RET Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
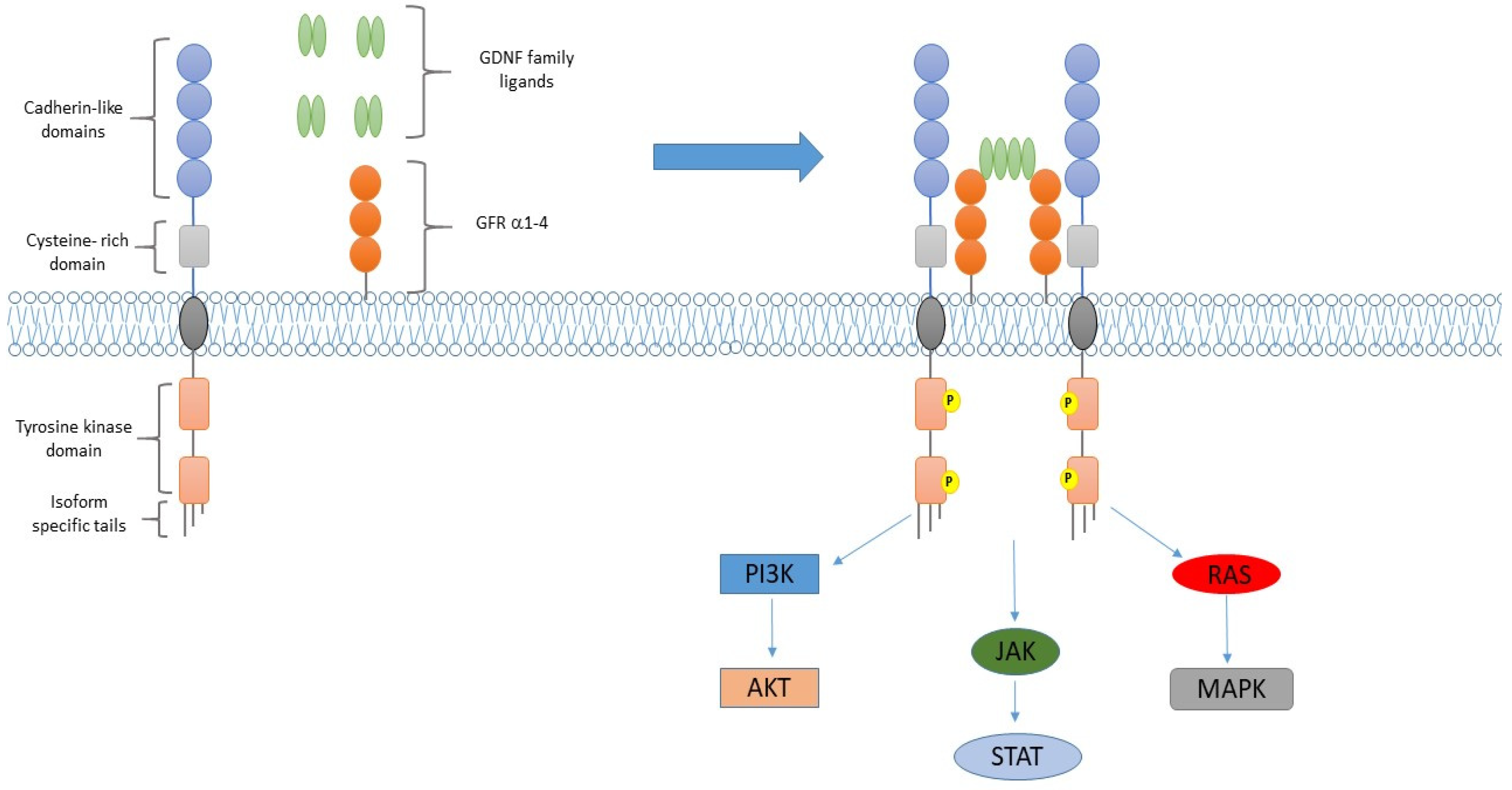
RET Rearrangements in NSCLC
2. Non-Selective RET Inhibitors
2.1. Cabozantinib
2.2. Vandetanib
2.3. Lenvatinib
| Author | Regimen | Setting | Pts | ORR (%) | Median PFS (Months) | Median OS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drilon, A. et al., 2016 [24] | Cabozantinib 60 mg/day | Pretreated or untreated | 26 | 28 | 5.5 | 9.9 |
| Neal, J.W. et al., 2016 [27] | Cabozantinib 60 mg/day vs. cabozantinib 40 mg/day + erlotinib 150 mg/day Vs. erlotinib 150 mg/day | Pretreated | 125 | 11 vs. 3 vs. 3 | 4.3 vs. 4.7 vs. 1.8 | 9.2 vs. 13.3 vs. 5.1 |
| Lee, S.H. et al., 2017 [33] | Vandetanib 300 mg/day | Pretreated | 18 (17 evaluable) | 18 | 4.5 | 11.6 |
| Yoh, K, et al., 2017 [34] | Vandetanib 300 mg/day | Pretreated | 19 | 47 | 4.7 | 11.1 |
| Hida, T, et al., 2019 [37] | Lenvatinib 24 mg/day | Pretreated | 25 | 16% | 7.3 | - |
3. Selective RET Inhibitors
3.1. Selpercatinib
3.2. Pralsetinib
| Author | Phase | Regimen | Setting | Pts | ORR (%) | Median PFS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drilon, A. et al., 2020 [41] | I–II | Selpercatinib 160 mg twice daily | Platinum pretreated | 105 | 64 (95% CI: 54–73%) | 16.5 (95% CI: 17.7–n.r.) |
| II | Selpercatinib 160 mg twice daily | Untreated | 39 | 85 (95% CI: 70–94%) | n.r. (95% CI: 13.8–n.r.) | |
| Gainor, J.F. et al., 2020 [47] | I–II | Pralsetinib 400 mg daily | Pretreated | 80 | 61 (95% CI: 50–72) | - |
| II | Pralsetinib 400 mg daily | Untreated | 26 | 73 (95% CI: 52–88) | - |
4. Discussion
| Trial | Phase | Setting | Stage | Pts | Treatment | Primary End Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04194944 (LIBRETTO-431) [49] | Phase III | First line | Stage IV or IIIB-C * | 250 | Selpercatinib vs. platinum + pemetrexed with or without pembrolizumab | PFS |
| NCT04222972(ACCELE-RET) [50] | Phase III | First line | Stage IV or IIIB-C * | 250 | Pralsetinib vs. platinum + pemetrexed with or without pembrolizumab (if non squamous) or platinum + gemcitabine | PFS |
| NCT03178552 (B-FAST) [51] | Phase I/II | First line | Stage IV or stage III * | 50 | Alectinib | ORR |
| NCT04591431ROME [52] | Phase II | Second line | Stage IV | 384 | Alectinib or brigatinib | ORR |
| NCT04268550 (LUNG-MAP) [53] | Phase II | Second or subsequent lines | Stage IV or stage III * | 124 | Selpercetinib | ORR |
| NCT04131543 (CRETA) [54] | Phase II | Second or subsequent lines | Stage IV or stage III * | 25 | Cabozantinib | ORR |
| NCT03445000 (ALERT-LUNG) [55] | Phase II | Second or subsequent lines | Stage IV or stage III * | 44 | Alectinib | ORR |
| NCT03468985 [56] | Phase II | Pretreated | Stage IV | 169 | Nivolumab + cabozantinib | PFS |
| NCT04161391 [64] | Phase I-II | Naive or pretreated | Stage IV | 362 | TPX-0046 | ORR |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amoresano, A.; Incoronato, M.; Monti, G.; Pucci, P.; de Franciscis, V.; Cerchia, L. Direct Interactions among Ret, GDNF and GFRα1 Molecules Reveal New Insights into the Assembly of a Functional Three-Protein Complex. Cell Signal 2005, 17, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; McCusker, M.G.; Russo, A.; Scilla, K.A.; Gittens, A.; Arensmeyer, K.; Mehra, R.; Adamo, V.; Rolfo, C. RET Fusions in Solid Tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, C.; Anand, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Subbiah, V.; Drilon, A.; Andrè, F.; Curigliano, G. Progresses Toward Precision Medicine in RET-Altered Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6102–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Clinicopathologic Characteristics, Genetic Variability and Therapeutic Options of RET Rearrangements Patients in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2016, 101, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, S.; Scheel, A.H.; Scheffler, M.; Schultheis, A.M.; Gautschi, O.; Aebersold, F.; Diebold, J.; Pall, G.; Rothschild, S.; Bubendorf, L.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of RET Rearranged Lung Cancer in European Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Subbiah, V.; Marchlik, E.; Elkin, S.K.; Carter, J.L.; Kurzrock, R. RET Aberrations in Diverse Cancers: Next-Generation Sequencing of 4,871 Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Isozaki, H.; Lennerz, J.K.; Gainor, J.F.; Lennes, I.T.; Zhu, V.W.; Marcoux, N.; Banwait, M.K.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Su, W.; et al. Landscape of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC and Clinical Validation of Combined EGFR and RET Inhibition with Osimertinib and BLU-667 for Acquired RET Fusion. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempner, S.J.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Braiteh, F.S.; Nikolinakos, P.G.; Gowen, K.; Cervantes, C.M.; Chmielecki, J.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.J.; et al. Emergence of RET Rearrangement Co-Existing with Activated EGFR Mutation in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Patients Who Had Progressed on First- or Second-Generation EGFR TKI. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, R.; Auger, N.; Auclin, E.; Besse, B. Clinical and Translational Implications of RET Rearrangements in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esagian, S.M.; Grigoriadou, G.I.; Nikas, I.P.; Boikou, V.; Sadow, P.M.; Won, J.-K.; Economopoulos, K.P. Comparison of Liquid-Based to Tissue-Based Biopsy Analysis by Targeted next Generation Sequencing in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, H.; Jung, Y.J.; Kang, H.W.; Park, I.-K.; Kang, C.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Ju, Y.S.; Seo, J.-S.; Chung, D.H.; Kim, Y.T. Diagnostic Method for the Detection of KIF5B-RET Transformation in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, T.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. RET Fusions Define a Unique Molecular and Clinicopathologic Subtype of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugay, F.; Llamas-Gutierrez, F.; Gournay, M.; Medane, S.; Mazet, F.; Chiforeanu, D.C.; Becker, E.; Lamy, R.; Léna, H.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of ROS1 - and RET -Rearranged NSCLC in Caucasian Patients: Data from a Cohort of 713 Non-Squamous NSCLC Lacking KRAS/EGFR/HER2/BRAF/PIK3CA/ALK Alterations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53336–53351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.M.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.E.; Bhandari, N.R.; Sireci, A. Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with RET-Fusion Positive Non-Small Lung Cancer in Real-World Practice in the United States. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacic, S.; Luvison, A.; Evdokimova, V.; Kelly, L.; Siegfried, J.M.; Villaruz, L.C.; Socinski, M.A.; Nikiforov, Y.E. RET Rearrangements in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Radiation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsuta, K.; Kohno, T.; Yoshida, A.; Shimada, Y.; Asamura, H.; Furuta, K.; Kushima, R. RET-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Clinicopathological and Molecular Analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Pennell, N.A.; Ali, S.M.; Ross, J.S.; Ma, P.C.; Velcheti, V. RET-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinomas with Lymphangitic Spread, Psammoma Bodies, and Clinical Responses to Cabozantinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digumarthy, S.R.; Mendoza, D.P.; Lin, J.J.; Rooney, M.; Do, A.; Chin, E.; Yeap, B.Y.; Shaw, A.T.; Gainor, J.F. Imaging Features and Patterns of Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with RET Rearrangements. Cancers 2020, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Ma, Z. Driver Genes as Predictive Indicators of Brain Metastasis in Patients with Advanced NSCLC: EGFR, ALK, and RET Gene Mutations. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offin, M.; Guo, R.; Wu, S.L.; Sabari, J.; Land, J.D.; Ni, A.; Montecalvo, J.; Halpenny, D.F.; Buie, L.W.; Pak, T.; et al. Immunophenotype and Response to Immunotherapy of RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.18.00386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakes, F.M.; Chen, J.; Tan, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shi, Y.; Yu, P.; Qian, F.; Chu, F.; Bentzien, F.; Cancilla, B.; et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a Novel MET and VEGFR2 Inhibitor, Simultaneously Suppresses Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.S.; Lee, W.-C.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, S.; Bleazard, T.; Won, J.-K.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, J.-I.; Kang, J.-H.; Seo, J.-S. A Transforming KIF5B and RET Gene Fusion in Lung Adenocarcinoma Revealed from Whole-Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Wang, L.; Hasanovic, A.; Suehara, Y.; Lipson, D.; Stephens, P.; Ross, J.; Miller, V.; Ginsberg, M.; Zakowski, M.F.; et al. Response to Cabozantinib in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Adenocarcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, A.; Albano, M.; Van Voorthuysen, M.; Somwar, R.; Smith, R.S.; Montecalvo, J.; et al. A Phase 2 Single Arm Trial of Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Lancet Oncol 2016, 17, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Schubert, L.; Rix, U.; Marek, L.A.; Le, A.T.; Keysar, S.B.; Glogowska, M.J.; Smith, M.A.; Kako, S.; Sumi, N.J.; et al. EGFR Mediates Responses to Small Molecule Drugs Targeting Oncogenic Fusion Kinases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3551–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakelee, H.A.; Gettinger, S.; Engelman, J.; Jänne, P.A.; West, H.; Subramaniam, D.S.; Leach, J.; Wax, M.; Yaron, Y.; Miles, D.R.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of Cabozantinib (XL184) with or without Erlotinib in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.W.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Wakelee, H.A.; Aisner, S.C.; Bowden, M.; Huang, Y.; Carbone, D.P.; Gerstner, G.J.; Lerner, R.E.; Rubin, J.L.; et al. Erlotinib, Cabozantinib, or Erlotinib plus Cabozantinib as Second- or Third-Line Treatment of Patients with EGFR Wild-Type Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ECOG-ACRIN 1512): A Phase 2 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, F.; Vitagliano, D.; Guida, T.; Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G.; Vecchio, G.; Ryan, A.J.; Fontanini, G.; Fusco, A.; Santoro, M. ZD6474, an Orally Available Inhibitor of KDR Tyrosine Kinase Activity, Efficiently Blocks Oncogenic RET Kinases. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7284–7290. [Google Scholar]
- Natale, R.B.; Thongprasert, S.; Greco, F.A.; Thomas, M.; Tsai, C.-M.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Ferry, D.; Mulatero, C.; Whorf, R.; Thompson, J.; et al. Phase III Trial of Vandetanib Compared with Erlotinib in Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hirsh, V.; Park, K.; Qin, S.; Blajman, C.R.; Perng, R.-P.; Chen, Y.-M.; Emerson, L.; Langmuir, P.; Manegold, C. Vandetanib Versus Placebo in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer after Prior Therapy with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: A Randomized, Double-Blind Phase III Trial (ZEPHYR). J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Sun, Y.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Germonpré, P.; Saijo, N.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Kabbinavar, F.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Vandetanib plus Docetaxel versus Docetaxel as Second-Line Treatment for Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ZODIAC): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, R.H.; Arrieta, Ó.; Yang, C.-H.; Gottfried, M.; Chan, V.; Raats, J.; de Marinis, F.; Abratt, R.P.; Wolf, J.; Blackhall, F.H.; et al. Vandetanib plus Pemetrexed for the Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Sun, J.-M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Choi, Y.-L.; et al. Vandetanib in Pretreated Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Harboring RET Rearrangement: A Phase II Clinical Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, K.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Nishio, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, H.; Nogami, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Kohno, T.; Tsuta, K.; et al. Vandetanib in Patients with Previously Treated RET-Rearranged Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LURET): An Open-Label, Multicentre Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, P. Lenvatinib in Management of Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2020, 25, e302–e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, L.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Bidoli, P.; Kim, J.-H.; Ferry, D.; Kim, Y.-C.; Losonczy, G.; Steele, N.; Woo, I.S.; et al. E7080 (Lenvatinib) in Addition to Best Supportive Care (BSC) versus BSC Alone in Third-Line or Greater Nonsquamous, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Velcheti, V.; Reckamp, K.L.; Nokihara, H.; Sachdev, P.; Kubota, T.; Nakada, T.; Dutcus, C.E.; Ren, M.; Tamura, T. A Phase 2 Study of Lenvatinib in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Makker, V.; Rasco, D.; Dutcus, C.E.; Wu, J.; Stepan, D.E.; Shumaker, R.C.; Motzer, R.J. Phase IB/II Trial of Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma, Endometrial Cancer, and Other Selected Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Velcheti, V.; Tuch, B.B.; Ebata, K.; Busaidy, N.L.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Wirth, L.J.; Stock, S.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; et al. Selective RET Kinase Inhibition for Patients with RET-Altered Cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Milia, J.; Filleron, T.; Wolf, J.; Carbone, D.P.; Owen, D.; Camidge, R.; Narayanan, V.; Doebele, R.C.; Besse, B.; et al. Targeting RET in Patients With RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers: Results From the Global, Multicenter RET Registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Loong, H.H.F.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.E.; Subbiah, V.; Oxnard, G.R.; Bauer, T.M.; Velcheti, V.; Lakhani, N.J.; Besse, B.; Park, K.; Patel, J.D.; Cabanillas, M.E.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of LOXO-292, a Potent and Highly Selective RET Inhibitor, in Patients with RET-Altered Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Lin, J.J.; Filleron, T.; Ni, A.; Milia, J.; Bergagnini, I.; Hatzoglou, V.; Velcheti, V.; Offin, M.; Li, B.; et al. Brief Report: Frequency of Brain Metastases and Multikinase Inhibitor Outcomes in Patients with RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Gainor, J.F.; Rahal, R.; Brubaker, J.D.; Kim, J.L.; Maynard, M.; Hu, W.; Cao, Q.; Sheets, M.P.; Wilson, D.; et al. Precision Targeted Therapy with BLU-667 for RET-Driven Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Lee, D.H.; Curigliano, G.; Doebele, R.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Baik, C.S.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lopes, G.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cassier, P.A.; et al. Clinical Activity and Tolerability of BLU-667, a Highly Potent and Selective RET Inhibitor, in Patients (Pts) with Advanced RET-Fusion+ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Subbiah, V.; Gainor, J.F.; Taylor, M.H.; Zhu, V.W.; Doebele, R.C.; Lopes, G.; Baik, C.; Garralda, E.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Treatment with Pralsetinib (Formerly BLU-667), a Potent and Selective RET Inhibitor, Provides Rapid Clearance of CtDNA in Patients with RET-Altered Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ix122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Curigliano, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, D.H.; Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Cassier, P.A.; Lopes, G.; Tan, D.S.-W.; et al. Registrational Dataset from the Phase I/II ARROW Trial of Pralsetinib (BLU-667) in Patients (Pts) with Advanced RET Fusion+ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Pralsetinib: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Zhou, C.C.; Drilon, A.; Park, K.; Wolf, J.; Elamin, Y.; Davis, H.M.; Soldatenkova, V.; Sashegyi, A.; Lin, A.B.; et al. Phase III Study of Selpercatinib versus Chemotherapy ± Pembrolizumab in Untreated RET Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-La Roche. A Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label Study of Pralsetinib Versus Standard of Care for First-Line Treatment of RET Fusion-Positive, Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04222972 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Hoffmann-La Roche. A Phase II/III Multicenter Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Multiple Targeted Therapies as Treatments for Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring Actionable Somatic Mutations Detected in Blood (B-FAST: Blood-First Assay Screening Trial). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03178552 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Fondazione per la Medicina Personalizzata. The Rome Trial from Histology to Target: The Road to Personalize Target Therapy and Immunotherapy. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04591431 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Southwest Oncology Group. A Phase II Study of LOXO-292 in Patients With RET Fusion-Positive Stage IV or Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (LUNG-MAP Sub-Study). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04268550 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Ardizzoni, A. Phase II Study to Evaluate the Activity and Safety of Cabozantinib in Pretreated, Advanced RET-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: CRETA Trial. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04131543 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- European Thoracic Oncology Platform. A Single Arm Phase II Trial Evaluating the Activity of Alectinib for the Treatment of Pretreated RET-Rearranged Advanced NSCLC. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03445000 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). A Randomized Phase II Trial of Nivolumab, Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab, and Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Previously Treated Non-Squamous NSCLC. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03468985 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Phase III Study of Anlotinib Hydrochloride Capsule Combined With Chemotherapy Versus Placebo Combined With Chemotherapy in Subjects With Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04439890 (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of Pembrolizumab (MK-3475) With or Without Lenvatinib (E7080/MK-7902) in Participants With Treatment-Naïve, Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Whose Tumors Have a Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) Greater Than or Equal to 1% (LEAP-007). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03829332 (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Fujimura, T.; Furugaki, K.; Harada, N.; Yoshimura, Y. Enhanced Antitumor Effect of Alectinib in Combination with Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor against RET-Fusion–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2020, 21, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Cascone, T.; Hess, K.R.; Subbiah, I.M.; Nelson, S.; Morikawa, N.; Nilsson, M.B.; Bhatt, T.; Ali, S.; William, W.N.; et al. Multi-Kinase RET Inhibitor Vandetanib Combined with MTOR Inhibitor Everolimus in Patients with RET Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Tan, L.; Lin, J.J.; Wong, S.Q.; Hollizeck, S.; Ebata, K.; Tuch, B.B.; Yoda, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. RET Solvent Front Mutations Mediate Acquired Resistance to Selective RET Inhibition in RET-Driven Malignancies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Liu, S.V.; McCoach, C.E.; Zhu, V.W.; Tan, A.C.; Yoda, S.; Peterson, J.; Do, A.; Prutisto-Chang, K.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Selective RET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.Y.; Johnson, M.L.; Clifford, S.E.; Somwar, R.; Kherani, J.F.; Son, J.; Bertram, A.A.; Davare, M.A.; Gladstone, E.; Ivanova, E.V.; et al. Overcoming MET-Dependent Resistance to Selective RET Inhibition in Patients with RET Fusion–Positive Lung Cancer by Combining Selpercatinib with Crizotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.E.; Zhai, D.; Rogers, E.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Ung, J.; Lee, D.; Rodon, L.; Graber, A.; Zimmerman, Z.F.; et al. The Next-Generation RET Inhibitor TPX-0046 Is Active in Drug-Resistant and Naïve RET-Driven Cancer Models. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.J.; Drilon, A. Decade in Review: A New Era for RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cascetta, P.; Sforza, V.; Manzo, A.; Carillio, G.; Palumbo, G.; Esposito, G.; Montanino, A.; Costanzo, R.; Sandomenico, C.; De Cecio, R.; et al. RET Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174415
Cascetta P, Sforza V, Manzo A, Carillio G, Palumbo G, Esposito G, Montanino A, Costanzo R, Sandomenico C, De Cecio R, et al. RET Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174415
Chicago/Turabian StyleCascetta, Priscilla, Vincenzo Sforza, Anna Manzo, Guido Carillio, Giuliano Palumbo, Giovanna Esposito, Agnese Montanino, Raffaele Costanzo, Claudia Sandomenico, Rossella De Cecio, and et al. 2021. "RET Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174415
APA StyleCascetta, P., Sforza, V., Manzo, A., Carillio, G., Palumbo, G., Esposito, G., Montanino, A., Costanzo, R., Sandomenico, C., De Cecio, R., Piccirillo, M. C., La Manna, C., Totaro, G., Muto, P., Picone, C., Bianco, R., Normanno, N., & Morabito, A. (2021). RET Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 13(17), 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174415










