Identification of a Two-MicroRNA Signature in Plasma as a Novel Biomarker for Very Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.2. MiRNA Extraction
2.3. Retrotranscription and Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Target Prediction Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
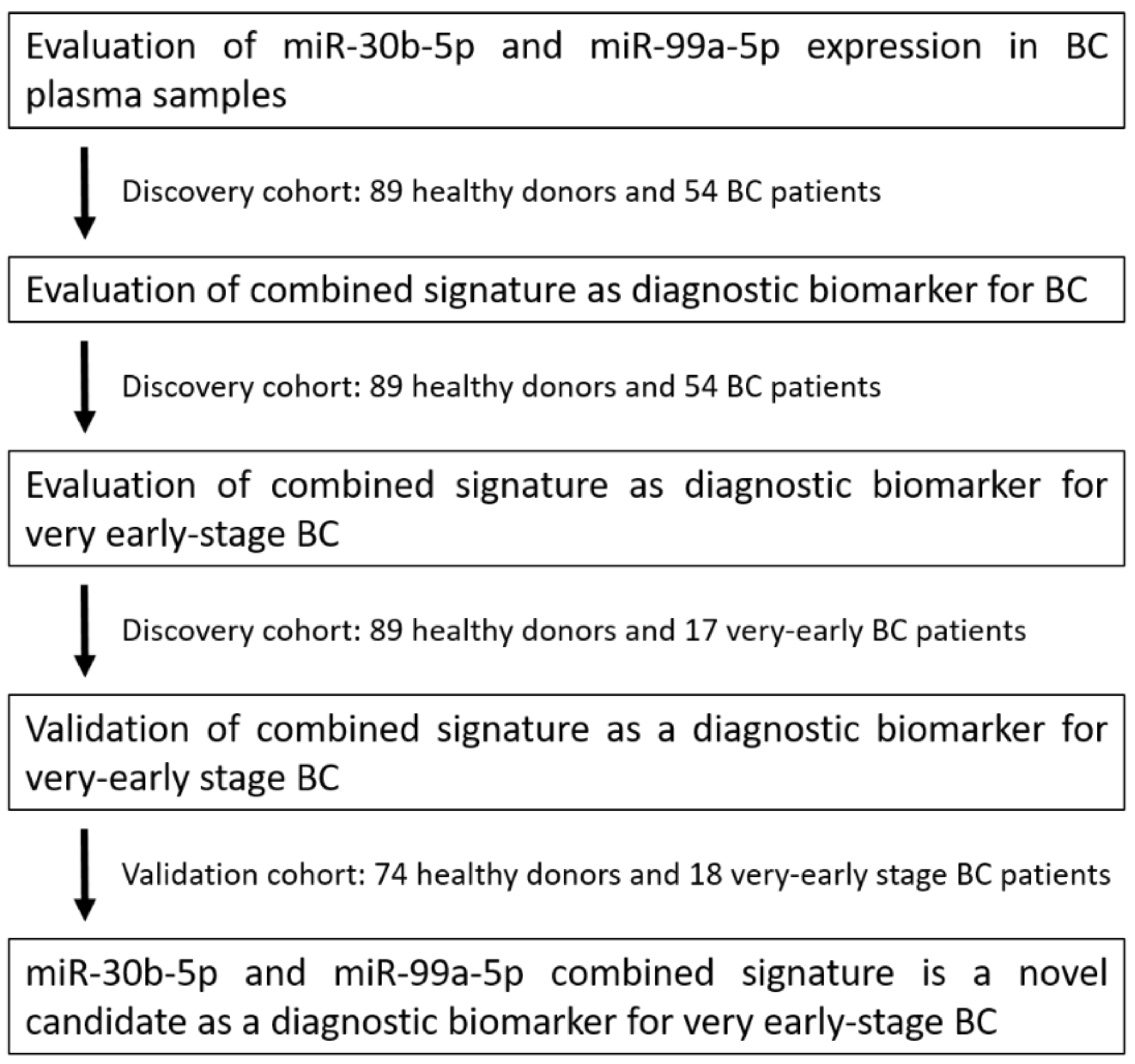
3.1. Study Workflow
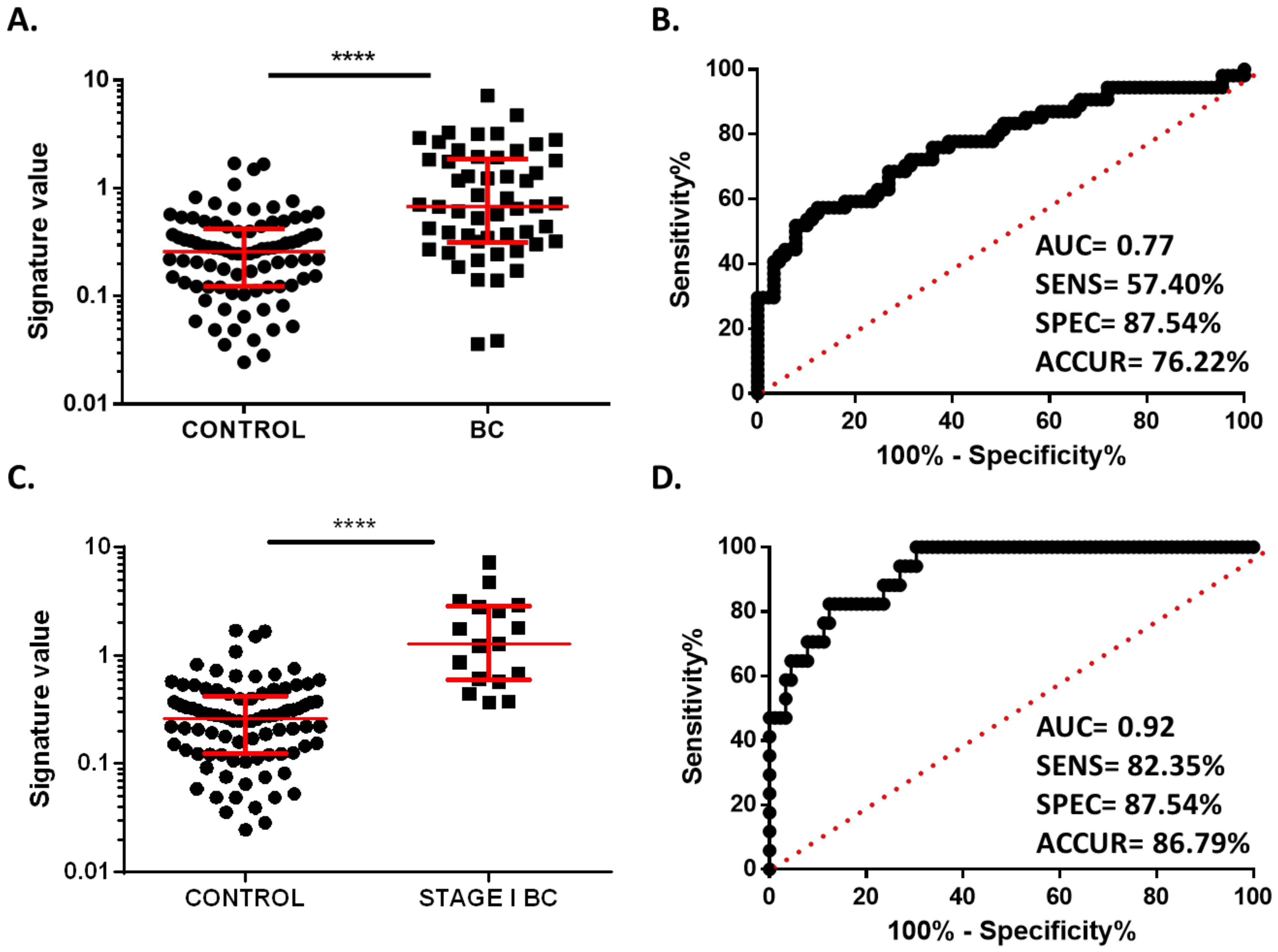
3.2. Circulating miR-30b-5p and miR-99a-5p Levels in Plasma Samples from BC and Healthy Patients
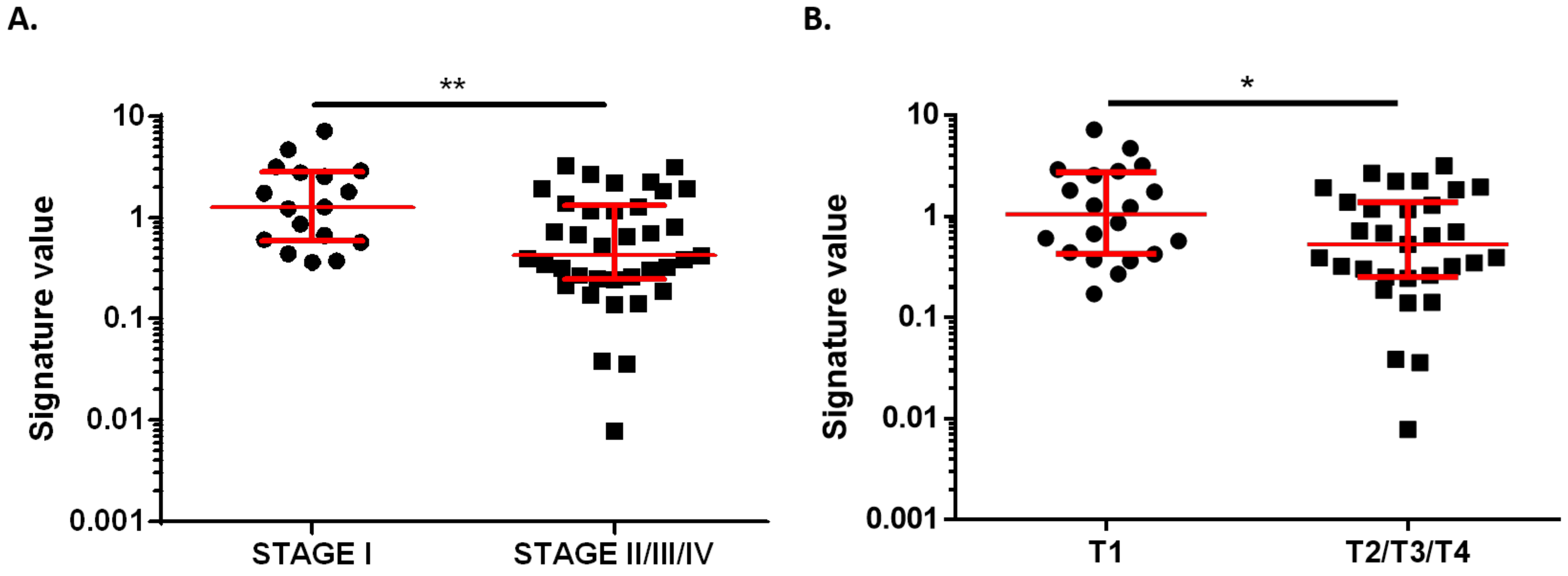
3.3. Two-MicroRNA Signature as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Very Early-Stage BC Patients
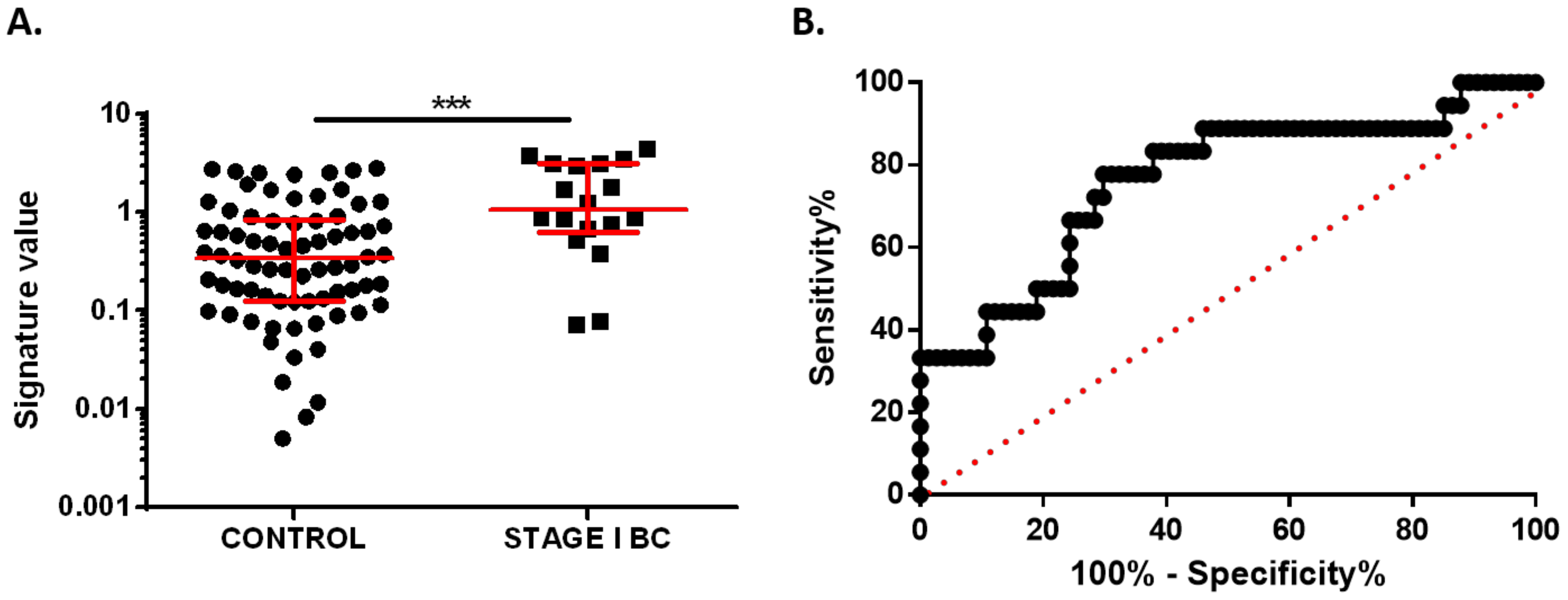
3.4. Validation of Plasma miRNA Signature as an Early Diagnosis BC Biomarker
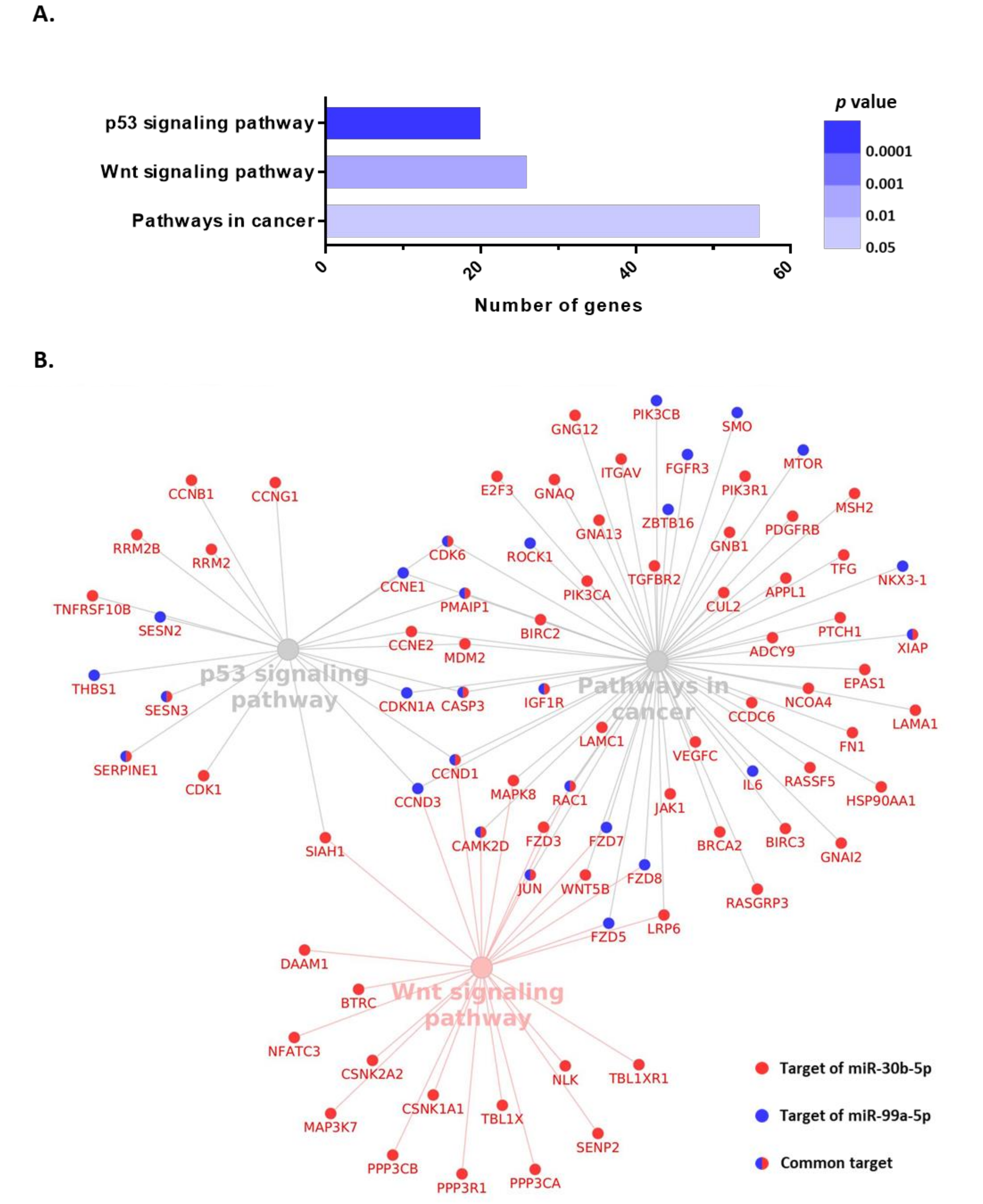
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis for miR-30b-5p and miR-99a-5p
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, O.; Yip, C.; Brooks, A.; Cabanes, A.; Caleffi, M.; Yataco, J.A.D.; Gyawali, B.; McCormack, V.; de Anderson, M.M.; Mehrotra, R.; et al. Breast cancer early detection: A phased approach to implementation. Cancer 2020, 126, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Mariotto, A.B.; Rowland, J.H.; Yabroff, K.R.; Alfano, C.M.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellquist, B.N.; Czene, K.; Hjälm, A.; Nyström, L.; Jönsson, H. Effectiveness of population-based service screening with mammography for women ages 40 to 49 years with a high or low risk of breast cancer: Socioeconomic status, parity, and age at birth of first child. Cancer 2015, 121, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Sensors 2017, 17, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramassone, A.; Pagotto, S.; Veronese, A.; Visone, R. Epigenetics and MicroRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Jucoski, T.S.; Vieira, E.; Carvalho, T.M.; Malheiros, D.; Ribeiro, E.M.D.S.F. Liquid biopsy for breast cancer using extracellular vesicles and cell-free microRNAs as biomarkers. Transl. Res. 2020, 223, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranwal, S.; Alahari, S.K. miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormo, E.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Ballester, S.; Pineda, B.; Zazo, S.; González-Alonso, P.; Albanell, J.; Rovira, A.; Rojo, F.; Lluch, A.; et al. The role of miR-26a and miR-30b in HER2+ breast cancer trastuzumab resistance and regulation of the CCNE2 gene. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormo, E.; Ballester, S.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Burgués, O.; Alonso, E.; Bermejo, B.; Menéndez, S.; Zazo, S.; Madoz-Gúrpide, J.; Rovira, A.; et al. The miRNA-449 family mediates doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating cell cycle factors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarra, D.; Constâncio, V.; Barros-Silva, D.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Antunes, L.; Maurício, J.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection and Metastasis Development Prediction. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.K.O.; Li, R.; Shin, V.Y.; Jin, H.C.; Leung, C.P.H.; Ma, E.S.K.; Pang, R.; Chua, D.; Chu, K.M.; Law, W.L.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Specific Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Detection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Bernal, A.; Lavado-Valenzuela, R.; Domínguez-Recio, M.E.; Jiménez-Rodriguez, B.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Alba, E.; Comino-Méndez, I. Challenges and achievements of liquid biopsy technologies employed in early breast cancer. EBioMedicine 2020, 62, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojbjerg, J.A.; Ebert, E.B.F.; Clement, M.S.; Winther-Larsen, A.; Meldgaard, P.; Sorensen, B. Circulating miR-30b and miR-30c predict erlotinib response in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2019, 135, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Stevic, I.; Pan, C.; Müller, V.; Oliviera-Ferrer, L.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Different signatures of miR-16, miR-30b and miR-93 in exosomes from breast cancer and DCIS patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Qin, F.; Hu, F.; Xu, H.; Sun, G.; Han, G.; Wang, T.; Guo, M. Characterization and selective incorporation of small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular vesicles. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam-Artigues, A.; Garrido-Cano, I.; Simón, S.; Ortega, B.; Moragón, S.; Lameirinhas, A.; Constâncio, V.; Salta, S.; Burgués, O.; Bermejo, B.; et al. Circulating miR-30b-5p levels in plasma as a novel potential biomarker for early detection of breast cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Kang, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Yang, P.; Yu, Z. MicroRNA-99a acts as a tumor suppressor and is down-regulated in bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holubekova, V.; Kolkova, Z.; Grendar, M.; Brany, D.; Dvorska, D.; Stastny, I.; Jagelkova, M.; Zelinova, K.; Samec, M.; Liskova, A.; et al. Pathway analysis of selected circulating mirnas in plasma of breast cancer patients: A preliminary study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Cano, I.; Constâncio, V.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Lameirinhas, A.; Simón, S.; Ortega, B.; Martínez, M.T.; Hernando, C.; Bermejo, B.; Lluch, A.; et al. Circulating mir-99a-5p expression in plasma: A potential biomarker for early diagnosis of breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Ishinaga, H.; Midorikawa, K.; Shah, S.A.; Nakamura, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M.; Takeuchi, K. Circulating microRNAs as novel prognosis biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gablo, N.; Trachtova, K.; Prochazka, V.; Hlavsa, J.; Grolich, T.; Kiss, I.; Srovnal, J.; Rehulkova, A.; Lovecek, M.; Skalicky, P.; et al. Identification and Validation of Circulating Micrornas as Prognostic Biomarkers in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients Undergoing Surgical Resection. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Gress, D.M.; Vega, L.R.M.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Compton, C.C. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, J.J.; Quadri, R.S.; Kalva, S.P.; Shah, H.; Sanjeeviah, A.R.; Beg, M.S.; Sutphin, P.D. Liquid biopsy for cancer: Review and implications for the radiologist. Radiology 2020, 294, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Circulating tumor cells: Moving biological insights into detection. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2606–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanasuriya, S.; Lambros, M.B.; de Bono, J.S. Application of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Targeted Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Hayes, D.F.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; Briant, K.C.O.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubor, P.; Kubatka, P.; Kajo, K.; Dankova, Z.; Polacek, H.; Bielik, T.; Kudela, E.; Samec, M.; Liskova, A.; Vlcakova, D.; et al. Why the gold standard approach by mammography demands extension by multiomics? Application of liquid biopsy mirna profiles to breast cancer disease management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, L.; Wszolek, M.F.; Liu, C.G.; Jing, W.; Diao, L.; Zien, A.; Zhang, J.D.; Jackson, D.; Dinney, C.P.N. Plasma microRNA profiles for bladder cancer detection. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2013, 31, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Song, G.; Zou, X.; Shan, X.; Liu, Q.; Xia, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W. Circulating plasma microRNA signature for the diagnosis of cervical cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 26, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.S.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Wong, D.V.T.; Mello, J.B.H.; Nobre, L.M.S.; Wanderley, C.W.S.; Lucetti, L.T.; Muniz, H.A.; Paiva, I.K.D.; Kuasne, H.; et al. Circulating let-7e-5p, mir-106a-5p, mir-28-3p, and mir-542-5p as a promising microrna signature for the detection of colorectal cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Martín, A.C.; Pérez-Palacios, R.; Vila-Navarro, E.; Marcuello, M.; Diaz-Centeno, M.; Cubiella, J.; Diez, M.S.; Bujanda, L.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA Signature Validation for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanutto, S.; Ciniselli, C.M.; Belfiore, A.; Lecchi, M.; Masci, E.; Delconte, G.; Primignani, M.; Tosetti, G.; Dal Fante, M.; Fazzini, L.; et al. Plasma miRNA-based signatures in CRC screening programs. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, V.Y.; Ng, E.K.O.; Chan, V.W.; Kwong, A.; Chu, K.M. A three-miRNA signature as promising non-invasive diagnostic marker for gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Wen, W.; Cheng, W.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; Qi, L.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Diagnostic value of a plasma microRNA signature in gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Miao, Y. Plasma miRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer: A miRNA expression analysis. Gene 2018, 673, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Ye, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. A three-plasma miRNA signature serves as novel biomarkers for osteosarcoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.A.; Weng, S.L.; Yang, S.F.; Chou, C.H.; Huang, W.C.; Tu, S.J.; Chang, T.H.; Huang, C.N.; Jong, Y.J.; Huang, H. Da A three–MicroRNA signature as a potential biomarker for the early detection of oral cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, D.; Chang, A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q. Plasma microRNA expression signature involving miR-548q, miR-630 and miR-940 as biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Q.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, F.; Lee, C.J.; Zhan, M.; Fang, H.B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F. A plasma miRNA signature for lung cancer early detection. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111902–111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hu, Q.; Schrauder, M.; Yan, L.; Wang, D.; Medico, L.; Guo, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, B.; et al. Circulating miR-148b and miR-133a as biomarkers for breast cancer detection. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5284–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuk, K.; Zucknick, M.; Heil, J.; Madhavan, D.; Schott, S.; Turchinovich, A.; Arlt, D.; Rath, M.; Sohn, C.; Benner, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. Plasma-based microRNA signatures in early diagnosis of breast cancer. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frères, P.; Wenric, S.; Boukerroucha, M.; Fasquelle, C.; Thiry, J.; Bovy, N.; Struman, I.; Geurts, P.; Collignon, J.; Schroeder, H.; et al. Circulating microRNA-based screening tool for breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5416–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, T.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Ding, Q.; Wang, S. Circulating microRNAs from the miR-106a–363 cluster on chromosome X as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, L.; Khadka, V.S.; Ai, J.; Zou, H.; Ju, D.; Jiang, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, X. Plasma microRNA pair panels as novel biomarkers for detection of early stage breast cancer. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.W.; Jacks, T.; Housman, D.E.; Ruley, H.E. Abrogation of oncogene-associated apoptosis allows transformation of p53-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2026–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal Heterogeneity and Tumor Evolution: Past, Present, and the Future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walerych, D.; Napoli, M.; Collavin, L.; Del Sal, G. The rebel angel: Mutant p53 as the driving oncogene in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; McGowan, P.M.; Crown, J.; O’Connor, D.; Gallagher, W.M. P53 as a target for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.C.; Verheyen, E.M.; Zeng, Y.A. Mammary development and breast cancer: A Wnt perspective. Cancers 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.F.; Chen, P.M.; Chu, P.Y. LGR5 overexpression confers poor relapse-free survival in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ghia, E.M.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Lei, Y.; He, J.; Cui, B.; et al. Inhibition of chemotherapy resistant breast cancer stem cells by a ROR1 specific antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, L.; Tagliabue, E.; Pupa, S.M. Inhibition of the Wnt signalling pathway: An avenue to control breast cancer aggressiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schie, E.H.; van Amerongen, R. Aberrant WNT/CTNNB1 Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Human Breast Cancer: Weighing the Evidence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | N (%) | Median (95% CI) | p Value (vs. Control) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy controls | 89 | 0.6787 (0.3943–1.234) | ||
| BC patients | 54 | 0.2593 (0.2073–0.3098) | <0.0001 | |
| Molecular subtype | ||||
| Luminal | 32 (59.26%) | 0.7656 (0.3228–1.383) | <0.0001 | 0.2750 |
| TNBC | 10 (18.52%) | 0.4252 (0.1722–1.177) | 0.02 | |
| HER2 | 12 (22.22%) | 1.233 (0.4249–2.229) | <0.0001 | |
| Grade | ||||
| 1 | 2 (3.70%) | 0.3232 (0.2711–0.3753) | 0.9697 | 0.4094 |
| 2 | 24 (44.44%) | 0.8368 (0.3654–1.954) | <0.0001 | |
| 3 | 25 (46.30%) | 0.4424 (0.3024–1.234) | <0.0001 | |
| Not available | 3 (5.56%) | |||
| Stage | ||||
| I | 17 (31.48%) | 1.287 (0.6117–2.809) | <0.0001 | 0.0523 |
| II | 15 (27.78%) | 0.3205 (0.1722–1.8498 | <0.0001 | |
| III | 11 (20.37%) | 0.4542 (0.2155–1.383) | 0.0026 | |
| IV | 12 (22.22%) | 0.7656 (0.3475–1.934) | <0.0001 | |
| T | ||||
| T1 | 20 (37.04%) | 1.049 (0.4424–2.566) | <0.0001 | 0.2170 |
| T2 | 15 (27.78%) | 0.6770 (0.3024–1.954) | <0.0001 | |
| T3 | 11 (20.37%) | 0.2620 (0.0387–1.934) | 0.0089 | |
| T4 | 5 (9.26%) | 0.7220 (0.3475–3.180) | <0.0001 | |
| Not available | 3 (5.55%) | |||
| N | ||||
| Positive | 26 (48.15%) | 0.4774 (0.3024–1.288) | <0.0001 | 0.0584 |
| Negative | 26 (48.15%) | 1.021 (0.4424–2.566) | <0.0001 | |
| Not available | 2 (3.70%) | |||
| Metastasis | ||||
| Yes | 11 (20.37%) | 0.7656 (0.3475–1.934) | <0.0001 | 0.5168 |
| No | 41 (75.93%) | 0.6612 (0.3753–1.287) | <0.0001 | |
| Not available | 2 (3.70%) |
| Characteristics | BC Patients | Healthy Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 18 | 74 |
| Median age in years (range) | 54 (34–69) | 55 (32–90) |
| Molecular subtype, N (%) | ||
| Luminal | 11 (61.11%) | |
| TNBC | 3 (16.67%) | |
| HER2 | 3 (16.67%) | |
| Not available | 1 (5.55%) | |
| Grade, N (%) | ||
| 1 | 5 (27.78%) | |
| 2 | 9 (50%) | |
| 3 | 4 (22.22%) | |
| Stage, N (%) | ||
| I | 18 (100%) | |
| T, N (%) | ||
| T1 | 18 (100%) | |
| N, N (%) | ||
| Positive | 18 (100%) | |
| Metastasis, N (%) | ||
| No | 18 (100%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adam-Artigues, A.; Garrido-Cano, I.; Carbonell-Asins, J.A.; Lameirinhas, A.; Simón, S.; Ortega-Morillo, B.; Martínez, M.T.; Hernando, C.; Constâncio, V.; Burgues, O.; et al. Identification of a Two-MicroRNA Signature in Plasma as a Novel Biomarker for Very Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112848
Adam-Artigues A, Garrido-Cano I, Carbonell-Asins JA, Lameirinhas A, Simón S, Ortega-Morillo B, Martínez MT, Hernando C, Constâncio V, Burgues O, et al. Identification of a Two-MicroRNA Signature in Plasma as a Novel Biomarker for Very Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112848
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdam-Artigues, Anna, Iris Garrido-Cano, Juan Antonio Carbonell-Asins, Ana Lameirinhas, Soraya Simón, Belén Ortega-Morillo, María Teresa Martínez, Cristina Hernando, Vera Constâncio, Octavio Burgues, and et al. 2021. "Identification of a Two-MicroRNA Signature in Plasma as a Novel Biomarker for Very Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112848
APA StyleAdam-Artigues, A., Garrido-Cano, I., Carbonell-Asins, J. A., Lameirinhas, A., Simón, S., Ortega-Morillo, B., Martínez, M. T., Hernando, C., Constâncio, V., Burgues, O., Bermejo, B., Henrique, R., Lluch, A., Jerónimo, C., Eroles, P., & Cejalvo, J. M. (2021). Identification of a Two-MicroRNA Signature in Plasma as a Novel Biomarker for Very Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Cancers, 13(11), 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112848








