Glioblastomas within the Subventricular Zone Are Region-Specific Enriched for Mesenchymal Transition Markers: An Intratumoral Gene Expression Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
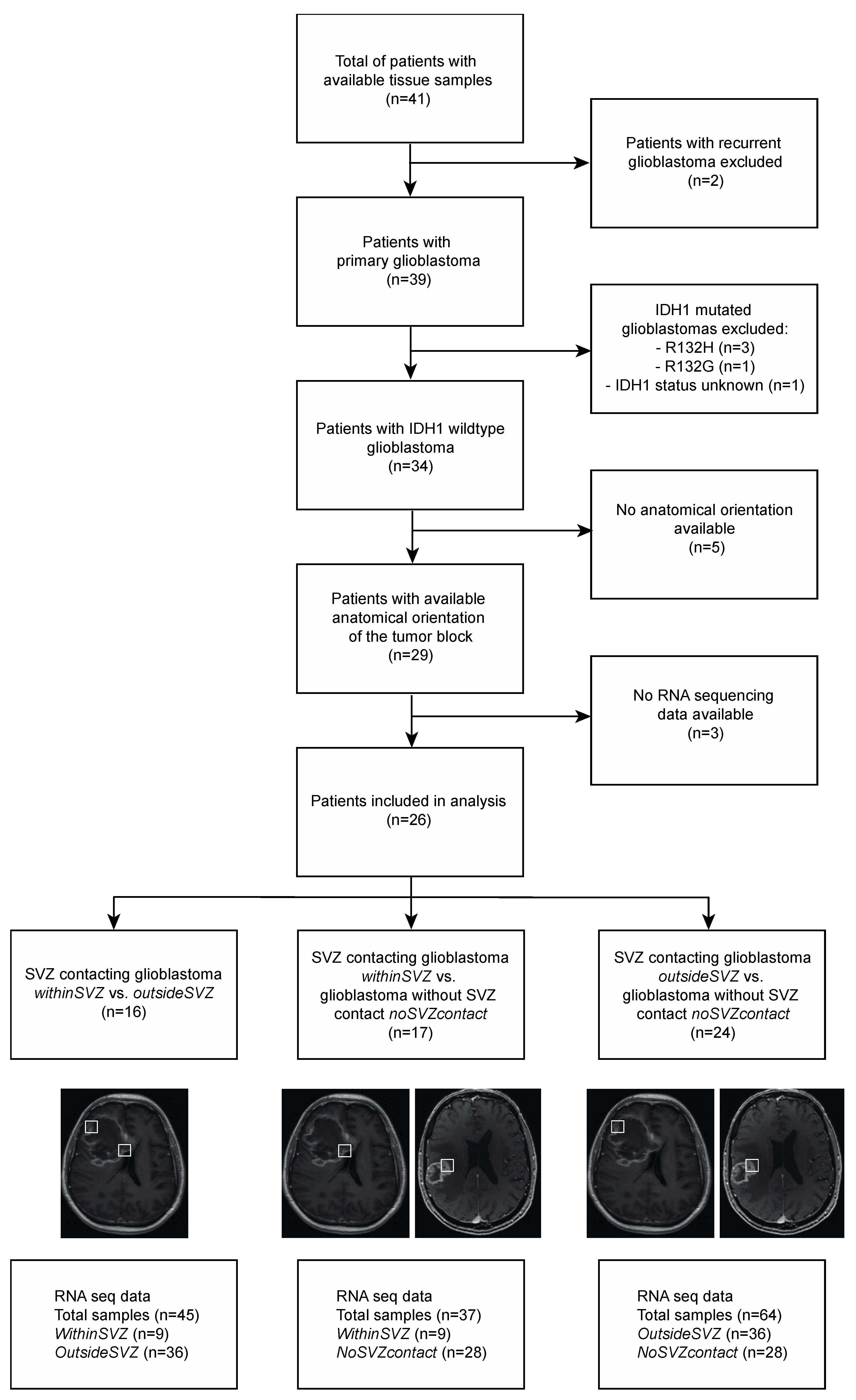
2.1. Patient Cohort and Baseline Characteristics
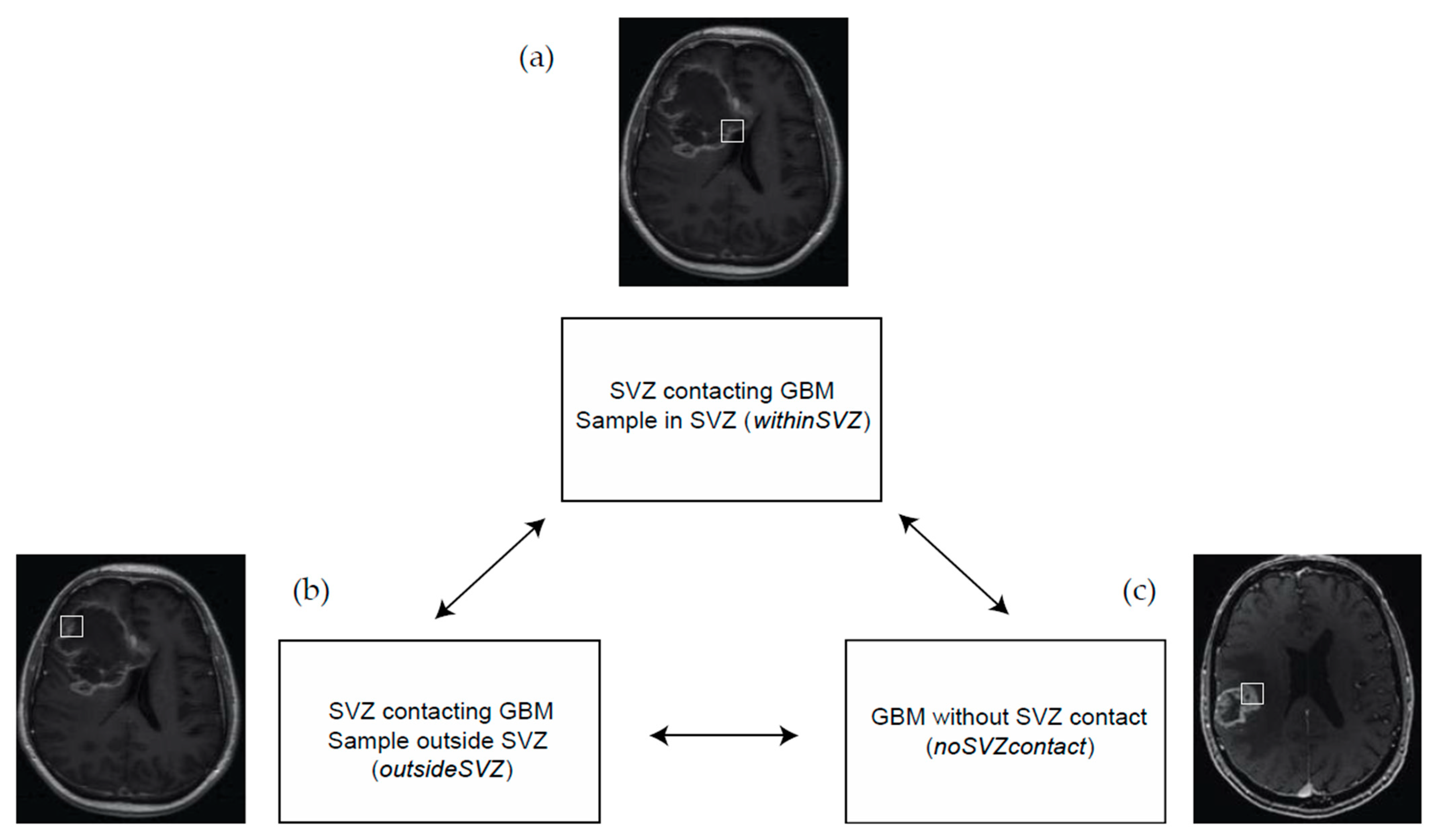
2.2. MRI Analysis and Tissue Block Selection
2.3. RNA Sequencing Data Selection
2.4. RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
3. Results
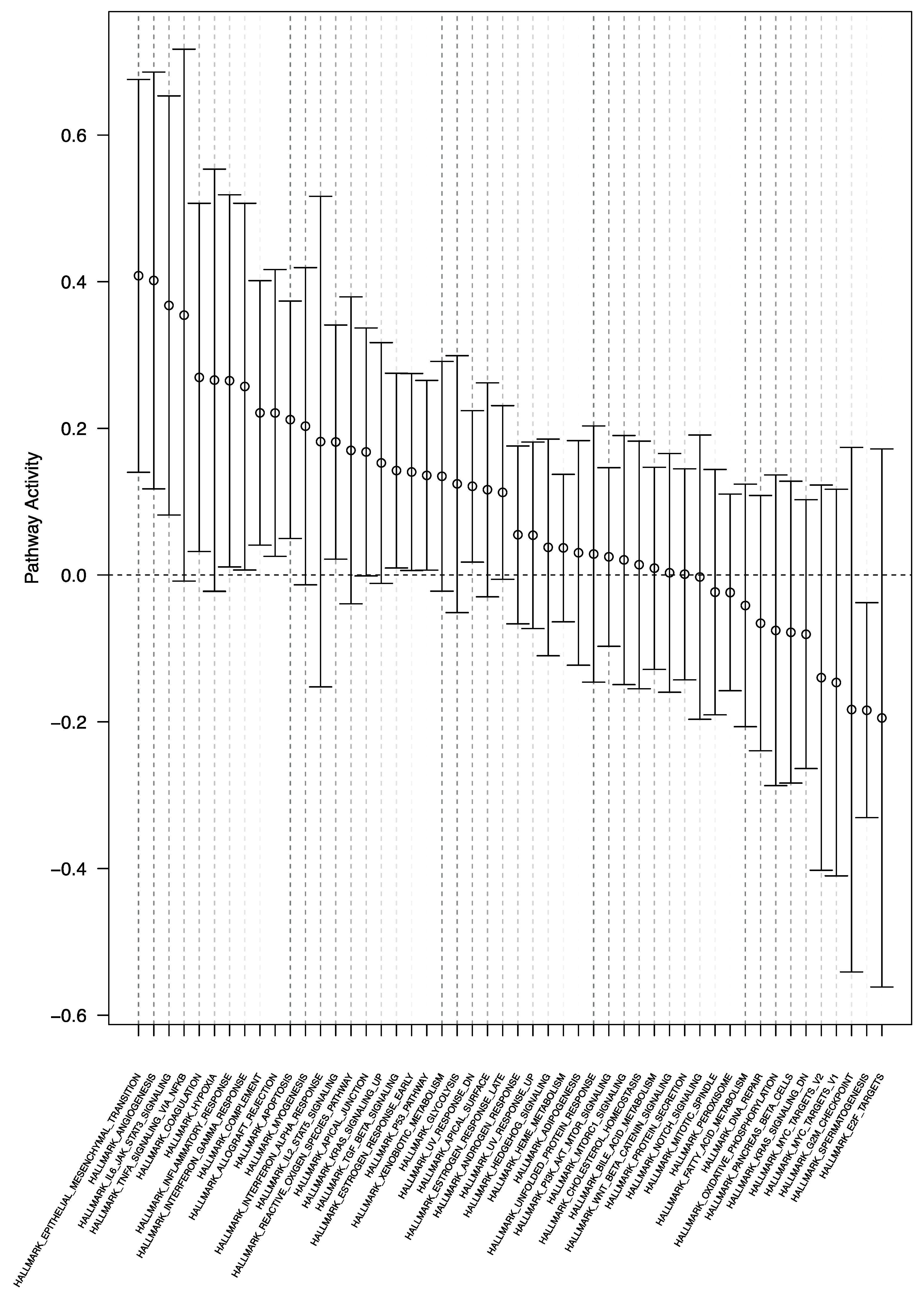
3.1. Differential Enrichment of Oncogenic Gene Sets across Tumor Regions: Intratumoral Analysis
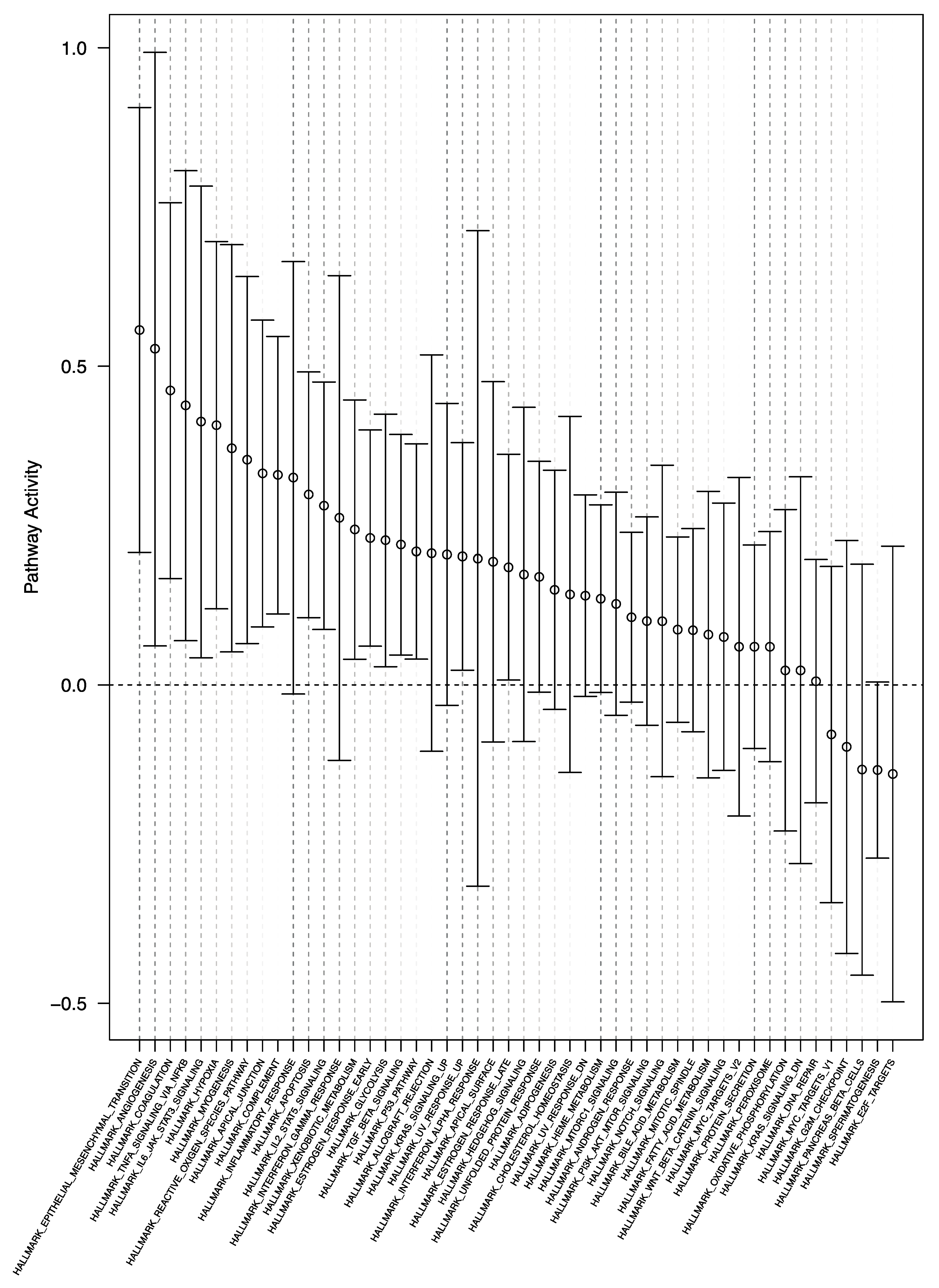
3.2. Differential Enrichment of Oncogenic Gene Sets in Glioblastomas in the SVZ Region: Intertumoral Analysis
3.3. No Difference in Oncogenic Signaling between Glioblastoma Samples from Outside the SVZ and Tumors without SVZ Contact: Intertumoral Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Tramontin, A.D.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Barbaro, N.M.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, S.; Lawton, M.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; et al. Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature 2004, 427, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaguno, S.A.; Chen, J.; Kwon, C.H.; Jackson, E.L.; Li, Y.; Burns, D.K.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Parada, L.F. Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kahng, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, S.J.; Um, J.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, J.K.; Park, J.; et al. Human glioblastoma arises from subventricular zone cells with low-level driver mutations. Nature 2018, 560, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, S.; van Bodegraven, E.; Seute, T.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Geurts, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Schoysman, L.; Huiszoon, W.B.; Varkila, M.; Rouss, S.; et al. Adverse prognosis of glioblastoma contacting the subventricular zone: Biological correlates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistry, A.M.; Wooten, D.J.; Davis, L.T.; Mobley, B.C.; Quaranta, V.; Ihrie, R.A. Ventricular-Subventricular Zone Contact by Glioblastoma is Not Associated with Molecular Signatures in Bulk Tumor Data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungk, C.; Mock, A.; Exner, J.; Geisenberger, C.; Warta, R.; Capper, D.; Abdollahi, A.; Friauf, S.; Lahrmann, B.; Grabe, N.; et al. Spatial transcriptome analysis reveals Notch pathway-associated prognostic markers in IDH1 wild-type glioblastoma involving the subventricular zone. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denicolaï, E.; Tabouret, E.; Colin, C.; Metellus, P.; Nanni, I.; Boucard, C.; Tchoghandjian, A.; Meyronet, D.; Baeza-Kallee, N.; Chinot, O.; et al. Molecular heterogeneity of glioblastomas; does location matter? Oncotarget 2016, 7, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, N.; Diehn, M.; Bredel, M.; Kuo, M.D. Illuminating radiogenomic characteristics of glioblastoma multiforme through integration of MR imaging, messenger RNA expression, and DNA copy number variation. Radiology 2014, 270, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappadakunnel, M.; Eskin, A.; Dong, J.; Nelson, S.F.; Mischel, P.S.; Liau, L.M.; Ngheimphu, A.L.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Goldin, J.; Pope, W.B. Stem cell associated gene expression in glioblastoma multiforme: Relationship to survival and the subventricular zone. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 96, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Li, X.; Qiu, B.; Jiang, T.; Wu, A. Can lateral ventricle contact predict the ontogeny and prognosis of glioblastoma? J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollapalli, K.; Ghantasala, S.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, R.; Rapole, S.; Moiyadi, S.E.; Srivastava, S. Subventricular zone involvement in Glioblastoma—A proteomic evaluation and clinicoradiological correlation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sottoriva, A.; Spiteri, I.; Piccirillo, S.G.; Peter Collins, V.; Marioni, J.C.; Curtis, C.; Watts, C.; Tavaré, S. Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4009–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonavia, R.; Inda, M.; Cavenee, W.K.; Furnari, F.B. Heterogeneity maintenance in glioblastoma: A social network. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4055–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puchalski, R.B.; Shah, N.; Miller, J.; Dalley, R.; Nomura, S.R.; Yoon, J.; Smith, K.A.; Lankerovich, M.; Bertagnolli, D.; Brickley, K.; et al. An anatomic transcriptional atlas of human glioblastoma. Science 2018, 11, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goffart, N.; Kroonen, J.; Di Valentin, E.; Dedobbeleer, M.; Denne, A.; Martinive, P.; Rogister, B. Adult mouse subventricular zones stimulate glioblastoma stem cells specific invasion through CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goffart, N.; Lombard, A.; Lallemand, F.; Kroonen, J.; Nassen, J.; Di Valentin, E.; Berendsen, S.; Dedobbeleer, M.; Willems, E.; Robe, P.A.; et al. CXCL12 mediates glioblastoma resistance to radiotherapy in the subventricular zone. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccirillo, S.G.M.; Spiteri, I.; Sottoriva, A.; Touloumis, A.; Ber, S.; Price, S.J.; Heywood, R.; Francis, N.; Howarth, K.D.; Collins, V.P.; et al. Contributions to drug resistance in glioblastoma derived from malignant cells in the sub-ependymal zone. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroonen, J.; Nassen, J.; Boulanger, Y.G.; Provenzano, F.; Capraro, V.; Bours, V.; Martin, D.; Deprez, M.; Robe, P.A.; Rogister, B. Human glioblastoma-initiating cells invade specifically the subventricular zones and olfactory bulbs of mice after striatal injection. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, K.P.L.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Vaillant, B.; Ezhilarasan, R.; Hummelink, K.; Hollingsworth, F.; Wani, K.; Heathcock, L.; James, J.D.; Goodman, L.D.; et al. Mesenchymal differentiation mediated by NF-kappaB promotes radiation resistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, E.Y.; Cooper, D.D.; Abbott, K.L.; Lennon, J.; Nagaraja, S.; Mackay, A.; Jones, C.; Vogel, H.; Jackson, P.K.; Monje, M. Neural precursor-derived pleiotrophin mediates subventricular zone invasion by glioma. Cell 2017, 170, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, S.; Kruyt, F.A.E.; Wagemakers, M.; Bhat, K.P.L.; den Dunnen, W.F.A. IL-8 associates with a pro-angiogenic and mesenchymal subtype in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15721–15731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.X.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, N.; Gong, W.; Huang, S. Constitutive NF-kappaB activity regulates the expression of VEGF and IL-8 and tumor angiogenesis of human glioblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Talasila, K.M.; Røsland, G.V.; Hagland, H.R.; Eskilsson, E.; Flones, I.H.; Fritah, S.; Azuaje, F.; Atai, N.; Harter, P.N.; Mittelbronn, M.; et al. The angiogenic switch leads to a metabolic shift in human glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, J.V.; Conroy, S.; Pavlov, K.; Sontakke, P.; Tomar, T.; Eggens-Meijer, E.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Wagemakers, M.; den Dunnen, W.F.A.; Kruyt, F.A.E. Hypoxia enhances migration and invasion in glioblastoma by promoting a mesenchymal shift mediated by the HIF1alpha-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnus, N.; Gerges, N.; Jabado, N.; Rak, J. Coagulation-related gene expression profile in glioblastoma is defined by molecular disease subtype. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carro, M.S.; Lim, W.K.; Alvarez, M.J.; Bollo, R.J.; Zhao, X.; Snyder, E.Y.; Sulman, E.P.; Anne, S.L.; Doetsch, F.; Colman, H.; et al. The transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain tumours. Nature 2010, 463, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.A.D.; Gutman, D.A.; Chisolm, C.; Appin, C.; Kong, J.; Rong, Y.; Kurc, T.; van Meir, E.; Saltz, J.H.; Moreno, C.S.; et al. The tumor microenvironment strongly impacts master transcriptional regulators and gene expression class of glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halliday, J.; Helmy, K.; Pattwell, S.S.; Pitter, K.L.; LaPlant, Q.; Ozawa, T.; Holland, E.C. In vivo radiation response of proneural glioma characterized by protective p53 transcriptional program and proneural-mesenchymal shift. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5248–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherry, M.M.; Reeves, A.; Wu, J.K.; Cochran, B.H. STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singer, E.; Judkins, J.; Salomonis, N.; Matlaf, L.; Soteropoulos, P.; McAllister, S.; Soroceanu, L. Reactive oxygen species-mediated therapeutic response and resistance in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Zhou, P. DCAFs, the missing link of the CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, M.; Kwon, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jen, K.; et al. CUL4A induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Han, J.; Meng, Q.; Xi, Q.; Wu, G.; Zhang, B. DCAF4L2 promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis via mediating degradation of NFkappab negative regulator PPM1B. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mangino, M.; Christiansen, L.; Stone, R.; Hunt, S.C.; Horvath, K.; Eisenberg, D.T.A.; Kimura, M.; Petersen, I.; Kark, J.D.; Herbig, U.; et al. DCAF4, a novel gene associated with leucocyte telomere length. J. Med. Genet 2015, 52, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellwege, J.N.; Russell, S.B.; Williams, S.M.; Edwards, T.L.; Velez Edwards, D.R. Gene-based evaluation of low-frequency variation and genetically-predicted gene expression impacting risk of keloid formation. Ann. Hum. Genet 2018, 82, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Owzar, K.; Han, Y.; Hung, R.J.; Brhane, Y.; McLaughlin, J.; Brennan, P.; et al. Functional variants in DCAF4 associated with lung cancer risk in European populations. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SVZ (n = 16) | Non-SVZ (n = 10) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender n (%) | 0.68 | ||
| Male | 7 (43.8%) | 3 (30%) | |
| Female | 9 (56.3%) | 7 (70%) | |
| Age mean (SD) | 62.1 (6.3) | 60.2 (8.4) | 0.51 |
| Initial KPS median (IQR) | 90 (28) | 90 (20) | 0.76 |
| Extent of resection n (%) | 0.35 | ||
| Total | 11 (68.8%) | 9 (90%) | |
| Subtotal | 5 (31.3%) | 1 (10%) | |
| Chemo and/or radiotherapy n (%) | 0.29 | ||
| Both | 14 (87.5%) | 9 (90%) | |
| Only chemotherapy | 0 | 1 (10%) | |
| Only radiotherapy | 0 | 0 | |
| None | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | |
| PTEN n (%) | 0.52 | ||
| Loss | 11 (68.8%) | 7 (70%) | |
| Normal | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | |
| Gain | 1 (6.2%) | 1 (10%) | |
| Missing | 2 (12.5%) | 2 (20%) | |
| MGMT Methylation n (%) | 0.4 | ||
| Yes | 7 (43.8%) | 2 (20%) | |
| No | 9 (56.3%) | 8 (80%) | |
| EGFR Amplification n (%) | 1 | ||
| Yes | 8 (50.0%) | 4 (40%) | |
| No | 6 (37.5%) | 4 (40%) | |
| Missing | 2 (12.5%) | 2 (20%) | |
| EGFR vIII n (%) | 0.62 | ||
| Yes | 3 (18.8%) | 3 (30%) | |
| No | 11 (68.8%) | 5 (50%) | |
| Missing | 2 (12.5%) | 2 (20%) | |
| Survival in days, median (IQR) | 442 (119) | 544 (137) | 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalemans, D.J.Z.; Berendsen, S.; Draaisma, K.; Robe, P.A.; Snijders, T.J. Glioblastomas within the Subventricular Zone Are Region-Specific Enriched for Mesenchymal Transition Markers: An Intratumoral Gene Expression Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153764
Dalemans DJZ, Berendsen S, Draaisma K, Robe PA, Snijders TJ. Glioblastomas within the Subventricular Zone Are Region-Specific Enriched for Mesenchymal Transition Markers: An Intratumoral Gene Expression Analysis. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153764
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalemans, Diana J. Z., Sharon Berendsen, Kaspar Draaisma, Pierre A. Robe, and Tom J. Snijders. 2021. "Glioblastomas within the Subventricular Zone Are Region-Specific Enriched for Mesenchymal Transition Markers: An Intratumoral Gene Expression Analysis" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153764
APA StyleDalemans, D. J. Z., Berendsen, S., Draaisma, K., Robe, P. A., & Snijders, T. J. (2021). Glioblastomas within the Subventricular Zone Are Region-Specific Enriched for Mesenchymal Transition Markers: An Intratumoral Gene Expression Analysis. Cancers, 13(15), 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153764






