CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis through ERK–ZEB1 Signaling
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Tissue Sections and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. XTT Colorimetric Assay
2.5. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assays
2.6. Flow Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis and CD44 Expression
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. In Vivo Metastasis Mouse Model
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
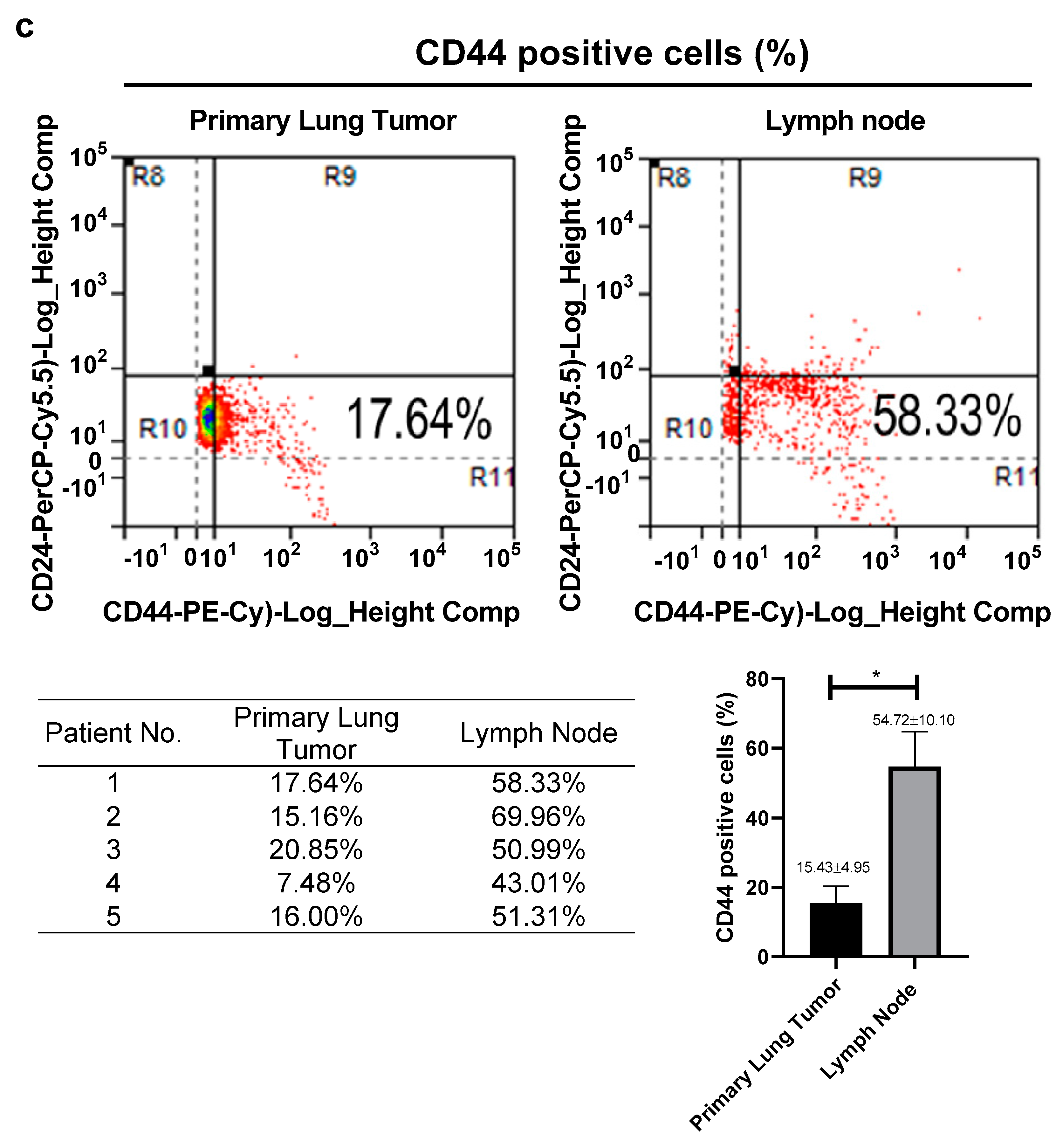
3.1. High Expression of CD44 in Primary Tumors and Lymph Nodes Is Associated with Poor Survival of Lung Cancer Patients
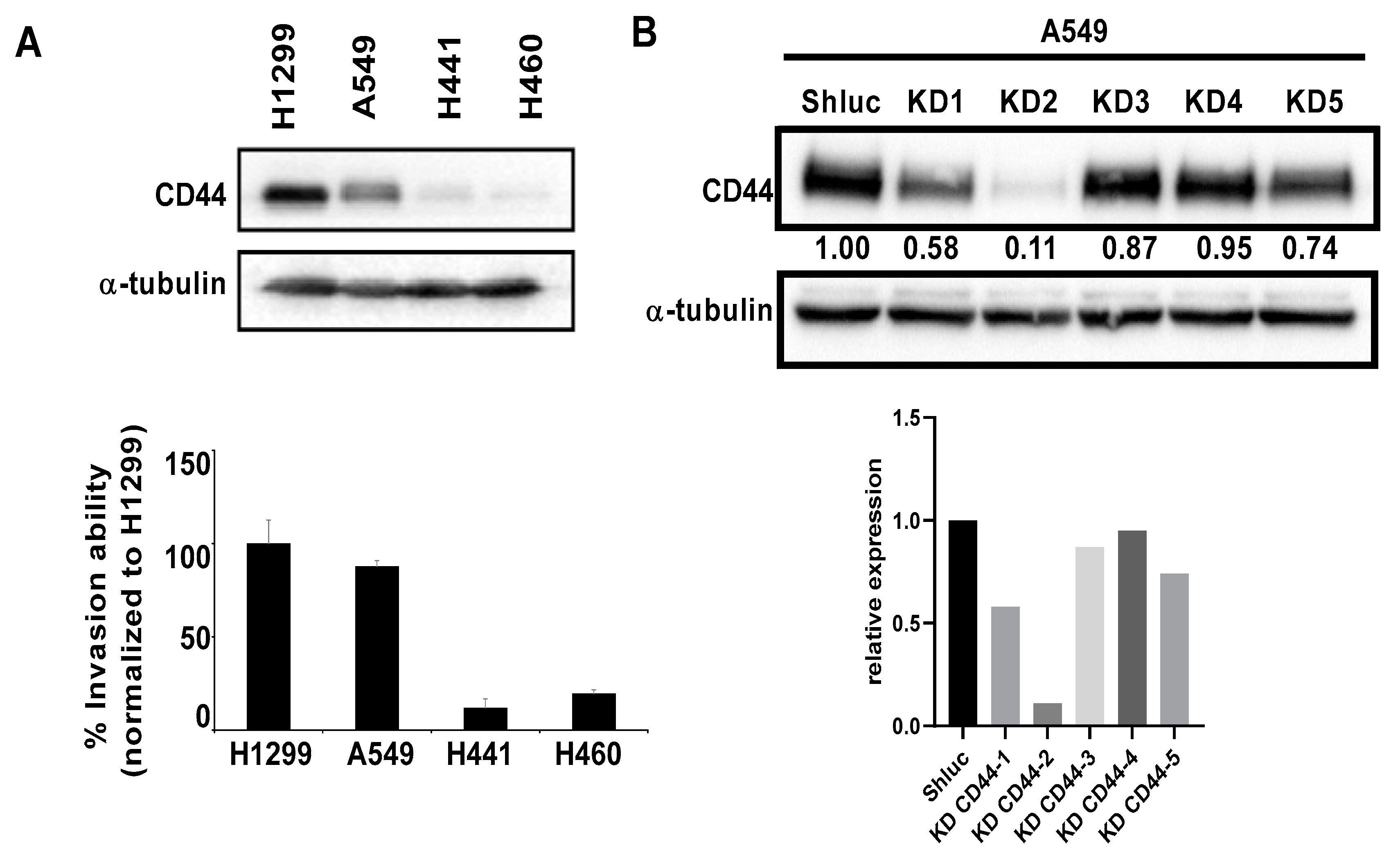
3.2. The Migration and Invasion Abilities of Lung Cancer Cells Were Reduced after CD44 Knockdown In Vitro
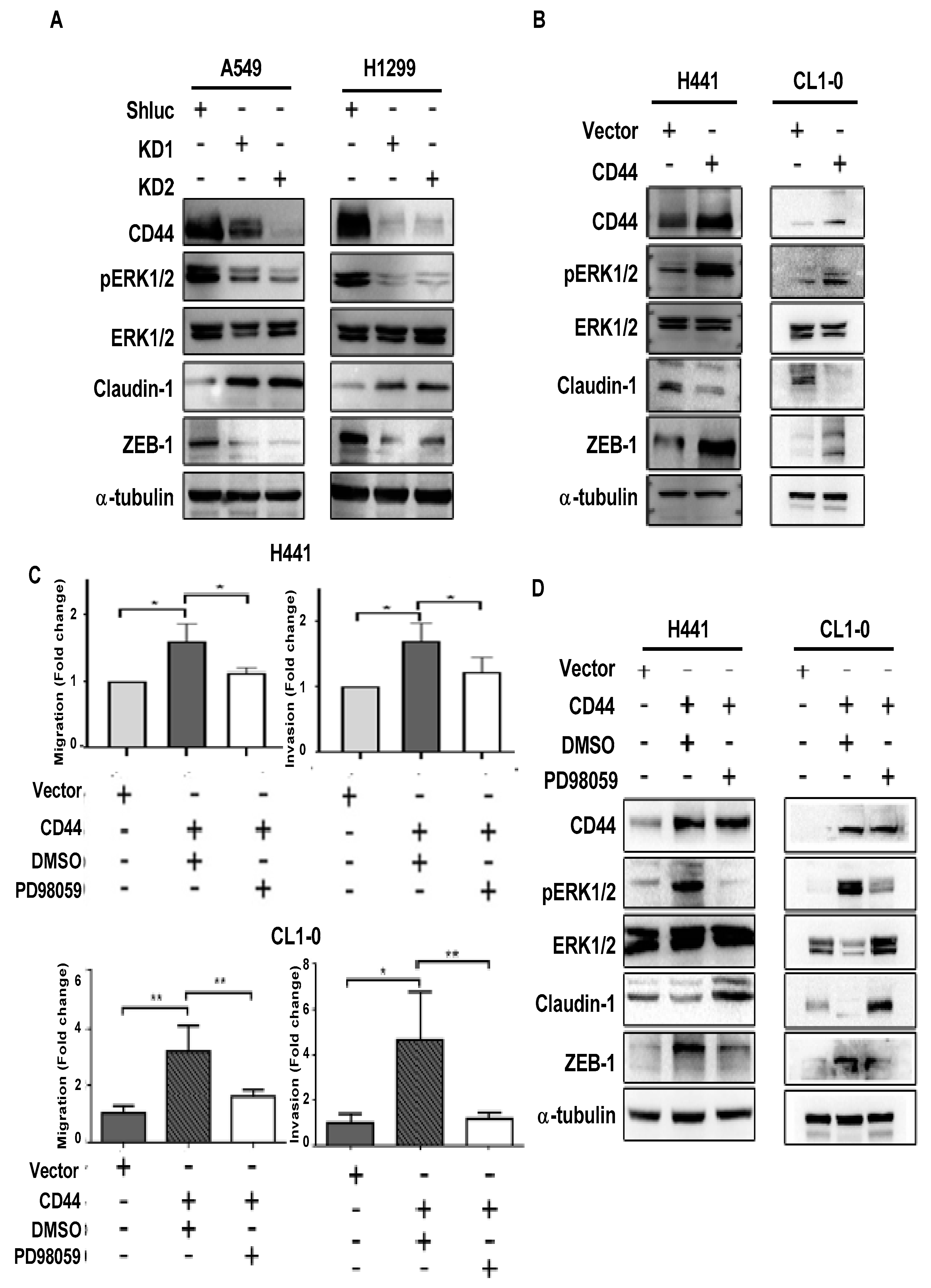
3.3. CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through ERK Pathway
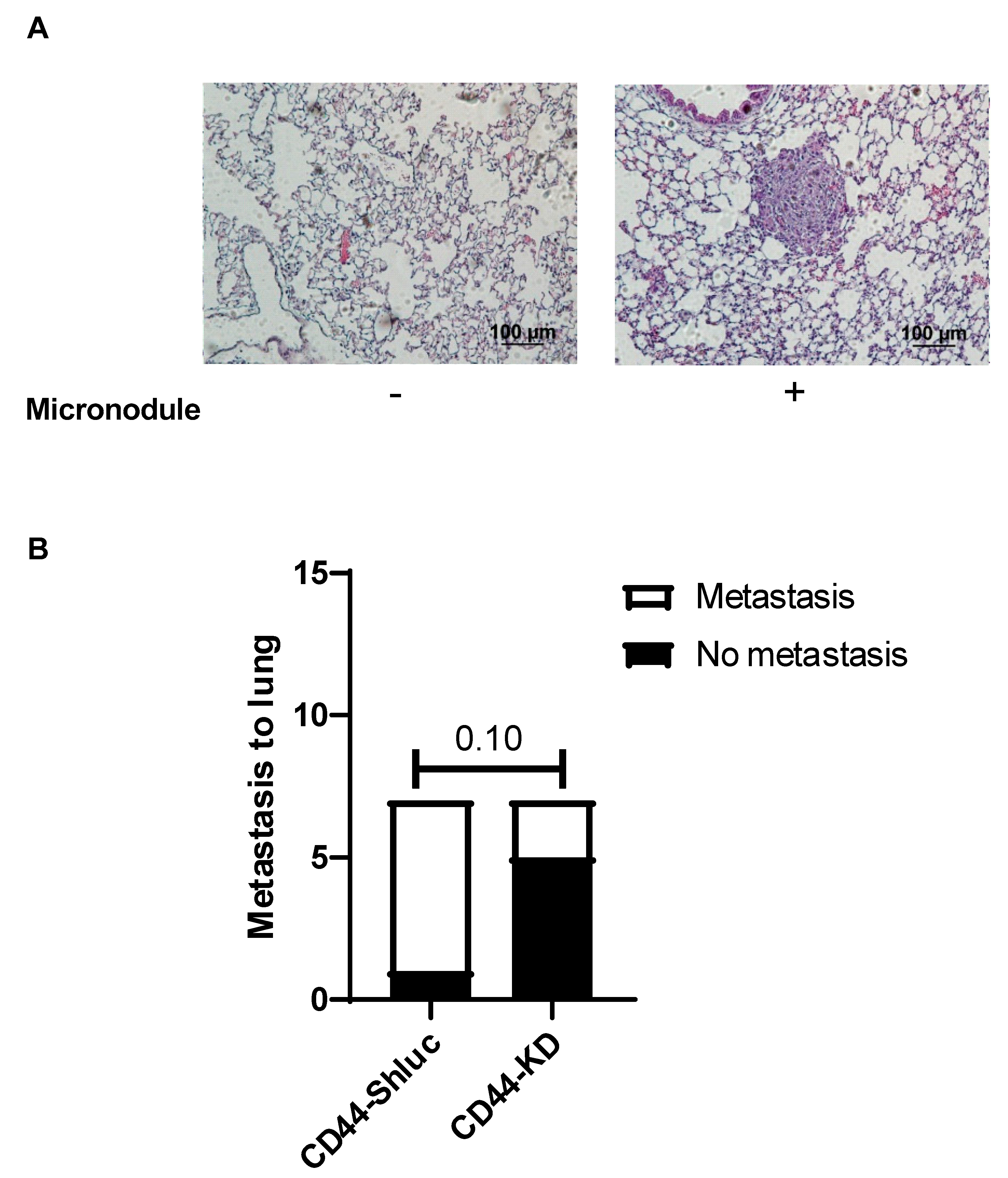
3.4. Effect of CD44 on Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mittal, V. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in aggressive lung cancers. In Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine: Novel Therapies and Clinical Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloza, E.M.; Harpole, L.; McCrory, D.C. Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of the current evidence. Chest 2003, 123, 137S–146S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, H.; Nichols, F.C.; Yang, P.; Allen, M.S.; Cassivi, S.D.; Deschamps, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pairolero, P.C. Survival after recurrent nonsmall-cell lung cancer after complete pulmonary resection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morath, I.; Hartmann, T.; Orian-Rousseau, V. CD44: More than a mere stem cell marker. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wang, G.; He, S.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Human cancer cells with stem cell-like phenotype exhibit enhanced sensitivity to the cytotoxicity of IL-2 and IL-15 activated natural killer cells. Cell. Immunol. 2016, 300, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazka, L.; Tesarik, R.; Turanek, J. Regulation of alternative splicing of CD44 in cancer. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Modi, S.; McGinn, O.; Zhao, X.; Dudeja, V.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Saluja, A.K. Impaired synthesis of stromal components in response to minnelide improves vascular function, drug delivery, and survival in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponta, H.; Sherman, L.; Herrlich, P.A. CD44: From adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Keller, E.T.; Garfield, D.H.; Shen, K.; Wang, J. Stromal cells in tumor microenvironment and breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, B.P. Activation of β-catenin and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kane, K.T.; Collins, M.A.; Simeone, D.M.; di Magliano, M.P.; Nguyen, K.T. CD44 regulates pancreatic cancer invasion through MT1-MMP. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.H.; Lim, S.W.; Huh, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.R. CD44 enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in association with colon cancer invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, B.; Pan, J.; Zhao, T.; Ji, J.; Zhang, C.; Che, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Chitinase 3-like 1-CD44 interaction promotes metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through β-catenin/Erk/Akt signaling in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Ishi, Y.; Motegi, H.; Okamoto, M.; Ou, Y.; Chen, J.; Yamaguchi, S. Overexpression of CD44 is associated with a poor prognosis in grade II/III gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 145, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wu, G.S.; Wu, K. Enrichment of CD44 in basal-type breast cancer correlates with EMT, cancer stem cell gene profile, and prognosis. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Zheng, L.Z.; Guo, W.J. Expression of CD44 in pancreatic cancer and its significance. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6724–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wu, R.-R.; Lv, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Hao, Q.-L.; Li, W. Prognostic value of CD44 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3632. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Si, J.; Xiong, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y. Blockade of Notch3 inhibits the stem-like property and is associated with ALDH1A1 and CD44 via autophagy in non-small lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.L.-H.; Fiscus, R.R.; Tung, J.W.; Tin, V.P.-C.; Cheng, L.C.; Sihoe, A.D.-L.; Fink, L.M.; Ma, Y.; Wong, M.P. Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Hsu, H.; Tyan, S.; Li, F.; Shew, J.; Lee, W.; Chen, J. Serglycin in tumor microenvironment promotes non-small cell lung cancer aggressiveness in a CD44-dependent manner. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Yo, Y.-T.; Lee, H.-Y.; Liao, Y.-P.; Chao, T.-K.; Su, P.-H.; Lai, H.-C. ALDH1-bright epithelial ovarian cancer cells are associated with CD44 expression, drug resistance, and poor clinical outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, M.; Nagano, O.; Tateyama, S.; Ohmura, M.; Yae, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Sugihara, E.; Onishi, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Yanagawa, H. Modulation of glucose metabolism by CD44 contributes to antioxidant status and drug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, B.P.; Slomiany, M.G. Hyaluronan, CD44 and Emmprin: Partners in cancer cell chemoresistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2008, 11, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, R.; Takahashi, F.; Cui, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Gu, T.; Sasaki, S.; Tominaga, S.; Nishio, K.; Tanabe, K.K.; Takahashi, K. Interaction between CD44 and hyaluronate induces chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-S.F.; Hou, M.-F.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lo, S. Role of MRE11 in Cell Proliferation, Tumor Invasion, and DNA Repair in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lo, S.; Tseng, L.-M.; Chen, D.-R.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Yuan, S.-S.F. Visfatin Mediates Malignant Behaviors through Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Intermediary in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Győrffy, B.; Surowiak, P.; Budczies, J.; Lánczky, A. Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.; Hsin, I.; Yang, T.; Sung, W.; Chi, J.; Chang, J.; Ko, J.; Sheu, G. The ERK–ZEB1 pathway mediates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in pemetrexed resistant lung cancer cells with suppression by vinca alkaloids. Oncogene 2017, 36, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian-Rousseau, V. CD44 acts as a signaling platform controlling tumor progression and metastasis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhaba, R.; Zöller, M. CD44 in cancer progression: Adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J. Mol. Histol. 2004, 35, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zou, Q.; Ge, R.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y. The critical role of CD133+ CD44+/high tumor cells in hematogenous metastasis of liver cancers. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ruan, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Duan, J.; Zhang, F.; Ding, R.; et al. Knockdown of CD44 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma both in vitro and in vivo by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7828–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Oh, S.; Lee, K.-m.; Yoo, S.-a.; Shin, I. CD44 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via modulation of c-Src transcription in human breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cui, R.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J. Overexpression of CD44 is associated with the occurrence and migration of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Guo, T. CD44 is functionally crucial for driving lung cancer stem cells metastasis through Wnt/β-catenin-FoxM1-Twist signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Yang, Y.-P.; Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wu, W.-W.; Lu, K.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-L.; Lee, S.-D.; et al. The subpopulation of CD44-positive cells promoted tumorigenicity and metastatic ability in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Murakami, I.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Tan, A.-C.; Mizuuchi, H.; Rozeboom, L.; Ellison, K.; Rivard, C.J.; Mitsudomi, T. CD44 facilitates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotypic change at acquisition of resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Nan, Y. ADAMTS8 targets ERK to suppress cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, T.; Pramanik, K.K.; Nath, N.; Mishra, P.; Singh, A.K.; Nagini, S.; Rana, A.; Mishra, R. Crosstalk between Raf-MEK-ERK and PI3K-Akt-GSK3β signaling networks promotes chemoresistance, invasion/migration and stemness via expression of CD44 variants (v4 and v6) in oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2018, 86, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Ohuchida, K.; Fei, S.; Zheng, B.; Guan, W.; Feng, H.; Kibe, S.; Ando, Y.; Koikawa, K.; Abe, T. Inhibition of ERK1/2 in cancer-associated pancreatic stellate cells suppresses cancer–stromal interaction and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Liu, H.; Kong, Q.; Li, B. Overexpression of ZEB1 associated with metastasis and invasion in patients with gastric carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 366, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Dai, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Overexpression of zinc finger E-box binding homeobox factor 1 promotes tumor invasiveness and confers unfavorable prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 11977–11984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, R.; Huang, G. Overexpression of ZEB1 relates to metastasis and invasion in osteosarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, N.; Pang, X.; Cao, J.; Ma, N.; Pang, H.; Liu, L.; et al. Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 promotes invasion and bone metastasis of small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.C.; Pan, S.H.; Yang, S.C.; Yu, S.L.; Che, T.F.; Lin, C.W.; Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.C.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; et al. Claudin-1 is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.E.; Nathan, V.; Osborne, J.K.; Farrow, R.K.; Deb, D.; Sullivan, J.P.; Dospoy, P.D.; Augustyn, A.; Hight, S.K.; Sato, M. ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3219–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Lu, L.; Huang, C. CD44 inhibition attenuates EGFR signaling and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in human EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-Y.; Vadhan, A.; Chen, P.-H.; Lee, Y.-L.; Chao, C.-Y.; Cheng, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hu, S.C.-S.; Yuan, S.-S.F. CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis through ERK–ZEB1 Signaling. Cancers 2021, 13, 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164057
Wang Y-Y, Vadhan A, Chen P-H, Lee Y-L, Chao C-Y, Cheng K-H, Chang Y-C, Hu SC-S, Yuan S-SF. CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis through ERK–ZEB1 Signaling. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164057
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yen-Yun, Anupama Vadhan, Ping-Ho Chen, Yen-Lung Lee, Chih-Yeh Chao, Kuang-Hung Cheng, Yu-Chiuan Chang, Stephen Chu-Sung Hu, and Shyng-Shiou F. Yuan. 2021. "CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis through ERK–ZEB1 Signaling" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164057
APA StyleWang, Y.-Y., Vadhan, A., Chen, P.-H., Lee, Y.-L., Chao, C.-Y., Cheng, K.-H., Chang, Y.-C., Hu, S. C.-S., & Yuan, S.-S. F. (2021). CD44 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis through ERK–ZEB1 Signaling. Cancers, 13(16), 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164057






