Genomic, Microbial and Immunological Microenvironment of Colorectal Polyps
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
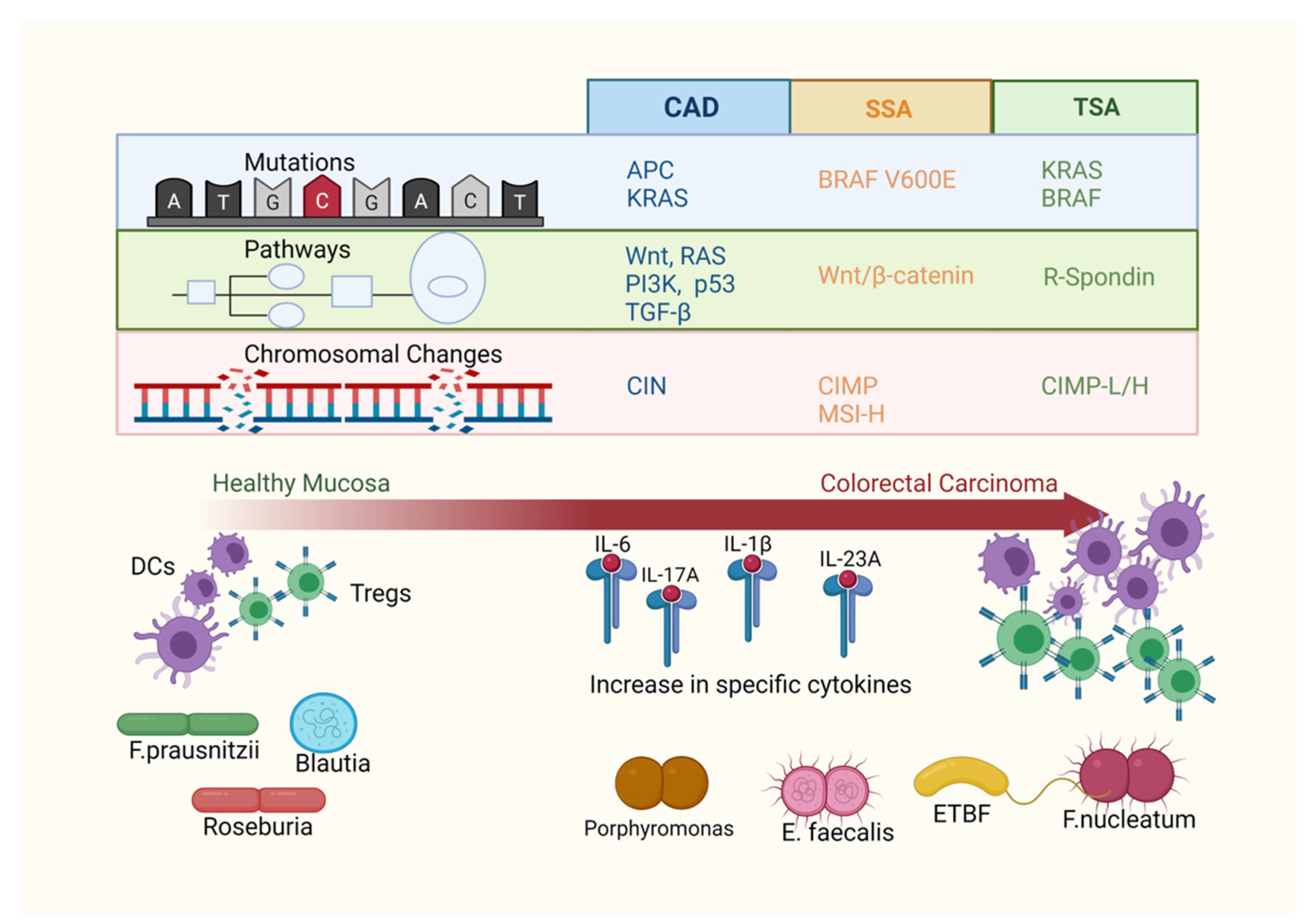
2. Gene Mutations in Colorectal Polyps
3. Tumour Mutational Burden
4. Immunological Environment within Polyps
| Immune Cell Subset | Associations in Polyps | Associations in CRC |
|---|---|---|
| T cells | T cell numbers in the tumour centre are associated with improved disease-free survival [95]. | |
| Cytotoxic T cells | Cytotoxic T cells in the tumour centre are associated with improved disease-free survival and overall survival [95,96]. | |
| Helper T cells | High expression of Th1-related genes is associated with increased disease-free survival, whilst a high expression of Th17-related genes is associated with poor prognosis [82]. | |
| Regulatory T cells | Increases in number with malignant transformation [73,74]. | Increase in number in tumour compared to normal mucosa [97]. High infiltrate within the tumour stroma and centre is associated with improved overall survival [95,96]. |
| Mucosa-associated invariant T cells | Accumulate in tumour tissue irrespective of stage [98]. | |
| Natural killer T cells | Increase in number in CRC. Patients with high natural killer T cell infiltration associated with better overall survival [99]. | |
| B cells | Higher numbers of infiltrating B cells seen in tumours of the right colon and associated with better disease-free survival [100]. | |
| Dendritic cells | Reduced numbers of mature dendritic cells and increased numbers of immature dendritic cells seen in conventional adenomas [64]. | Infiltration of dendritic cells is higher in MSI-H lesions [101]. Improved survival of patients with high infiltration of dendritic cells [102]. |
| Macrophages | High macrophage infiltration is associated with improved survival in colon cancer and reduced liver metastasis [85,86]. | |
| Neutrophils | High neutrophil infiltration in the tumour front is associated with better prognosis in patients with stage I-II CRC [87]. | |
| Natural killer cells | CRCs contain fewer natural killer cells than adjacent normal mucosa [88]. Patients with extensive natural killer cell infiltration have higher rates of overall survival [89]. |
5. Microbiota and Colorectal Polyps
6. Interaction of Microbiota and the Immune System in CRC Tumorigenesis
7. Potential Clinical Uses of Polyp Molecular Characteristics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.A.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Colorectal cancer. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shussman, N.; Wexner, S.D. Colorectal polyps and polyposis syndromes. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2014, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bettington, M.; Walker, N.; Clouston, A.; Brown, I.; Leggett, B.; Whitehall, V. The serrated pathway to colorectal carcinoma: Current concepts and challenges. Histopathology 2013, 62, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggett, B.; Whitehall, V. Role of the serrated pathway in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2088–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, R.K.; Bettington, M.; Srivastava, A.; Rosty, C. An update on the morphology and molecular pathology of serrated colorectal polyps and associated carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1390–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, F.D.E.; D’Argenio, V.; Pol, J.; Kroemer, G.; Maiuri, M.C.; Salvatore, F. The molecular hallmarks of the serrated pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aherne, S.T.; Madden, S.F.; Hughes, D.J.; Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A.; Levy, M.; Vodicka, P.; Neary, P.; Dowling, P.; Clynes, M. Circulating miRNAs miR-34a and miR-150 associated with colorectal cancer progression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gattolliat, C.H.; Uguen, A.; Pesson, M.; Trillet, K.; Simon, B.; Doucet, L.; Robaszkiewicz, M.; Corcos, L. MicroRNA and targeted mRNA expression profiling analysis in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatani, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Akao, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Nagasaka, M.; Shibata, T.; Tahara, T.; Hirata, I. Downregulation of anti-oncomirs miR-143/145 cluster occurs before APC gene aberration in the development of colorectal tumors. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2013, 46, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, Z.; Barnett, R.; Gardner, S.; Keskey, B.; Druen, D.; Billeter, A.; Cheadle, W.G. Differential microRNA (miRNA) expression could explain microbial tolerance in a novel chronic peritonitis model. Innate Immun. 2013, 19, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R.; le Sage, C.; Diosdado, B.; van der Waal, M.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.; Bolijn, A.; Meijer, G.A.; Agami, R. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberg, A.L.; French, A.J.; Sarver, A.L.; Subramanian, S.; Morlan, B.W.; Riska, S.M.; Borralho, P.M.; Cunningham, J.M.; Boardman, L.A.; Wang, L.; et al. miRNA expression in colon polyps provides evidence for a multihit model of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uratani, R.; Toiyama, Y.; Kitajima, T.; Kawamura, M.; Hiro, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Mohri, Y.; Mori, T.; et al. Diagnostic Potential of Cell-Free and Exosomal MicroRNAs in the identification of patients with high-risk colorectal adenomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Raju, G.S.; Chang, D.W.; Lin, S.H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X. Global and targeted circulating microRNA profiling of colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer. Cancer 2018, 124, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartley, A.N.; Yao, H.; Barkoh, B.A.; Ivan, C.; Mishra, B.M.; Rashid, A.; Calin, G.A.; Luthra, R.; Hamilton, S.R. Complex patterns of altered MicroRNA expression during the adenoma-adenocarcinoma sequence for microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7283–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slattery, M.L.; Herrick, J.S.; Wolff, R.K.; Mullany, L.E.; Stevens, J.R.; Samowitz, W. The miRNA landscape of colorectal polyps. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsikitis, V.L.; Potter, A.; Mori, M.; Buckmeier, J.A.; Preece, C.R.; Harrington, C.A.; Bartley, A.N.; Bhattacharyya, A.K.; Hamilton, S.R.; Lance, M.P.; et al. MicroRNA signatures of colonic polyps on screening and histology. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strubberg, A.M.; Madison, B.B. MicroRNAs in the etiology of colorectal cancer: Pathways and clinical implications. Dis. Models Mech. 2017, 10, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yang, W. Regulatory miRNAs in colorectal carcinogenesis and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anvarnia, A.; Mohaddes-Gharamaleki, F.; Asadi, M.; Akbari, M.; Yousefi, B.; Shanehbandi, D. Dysregulated microRNAs in colorectal carcinogenesis: New insight to cell survival and apoptosis regulation. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 21683–21693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, S.I.; Sotiriou, S.K.; Pateras, I.S.; Santoni, F.; Sougioultzis, S.; Edgren, H.; Almusa, H.; Robyr, D.; Guipponi, M.; Saarela, J.; et al. A single-nucleotide substitution mutator phenotype revealed by exome sequencing of human colon adenomas. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6279–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, L.; Zheng, L.; Ge, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Exome capture sequencing of adenoma reveals genetic alterations in multiple cellular pathways at the early stage of colorectal tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Raju, G.S.; Huff, C.; Ye, Y.; Gu, J.; Chen, J.S.; Hildebrandt, M.A.T.; Liang, H.; Menter, D.G.; Morris, J.; et al. The somatic mutation landscape of premalignant colorectal adenoma. Gut 2018, 67, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Yoo, J.; Song, Y.S.; Lim, C.H.; Kim, T.M. Mutation analysis of colorectal and gastric carcinomas originating from adenomas: Insights into genomic evolution associated with malignant progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaqué, J.P.; Martínez, N.; Varela, I.; Fernández, F.; Mayorga, M.; Derdak, S.; Beltrán, S.; Moreno, T.; Almaraz, C.; De Las Heras, G.; et al. Colorectal adenomas contain multiple somatic mutations that do not coincide with synchronous adenocarcinoma specimens. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Raju, G.S.; Jogunoori, W.; Menon, V.; Majumdar, A.; Chen, J.S.; Gi, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.S.; Phan, L.; Belkin, M.; et al. Mutational profiles reveal an aberrant TGF-beta-CEA regulated pathway in colon adenomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intarajak, T.; Udomchaiprasertkul, W.; Bunyoo, C.; Yimnoon, J.; Soonklang, K.; Wiriyaukaradecha, K.; Lamlertthon, W.; Sricharunrat, T.; Chaiwiriyawong, W.; Siriphongpreeda, B.; et al. Genetic aberration analysis in thai colorectal adenoma and early-stage adenocarcinoma patients by whole-exome sequencing. Cancers 2019, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, T.M.; Rhee, J.K.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.S.; An, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, Y.J. Whole-exome sequencing identified mutational profiles of high-grade colon adenomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6579–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Sekine, S.; Ogawa, R.; Taniguchi, H.; Kushima, R.; Tsuda, H.; Kanai, Y. Frequent activating GNAS mutations in villous adenoma of the colorectum. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.H.N.; Lai, J.C.W.; Ho, S.L.; Leung, W.K.; Law, W.L.; Lee, J.F.Y.; Chan, A.K.W.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, A.S.Y.; Lee, B.C.H.; et al. RNF43 germline and somatic mutation in serrated neoplasia pathway and its association with BRAF mutation. Gut 2017, 66, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, J.H.; Liau, J.Y.; Yuan, C.T.; Lin, Y.L.; Tseng, L.H.; Cheng, M.L.; Jeng, Y.M. RNF43 Is an Early and Specific Mutated Gene in the Serrated Pathway, With Increased Frequency in Traditional Serrated Adenoma and Its Associated Malignancy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, S.; Yamashita, S.; Tanabe, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yoshida, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kojima, M.; Shinmura, K.; Saito, Y.; Hiraoka, N.; et al. Frequent PTPRK-RSPO3 fusions and RNF43 mutations in colorectal traditional serrated adenoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borowsky, J.; Dumenil, T.; Bettington, M.; Pearson, S.A.; Bond, C.; Fennell, L.; Liu, C.; McKeone, D.; Rosty, C.; Brown, I.; et al. The role of APC in WNT pathway activation in serrated neoplasia. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, T.; Yamashita, S.; Yoshida, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Ushijima, T.; Yamada, T.; Saito, Y.; Ochiai, A.; Sekine, S.; Hiraoka, N. WNT pathway gene mutations are associated with the presence of dysplasia in colorectal sessile serrated adenoma/polyps. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, S.; Yamashita, S.; Yamada, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Ogawa, R.; Yoshida, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kojima, M.; Ushijima, T.; Saito, Y. Clinicopathological and molecular correlations in traditional serrated adenoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquati, C.; Prossomariti, A.; Piazzi, G.; Buttitta, F.; Bazzoli, F.; Laghi, L.; Ricciardiello, L. Discovering the mutational profile of early colorectal lesions: A translational impact. Cancers 2021, 13, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, C.E.; Ramalingam, S.S. Tumor Mutation Burden: Leading Immunotherapy to the Era of Precision Medicine? J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, D.M.; McShane, L.M.; Fabrizio, D.; Funari, V.; Chen, S.J.; White, J.R.; Wenz, P.; Baden, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Chaudhary, R.; et al. Establishing guidelines to harmonize tumor mutational burden (TMB): In silico assessment of variation in TMB quantification across diagnostic platforms: Phase I of the Friends of Cancer Research TMB Harmonization Project. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Fang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Hao, S.; Yu, Z.; et al. Influence of low tumor content on tumor mutational burden estimation by whole-exome sequencing and targeted panel sequencing. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Powles, T.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Balar, A.V.; Necchi, A.; Dawson, N.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Balmanoukian, A.; Loriot, Y.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nghiem, P.T.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Miller, N.J.; Annamalai, L.; Berry, S.; Chartash, E.K.; Daud, A.; Fling, S.P.; et al. PD-1 blockade with pembrolizumab in advanced merkel-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, T.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, F.; Ou, F.S.; Qu, X.; Zemla, T.J.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Tam, R.; Mahajan, S.; Goldberg, R.M.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Blanke, C.D.; et al. Mutational analysis of patients with colorectal cancer in CALGB/SWOG 80405 identifies new roles of microsatellite instability and tumor mutational burden for patient outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samstein, R.M.; Lee, C.H.; Shoushtari, A.N.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shen, R.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Barron, D.A.; Zehir, A.; Jordan, E.J.; Omuro, A.; et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Guo, T.; Ge, W. High tumor mutation burden predicts better efficacy of immunotherapy: A pooled analysis of 103078 cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1629258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, D.L.; He, M.M.; Yang, L.P.; Wang, Y.N.; Jin, Y.; Ren, C.; Luo, H.Y.; et al. Tumor mutational and indel burden: A systematic pan-cancer evaluation as prognostic biomarkers. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras, E.; San Lucas, F.A.; Chang, K.; Zhou, R.; Masand, G.; Fowler, J.; Mork, M.E.; You, Y.N.; Taggart, M.W.; McAllister, F.; et al. Genomic Landscape of Colorectal Mucosa and Adenomas. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karczmarski, J.; Goryca, K.; Pachlewski, J.; Dabrowska, M.; Pysniak, K.; Paziewska, A.; Kulecka, M.; Lenarcik, M.; Mroz, A.; Mikula, M.; et al. Mutation profiling of premalignant colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 2542640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, H.; Vesely, M.D.; Koboldt, D.C.; Rickert, C.G.; Uppaluri, R.; Magrini, V.J.; Arthur, C.D.; White, J.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Shea, L.K.; et al. Cancer exome analysis reveals a T-cell-dependent mechanism of cancer immunoediting. Nature 2012, 482, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, V.; Ikeda, H.; Bruce, A.T.; White, J.M.; Swanson, P.E.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 2001, 410, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, C.M.; Vermi, W.; Swann, J.B.; Zerafa, N.; Rodig, S.J.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature 2007, 450, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Pages, F.; Marincola, F.M.; Angell, H.K.; Thurin, M.; Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I.; Berger, A.; Bifulco, C.; Botti, G.; et al. Cancer classification using the Immunoscore: A worldwide task force. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Angell, H.K.; Bedognetti, D.; Marincola, F.M. The continuum of cancer immunosurveillance: Prognostic, predictive, and mechanistic signatures. Immunity 2013, 39, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Berger, A.; Bindea, G.; Meatchi, T.; Bruneval, P.; Trajanoski, Z.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; et al. Histopathologic-based prognostic factors of colorectal cancers are associated with the state of the local immune reaction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pages, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Asslaber, M.; Tosolini, M.; Bindea, G.; Lagorce, C.; Wind, P.; Marliot, F.; Bruneval, P.; et al. In situ cytotoxic and memory T cells predict outcome in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5944–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Gonzalez, G.; Ouseph, M.; Lombardo, K.; Lu, S.; Glickman, J.; Resnick, M.B. Immune environment in serrated lesions of the colon: Intraepithelial lymphocyte density, PD-1, and PD-L1 expression correlate with serrated neoplasia pathway progression. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 83, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Mitomi, H.; Yao, T.; Saito, T.; Shibuya, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Osada, T.; Watanabe, S. Distinct histopathological characteristics in colorectal submucosal invasive carcinoma arising in sessile serrated adenoma/polyp and conventional tubular adenoma. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.; Steigen, S.E.; Goll, R.; Vonen, B.; Husbekk, A.; Cui, G.; Florholmen, J. Dendritic cell infiltration pattern along the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2008, 116, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, M.R.; Phelan, J.J.; Michielsen, A.J.; Maguire, A.A.; Dunne, C.; Martin, P.; Noonan, S.; Tosetto, M.; Geraghty, R.; Fennelly, D.; et al. Characterising the prognostic potential of HLA-DR during colorectal cancer development. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.B.; Sun, G.P. Expression of COX-2 and HER-2 in colorectal cancer and their correlation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6206–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyravian, N.; Gharib, E.; Moradi, A.; Mobahat, M.; Tarban, P.; Azimzadeh, P.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H. Evaluating the expression level of co-stimulatory molecules CD 80 and CD 86 in different types of colon polyps. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2018, 66, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enarsson, K.; Lundin, B.S.; Johnsson, E.; Brezicka, T.; Quiding-Jarbrink, M. CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells reduce T cell transendothelial migration in cancer patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, P.; Stenstad, H.; Langenes, V.; Ahlmanner, F.; Theander, L.; Ndah, T.G.; Fredin, K.; Borjesson, L.; Gustavsson, B.; Bastid, J.; et al. Regulatory T cells from colon cancer patients inhibit effector T-cell migration through an adenosine-dependent mechanism. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, H.; Olofsson, V.; Lundin, S.; Yakkala, C.; Bjorck, S.; Borjesson, L.; Gustavsson, B.; Quiding-Jarbrink, M. Accumulation of CCR4(+)CTLA-4 FOXP3(+)CD25(hi) regulatory T cells in colon adenocarcinomas correlate to reduced activation of conventional T cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlmanner, F.; Sundstrom, P.; Akeus, P.; Eklof, J.; Borjesson, L.; Gustavsson, B.; Lindskog, E.B.; Raghavan, S.; Quiding-Jarbrink, M. CD39(+) regulatory T cells accumulate in colon adenocarcinomas and display markers of increased suppressive function. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36993–37007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaqub, S.; Henjum, K.; Mahic, M.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Aandahl, E.M.; Bjornbeth, B.A.; Tasken, K. Regulatory T cells in colorectal cancer patients suppress anti-tumor immune activity in a COX-2 dependent manner. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinkiewicz, M.; Migaczewski, M.; Hankus, J.; Dembinski, M.; Pedziwiatr, M.; Okon, K.; Pisarska, M.; Budzynski, A. The number of regulatory Foxp3+ T-cells in different stages of malignant transformation of large intestinal polyps. Adv. Med. Sci. 2016, 61, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.W.; Zhu, H.Z.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Feng, M.H.; Qi, J.; Chen, Z.F. Foxp3 expression in CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells promotes development of colorectal cancer by inhibiting tumor immunity. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Spaans, L.; Miranda, S.; Goncalves, G.; Reis, J.; Costa, J.L.; Duraes, C.; Carneiro, F.; Machado, J.C. The influence of the genetic and immunologic context in the development of colorectal adenoma: A case series report. Acta Med. Port. 2020, 33, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Yuan, A.; Zheng, W.; Li, C.; Cui, J.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Goll, R.; Cui, G. Accumulation of FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in the tumor microenvironment of human colorectal adenomas. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johdi, N.A.; Ait-Tahar, K.; Sagap, I.; Jamal, R. Molecular signatures of human regulatory T cells in colorectal cancer and polyps. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, A.; Florholmen, J. Elevated proinflammatory cytokine IL-17A in the adjacent tissues along the adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2015, 21, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yuan, A.; Goll, R.; Florholmen, J. IL-17A in the tumor microenvironment of the human colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Qu, Y.; Leng, Y.; Sun, W.; Ma, S.; Wei, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X. Human colon carcinogenesis is associated with increased interleukin-17-driven inflammatory responses. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Goll, R.; Olsen, T.; Steigen, S.E.; Husebekk, A.; Vonen, B.; Florholmen, J. Reduced expression of microenvironmental Th1 cytokines accompanies adenomas-carcinomas sequence of colorectum. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Fredriksen, T.; Mauger, S.; Bindea, G.; Berger, A.; Bruneval, P.; Fridman, W.H.; Pages, F.; et al. Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contasta, I.; Berghella, A.M.; Pellegrini, P.; Adorno, D. Passage from normal mucosa to adenoma and colon cancer: Alteration of normal sCD30 mechanisms regulating TH1/TH2 cell functions. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2003, 18, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, P.; Berghella, A.M.; Del Beato, T.; Cicia, S.; Adorno, D.; Casciani, C.U. Disregulation in TH1 and TH2 subsets of CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients and involvement in cancer establishment and progression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1996, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forssell, J.; Oberg, A.; Henriksson, M.L.; Stenling, R.; Jung, A.; Palmqvist, R. High macrophage infiltration along the tumor front correlates with improved survival in colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Peng, R.Q.; Wu, X.J.; Xia, Q.; Hou, J.H.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Q.M.; Zhang, X.; Pang, Z.Z.; Wan, D.S.; et al. The density of macrophages in the invasive front is inversely correlated to liver metastasis in colon cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikberg, M.L.; Ling, A.; Li, X.; Oberg, A.; Edin, S.; Palmqvist, R. Neutrophil infiltration is a favorable prognostic factor in early stages of colon cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 68, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halama, N.; Braun, M.; Kahlert, C.; Spille, A.; Quack, C.; Rahbari, N.; Koch, M.; Weitz, J.; Kloor, M.; Zoernig, I.; et al. Natural killer cells are scarce in colorectal carcinoma tissue despite high levels of chemokines and cytokines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coca, S.; Perez-Piqueras, J.; Martinez, D.; Colmenarejo, A.; Saez, M.A.; Vallejo, C.; Martos, J.A.; Moreno, M. The prognostic significance of intratumoral natural killer cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 79, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Bothwell, A.L.M. Stat6 Promotes Intestinal Tumorigenesis in a Mouse Model of Adenomatous Polyposis by Expansion of MDSCs and Inhibition of Cytotoxic CD8 Response. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, E.; Lavoie, S.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Kim, J.; Soucy, G.; Odze, R.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. CCL2 Promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by enhancing polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cell population and function. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sedimbi, S.; Lofbom, L.; Singh, A.K.; Porcelli, S.A.; Cardell, S.L. Unique invariant natural killer T cells promote intestinal polyps by suppressing TH1 immunity and promoting regulatory T cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sedimbi, S.K.; Lofbom, L.; Besra, G.S.; Porcelli, S.A.; Cardell, S.L. Promotion or suppression of murine intestinal polyp development by iNKT cell directed immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Tumor Immunology and Tumor Evolution: Intertwined Histories. Immunity 2020, 52, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idos, G.E.; Kwok, J.; Bonthala, N.; Kysh, L.; Gruber, S.B.; Qu, C. The prognostic implications of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ge, X.; He, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, L. The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer differs by anatomical subsite: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salama, P.; Phillips, M.; Grieu, F.; Morris, M.; Zeps, N.; Joseph, D.; Platell, C.; Iacopetta, B. Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, P.; Ahlmanner, F.; Akeus, P.; Sundquist, M.; Alsen, S.; Yrlid, U.; Borjesson, L.; Sjoling, A.; Gustavsson, B.; Wong, S.B.; et al. Human mucosa-associated invariant T cells accumulate in colon adenocarcinomas but produce reduced amounts of IFN-gamma. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3472–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachibana, T.; Onodera, H.; Tsuruyama, T.; Mori, A.; Nagayama, S.; Hiai, H.; Imamura, M. Increased intratumor Valpha24-positive natural killer T cells: A prognostic factor for primary colorectal carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7322–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edin, S.; Kaprio, T.; Hagstrom, J.; Larsson, P.; Mustonen, H.; Bockelman, C.; Strigard, K.; Gunnarsson, U.; Haglund, C.; Palmqvist, R. The Prognostic Importance of CD20(+) B lymphocytes in Colorectal Cancer and the Relation to Other Immune Cell subsets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.; Michel, S.; Reuschenbach, M.; Nelius, N.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M.; Kloor, M. Dendritic cell and macrophage infiltration in microsatellite-unstable and microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer. Fam. Cancer 2011, 10, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagorsen, D.; Voigt, S.; Berg, E.; Stein, H.; Thiel, E.; Loddenkemper, C. Tumor-infiltrating macrophages and dendritic cells in human colorectal cancer: Relation to local regulatory T cells, systemic T-cell response against tumor-associated antigens and survival. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costello, E.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Fierer, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Jia, H.; Stadlmayr, A.; Tang, L.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, X.; Jie, Z.; et al. Gut microbiome development along the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durban, A.; Abellan, J.J.; Jimenez-Hernandez, N.; Ponce, M.; Ponce, J.; Sala, T.; D’Auria, G.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. Assessing gut microbial diversity from feces and rectal mucosa. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, Y.; Maharshak, N.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Wolber, E.A.; Sartor, R.B.; Carroll, I.M. High throughput sequencing reveals distinct microbial populations within the mucosal and luminal niches in healthy individuals. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pleguezuelos-Manzano, C.; Puschhof, J.; Rosendahl Huber, A.; van Hoeck, A.; Wood, H.M.; Nomburg, J.; Gurjao, C.; Manders, F.; Dalmasso, G.; Stege, P.B.; et al. Mutational signature in colorectal cancer caused by genotoxic pks(+) E. coli. Nature 2020, 580, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Rawls, J.F.; Randall, T.; Burcal, L.; Mpande, C.N.; Jenkins, N.; Jovov, B.; Abdo, Z.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Molecular characterization of mucosal adherent bacteria and associations with colorectal adenomas. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangifesta, M.; Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Gaiani, F.; de’Angelis, N.; de’Angelis, G.L.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M.; Turroni, F. Mucosal microbiota of intestinal polyps reveals putative biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanapareddy, N.; Legge, R.M.; Jovov, B.; McCoy, A.; Burcal, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Randall, T.A.; Galanko, J.; Benson, A.; Sandler, R.S.; et al. Increased rectal microbial richness is associated with the presence of colorectal adenomas in humans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.J.; Zhou, Y.L.; He, J.; Feng, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Lai, X.B.; Zhou, J.X.; Wang, H. Characterizing the composition of intestinal microflora by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, E.; Sikaroodi, M.; Korman, L.; Hardi, R.; Baybick, J.; Hanzel, D.; Kuehn, G.; Kuehn, T.; Gillevet, P.M. Gut microbiome identifies risk for colorectal polyps. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nugent, J.L.; McCoy, A.N.; Addamo, C.J.; Jia, W.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Altered tissue metabolites correlate with microbial dysbiosis in colorectal adenomas. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.M.; Liu, H.L. Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.N.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Azcarate-Peril, A.; Yeh, J.J.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Fusobacterium is associated with colorectal adenomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, M.; Kanno, S.; Nosho, K.; Sukawa, Y.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Kurihara, H.; Igarashi, H.; Takahashi, T.; Tachibana, M.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Association of Fusobacterium nucleatum with clinical and molecular features in colorectal serrated pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, N.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Comparisons of gut microbiota among healthy control, patients with conventional adenoma, sessile serrated adenoma, and colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tjalsma, H.; Boleij, A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dutilh, B.E. A bacterial driver-passenger model for colorectal cancer: Beyond the usual suspects. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, K.M.; Greiner, K.A.; Umar, S. Deciphering the colorectal cancer gut microbiota: Association vs. causality. Curr. Colorect. Canc. R. 2019, 15, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, S.M.; Dethlefsen, L.; Huber, J.A.; Mark Welch, D.; Relman, D.A.; Sogin, M.L. Exploring microbial diversity and taxonomy using SSU rRNA hypervariable tag sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignard, S.; Flandrois, J.P. 16S rRNA sequencing in routine bacterial identification: A 30-month experiment. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 67, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira-Pascual, L.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Ocon, S.; Costales, P.; Parra, A.; Suarez, A.; Moris, F.; Rodrigo, L.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C. Microbial mucosal colonic shifts associated with the development of colorectal cancer reveal the presence of different bacterial and archaeal biomarkers. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Lou, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y. Mucosal adherent bacterial dysbiosis in patients with colorectal adenomas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaden, J.A.; Abrams, K.R.; Mayberry, J.F. The risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis. Gut 2001, 48, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arthur, J.C.; Perez-Chanona, E.; Mühlbauer, M.; Tomkovich, S.; Uronis, J.M.; Fan, T.J.; Campbell, B.J.; Abujamel, T.; Dogan, B.; Rogers, A.B.; et al. Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota. Science 2012, 338, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennis, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Blatner, N.R.; Wang, S.; Saadalla, A.; Trudeau, E.; Roers, A.; Weaver, C.T.; Lee, J.J.; Gilbert, J.A.; et al. Adenomatous polyps are driven by microbe-instigated focal inflammation and are controlled by IL-10-producing T cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5905–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomkovich, S.; Yang, Y.; Winglee, K.; Gauthier, J.; Muhlbauer, M.; Sun, X.; Mohamadzadeh, M.; Liu, X.; Martin, P.; Wang, G.P.; et al. Locoregional effects of microbiota in a preclinical model of colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2620–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huycke, M.M.; Joyce, W.; Wack, M.F. Augmented production of extracellular superoxide by blood isolates of Enterococcus faecalis. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, P.A.; Shkoda, A.; Kim, S.C.; Sartor, R.B.; Haller, D. IL-10 gene-deficient mice lack TGF-beta/Smad signaling and fail to inhibit proinflammatory gene expression in intestinal epithelial cells after the colonization with colitogenic Enterococcus faecalis. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2990–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obiso, R.J., Jr.; Azghani, A.O.; Wilkins, T.D. The Bacteroides fragilis toxin fragilysin disrupts the paracellular barrier of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Rhee, K.J.; Albesiano, E.; Rabizadeh, S.; Wu, X.; Yen, H.R.; Huso, D.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wick, E.; McAllister, F.; et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, A.L.; Fan, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, S.; Huso, D.L.; Wolfe, J.L.; Sears, C.L.; Pardoll, D.M.; Housseau, F. Regulatory T-cell response to enterotoxigenic bacteroides fragilis colonization triggers IL17-dependent colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Weng, W.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum increases proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and tumor development in mice by activating toll-like receptor 4 signaling to nuclear factor-kappaB, and up-regulating expression of MicroRNA-21. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 851–866.e824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, M.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Cai, G.; Han, Y.W. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by modulating E-cadherin/beta-catenin signaling via its FadA adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gur, C.; Ibrahim, Y.; Isaacson, B.; Yamin, R.; Abed, J.; Gamliel, M.; Enk, J.; Bar-On, Y.; Stanietsky-Kaynan, N.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; et al. Binding of the Fap2 protein of Fusobacterium nucleatum to human inhibitory receptor TIGIT protects tumors from immune cell attack. Immunity 2015, 42, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biarc, J.; Nguyen, I.S.; Pini, A.; Gosse, F.; Richert, S.; Thierse, D.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Leize-Wagner, E.; Raul, F.; Klein, J.P.; et al. Carcinogenic properties of proteins with pro-inflammatory activity from Streptococcus infantarius (formerly S.bovis). Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, J.; Rolhion, N.; Dubois, A.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Bringer, M.A. Intracellular colon cancer-associated Escherichia coli promote protumoral activities of human macrophages by inducing sustained COX-2 expression. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Wang, K.; Mucida, D.; Stewart, C.A.; Schnabl, B.; Jauch, D.; Taniguchi, K.; Yu, G.Y.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Hung, K.E.; et al. Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature 2012, 491, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aceto, G.M.; Catalano, T.; Curia, M.C. Molecular aspects of colorectal adenomas: The interplay among microenvironment, oxidative stress, and predisposition. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1726309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pitmon, E.; Wang, K. Microbiome, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 32, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Subjects | Method | Families and Genera Enriched in Adenoma | Families and Genera Depleted in Adenoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shen et al. [112] | 4 CA, 4 HC | T-RFLP, 16S rRNA | Dorea, Faecalibacterium | Bacteroides, Coprococcus |
| Mira-Pascual et al. [129] | 11 CA, 7 CRC, 10 HC | V1-V3 16S rRNA | Akkermansia, Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Enterobacteriaceae, Fusobacterium | Faecalibacterium |
| Dadkhah et al. [116] | 122 CA | V1-V2 16S rRNA | Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Faecalibacterium | |
| Sanarpeddy et al. [114] | 33 CA, 38 HC | V1-V2 16S rRNA | Acidovorax, Aquabacterium, Cloacibacterium, Helicobacter, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Pseudomonas | Streptococcus |
| Lu et al. [130] | 31 CA, 20 HC | V3-V4 16S rRNA | Lactococcus, Pseudomonas | Bacillus, Enterococcus, Solibacillus |
| Nugent et al. [117] | 15 CA, 15 HC | MS, qPCR | Bifidobacterium, Eubacteria | |
| Mangifesta et al. [113] | 12 CA | V3 16S rRNA | Helicobacter, Lactobacillus, Klebsiella, Prevotella | Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Escherichia-Shigella, Faecalibacterium, Romboutsia, Ruminococcaceae |
| Wang et al. [115] | 49 Advanced-CA, 36 HC | V4 16S rRNA | Halomonas, Oceanospirillales, Shewanella algae | Bacteroides, Blautia, Coprococcus, Fusobacterium |
| Kostic et al. [120] | 28 CA, 27 CRC, 31 HC | qPCR | Fusobacterium | |
| McCoy et al. [119] | 48 CA, 67 HC | qPCR | Fusobacterium | |
| Ito et al. [121] | 343 SSA, 122 CA, 511 CRC | qPCR | Fusobacterium nucleatum |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tse, B.C.Y.; Welham, Z.; Engel, A.F.; Molloy, M.P. Genomic, Microbial and Immunological Microenvironment of Colorectal Polyps. Cancers 2021, 13, 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143382
Tse BCY, Welham Z, Engel AF, Molloy MP. Genomic, Microbial and Immunological Microenvironment of Colorectal Polyps. Cancers. 2021; 13(14):3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143382
Chicago/Turabian StyleTse, Benita C. Y., Zoe Welham, Alexander F. Engel, and Mark P. Molloy. 2021. "Genomic, Microbial and Immunological Microenvironment of Colorectal Polyps" Cancers 13, no. 14: 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143382
APA StyleTse, B. C. Y., Welham, Z., Engel, A. F., & Molloy, M. P. (2021). Genomic, Microbial and Immunological Microenvironment of Colorectal Polyps. Cancers, 13(14), 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143382







