Perivascular T-Cell Infiltrate Predicts Survival in Primary Central Nervous System B-Cell Lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, A.; Sumrall, A.; Phuphanich, S.; Spetzler, D.; Gatalica, Z.; Xiu, J.; Michelhaugh, S.; Brenner, A.; Pandey, M.; Kesari, S.; et al. Primary CNS Lymphoma Commonly Expresses Immune Response Biomarkers. Neurooncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alame, M.; Cornillot, E.; Cacheux, V.; Rigau, V.; Costes-Martineau, V.; Lacheretz-Szablewski, V.; Colinge, J. The Immune Contexture of Primary Central Nervous System Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Associates with Patient Survival and Specific Cell Signaling. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3565–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alame, M.; Pirel, M.; Costes-Martineau, V.; Bauchet, L.; Fabbro, M.; Tourneret, A.; De Oliveira, L.; Durand, L.; Roger, P.; Gonzalez, S.; et al. Characterisation of Tumour Microenvironment and Immune Checkpoints in Primary Central Nervous System Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphomas. Virchows Arch. 2020, 476, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelis, L.; Antoranz, A.; Delsupehe, A.-M.; Biesemans, P.; Ferreiro, J.F.; Debackere, K.; Vandenberghe, P.; Verhoef, G.; Gheysens, O.; Cattoretti, G.; et al. In-Depth Characterization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Central Nervous System Lymphoma Reveals Implications for Immune-Checkpoint Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Chang, J.H.; Yang, W.-I.; Suh, C.-O.; Kim, Y.R.; Jang, J.E.; Cheong, J.-W.; Min, Y.H.; et al. Programmed Cell Death 1 Expression Is Associated with Inferior Survival in Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87317–87328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasato, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Takeya, H.; Yano, H.; Hayano, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Makino, K.; Takeya, M.; Yamanaka, R.; Komohara, Y. The Expression of PD-1 Ligands and IDO1 by Macrophage/Microglia in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2018, 58, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasayama, T.; Tanaka, K.; Mizowaki, T.; Nagashima, H.; Nakamizo, S.; Tanaka, H.; Nishihara, M.; Mizukawa, K.; Hirose, T.; Itoh, T.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Associate with Cerebrospinal Fluid Interleukin-10 and Survival in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL). Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Balakrishnan, L.; Sharma, K.; Khan, A.A.; Advani, J.; Gowda, H.; Tripathy, S.P.; Suar, M.; Pandey, A.; Gandotra, S.; et al. A Network Map of Interleukin-10 Signaling Pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Them, L.; Costopoulos, M.; Tanguy, M.-L.; Houillier, C.; Choquet, S.; Benanni, H.; Elias-Shamieh, R.; Armand, M.; Faivre, G.; Glaisner, S.; et al. The CSF IL-10 Concentration Is an Effective Diagnostic Marker in Immunocompetent Primary CNS Lymphoma and a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Treatment-Responsive Patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D. Cerebrospinal Fluid IL-10 and IL-10/IL-6 as Accurate Diagnostic Biomarkers for Primary Central Nervous System Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetz, D.; Ponzoni, M.; Schiraldi, M.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Bertoni, F.; Doglioni, C.; Uguccioni, M. Perivascular Expression of CXCL9 and CXCL12 in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: T-Cell Infiltration and Positioning of Malignant B Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2300–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathé, G.; Amiel, J.L.; Schwarzenberg, L.; Cattan, A.; Schneider, M. Haematopoietic Chimera in Man After Allogenic (Homologous) Bone-Marrow Transplantation. Br. Med. J. 1963, 2, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varadi, G.; Or, R.; Kapelushnik, J.; Naparstek, E.; Nagler, A.; Brautbar, C.; Amar, A.; Kirschbaum, M.; Samuel, S.; Slavin, S.; et al. Graft-versus-Lymphoma Effect after Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 1999, 34, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, T.; Ladigan, S.; Baraniskin, A.; Vangala, D.; Seidel, S.; Hopfer, O.; Kiehl, M.; Schroers, R. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Haematologica 2020, 105, e160–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karschnia, P.; Blobner, J.; Teske, N.; Schöberl, F.; Fitzinger, E.; Dreyling, M.; Tonn, J.-C.; Thon, N.; Subklewe, M.; von Baumgarten, L. CAR T-Cells for CNS Lymphoma: Driving into New Terrain? Cancers 2021, 13, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Briere, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. CHOP Chemotherapy plus Rituximab Compared with CHOP Alone in Elderly Patients with Diffuse Large-B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilly, H.; Gomes da Silva, M.; Vitolo, U.; Jack, A.; Meignan, M.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Walewski, J.; André, M.; Johnson, P.W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. 5), v116–v125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Pittaluga, S. Primary Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System: Epidemiology, Pathology and Current Approaches to Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muldoon, L.L.; Soussain, C.; Jahnke, K.; Johanson, C.; Siegal, T.; Smith, Q.R.; Hall, W.A.; Hynynen, K.; Senter, P.D.; Peereboom, D.M.; et al. Chemotherapy Delivery Issues in Central Nervous System Malignancy: A Reality Check. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahnke, K.; Muldoon, L.L.; Varallyay, C.G.; Lewin, S.J.; Brown, R.D.; Kraemer, D.F.; Soussain, C.; Neuwelt, E.A. Efficacy and MRI of Rituximab and Methotrexate Treatment in a Nude Rat Model of CNS Lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batchelor, T.T.; Grossman, S.A.; Mikkelsen, T.; Ye, X.; Desideri, S.; Lesser, G.J. Rituximab Monotherapy for Patients with Recurrent Primary CNS Lymphoma. Neurology 2011, 76, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birnbaum, T.; Stadler, E.A.; von Baumgarten, L.; Straube, A. Rituximab Significantly Improves Complete Response Rate in Patients with Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 109, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdhoff, M.; Ambady, P.; Abdelaziz, A.; Sarai, G.; Bonekamp, D.; Blakeley, J.; Grossman, S.A.; Ye, X. High-Dose Methotrexate with or without Rituximab in Newly Diagnosed Primary CNS Lymphoma. Neurology 2014, 83, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bromberg, J.E.C.; Issa, S.; Bakunina, K.; Minnema, M.C.; Seute, T.; Durian, M.; Cull, G.; Schouten, H.C.; Stevens, W.B.C.; Zijlstra, J.M.; et al. Rituximab in Patients with Primary CNS Lymphoma (HOVON 105/ALLG NHL 24): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Intergroup Study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Herbrand, A.K.; Fox, C.P.; Bakunina, K.; Bromberg, J.E.C.; Cwynarski, K.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Illerhaus, G.; Issa, S.; et al. Rituximab in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutter, J.A.; Alig, S.; Lauer, E.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Mitschke, J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Olsen, M.; Liu, C.L.; Jin, M.C.; Bleul, S.; et al. Matrix induction followed by autologous stem cell transplant or whole-brain irradiation in primary cns lymphoma. 7-year results of the ielsg32 randomized trial. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postow, M.A.; Chesney, J.; Pavlick, A.C.; Robert, C.; Grossmann, K.; McDermott, D.; Linette, G.P.; Meyer, N.; Giguere, J.K.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Engert, A.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Collins, G.P.; Ramchandren, R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Lee, H.J.; Armand, P.; Johnson, N.A.; Brice, P.; Radford, J.; Ribrag, V.; Molin, D.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: 2-Year Follow-up of KEYNOTE-087. Blood 2019, 134, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roemer, M.G.M.; Advani, R.H.; Ligon, A.H.; Natkunam, Y.; Redd, R.A.; Homer, H.; Connelly, C.F.; Sun, H.H.; Daadi, S.E.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 Genetic Alterations Define Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Predict Outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2690–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roemer, M.G.M.; Redd, R.A.; Cader, F.Z.; Pak, C.J.; Abdelrahman, S.; Ouyang, J.; Sasse, S.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; et al. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II and Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression Predict Outcome After Programmed Death 1 Blockade in Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Iwamoto, F.M.; LaCasce, A.; Mukundan, S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Chapuy, B.; Armand, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Shipp, M.A. PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed/Refractory Primary Central Nervous System and Testicular Lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 3071–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavrilenko, A.N.; Volkov, N.P.; Shmidt, D.I.; Polushin, A.Y.; Kondakova, E.; Lepik, K.V.; Zalaylov, Y.R.; Popova, M.O.; Kulagin, A.D.; Afanasyev, B.V.; et al. Nivolumab in Primary CNS Lymphoma and Primary Testicular Lymphoma with CNS Involvement: Single Center Experience. Blood 2020, 136, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Houot, R.; Soussain, C.; Blonski, M.; Schmitt, A.; Delwail, V.; Damaj, G.L.; Ghesquieres, H.; Peyrade, F.; Tempescul, A.; et al. First Results of the Acsé Pembrolizumab Phase II in the Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL) Cohort. Blood 2020, 136, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadelain, M.; Rivière, I.; Brentjens, R. Targeting Tumours with Genetically Enhanced T Lymphocytes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1-2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.A.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Mehta, A.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; et al. Lisocabtagene Maraleucel for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A Multicentre Seamless Design Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.C.; Neelapu, S.S.; Giavridis, T.; Sadelain, M. Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.J.; Dietrich, J.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Leick, M.; Choi, B.D.; DeFilipp, Z.; Chen, Y.-B.; Abramson, J.; Crombie, J.; Armand, P.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Secondary CNS Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, L.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Long, X.; et al. CAR T-Cell Therapy Is Effective but Not Long-Lasting in B-Cell Lymphoma of the Brain. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, M.; Houillier, C.; Le Garff-Tavernier, M.; Souchet, L.; Roos-Weil, D.; Morel, V.; Uzunov, M.; Metz, C.; Nguyen-Quoc, S.; Jacque, N.; et al. CAR-T Cell Therapy in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): The Experience of the French Network for Oculo-Cerebral Lymphomas (LOC). In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma, Online, 18–22 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, K.R.; Migliorini, D.; Perkey, E.; Yost, K.E.; Bhaduri, A.; Bagga, P.; Haris, M.; Wilson, N.E.; Liu, F.; Gabunia, K.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies. Cell 2020, 183, 126–142.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrey, L.E.; Batchelor, T.T.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Pulczynski, E.J.; Zucca, E.; Smith, J.R.; Korfel, A.; Soussain, C.; DeAngelis, L.M.; et al. Report of an International Workshop to Standardize Baseline Evaluation and Response Criteria for Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5034–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.J.; Jain, M.D.; Figura, N.B.; Chavez, J.C.; Shah, B.D.; Khimani, F.; Lazaryan, A.; Krivenko, G.; Davila, M.L.; Liu, H.D.; et al. Radiation Therapy as a Bridging Strategy for CAR T Cell Therapy With Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnix, C.C.; Gunther, J.R.; Dabaja, B.S.; Strati, P.; Fang, P.; Hawkins, M.C.; Adkins, S.; Westin, J.; Ahmed, S.; Fayad, L.; et al. Bridging Therapy Prior to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouzoulet, F.; Rezai, K.; Li, Z.; Yushi, Q.; Tun, H.W.; Labiod, D.; Bonnet-Boissinot, S.; Soussain, C. Preclinical Evaluation of Ibrutinib for Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldwirt, L.; Beccaria, K.; Ple, A.; Sauvageon, H.; Mourah, S. Ibrutinib Brain Distribution: A Preclinical Study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoun, K.; Choquet, S.; Boyle, E.; Houillier, C.; Larrieu-Ciron, D.; Al Jijakli, A.; Delrieu, V.; Delwail, V.; Morschhauser, F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; et al. Ibrutinib Monotherapy in Relapsed/Refractory CNS Lymphoma: A Retrospective Case Series. Neurology 2017, 88, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Pastore, A.; Palaskas, N.; Tang, S.S.; Campos, C.; Schartz, D.; Codega, P.; Nichol, D.; Clark, O.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; et al. Ibrutinib Unmasks Critical Role of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Dunleavy, K.; Roschewski, M.; Widemann, B.C.; Butman, J.A.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Cole, D.E.; Melani, C.; Higham, C.S.; et al. Inhibition of B Cell Receptor Signaling by Ibrutinib in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 833–843.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soussain, C.; Choquet, S.; Blonski, M.; Leclercq, D.; Houillier, C.; Rezai, K.; Bijou, F.; Houot, R.; Boyle, E.; Gressin, R.; et al. Ibrutinib Monotherapy for Relapse or Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma and Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma: Final Analysis of the Phase II “proof-of-Concept” ILOC Study by the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA) and the French Oculo-Cerebral Lymphoma (LOC) Network. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 117, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Nagane, M.; Mishima, K.; Terui, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Yonezawa, H.; Asai, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Shinojima, N.; et al. Phase I/II Study of Tirabrutinib, a Second-Generation Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Relapsed/Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Geng, H.; Fraser, E.J.; Formaker, P.; Chen, L.; Sharma, J.; Killea, P.; Choi, K.; Ventura, J.; Kurhanewicz, J.; et al. Phase 1 Investigation of Lenalidomide/Rituximab plus Outcomes of Lenalidomide Maintenance in Relapsed CNS Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghesquieres, H.; Chevrier, M.; Laadhari, M.; Chinot, O.; Choquet, S.; Moluçon-Chabrot, C.; Beauchesne, P.; Gressin, R.; Morschhauser, F.; Schmitt, A.; et al. Lenalidomide in Combination with Intravenous Rituximab (REVRI) in Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma or Primary Intraocular Lymphoma: A Multicenter Prospective “proof of Concept” Phase II Study of the French Oculo-Cerebral Lymphoma (LOC) Network and the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.W.; Johnston, P.B.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Atherton, P.J.; Pederson, L.D.; Koenig, P.A.; Reeder, C.B.; Omuro, A.M.P.; Schiff, D.; O’Neill, B.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS or Vitreoretinal Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovsky, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Natarajan, G.; Woyach, J.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Zhong, Y.; Hessler, J.D.; Liu, T.-M.; Chang, B.Y.; Larkin, K.M.; et al. Ibrutinib Is an Irreversible Molecular Inhibitor of ITK Driving a Th1-Selective Pressure in T Lymphocytes. Blood 2013, 122, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, M.; Beckwith, K.; Do, P.; Mundy, B.L.; Gordon, A.; Lehman, A.M.; Maddocks, K.J.; Cheney, C.; Jones, J.A.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. Ibrutinib Treatment Improves T Cell Number and Function in CLL Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3052–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, H.M.; Mirajkar, N.; Cutmore, N.; Zuo, J.; Long, H.; Kwok, M.; Oldrieve, C.; Hudson, C.; Stankovic, T.; Paneesha, S.; et al. Long-Term Ibrutinib Therapy Reverses CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiff, A.; Trikha, P.; Wesolowski, R.; Kendra, K.; Hsu, V.; Uppati, S.; McMichael, E.; Duggan, M.; Campbell, A.; Keller, K.; et al. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Express Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and Can Be Depleted in Tumor Bearing Hosts by Ibrutinib Treatment. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aue, G.; Sun, C.; Liu, D.; Park, J.-H.; Pittaluga, S.; Tian, X.; Lee, E.; Soto, S.; Valdez, J.; Maric, I.; et al. Activation of Th1 Immunity within the Tumor Microenvironment Is Associated with Clinical Response to Lenalidomide in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luptakova, K.; Rosenblatt, J.; Glotzbecker, B.; Mills, H.; Stroopinsky, D.; Kufe, T.; Vasir, B.; Arnason, J.; Tzachanis, D.; Zwicker, J.I.; et al. Lenalidomide Enhances Anti-Myeloma Cellular Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, C.; Rossille, D.; Dulong, J.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Papa, I.; Latour, M.; Bescher, N.; Bezier, I.; Chouteau, M.; Fest, T.; et al. Lenalidomide Triggers T-Cell Effector Functions in Vivo in Patients with Follicular Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Personett, D.; Huang, P.; Edenfield, B.; Katz, J.; Babusis, D.; Tang, Y.; Shirely, M.A.; Moghaddam, M.F.; et al. Pomalidomide Shows Significant Therapeutic Activity against CNS Lymphoma with a Major Impact on the Tumor Microenvironment in Murine Models. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrue, K.; Carisey, A.; Morgan, D.J.; Chopra, R.; Davis, D.M. Lenalidomide Augments Actin Remodeling and Lowers NK-Cell Activation Thresholds. Blood 2015, 126, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruella, M.; Kenderian, S.S.; Shestova, O.; Fraietta, J.A.; Qayyum, S.; Zhang, Q.; Maus, M.V.; Liu, X.; Nunez-Cruz, S.; Klichinsky, M.; et al. The Addition of the BTK Inhibitor Ibrutinib to Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells (CART19) Improves Responses against Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuramitsu, S.; Ohno, M.; Ohka, F.; Shiina, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kato, A.; Tanahashi, K.; Motomura, K.; Kondo, G.; Kurimoto, M.; et al. Lenalidomide Enhances the Function of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells against the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III by Enhancing Immune Synapses. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Walter, M.; Urak, R.; Weng, L.; Huynh, C.; Lim, L.; Wong, C.W.; Chang, W.-C.; Thomas, S.H.; Sanchez, J.F.; et al. Lenalidomide Enhances the Function of CS1 Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Redirected T Cells Against Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, J.; Hirayama, A.V.; Purushe, J.; Hay, K.A.; Lymp, J.; Li, D.; Yeung, C.; Sheih, A.; Pender, B.S.; Hawkins, R.M.; et al. Feasibility and Efficacy of CD19-Targeted CAR-T Cells with Concurrent Ibrutinib for CLL after Ibrutinib Failure. Blood 2020, 135, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Vernau, L.; Grupp, S.A.; Barrett, D.M. Naïve T-Cell Deficits at Diagnosis and after Chemotherapy Impair Cell Therapy Potential in Pediatric Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Dickinson, M.; Ulrickson, M.L.; Oluwole, O.O.; Herrera, A.F.; Thieblemont, C.; Ujjani, C.S.; Lin, Y.; Riedell, P.A.; Kekre, N.; et al. Interim Analysis of ZUMA-12: A Phase 2 Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) as First-Line Therapy in Patients (Pts) With High-Risk Large B Cell Lymphoma (LBCL). Blood 2020, 136, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Zhang, H.; Barrios, C.H.; Saji, S.; Jung, K.H.; Hegg, R.; Koehler, A.; Sohn, J.; Iwata, H.; Telli, M.L.; et al. Neoadjuvant Atezolizumab in Combination with Sequential Nab-Paclitaxel and Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy versus Placebo and Chemotherapy in Patients with Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (IMpassion031): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab Combined with Two Cycles of Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (CheckMate 9LA): An International, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Fridlyand, J.; Abrey, L.; Shen, A.; Karch, J.; Wang, E.; Issa, S.; Damon, L.; Prados, M.; McDermott, M.; et al. Phase I Study of Intraventricular Administration of Rituximab in Patients with Recurrent CNS and Intraocular Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Advani, R.; Drappatz, J.; Gerstner, E.; Batchelor, T.; Krouwer, H.; Hwang, J.; Auerback, G.; et al. Multicenter Phase 1 Trial of Intraventricular Immunochemotherapy in Recurrent CNS Lymphoma. Blood 2013, 121, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadoch, C.; Li, J.; Wong, V.S.; Chen, L.; Cha, S.; Munster, P.; Lowell, C.A.; Shuman, M.A.; Rubenstein, J.L. Complement Activation and Intraventricular Rituximab Distribution in Recurrent Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulazzani, M.; Fräßle, S.P.; von Mücke-Heim, I.; Langer, S.; Zhou, X.; Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H.; Leube, J.; Zhang, W.; Dötsch, S.; Svec, M.; et al. Long-Term in Vivo Microscopy of CAR T Cell Dynamics during Eradication of CNS Lymphoma in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24275–24284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Huynh, C.; Urak, R.; Weng, L.; Walter, M.; Lim, L.; Vyas, V.; Chang, W.-C.; Aguilar, B.; Brito, A.; et al. The Cerebroventricular Environment Modifies CAR T Cells for Potent Activity against Both Central Nervous System and Systemic Lymphoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulch, M.; Cazaux, M.; Loe-Mie, Y.; Thibaut, R.; Corre, B.; Lemaître, F.; Grandjean, C.L.; Garcia, Z.; Bousso, P. A Cross-Talk between CAR T Cell Subsets and the Tumor Microenvironment Is Essential for Sustained Cytotoxic Activity. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabd4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinicaltrials.gov Identification | Study Design | Treatment | Objective | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04609046 | Phase I PCNSL first-line | Induction: methotrexate, rituximab, lenalidomide and nivolumab Maintenance: lenalidomide and nivolumab | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 27 patients) | |
| NCT03703167 | Phase Ib R/R PCNSL and R/R sCNSL | Combination of ibrutinib with rituximab and lenalidomide with dose expansion of ibrutinib and lenalidomide | MTD of ibrutinib PFS | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 40 patients) |
| NCT04938297 | Phase II PCNSL and sCNSL | Rituximab, zanubrutinib in combination with lenalidomide, followed by zanubrutinib or lenalidomide maintenance | ORR | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 100 patients) |
| NCT04899427 | Phase II R/R PCNSL | Orelabrutinib combined with PD-1 inhibitor | ORR | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 32 patients) |
| NCT04831658 | Phase II PCNSL first-line | BTK inhibitor, PD-1 inhibitor and formustine | CR rate | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 40 patients) |
| NCT04737889 | Phase II PCNSL | Rituximab, lenalidomide combined with methotrexate and temozolomide | 2-year PFS | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 30 patients) |
| NCT04688151 | Phase I PCNSL | Rituximab, acalabrutinib and durvalumab (RAD) | MTD Acalabrutinib | Ongoing |
| NCT04462328 | Phase I PCNSL and sCNSL R/R and first-line | Dose expansion of acalabrutinib and durvalumab | MTD Acalabrutinib | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 21 patients) |
| NCT04421560 | Phase Ib/II R/R PCNSL | Pembrolizumab, ibrutinib and rituximab | 6-month PFS | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 37 patients) |
| NCT03770416 | Phase I R/R PCNSL and sCNSL | Nivolumab and ibrutinib | ORR | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 40 patients) |
| NCT04446962 | Phase Ib/II PCNSL first-line | Lenalidomide or ibrutinib in association with rituximab–methotrexate–procarbazine–vincristine (R-MPV) | MTD lenalidomide/ibrutinib CR rate at the end of induction | Ongoing (estimated enrolment: 92 patients in phase II) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcantara, M.; Fuentealba, J.; Soussain, C. Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205061
Alcantara M, Fuentealba J, Soussain C. Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(20):5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205061
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcantara, Marion, Jaime Fuentealba, and Carole Soussain. 2021. "Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma" Cancers 13, no. 20: 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205061
APA StyleAlcantara, M., Fuentealba, J., & Soussain, C. (2021). Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers, 13(20), 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205061





