Real-World Analysis of the Impact of Radiotherapy on Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Statistics
2.3. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. XRT Timing Impact on IO-Treated Patients
3.3. XRT Parameters Impact on Outcome of IO-Treated Patients
3.4. Patient and Treatment Characteristics’ Impact on Outcome of IO-Treated Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez–Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Updated Analysis of KEYNOTE-024: Pembrolizumab Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer With PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score of 50% or Greater. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Speranza, G.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; Dómine, M.; Hui, R.; Hochmair, M.J.; Clingan, P.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Updated Analysis From KEYNOTE-189: Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Pemetrexed and Platinum for Previously Untreated Metastatic Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.; de Marinis, F.; Giaccone, G.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.G.; Geater, S.; et al. IMpower110: Interim overall survival (OS) analysis of a phase III study of atezolizumab (atezo) vs platinum-based chemotherapy (chemo) as first-line (1L) treatment (tx) in PD-L1–selected NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.; McCleod, M.; Hussein, M.; Morabito, A.; Rittmeyer, A.; Conter, H.J.; Kopp, H.-G.; Daniel, D.; McCune, S.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 tria. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yu, J.X.; Hubbard-Lucey, V.M.; Neftelinov, S.T.; Hodge, J.P.; Lin, Y. The clinical trial landscape for PD1/PDL1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, E.B.; Demaria, S.; Schiff, P.B.; Chachoua, A.; Formenti, S.C. An abscopal response to radiation and ipilimumab in a patient with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, S.; Ng, B.; Devitt, M.L.; Babb, J.S.; Kawashima, N.; Liebes, L.; Formenti, S.C. Ionizing radiation inhibition of distant untreated tumors (abscopal effect) is immune mediated. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 58, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camphausen, K.; Moses, M.A.; Ménard, C.; Sproull, M.; Beecken, W.D.; Folkman, J.; O’Reilly, M.S. Radiation abscopal antitumor effect is mediated through p53. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Lam, R.K.K.; Calaf, G.M.; Zhou, H.; Amundson, S.; Hei, T.K. Radiation-induced non-targeted response in vivo: Role of the TGFβ-TGFBR1-COX-2 signalling pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.M.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Spada, S.; Rudqvist, N.-P.; Chapman, J.R.; Ueberheide, B.M.; Pilones, K.A.; Sarfraz, Y.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Exosomes Shuttle TREX1-Sensitive IFN-Stimulatory dsDNA from Irradiated Cancer Cells to DCs. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.; Patin, E.C.; Pedersen, M.; Wilkins, A.; Dillon, M.T.; Melcher, A.A.; Harrington, K.J. Inflammatory microenvironment remodelling by tumour cells after radiotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Kim, S.; Arrington, J.; Naghavi, A.O.; Dilling, T.J.; Creelan, B.C.; Antonia, S.J.; Caudell, J.J.; Harrison, L.B.; Sahebjam, S.; et al. Outcomes targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in conjunction with stereotactic radiation for patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaverdian, N.; Lisberg, A.E.; Bornazyan, K.; Veruttipong, D.; Goldman, J.W.; Formenti, S.C.; Garon, E.B.; Lee, P. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: A secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Douglass, J.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.; Sharfman, W.; Hammers, H.; et al. Concurrent Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Melanoma, and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastina, P.; Nardone, V.; Botta, C.; Croci, S.; Tini, P.; Battaglia, G.; Ricci, V.; Cusi, M.G.; Gandolfo, C.; Misso, G.; et al. Radiotherapy prolongs the survival of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients undergone to an immune-modulating treatment with dose-fractioned cisplatin and metronomic etoposide and bevacizumab (mPEBev). Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75904–75913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Golden, E.B.; Chhabra, A.; Chachoua, A.; Adams, S.; Donach, M.; Fenton-Kerimian, M.; Friedman, K.; Ponzo, F.; Babb, J.S.; Goldberg, J.; et al. Local radiotherapy and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to generate abscopal responses in patients with metastatic solid tumours: A proof-of-principle trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, J.D.; Ai, W.Z.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Torchia, J.A.; Levy, M.; Advani, R.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Hoppe, R.T.; Knox, S.J.; Shin, L.K.; et al. In Situ Vaccination With a TLR9 Agonist Induces Systemic Lymphoma Regression: A Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4324–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.-L.N.; de Langen, A.J.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Jin, T.; Li, M.; Xue, J.; Lu, B. Synergistic effect of immunotherapy and radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Current clinical trials and prospective challenges. Precis. Clin. Med. 2019, 2, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Liang, H.; Deng, L.; Fu, Y.-X. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy: A beneficial liaison? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccheri, G.; Ferrigno, D.; Tamburini, M. Karnofsky and ECOG performance status scoring in lung cancer: A prospective, longitudinal study of 536 patients from a single institution. Eur. J. Cancer Part A 1996, 32, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, K.E. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with inoperable lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1980, 65, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, E.; Feliu, J.; Zamora, P.; Barón, M.G.; Sánchez, J.J.; Ordónez, A.; Espinosa, J. Serum albumin and other prognostic factors related to response and survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 1995, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, S.; Schmid, S.; Krapf, M.; Flatz, L.; Born, D.; Jochum, W.; Templeton, A.J.; Früh, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Auclin, E.; Ferrara, R.; Charrier, M.; Remon, J.; Planchard, D.; Ponce, S.; Ares, L.P.; Leroy, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; et al. Association of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes in Patients With Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Alley, E.W.; Evans, T.L.; Kosteva, J.A.; Ciunci, C.A.; Gabriel, P.E.; Thompson, J.C.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.; Benjamin, K.T.; Ko, E.C. Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Combinations for Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frak, M.; Krawczyk, P.; Kalinka, E.; Milanowski, J. Molecular and clinical premises for the combination therapy consisting of radiochemotherapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Hernandez, M.; Jack Lee, J.; Ye, R.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V.; Ross Camidge, D.; et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. Maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non–small-cell lung cancer: Long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Demaria, S.; Formenti, S. Current clinical trials testing the combination of immunotherapy with radiotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Galloway, A.E.; Kawashima, N.; Dewyngaert, J.K.; Babb, J.S.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5379–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, K.T. Evolution of the Supermodel: Progress in Modelling Radiotherapy Response in Mice. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.A.; Wilhite, T.J.; Balboni, T.A.; Alexander, B.M.; Spektor, A.; Ott, P.A.; Ng, A.K.; Hodi, F.S.; Schoenfeld, J.D. A systematic evaluation of abscopal responses following radiotherapy in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with ipilimumab. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chajon, E.; Castelli, J.; Marsiglia, H.; De Crevoisier, R. The synergistic effect of radiotherapy and immunotherapy: A promising but not simple partnership. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 111, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agg, H.; Winfree, K.B.; Zhu, Y.E.; Muehlenbein, C. A real-world analysis of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab or pembrolizumab in combination with pemetrexed and platinum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | All Patients | No XRT | XRT before IO | XRT after IO | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 453 (100) | 167 (100) | 182 (100) | 104 (100) | |
| Age (years) median (range) | 67 (34–96) | 69 (38–96) | 67 (43–89) | 66 (34–83) | 0.0369 * |
| Sex-male (%) | 296 (65.3) | 107 (64.1) | 116 (63.7) | 73 (70.2) | 0.495 § |
| ECOG-PS—N (%) | 0.025 § | ||||
| 0–1 | 312 (68.7) | 112 (67.1) | 117 (64.3) | 83 (79.8) | |
| 2–3 | 137 (30.2) | 52 (31.1) | 64 (35.2) | 21 (20.2) | |
| 4 | 4 (0.9) | 3 (1.8) | 1 (0.5) | 0 | |
| XRT site—N (%) | 0.049 § | ||||
| None | 167 (36.9) | 167 (100) | |||
| Bone | 126 (27.8) | 86 (47.3) | 40 (38.5) | ||
| Cranium | 23 (5.1) | 10 (5.5) | 13 (12.5) | ||
| Gastro-intestinal | 9 (2.0) | 4 (2.2) | 5 (4.8) | ||
| Lung and Mediastinum | 116 (25.6) | 77 (42.3) | 39 (37.5) | ||
| Soft tissue | 12 (2.6) | 5 (2.7) | 7 (6.7) | ||
| Total XRT dose (Gy)—N (%) | <0.001 § | ||||
| None | 167 (36.9) | 167 (100) | |||
| 1 < dose ≤ 10 | 41 (9.1) | 19 (10.4) | 22 (21.2) | ||
| 10 < dose ≤ 20 | 75 (16.6) | 47 (25.8) | 28 (26.9) | ||
| 20 < dose ≤ 30 | 71 (15.7) | 45 (24.7) | 26 (25.0) | ||
| 30 < dose ≤ 40 | 21 (4.6) | 8 (4.4) | 13 (12.5) | ||
| 40 < dose ≤ 50 | 29 (6.4) | 18 (9.9) | 11 (10.6) | ||
| 50 < dose | 49 (10.8) | 45 (24.7) | 4 (3.8) | ||
| Fraction size (Gy)—N (%) | <0.001 § | ||||
| None | 167 (36.9) | 167 (100) | |||
| Fraction ≤ 2 | 54 (11.9) | 49 (26.9) | 5 (4.8) | ||
| 2 < fraction ≤ 4 | 144 (31.8) | 85 (46.7) | 59 (56.7) | ||
| 4 < fraction ≤ 8 | 60 (13.2) | 32 (17.6) | 28 (26.9) | ||
| 8 ≤ Fraction | 28 (6.2) | 16 (8.8) | 12 (11.5) | ||
| IO—N (%) | 0.136 § | ||||
| Nivolumab | 176 (38.9) | 66 (39.5) | 64 (35.2) | 46 (44.2) | |
| Atezolizumab | 32 (7.1) | 8 (4.8) | 19 (10.4) | 5 (4.8) | |
| IO plus Chemotherapy | 101 (22.3) | 38 (22.8) | 48 (26.4) | 15 (14.4) | |
| IO plus IO | 5 (1.1) | 2 (1.2) | 2 (1.1) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Pembrolizumab | 139 (30.7) | 53 (31.7) | 49 (26.9) | 37 (35.6) | |
| Treatment line of IO—N (%) | 0.755 *,‡ | ||||
| 1 | 226 (49.9) | 86 (51.5) | 89 (48.9) | 51 (49.0) | |
| ≥2 | 227 (50.1) | 81 (48.5) | 93 (51.1) | 53 (51.0) | |
| Albumin—gr/dL, mean (95%CI) | 3.54 (3.48–3.60) | 3.46 (3.35–3.57) | 3.51 (3.43–3.59) | 3.72 (3.60–3.84) | 0.005 * |
| NLR—mean (95%CI) | 6.77 (6.21–7.34) | 6.01 (5.23–6.78) | 8.02 (7.06–8.99) | 5.52 (4.33–6.71) | <0.001 * |
| Histology—N (%) | 0.625 § | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 309 (68.2) | 118 (70.7) | 123 (67.6) | 68 (65.4) | |
| Squamous cell | 92 (20.3) | 31 (18.6) | 35 (19.2) | 26 (25.0) | |
| NSCLC-NOS | 52 (11.5) | 18 (10.8) | 24 (13.2) | 10 (9.6) | |
| Mutation—N (%) | 0.660 §,# | ||||
| None | 349 (77.0) | 125 (74.9) | 144 (79.1) | 80 (76.9) | |
| KRAS | 43 (9.5) | 19 (11.4) | 14 (7.7) | 10 (9.6) | |
| EGFR | 31 (6.8) | 11 (6.6) | 15 (8.2) | 5 (4.8) | |
| ALK | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (1.0) | |
| BRAF | 13 (2.9) | 6 (3.6) | 3 (1.6) | 4 (3.8) | |
| c-MET | 6 (1.3) | 2 (1.2) | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.0) | |
| ROS1 | 5 (1.1) | 1 (0.6) | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1.9) | |
| Other | 4 (0.9) | 3 (1.8) | 0 | 1 (1.0) |
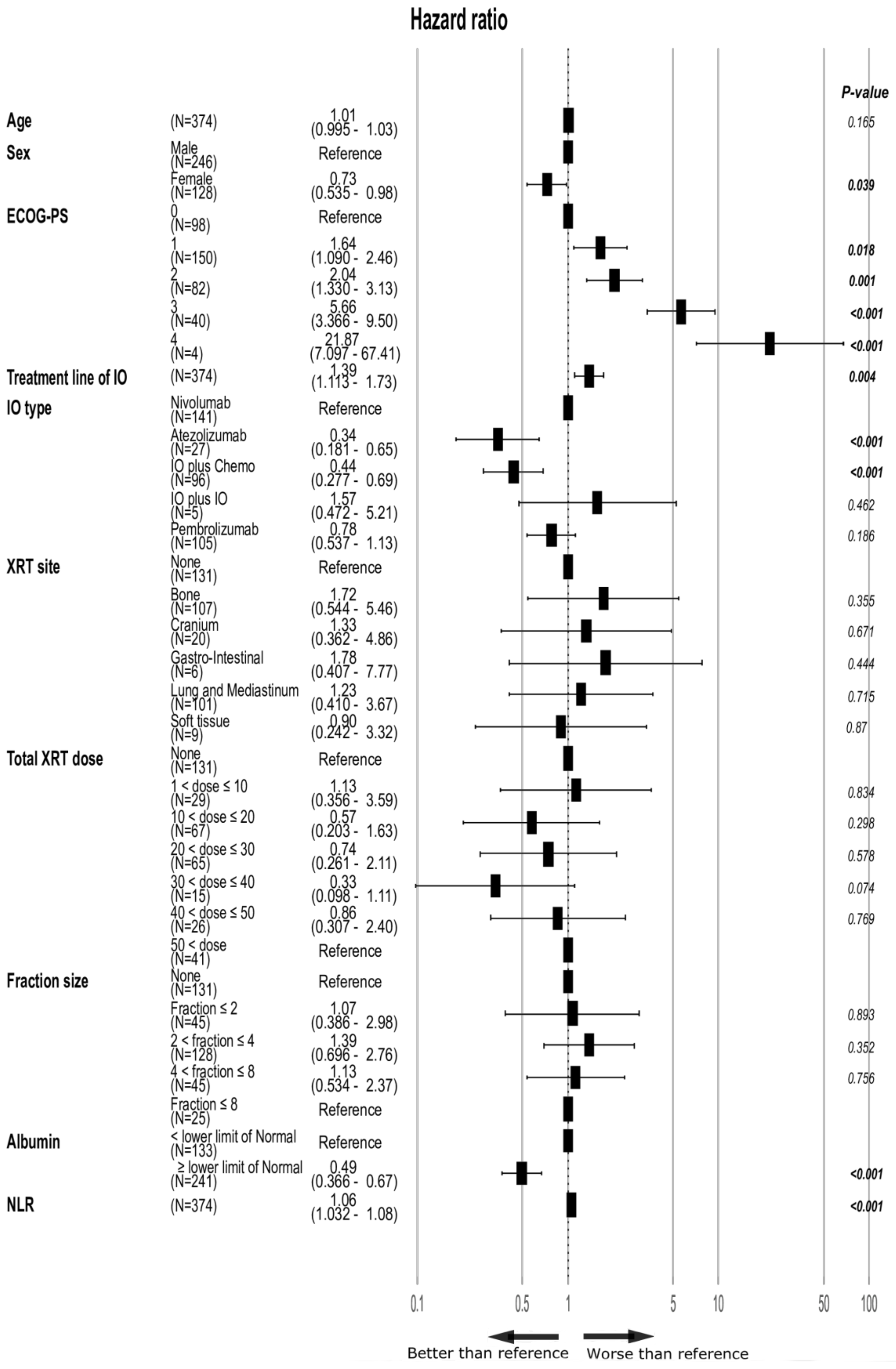
| Parameters | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.0 (0.99–1.0) | 0.196 |
| Sex (men—reference) | 0.81 (0.63–1.04) | 0.110 |
| ECOG-PS | ||
| 0 | Reference | |
| 1 | 1.77 (1.29–2.42) | <0.001 |
| 2 | 3.03 (2.15–4.27) | <0.001 |
| 3 | 6.37 (4.19–9.68) | <0.001 |
| 4 | 31.81 (11.15–90.79) | <0.001 |
| XRT site | ||
| None | Reference | |
| Bone | 1.36 (1.01–1.83) | 0.040 |
| Cranium | 0.99 (0.57–1.75) | 0.988 |
| Gastro-intestine | 0.71 (0.31–1.62) | 0.417 |
| Lung and Mediastinum | 1.00 (0.74–1.36) | 0.988 |
| Soft Tissue | 0.90 (0.45–1.79) | 0.765 |
| Total XRT dose (Gray) | ||
| None | Reference | |
| 1< dose ≤ 10 | 1.66 (1.13–2.46) | 0.010 |
| 10 < dose ≤ 20 | 1.33 (0.95–1.86) | 0.099 |
| 20 < dose ≤ 30 | 1.18 (0.82–1.69) | 0.376 |
| 30 < dose ≤ 40 | 0.50 (0.25–0.99) | 0.048 |
| 40 < dose ≤ 50 | 0.97 (0.59–1.58) | 0.891 |
| 50 < dose | 0.85 (0.55–1.31) | 0.470 |
| Fraction size (Gray) | ||
| None | Reference | |
| Fraction ≤ 2 | 0.87 (0.57–1.32) | 0.513 |
| 2 < Fraction ≤ 4 | 1.14 (0.85–1.52) | 0.370 |
| 4 < Fraction ≤ 8 | 1.48 (1.04–2.10) | 0.027 |
| 8 < Fraction | 0.82 (0.49–1.37) | 0.452 |
| XRT Timing | ||
| No XRT | Reference | |
| XRT after IO | 1.20 (0.91–1.58) | 0.188 |
| XRT before IO | 1.00 (0.74–1.36) | 0.990 |
| Timing Cohorts—time window: * | ||
| XRT after IO | Reference | |
| One month | 0.72 (0.44–1.16) | 0.179 |
| Three months | 0.76 (0.50–1.14) | 0.188 |
| Six months | 0.77 (0.54–1.09) | 0.139 |
| Treatment-line of IO | 1.32 (1.15–1.52) | <0.001 |
| Albumin | ||
| < lower limit of Normal | Reference | |
| ≥ lower limit of Normal | 0.34 (0.26–0.45) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 1.06 (1.04–1.07) | <0.001 |
| Histology | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | Reference | |
| Squamous cell | 1.01 (0.75–1.36) | 0.940 |
| NSCLC NOS | 1.20 (0.85–1.72) | 0.290 |
| Mutation | ||
| None | Reference | |
| KRAS | 9.20 (0.60–1.41) | 0.706 |
| EGFR | 1.15 (0.73–1.82) | 0.552 |
| ALK | 2.34 (0.58–9.44) | 0.231 |
| BRAF | 8.71 (0.43–1.76) | 0.701 |
| c-MET | 7.31 (0.27–1.97) | 0.536 |
| ROS1 | 1.06 (0-Inf) | 0.990 |
| Others | 5.25 (0.13–2.11) | 0.364 |
| IO type: | ||
| Nivolumab | Reference | |
| Pembrolizumab | 0.71 (0.54–0.92) | 0.011 |
| IO plus Chemotherapy | 0.36 (0.24–0.54) | <0.001 |
| Atezolizumab | 0.79 (0.47–1.34) | 0.386 |
| IO plus IO | 0.56 (0.178–1.75) | 0.315 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onn, A.; Gottfried, T.; Stemmer, A.; Appel, S.; Lawrence, Y.R.; Urban, D.; Beller, T.; Daher, S.; Bar, J. Real-World Analysis of the Impact of Radiotherapy on Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112800
Onn A, Gottfried T, Stemmer A, Appel S, Lawrence YR, Urban D, Beller T, Daher S, Bar J. Real-World Analysis of the Impact of Radiotherapy on Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112800
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnn, Amir, Teodor Gottfried, Amos Stemmer, Sarit Appel, Yaacov R. Lawrence, Damien Urban, Tamar Beller, Sameh Daher, and Jair Bar. 2021. "Real-World Analysis of the Impact of Radiotherapy on Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112800
APA StyleOnn, A., Gottfried, T., Stemmer, A., Appel, S., Lawrence, Y. R., Urban, D., Beller, T., Daher, S., & Bar, J. (2021). Real-World Analysis of the Impact of Radiotherapy on Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 13(11), 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112800






