Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
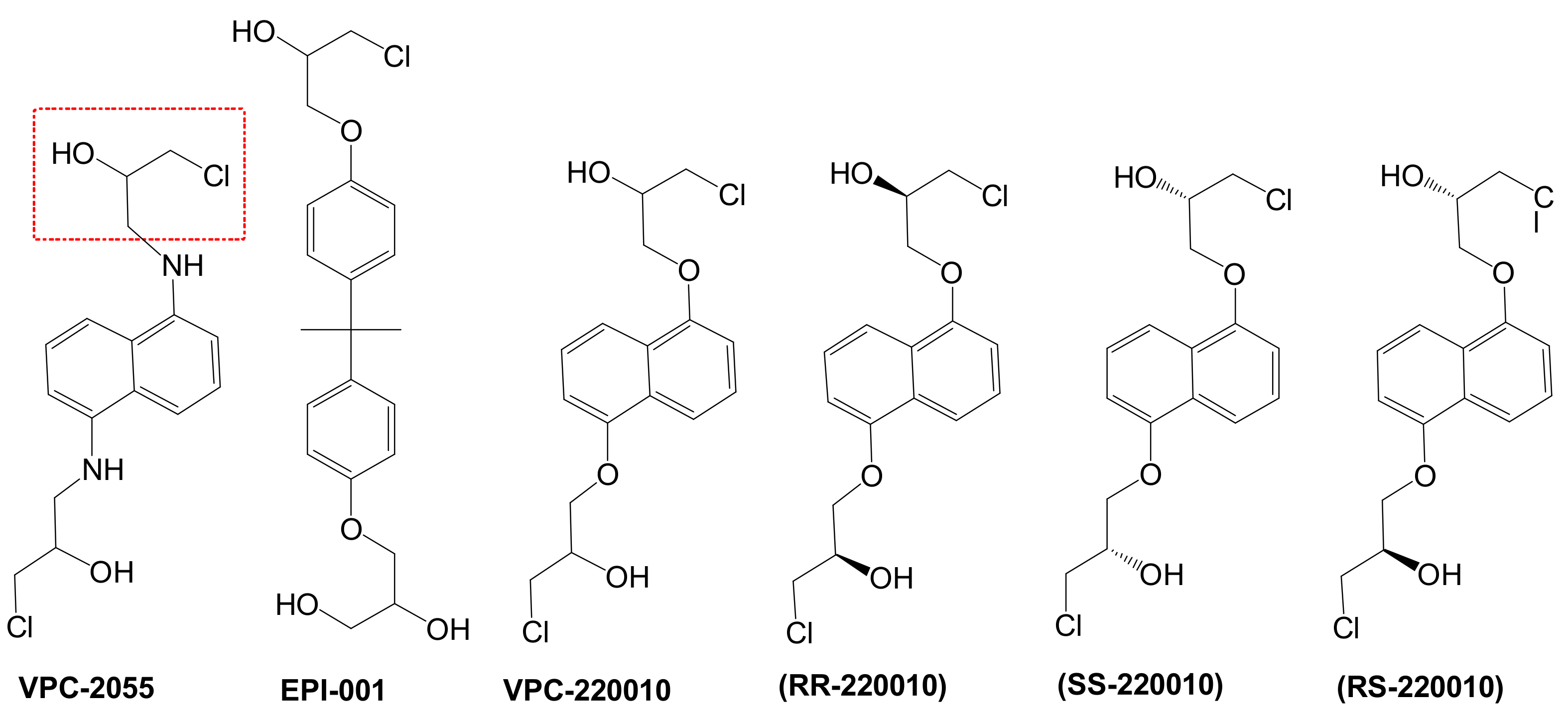
3.1. Determination of VPC-2055 as an AR-NTD Inhibitor
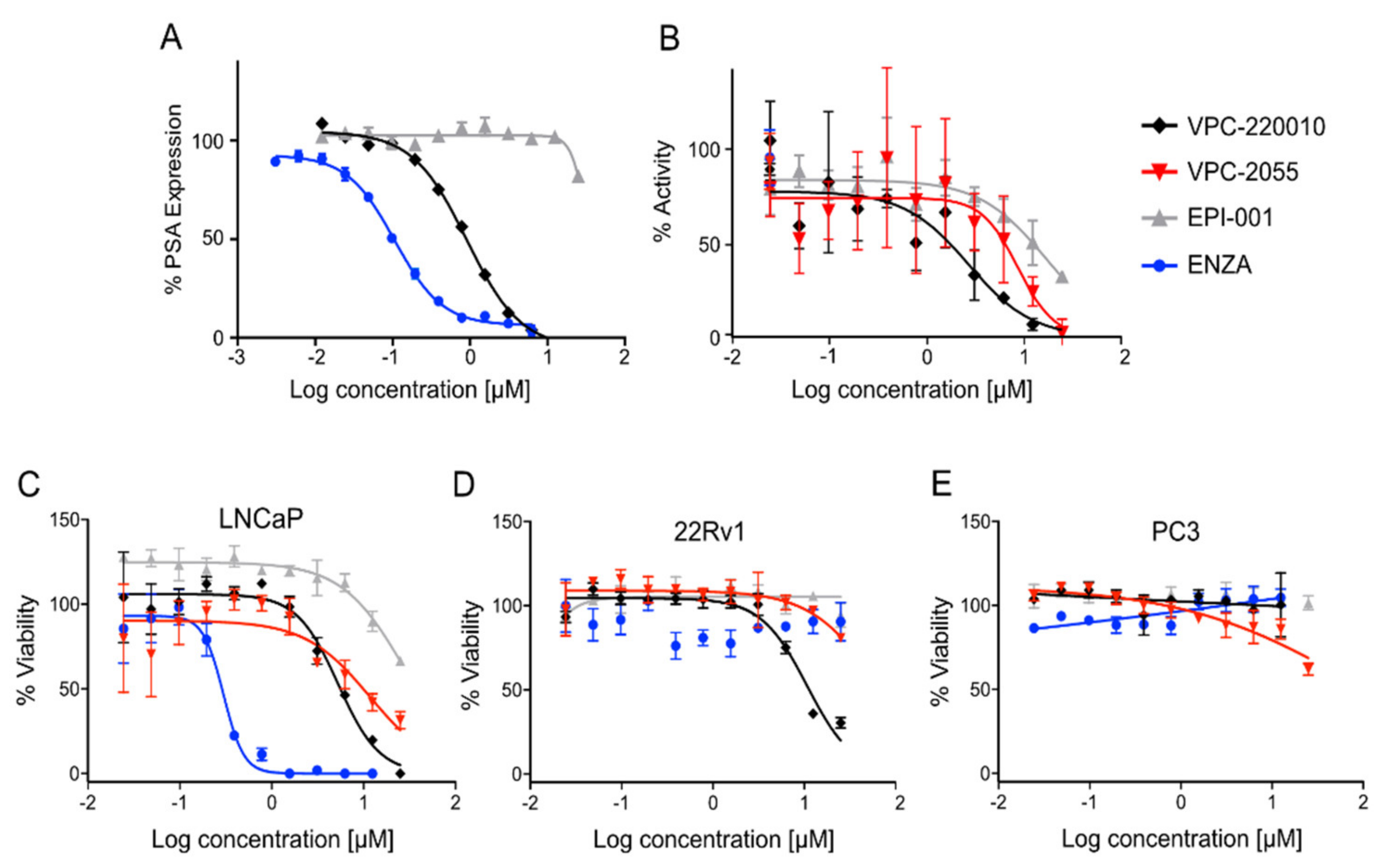
3.2. Identification of VPC-220010 as a Pan-Inhibitor of the AR
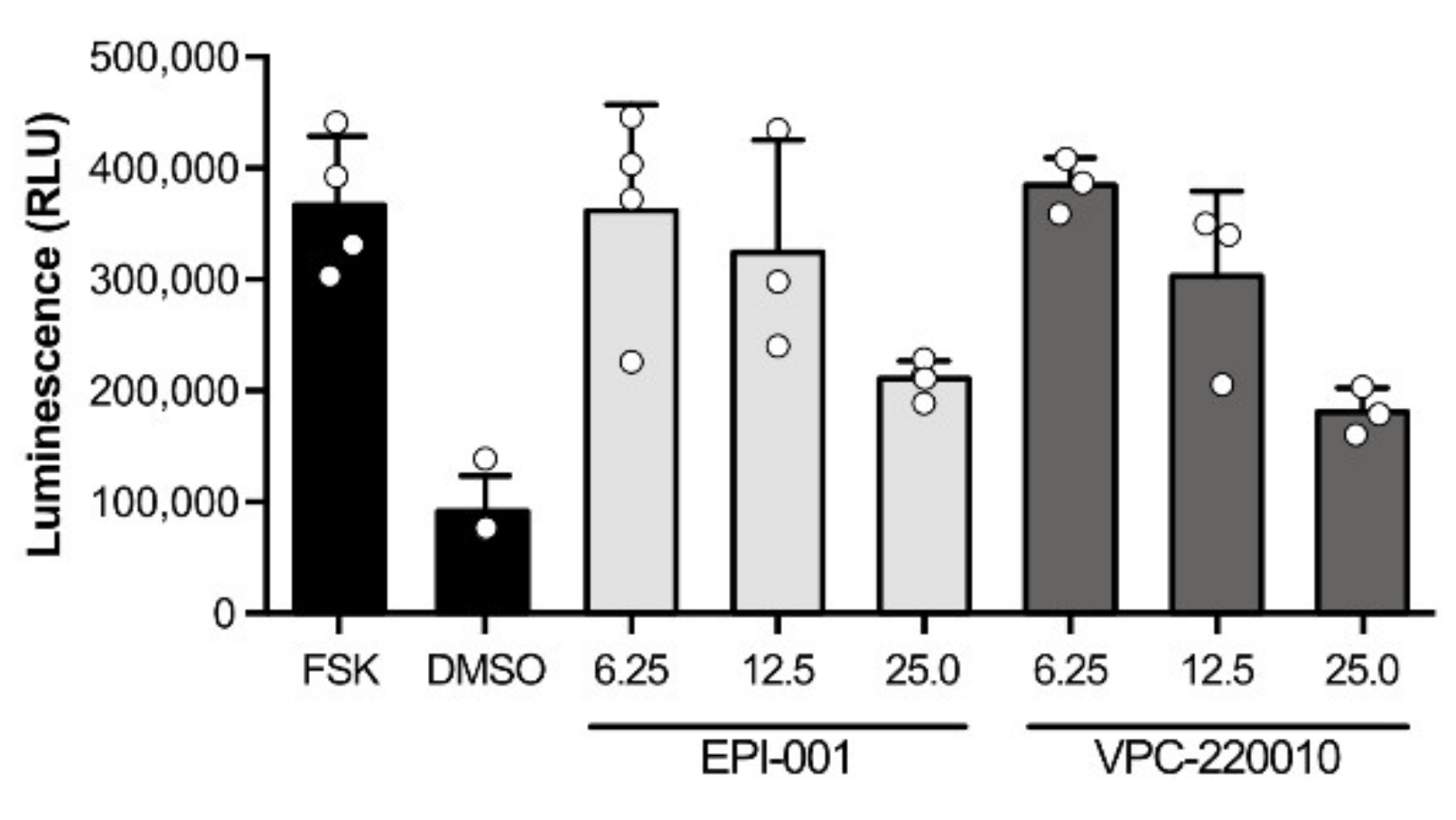
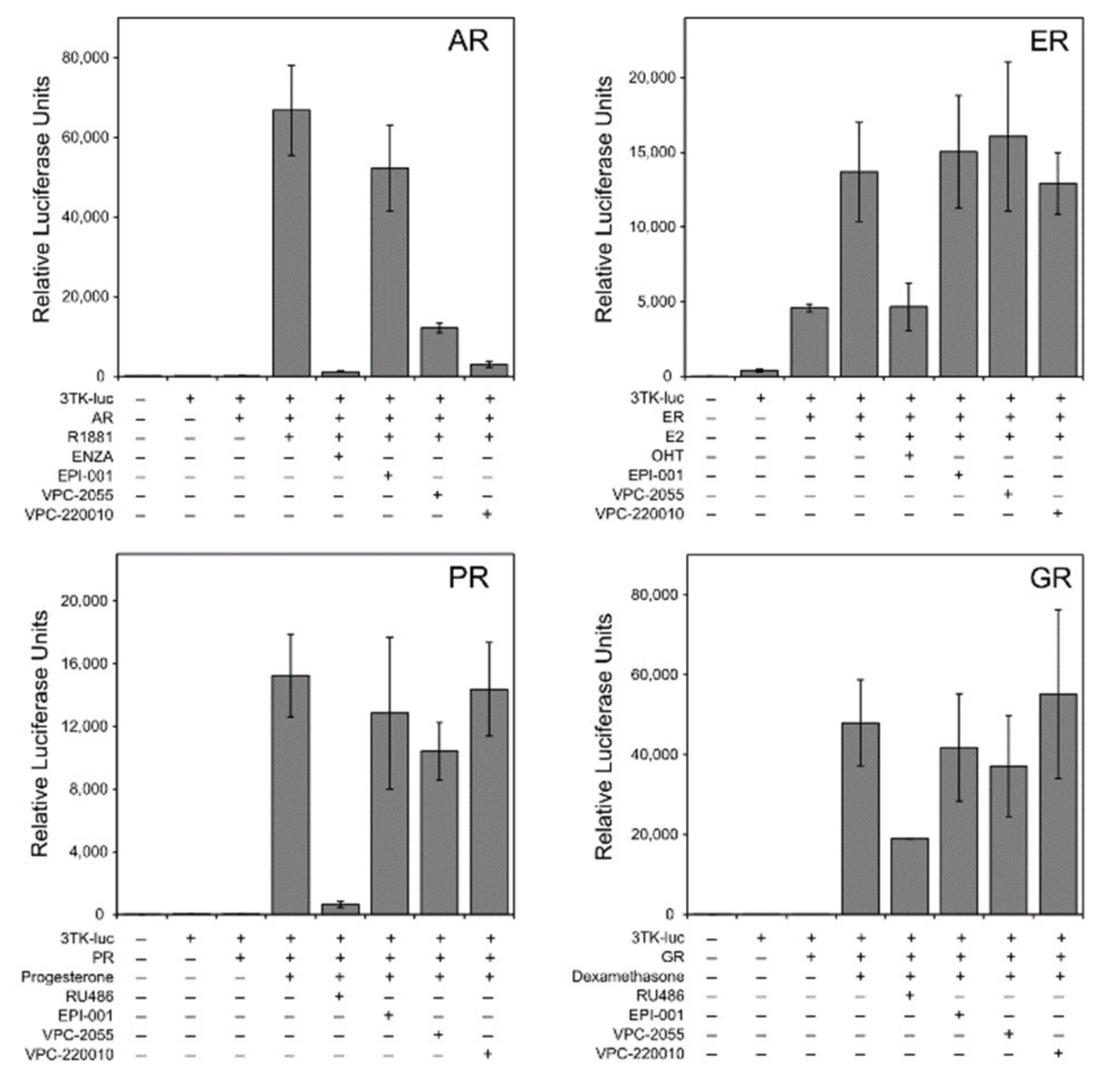
3.3. Specificity of VPC-220010 for the Androgen Receptor
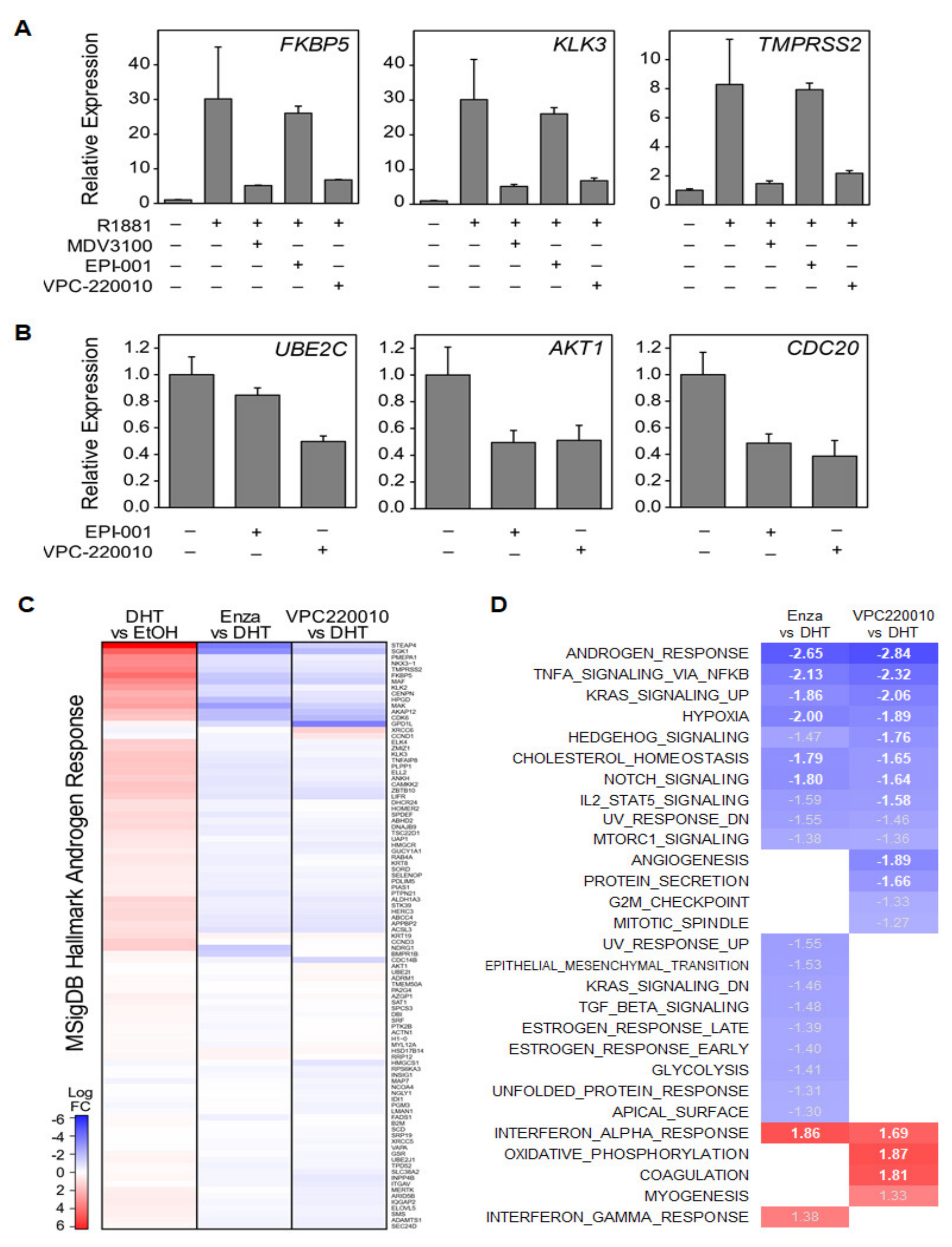
3.4. VPC-220010 Reduces DNA Binding and Expression of Androgen Response Genes
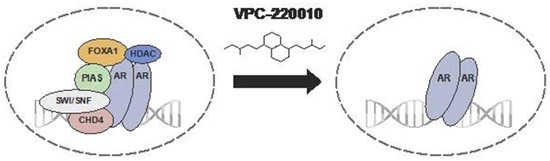
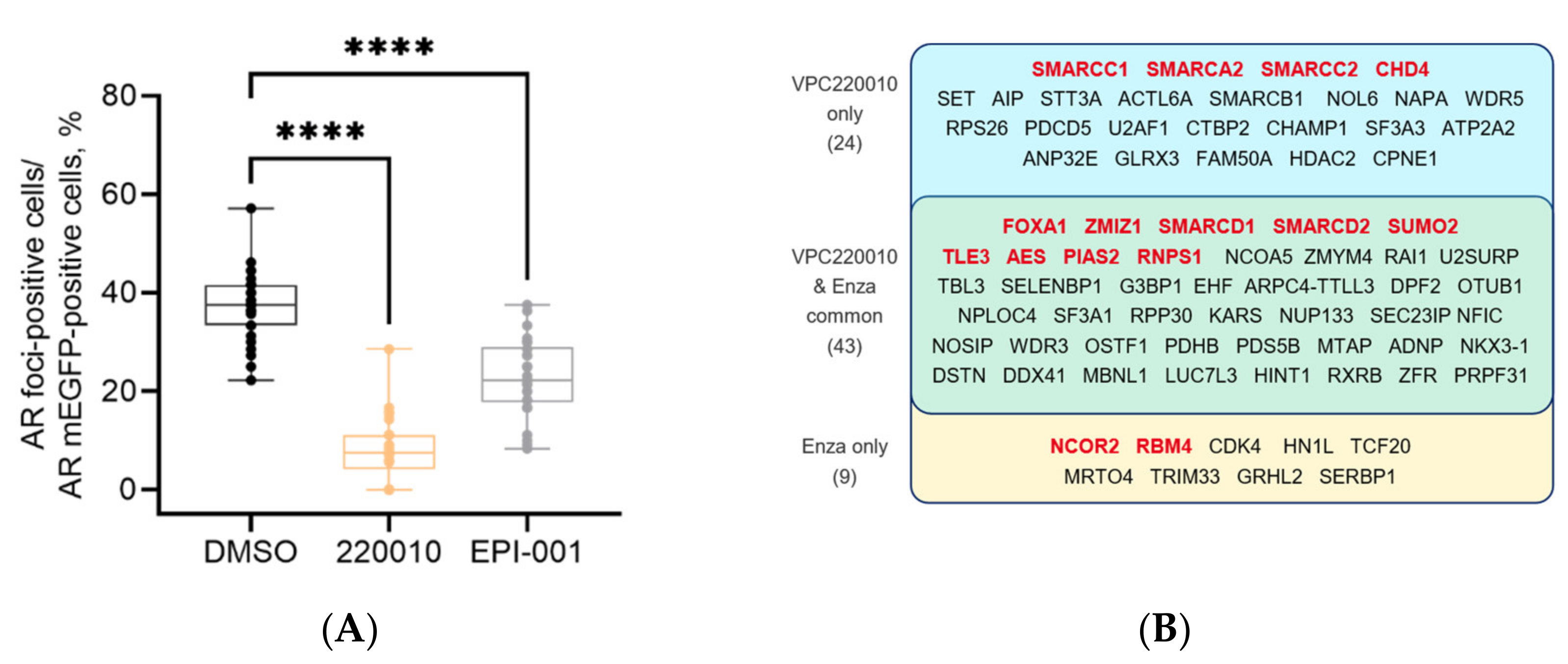
3.5. VPC-220010 Disrupts Interactions of AR with Its Cofactors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, D.A.; Dang, H.X.; Zhao, S.G.; Lloyd, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Alumkal, J.J.; Foye, A.; Kothari, V.; Perry, M.D.; Bailey, A.M.; et al. Genomic Hallmarks and Structural Variation in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, D.Y.; Spisák, S.; Seo, J.-H.; Bell, C.; O’Connor, E.; Korthauer, K.; Ribli, D.; Csabai, I.; Solymosi, N.; Szallasi, Z.; et al. A Somatically Acquired Enhancer of the Androgen Receptor Is a Noncoding Driver in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Sprenger, C.C.; Vessella, R.L.; Haugk, K.; Soriano, K.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Page, S.T.; Coleman, I.M.; Nguyen, H.M.; Sun, H.; et al. Castration resistance in human prostate cancer is conferred by a frequently occurring androgen receptor splice variant. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2715–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Chan, S.C.; Brand, L.J.; Hwang, T.H.; Silverstein, K.A.T.; Dehm, S.M. Androgen Receptor Splice Variants Mediate Enzalutamide Resistance in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simental, J.A.; Sar, M.; Lane, M.V.; French, F.S.; Wilson, E.M. Transcriptional activation and nuclear targeting signals of the human androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, D.N.; McEwan, I.J. Functional Characterization of the Native NH2-Terminal Transactivation Domain of the Human Androgen Receptor: Binding Kinetics for Interactions with TFIIF and SRC-1a. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3352–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, I.J.; Monaghan, A.E. A sting in the tail: The N-terminal domain of the androgen receptor as a drug target. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.J.; Mawji, N.R.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Haile, S.; Myung, J.-K.; Watt, K.; Tam, T.; Yang, Y.; Bañuelos, C.A.; et al. Regression of Castrate-Recurrent Prostate Cancer by a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Amino-Terminus Domain of the Androgen Receptor. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Chandhasin, C.; Osbourne, E.; Luo, J.; Sadar, M.D.; Perabo, F. Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of the Androgen Receptor: A New Approach for the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Moigne, R.; Zhou, H.-J.; Obst, J.K.; Banuelos, C.A.; Jian, K.; Williams, D.; Virsik, P.; Andersen, R.J.; Sadar, M.; Perabo, F.; et al. Lessons learned from the metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer phase I trial of EPI-506, a first-generation androgen receptor N-terminal domain inhibitor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 7). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, P.; Snoek, R.; Ray, M.; Rao, L.G.; Rennie, P.S. Rapid, non-destructive, cell-based screening assays for agents that modulate growth, death, and androgen receptor activation in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2007, 67, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimand, J.; Isserlin, R.; Voisin, V.; Kucera, M.; Tannus-Lopes, C.; Rostamianfar, A.; Wadi, L.; Meyer, M.; Wong, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Pathway enrichment analysis and visualization of omics data using g:Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 482–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelloo, S.; Nevedomskaya, E.; Kim, Y.; Hoekman, L.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Mirza, T.; Wessels, L.F.A.; van Weerden, W.M.; Altelaar, A.F.M.; Bergman, A.M.; et al. Endogenous androgen receptor proteomic profiling reveals genomic subcomplex involved in prostate tu-morigenesis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hassona, M.D.H.; Lack, N.A.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; Leblanc, E.; Tavassoli, P.; Kanaan, N.; Frewin, K.; Singh, K.; Adomat, H.; et al. Characterization of a new class of androgen receptor antagonists with potential therapeutic application in ad-vanced prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalal, K.; Ban, F.; Li, H.; Morin, H.; Roshan-Moniri, M.; Tam, K.J.; Shepherd, A.; Sharma, A.; Peacock, J.; Carlson, M.L.; et al. Selectively targeting the dimerization interface of human androgen receptor with small-molecules to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 437, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munuganti, R.S.N.; Leblanc, E.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; Labriere, C.; Frewin, K.; Singh, K.; Hassona, M.D.H.; Lack, N.A.; Li, H.; Ban, F.; et al. Targeting the Binding Function 3 (BF3) Site of the Androgen Receptor Through Virtual Screening. 2. Development of 2-((2-phenoxyethyl) thio)-1H-benzimidazole Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munuganti, R.S.; Hassona, M.D.; Leblanc, E.; Frewin, K.; Singh, K.; Ma, D.; Ban, F.; Hsing, M.; Adomat, H.; Lallous, N.; et al. Identification of a Potent Antiandrogen that Targets the BF3 Site of the Androgen Receptor and Inhibits Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lack, N.A.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; Tavassoli, P.; Han, F.Q.; Chan, K.H.; Feau, C.; Leblanc, E.; Guns, E.T.; Guy, R.; Rennie, P.S.; et al. Targeting the Binding Function 3 (BF3) Site of the Human Androgen Receptor through Virtual Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8563–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heemers, H.V.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen Receptor (AR) Coregulators: A Diversity of Functions Converging on and Regulating the AR Transcriptional Complex. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 778–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boija, A.; Klein, I.A.; Sabari, B.R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Coffey, E.L.; Zamudio, A.V.; Li, C.H.; Shrinivas, K.; Manteiga, J.C.; Hannett, N.M.; et al. Transcription Factors Activate Genes through the Phase-Separation Capacity of Their Activation Domains. Cell 2018, 175, 1842–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabari, B.R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Boija, A.; Klein, I.A.; Coffey, E.L.; Shrinivas, K.; Abraham, B.J.; Hannett, N.M.; Zamudio, A.V.; Manteiga, J.C.; et al. Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science 2018, 361, eaar3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradner, J.E.; Hnisz, D.; Young, R.A. Transcriptional Addiction in Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wong, S.; Lee, J.; Lingadahalli, S.; Wells, C.; Saxena, N.; Sanchez, C.; Sun, B.; Parra-Nuñez, A.K.; Chan, N.; et al. Dynamic phase separation of the androgen receptor and its coactivators to regulate gene expression. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Taylor, C.; Brown, G.D.; Papachristou, E.; Carroll, J.; D’Santos, C.S. Rapid immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry of endogenous proteins (RIME) for analysis of chromatin complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenster, G.; van der Korput, H.A.G.M.; Trapman, J.; Brinkmann, A.O. Identification of Two Transcription Activation Units in the N-terminal Domain of the Human Androgen Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7341–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Tu, W.H.; Yang, N.; Qin, H.; Sun, Z. ZMIZ1 Preferably Enhances the Transcriptional Activity of Androgen Receptor with Short Polyglutamine Tract. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, K.A.; Brown, G.D.; Carroll, J.S. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (ChIP-seq) for Mapping of Estrogen Receptor-Chromatin Interactions in Breast Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1366, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marshall, T.W.; Link, K.A.; Petre-Draviam, C.E.; Knudsen, K.E. Differential Requirement of SWI/SNF for Androgen Receptor Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30605–30613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
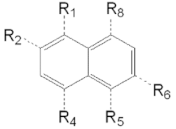
| VPCID | R1 | R2 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R8 | eGFP IC50 (μM) | PSA IC50 (μM) | PC3-iV7 IC50 (μM) | T1/2 (min.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220009 |  | 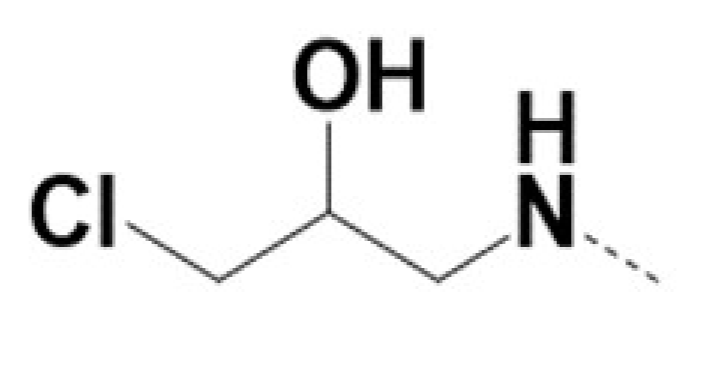 | 1 | 1 | NA | |||||
| 220010 | 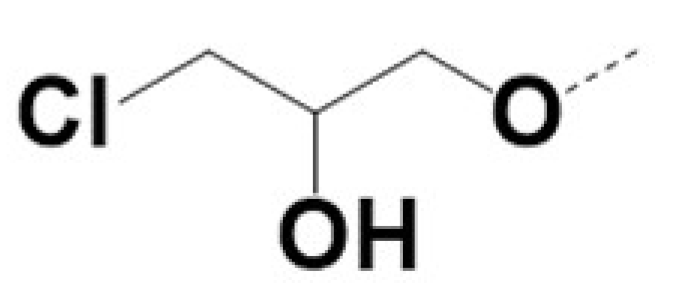 | 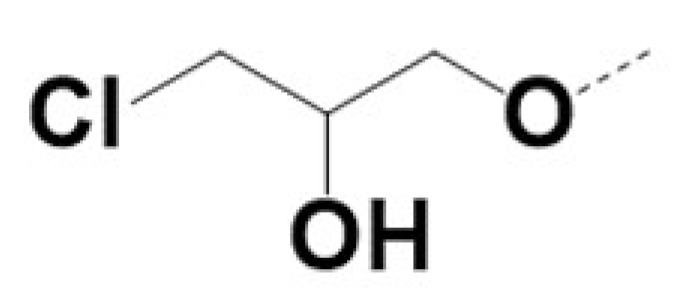 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 30 | ||||
| 220027 | 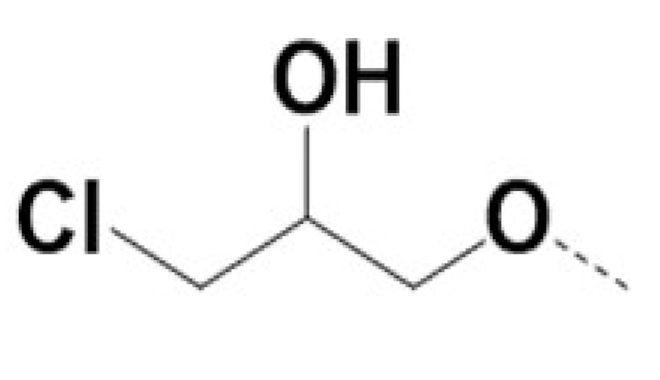 | Br |  | Br | 3 | 4 | 4 | TBD | ||
| 220028 | 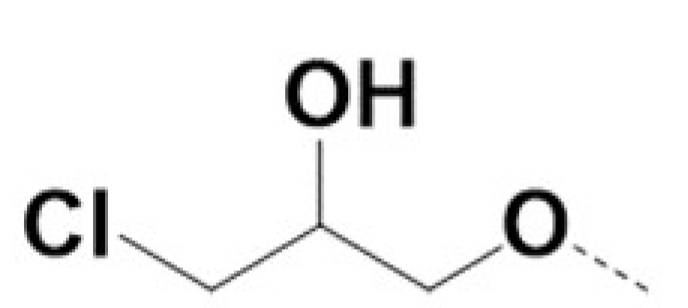 | Br | 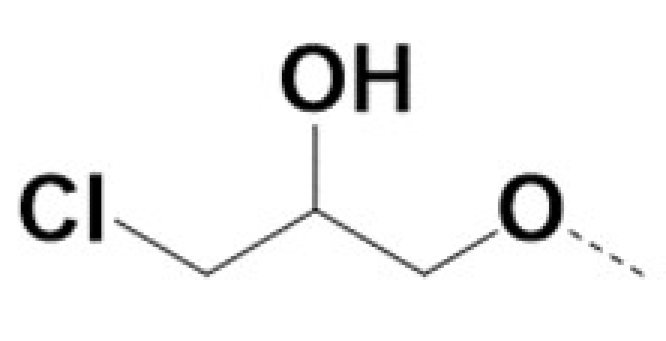 | Br | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3 | NA | ||
| 220054 | 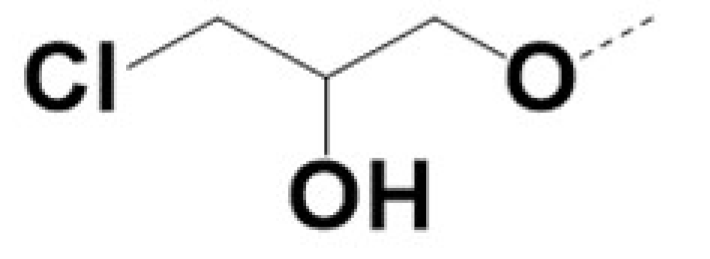 | 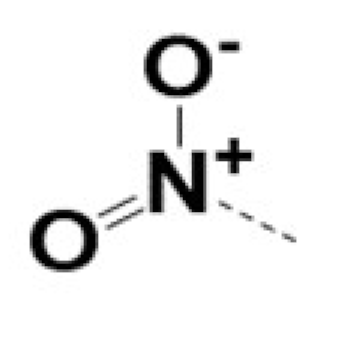 | 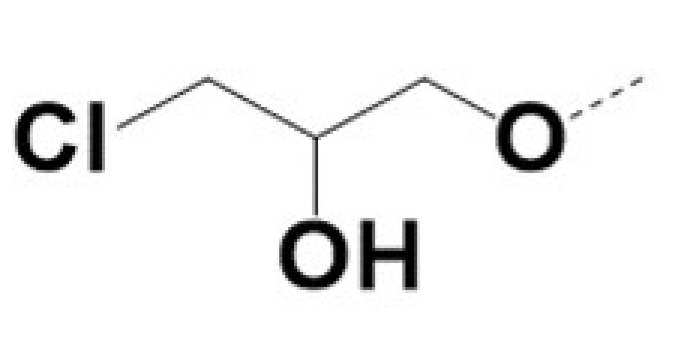 | 5 | 5 | 3 | NA | |||
| 220057 | 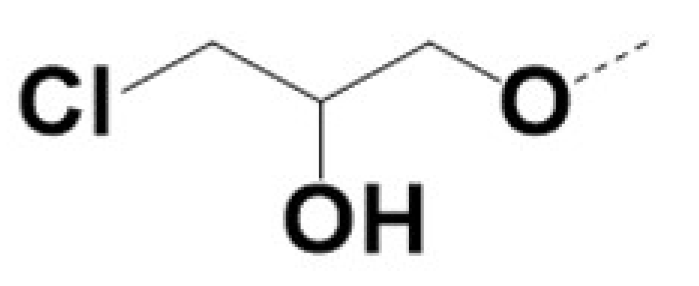 | 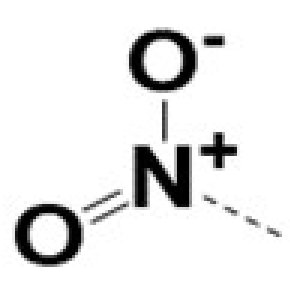 | 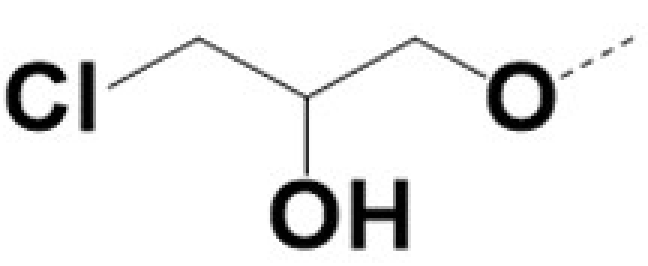 | 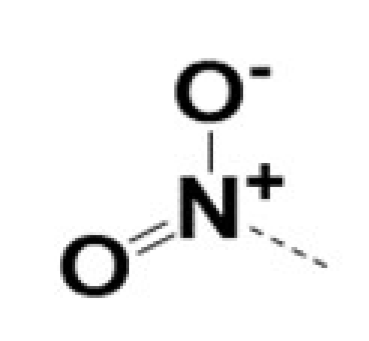 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 462 | ||
| 220062 | 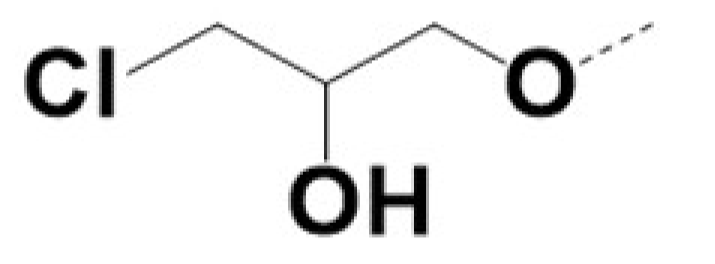 | Br | 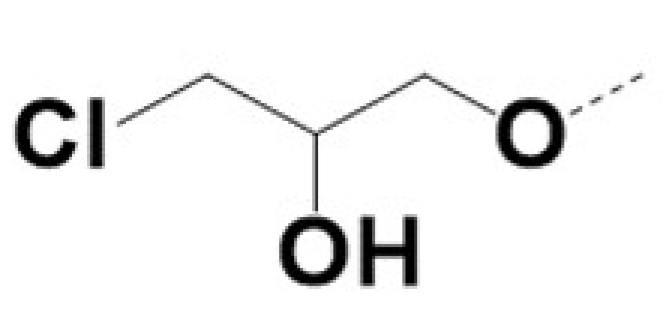 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 36 | |||
| 220075 | 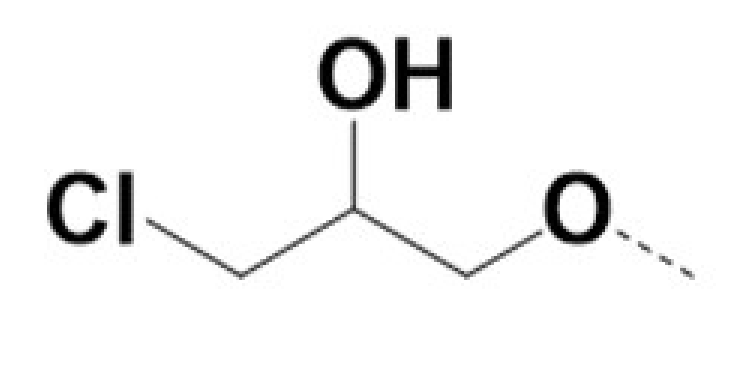 | 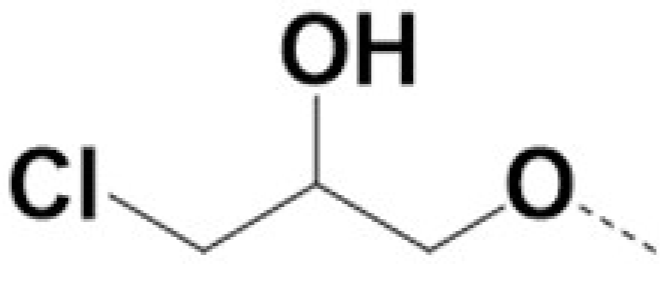 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 12 | 18 | ||||
| RR-220010 | 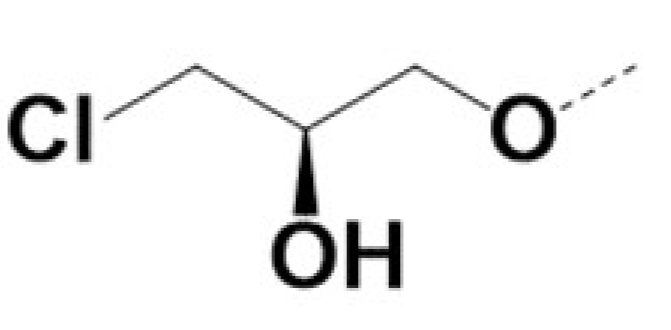 | 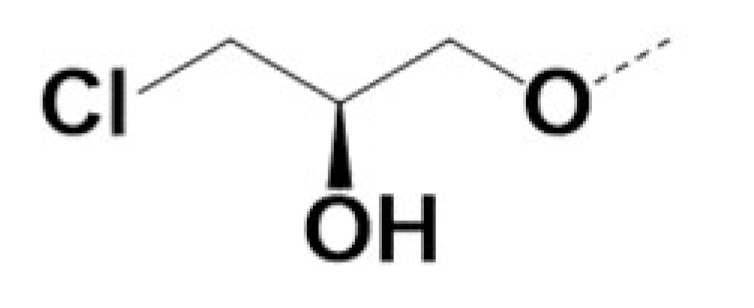 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 5 | 11 | ||||
| SS-220010 | 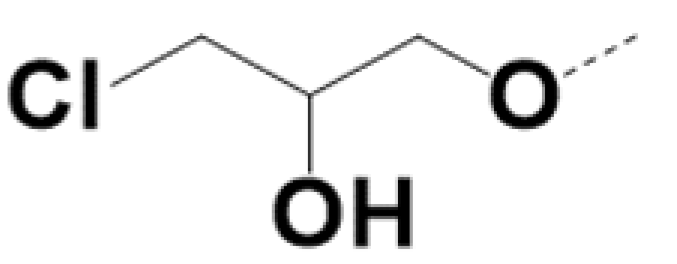 | 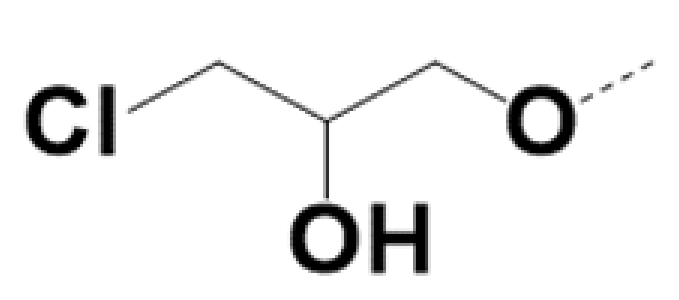 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 6 | 12 | ||||
| RS-220010 | 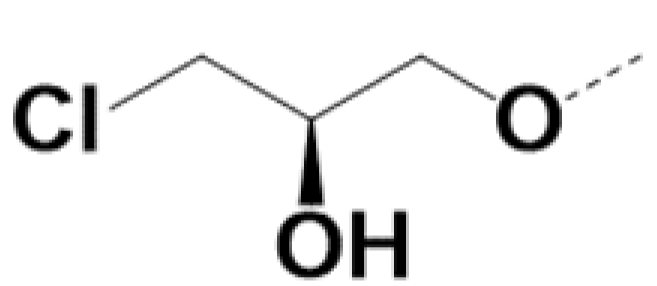 | 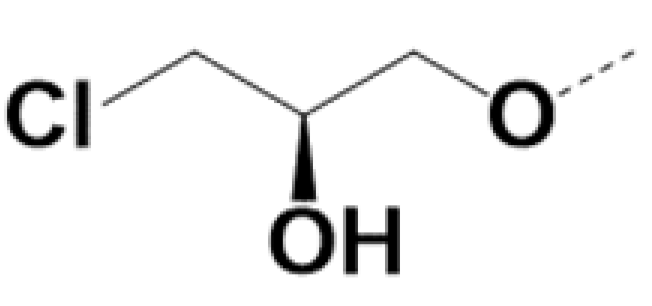 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 5 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ban, F.; Leblanc, E.; Cavga, A.D.; Huang, C.-C.F.; Flory, M.R.; Zhang, F.; Chang, M.E.K.; Morin, H.; Lallous, N.; Singh, K.; et al. Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143488
Ban F, Leblanc E, Cavga AD, Huang C-CF, Flory MR, Zhang F, Chang MEK, Morin H, Lallous N, Singh K, et al. Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(14):3488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143488
Chicago/Turabian StyleBan, Fuqiang, Eric Leblanc, Ayse Derya Cavga, Chia-Chi Flora Huang, Mark R. Flory, Fan Zhang, Matthew E. K. Chang, Hélène Morin, Nada Lallous, Kriti Singh, and et al. 2021. "Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 14: 3488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143488
APA StyleBan, F., Leblanc, E., Cavga, A. D., Huang, C.-C. F., Flory, M. R., Zhang, F., Chang, M. E. K., Morin, H., Lallous, N., Singh, K., Gleave, M. E., Mohammed, H., Rennie, P. S., Lack, N. A., & Cherkasov, A. (2021). Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 13(14), 3488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143488