Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methylation Profiling
2.2. Transcriptome Profiling
2.3. Integration of Methylation and Expression Data
2.4. Microarray Screening
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. siRNA Gene Knockdown
2.7. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout
2.8. Overexpression of NFATc1
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Migration Assay
2.12. Colony Assay
2.13. Demethylation Treatment, DNA Bisulfite Conversion and Sequencing
2.14. Luciferase Assay
2.15. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
3. Results
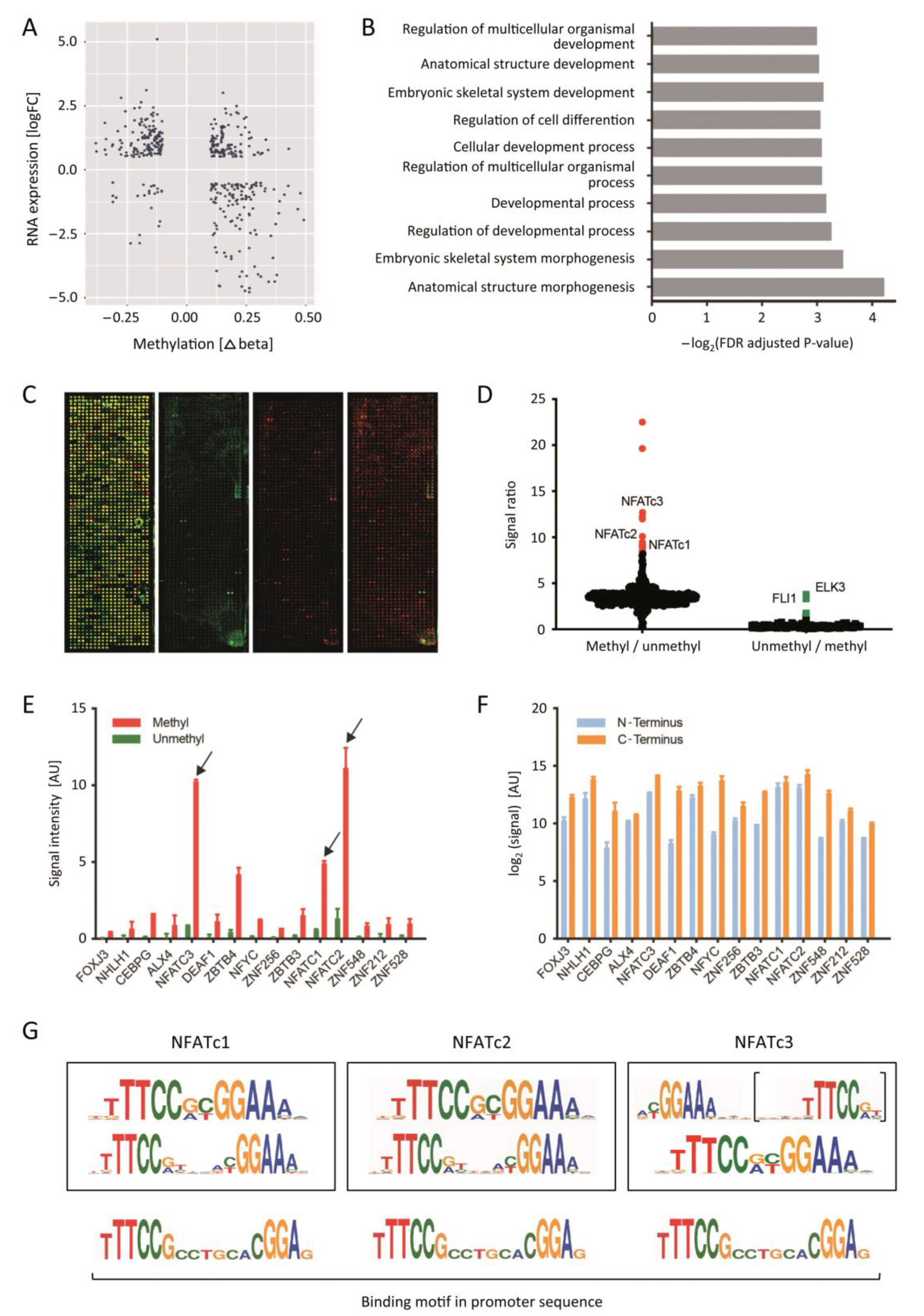
3.1. Identification of Genes with Changes in Both Promoter Methylation and RNA Expression
3.2. The NFAT TF-Family Binds to DNA in a Methylation-Dependent Differential Manner
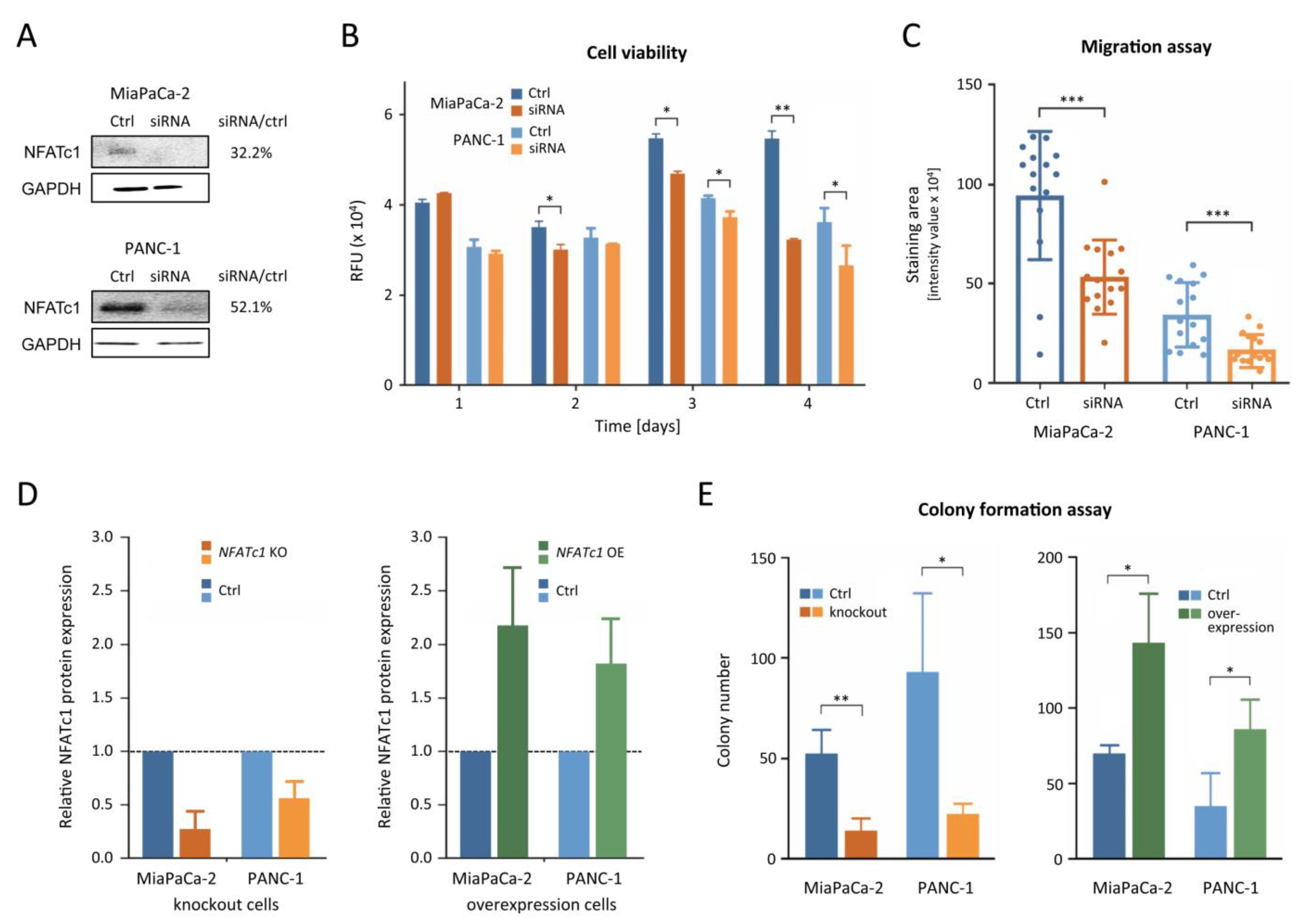
3.3. NFATc1 Is Playing an Oncogenic Role
3.4. Identification of ALDH1A3 as a Target Gene of NFATc1
3.5. NFATc1 Regulates ALDH1A3 in a Methylation-Dependent Way
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kleeff, J.; Michl, P.; Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Palmer, D.H. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinlade, O.; Wei, S.; Kammers, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, D.; Huang, Z.Y.; Qian, J.; Zhu, H.; Wan, J.; et al. Analysis of KLF4 regulated genes in cancer cells reveals a role of DNA methylation in promoter-enhancer interactions. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Schrimpf, D.; Sturm, D.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Chavez, L.; Reuss, D.E.; et al. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Jia, Y.; Yu, Z.; House, M.G.; Esteller, M.; Brock, M.V.; Herman, J.G. Epigenetic changes associated with neoplasms of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas. Discov. Med. 2014, 17, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, R.; Vinson, C. CpG methylation recruits sequence specific transcription factors essential for tissue specific gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, M.; Hellmann, I.; Stadler, M.B.; Ramos, L.; Pääbo, S.; Rebhan, M.; Schübeler, D. Distribution, silencing potential and evolutionary impact of promoter DNA methylation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2017, 32, 185–203.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newell-Price, J.; Clark, A.J.; King, P. DNA methylation and silencing of gene expression. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, J.; Bird, A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell 1991, 64, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wan, J.; Su, Y.; Song, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Nguyen, H.N.; Shin, J.; Cox, E.; Rho, H.S.; Woodard, C.; et al. DNA methylation presents distinct binding sites for human transcription factors. eLife 2013, 2, e00726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Qian, J. Transcription factors as readers and effectors of DNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Su, Y.; Song, Q.; Tung, B.; Oyinlade, O.; Liu, S.; Ying, M.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H.; Qian, J.; et al. Methylated cis-regulatory elements mediate KLF4-dependent gene transactivation and cell migration. eLife 2017, 6, e20068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi, A.; Garcia, M.F.; Jaroszewicz, A.; Osman, N.; Pellegrini, M.; Zaret, K.S. Pioneer transcription factors target partial DNA motifs on nucleosomes to initiate reprogramming. Cell 2015, 161, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maunakea, A.K.; Chepelev, I.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K. Intragenic DNA methylation modulates alternative splicing by recruiting MeCP2 to promote exon recognition. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Morgunova, E.; Jolma, A.; Kaasinen, E.; Sahu, B.; Khund-Sayeet, S.; Das, P.K.; Kivioja, T.; Dave, K.; Zhong, F.; et al. Impact of cytosine methylation on DNA binding specificities of human transcription factors. Science 2017, 356, eaaj2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.S.; Nazarov, P.V.; Giese, N.A.; Beghelli, S.; Heller, A.; Greenhalf, W.; Costello, E.; Muller, A.; Bier, M.; Strobel, O.; et al. Transcriptional variations in the wider peritumoral tissue environment of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assenov, Y.; Müller, F.; Lutsik, P.; Walter, J.; Lengauer, T.; Bock, C. Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data with RnBeads. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Huang, X.; Ebert, D.; Mills, C.; Guo, X.; Thomas, P.D. Protocol update for large-scale genome and gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system (v.14.0). Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueong, S.S.; Di, C.; Schäfer, J.V.; Plückthun, A.; Hoheisel, J.D. Personalised proteome analysis by means of protein microarrays made from individual patient samples. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 39756. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, B.; Bauer, A.S.; Hufnagel, K.; Wu, Y.; Trajkovic-Arsic, M.; Pirona, A.C.; Giese, N.; Taipale, J.; Siveke, J.T.; Hoheisel, J.D.; et al. The transcription factor FLI1 promotes cancer progression by affecting cell cycle regulation. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufnagel, K.; Reininger, D.; Ng, S.W.; Gassert, N.; Rohland, J.K.; Shahryarhesami, S.; Bauer, A.S.; Waterboer, T.; Hoheisel, J.D. In situ, cell-free protein expression on microarrays and their use for the detection of immune responses. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirona, A.C.; Oktriani, R.; Boettcher, M.; Hoheisel, J.D. Process for an efficient lentiviral cell transduction. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2020, 5, bpaa005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bock, C.; Reither, S.; Mikeska, T.; Paulsen, M.; Walter, J.; Lengauer, T. BiQ Analyzer: Visualization and quality control for DNA methylation data from bisulfite sequencing. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 4067–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, M.; Rehli, M. Functional analysis of promoter CpG methylation using a CpG-free luciferase reporter vector. Epigenetics 2006, 1, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Xia, S.; Zhu, H.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y. MeDReaders: A database for transcription factors that bind to methylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D146–D151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Furukawa, T.; Kobari, M.; Tsao, M.S. Comparative phenotypic studies of duct epithelial cell lines derived from normal human pancreas and pancreatic carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, C.E.; Bailey, T.L.; Noble, W.S. FIMO: Scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1017–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.J.; Cai, J.; Guo, J.F.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. ALDH1A3, a metabolic target for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomberk, G.; Dusetti, N.; Iovanna, J.; Urrutia, R. Emerging epigenomic landscapes of pancreatic cancer in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Sen, S.; Weeks, R.J.; Eccles, M.R.; Chatterjee, A. Promoter DNA hypermethylation and paradoxical gene activation. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, X.; Ng, H.H.; Johnson, C.A.; Laherty, L.D.; Turner, B.M.; Eisenmann, B.M.; Bird, A. Transcriptional repression by the methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 involves a histone deacetylase complex. Nature 1998, 393, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Xu, Y.; He, T.; Qin, C.; Xu, J. Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, C.M.; Tran, M.A.; Pitruzzello, M.C.; Wen, W.; Loeza, J.; Dellinger, T.H.; Mor, G.; Glackin, C.A. TWIST1 drives cisplatin resistance and cell survival in an ovarian cancer model, via upregulation of GAS6, L1CAM, and Akt signalling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.X.; Yin, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Rong, Z.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Du, D.D.; Wang, Y.D.; Gao, R.X.; Xian, G.Z. TWIST1 transcriptionally regulates glycolytic genes to promote the Warburg metabolism in pancreatic cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 386, 111713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Luo, C.; Hogan, P.G. Transcription factors of the NFAT family: Regulation and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 707–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, P.G.; Chen, L.; Nardone, J.; Rao, A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2205–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchholz, M.; Schatz, A.; Wagner, M.; Michl, P.; Linhart, T.; Adler, G.; Gress, T.M.; Ellenrieder, V. Overexpression of c-myc in pancreatic cancer caused by ectopic activation of NFATc1 and the Ca2+/calcineurin signaling pathway. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Singh, S.K.; König, A.; Reutlinger, K.; Nye, M.D.; Adhikary, T.; Eilers, M.; Gress, T.M.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; Ellenrieder, V. Sequential activation of NFAT and c-Myc transcription factors mediates the TGF-β switch from a suppressor to a promoter of cancer cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27241–27250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.M.; Singh, G.; König, A.; Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P.; Zhang, J.S.; Regul, L.; Nagarajan, S.; Kühnemuth, B.; Johnsen, S.A.; et al. NFATc1 links EGFR signaling to induction of Sox9 transcription and acinar–ductal transdifferentiation in the pancreas. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1024–1034.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.M.; Neesse, A.; Dyck, M.L.; Steuber, B.; Koening, A.O.; Lubeseder-Martellato, C.; Winter, T.; Forster, T.; Bohnenberger, H.; Kitz, J.; et al. Context-dependent epigenetic regulation of nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 in pancreatic plasticity. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1507–1520.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mognol, G.; Carneiro, F.R.G.; Robbs, B.K.; Faget, D.V.; Viola, J.P.B. Cell cycle and apoptosis regulation by NFAT transcription factors: New roles for an old player. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.M.; La Thangue, N.B. p300/CBP proteins: HATs for transcriptional bridges and scaffolds. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Kröller, L.; Miao, B.; Boekhoff, H.; Bauer, A.S.; Büchler, M.W.; Hackert, T.; Giese, N.A.; Taipale, J.; Hoheisel, J.D. Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184569
Wu Y, Kröller L, Miao B, Boekhoff H, Bauer AS, Büchler MW, Hackert T, Giese NA, Taipale J, Hoheisel JD. Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184569
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yenan, Lea Kröller, Beiping Miao, Henning Boekhoff, Andrea S. Bauer, Markus W. Büchler, Thilo Hackert, Nathalia A. Giese, Jussi Taipale, and Jörg D. Hoheisel. 2021. "Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184569
APA StyleWu, Y., Kröller, L., Miao, B., Boekhoff, H., Bauer, A. S., Büchler, M. W., Hackert, T., Giese, N. A., Taipale, J., & Hoheisel, J. D. (2021). Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 13(18), 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184569







