Adipsin-Dependent Secretion of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates the Adipocyte-Cancer Stem Cell Interaction
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements
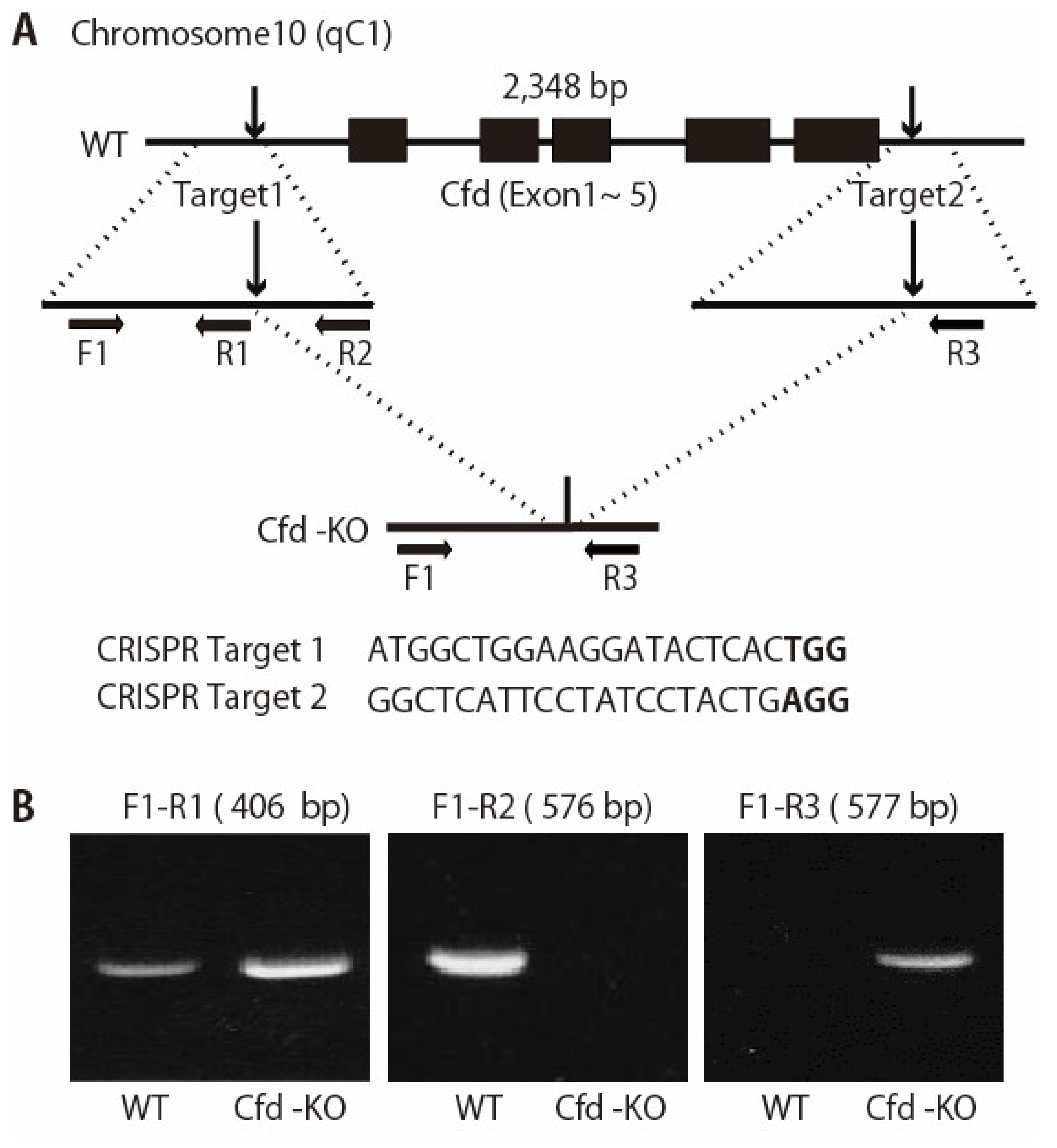
2.2. Generation of Cfd-Knockout (KO) Mouse
2.3. Reverse Transcription PCR Analysis
2.4. Establishment of Murine mADSCs
2.5. Establishment of Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Tumor Xenografts (PDXs)
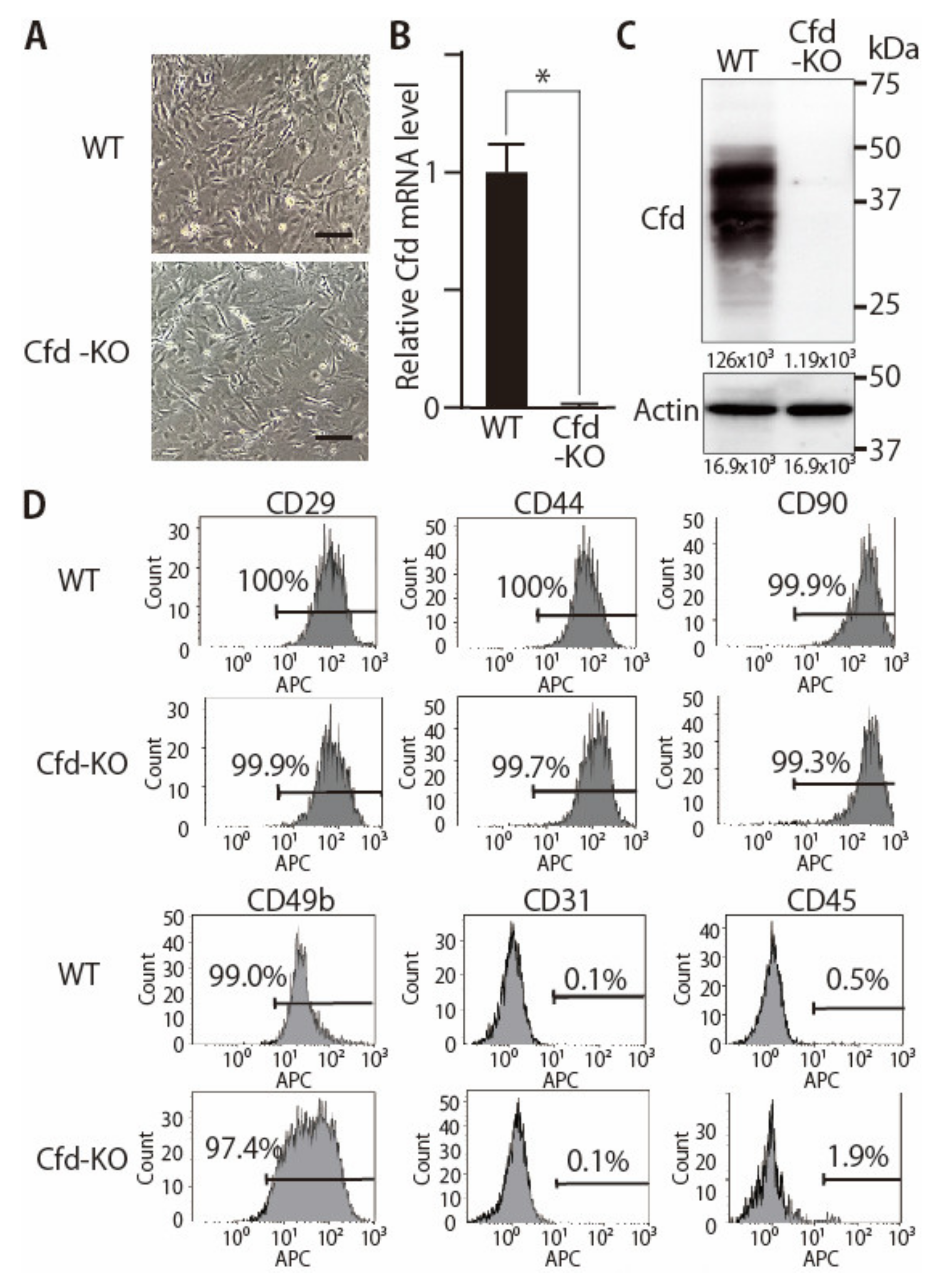
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Coculture of PDX Cells and mADSCs
2.8. Adipsin Purification
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Cytokine Array
2.11. Xenotransplantation Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Adipsin-KO Mouse and Mammary ADSCs
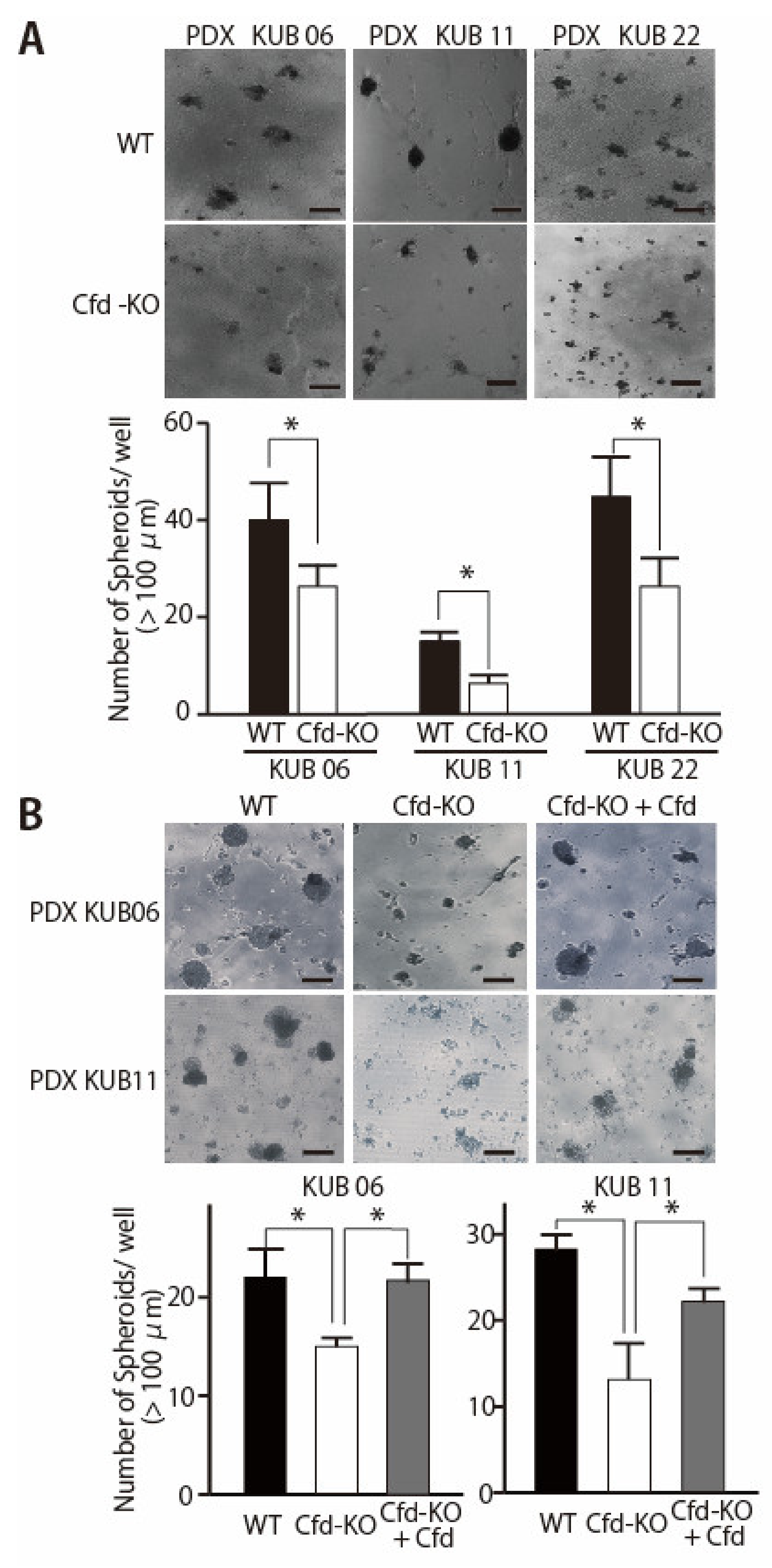
3.2. Adipokine Cfd-Dependent Tumorsphere Formation by Breast Cancer PDX Cells
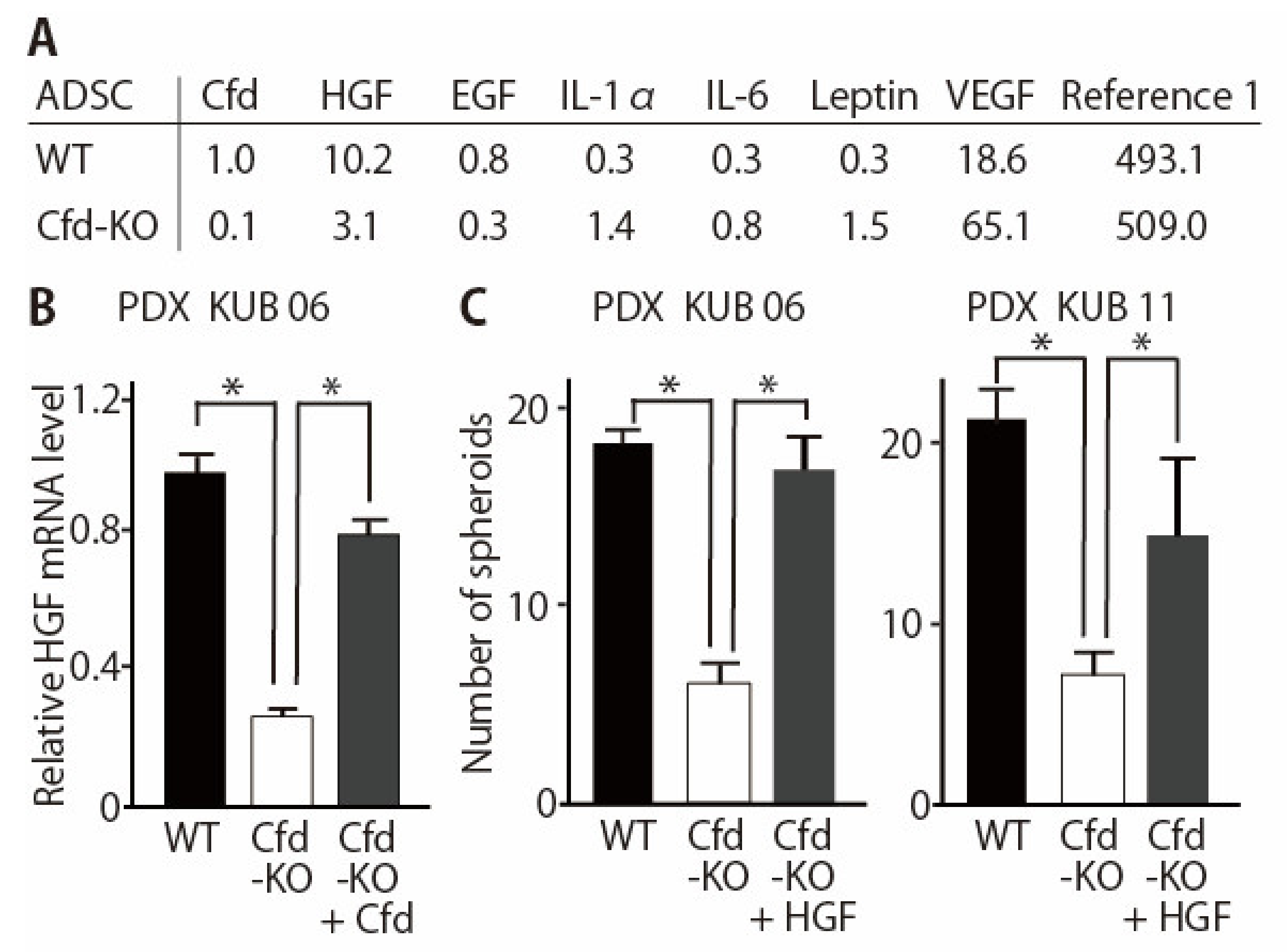
3.3. HGF Alleviated the Reduced Ability of Cfd-KO mADSCs to Promote Tumorsphere Formation
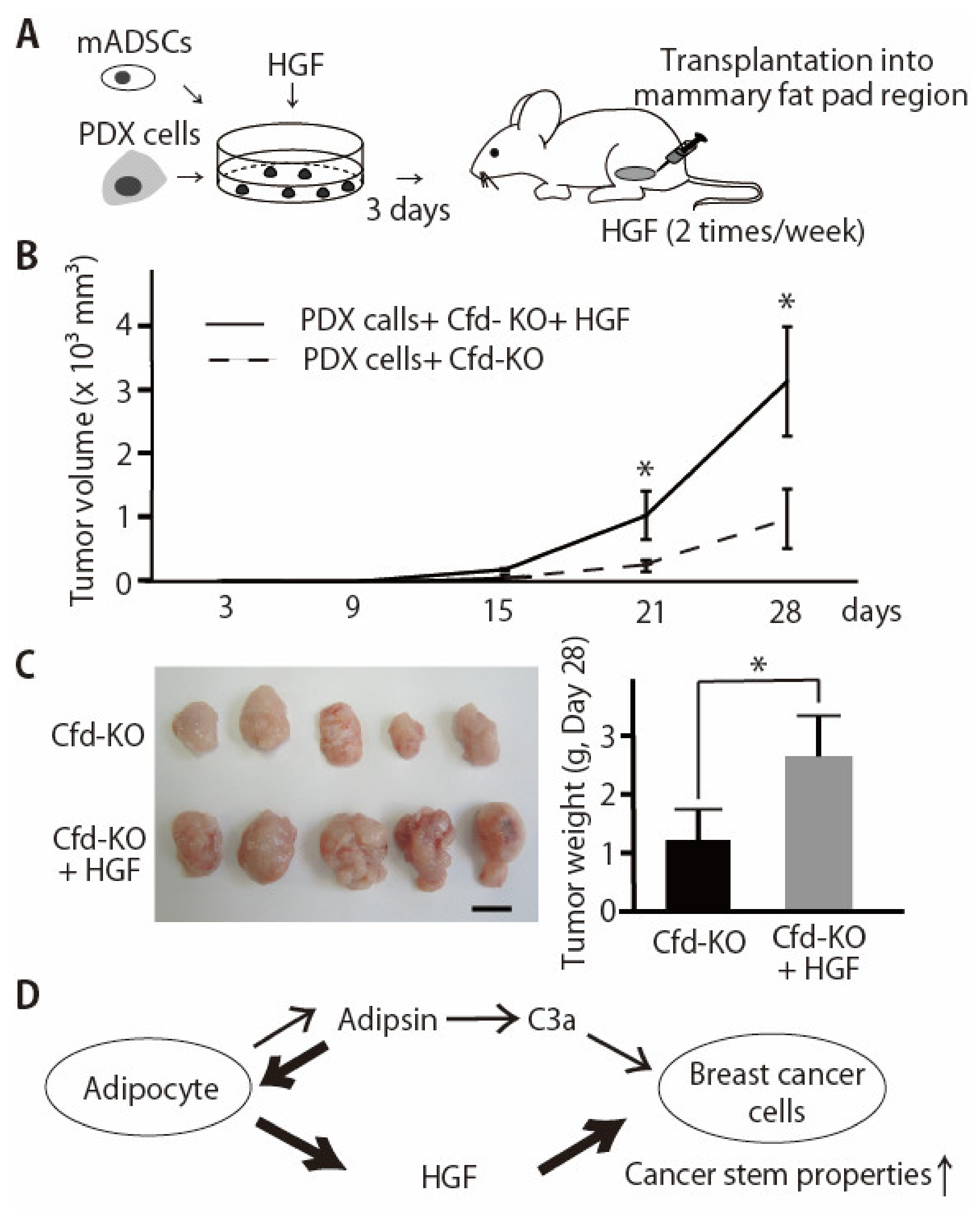
3.4. HGF Alleviated the Reduced Effect of Cfd-KO mADSCs on Tumor Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimono, Y.; Mukohyama, J.; Nakamura, S.; Minami, H. MicroRNA Regulation of Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, N.A.; Shimono, Y.; Qian, D.; Clarke, M.F. The biology of cancer stem cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 675–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Hisamori, S.; Hogan, D.J.; Zabala, M.; Hendrickson, D.G.; Dalerba, P.; Cai, S.; Scheeren, F.; Kuo, A.H.; Sikandar, S.S.; et al. miR-142 regulates the tumorigenicity of human breast cancer stem cells through the canonical WNT signaling pathway. eLife 2014, 3, e01977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, Y.; Zabala, M.; Cho, R.W.; Lobo, N.; Dalerba, P.; Qian, D.; Diehn, M.; Liu, H.; Panula, S.P.; Chiao, E.; et al. Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Nishimura, T.; Hayashi, T.; Kono, S.; Tsuchida, H.; Hirata, M.; Kijima, Y.; Takao, S.; Okada, S.; et al. Upregulation of S100A10 in metastasized breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4359–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, N.; Kakeji, Y.; Shimono, Y. MicroRNA-93 targets WASF3 and functions as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Spradling, A.C. Stem cells and niches: Mechanisms that promote stem cell maintenance throughout life. Cell 2008, 132, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stingl, J.; Eirew, P.; Ricketson, I.; Shackleton, M.; Vaillant, F.; Choi, D.; Li, H.I.; Eaves, C.J. Purification and unique properties of mammary epithelial stem cells. Nature 2006, 439, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, M.; Vaillant, F.; Simpson, K.J.; Stingl, J.; Smyth, G.K.; Asselin-Labat, M.L.; Wu, L.; Lindeman, G.J.; Visvader, J.E. Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell. Nature 2006, 439, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Shimono, Y.; Funakoshi, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Toyoda, M.; Kiyota, N.; Kono, S.; Takao, S.; Mukohara, T.; Minami, H. Adipose-derived stem cells enhance human breast cancer growth and cancer stem cell-like properties through adipsin. Oncogene 2019, 38, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.T.; Damm, D.; Hancock, N.; Rosen, B.S.; Lowell, B.B.; Usher, P.; Flier, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Human adipsin is identical to complement factor D and is expressed at high levels in adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9210–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, W.; Brestoff, J.R.; Rohatgi, N.; Wu, X.; Atkinson, J.P.; Harris, C.A.; Teitelbaum, S.L. Fat-Produced Adipsin Regulates Inflammatory Arthritis. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveridge, C.J.; Slater, S.; Campbell, K.J.; Nam, N.A.; Knight, J.; Ahmad, I.; Hedley, A.; Lilla, S.; Repiscak, P.; Patel, R.; et al. BRF1 accelerates prostate tumourigenesis and perturbs immune infiltration. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.J.; Kim, S.; Jang, B.H.; Chang, S.H.; Yun, U.J.; Park, K.M.; Waki, H.; Li, D.Y.; Tontonoz, P.; Park, K.W. Small Molecule-Induced Complement Factor D (Adipsin) Promotes Lipid Accumulation and Adipocyte Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Ljubicic, S.; Leibiger, B.; Kern, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kelly, M.E.; Chatterjee Bhowmick, D.; Murano, I.; Cohen, P.; et al. Adipsin is an adipokine that improves β cell function in diabetes. Cell 2014, 158, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, N.; Kraakman, M.J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Costa, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; et al. Adipsin promotes bone marrow adiposity by priming mesenchymal stem cells. eLife 2021, 10, e69209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuru, H.; Osaka, M.; Hiraoka, Y.; Yoshida, M. HFD-induced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation are decreased in Factor D deficient mouse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Banoy, N.; Guseh, J.S.; Li, G.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Chen, T.; Poirier, B.; Putzel, G.; Rosselot, C.; Pabon, M.A.; Camporez, J.P.; et al. Adipsin preserves beta cells in diabetic mice and associates with protection from type 2 diabetes in humans. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Tsukaguchi, H.; Morita, H.; Higasa, K.; Tran, M.T.N.; Hamada, M.; Usui, T.; Morito, N.; Horita, S.; Hayashi, T.; et al. A mutation in transcription factor MAFB causes Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis with Duane Retraction Syndrome. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, B.A.; Flaat, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Patel, B.; Ripoll, C. Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 2008, 45, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, Y.; Mukohara, T.; Shimono, Y.; Funakoshi, Y.; Chayahara, N.; Toyoda, M.; Kiyota, N.; Takao, S.; Kono, S.; Nakatsura, T.; et al. Comparison of 2D- and 3D-culture models as drug-testing platforms in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Hattori, S.; Kariya, R.; Iwanaga, S.; Taura, M.; Harada, H.; Suzu, S.; Okada, S. Comparative study of human hematopoietic cell engraftment into BALB/c and C57BL/6 strain of Rag-2/Jak3 double-deficient mice. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 539748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrick, M.; Luckett, J.; Yue, L.; Stover, C. Dual role of complement in adipose tissue. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nae, S.; Bordeianu, I.; Stancioiu, A.T.; Antohi, N. Human adipose-derived stem cells: Definition, isolation, tissue-engineering applications. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 919–924. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hutson, I.; Akk, A.M.; Mascharak, S.; Pham, C.T.N.; Hourcade, D.E.; Brown, R.; Atkinson, J.P.; Harris, C.A. Contribution of Adipose-Derived Factor D/Adipsin to Complement Alternative Pathway Activation: Lessons from Lipodystrophy. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divella, R.; De Luca, R.; Abbate, I.; Naglieri, E.; Daniele, A. Obesity and cancer: The role of adipose tissue and adipo-cytokines-induced chronic inflammation. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 2346–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, S.; Catalano, S. The multifactorial role of leptin in driving the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 8, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Adipocyte biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active facilitator. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 69, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, A.J.; Balaban, S.; Saunders, D.N. Adipocyte-Tumor Cell Metabolic Crosstalk in Breast Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzoros, C.; Petridou, E.; Dessypris, N.; Chavelas, C.; Dalamaga, M.; Alexe, D.M.; Papadiamantis, Y.; Markopoulos, C.; Spanos, E.; Chrousos, G.; et al. Adiponectin and breast cancer risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.; Koo, J.S. The Role of Adipokines and Bone Marrow Adipocytes in Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnoni, A.; Brunetti, O.; Longo, V.; Calabrese, A.; Argentiero, A.L.; Calbi, R.; Solimando Antonio, G.; Licchetta, A. Immune system and bone microenvironment: Rationale for targeted cancer therapies. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yan, B.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Chen, K.; Zhou, C.; Sun, L.; Qian, W.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, Q.; et al. Paracrine HGF/c-MET enhances the stem cell-like potential and glycolysis of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of YAP/HIF-1α. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, G.; Hackenberg, M.; Catalina, P.; Boulaiz, H.; Grinan-Lison, C.; Garcia, M.A.; Peran, M.; Lopez-Ruiz, E.; Ramirez, A.; Morata-Tarifa, C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell’s secretome promotes selective enrichment of cancer stem-like cells with specific cytogenetic profile. Cancer Lett. 2018, 429, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, E.; Weller, M.; Weiss, T.; Ventura, E.; Burghardt, I.; Szabo, E. Negative control of the HGF/c-MET pathway by TGF-β: A new look at the regulation of stemness in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bacco, F.; Casanova, E.; Medico, E.; Pellegatta, S.; Orzan, F.; Albano, R.; Luraghi, P.; Reato, G.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Porrati, P.; et al. The MET oncogene is a functional marker of a glioblastoma stem cell subtype. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.; Gaggianesi, M.; Catalano, V.; Benfante, A.; Iovino, F.; Biffoni, M.; Apuzzo, T.; Sperduti, I.; Volpe, S.; Cocorullo, G.; et al. CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leenders, G.J.; Sookhlall, R.; Teubel, W.J.; de Ridder, C.M.; Reneman, S.; Sacchetti, A.; Vissers, K.J.; van Weerden, W.; Jenster, G. Activation of c-MET induces a stem-like phenotype in human prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26753. [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio, A.M. VEGF/Neuropilin Signaling in Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Shimokawa, M.; Date, S.; Takano, A.; Matano, M.; Nanki, K.; Ohta, Y.; Toshimitsu, K.; Nakazato, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; et al. A Colorectal Tumor Organoid Library Demonstrates Progressive Loss of Niche Factor Requirements during Tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Liu, Y.; Sharma, S.; Wu, K.; Chan, M.D.; Lo, H.W.; Carpenter, R.L.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Zhou, X.; Qasem, S.A.; et al. Activation of the c-Met Pathway Mobilizes an Inflammatory Network in the Brain Microenvironment to Promote Brain Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4970–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, S.V.; Carson, M.; el-Kabbani, O.; Kilpatrick, J.M.; Moore, D.; Chen, X.; Bugg, C.E.; Volanakis, J.E.; DeLucas, L.J. Structure of human factor D. A complement system protein at 2.0 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizuno, M.; Khaledian, B.; Maeda, M.; Hayashi, T.; Mizuno, S.; Munetsuna, E.; Watanabe, T.; Kono, S.; Okada, S.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Adipsin-Dependent Secretion of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates the Adipocyte-Cancer Stem Cell Interaction. Cancers 2021, 13, 4238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164238
Mizuno M, Khaledian B, Maeda M, Hayashi T, Mizuno S, Munetsuna E, Watanabe T, Kono S, Okada S, Suzuki M, et al. Adipsin-Dependent Secretion of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates the Adipocyte-Cancer Stem Cell Interaction. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164238
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizuno, Masahiro, Behnoush Khaledian, Masao Maeda, Takanori Hayashi, Seiya Mizuno, Eiji Munetsuna, Takashi Watanabe, Seishi Kono, Seiji Okada, Motoshi Suzuki, and et al. 2021. "Adipsin-Dependent Secretion of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates the Adipocyte-Cancer Stem Cell Interaction" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164238
APA StyleMizuno, M., Khaledian, B., Maeda, M., Hayashi, T., Mizuno, S., Munetsuna, E., Watanabe, T., Kono, S., Okada, S., Suzuki, M., Takao, S., Minami, H., Asai, N., Sugiyama, F., Takahashi, S., & Shimono, Y. (2021). Adipsin-Dependent Secretion of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates the Adipocyte-Cancer Stem Cell Interaction. Cancers, 13(16), 4238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164238









