Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Neoangiogenesis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.2.1. EMT Markers
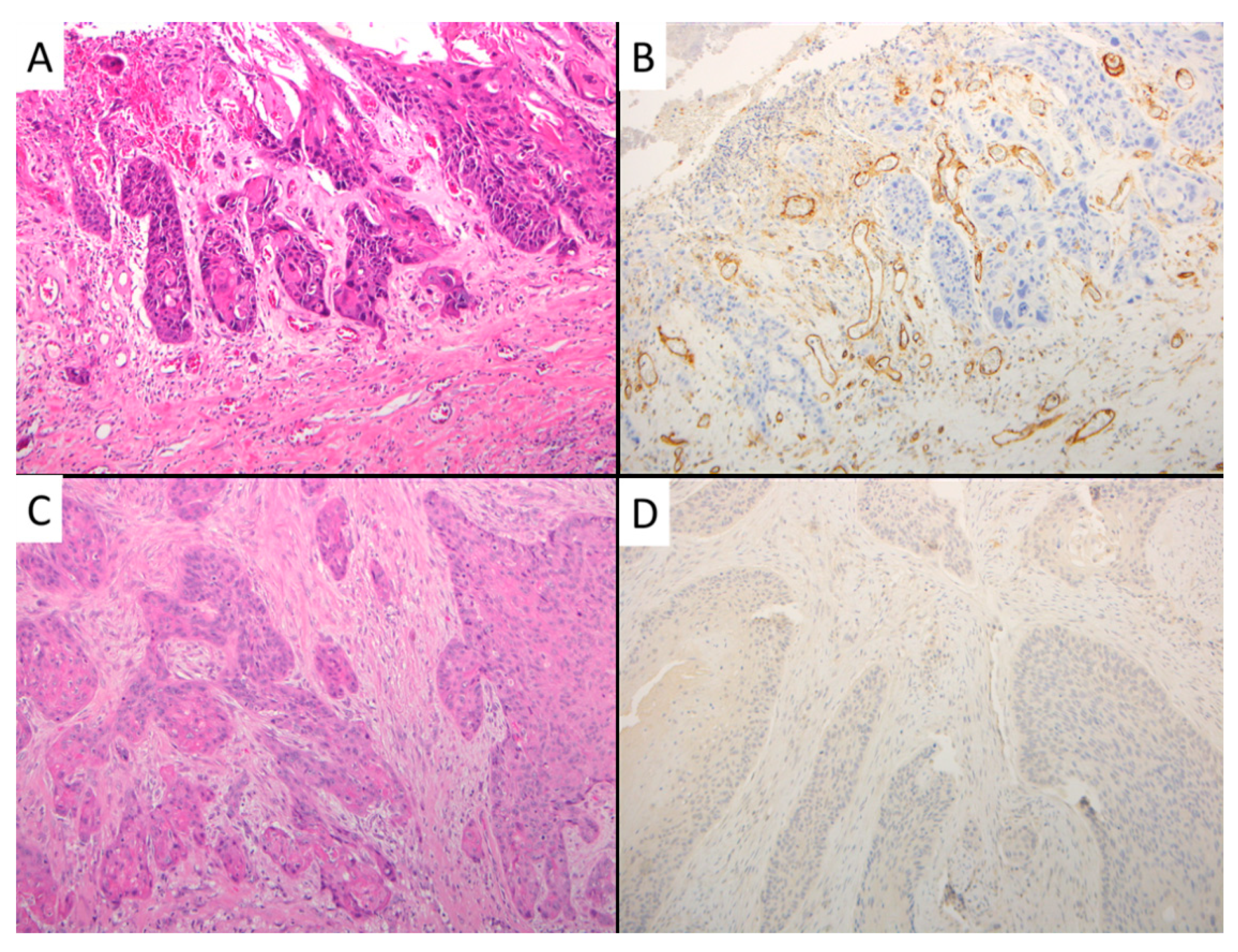
2.2.2. CD105-Assessed Microvessel Density (MVD)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes
3.2. Univariate Survival Analysis
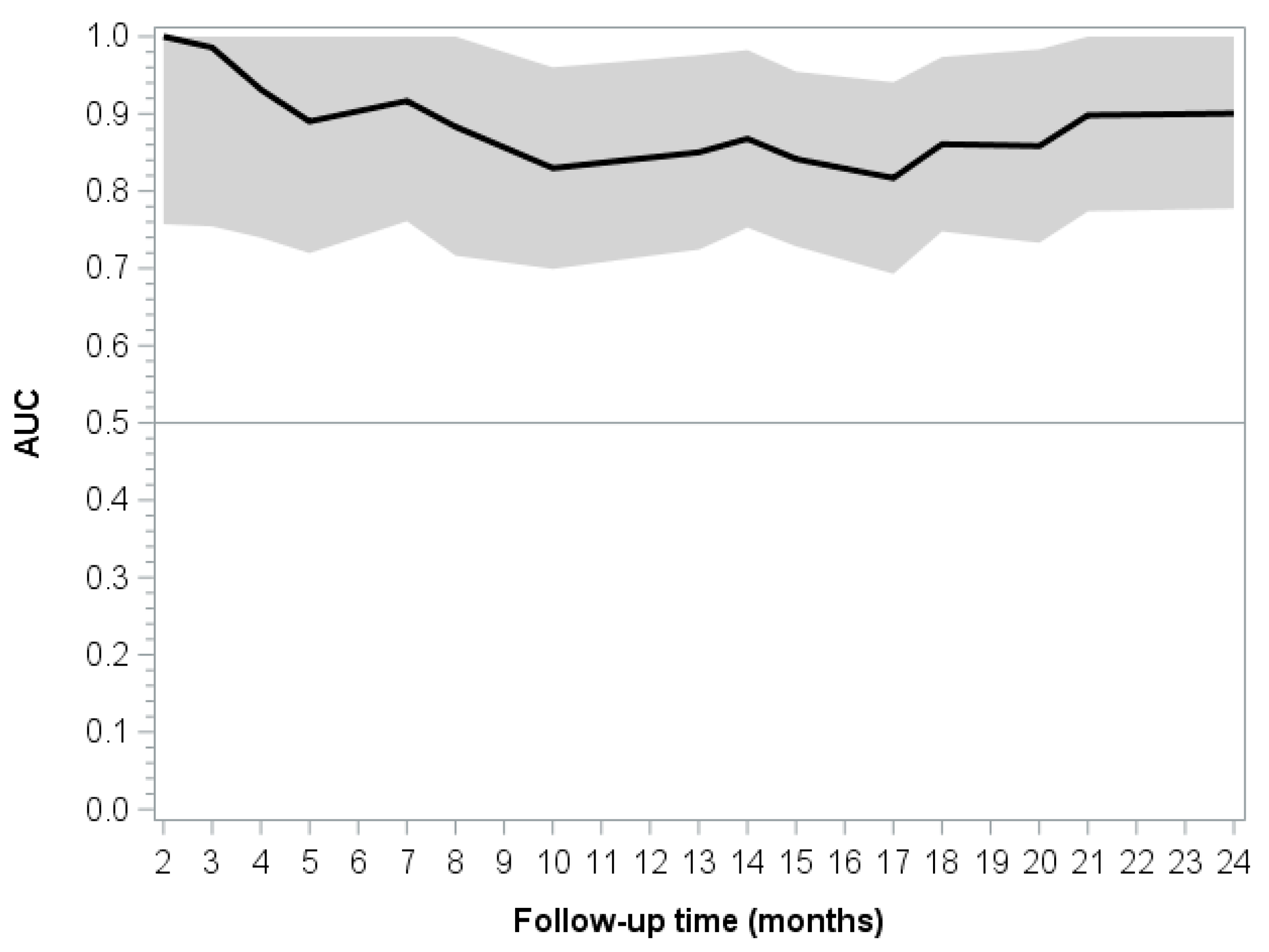
3.3. Multivariate Prognostic Model
3.4. Association between EMT Proteins, Angiogenesis, and Other Clinical-Pathological Variables in LSCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribatti, D. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Morphogenesis, Cancer Progression and Angiogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 353, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, E.F.; Rolim, L.S.A.; de Melo, F.A.D.R.; de Farias Morais, H.G.; de Souza, L.B.; de Almeida Freitas, R. Biological Role of Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition-Inducing Transcription Factors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 119, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, J.; Ladanyi, A.; Ingruber, J.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Riechelmann, H. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: A Mechanism that Fuels Cancer Radio/Chemoresistance. Cells 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xie, N.; Liu, X.; Hou, J.; et al. Prognostic Value of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Inducing Transcription Factors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Cheng, B.; Tao, X. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Cancer. 2021, 148, 1548–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, G.; Nicolè, L.; Cappellesso, R.; Marchese-Ragona, R.; Fasanaro, E.; Di Carlo, R.; La Torre, F.B.; Nardello, E.; Sanavia, T.; Ottaviano, G.; et al. β-Arrestin-1 Expression and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Laryngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2019, 34, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.; Teknos, T.N.; Pan, Q. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappellesso, R.; Marioni, G.; Crescenzi, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Guzzardo, V.; Mussato, A.; Staffieri, A.; Martini, A.; Blandamura, S.; Fassina, A. The Prognostic Role of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers E-Cadherin and Slug in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Histopathology 2015, 67, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, R.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Nathan, G.; Celebrezze, J.; Medich, D.; Silverman, J.F. Endoglin (CD105) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor as Prognostic Markers in Colorectal Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollauri-Ibáñez, C.; Ayuso-Íñigo, B.; Pericacho, M. Hot and Cold Tumors: Is Endoglin (CD105) a Potential Target for Vessel Normalization? Cancers 2021, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, G.; Franz, L.; Ottaviano, G.; Contro, G.; Tealdo, G.; Carli, A.; Frigo, A.C.; Nicolai, P.; Alessandrini, L. Prognostic Significance of CD105- and CD31-Sssessed Microvessel Density in Paired Biopsies and Surgical Samples of Laryngeal Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B. AJCC Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Uno, H.; Cai, T.; Pencina, M.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wei, L.J. On the C-Statistics for Evaluating Overall Adequacy of Risk Prediction Procedures with Censored Survival Data. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greco, A.; De Virgilio, A.; Rizzo, M.I.; Pandolfi, F.; Rosati, D.; de Vincentiis, M. The Prognostic Role of E-Cadherin and Β-Catenin Overexpression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, E148–E155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wen, J.; Lei, M.; Wen, M.; Li, S.; Lv, X.; Luo, Z.; Wen, G. Hypoxia Promotes the Invasion and Metastasis of Laryngeal Cancer Cells via EMT. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.J.; Song, P.P.; Zhou, H.; Shen, X.H.; Wang, J.G.; Ma, X.F.; Gu, Y.J.; Liu, D.D.; Feng, A.N.; Qian, X.Y.; et al. Role of epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers E-Cadherin, N-Cadherin, β-Catenin and ZEB2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3472–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S. Clinicopathological Significance of SOX4 and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers in Patients with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Medicine 2021, 100, e25028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and Metastasis of Lung Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bin, M.; Chen, J.; Yng, N.; Peng, Y. The Regulatory Mechanism and Biological Significance of the Snail-Mir590-VEGFR-NRP1 Axis in the Angiogenesis, Growth and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer. Cell Death Disease 2020, 11, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Soltermann, A.; Tischler, V.; Arbogast, S.; Braun, J.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Weder, W.; Moch, H.; Kristiansen, G. Prognostic Significance of Epithelial-Mesenchymal and Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Protein Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7430–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurzu, S.; Kobori, L.; Fodor, D.; Jung, I. Epithelial Mesenchymal and Endothelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2962580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Chen, C.L.; Chau, G.Y.; Chiou, S.H.; Su, C.W.; Chou, T.Y.; Peng, W.L.; Wu, J.C. Comprehensive Analysis of the Independent Effect of Twist and Snail in Promoting Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, D.; Kim, S. Cooperation between ZEB2 and Sp1 Promotes Cancer Cell Survival and Angiogenesis during Metastasis Through Induction of Survivin and VEGF. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Fu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wei, T.; Yang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α/interleukin-1β Signaling Enhances Hepatoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Macrophages in a Hypoxic Inflammatory Microenvironment. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1872–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| LSCC Recurrence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | No (No. = 21) | Yes (No. = 16) | As a Whole (No. = 37) | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 19 (90.5) | 14 (87.5) | 33 (89.2) | 1 | 0.6032 |
| Female | 02 (9.5) | 02 (12.5) | 04 (10.8) | 1.48 (0.336–6.542) | |
| Age (years) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 61.52 (9.39) | 66.31 (6.99) | 63.59 (8.67) | 1.040 (0.982–1.103) | 0.1825 |
| Median (IQR) | 61.00 (58.00–68.00) | 66.00 (61.50–71.50) | 64.00 (59.00–70.00) | ||
| pT | |||||
| pT1-T2 | 05 (23.8) | 04 (25.0) | 09 (24.3) | 1 | 0.9012 |
| pT3-T4 | 16 (76.2) | 12 (75.0) | 28 (75.7) | 0.931 (0.300–2.889) | |
| pN-status | |||||
| pN0 | 12 (57.1) | 04 (25.0) | 16 (43.2) | 1 | 0.0343 |
| pN+ | 09 (42.9) | 12 (75.0) | 21 (56.8) | 3.418 (1.095–10.668) | |
| CD105-assessed MVD % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 5.01 (6.13) | 11.15 (9.99) | 7.66 (8.48) | 1.036 (0.995–1.079) | 0.0869 |
| Median (IQR) | 3.32 (0.01–6.67) | 9.87 (5.43–13.82) | 5.70 (2.12–10.43) | ||
| E-Cadherin expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 43.10 (36.52) | 29.69 (31.44) | 37.30 (34.61) | 0.992 (0.976–1.007) | 0.3029 |
| Median (IQR) | 40.00 (10.00–80.00) | 15.00 (0.00–60.00) | 20.00 (5.00–70.00) | ||
| N-Cadherin expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.81 (13.22) | 13.13 (21.12) | 7.84 (17.46) | 1.018 (0.997–1.040) | 0.0911 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–25.00) | 0.00 (0.00–5.00) | ||
| Snail expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 11.67 (14.08) | 23.13 (28.45) | 16.62 (21.92) | 1.015 (0.994–1.036) | 0.1551 |
| Median (IQR) | 10.00 (0.00–20.00) | 5.00 (0.00–55.00) | 5.00 (0.00–30.00) | ||
| Slug expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 30.48 (31.38) | 5.00 (9.13) | 19.46 (27.30) | 0.946 (0.901–0.994) | 0.0268 |
| Median (IQR) | 20.00 (0.00–50.00) | 0.00 (0.00–7.50) | 10.00 (0.00–30.00) | ||
| Zeb1 expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.90 (4.87) | 3.75 (5.63) | 2.70 (5.22) | 1.028 (0.952–1.109 ) | 0.4798 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–5.00) | 0.00 (0.00–5.00) | ||
| Zeb2 expression % | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.57 (6.73) | 8.44 (9.78) | 5.68 (8.43) | 1.042 (0.991–1.096) | 0.1073 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.00 (0.00–5.00) | 5.00 (0.00–17.50) | 0.00 (0.00–10.00) | ||
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| pN status | 3.717 (1.100–12.558) | 0.0346 |
| CD105-assessed MVD % | 1.013 (0.973–1.054) | 0.5291 |
| N-Cadherin % | 1.027 (1.001–1.054) | 0.0430 |
| Slug % | 0.924 (0.865–0.988) | 0.0214 |
| Time (Months) | Uno’s Concordance Coefficient (SE) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.8949 (0.0797) | 0.7387–1.0000 |
| 12 | 0.8320 (0.0951) | 0.6456–1.0000 |
| 18 | 0.8120 (0.0884) | 0.6387–0.9853 |
| 24 | 0.8252 (0.0800) | 0.6684–0.9820 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franz, L.; Nicolè, L.; Frigo, A.C.; Ottaviano, G.; Gaudioso, P.; Saccardo, T.; Visconti, F.; Cappellesso, R.; Blandamura, S.; Fassina, A.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Neoangiogenesis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133339
Franz L, Nicolè L, Frigo AC, Ottaviano G, Gaudioso P, Saccardo T, Visconti F, Cappellesso R, Blandamura S, Fassina A, et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Neoangiogenesis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133339
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranz, Leonardo, Lorenzo Nicolè, Anna Chiara Frigo, Giancarlo Ottaviano, Piergiorgio Gaudioso, Tommaso Saccardo, Francesca Visconti, Rocco Cappellesso, Stella Blandamura, Ambrogio Fassina, and et al. 2021. "Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Neoangiogenesis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133339
APA StyleFranz, L., Nicolè, L., Frigo, A. C., Ottaviano, G., Gaudioso, P., Saccardo, T., Visconti, F., Cappellesso, R., Blandamura, S., Fassina, A., & Marioni, G. (2021). Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Neoangiogenesis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 13(13), 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133339







