Unraveling How Tumor-Derived Galectins Contribute to Anti-Cancer Immunity Failure
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Do Circulating Tumor-Derived Galectins Have Any Impact on Naïve T Cell Production?
1.2. T Lymphocyte Regulation by Galectins at the Periphery
1.2.1. Galectins’ Functions in Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes
1.2.2. Galectin Functions inside the Tumor
2. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianconi, E.; Piovesan, A.; Facchin, F.; Beraudi, A.; Casadei, R.; Frabetti, F.; Vitale, L.; Pelleri, M.C.; Tassani, S.; Piva, F.; et al. An estimation of the number of cells in the human body. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2013, 40, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, P.; Davis, M.M. Human immune system variation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laderach, D.J.; Compagno, D.; Toscano, M.A.; Croci, D.O.; Dergan-Dylon, S.; Salatino, M.; Rabinovich, G.A. Dissecting the signal transduction pathways triggered by galectin-glycan interactions in physiological and pathological settings. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, D.; Jaworski, F.M.; Gentilini, L.; Contrufo, G.; Gonzalez Perez, I.; Elola, M.T.; Pregi, N.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Laderach, D.J. Galectins: Major signaling modulators inside and outside the cell. Curr. Mol. Med. 2014, 14, 630–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nio-Kobayashi, J. Tissue- and cell-specific localization of galectins, beta-galactose-binding animal lectins, and their potential functions in health and disease. Anat. Sci. Int. 2017, 92, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Hoeven, N.W.; Hollander, M.R.; Yildirim, C.; Jansen, M.F.; Teunissen, P.F.; Horrevoets, A.J.; van der Pouw Kraan, T.C.; van Royen, N. The emerging role of galectins in cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Pharm. 2016, 81, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.J.; Cao, Z.Q.; Leng, P. The roles of galectins in hepatic diseases. J. Mol. Histol. 2020, 51, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Mei, X.; Zhao, Y. Galectins as potential pharmacological targets in renal injuries of diverse etiology. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 881, 173213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Hsu, Y.A.; Wei, C.C.; Liu, F.T. Galectins in allergic inflammatory diseases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 189, 100925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez Hernandez, E.; Sanchez-Maldonado, C.; Mayoral Chavez, M.A.; Hernandez-Zimbron, L.F.; Patricio Martinez, A.; Zenteno, E.; Limon Perez de Leon, I.D. The therapeutic potential of galectin-1 and galectin-3 in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanna, F.; Veronesi, F.; Frizziero, A.; Fini, M. Role and translational implication of galectins in arthritis pathophysiology and treatment: A systematic literature review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1588–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.L.; Liu, F.T. The expression and function of galectins in skin physiology and pathology. Exp. Derm. 2018, 27, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, M.R.; Urbina, A.N.; Assavalapsakul, W.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, F.T.; Wang, S.F. The role of galectins in virus infection—A systemic literature review. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Xue, C.; Su, X.Z.; Lu, F. The roles of galectins in parasitic infections. Acta. Trop. 2018, 177, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, M.R.; Salatino, M.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Rabinovich, G.A. Sweetening the hallmarks of cancer: Galectins as multifunctional mediators of tumor progression. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20182041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elola, M.T.; Ferragut, F.; Cardenas Delgado, V.M.; Nugnes, L.G.; Gentilini, L.; Laderach, D.; Troncoso, M.F.; Compagno, D.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Rabinovich, G.A. Expression, localization and function of galectin-8, a tandem-repeat lectin, in human tumors. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, V.L.; Heusschen, R.; Caers, J.; Griffioen, A.W. Galectin expression in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: A systematic review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bosch, N.; Navarro, P. Galectins in the Tumor Microenvironment: Focus on Galectin-1. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1259, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, V.L.; Barkan, B.; Shoji, H.; Aries, I.M.; Mathieu, V.; Deltour, L.; Hackeng, T.M.; Kiss, R.; Kloog, Y.; Poirier, F.; et al. Tumor cells secrete galectin-1 to enhance endothelial cell activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6216–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, D.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Xue, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tai, G. The two endocytic pathways mediated by the carbohydrate recognition domain and regulated by the collagen-like domain of galectin-3 in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepur, A.; Carlsson, M.C.; Novak, R.; Dumic, J.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H. Galectin-3 endocytosis by carbohydrate independent and dependent pathways in different macrophage like cell types. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Q.T.; Shi, G.; Cao, H.; Nelson, D.W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhao, S.; Kong, C.; Richardson, D.; O’Byrne, K.J.; et al. Galectin-1: A link between tumor hypoxia and tumor immune privilege. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8932–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Xia, L.; Guo, M.; Xu, Y.; Yue, F.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, G.Q.; Zhao, K.W. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 mediates expression of galectin-1: The potential role in migration/invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, D.O.; Salatino, M.; Rubinstein, N.; Cerliani, J.P.; Cavallin, L.E.; Leung, H.J.; Ouyang, J.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Toscano, M.A.; Domaica, C.I.; et al. Disrupting galectin-1 interactions with N-glycans suppresses hypoxia-driven angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in Kaposi’s sarcoma. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemori, R.Y.; Machado, C.M.; Furuzawa, K.M.; Nonogaki, S.; Osinaga, E.; Umezawa, K.; de Carvalho, M.A.; Verinaud, L.; Chammas, R. Galectin-3 up-regulation in hypoxic and nutrient deprived microenvironments promotes cell survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saussez, S.; Glinoer, D.; Chantrain, G.; Pattou, F.; Carnaille, B.; Andre, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Laurent, G. Serum galectin-1 and galectin-3 levels in benign and malignant nodular thyroid disease. Thyroid 2008, 18, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno-Laurent, F.; Watanabe, R.; Teague, J.E.; Kupper, T.S.; Clark, R.A.; Dimitroff, C.J. Galectin-1 inhibits the viability, proliferation, and Th1 cytokine production of nonmalignant T cells in patients with leukemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 3534–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bosch, N.; Barranco, L.E.; Orozco, C.A.; Moreno, M.; Visa, L.; Iglesias, M.; Oldfield, L.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Greenhalf, W.; Earl, J.; et al. Increased plasma levels of galectin-1 in pancreatic cancer: Potential use as biomarker. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32984–32996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, N.; Zhao, X.; Ji, J.; Xu, M.; Jiao, Y.; Qian, T.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; Xiao, M. Serum galectin-3 as a biomarker for screening, early diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11583–11591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cymbaluk-Ploska, A.; Gargulinska, P.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Pius-Sadowska, E.; Machalinski, B. Could Galectin 3 Be a Good Prognostic Factor in Endometrial Cancer? Diagnostics 2020, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Qian, K. Expression and Clinical Significance of Galcetin-3 in the Serum of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2020, 23, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurisci, I.; Tinari, N.; Natoli, C.; Angelucci, D.; Cianchetti, E.; Iacobelli, S. Concentrations of galectin-3 in the sera of normal controls and cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Duckworth, C.A.; Fu, B.; Pritchard, D.M.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.G. Circulating galectins -2, -4 and -8 in cancer patients make important contributions to the increased circulation of several cytokines and chemokines that promote angiogenesis and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, H.; Guo, X.; Wandall, H.H.; Pedersen, J.W.; Fu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.G. Serum galectin-2, -4, and -8 are greatly increased in colon and breast cancer patients and promote cancer cell adhesion to blood vascular endothelium. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7035–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, A.M.; Reiche, C.; Heiduk, M.; Tannert, A.; Meinecke, A.C.; Baier, S.; von Renesse, J.; Kahlert, C.; Distler, M.; Welsch, T.; et al. Detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with galectin-9 serum levels. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3102–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowiak, K.; Gallego-Colon, E.; Francuz, T.; Czajka-Francuz, P.; Ruiz-Agamez, N.; Kubeczko, M.; Grochola, I.; Wybraniec, M.T.; Chudek, J.; Wojnar, J. Increased serum levels of Galectin-9 in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, L.B.; Silva-Filho, A.F.; Martins, M.R.; Vilar, K.M.; Pitta, M.G.R.; Rego, M. Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Have High Serum Galectin-9 Levels: A Sweet Molecule to Keep an Eye On. Pancreas 2018, 47, e59–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brule, F.A.; Waltregny, D.; Castronovo, V. Increased expression of galectin-1 in carcinoma-associated stroma predicts poor outcome in prostate carcinoma patients. J. Pathol. 2001, 193, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoke, T.; Kayser, K.; Baumhakel, J.D.; Trojan, I.; Furak, J.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Horvath, A.; Szluha, K.; Gabius, H.J.; Andre, S. Prognostic significance of endogenous adhesion/growth-regulatory lectins in lung cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube-Delarosbil, C.; St-Pierre, Y. The emerging role of galectins in high-fatality cancers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, D.; Tiraboschi, C.; Garcia, J.D.; Rondon, Y.; Corapi, E.; Velazquez, C.; Laderach, D.J. Galectins as Checkpoints of the Immune System in Cancers, Their Clinical Relevance, and Implication in Clinical Trials. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Toscano, M.A.; Jackson, S.S.; Vasta, G.R. Functions of cell surface galectin-glycoprotein lattices. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, O.B.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-glycan lattices regulate cell-surface glycoprotein organization and signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Ariel, A.; Hershkoviz, R.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K.I.; Lider, O. Specific inhibition of T-cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and proinflammatory cytokine secretion by human recombinant galectin-1. Immunology 1999, 97, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Baum, L.G. Presentation of galectin-1 by extracellular matrix triggers T cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4705–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Baum, L.G. Galectin interactions with extracellular matrix and effects on cellular function. Methods Enzym. 2006, 417, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Sanchez-Ruderisch, H.; Welzel, M.; Wiedenmann, B.; Sakai, T.; Andre, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Khachigian, L.; Detjen, K.M.; Rosewicz, S. Galectin-1 interacts with the {alpha}5{beta}1 fibronectin receptor to restrict carcinoma cell growth via induction of p21 and p27. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37266–37277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Wang, W.; Song, W.K.; Cooper, D.N.; Kaufman, S.J. Selective modulation of the interaction of alpha 7 beta 1 integrin with fibronectin and laminin by L-14 lectin during skeletal muscle differentiation. J. Cell. Sci. 1994, 107 Pt 1, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elola, M.T.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Troncoso, M.F.; Vasta, G.R.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins: Matricellular glycan-binding proteins linking cell adhesion, migration, and survival. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1679–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.H.; Ying, N.W.; Wu, M.H.; Chiang, W.F.; Hsu, C.L.; Wong, T.Y.; Jin, Y.T.; Hong, T.M.; Chen, Y.L. Galectin-1, a novel ligand of neuropilin-1, activates VEGFR-2 signaling and modulates the migration of vascular endothelial cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, D.O.; Cerliani, J.P.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Mendez-Huergo, S.P.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Dergan-Dylon, S.; Toscano, M.A.; Caramelo, J.J.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Ouyang, J.; et al. Glycosylation-dependent lectin-receptor interactions preserve angiogenesis in anti-VEGF refractory tumors. Cell 2014, 156, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseeva, E.P.; Spring, E.L.; Baron, J.H.; de Bono, D.P. Galectin 1 modulates attachment, spreading and migration of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells via interactions with cellular receptors and components of extracellular matrix. J. Vasc. Res. 1999, 36, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.M.; Yoshizaki, L.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Fink, N.E. Isolation of galectin-1 from human platelets: Its interaction with actin. Protein J. 2012, 31, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, K.E.; Lee, C.; Stewart, P.L.; Baum, L.G. Restricted receptor segregation into membrane microdomains occurs on human T cells during apoptosis induced by galectin-1. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar]
- Walzel, H.; Schulz, U.; Neels, P.; Brock, J. Galectin-1, a natural ligand for the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45. Immunol. Lett. 1999, 67, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzel, H.; Blach, M.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K.I.; Brock, J. Involvement of CD2 and CD3 in galectin-1 induced signaling in human Jurkat T-cells. Glycobiology 2000, 10, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, K.E.; Hahn, H.P.; Pang, M.; Nguyen, J.T.; Baum, L.G. CD7 delivers a pro-apoptotic signal during galectin-1-induced T cell death. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.D.; Nguyen, J.T.; He, J.; Wang, W.; Ardman, B.; Green, J.M.; Fukuda, M.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-1 binds different CD43 glycoforms to cluster CD43 and regulate T cell death. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5328–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.J.; Chen, H.L.; Demetriou, M. Lateral compartmentalization of T cell receptor versus CD45 by galectin-N-glycan binding and microfilaments coordinate basal and activation signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35361–35372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ose, R.; Oharaa, O.; Nagase, T. Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 Mediate Protocadherin-24-Dependent Membrane Localization of beta-catenin in Colon Cancer Cell Line HCT116. Curr. Chem. Genom. 2012, 6, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.H.; Gabius, H.J.; Rohowsky-Kochan, C.; Ledeen, R.W.; Wu, G. Cross-linking of GM1 ganglioside by galectin-1 mediates regulatory T cell activity involving TRPC5 channel activation: Possible role in suppressing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Gabius, H.J.; Ledeen, R.W.; Bleich, D. Ganglioside GM1 deficiency in effector T cells from NOD mice induces resistance to regulatory T-cell suppression. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Haklai, R.; Elad-Sfadia, G.; Ballan, E.; Kloog, Y. Galectin-1 binds oncogenic H-Ras to mediate Ras membrane anchorage and cell transformation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7486–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazevits, O.; Mideksa, Y.G.; Solman, M.; Ligabue, A.; Ariotti, N.; Nakhaeizadeh, H.; Fansa, E.K.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Wittinghofer, A.; Ahmadian, M.R.; et al. Galectin-1 dimers can scaffold Raf-effectors to increase H-ras nanoclustering. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyakarnam, A.; Lenneman, A.J.; Lakkides, K.M.; Patterson, R.J.; Wang, J.L. A comparative nuclear localization study of galectin-1 with other splicing components. Exp. Cell. Res. 1998, 242, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Voss, P.G.; Grabski, S.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. Association of galectin-1 and galectin-3 with Gemin4 in complexes containing the SMN protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, R.J.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.L. Understanding the biochemical activities of galectin-1 and galectin-3 in the nucleus. Glycoconj. J. 2002, 19, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, P.G.; Gray, R.M.; Dickey, S.W.; Wang, W.; Park, J.W.; Kasai, K.; Hirabayashi, J.; Patterson, R.J.; Wang, J.L. Dissociation of the carbohydrate-binding and splicing activities of galectin-1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 478, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Park, J.W.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. Immunoprecipitation of spliceosomal RNAs by antisera to galectin-1 and galectin-3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboni, E.A.; Bawumia, S.; Hughes, R.C. Kinetic measurements of binding of galectin 3 to a laminin substratum. Glycoconj. J. 1999, 16, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Alonso, M.; Hirsch, T.; Wildmann, C.; van der Bruggen, P. Galectin-3 captures interferon-gamma in the tumor matrix reducing chemokine gradient production and T-cell tumor infiltration. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.; Granovsky, M.; Quaggin, S.; Dennis, J.W. Negative regulation of T-cell activation and autoimmunity by Mgat5 N-glycosylation. Nature 2001, 409, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillman, B.N.; Hsu, D.K.; Pang, M.; Brewer, C.F.; Johnson, P.; Liu, F.T.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-3 and galectin-1 bind distinct cell surface glycoprotein receptors to induce T cell death. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demotte, N.; Stroobant, V.; Courtoy, P.J.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Colau, D.; Luescher, I.F.; Hivroz, C.; Nicaise, J.; Squifflet, J.L.; Mourad, M.; et al. Restoring the association of the T cell receptor with CD8 reverses anergy in human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Immunity 2008, 28, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, A.E.; Demotte, N.; Scheid, B.; Wildmann, C.; Bigirimana, R.; Gordon-Alonso, M.; Carrasco, J.; Valitutti, S.; Godelaine, D.; van der Bruggen, P. A major secretory defect of tumour-infiltrating T lymphocytes due to galectin impairing LFA-1-mediated synapse completion. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomb, F.; Wang, W.; Simpson, D.; Zafar, M.; Beynon, R.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.G. Galectin-3 interacts with the cell-surface glycoprotein CD146 (MCAM, MUC18) and induces secretion of metastasis-promoting cytokines from vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8381–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguillos, M.A.; Svensson, M.; Schulte, T.; Boza-Serrano, A.; Garcia-Quintanilla, A.; Kavanagh, E.; Santiago, M.; Viceconte, N.; Oliva-Martin, M.J.; Osman, A.M.; et al. Microglia-Secreted Galectin-3 Acts as a Toll-like Receptor 4 Ligand and Contributes to Microglial Activation. Cell. Rep. 2015, 10, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouo, T.; Huang, L.; Pucsek, A.B.; Cao, M.; Solt, S.; Armstrong, T.; Jaffee, E. Galectin-3 Shapes Antitumor Immune Responses by Suppressing CD8+ T Cells via LAG-3 and Inhibiting Expansion of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska, A.I.; Jefferies, K.C.; Panjwani, N. Galectin-3 protein modulates cell surface expression and activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29913–29921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magescas, J.; Sengmanivong, L.; Viau, A.; Mayeux, A.; Dang, T.; Burtin, M.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H.; Poirier, F.; Terzi, F.; et al. Spindle pole cohesion requires glycosylation-mediated localization of NuMA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalom-Feuerstein, R.; Plowman, S.J.; Rotblat, B.; Ariotti, N.; Tian, T.; Hancock, J.F.; Kloog, Y. K-ras nanoclustering is subverted by overexpression of the scaffold protein galectin-3. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6608–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Takenaka, Y.; Tsutsumi, S.; Hogan, V.; Kikuchi, A.; Raz, A. Galectin-3, a novel binding partner of beta-catenin. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6363–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Takenaka, Y.; Fukumori, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Okada, K.; Hogan, V.; Kikuchi, A.; Kuwano, H.; Raz, A. Implication of galectin-3 in Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3535–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Fermin, A.; Vardhana, S.; Weng, I.C.; Lo, K.F.; Chang, E.Y.; Maverakis, E.; Yang, R.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Dustin, M.L.; et al. Galectin-3 negatively regulates TCR-mediated CD4+ T-cell activation at the immunological synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14496–14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hsu, D.K.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, R.Y.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Isseroff, R.R.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-3 regulates intracellular trafficking of EGFR through Alix and promotes keratinocyte migration. J. Investig. Derm. 2012, 132, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Joo, E.J.; Tarighat, S.S.; Schiffer, I.; Paz, H.; Fabbri, M.; Abdel-Azim, H.; Groffen, J.; Heisterkamp, N. B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and stromal cells communicate through Galectin-3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11378–11394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Boussac, M.; Veron, P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Garin, J.; Amigorena, S. Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: A secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7309–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, J.L.; Khanna, S.; Giles, P.J.; Brennan, P.; Brewis, I.A.; Staffurth, J.; Mason, M.D.; Clayton, A. Proteomics analysis of bladder cancer exosomes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Poirier, F.; Jacob, R.; Delacour, D. Galectin-3, a novel centrosome-associated protein, required for epithelial morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2010, 21, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Finley, R.L., Jr.; Raz, A.; Kim, H.R. Galectin-3 translocates to the perinuclear membranes and inhibits cytochrome c release from the mitochondria. A role for synexin in galectin-3 translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15819–15827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumori, T.; Takenaka, Y.; Oka, N.; Yoshii, T.; Hogan, V.; Inohara, H.; Kanayama, H.O.; Kim, H.R.; Raz, A. Endogenous galectin-3 determines the routing of CD95 apoptotic signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3376–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.W.; Gu Kang, H.; La, S.H.; Choi, I.J.; Ro, J.Y.; Bresalier, R.S.; Song, J.; Chun, K.H. Ablation of galectin-3 induces p27(KIP1)-dependent premature senescence without oncogenic stress. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.G.; Lee, H.W.; Chun, K.H. Ablation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) induces cellular senescence in gastric cancer through a galectin-3 dependent mechanism. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57117–57130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, K.H.; Yoo, B.C.; Hong, S.H.; Lim, Y.C.; Shin, Y.K.; Park, J.G. Identification of mitochondrial F(1)F(0)-ATP synthase interacting with galectin-3 in colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagher, S.F.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. Identification of galectin-3 as a factor in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudek, K.C.; Voss, P.G.; Locascio, L.E.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. A mechanism for incorporation of galectin-3 into the spliceosome through its association with U1 snRNP. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7705–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chang, C.W.; Tsay, Y.G.; Huang, L.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Cheng, L.H.; Yang, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Teo, W.H.; Hung, K.F.; et al. HSP40 co-chaperone protein Tid1 suppresses metastasis of head and neck cancer by inhibiting Galectin-7-TCF3-MMP9 axis signaling. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3841–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, C.; Baricault, L.; Canelle, L.; Barboule, N.; Racca, C.; Monsarrat, B.; Magnaldo, T.; Larminat, F. Mitochondrial proteomic approach reveals galectin-7 as a novel BCL-2 binding protein in human cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2011, 22, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, Y.; Higashi, K.; Kushida, M.; Hong, Y.Y.; Nakao, S.; Higashiyama, R.; Moro, T.; Itoh, J.; Mikami, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses profibrogenic signal transduction via nuclear export of Smad3 with galectin-7. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Nishi, N.; Shoji, H.; Itoh, A.; Lu, L.H.; Hirashima, M.; Nakamura, T. Induction of cell adhesion by galectin-8 and its target molecules in Jurkat T-cells. J. Biochem. 2008, 143, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadari, Y.R.; Arbel-Goren, R.; Levy, Y.; Amsterdam, A.; Alon, R.; Zakut, R.; Zick, Y. Galectin-8 binding to integrins inhibits cell adhesion and induces apoptosis. J. Cell. Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 13, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, M.F.; Ferragut, F.; Bacigalupo, M.L.; Cardenas Delgado, V.M.; Nugnes, L.G.; Gentilini, L.; Laderach, D.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Compagno, D.; Rabinovich, G.A.; et al. Galectin-8: A matricellular lectin with key roles in angiogenesis. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.M.; Ferragut, F.; Cardenas Delgado, V.M.; Bracalente, C.; Bravo, A.I.; Cagnoni, A.J.; Nunez, M.; Morosi, L.G.; Quinta, H.R.; Espelt, M.V.; et al. Glycosylation-dependent binding of galectin-8 to activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM/CD166) promotes its surface segregation on breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueni, L.N.; Detmar, M. Galectin-8 interacts with podoplanin and modulates lymphatic endothelial cell functions. Exp. Cell. Res. 2009, 315, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshkar Sebban, L.; Ronen, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Elkayam, O.; Caspi, D.; Aamar, S.; Amital, H.; Rubinow, A.; Golan, I.; Naor, D.; et al. The involvement of CD44 and its novel ligand galectin-8 in apoptotic regulation of autoimmune inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.W.; Hong, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Song, H.K. Structural basis for recognition of autophagic receptor NDP52 by the sugar receptor galectin-8. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.H.; Weng, I.C.; Li, F.Y.; Lin, W.H.; Liu, F.T. Intracellular galectins sense cytosolically exposed glycans as danger and mediate cellular responses. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Anderson, A.C.; Schubart, A.; Xiong, H.; Imitola, J.; Khoury, S.J.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Li, C.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Yao, J.; Li, H.; Yan, M.; Chang, W.C.; Hsu, J.M.; Cha, J.H.; et al. Galectin-9 interacts with PD-1 and TIM-3 to regulate T cell death and is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, K.; Arikawa, T.; Oomizu, S.; Kontani, K.; Nobumoto, A.; Tateno, H.; Watanabe, K.; Niki, T.; Katoh, S.; Miyake, M.; et al. Galectin-9 increases Tim-3+ dendritic cells and CD8+ T cells and enhances antitumor immunity via galectin-9-Tim-3 interactions. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7660–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, S.; Ishii, N.; Nobumoto, A.; Takeshita, K.; Dai, S.Y.; Shinonaga, R.; Niki, T.; Nishi, N.; Tominaga, A.; Yamauchi, A.; et al. Galectin-9 inhibits CD44-hyaluronan interaction and suppresses a murine model of allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Thalhamer, T.; Franca, R.F.; Xiao, S.; Wang, C.; Hotta, C.; Zhu, C.; Hirashima, M.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K. Galectin-9-CD44 interaction enhances stability and function of adaptive regulatory T cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasinska, I.M.; Meyer, N.H.; Schlichtner, S.; Hussain, R.; Siligardi, G.; Casely-Hayford, M.; Fiedler, W.; Wellbrock, J.; Desmet, C.; Calzolai, L.; et al. Ligand-Receptor Interactions of Galectin-9 and VISTA Suppress Human T Lymphocyte Cytotoxic Activity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madireddi, S.; Eun, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Nemcovicova, I.; Mehta, A.K.; Zajonc, D.M.; Nishi, N.; Niki, T.; Hirashima, M.; Croft, M. Galectin-9 controls the therapeutic activity of 4-1BB-targeting antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1433–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitaitis, G.M.; Wagner, D.H., Jr. Galectin-9 controls CD40 signaling through a Tim-3 independent mechanism and redirects the cytokine profile of pathogenic T cells in autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madireddi, S.; Eun, S.Y.; Mehta, A.K.; Birta, A.; Zajonc, D.M.; Niki, T.; Hirashima, M.; Podack, E.R.; Schreiber, T.H.; Croft, M. Regulatory T Cell-Mediated Suppression of Inflammation Induced by DR3 Signaling Is Dependent on Galectin-9. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Hong, P.W.; Lee, B.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-9 binding to cell surface protein disulfide isomerase regulates the redox environment to enhance T-cell migration and HIV entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10650–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, T.; Tsutsui, S.; Hirose, S.; Aradono, S.; Sugimoto, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Nishi, N.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 is a high affinity IgE-binding lectin with anti-allergic effect by blocking IgE-antigen complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32344–32352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Takamatsu, S.; Minowa, M.T.; Yoshida, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Marth, J.D. Dietary and genetic control of glucose transporter 2 glycosylation promotes insulin secretion in suppressing diabetes. Cell 2005, 123, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, A.; Tsukada, J.; Mizobe, T.; Higashi, T.; Mouri, F.; Tanikawa, R.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M.; Tanaka, Y. Intracellular galectin-9 activates inflammatory cytokines in monocytes. Genes Cells 2009, 14, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Braber, I.; Mugwagwa, T.; Vrisekoop, N.; Westera, L.; Mogling, R.; de Boer, A.B.; Willems, N.; Schrijver, E.H.; Spierenburg, G.; Gaiser, K.; et al. Maintenance of peripheral naive T cells is sustained by thymus output in mice but not humans. Immunity 2012, 36, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, I.; Antia, R.; Callard, R.; Yates, A.J. Quantifying the development of the peripheral naive CD4+ T-cell pool in humans. Blood 2009, 113, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, B.; Yates, A.J. The natural history of naive T cells from birth to maturity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting: Integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, I.; Bhuniya, A.; Shukla, D.; Patidar, A.; Nandi, P.; Saha, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Ganguly, N.; Ghosh, S.; Nair, A.; et al. Tumor Arrests DN2 to DN3 Pro T Cell Transition and Promotes Its Conversion to Thymic Dendritic Cells by Reciprocally Regulating Notch1 and Ikaros Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, R.M.; Graf, M.R.; Merchant, R.E.; Black, K.L.; Wheeler, C.J. Thymic function and output of recent thymic emigrant T cells during intracranial glioma progression. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 64, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronne-Bar-On, A.; Zipori, D.; Haran-Ghera, N. Increased regulatory versus effector T cell development is associated with thymus atrophy in mouse models of multiple myeloma. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Geng, S.; Wu, X.; Zhong, L.; Schmidt, C.A.; Przybylski, G.K. Reduced levels of recent thymic emigrants in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, A.; Singh, S.M.; Sodhi, A. Ascitic growth of a spontaneous transplantable T cell lymphoma induces thymic involution. 1. Alterations in the CD4/CD8 distribution in thymocytes. Tumour Biol. 2000, 21, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Taguchi, C.; Sasaguri, K.; Kubo, K.Y.; Horie, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Onozuka, M.; Sato, S.; Kadoya, T. The Galectin-1 level in serum as a novel marker for stress. Glycoconj. J. 2010, 27, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaguri, K.; Yamada, K.; Narimatsu, Y.; Oonuki, M.; Oishi, A.; Koda, K.; Kubo, K.Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kadoya, T. Stress-induced galectin-1 influences immune tolerance in the spleen and thymus by modulating CD45 immunoreactive lymphocytes. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, S.R.; Teh, C.; Hu, D.Y.; Strasser, A.; Gray, D.H.D. Cell death and thymic tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, L.G.; Pang, M.; Perillo, N.L.; Wu, T.; Delegeane, A.; Uittenbogaart, C.H.; Fukuda, M.; Seilhamer, J.J. Human thymic epithelial cells express an endogenous lectin, galectin-1, which binds to core 2 O-glycans on thymocytes and T lymphoblastoid cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Baum, L.G. Endothelial cell expression of galectin-1 induced by prostate cancer cells inhibits T-cell transendothelial migration. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perillo, N.L.; Uittenbogaart, C.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-1, an endogenous lectin produced by thymic epithelial cells, induces apoptosis of human thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, G.N.; Lewis, L.A.; Kozak, K.R.; Moran, M.; Nguyen, J.T.; Baum, L.G.; Miceli, M.C. Galectin-1 specifically modulates TCR signals to enhance TCR apoptosis but inhibit IL-2 production and proliferation. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 799–806. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, S.; Earl, L.A.; Jacobs, L.; Baum, L.G. Structural features of galectin-9 and galectin-1 that determine distinct T cell death pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12248–12258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, N.L.; Pace, K.E.; Seilhamer, J.J.; Baum, L.G. Apoptosis of T cells mediated by galectin-1. Nature 1995, 378, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.T.; Evans, D.P.; Galvan, M.; Pace, K.E.; Leitenberg, D.; Bui, T.N.; Baum, L.G. CD45 modulates galectin-1-induced T cell death: Regulation by expression of core 2 O-glycans. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Cummings, R.D. Galectin-1, a beta-galactoside-binding lectin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. I. Physical and chemical characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5198–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Cummings, R.D. Characterization of monomeric forms of galectin-1 generated by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13081–13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battig, P.; Saudan, P.; Gunde, T.; Bachmann, M.F. Enhanced apoptotic activity of a structurally optimized form of galectin-1. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Verde, D.M.; Silva-Monteiro, E.; Jasiulionis, M.G.; Farias-De-Oliveira, D.A.; Brentani, R.R.; Savino, W.; Chammas, R. Galectin-3 modulates carbohydrate-dependent thymocyte interactions with the thymic microenvironment. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumori, T.; Takenaka, Y.; Yoshii, T.; Kim, H.R.; Hogan, V.; Inohara, H.; Kagawa, S.; Raz, A. CD29 and CD7 mediate galectin-3-induced type II T-cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8302–8311. [Google Scholar]
- Matarrese, P.; Fusco, O.; Tinari, N.; Natoli, C.; Liu, F.T.; Semeraro, M.L.; Malorni, W.; Iacobelli, S. Galectin-3 overexpression protects from apoptosis by improving cell adhesion properties. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T. Expression of galectin-3 modulates T-cell growth and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6737–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashio, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Abedin, M.J.; Seki, M.; Nishi, N.; Yoshida, N.; Nakamura, T.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 induces apoptosis through the calcium-calpain-caspase-1 pathway. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribulatti, M.V.; Mucci, J.; Cattaneo, V.; Aguero, F.; Gilmartin, T.; Head, S.R.; Campetella, O. Galectin-8 induces apoptosis in the CD4(high)CD8(high) thymocyte subpopulation. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, J.; Ota, K.; Kumar, A.; Wallner, E.I.; Kanwar, Y.S. Developmental regulation, expression, and apoptotic potential of galectin-9, a beta-galactoside binding lectin. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, W.; Mendes-Da-Cruz, D.A.; Smaniotto, S.; Silva-Monteiro, E.; Villa-Verde, D.M. Molecular mechanisms governing thymocyte migration: Combined role of chemokines and extracellular matrix. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.D.; Whiting, C.C.; Tomassian, T.; Pang, M.; Bissel, S.J.; Baum, L.G.; Mossine, V.V.; Poirier, F.; Huflejt, M.E.; Miceli, M.C. Endogenous galectin-1 enforces class I-restricted TCR functional fate decisions in thymocytes. Blood 2008, 112, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martinez Allo, V.C.; Hauk, V.; Sarbia, N.; Pinto, N.A.; Croci, D.O.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Morales, R.M.; Gatto, S.G.; Manselle Cocco, M.N.; Stupirski, J.C.; et al. Suppression of age-related salivary gland autoimmunity by glycosylation-dependent galectin-1-driven immune inhibitory circuits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6630–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Perez, R.; Lopez-Santalla, M.; Sanchez-Dominguez, R.; Alberquilla, O.; Gutierrez-Canas, I.; Juarranz, Y.; Bueren, J.A.; Garin, M.I. Enhanced Susceptibility of Galectin-1 Deficient Mice to Experimental Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 687443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-de-Abreu, E.; Silva-Dos-Santos, D.; Lepletier, A.; Ramos, T.D.P.; Ferreira-Reis, R.; Vasconcelos-Fontes, L.; Ramos, M.T.; Torres, R.C.; Cotta-de-Almeida, V.; Carvalho, V.F.; et al. Lack of Galectin-3 Disrupts Thymus Homeostasis in Association to Increase of Local and Systemic Glucocorticoid Levels and Steroidogenic Machinery. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaldo, T.; Fowlis, D.; Darmon, M. Galectin-7, a marker of all types of stratified epithelia. Differentiation 1998, 63, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyakarnam, A.; Dagher, S.F.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. Evidence for a role for galectin-1 in pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 4730–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudek, K.C.; Voss, P.G.; Wang, J.L.; Patterson, R.J. A 10S galectin-3-U1 snRNP complex assembles into active spliceosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6391–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Patterson, R.J.; Wang, J.L. Intracellular functions of galectins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.G.; Kim, W.J.; Chun, K.H.; Kim, S.J. Galectin-3 Interacts with C/EBPbeta and Upregulates Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor Expression in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Chun, K.H. Non-classical role of Galectin-3 in cancer progression: Translocation to nucleus by carbohydrate-recognition independent manner. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, P.; Ferrarini, M.; Molina-Paris, C.; Lythe, G.; Vasseur, F.; Lim, A.; Rocha, B.; Azogui, O. A new mechanism shapes the naive CD8(+) T cell repertoire: The selection for full diversity. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 85, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greef, P.C.; Oakes, T.; Gerritsen, B.; Ismail, M.; Heather, J.M.; Hermsen, R.; Chain, B.; de Boer, R.J. The naive T-cell receptor repertoire has an extremely broad distribution of clone sizes. Elife 2020, 9, e49900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.J. Theories and quantification of thymic selection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Hu, Z.; Keskin, D.B.; Shukla, S.A.; Sun, J.; Bozym, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Luoma, A.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Peter, L.; et al. An immunogenic personal neoantigen vaccine for patients with melanoma. Nature 2017, 547, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.T.; Kessler, D.A.; Levine, H. Effects of thymic selection on T cell recognition of foreign and tumor antigenic peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7875–E7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittet, M.J.; Valmori, D.; Dunbar, P.R.; Speiser, D.E.; Lienard, D.; Lejeune, F.; Fleischhauer, K.; Cerundolo, V.; Cerottini, J.C.; Romero, P. High frequencies of naive Melan-A/MART-1-specific CD8(+) T cells in a large proportion of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2 individuals. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germeau, C.; Ma, W.; Schiavetti, F.; Lurquin, C.; Henry, E.; Vigneron, N.; Brasseur, F.; Lethe, B.; De Plaen, E.; Velu, T.; et al. High frequency of antitumor T cells in the blood of melanoma patients before and after vaccination with tumor antigens. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, M.P.; Patente, T.A.; Flatow, E.A.; Sallusto, F.; Barbuto, J.A.M. Frequency determination of breast tumor-reactive CD4 and CD8 T cells in humans: Unveiling the antitumor immune response. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1607674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A.J.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M. Immunobiology, 5th ed.; Garland Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 10:0-8153-3642-X. [Google Scholar]
- Keryer-Bibens, C.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Villemant, C.; Souquere, S.; Nishi, N.; Hirashima, M.; Middeldorp, J.; Busson, P. Exosomes released by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells convey the viral latent membrane protein 1 and the immunomodulatory protein galectin 9. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, L.V.; Sampaio, A.L.; Cooper, D.; Perretti, M. Inhibitory control of endothelial galectin-1 on in vitro and in vivo lymphocyte trafficking. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, D.K.; Aguilera, T.; Cao, H.; Kwok, S.; Kong, C.; Bloomstein, J.; Wang, Z.; Rangan, V.S.; Jiang, D.; von Eyben, R.; et al. Galectin-1-driven T cell exclusion in the tumor endothelium promotes immunotherapy resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5553–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.P.; Odell, A.F.; Karnezis, T.; Farnsworth, R.H.; Gould, C.M.; Li, J.; Paquet-Fifield, S.; Harris, N.C.; Walter, A.; Gregory, J.L.; et al. Genome-wide functional analysis reveals central signaling regulators of lymphatic endothelial cell migration and remodeling. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, S.; Man, J.H.; Chang, M.H.; Lee, B.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-1 regulates tissue exit of specific dendritic cell populations. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 22662–22677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilarregui, J.M.; Croci, D.O.; Bianco, G.A.; Toscano, M.A.; Salatino, M.; Vermeulen, M.E.; Geffner, J.R.; Rabinovich, G.A. Tolerogenic signals delivered by dendritic cells to T cells through a galectin-1-driven immunoregulatory circuit involving interleukin 27 and interleukin 10. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ye, Y.; Jia, J.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Geng, L.; Yin, S.; et al. Galectin-1-induced tolerogenic dendritic cells combined with apoptotic lymphocytes prolong liver allograft survival. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortner, D.; Grabher, D.; Hermann, M.; Kremmer, E.; Hofer, S.; Heufler, C. The adaptor protein Bam32 in human dendritic cells participates in the regulation of MHC class I-induced CD8+ T cell activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3972–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesone, A.J.; Rutkowski, M.R.; Brencicova, E.; Svoronos, N.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Stephen, T.L.; Allegrezza, M.J.; Payne, K.K.; Nguyen, J.M.; Wickramasinghe, J.; et al. Satb1 Overexpression Drives Tumor-Promoting Activities in Cancer-Associated Dendritic Cells. Cell. Rep. 2016, 14, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, N.; Alvarez, M.; Zwirner, N.W.; Toscano, M.A.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Bravo, A.; Mordoh, J.; Fainboim, L.; Podhajcer, O.L.; Rabinovich, G.A. Targeted inhibition of galectin-1 gene expression in tumor cells results in heightened T cell-mediated rejection; A potential mechanism of tumor-immune privilege. Cancer Cell. 2004, 5, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, R.; Berger, E.; Zenclussen, A.C.; Jorch, G.; Lode, H.N.; Salatino, M.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Fest, S. Neuroblastoma triggers an immunoevasive program involving galectin-1-dependent modulation of T cell and dendritic cell compartments. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno-Laurent, F.; Opperman, M.; Barthel, S.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Dimitroff, C.J. Galectin-1 triggers an immunoregulatory signature in Th cells functionally defined by IL-10 expression. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczynski, P.; Ouyang, J.; Monti, S.; Rodig, S.J.; Takeyama, K.; Abramson, J.; Chen, W.; Kutok, J.L.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Shipp, M.A. The AP1-dependent secretion of galectin-1 by Reed Sternberg cells fosters immune privilege in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13134–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motran, C.C.; Molinder, K.M.; Liu, S.D.; Poirier, F.; Miceli, M.C. Galectin-1 functions as a Th2 cytokine that selectively induces Th1 apoptosis and promotes Th2 function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3015–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, N.; Chong, Y.; Xu, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Yin, W.; et al. Apoptosis and anergy of T cell induced by pancreatic stellate cells-derived galectin-1 in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5617–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.D.; Tomassian, T.; Bruhn, K.W.; Miller, J.F.; Poirier, F.; Miceli, M.C. Galectin-1 tunes TCR binding and signal transduction to regulate CD8 burst size. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5283–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, P.T.; Montes de Oca, M.; Rivera, F.L.; Kumar, R.; Edwards, C.L.; Faleiro, R.J.; Ng, S.S.; Sheel, M.; Wang, Y.; Amante, F.H.; et al. Galectin-1 Impairs the Generation of Anti-Parasitic Th1 Cell Responses in the Liver during Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnberg, T.; Svensson, V.; James, K.R.; Fernandez-Ruiz, D.; Sebina, I.; Montandon, R.; Soon, M.S.; Fogg, L.G.; Nair, A.S.; Liligeto, U.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq and computational analysis using temporal mixture modelling resolves Th1/Tfh fate bifurcation in malaria. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaal2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corapi, E.; Carrizo, G.; Compagno, D.; Laderach, D. Endogenous Galectin-1 in T Lymphocytes Regulates Anti-prostate Cancer Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Croci, D.O.; Cerliani, J.P.; Martinez-Allo, V.C.; Dergan-Dylon, S.; Mendez Huergo, S.P.; Stupirski, J.C.; Mazal, D.; Osinaga, E.; Toscano, M.A.; et al. Targeting galectin-1 overcomes breast cancer associated immunosuppression and prevents metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, M.I.; Chu, C.C.; Golshayan, D.; Cernuda-Morollon, E.; Wait, R.; Lechler, R.I. Galectin-1: A key effector of regulation mediated by CD4+CD25+ T cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnoni, A.J.; Giribaldi, M.L.; Blidner, A.G.; Cutine, A.M.; Gatto, S.G.; Morales, R.M.; Salatino, M.; Abba, M.C.; Croci, D.O.; Marino, K.V.; et al. Galectin-1 fosters an immunosuppressive microenvironment in colorectal cancer by reprogramming CD8(+) regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102950118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, T.; Toelen, J.; Maes, W.; Poirier, F.; Boon, L.; Tousseyn, T.; Mathivet, T.; Gerhardt, H.; Mathieu, V.; Kiss, R.; et al. Glioma-derived galectin-1 regulates innate and adaptive antitumor immunity. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.J.; Chockley, P.; Zamler, D.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R. Natural killer cells require monocytic Gr-1(+)/CD11b(+) myeloid cells to eradicate orthotopically engrafted glioma cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1163461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Woensel, M.; Mathivet, T.; Wauthoz, N.; Rosiere, R.; Garg, A.D.; Agostinis, P.; Mathieu, V.; Kiss, R.; Lefranc, F.; Boon, L.; et al. Sensitization of glioblastoma tumor micro-environment to chemo- and immunotherapy by Galectin-1 intranasal knock-down strategy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, C.A.; Martinez-Bosch, N.; Guerrero, P.E.; Vinaixa, J.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Iglesias, M.; Moreno, M.; Djurec, M.; Poirier, F.; Gabius, H.J.; et al. Targeting galectin-1 inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by modulating tumor-stroma crosstalk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3769–E3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Han, B.; Meng, X.; Duan, C.; Yang, C.; Wu, Z.; Magafurov, D.; Zhao, S.; Safin, S.; Jiang, C.; et al. Immunogenomic analysis reveals LGALS1 contributes to the immune heterogeneity and immunosuppression in glioma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiraboschi, C.; Gentilini, L.; Corapi, E.; Jaworski, F.M.; Velazquez, C.; Chauchereau, A.; Laderach, D.J.; Compagno, D. Combining inhibition of Galectin-3 with and before a therapeutic vaccination is critical for the prostate-tumor free outcome. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljevic, G.; Jovanovic, I.; Majstorovic, I.; Mitrovic, M.; Lisnic, V.J.; Arsenijevic, N.; Jonjic, S.; Lukic, M.L. Deletion of galectin-3 in the host attenuates metastasis of murine melanoma by modulating tumor adhesion and NK cell activity. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.K.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Chen, H.Y.; Yu, L.; Grando, S.A.; Liu, F.T. Endogenous galectin-3 is localized in membrane lipid rafts and regulates migration of dendritic cells. J. Investig. Derm. 2009, 129, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuilh, L.; Vanhoutte, F.; Fontaine, J.; van Stijn, C.M.; Tillie-Leblond, I.; Capron, M.; Faveeuw, C.; Jouault, T.; van Die, I.; Gosset, P.; et al. Galectin-3 modulates immune and inflammatory responses during helminthic infection: Impact of galectin-3 deficiency on the functions of dendritic cells. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5148–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Yu, J.S.; Liu, F.T.; Miaw, S.C.; Wu-Hsieh, B.A. Galectin-3 negatively regulates dendritic cell production of IL-23/IL-17-axis cytokines in infection by Histoplasma capsulatum. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3427–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermin Lee, A.; Chen, H.Y.; Wan, L.; Wu, S.Y.; Yu, J.S.; Huang, A.C.; Miaw, S.C.; Hsu, D.K.; Wu-Hsieh, B.A.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-3 modulates Th17 responses by regulating dendritic cell cytokines. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.D.; Gude, R.P.; Kalraiya, R.D.; Chiplunkar, S.V. Endogenous galectin-3 expression levels modulate immune responses in galectin-3 transgenic mice. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, M.F.; Rolig, A.S.; Redmond, W.L. Intracellular Galectin-3 Is Essential for OX40-Mediated Memory CD8(+) T Cell Development. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.G.; Goedegebuure, P.S.; Sadanaga, N.; Nagoshi, M.; von Bernstorff, W.; Eberlein, T.J. Expression and function of galectin-3, a beta-galactoside-binding protein in activated T lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Melief, S.M.; Visser, M.; van der Burg, S.H.; Verdegaal, E.M.E. IDO and galectin-3 hamper the ex vivo generation of clinical grade tumor-specific T cells for adoptive cell therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.S.; Cao, Z.; Sugaya, S.; Lopez, M.J.; Sendra, V.G.; Laver, N.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Fu, J.; Song, J.; et al. Pathological lymphangiogenesis is modulated by galectin-8-dependent crosstalk between podoplanin and integrin-associated VEGFR-3. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniasz-Krzywiec, P.; Martin-Perez, R.; Ehling, M.; Garcia-Caballero, M.; Pinioti, S.; Pretto, S.; Kroes, R.; Aldeni, C.; Di Matteo, M.; Prenen, H.; et al. Podoplanin-Expressing Macrophages Promote Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphoinvasion in Breast Cancer. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 917–936.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, C.A.; Carabelli, J.; Campetella, O.; Tribulatti, M.V. Galectin-8 Enhances T cell Response by Promotion of Antigen Internalization and Processing. iScience 2020, 23, 101278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabelli, J.; Quattrocchi, V.; D’Antuono, A.; Zamorano, P.; Tribulatti, M.V.; Campetella, O. Galectin-8 activates dendritic cells and stimulates antigen-specific immune response elicitation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabelli, J.; Prato, C.A.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Aoki, M.P.; Campetella, O.; Tribulatti, M.V. Interleukin-6 signalling mediates Galectin-8 co-stimulatory activity of antigen-specific CD4 T-cell response. Immunology 2018, 155, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribulatti, M.V.; Cattaneo, V.; Hellman, U.; Mucci, J.; Campetella, O. Galectin-8 provides costimulatory and proliferative signals to T lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, J.F.; Suryawanshi, A.; Chen, W.S.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Panjwani, N. Galectin-8 promotes regulatory T-cell differentiation by modulating IL-2 and TGFbeta signaling. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 94, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribulatti, M.V.; Figini, M.G.; Carabelli, J.; Cattaneo, V.; Campetella, O. Redundant and antagonistic functions of galectin-1, -3, and -8 in the elicitation of T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2991–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Arikawa, T.; Shinonaga, R.; Oomizu, S.; Inagawa, H.; Soma, G.; Niki, T.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 signaling prolongs survival in murine lung-cancer by inducing macrophages to differentiate into plasmacytoid dendritic cell-like macrophages. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 142, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobumoto, A.; Nagahara, K.; Oomizu, S.; Katoh, S.; Nishi, N.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Tominaga, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 suppresses tumor metastasis by blocking adhesion to endothelium and extracellular matrices. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobumoto, A.; Oomizu, S.; Arikawa, T.; Katoh, S.; Nagahara, K.; Miyake, M.; Nishi, N.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Yamauchi, A.; et al. Galectin-9 expands unique macrophages exhibiting plasmacytoid dendritic cell-like phenotypes that activate NK cells in tumor-bearing mice. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, W.; Zhou, H.; Yuan, J.; Wu, K.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.K. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates CD8+ alloreactive T cell and prolongs survival of skin graft. Cell. Immunol. 2007, 250, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Oomizu, S.; Sakata, K.M.; Sakata, A.; Arikawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ito, K.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Saita, N.; et al. Galectin-9 suppresses the generation of Th17, promotes the induction of regulatory T cells, and regulates experimental autoimmune arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 127, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sundararajan, A.; Suryawanshi, A.; Kumar, N.; Veiga-Parga, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Thomas, P.G.; Sangster, M.Y.; Rouse, B.T. T cell immunoglobulin and mucin protein-3 (Tim-3)/Galectin-9 interaction regulates influenza A virus-specific humoral and CD8 T-cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19001–19006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.B.; Sehrawat, S.; Suryawanshi, A.; Rajasagi, N.K.; Mulik, S.; Hirashima, M.; Rouse, B.T. Influence of galectin-9/Tim-3 interaction on herpes simplex virus-1 latency. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5745–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritoki, M.; Kadowaki, T.; Niki, T.; Nakano, D.; Soma, G.; Mori, H.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Kohno, M.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 ameliorates clinical severity of MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice by inducing plasma cell apoptosis independently of Tim-3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooden, M.J.; Wiersma, V.R.; Samplonius, D.F.; Gerssen, J.; van Ginkel, R.J.; Nijman, H.W.; Hirashima, M.; Niki, T.; Eggleton, P.; Helfrich, W.; et al. Galectin-9 activates and expands human T-helper 1 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhuillier, C.; Barjon, C.; Niki, T.; Gelin, A.; Praz, F.; Morales, O.; Souquere, S.; Hirashima, M.; Wei, M.; Dellis, O.; et al. Impact of exogenous galectin-9 on human t cells: Contribution of the t cell receptor complex to antigen-independent activation but not to apoptosis induction. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16797–16811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, E.W.; Bi, S.; Kane, L.P. Galectin-9 regulates T helper cell function independently of Tim-3. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.Y.; Nakagawa, R.; Itoh, A.; Murakami, H.; Kashio, Y.; Abe, H.; Katoh, S.; Kontani, K.; Kihara, M.; Zhang, S.L.; et al. Galectin-9 induces maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Chou, F.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Yeh, L.T.; Lin, K.I.; Liu, F.T.; Sytwu, H.K. Intracellular Galectin-9 Enhances Proximal TCR Signaling and Potentiates Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomizu, S.; Arikawa, T.; Niki, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueno, M.; Nishi, N.; Yamauchi, A.; Hattori, T.; Masaki, T.; Hirashima, M. Cell surface galectin-9 expressing th cells regulate Th17 and Foxp3+ Treg development by galectin-9 secretion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomizu, S.; Arikawa, T.; Niki, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueno, M.; Nishi, N.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 suppresses Th17 cell development in an IL-2-dependent but Tim-3-independent manner. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 143, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbaz, S.; Dunsmore, G.; Koleva, P.; Xu, L.; Houston, S.; Elahi, S. Galectin-9 and VISTA Expression Define Terminally Exhausted T Cells in HIV-1 Infection. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2474–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardalhon, V.; Anderson, A.C.; Karman, J.; Apetoh, L.; Chandwaskar, R.; Lee, D.H.; Cornejo, M.; Nishi, N.; Yamauchi, A.; Quintana, F.J.; et al. Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway: Regulation of Th1 immunity through promotion of CD11b+Ly-6G+ myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wan, L.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.K. Tim-3-Galectin-9 pathway involves the suppression induced by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Jose, E.; Borroto, A.; Niedergang, F.; Alcover, A.; Alarcon, B. Triggering the TCR complex causes the downregulation of nonengaged receptors by a signal transduction-dependent mechanism. Immunity 2000, 12, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Costes, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Lagorce-Pages, C.; Tosolini, M.; Camus, M.; Berger, A.; Wind, P.; et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 2006, 313, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.T.; Adams, S.F.; Tahirovic, E.; Hagemann, I.S.; Coukos, G. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, J.A.; Fearon, D.T. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science 2015, 348, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banh, A.; Zhang, J.; Cao, H.; Bouley, D.M.; Kwok, S.; Kong, C.; Giaccia, A.J.; Koong, A.C.; Le, Q.T. Tumor galectin-1 mediates tumor growth and metastasis through regulation of T-cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, V.; de Lassalle, E.M.; Toelen, J.; Mohr, T.; Bellahcene, A.; Van Goietsenoven, G.; Verschuere, T.; Bouzin, C.; Debyser, Z.; De Vleeschouwer, S.; et al. Galectin-1 in melanoma biology and related neo-angiogenesis processes. J. Investig. Derm. 2012, 132, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno-Laurent, F.; Opperman, M.J.; Barthel, S.R.; Hays, D.; Schatton, T.; Zhan, Q.; He, X.; Matta, K.L.; Supko, J.G.; Frank, M.H.; et al. Metabolic inhibition of galectin-1-binding carbohydrates accentuates antitumor immunity. J. Investig. Derm. 2012, 132, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bosch, N.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Moreno, M.; Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Munne-Collado, J.; Iglesias, M.; Andre, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Hwang, R.F.; Poirier, F.; et al. Galectin-1 drives pancreatic carcinogenesis through stroma remodeling and Hedgehog signaling activation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3512–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, M.R.; Stephen, T.L.; Svoronos, N.; Allegrezza, M.J.; Tesone, A.J.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Brencicova, E.; Escovar-Fadul, X.; Nguyen, J.M.; Cadungog, M.G.; et al. Microbially driven TLR5-dependent signaling governs distal malignant progression through tumor-promoting inflammation. Cancer Cell. 2015, 27, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endharti, A.T.; Zhou, Y.W.; Nakashima, I.; Suzuki, H. Galectin-1 supports survival of naive T cells without promoting cell proliferation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, M.A.; Bianco, G.A.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Croci, D.O.; Correale, J.; Hernandez, J.D.; Zwirner, N.W.; Poirier, F.; Riley, E.M.; Baum, L.G.; et al. Differential glycosylation of TH1, TH2 and TH-17 effector cells selectively regulates susceptibility to cell death. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, S.R.; Qian, Y.; Karmakar, S.; Koyama, N.S.; Dias-Baruffi, M.; Leffler, H.; McEver, R.P.; Cummings, R.D. Differential roles of galectin-1 and galectin-3 in regulating leukocyte viability and cytokine secretion. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Karakhanova, S.; Werner, J.; Bazhin, A.V. Reactive oxygen species in cancer biology and anticancer therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 3677–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Cummings, R.D. Galectin-1, a beta-galactoside-binding lectin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. II. Localization and biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5207–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajka-Boja, R.; Blasko, A.; Kovacs-Solyom, F.; Szebeni, G.J.; Toth, G.K.; Monostori, E. Co-localization of galectin-1 with GM1 ganglioside in the course of its clathrin- and raft-dependent endocytosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, H.F.; Pace, K.E.; Cabrera, P.V.; White, R.; Porvari, K.; Kaija, H.; Vihko, P.; Baum, L.G. O-glycosylation regulates LNCaP prostate cancer cell susceptibility to apoptosis induced by galectin-1. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6155–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs-Solyom, F.; Blasko, A.; Fajka-Boja, R.; Katona, R.L.; Vegh, L.; Novak, J.; Szebeni, G.J.; Krenacs, L.; Uher, F.; Tubak, V.; et al. Mechanism of tumor cell-induced T-cell apoptosis mediated by galectin-1. Immunol. Lett. 2010, 127, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasko, A.; Fajka-Boja, R.; Ion, G.; Monostori, E. How does it act when soluble? Critical evaluation of mechanism of galectin-1 induced T-cell apoptosis. Acta Biol. Hung. 2011, 62, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchel, G.; Schulte, J.H.; Harrison, L.; Batzke, K.; Schuller, U.; Hansen, W.; Schramm, A. Immune response modulation by Galectin-1 in a transgenic model of neuroblastoma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 5, e1131378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, V.L.; Postel, R.; Brandwijk, R.J.; Dings, R.P.; Nesmelova, I.; Satijn, S.; Verhofstad, N.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Baum, L.G.; Bakkers, J.; et al. Galectin-1 is essential in tumor angiogenesis and is a target for antiangiogenesis therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15975–15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laderach, D.J.; Gentilini, L.D.; Giribaldi, L.; Delgado, V.C.; Nugnes, L.; Croci, D.O.; Al Nakouzi, N.; Sacca, P.; Casas, G.; Mazza, O.; et al. A Unique Galectin Signature in Human Prostate Cancer Progression Suggests Galectin-1 as a Key Target for Treatment of Advanced Disease. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saussez, S.; Decaestecker, C.; Cludts, S.; Ernoux, P.; Chevalier, D.; Smetana, K., Jr.; Andre, S.; Leroy, X.; Gabius, H.J. Adhesion/growth-regulatory tissue lectin galectin-1 in relation to angiogenesis/lymphocyte infiltration and prognostic relevance of stromal up-regulation in laryngeal carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clausse, N.; van den Brule, F.; Waltregny, D.; Garnier, F.; Castronovo, V. Galectin-1 expression in prostate tumor-associated capillary endothelial cells is increased by prostate carcinoma cells and modulates heterotypic cell-cell adhesion. Angiogenesis 1999, 3, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranjol, M.Z.I.; Zinovkin, D.A.; Maskell, A.R.T.; Stephens, L.J.; Achinovich, S.L.; Los, D.M.; Nadyrov, E.A.; Hannemann, M.; Gutowski, N.J.; Whatmore, J.L. Cathepsin L-induced galectin-1 may act as a proangiogenic factor in the metastasis of high-grade serous carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Gonzalez, R.; Cibrian, D.; Fernandez-Gallego, N.; Ramirez-Huesca, M.; Saiz, M.L.; Navarro, M.N.; Fresno, M.; de la Fuente, H.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Galectin-1 Expression in CD8(+) T Lymphocytes Controls Inflammation in Contact Hypersensitivity. J. Investig. Derm. 2020, 141, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, M.; Hornung, A.; Novak, J.; Demydenko, D.; Szabo, E.; Czibula, A.; Fajka-Boja, R.; Kriston-Pal, E.; Monostori, E.; Kovacs, L. Novel role for galectin-1 in T-cells under physiological and pathological conditions. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatar, D.; Olkhanud, P.B.; Wells, V.; Indig, F.E.; Mallucci, L.; Biragyn, A. Tregs utilize beta-galactoside-binding protein to transiently inhibit PI3K/p21ras activity of human CD8+ T cells to block their TCR-mediated ERK activity and proliferation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Ryu, D.B.; Park, S.S.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, B.S.; Min, C.K. Myeloma-secreted galectin-1 potently interacts with CD304 on monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, C.M.; Hamon, Y.; Gonnord, P.; Boularan, C.; Kagan, J.; Viaris de Lesegno, C.; Ruez, R.; Mailfert, S.; Bertaux, N.; Loew, D.; et al. Glycosylation-Dependent IFN-gammaR Partitioning in Lipid and Actin Nanodomains Is Critical for JAK Activation. Cell 2016, 166, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demotte, N.; Wieers, G.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Moser, M.; Schmidt, C.; Thielemans, K.; Squifflet, J.L.; Weynand, B.; Carrasco, J.; Lurquin, C.; et al. A galectin-3 ligand corrects the impaired function of human CD4 and CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and favors tumor rejection in mice. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7476–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.R.; Turnis, M.E.; Goldberg, M.V.; Bankoti, J.; Selby, M.; Nirschl, C.J.; Bettini, M.L.; Gravano, D.M.; Vogel, P.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubieta, M.R.; Furman, D.; Barrio, M.; Bravo, A.I.; Domenichini, E.; Mordoh, J. Galectin-3 expression correlates with apoptosis of tumor-associated lymphocytes in human melanoma biopsies. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilson, R.C.; Gunasinghe, S.D.; Johannes, L.; Gaus, K. Galectin-3 modulation of T-cell activation: Mechanisms of membrane remodelling. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2019, 76, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Kidoya, H.; Yamakawa, D.; Naito, H.; Takakura, N. Galectin-3 accelerates M2 macrophage infiltration and angiogenesis in tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, M.; Biron-Pain, K.; Hebert, J.; Lamarre, A.; Magnaldo, T.; St-Pierre, Y. Galectin-7 in lymphoma: Elevated expression in human lymphoid malignancies and decreased lymphoma dissemination by antisense strategies in experimental model. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ding, M.; Yu, M.L.; Feng, M.X.; Tan, L.J.; Zhao, F.K. Identification of galectin-7 as a potential biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by proteomic analysis. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cada, Z.; Chovanec, M.; Smetana, K.; Betka, J.; Lacina, L.; Plzak, J.; Kodet, R.; Stork, J.; Lensch, M.; Kaltner, H.; et al. Galectin-7: Will the lectin’s activity establish clinical correlations in head and neck squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas? Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, M.; Rose, A.A.; Grosset, A.A.; Biron-Pain, K.; Gaboury, L.; Siegel, P.M.; St-Pierre, Y. Overexpression of galectin-7, a myoepithelial cell marker, enhances spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebo, A.; Ditsch, N.; Kuhn, C.; Heidegger, H.H.; Zeder-Goess, C.; Kolben, T.; Czogalla, B.; Schmoeckel, E.; Mahner, S.; Jeschke, U.; et al. High Galectin-7 and Low Galectin-8 Expression and the Combination of both are Negative Prognosticators for Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Schmoeckel, E.; Kuhn, C.; Hofmann, S.; Mayr, D.; Mahner, S.; Jeschke, U. Galectins-1, -3, and -7 Are Prognostic Markers for Survival of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeon, H.K.; Lee, J.K.; Sung, C.O.; Do, I.G.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, B.G.; Bae, D.S.; Lee, J.W. Clinical significance of galectin-7 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Pergialiotis, V.; Papoutsi, E.; Androutsou, A.; Tzortzis, A.S.; Frountzas, M.; Papapanagiotou, A.; Kontzoglou, K. Galectins-1, -3, -7, -8 and -9 as prognostic markers for survival in epithelial ovarian cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obs. 2021, 152, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higareda-Almaraz, J.C.; Ruiz-Moreno, J.S.; Klimentova, J.; Barbieri, D.; Salvador-Gallego, R.; Ly, R.; Valtierra-Gutierrez, I.A.; Dinsart, C.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Stulik, J.; et al. Systems-level effects of ectopic galectin-7 reconstitution in cervical cancer and its microenvironment. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibens-Laulan, N.; St-Pierre, Y. Intracellular galectin-7 expression in cancer cells results from an autocrine transcriptional mechanism and endocytosis of extracellular galectin-7. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrie, M.; Vladoiu, M.C.; Grosset, A.A.; Gaboury, L.; St-Pierre, Y. Expression and functions of galectin-7 in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7705–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hiromasa, K.; Kabashima-Kubo, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Nakamura, M. Galectin-7, induced by cis-urocanic acid and ultraviolet B irradiation, down-modulates cytokine production by T lymphocytes. Exp. Derm. 2013, 22, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilini, L.D.; Jaworski, F.M.; Tiraboschi, C.; Perez, I.G.; Kotler, M.L.; Chauchereau, A.; Laderach, D.J.; Compagno, D. Stable and high expression of Galectin-8 tightly controls metastatic progression of prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44654–44668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinohl, C.; Barnard, S.J.; Fritz-Wolf, K.; Unger, M.; Porr, A.; Heipel, M.; Wirth, S.; Madlung, J.; Nordheim, A.; Menke, A.; et al. Galectin-8 binds to the Farnesylated C-terminus of K-Ras4B and Modifies Ras/ERK Signaling and Migration in Pancreatic and Lung Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferragut, F.; Cagnoni, A.J.; Colombo, L.L.; Sanchez Terrero, C.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Troncoso, M.F.; Vanzulli, S.I.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Marino, K.V.; Elola, M.T. Dual knockdown of Galectin-8 and its glycosylated ligand, the activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM/CD166), synergistically delays in vivo breast cancer growth. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2019, 1866, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatz-Azoulay, H.; Vinik, Y.; Isaac, R.; Kohler, U.; Lev, S.; Zick, Y. The Animal Lectin Galectin-8 Promotes Cytokine Expression and Metastatic Tumor Growth in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena, A.; Metz, C.; Vicuna, L.; Silva, A.; Pardo, E.; Oyanadel, C.; Massardo, L.; Gonzalez, A.; Soza, A. Galectin-8 induces apoptosis in Jurkat T cells by phosphatidic acid-mediated ERK1/2 activation supported by protein kinase A down-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12670–12679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, V.; Tribulatti, M.V.; Campetella, O. Galectin-8 tandem-repeat structure is essential for T-cell proliferation but not for co-stimulation. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Jing, D.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Zhao, J.; Yao, Z.; Lin, H. Galectin-9 Expression Predicts Favorable Clinical Outcome in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Kontani, K.; Kihara, M.; Liu, D.; Shirato, Y.; Seki, M.; Nishi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Yokomise, H.; et al. Galectin-9 as a prognostic factor with antimetastatic potential in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2962–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, A.; Kontani, K.; Kihara, M.; Nishi, N.; Yokomise, H.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9, a novel prognostic factor with antimetastatic potential in breast cancer. Breast J. 2006, 12, S196–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Iwama, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Okura, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Takano, J.; Katsura, A.; Tatsuta, M.; Maeda, E.; Mimura, S.; et al. Galectin-9 suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma via apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mingo Pulido, A.; Gardner, A.; Hiebler, S.; Soliman, H.; Rugo, H.S.; Krummel, M.F.; Coussens, L.M.; Ruffell, B. TIM-3 Regulates CD103(+) Dendritic Cell Function and Response to Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018, 33, 60–74.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headley, M.B.; Bins, A.; Nip, A.; Roberts, E.W.; Looney, M.R.; Gerard, A.; Krummel, M.F. Visualization of immediate immune responses to pioneer metastatic cells in the lung. Nature 2016, 531, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.W.; Broz, M.L.; Binnewies, M.; Headley, M.B.; Nelson, A.E.; Wolf, D.M.; Kaisho, T.; Bogunovic, D.; Bhardwaj, N.; Krummel, M.F. Critical Role for CD103(+)/CD141(+) Dendritic Cells Bearing CCR7 for Tumor Antigen Trafficking and Priming of T Cell Immunity in Melanoma. Cancer Cell. 2016, 30, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, H.; Idoyaga, J.; Rahman, A.; Leboeuf, M.; Remark, R.; Jordan, S.; Casanova-Acebes, M.; Khudoynazarova, M.; Agudo, J.; Tung, N.; et al. Expansion and Activation of CD103(+) Dendritic Cell Progenitors at the Tumor Site Enhances Tumor Responses to Therapeutic PD-L1 and BRAF Inhibition. Immunity 2016, 44, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, M.L.; Binnewies, M.; Boldajipour, B.; Nelson, A.E.; Pollack, J.L.; Erle, D.J.; Barczak, A.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Daud, A.; Barber, D.L.; et al. Dissecting the tumor myeloid compartment reveals rare activating antigen-presenting cells critical for T cell immunity. Cancer Cell. 2014, 26, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, D.; Mani, V.R.; Mohan, N.; Akkad, N.; Ochi, A.; Heindel, D.W.; Lee, K.B.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Pandian, G.S.B.; Savadkar, S.; et al. Dectin 1 activation on macrophages by galectin 9 promotes pancreatic carcinoma and peritumoral immune tolerance. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrizak, D.; Martin, N.; Barjon, C.; Jimenez-Pailhes, A.S.; Mustapha, R.; Niki, T.; Guigay, J.; Pancre, V.; de Launoit, Y.; Busson, P.; et al. Effect of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived exosomes on human regulatory T cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Liang, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, L. Tim-3 expression defines regulatory T cells in human tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuishi, K.; Ngiow, S.F.; Sullivan, J.M.; Teng, M.W.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Anderson, A.C. TIM3(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells are tissue-specific promoters of T-cell dysfunction in cancer. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e23849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages expressing galectin-9 identify immunoevasive subtype muscle-invasive bladder cancer with poor prognosis but favorable adjuvant chemotherapeutic response. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Munger, M.E.; Veenstra, R.G.; Weigel, B.J.; Hirashima, M.; Munn, D.H.; Murphy, W.J.; Azuma, M.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Coexpression of Tim-3 and PD-1 identifies a CD8+ T-cell exhaustion phenotype in mice with disseminated acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 4501–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, R.; Wang, P. TIM-3 plays a more important role than PD-1 in the functional impairments of cytotoxic T cells of malignant Schwannomas. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317698352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, K.L.; Haaland, M.S.; Douglas-Vail, M.B.; Mujib, S.; Chew, G.M.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Ostrowski, M.A. T cell Ig and mucin domain-containing protein 3 is recruited to the immune synapse, disrupts stable synapse formation, and associates with receptor phosphatases. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuishi, K.; Apetoh, L.; Sullivan, J.M.; Blazar, B.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommen, D.S.; Koelzer, V.H.; Herzig, P.; Roller, A.; Trefny, M.; Dimeloe, S.; Kiialainen, A.; Hanhart, J.; Schill, C.; Hess, C.; et al. A transcriptionally and functionally distinct PD-1(+) CD8(+) T cell pool with predictive potential in non-small-cell lung cancer treated with PD-1 blockade. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; van der Leun, A.M.; Yofe, I.; Lubling, Y.; Gelbard-Solodkin, D.; van Akkooi, A.C.J.; van den Braber, M.; Rozeman, E.A.; Haanen, J.; Blank, C.U.; et al. Dysfunctional CD8 T Cells Form a Proliferative, Dynamically Regulated Compartment within Human Melanoma. Cell 2019, 176, 775–789.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; van der Burg, S.H.; Melief, C.J.M.; Bhardwaj, N. Therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 125, 3401–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.A.; Glisson, B.S. New Hope for Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Modulation. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Blanc, C.; Granier, C.; Saldmann, A.; Tanchot, C.; Tartour, E. Therapeutic cancer vaccine: Building the future from lessons of the past. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyrek, K.; Richter, M.; Lavrik, I.N. Decoding the sweet regulation of apoptosis: The role of glycosylation and galectins in apoptotic signaling pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Hu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Cai, J. Inhibition of galectin-3 augments the antitumor efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in non-small-cell lung cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dings, R.P.; Williams, B.W.; Song, C.W.; Griffioen, A.W.; Mayo, K.H.; Griffin, R.J. Anginex synergizes with radiation therapy to inhibit tumor growth by radiosensitizing endothelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 115, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, P.; Martinez-Bosch, N.; Blidner, A.G.; Rabinovich, G.A. Impact of Galectins in Resistance to Anticancer Therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6086–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorgues-Xerri, L.; Riveiro, M.E.; Tijeras-Raballand, A.; Serova, M.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Bieche, I.; Vidaud, M.; de Gramont, A.; Martinet, M.; Cvitkovic, E.; et al. OTX008, a selective small-molecule inhibitor of galectin-1, downregulates cancer cell proliferation, invasion and tumour angiogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2463–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumori, T.; Oka, N.; Takenaka, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Elsamman, E.; Kasai, T.; Shono, M.; Kanayama, H.O.; Ellerhorst, J.; Lotan, R.; et al. Galectin-3 regulates mitochondrial stability and antiapoptotic function in response to anticancer drug in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3114–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mercier, M.; Lefranc, F.; Mijatovic, T.; Debeir, O.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Bontempi, G.; Decaestecker, C.; Kiss, R.; Mathieu, V. Evidence of galectin-1 involvement in glioma chemoresistance. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2008, 229, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Messaoudi, K.; Lemaire, L.; Benoit, J.P.; Lagarce, F. Combined anti-Galectin-1 and anti-EGFR siRNA-loaded chitosan-lipid nanocapsules decrease temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma: In vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 481, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, W. Knockdown of galectin-1 facilitated cisplatin sensitivity by inhibiting autophagy in neuroblastoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 297, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.I.; Whang, E.E.; Donner, D.B.; Jiang, X.; Price, B.D.; Carothers, A.M.; Delaine, T.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Nose, V.; et al. Galectin-3 targeted therapy with a small molecule inhibitor activates apoptosis and enhances both chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity in papillary thyroid cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harazono, Y.; Kho, D.H.; Balan, V.; Nakajima, K.; Hogan, V.; Raz, A. Extracellular galectin-3 programs multidrug resistance through Na+/K+-ATPase and P-glycoprotein signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19592–19604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Shao, Y.Y.; Ho, W.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Feng, W.C.; Chow, L.P. Integrated Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino Acids in Cell Culture (SILAC) and Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation (iTRAQ) Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Identifies Galectin-1 as a Potential Biomarker for Predicting Sorafenib Resistance in Liver Cancer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1527–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Li, K.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Gao, P.T.; Dong, Z.R.; Cai, J.B.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Tian, M.X.; Hu, Z.Q.; et al. Galectin-1 induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib resistance by activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Reversal of galectin-1 gene silencing on resistance to cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biomed. Pharm. 2016, 83, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.Y.; Tang, S.J.; Sun, G.H.; Chou, T.Y.; Yeh, T.S.; Yu, S.L.; Sun, K.H. Galectin-1 promotes lung cancer progression and chemoresistance by upregulating p38 MAPK, ERK, and cyclooxygenase-2. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Song, L.; Chen, X.L.; Zeng, X.F.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhu, C.R.; Huang, T.; Tan, X.P.; Lin, X.M.; Yang, Q.; et al. Identification of galectin-1 as a novel mediator for chemoresistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26709–26723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Li, G.; Podar, K.; Hideshima, T.; Neri, P.; He, D.; Mitsiades, N.; Richardson, P.; Chang, Y.; Schindler, J.; et al. A novel carbohydrate-based therapeutic GCS-100 overcomes bortezomib resistance and enhances dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8350–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, T.; Itamochi, H.; Kigawa, J.; Kanamori, Y.; Shimada, M.; Takahashi, M.; Shimogai, R.; Kawaguchi, W.; Sato, S.; Terakawa, N. Galectin-3 may contribute to Cisplatin resistance in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2007, 17, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirandola, L.; Yu, Y.; Cannon, M.J.; Jenkins, M.R.; Rahman, R.L.; Nguyen, D.D.; Grizzi, F.; Cobos, E.; Figueroa, J.A.; Chiriva-Internati, M. Galectin-3 inhibition suppresses drug resistance, motility, invasion and angiogenic potential in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; You, D.; Li, L. Galectin-3 regulates chemotherapy sensitivity in epithelial ovarian carcinoma via regulating mitochondrial function. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 44, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, G.; Halvaei, S.; Heidarian, Y.; Dehghani-Ghobadi, Z.; Hassani, M.; Hosseini, H.; Naderi, N.; Sheikh Hassani, S. Pectasol-C Modified Citrus Pectin targets Galectin-3-induced STAT3 activation and synergize paclitaxel cytotoxic effect on ovarian cancer spheroids. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4315–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkham, S.; Junking, M.; Wongkham, C.; Sripa, B.; Chur-In, S.; Araki, N. Suppression of galectin-3 expression enhances apoptosis and chemosensitivity in liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.B.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, C.W.; Hur, D.Y. Silencing of galectin-3 represses osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion through inhibition of FAK/Src/Lyn activation and beta-catenin expression and increases susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Shimura, T.; Yajima, T.; Kubo, N.; Araki, K.; Wada, W.; Tsutsumi, S.; Suzuki, H.; Kuwano, H.; Raz, A. Transient silencing of galectin-3 expression promotes both in vitro and in vivo drug-induced apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, X.; Gong, M.; Guo, G.; Han, K.; An, R. Galectin-3 inhibition sensitizes human renal cell carcinoma cells to arsenic trioxide treatment. Cancer Biol. 2013, 14, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagoshi, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, N.; Shimura, Y.; Horiike, S.; Kimura, S.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M.; et al. Targeting activating transcription factor 3 by Galectin-9 induces apoptosis and overcomes various types of treatment resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, N.; Kenerson, H.L.; Lausted, C.; Yan, X.; Meng, C.; Sullivan, K.M.; Baloni, P.; Bergey, D.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Hood, L.E.; et al. Modulation of Immune Checkpoints by Chemotherapy in Human Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cell. Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabioglu, N.; Onder, S.; Oner, G.; Karatay, H.; Tukenmez, M.; Muslumanoglu, M.; Igci, A.; Eralp, Y.; Aydiner, A.; Saip, P.; et al. TIM3 expression on TILs is associated with poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Zou, W. Galectin-3 induces ovarian cancer cell survival and chemoresistance via TLR4 signaling activation. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11883–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.G.; Alvero, A.B.; Chen, R.; Silasi, D.A.; Abrahams, V.M.; Chan, S.; Visintin, I.; Rutherford, T.; Mor, G. TLR-4 signaling promotes tumor growth and paclitaxel chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, M.; Jyoti, A.; Johnson, S.E.; Swindell, E.P.; Napier, D.; Sethi, P.; Chan, R.; Feddock, J.M.; Weiss, H.L.; O’Halloran, T.V.; et al. Radiation-enhanced therapeutic targeting of galectin-1 enriched malignant stroma in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41559–41574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.; Le, Q.T. Galectin-1 links tumor hypoxia and radiotherapy. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Lu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Bao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, B.; Wang, F.; et al. Noninvasive small-animal imaging of galectin-1 upregulation for predicting tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 158, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upreti, M.; Jamshidi-Parsian, A.; Apana, S.; Berridge, M.; Fologea, D.A.; Koonce, N.A.; Henry, R.L.; Griffin, R.J. Radiation-induced galectin-1 by endothelial cells: A promising molecular target for preferential drug delivery to the tumor vasculature. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaib, S.; Messai, Y.; Couve, S.; Escudier, B.; Hasmim, M.; Noman, M.Z. Hypoxia promotes tumor growth in linking angiogenesis to immune escape. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.A.; Kerbel, R.S. Improving immunotherapy outcomes with anti-angiogenic treatments and vice versa. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoud, N.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Kindgard, L.; Garcia, P.A.; Blidner, A.G.; Marino, K.V.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Croci, D.O. Hypoxia Supports Differentiation of Terminally Exhausted CD8 T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.C.; Sen, D.R.; Al Abosy, R.; Bi, K.; Virkud, Y.V.; LaFleur, M.W.; Yates, K.B.; Lako, A.; Felt, K.; Naik, G.S.; et al. Subsets of exhausted CD8(+) T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Normalizing tumor microenvironment to treat cancer: Bench to bedside to biomarkers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonce, N.A.; Griffin, R.J.; Dings, R.P.M. Galectin-1 Inhibitor OTX008 Induces Tumor Vessel Normalization and Tumor Growth Inhibition in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosset, A.A.; Labrie, M.; Vladoiu, M.C.; Yousef, E.M.; Gaboury, L.; St-Pierre, Y. Galectin signatures contribute to the heterogeneity of breast cancer and provide new prognostic information and therapeutic targets. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18183–18203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrie, M.; De Araujo, L.O.F.; Communal, L.; Mes-Masson, A.M.; St-Pierre, Y. Tissue and plasma levels of galectins in patients with high grade serous ovarian carcinoma as new predictive biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.G.; Doody, A.D.; Mihalyo, M.A.; Huang, C.T.; Kelleher, E.; Ravi, S.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Flies, D.B.; Kennedy, E.P.; Long, M.; et al. Androgen ablation mitigates tolerance to a prostate/prostate cancer-restricted antigen. Cancer Cell. 2005, 7, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, A.Z.; Dallos, M.C.; Zahurak, M.L.; Partin, A.W.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Ross, A.E.; Allaf, M.E.; Nirschl, T.R.; Liu, D.; Chapman, C.G.; et al. T-Cell Infiltration and Adaptive Treg Resistance in Response to Androgen Deprivation With or Without Vaccination in Localized Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3182–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallanzani, R.G.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Raffo Iraolagoitia, X.L.; Ziblat, A.; Domaica, C.I.; Avila, D.E.; Rossi, L.E.; Fuertes, M.B.; Battistone, M.A.; Rabinovich, G.A.; et al. Expansion of CD11b(+)Ly6G (+)Ly6C (int) cells driven by medroxyprogesterone acetate in mice bearing breast tumors restrains NK cell effector functions. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, G.R.; Sahores, A.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Perrotta, R.M.; Pataccini, G.; Vanzulli, S.I.; Polo, M.L.; Radisky, D.C.; Sartorius, C.A.; Novaro, V.; et al. Enhanced Antitumor Immunity via Endocrine Therapy Prevents Mammary Tumor Relapse and Increases Immune Checkpoint Blockade Sensitivity. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, S.M.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Tometten, M.; Garcia, M.; Orsal, A.S.; Cordo-Russo, R.; Toscano, M.A.; Bianco, G.A.; Kobelt, P.; Handjiski, B.; et al. A pivotal role for galectin-1 in fetomaternal tolerance. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramhorst, R.E.; Giribaldi, L.; Fraccaroli, L.; Toscano, M.A.; Stupirski, J.C.; Romero, M.D.; Durand, E.S.; Rubinstein, N.; Blaschitz, A.; Sedlmayr, P.; et al. Galectin-1 confers immune privilege to human trophoblast: Implications in recurrent fetal loss. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetti, M.; Bonezzi, K.; Frapolli, R.; Sala, F.; Borsotti, P.; Zangarini, M.; Cvitkovic, E.; Noel, K.; Ubezio, P.; Giavazzi, R.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and antineoplastic activity of galectin-1-targeting OTX008 in combination with sunitinib. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2013, 72, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Z.; Ko, F.C.F.; Tey, S.K.; Kwong, E.M.L.; Mao, X.; Liu, B.H.M.; Ma, A.P.Y.; Fung, Y.M.E.; Che, C.M.; Wong, D.K.H.; et al. Galectin-1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma and the combined therapeutic effect of OTX008 galectin-1 inhibitor and sorafenib in tumor cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, M.; Dzopalic, T.; Marjanovic, G.; Urosevic, I.; Milosevic, I. Immunomodulatory effects of galectin-1 in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cent. Eur J. Immunol. 2021, 46, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limagne, E.; Richard, C.; Thibaudin, M.; Fumet, J.D.; Truntzer, C.; Lagrange, A.; Favier, L.; Coudert, B.; Ghiringhelli, F. Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway and mMDSC control primary and secondary resistances to PD-1 blockade in lung cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1564505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, B.; Luo, Z.; Guo, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. Cocktail strategy for ‘cold’ tumors therapy via active recruitment of CD8+ T cells and enhancing their function. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.; Kouverianou, E.; Rooney, C.M.; McHugh, B.J.; Howie, S.E.M.; Gregory, C.D.; Forbes, S.J.; Henderson, N.C.; Zetterberg, F.R.; Nilsson, U.J.; et al. An Orally Active Galectin-3 Antagonist Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth and Augments Response to PD-L1 Blockade. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curti, B.D.; Koguchi, Y.; Leidner, R.S.; Rolig, A.S.; Sturgill, E.R.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Rajamanickam, V.; Bernard, B.; Hilgart-Martiszus, I.; et al. Enhancing clinical and immunological effects of anti-PD-1 with belapectin, a galectin-3 inhibitor. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capalbo, C.; Scafetta, G.; Filetti, M.; Marchetti, P.; Bartolazzi, A. Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Immunotherapy: The Galectin-3 Signature in NSCLCs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Connolly, E.M.; Liao, X.; Ouyang, J.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Lawrence, D.; McDermott, D.; Murphy, G.; Zhou, J.; et al. Combined Anti-VEGF and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapy Elicits Humoral Immunity to Galectin-1 Which Is Associated with Favorable Clinical Outcomes. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanami, T.; Hoshino, I.; Shiratori, F.; Yajima, S.; Oshima, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, M.; Hiwasa, T.; Kuwajima, A.; Shimada, H. Prevalence of serum galectin-1 autoantibodies in seven types of cancer: A potential biomarker. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Connolly, E.M.; Li, J.; Liao, X.; Severgnini, M.; Zhou, J.; Rodig, S.; Hodi, F.S. Anti-CTLA-4 based therapy elicits humoral immunity to galectin-3 in patients with metastatic melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1440930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladoiu, M.C.; Labrie, M.; Letourneau, M.; Egesborg, P.; Gagne, D.; Billard, E.; Grosset, A.A.; Doucet, N.; Chatenet, D.; St-Pierre, Y. Design of a peptidic inhibitor that targets the dimer interface of a prototypic galectin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40970–40980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurisci, I.; Cumashi, A.; Sherman, A.A.; Tsvetkov, Y.E.; Tinari, N.; Piccolo, E.; D’Egidio, M.; Adamo, V.; Natoli, C.; Rabinovich, G.A.; et al. Synthetic inhibitors of galectin-1 and -3 selectively modulate homotypic cell aggregation and tumor cell apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, H.; Yu, X.; Collins, P.M.; Bum-Erdene, K. Galectin-3 inhibitors: A patent review (2008-present). Expert Opin. Pat. 2014, 24, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Sanz, R.; Garcia-Fuentes, L.; Vargas-Berenguel, A. Human galectin-3 selective and high affinity inhibitors. Present state and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnoni, A.J.; Perez Saez, J.M.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Marino, K.V. Turning-Off Signaling by Siglecs, Selectins, and Galectins: Chemical Inhibition of Glycan-Dependent Interactions in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.N. Galectinomics: Finding themes in complexity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barondes, S.H.; Castronovo, V.; Cooper, D.N.; Cummings, R.D.; Drickamer, K.; Feizi, T.; Gitt, M.A.; Hirabayashi, J.; Hughes, C.; Kasai, K.; et al. Galectins: A family of animal beta-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell 1994, 76, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inohara, H.; Raz, A. Effects of natural complex carbohydrate (citrus pectin) on murine melanoma cell properties related to galectin-3 functions. Glycoconj J. 1994, 11, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnoni, A.J.; Kovensky, J.; Uhrig, M.L. Design and synthesis of hydrolytically stable multivalent ligands bearing thiodigalactoside analogues for peanut lectin and human galectin-3 binding. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocibalova, Z.; Guzyova, M.; Borovska, I.; Messingerova, L.; Copakova, L.; Sulova, Z.; Breier, A. Development of Multidrug Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Is Associated with Alterations of the LPHN1/GAL-9/TIM-3 Signaling Pathway. Cancers 2021, 13, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Scott, S.A.; Cutler, S.; Dong, L.F.; Neuzil, J.; Blanchard, H.; Ralph, S.J. Thiodigalactoside inhibits murine cancers by concurrently blocking effects of galectin-1 on immune dysregulation, angiogenesis and protection against oxidative stress. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Ralph, S.J. Inhibiting galectin-1 reduces murine lung metastasis with increased CD4(+) and CD8 (+) T cells and reduced cancer cell adherence. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Suzuki, M.; Andoh, S.; Monzen, H.; Terai, K.; Williams, B.; Song, C.W.; Mayo, K.H.; Hasegawa, T.; Dings, R.P.; et al. Antiangiogenesis therapy using a novel angiogenesis inhibitor, anginex, following radiation causes tumor growth delay. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 12, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dings, R.P.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Griffioen, A.W.; Mayo, K.H. The designed angiostatic peptide anginex synergistically improves chemotherapy and antiangiogenesis therapy with angiostatin. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo, K.H.; Dings, R.P.; Flader, C.; Nesmelova, I.; Hargittai, B.; van der Schaft, D.W.; van Eijk, L.I.; Walek, D.; Haseman, J.; Hoye, T.R.; et al. Design of a partial peptide mimetic of anginex with antiangiogenic and anticancer activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45746–45752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dings, R.P.; Kumar, N.; Miller, M.C.; Loren, M.; Rangwala, H.; Hoye, T.R.; Mayo, K.H. Structure-based optimization of angiostatic agent 6DBF7, an allosteric antagonist of galectin-1. J. Pharm. Exp. 2013, 344, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dings, R.P.; Van Laar, E.S.; Webber, J.; Zhang, Y.; Griffin, R.J.; Waters, S.J.; MacDonald, J.R.; Mayo, K.H. Ovarian tumor growth regression using a combination of vascular targeting agents anginex or topomimetic 0118 and the chemotherapeutic irofulven. Cancer Lett. 2008, 265, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.V.; Wurtzel, J.G.; Goldfinger, L.E. Inhibition of Galectin-1 Sensitizes HRAS-driven Tumor Growth to Rapamycin Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5053–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Juszczynski, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Green, M.R.; O’Donnell, E.; Currie, T.; Armant, M.; Takeyama, K.; Monti, S.; Rabinovich, G.A.; et al. Viral induction and targeted inhibition of galectin-1 in EBV+ posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2011, 117, 4315–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Saez, J.M.; Hockl, P.F.; Cagnoni, A.J.; Mendez Huergo, S.P.; Garcia, P.A.; Gatto, S.G.; Cerliani, J.P.; Croci, D.O.; Rabinovich, G.A. Characterization of a neutralizing anti-human galectin-1 monoclonal antibody with angioregulatory and immunomodulatory activities. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demotte, N.; Bigirimana, R.; Wieers, G.; Stroobant, V.; Squifflet, J.L.; Carrasco, J.; Thielemans, K.; Baurain, J.F.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Courtoy, P.J.; et al. A short treatment with galactomannan GM-CT-01 corrects the functions of freshly isolated human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgill, E.R.; Rolig, A.S.; Linch, S.N.; Mick, C.; Kasiewicz, M.J.; Sun, Z.; Traber, P.G.; Shlevin, H.; Redmond, W.L. Galectin-3 inhibition with belapectin combined with anti-OX40 therapy reprograms the tumor microenvironment to favor anti-tumor immunity. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1892265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton-Northup, J.R.; Dickerson, M.T.; Ma, L.; Besch-Williford, C.L.; Deutscher, S.L. Inhibition of metastatic tumor formation in vivo by a bacteriophage display-derived galectin-3 targeting peptide. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; He, S.; Fan, T.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Huang, Y. Treatment of prostate carcinoma with (galectin-3)-targeted HPMA copolymer-(G3-C12)-5-Fluorouracil conjugates. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2260–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y. Targeting prostate carcinoma by G3-C12 peptide conjugated N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y. Polymeric nanomedicine for tumor-targeted combination therapy to elicit synergistic genotoxicity against prostate cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6661–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, L.; Yang, Q.; Shan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. G3-C12 Peptide Reverses Galectin-3 from Foe to Friend for Active Targeting Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4124–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, D.; Raz, A. Modulation of the lung colonization of B16-F1 melanoma cells by citrus pectin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienta, K.J.; Naik, H.; Akhtar, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Replogle, T.S.; Lehr, J.; Donat, T.L.; Tait, L.; Hogan, V.; Raz, A. Inhibition of spontaneous metastasis in a rat prostate cancer model by oral administration of modified citrus pectin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, A.; Gillen, A.C.; Lott, J.R. Effects of daily oral administration of quercetin chalcone and modified citrus pectin on implanted colon-25 tumor growth in Balb-c mice. Altern. Med. Rev. 2000, 5, 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Nangia-Makker, P.; Hogan, V.; Honjo, Y.; Baccarini, S.; Tait, L.; Bresalier, R.; Raz, A. Inhibition of human cancer cell growth and metastasis in nude mice by oral intake of modified citrus pectin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Huang, Z.L.; Yang, G.H.; Lu, W.Q.; Yu, N.R. Inhibitory effect of modified citrus pectin on liver metastases in a mouse colon cancer model. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 7386–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, C.; Wilk, B.J.; Hotchkiss, A.; Chau, H.; Eliaz, I.; Melnick, S.J. Activation of human T-helper/inducer cell, T-cytotoxic cell, B-cell, and natural killer (NK)-cells and induction of natural killer cell activity against K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells with modified citrus pectin. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Katz, A. PectaSol-C modified citrus pectin induces apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in human and mouse androgen-dependent and- independent prostate cancer cells. Integr. Cancer 2010, 9, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranian, N.; Sepehri, H.; Mehdipour, P.; Biramijamal, F.; Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Sarrafnejad, A.; Hajizadeh, E. Combination effect of PectaSol and Doxorubicin on viability, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in DU-145 and LNCaP prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streetly, M.J.; Maharaj, L.; Joel, S.; Schey, S.A.; Gribben, J.G.; Cotter, F.E. GCS-100, a novel galectin-3 antagonist, modulates MCL-1, NOXA, and cell cycle to induce myeloma cell death. Blood 2010, 115, 3939–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Balan, V.; Hogan, V.; Raz, A. Calpain activation through galectin-3 inhibition sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.C.; Pang, M.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T.; de Vos, S.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Said, J.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-3 binds to CD45 on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to regulate susceptibility to cell death. Blood 2012, 120, 4635–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvolo, P.P.; Ruvolo, V.R.; Benton, C.B.; AlRawi, A.; Burks, J.K.; Schober, W.; Rolke, J.; Tidmarsh, G.; Hail, N., Jr.; Davis, R.E.; et al. Combination of galectin inhibitor GCS-100 and BH3 mimetics eliminates both p53 wild type and p53 null AML cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
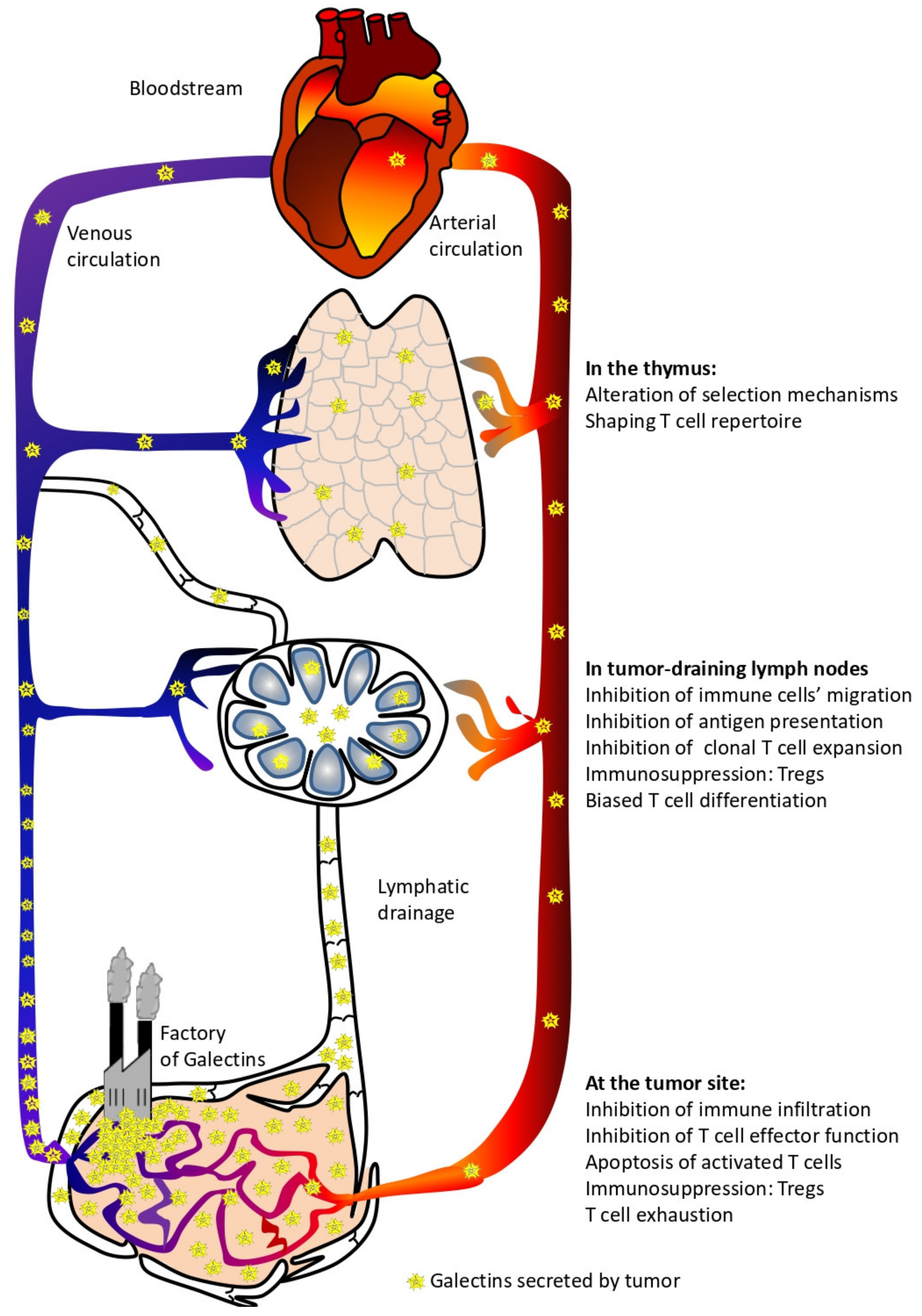
| Member | Recognition Motif | Interactors | Described Biological Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galectin-1 | Carbohydrate-dependent Long poly-N-acetyllactosamine chains with a terminal β-galactose residue Carbohydrate-independent | Proteins of the extracellular matrix: Laminin, fibronectin, collagen, vitronectin, thrombospondin, osteopontin Membrane receptors: Neuropilin-1, VEGF-R2, integrins α1β1 and αMβ2, actin, CD43, CD3,CD4, CD2, CD7, and CD45 Protocadherin-24 GM1 H-RAS Gemin-4, Transcription Factor II-I (TFII-I), snRNP | Involved in ligand crosslinking and the formation of cell surface lattices Induction and maintenance of multiple signaling pathways Modulation of cell adhesion and migration Modulation of vascular function and immune cell migration Modulation of T cell activation, survival and acquisition of effector functions Regulation Wnt signaling Modulation of Treg function Enhance signaling through GTP-H-RAS nanoscale signaling hubs Nuclear splicing of pre-mRNA and control of gene expression | [43,44] [45,46,47] [48,49,50] [51,52,53,54] [55,56,57,58,59,60] [61] [62,63] [64,65] [66,67,68,69,70] |
| Galectin-3 | Carbohydrate-dependent Repeating [-3Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ1-]n or poly-N-acetyllactosamine sequences regardless of the presence of a terminal β-galactose residue Carbohydrate-independent | Proteins of the extracellular matrix: Laminin, vitronectin, collagens I and IV Soluble cytokines Membrane receptors: TCR complex, CD45, CD71, LFA-1, MCAM, TLR-4 LAG-3, VEGF-R2 Nuclear mitotic aparatus (NuMa) K-RAS β-catenin, Protocadherin-24 Endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) or Alix Centrin-2 in basal bodies and centrosomas Synexin, CD95 (APO-1/FAS) Cyclin D1/CDK4 complex, hTERT, ATP synthase Gemin-4, snRNP, transcription factor II-I (TFII-I) | Involved in ligand crosslinking and the formation of cell surface lattices Impact on induction and maintenance of multiple signaling pathways: cell adhesion and migration Reduces cell migration by trapping cytokines Modulation of T cell migration, activation, and functional secretory synapse Cell division Determine membrane nanostructure: impact on signal transduction Wnt signaling TCR downregulation, EGFR trafficking, biogenesis of multivesicular bodies-Exosomes Microtubule organization Apoptosis Cell cycle and senescence Nuclear splicing of pre-mRNA and control of gene expression | [43,44] [50,71,72] [72] [73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] [81] [82] [61,83,84] [85,86,87,88,89] [90] [91,92] [93,94,95] [67,68,69,70,96,97] |
| Galectin-7 | Internal or terminal LacNAc repeats | Tid1 Bcl-2 Smad 3 | Tid1 regulates the nuclear translocation of Galectin-7: role in tumorigenesis and metastasis Sensitize mitochondria to apoptosis signals Decrease expression of TGF-β responsive genes | [98] [99] [100] |
| Galectin-8 | Human blood groups A and B glycans and sialylated lactose or lactosamine | Proteins of the extracellular matrix: Laminin, fibronectin, vitronectin, collagen IV Integrins (α3β1 and α6β1), CD166, podoplanin, CD44 NDP52 | Modulation of cell adhesive and signaling properties Regulation of cell adhesion to endothelium and migration Regulation of apoptosis and inflammation Regulation of bacteria-specific autophagy | [50,101] [102,103,104,105] [106] [107,108] |
| Galectin-9 | Poly N-acetyllactosamine units | TIM-3, PD-1, CD44, VISTA, 4-1BB, CD40, DR3 Cell surface protein disulfide isomerase, β3 integrin IgE Glut-2 NF-IL6 transcription factor | Regulation of T-helper 1 cell immunity and tolerance induction Regulation of the redox environment and T cell migration Anti-allergic effects Determines Glut-2 cell-surface half-life, metabolism regulation Regulation of inflammatory cytokines | [109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117] [118] [119] [120] [121] |
| Member | Inhibitor | Reported Biological Effects | Phase of The Study | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galectin-1 | Thiodigalactoside (TDG) | Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis Reduction of angiogenesis Activation of anti-tumor immunosurveillance | Pre-clinic | [380,381] |
| Anginex (βpep-25) | Inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis and migration Increase sensitivity to radiotherapy, chemotherapy and anti-angiogenesis therapy | Pre-clinic | [20,254,313,341,382,383] | |
| Anginex analogues (6DBF7; DB16; DB21) | Inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis | Pre-clinic | [384,385] | |
| OTX008 | Inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis and migration Synergic effects with chemo- and immunotherapy | Pre-clinic Phase I | [315,359,386,387] NCT01724320 | |
| Galectin-1–specific neutralizing mAb | Inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis | Pre-clinic | [25,52,388,389] | |
| Increased immune infiltration of tumors | ||||
| Galectins-1 and -3 | GM-CT-01 (DAVANAT®) | Inhibition of tumor growth Restoration of anti-tumor immune surveillance | Pre-clinic Phase I and II | [390] NCT00054977, NCT00388700, NCT00386516, NCT01723813 |
| GR-MD-02 (modified version of the DAVANAT®) | Inhibition of tumor growth, improve survival of tumor-bearing mice Restoration of anti-tumor immune surveillance, improve immune checkpoint blockade | Pre-clinic Phase I | [365,391] NCT02117362, NCT02575404 | |
| Galectin-3 | G3–C12 | Inhibition of tumor growth and mestastasis Synergic effects with chemotherapy | Pre-clinic | [392,393,394,395,396] |
| Modified citrus peptin (MCP) | Inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis | Pre-clinic | [397,398,399,400,401,402] | |
| Immune activation | ||||
| Increased sensitivity to chemotherapy | ||||
| PectaSol-C Modified Citrus Peptin | Synergic effects with chemotherapy | Pre-clinic | [331,403,404] | |
| Phase III | NCT01681823 | |||
| GCS-100 | Inhibition of tumor growth | Pre-clinic | [265,327,405,406,407,408] | |
| Correction of impaired anti-tumor immune functions | Phase I | NCT00609817 | ||
| Increased sensitivity to Immuno-chemotherapy | Phase II | NCT00514696, NCT00776802 | ||
| Galectin-7 | Inhibitory peptide | Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis | Pre-clinic | [370] |
| Restoration of anti-tumor immune surveillance, improve immune checkpoint blockade |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laderach, D.J.; Compagno, D. Unraveling How Tumor-Derived Galectins Contribute to Anti-Cancer Immunity Failure. Cancers 2021, 13, 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184529
Laderach DJ, Compagno D. Unraveling How Tumor-Derived Galectins Contribute to Anti-Cancer Immunity Failure. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184529
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaderach, Diego José, and Daniel Compagno. 2021. "Unraveling How Tumor-Derived Galectins Contribute to Anti-Cancer Immunity Failure" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184529
APA StyleLaderach, D. J., & Compagno, D. (2021). Unraveling How Tumor-Derived Galectins Contribute to Anti-Cancer Immunity Failure. Cancers, 13(18), 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184529






