Crosstalk between Environmental Inflammatory Stimuli and Non-Coding RNA in Cancer Occurrence and Development
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
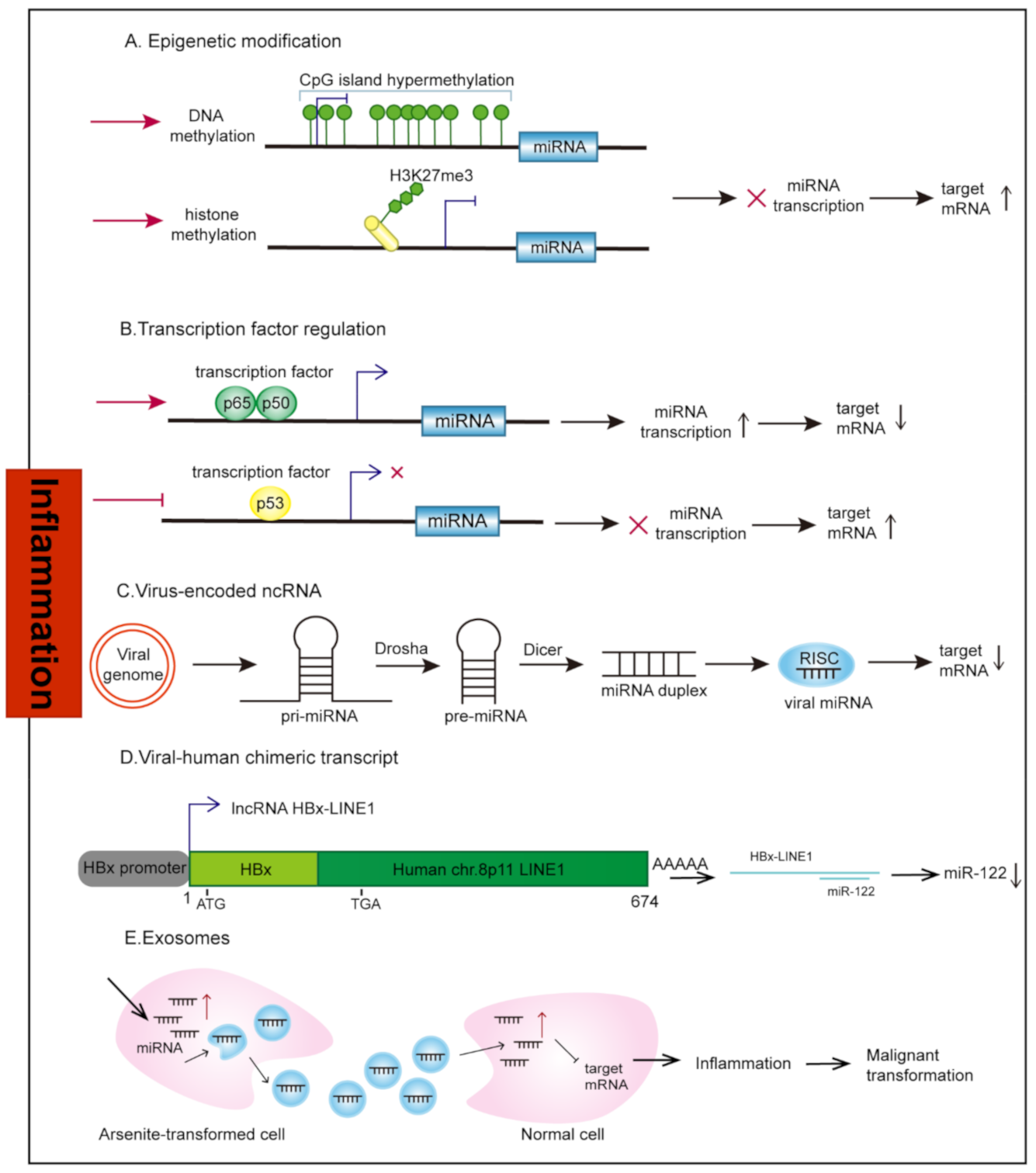
2. Aberrant Regulation of ncRNAs under Inflammation Stimuli
2.1. Transcriptional Regulation
2.1.1. Epigenetic Modification
2.1.2. Transcription Factors
2.2. Virus-Encoded ncRNAs
2.3. Human-Virus Fusion ncRNAs
2.4. Exosomes
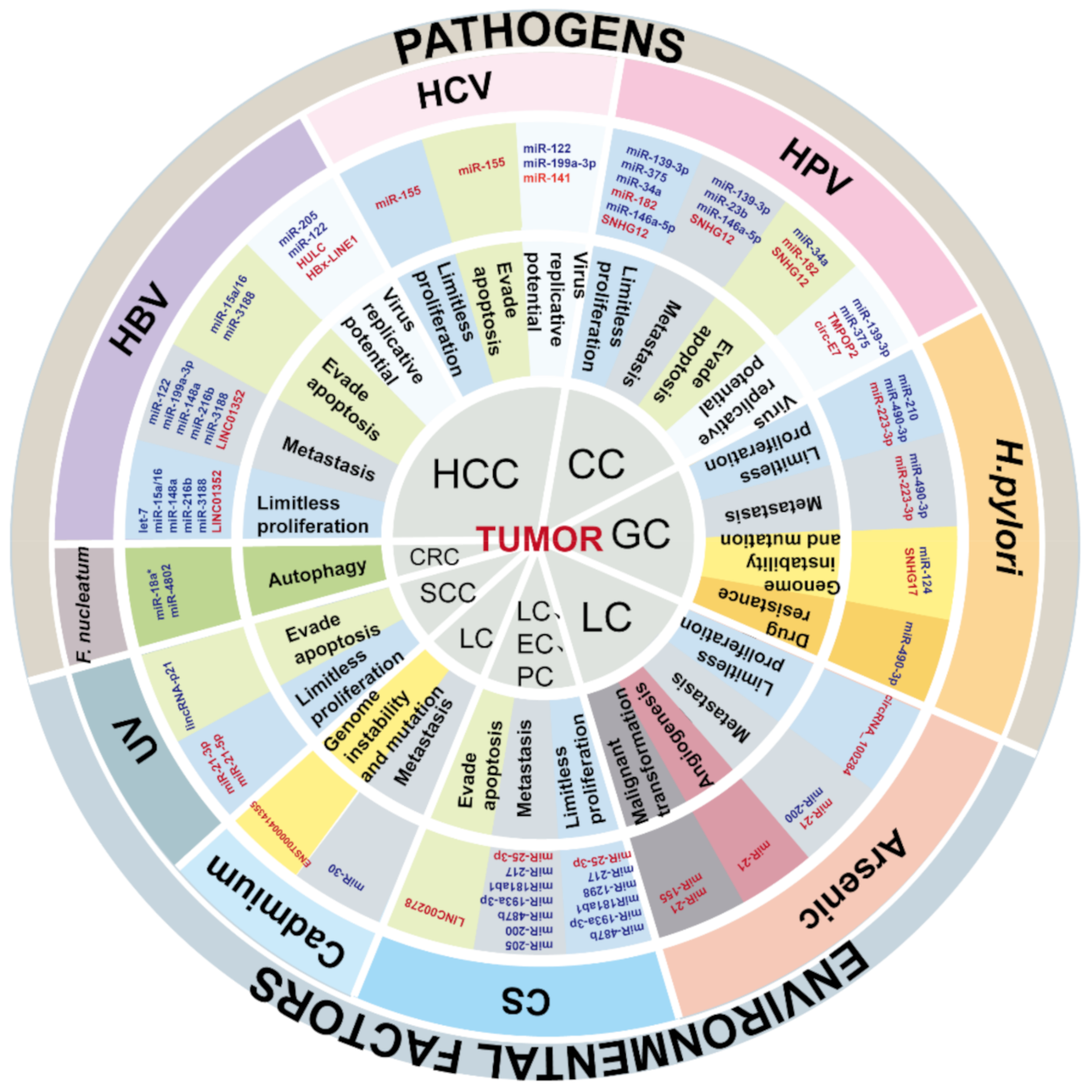
3. Cancers Caused by Pathogens
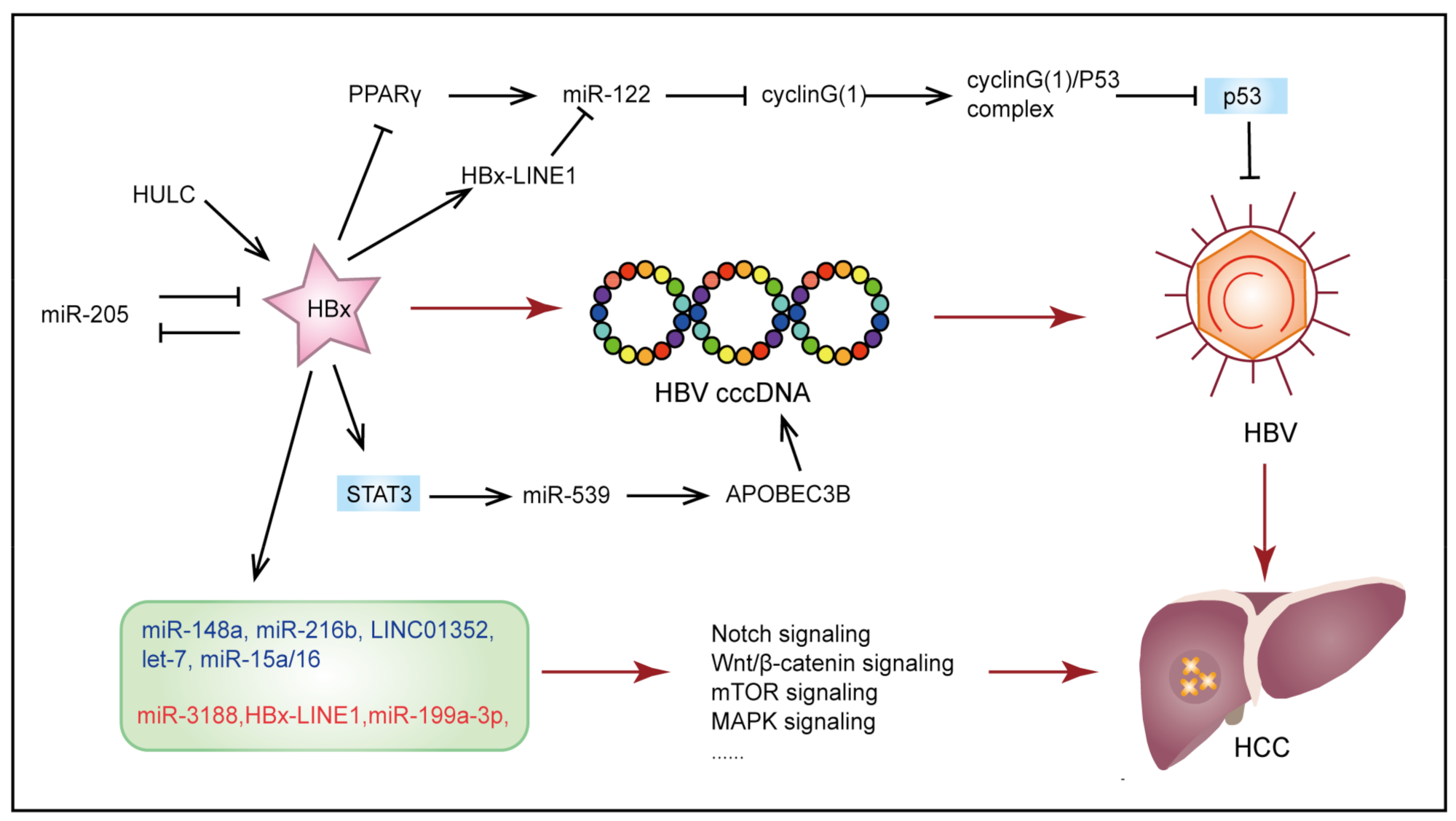
3.1. Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.2. Human Papillomavirus-Induced Cervical Cancer
3.3. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer
3.4. Cancers Associated with Other Pathogens
3.4.1. Intestinal Flora-Induced Colorectal Cancer
3.4.2. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4. Cancers Associated with Environmental Factors
4.1. Inhalation Exposure-Induced Cancer
4.1.1. Cigarette Smoke
4.1.2. Lung Cancer
4.1.3. Esophageal Cancer
4.1.4. Pancreatic Cancer
4.2. Ingestion Exposure-Induced Cancers
4.2.1. Arsenic
4.2.2. Cadmium
4.3. Dermal Contact Exposure-Induced Cancers
Ultraviolet
5. ncRNAs as Therapeutic Targets
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and Cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet Lond. Engl. 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P. Human Gastric Carcinogenesis: A Multistep and Multifactorial Process—First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 6735–6740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terzić, J.; Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Karin, M. Inflammation and Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2101–2114.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, F. Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. Nature 1970, 227, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. Elegans Heterochronic Gene Lin-4 Encodes Small RNAs with Antisense Complementarity to Lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.P.; Fang, G.; Rozowsky, J.; Snyder, M.; Gerstein, M.B. Annotating Non-Coding Regions of the Genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.D.; Parsons, C.; Walker, L.; Zhang, W.C.; Slack, F.J. Targeting Noncoding RNAs in Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique Features of Long Non-Coding RNA Biogenesis and Function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, A.; Colleran, A.; Ryan, A.; Mann, J.; Egan, L.J. Regulation of NF-KappaB Responses by Epigenetic Suppression of IkappaBalpha Expression in HCT116 Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G96–G105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.; Niwa, T.; Toyoda, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Tatematsu, M.; Yang, H.-K.; Ushijima, T. Insufficient Role of Cell Proliferation in Aberrant DNA Methylation Induction and Involvement of Specific Types of Inflammation. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Toyoda, T.; Mori, A.; Tanaka, H.; Maekita, T.; Ichinose, M.; Tatematsu, M.; Ushijima, T. Inflammatory Processes Triggered by Helicobacter Pylori Infection Cause Aberrant DNA Methylation in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, O.G.; Wu, H.; Timp, W.; Doi, A.; Feinberg, A.P. Genome-Scale Epigenetic Reprogramming during Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulakowski, P.; Crowther, A.J.L.; Jiménez, L.A.; Donaldson, K.; Mayer, R.; Leonard, T.B.; MacNee, W.; Drost, E.M. The Effect of Smoking on the Transcriptional Regulation of Lung Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, I.K.; Nevid, M.Z.; Friedman, A.E.; Rahman, I. Cigarette Smoke Induces Distinct Histone Modifications in Lung Cells: Implications for the Pathogenesis of COPD and Lung Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-ΚB and STAT3—Key Players in Liver Inflammation and Cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, D.R.; Hurt, E.M.; Farrar, W.L. The Role of IL-6 and STAT3 in Inflammation and Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.; Hennessy, E.J.; Martin, C.; O’Leary, J.J.; Ruan, Q.; Johnson, D.S.; Chen, Y.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Negative Regulation of TLR4 via Targeting of the Proinflammatory Tumor Suppressor PDCD4 by the MicroRNA MiR-21. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Jaeger, S.A.; Hirsch, H.A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Struhl, K. STAT3 Activation of MiR-21 and MiR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD Are Part of the Epigenetic Switch Linking Inflammation to Cancer. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, C.M.; Roy, S.; Deep, G.; Guillermo-Lagae, R.; Jain, A.K.; Dhar, D.; Orlicky, D.J.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Role of P53 in Silibinin-Mediated Inhibition of Ultraviolet B Radiation-Induced DNA Damage, Inflammation and Skin Carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooks, T.; Harris, C.C.; Oren, M. Caught in the Cross Fire: P53 in Inflammation. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The First 30 Years of P53: Growing Ever More Complex. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. The P53/MiR-34 Axis in Development and Disease. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.; Zavolan, M.; Grässer, F.A.; Chien, M.; Russo, J.J.; Ju, J.; John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Marks, D.; Sander, C.; et al. Identification of Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs. Science 2004, 304, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbach, J.L.; Nagel, M.A.; Cohrs, R.J.; Gilden, D.H.; Cullen, B.R. Analysis of Human Alphaherpesvirus MicroRNA Expression in Latently Infected Human Trigeminal Ganglia. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10677–10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cullen, B.R. Analysis of the Interaction of Primate Retroviruses with the Human RNA Interference Machinery. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12218–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, B.R. Five Questions about Viruses and MicroRNAs. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, S.; Sewer, A.; Lagos-Quintana, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sander, C.; Grässer, F.A.; van Dyk, L.F.; Ho, C.K.; Shuman, S.; Chien, M.; et al. Identification of MicroRNAs of the Herpesvirus Family. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, C.C.; Tarrant-Elorza, M.; Verma, S.; Purushothaman, P.; Pari, G.S. Regulation of Viral and Cellular Gene Expression by Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Polyadenylated Nuclear RNA. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5540–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, P.; Morris, K.V. Long Noncoding RNAs in Viral Infections. Virus Res. 2016, 212, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, B.R. Viruses and MicroRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, S25–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-C.; Sun, T.; Ching, A.K.K.; He, M.; Li, J.-W.; Wong, A.M.; Co, N.N.; Chan, A.W.H.; Li, P.-S.; Lung, R.W.M.; et al. Viral-Human Chimeric Transcript Predisposes Risk to Liver Cancer Development and Progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello-Morales, R.; Praena, B.; de la Nuez, C.; Rejas, M.T.; Guerra, M.; Galán-Ganga, M.; Izquierdo, M.; Calvo, V.; Krummenacher, C.; López-Guerrero, J.A. Role of Microvesicles in the Spread of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 in Oligodendrocytic Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00088-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Exosomes Mediate Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Transmission and NK-Cell Dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from Hepatitis C Infected Patients Transmit HCV Infection and Contain Replication Competent Viral RNA in Complex with Ago2-MiR122-HSP90. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Willemsen, R.; Demmers, J.A.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus between Human Hepatoma Huh7.5 Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13109–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, A.J.; Hoshino, D.; Hong, N.H.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; Weaver, A.M. KRAS-MEK Signaling Controls Ago2 Sorting into Exosomes. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated HnRNPA2B1 Controls the Sorting of MiRNAs into Exosomes through Binding to Specific Motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-Box Protein 1 Is Required to Sort MicroRNAs into Exosomes in Cells and in a Cell-Free Reaction. eLife 2016, 5, e19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, H.; Bording-Jorgensen, M.; Dijk, S.; Wine, E. The Complex Interplay between Chronic Inflammation, the Microbiome, and Cancer: Understanding Disease Progression and What We Can Do to Prevent It. Cancers 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuper, H.; Adami, H.O.; Trichopoulos, D. Infections as a Major Preventable Cause of Human Cancer. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 248, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullman, S.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Sicinska, E.; Clancy, T.E.; Zhang, X.; Cai, D.; Neuberg, D.; Huang, K.; Guevara, F.; Nelson, T.; et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium Persistence and Antibiotic Response in Colorectal Cancer. Science 2017, 358, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A Review of Human Carcinogens--Part B: Biological Agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.B.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.-P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of CccDNA Function in Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollicino, T.; Belloni, L.; Raffa, G.; Pediconi, N.; Squadrito, G.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Hepatitis B Virus Replication Is Regulated by the Acetylation Status of Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA-Bound H3 and H4 Histones. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Is Essential to Initiate and Maintain Virus Replication after Infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Pollicino, T.; De Nicola, F.; Guerrieri, F.; Raffa, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Nuclear HBx Binds the HBV Minichromosome and Modifies the Epigenetic Regulation of CccDNA Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19975–19979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrieri, F.; Belloni, L.; D’Andrea, D.; Pediconi, N.; Le Pera, L.; Testoni, B.; Scisciani, C.; Floriot, O.; Zoulim, F.; Tramontano, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Direct HBx Genomic Targets. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Cui, M.; Liu, F.; You, X.; Du, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Z.; Ye, L.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Inhibits Tumor Suppressor MiR-205 through Inducing Hypermethylation of MiR-205 Promoter to Enhance Carcinogenesis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Yang, G.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Long Non-Coding RNA HULC Activates HBV by Modulating HBx/STAT3/MiR-539/APOBEC3B Signaling in HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Dash, S.; Feitelson, M.; Lim, K.; Wu, T. Epigenetic Regulation of MiR-122 by PPARγ and Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Diao, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus-Human Chimeric Transcript HBx-LINE1 Promotes Hepatic Injury via Sequestering Cellular MicroRNA-122. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yan, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, E.; Ye, X.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, F.; et al. Loss of MicroRNA 122 Expression in Patients with Hepatitis B Enhances Hepatitis B Virus Replication through Cyclin G(1)-Modulated P53 Activity. Hepatology 2012, 55, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.-S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Liao, Z.-B.; Zhang, H.-W.; Liang, H.-F.; Chen, X.-P.; Dong, H.-H. TGF-Β1 Accelerates the Hepatitis B Virus X-Induced Malignant Transformation of Hepatic Progenitor Cells by Upregulating MiR-199a-3p. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1807–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Song, E. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Downregulates Expression of the MiR-16 Family in Malignant Hepatocytes in Vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Toh, S.T.; Sung, W.-K.; Tan, P.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.Y.F.; Jooi, L.L.P.; Lee, C.G.L. Lethal-7 Is down-Regulated by the Hepatitis B Virus x Protein and Targets Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fan, Z.; Kang, L.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, H.; Lin, J.; Jiang, K.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Represses MiRNA-148a to Enhance Tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Zhou, S.-J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, E.-L.; Wu, Z.-B.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Chen, X.-P. MiR-216b Is Involved in Pathogenesis and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through HBx-MiR-216b-IGF2BP2 Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Liang, H.-F.; Jaoude, J.C.; Liu, F.-Y. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes CREB-Mediated Activation of MiR-3188 and Notch Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xu, Q.; Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Ou, B.; Zhang, H.; Mao, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. HBx/ERα Complex-Mediated LINC01352 Downregulation Promotes HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the MiR-135b-APC Axis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3774–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, N.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjosé, S.; Herrero, R.; Castellsagué, X.; Shah, K.V.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical Cancer Study Group. Epidemiologic Classification of Human Papillomavirus Types Associated with Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazibrada, J.; Rittà, M.; Mondini, M.; De Andrea, M.; Azzimonti, B.; Borgogna, C.; Ciotti, M.; Orlando, A.; Surico, N.; Chiusa, L.; et al. Interaction between Inflammation and Angiogenesis during Different Stages of Cervical Carcinogenesis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 108, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, S.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Schulkens, I.A.; Thijssen, V.L.; Osse, E.M.; de Kroon, C.D.; Griffioen, A.W.; Fleuren, G.J.; Gorter, A.; Jordanova, E.S. Correlations between Immune Response and Vascularization QRT-PCR Gene Expression Clusters in Squamous Cervical Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walch-Rückheim, B.; Ströder, R.; Theobald, L.; Pahne-Zeppenfeld, J.; Hegde, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Bohle, R.M.; Juhasz-Böss, I.; Solomayer, E.-F.; Smola, S. Cervical Cancer-Instructed Stromal Fibroblasts Enhance IL23 Expression in Dendritic Cells to Support Expansion of Th17 Cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröer, N.; Pahne, J.; Walch, B.; Wickenhauser, C.; Smola, S. Molecular Pathobiology of Human Cervical High-Grade Lesions: Paracrine STAT3 Activation in Tumor-Instructed Myeloid Cells Drives Local MMP-9 Expression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, D.; de Martel, C.; Lacey, C.J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Bruni, L.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Plummer, M.; et al. Global Burden of Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases. Vaccine 2012, 30 (Suppl. 5), F12–F23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Bossler, F.; Braun, J.A.; Herrmann, A.L.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Munger, K. The Papillomavirus E7 Proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 138–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Pol, S.B.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Papillomavirus E6 Oncoproteins. Virology 2013, 445, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannigrahi, M.K.; Sharma, R.; Singh, V.; Panda, N.K.; Rattan, V.; Khullar, M. Role of Host MiRNA Hsa-MiR-139-3p in HPV-16-Induced Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.M.; Phillips, B.L.; Chan, E.K. MiR-375 Activates P21 and Suppresses Telomerase Activity by Coordinately Regulating HPV E6/E7, E6AP, CIP2A, and 14-3-3ζ. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Vierstra, R.D.; Howley, P.M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP Complex Functions as a Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase in the Ubiquitination of P53. Cell 1993, 75, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lai, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Wang, N.; Luo, X.-G.; et al. Human Papillomavirus E6/E7 and Long Noncoding RNA TMPOP2 Mutually Upregulated Gene Expression in Cervical Cancer Cells. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01808-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Pietilä, T.; Rönty, M.; Michon, F.; Frilander, M.J.; Ritari, J.; Tarkkanen, J.; Paulín, L.; Auvinen, P.; Auvinen, E. Identification and Validation of Human Papillomavirus Encoded MicroRNAs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lee, E.E.; Kim, J.; Yang, R.; Chamseddin, B.; Ni, C.; Gusho, E.; Xie, Y.; Chiang, C.-M.; Buszczak, M.; et al. Transforming Activity of an Oncoprotein-Encoding Circular RNA from Human Papillomavirus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.-K.; McCoy, J.P.; Banerjee, N.S.; Rader, J.S.; Broker, T.R.; Meyers, C.; Chow, L.T.; Zheng, Z.-M. Oncogenic HPV Infection Interrupts the Expression of Tumor-Suppressive MiR-34a through Viral Oncoprotein E6. RNA 2009, 15, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, C.L.; Tsang, T.Y.; Yau, P.L.; Kwok, T.T. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Induces Cervical Cancer Cell Migration through the P53/MicroRNA-23b/Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Pathway. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Deng, Y.; Ao, L.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Choy, K.W.; Tony Chung, K.H.; Du, Q.; Sui, Y.; et al. The High-Risk HPV Oncogene E7 Upregulates MiR-182 Expression through the TGF-β/Smad Pathway in Cervical Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peta, E.; Sinigaglia, A.; Masi, G.; Di Camillo, B.; Grassi, A.; Trevisan, M.; Messa, L.; Loregian, A.; Manfrin, E.; Brunelli, M.; et al. HPV16 E6 and E7 Upregulate the Histone Lysine Demethylase KDM2B through the C-MYC/MiR-146a-5p Axys. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1654–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-Y.; Guan, H.-M.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.-J.; Hu, X.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, J.-Y. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG12 Modulated by Human Papillomavirus 16 E6/E7 Promotes Cervical Cancer Progression via ERK/Slug Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 7911–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, W.; Malfertheiner, P. Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Dtsch. Arzteblatt Int. 2018, 115, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schistosomes, Liver Flukes and Helicobacter Pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7–14 June 1994. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1994, 61, 1–241. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.K.K.; Wang, M.H.; To, K.F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, M.S.M.; Shin, V.Y.; Tong, J.H.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of MiR-490-3p Reactivates the Chromatin Remodeler SMARCD1 to Promote Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Gastric Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Khalafi, S.; Chen, Z.; Poveda, J.; Peng, D.; Lu, H.; Soutto, M.; Que, J.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.; Zaika, A.; et al. Silencing of MiR490-3p by H. Pylori Activates DARPP-32 and Induces Resistance to Gefitinib. Cancer Lett. 2020, 491, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiga, K.; Mimuro, H.; Suzuki, M.; Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Sanada, T.; Kim, M.; Ogawa, M.; Iwasaki, Y.W.; Kayo, H.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of MiR-210 Increases the Proliferation of Gastric Epithelium during Chronic Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray-Stewart, T.; Sierra, J.C.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Mera, R.M.; Chaturvedi, R.; Bravo, L.E.; Correa, P.; Schneider, B.G.; Wilson, K.T.; Casero, R.A. Epigenetic Silencing of MiR-124 Prevents Spermine Oxidase Regulation: Implications for Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5480–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Taylor, J.D.; Wyatt, J.I.; Heatley, R.V.; Shallcross, T.M.; Tompkins, D.S.; Rathbone, B.J. Mucosal IgA Recognition of Helicobacter Pylori 120 KDa Protein, Peptic Ulceration, and Gastric Pathology. Lancet 1991, 338, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Selbach, M. Role of Type IV Secretion in Helicobacter Pylori Pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter Pylori CagA and Gastric Cancer: A Paradigm for Hit-and-Run Carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, C.; Zou, S.; Xu, X.; Jia, J.; Liu, Z. NF-ΚB/MiR-223-3p/ARID1A Axis Is Involved in Helicobacter Pylori CagA-Induced Gastric Carcinogenesis and Progression. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Jing, X.; Bao, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, A.; Miao, R.; Guo, H.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; et al. H. Pylori Infection Alters Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks via SNHG17. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3901–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kundu, P.; Seow, S.W.; de Matos, C.T.; Aronsson, L.; Chin, K.C.; Kärre, K.; Pettersson, S.; Greicius, G. Gut Microbiota Accelerate Tumor Growth via C-Jun and STAT3 Phosphorylation in APCMin/+ Mice. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, L.; Stepankova, R.; Kozakova, H.; Fiserova, A.; Rossmann, P.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Colorectal Carcinogenesis in Germ-Free and Conventionally Reared Rats: Different Intestinal Environments Affect the Systemic Immunity. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Rhee, K.-J.; Albesiano, E.; Rabizadeh, S.; Wu, X.; Yen, H.-R.; Huso, D.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wick, E.; McAllister, F.; et al. A Human Colonic Commensal Promotes Colon Tumorigenesis via Activation of T Helper Type 17 T Cell Responses. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, M.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Cai, G.; Han, Y.W. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Promotes Colorectal Carcinogenesis by Modulating E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Signaling via Its FadA Adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Ma, D.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Kryczek, I.; Sun, D.; Nagarsheth, N.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; da Cunha, A.P.; Rezende, R.M.; Cialic, R.; Wei, Z.; Bry, L.; Comstock, L.E.; Gandhi, R.; Weiner, H.L. The Host Shapes the Gut Microbiota via Fecal MicroRNA. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics, 2012. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cortese, M.; Acosta, E.G.; Bartenschlager, R. Rewiring Cellular Networks by Members of the Flaviviridae Family. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niepmann, M.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Rossbach, O. Signals Involved in Regulation of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Genome Translation and Replication. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niepmann, M.; Gerresheim, G.K. Hepatitis C Virus Translation Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, J.M.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Danino, T.; Shaw, K.S.; Mele, A.; Fak, J.J.; Nishiuchi, E.; Takacs, C.N.; Catanese, M.T.; de Jong, Y.P.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus RNA Functionally Sequesters MiR-122. Cell 2015, 160, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaudha, K.; Kaliszewski, M.; Korolnek, T.; Florea, L.; Yeung, M.L.; Jeang, K.-T.; Kumar, A. MicroRNA Silencing of Tumor Suppressor DLC-1 Promotes Efficient Hepatitis C Virus Replication in Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2011, 53, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Aly, H.H.; Tajima, A.; Inoue, I.; Shimotohno, K. Regulation of the Hepatitis C Virus Genome Replication by MiR-199a. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Cheng, N.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Sun, S. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced up-Regulation of MicroRNA-155 Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis by Activating Wnt Signaling. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stämpfli, M.R.; Anderson, G.P. How Cigarette Smoke Skews Immune Responses to Promote Infection, Lung Disease and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopland, D.R. Tobacco Use and Its Contribution to Early Cancer Mortality with a Special Emphasis on Cigarette Smoking. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103 (Suppl. 8), 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, K.R.; D’hulst, A.I.; Maes, T.; Moerloose, K.B.; Demedts, I.K.; Lebecque, S.; Joos, G.F.; Brusselle, G.G. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Emphysema Are Attenuated in CCR6-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4350–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopori, M. Effects of Cigarette Smoke on the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzk, N.; Lubojemska, A.; Hardison, S.E.; Wang, Q.; Gutierrez, M.G.; Brown, G.D.; Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophils Sense Microbe Size and Selectively Release Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Response to Large Pathogens. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.; Thompson, P.R.; Segal, B.H.; Urban, C.F. Nicotine Induces Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, M.D. Differential Allelic Expression of Dopamine D1 Receptor Gene (DRD1) Is Modulated by MicroRNA MiR-504. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Stidley, C.A.; Bernauer, A.M.; Picchi, M.A.; Sheng, X.; Frasco, M.A.; Van Den Berg, D.; Gilliland, F.D.; Crowell, R.E.; Belinsky, S.A. Haplotypes of DNMT1 and DNMT3B Are Associated with Mutagen Sensitivity Induced by Benzo[a]Pyrene Diol Epoxide among Smokers. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, S.-R.; Chida, A.S.; Bauter, M.R.; Shafiq, N.; Seweryniak, K.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Kilty, I.; Rahman, I. Cigarette Smoke Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Release by Activation of NF-KappaB and Posttranslational Modifications of Histone Deacetylase in Macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L46–L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Boggs, S.E.; Belinsky, S.A.; Liu, J. Cigarette Smoke Induces Demethylation of Prometastatic Oncogene Synuclein-Gamma in Lung Cancer Cells by Downregulation of DNMT3B. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5900–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Breitling, L.P.; Brenner, H. DNA Methylation Changes of Whole Blood Cells in Response to Active Smoking Exposure in Adults: A Systematic Review of DNA Methylation Studies. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cui, S.; Ma, J.; Lu, Q.; Kong, C.; Liu, T.; Sun, Z. Cigarette Smoking Extract Causes Hypermethylation and Inactivation of WWOX Gene in T-24 Human Bladder Cancer Cells. Neoplasma 2012, 59, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez, C.S.; Juri, D.E.; Do, K.; Bernauer, A.M.; Thomas, C.L.; Damiani, L.A.; Tessema, M.; Leng, S.; Belinsky, S.A. EMT and Stem Cell-like Properties Associated with MiR-205 and MiR-200 Epigenetic Silencing Are Early Manifestations during Carcinogen-Induced Transformation of Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Xu, H.; Shan, J.; Tao, Y.; Hong, J.A.; Inchauste, S.; Zhang, M.; Kunst, T.F.; Mercedes, L.; Schrump, D.S. Cigarette Smoke Mediates Epigenetic Repression of MiR-487b during Pulmonary Carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1241–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vähäkangas, K.H.; Bennett, W.P.; Castrén, K.; Welsh, J.A.; Khan, M.A.; Blömeke, B.; Alavanja, M.C.; Harris, C.C. P53 and K-Ras Mutations in Lung Cancers from Former and Never-Smoking Women. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4350–4356. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, A.M.; Sun, K.Y.; Ruestow, P.; Cowan, D.M.; Madl, A.K. Lung Cancer Mutation Profile of EGFR, ALK, and KRAS: Meta-Analysis and Comparison of Never and Ever Smokers. Lung Cancer 2016, 102, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Schiller, J.H.; Gazdar, A.F. Lung Cancer in Never Smokers—A Different Disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.J.; Ratner, E.; Leng, S.; Zhai, R.; Nallur, S.; Babar, I.; Muller, R.-U.; Straka, E.; Su, L.; Burki, E.A.; et al. A SNP in a Let-7 MicroRNA Complementary Site in the KRAS 3’ Untranslated Region Increases Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Risk. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8535–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seviour, E.G.; Sehgal, V.; Mishra, D.; Rupaimoole, R.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Lee, J.-S.; Sood, A.K.; Kim, M.P.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Targeting KRas-Dependent Tumour Growth, Circulating Tumour Cells and Metastasis in Vivo by Clinically Significant MiR-193a-3p. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, K.; Erice, O.; Kostyrko, K.; Hausmann, S.; Guruceaga, E.; Tathireddy, A.; Flores, N.M.; Sayles, L.C.; Lee, A.G.; Fragoso, R.; et al. The Mir181ab1 Cluster Promotes KRAS-Driven Oncogenesis and Progression in Lung and Pancreas. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1879–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Dang, J.; Chang, K.-Y.; Yau, E.; Aza-Blanc, P.; Moscat, J.; Rana, T.M. MiR-1298 Inhibits Mutant KRAS-Driven Tumor Growth by Repressing FAK and LAMB3. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5777–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, L.S.; Chow, W.-H.; Vaughan, T.L.; Gammon, M.D.; Risch, H.A.; Stanford, J.L.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Mayne, S.T.; Dubrow, R.; Rotterdam, H.; et al. Population Attributable Risks of Esophageal and Gastric Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleypriest, B.J.; Ward, S.G.; Tosh, D. How Does Inflammation Cause Barrett’s Metaplasia? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardikar, S.; Onstad, L.; Song, X.; Wilson, A.M.; Montine, T.J.; Kratz, M.; Anderson, G.L.; Blount, P.L.; Reid, B.J.; White, E.; et al. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Markers and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Incidence in a Barrett’s Esophagus Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cook, M.B.; Barnett, M.J.; Bock, C.H.; Cross, A.J.; Goodman, P.J.; Goodman, G.E.; Haiman, C.A.; Khaw, K.-T.; McCullough, M.L.; Newton, C.C.; et al. Prediagnostic Circulating Markers of Inflammation and Risk of Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Study within the National Cancer Institute Cohort Consortium. Gut 2019, 68, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, S.; Inchauste, S.; Guo, H.; Shan, J.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, H.; Miettenen, M.; Zhang, M.R.; Hong, J.A.; Raiji, M.T.; et al. Cigarette Smoke Mediates Epigenetic Repression of MiR-217 during Esophageal Adenocarcinogenesis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5548–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer Statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hsia, J.; Yang, G. Prevalence of Smoking in China in 2010. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2469–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennathur, A.; Gibson, M.K.; Jobe, B.A.; Luketich, J.D. Oesophageal Carcinoma. Lancet 2013, 381, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Deng, J.; Guo, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y. A Novel Micropeptide Encoded by Y-Linked LINC00278 Links Cigarette Smoking and AR Signaling in Male Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2790–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The Epidemiology of Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Zhong, R.; Shen, N.; Chen, W.; Zhu, B.; Ke, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, T.; Lou, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Non-Linear Dose-Response Relationship between Cigarette Smoking and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis of 42 Observational Studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Babic, A.; Clish, C.B.; Kraft, P.; Bao, Y.; Qian, Z.R.; Rubinson, D.A.; Ng, K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; et al. Cigarette Smoking and Pancreatic Cancer Survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, R.; Li, M.; Ye, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Tan, L.; Mai, D.; Li, G.; et al. Excessive MiR-25-3p Maturation via N6-Methyladenosine Stimulated by Cigarette Smoke Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Bagchi, D. Oxidative Mechanisms in the Toxicity of Metal Ions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebel, T.W. Arsenic and Drinking Water Contamination. Science 1999, 283, 1458–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebel, T.W. Genotoxicity of Arsenical Compounds. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2001, 203, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, M.J.; Wang, L. Arsenic Alters Cytosine Methylation Patterns of the Promoter of the Tumor Suppressor Gene P53 in Human Lung Cells: A Model for a Mechanism of Carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 1997, 386, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treas, J.; Tyagi, T.; Singh, K.P. Chronic Exposure to Arsenic, Estrogen, and Their Combination Causes Increased Growth and Transformation in Human Prostate Epithelial Cells Potentially by Hypermethylation-Mediated Silencing of MLH1. Prostate 2013, 73, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Arita, A.; Sun, H.; Costa, M. Effects of Nickel, Chromate, and Arsenite on Histone 3 Lysine Methylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.; Luo, F.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liu, Q. Involvement of HIF-2α-Mediated Inflammation in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, F.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q.; Xue, J.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, A.; et al. NF-KB-Regulated Exosomal MiR-155 Promotes the Inflammation Associated with Arsenite Carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, F.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, P.; Xue, J.; Dai, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.; et al. NF-ΚB-Regulated MiR-155, via Repression of QKI, Contributes to the Acquisition of CSC-like Phenotype during the Neoplastic Transformation of Hepatic Cells Induced by Arsenite. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Chen, C.; Yang, Q.; Xue, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Luo, F.; Liu, X.; Xiao, T.; Xu, H.; et al. Exosomal CircRNA_100284 from Arsenite-Transformed Cells, via MicroRNA-217 Regulation of EZH2, Is Involved in the Malignant Transformation of Human Hepatic Cells by Accelerating the Cell Cycle and Promoting Cell Proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; et al. The IL-6/STAT3 Pathway via MiR-21 Is Involved in the Neoplastic and Metastatic Properties of Arsenite-Transformed Human Keratinocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Jing, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.; et al. MicroRNA-21, up-Regulated by Arsenite, Directs the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Enhances the Invasive Potential of Transformed Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells by Targeting PDCD4. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Ling, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.; Liang, X.; Jiang, R.; Wang, B.; Bian, Q.; Liu, Q. Arsenite Evokes IL-6 Secretion, Autocrine Regulation of STAT3 Signaling, and MiR-21 Expression, Processes Involved in the EMT and Malignant Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Angiogenesis, Mediated by MiR-21, Is Involved Arsenite-Induced Carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 223, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Q. Exosomal MiR-21 Derived from Arsenite-Transformed Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Promotes Cell Proliferation Associated with Arsenite Carcinogenesis. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, U.; Schubert, J.; Wellner, U.; Schmalhofer, O.; Vincan, E.; Spaderna, S.; Brabletz, T. A Reciprocal Repression between ZEB1 and Members of the MiR-200 Family Promotes EMT and Invasion in Cancer Cells. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, C.P.; Gregory, P.A.; Kolesnikoff, N.; Bert, A.G.; Wang, J.; Shannon, M.F.; Goodall, G.J. A Double-Negative Feedback Loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the MicroRNA-200 Family Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7846–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Smith, E.; Goodall, G.J.; Drew, P.A.; Brabletz, T.; Yang, C. Reversal and Prevention of Arsenic-Induced Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Malignant Transformation by MicroRNA-200b. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 121, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Humphries, B.; Xiao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, C. MicroRNA-200b Suppresses Arsenic-Transformed Cell Migration by Targeting Protein Kinase Cα and Wnt5b-Protein Kinase Cα Positive Feedback Loop and Inhibiting Rac1 Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18373–18386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipic, M.; Fatur, T.; Vudrag, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Cadmium Induced Mutagenicity. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waalkes, M.P. Cadmium Carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2003, 533, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Cai, D.; Li, P.; Jin, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, L.; Chen, G.; Sun, J.; et al. Chronic Oral Exposure to Cadmium Causes Liver Inflammation by NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Pubertal Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2021, 148, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Zurac, S. MiRNAs in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Skin Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Kimura-Masuda, K.; Masuda, Y. The Role and Function of MicroRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Xiao, S.; Wu, T.; Xie, M.; Zhang, W. Continuous Cadmium Exposure from Weaning to Maturity Induces Downregulation of Ovarian Follicle Development-Related SCF/c-Kit Gene Expression and the Corresponding Changes of DNA Methylation/MicroRNA Pattern. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 225, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, V.S.; Zhang, X.; Jagannathan, L.; Jose, C.C.; Cuddapah, S. Cadmium Exposure Upregulates SNAIL through MiR-30 Repression in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 373, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Onuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Torimura, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Surrogate Indicators for Chemical Stress Responses in Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Lei, Y. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Expression Signatures Modulate DNA Damage and Repair in Cadmium Toxicology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghissassi, F.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A Review of Human Carcinogens—Part D: Radiation. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.K.; Kricker, A. The Epidemiology of UV Induced Skin Cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 63, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Weng, Q.Y.; Fisher, D.E. UV Signaling Pathways within the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2080–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.J.; Ray, A. Epigenetic Regulation of MiRNA Genes and Their Role in Human Melanomas. Epigenomics 2012, 4, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bald, T.; Quast, T.; Landsberg, J.; Rogava, M.; Glodde, N.; Lopez-Ramos, D.; Kohlmeyer, J.; Riesenberg, S.; van den Boorn-Konijnenberg, D.; Hömig-Hölzel, C.; et al. Ultraviolet-Radiation-Induced Inflammation Promotes Angiotropism and Metastasis in Melanoma. Nature 2014, 507, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.R.; Davis, S.; Noonan, F.P.; Graff-Cherry, C.; Hawley, T.S.; Walker, R.L.; Feigenbaum, L.; Fuchs, E.; Lyakh, L.; Young, H.A.; et al. Interferon-γ Links Ultraviolet Radiation to Melanomagenesis in Mice. Nature 2011, 469, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.J.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; Nakatsuji, T.; Muehleisen, B.; Muto, J.; Borkowski, A.W.; Martinez, L.; Greidinger, E.L.; Yu, B.D.; Gallo, R.L. Ultraviolet Radiation Damages Self Noncoding RNA and Is Detected by TLR3. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degueurce, G.; D’Errico, I.; Pich, C.; Ibberson, M.; Schütz, F.; Montagner, A.; Sgandurra, M.; Mury, L.; Jafari, P.; Boda, A.; et al. Identification of a Novel PPARβ/δ/MiR-21-3p Axis in UV-induced Skin Inflammation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, L.; Nikolova, M.; Reva, B.; Fuchs, E. Strand-Specific in Vivo Screen of Cancer-Associated MiRNAs Unveils a Role for MiR-21(∗) in SCC Progression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Huang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-W.; Deng, Q.-K.; Yan, W.; Zhou, M.-J.; Ou, C.-S.; Ding, Z.-H. Differential Expression Profiles of MicroRNAs in NIH3T3 Cells in Response to UVB Irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darido, C.; Georgy, S.R.; Wilanowski, T.; Dworkin, S.; Auden, A.; Zhao, Q.; Rank, G.; Srivastava, S.; Finlay, M.J.; Papenfuss, A.T.; et al. Targeting of the Tumor Suppressor GRHL3 by a MiR-21-Dependent Proto-Oncogenic Network Results in PTEN Loss and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.R.; Messenger, Z.J.; Tam, H.W.; Phillips, S.L.; Recio, L.; Smart, R.C. Long Noncoding RNA LincRNA-P21 Is the Major Mediator of UVB-Induced and P53-Dependent Apoptosis in Keratinocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramata, P.; Lu, Y.-P.; Lou, Y.-R.; Singh, R.N.; Kwon, S.M.; Conney, A.H. Patches of Mutant P53-Immunoreactive Epidermal Cells Induced by Chronic UVB Irradiation Harbor the Same P53 Mutations as Squamous Cell Carcinomas in the Skin of Hairless SKH-1 Mice. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Corey, D.R. Non-Coding RNAs as Drug Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussecker, D.; Kay, M.A. MiR-122 Continues to Blaze the Trail for MicroRNA Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2010, 18, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, M.S.; Neilson, J.R.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA Sponges: Competitive Inhibitors of Small RNAs in Mammalian Cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, I.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional Sequestration of MicroRNA-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by Circular RNA Sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G.; Shair, K.H.Y.; Marquitz, A.R.; Kung, C.-P.; Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Human Tumor Virus Utilizes Exosomes for Intercellular Communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20370–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional Delivery of Viral MiRNAs via Exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlgren, J.; De L Karlson, T.; Brisslert, M.; Vaziri Sani, F.; Telemo, E.; Sunnerhagen, P.; Valadi, H. Plasma Exosomes Can Deliver Exogenous Short Interfering RNA to Monocytes and Lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtam, T.A.; Kovalev, R.A.; Varfolomeeva, E.Y.; Makarov, E.M.; Kil, Y.V.; Filatov, M.V. Exosomes Are Natural Carriers of Exogenous SiRNA to Human Cells in Vitro. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2013, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Na’ara, S.; Gil, Z. Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2015, 23, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Arora, S.; Prakasam, G.; Calin, G.A.; Syed, M.A. MicroRNA in Lung Cancer: Role, Mechanisms, Pathways and Therapeutic Relevance. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 70, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varn, F.S.; Schaafsma, E.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C. Genomic Characterization of Six Virus-Associated Cancers Identifies Changes in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Altered Genetic Programs. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6413–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Farmer, E.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.-F. Perspectives for Therapeutic HPV Vaccine Development. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Nimura, K.; Ito, R.; Saga, K.; Inohara, H.; Kaneda, Y. Evaluation of HPV16 E7 Expression in Head and Neck Carcinoma Cell Lines and Clinical Specimens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| miRNA | Expression | Target | Related Cancers | Related Inflammation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-205 | ↓ 18 | HBx mRNA | HCC 1 | HBV 11 | [51] |
| miR-205 | ↓ | unknown | LC 2 | CS 12 | [120] |
| miR-122 | ↓ | cyclin G(1) | HCC | HBV | [53,54,55] |
| miR-122 | ↓ | HCV mRNA | HCC | HCV 13 | [102,103,104] |
| miR-199a-3p | ↑ 19 | unknown | HCC | HBV | [56] |
| miR-199a-3p | ↓ | HCV mRNA | unknown | HCV | [106] |
| let-7 | ↓ | STAT3 | HCC | HBV | [58] |
| let7 | ↓ | KRAS | LC | CS | [125] |
| miR-15a/16 | ↓ | cyclin D1 | HCC | HBV | [57] |
| miR-148a | ↓ | HPIP | HCC | HBV | [59] |
| miR-216b | ↓ | IGF2BP2 | HCC | HBV | [60] |
| miR-3188 | ↑ | ZHX2 | HCC | HBV | [61] |
| miR-139-3p | ↓ | E6/E7 | CC 3, HNC 4 | HPV 14 | [72] |
| miR-375 | ↓ | E6AP | CC | HPV | [73] |
| miR-34a | ↓ | unknown | CC | HPV | [78] |
| miR-23b | ↓ | uPA | CC | HPV | [79] |
| miR-182 | ↑ | unknown | CC | HPV | [80] |
| miR-146a-5p | ↓ | KDM2B | CC | HPV | [81] |
| miR-210 | ↓ | STMN1, DIMT1 | GC 5 | H. pylori15 | [87] |
| miR-490-3p | ↓ | SMARCD1, DARPP-32 | GC | H. pylori | [85,86] |
| miR-124 | ↓ | SMOX | GC | H. pylori | [88] |
| miR-223-3p | ↑ | ARID1A | GC | H. pylori | [92] |
| miR-18a* | ↓ | ULK1 | CRC 6 | F. nucleatum | [98] |
| miR-4802 | ↓ | ATG7 | CRC | F. nucleatum | [98] |
| miR-515-5p | unknown | unknown | unknown | Escherichia coli and F. nucleatum 16 | [99] |
| miR-1226-5p | unknown | unknown | unknown | Escherichia coli and F. nucleatum | [99] |
| miR-141 | ↑ | DLC-1 | unknown | HCV | [105] |
| miR-155 | ↑ | unknown | HCC | HCV | [107] |
| miR-155 | ↑ | QKI | unknown | Arsenic | [150,151] |
| miR-504 | unknown | DRD1 | unknown | CS | [114] |
| miR-200b, miR-200c | ↓ | unknown | LC | CS | [120] |
| miR-200b | ↓ | PKCα | unknown | Arsenic | [161] |
| miR-487b | ↓ | SUZ12, BMI1, WNT5A, MYC, and KRAS | LC | CS | [121] |
| miR-193a-3p | ↓ | KRAS | LC | CS | [126] |
| miR181ab1 | ↓ | unknown | LC, PDAC 7 | CS | [127] |
| miR-1298 | ↓ | FAK, LAMB3 | LC | CS | [128] |
| miR-217 | ↓ | KLK7 | EC 8 | CS | [133] |
| miR-25-3p | ↑ | PHLPP2 | PC 9 | CS | [142] |
| miR-221 | ↑ | unknown | unknown | Cadmium | [167] |
| miR-30 | ↓ | Snail | unknown | Cadmium | [168] |
| miR-21 | ↑ | PDCD4 | LC | Arsenic | [153,154,155,156,157] |
| miR-21-3p | ↑ | SMAD7 | unknown | UV 17 | [178] |
| miR-21-3p | ↑ | PHACTR4 | SCC 10 | unknown | [179] |
| miR-21-5p | ↑ | GRHL3, PTEN | SCC | UV | [180,181] |
| lncRNA | Expression | Target | Related Diseases | Related Inflammation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HULC | ↑ 10 | unknown | HCC 1 | HBV 5 | [52] |
| HBx-LINE1 | ↑ | miR-122 | HCC | HBV | [54] |
| LINC01352 | ↓ 11 | miR-135b | HCC | HBV | [62] |
| TMPOP2 | ↑ | miR-375, miR-139 | CC 2 | HPV 6 | [75] |
| SNHG12 | ↑ | unknown | CC | HPV | [82] |
| SNHG17 | ↑ | NONO, miR-3909 | GC 3 | H. pylori7 | [93] |
| LINC00278 | ↓ | unknown | EC 4 | CS 8 | [137] |
| GABPB1-AS1 | ↑ | unknown | unknown | Cadmium | [169] |
| LINC00152 | ↑ | unknown | unknown | Cadmium | [169] |
| ENST00000414355 | ↑ | unknown | unknown | Cadmium | [170] |
| lincRNA-p21 | ↓ | unknown | unknown | UV 9 | [182] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Xie, M.; Jing, X.; Cui, J.; Wu, X.; Shu, Y. Crosstalk between Environmental Inflammatory Stimuli and Non-Coding RNA in Cancer Occurrence and Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 4436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174436
Xu T, Xie M, Jing X, Cui J, Wu X, Shu Y. Crosstalk between Environmental Inflammatory Stimuli and Non-Coding RNA in Cancer Occurrence and Development. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174436
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tingting, Mengyan Xie, Xinming Jing, Jiahua Cui, Xi Wu, and Yongqian Shu. 2021. "Crosstalk between Environmental Inflammatory Stimuli and Non-Coding RNA in Cancer Occurrence and Development" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174436
APA StyleXu, T., Xie, M., Jing, X., Cui, J., Wu, X., & Shu, Y. (2021). Crosstalk between Environmental Inflammatory Stimuli and Non-Coding RNA in Cancer Occurrence and Development. Cancers, 13(17), 4436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174436






