Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
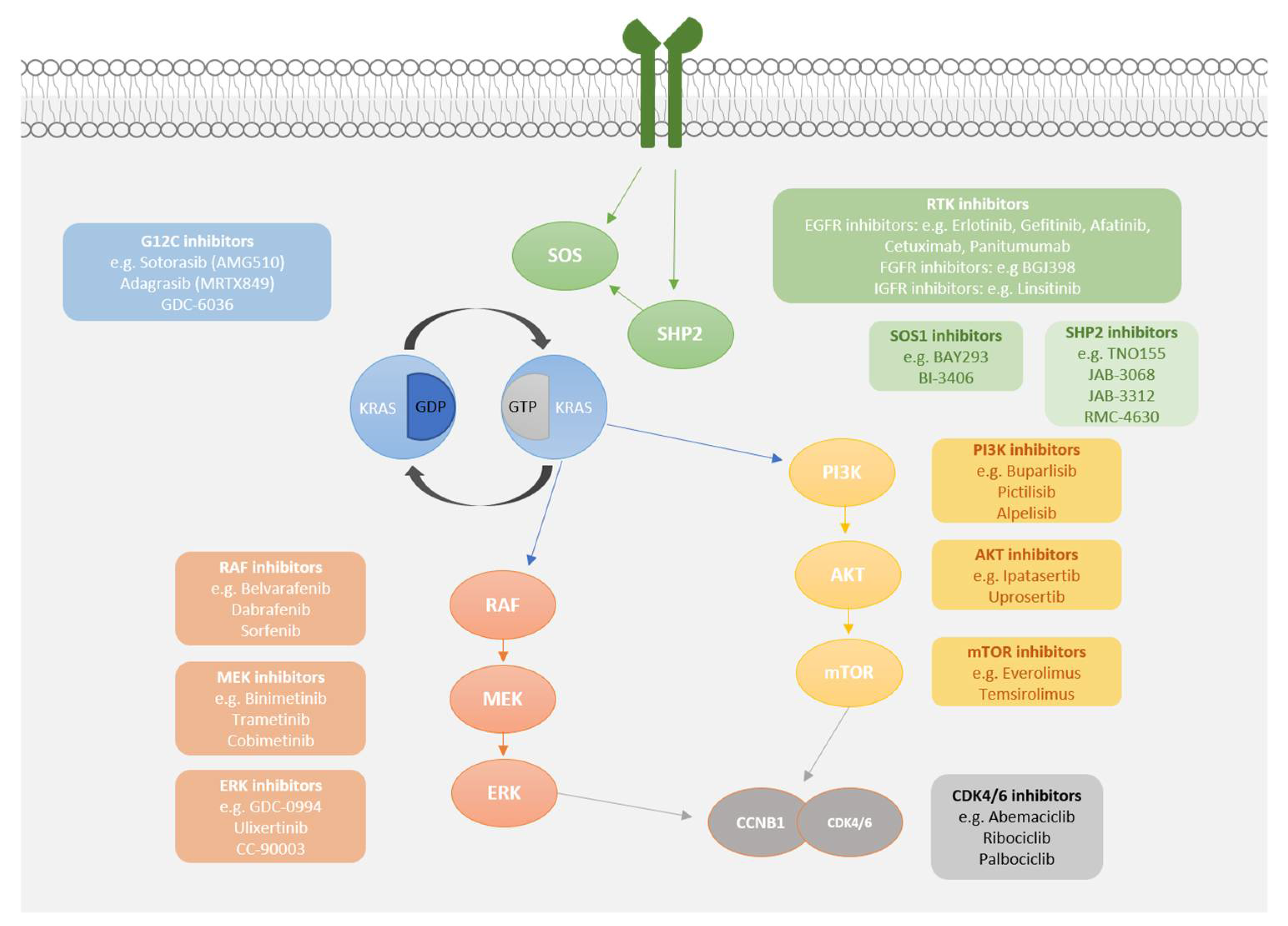
2. G12C Inhibitors
3. Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors
4. Maximising the Potential of G12C Inhibitors
4.1. Upstream Co-Inhibition
4.2. Downstream Co-Inhibition
4.3. Cell Cycle Checkpoint Co-Inhibition
4.4. Immune Checkpoint Co-Inhibition
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hobbs, G.A.; Der, C.J.; Rossman, K.L. RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanshu, D.K.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F. RAS Proteins and Their Regulators in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherfils, J.; Zeghouf, M. Regulation of Small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 269–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, M.; Dhawahir, A.; Sum, E.Y.M.; Urosevic, J.; Lechuga, C.G.; Esteban, L.M.; Castellano, E.; Guerra, C.; Santos, E.; Barbacid, M. Genetic analysis of Ras signalling pathways in cell proliferation, migration and survival. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data: Figure 1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkala, S.; Ramalingam, S.S. Personalized therapy for lung cancer: Striking a moving target. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 120858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffzek, K.; Ahmadian, M.R.; Kabsch, W.; Wiesmüller, L.; Lautwein, A.; Schmitz, F.; Wittinghofer, A. The Ras-RasGAP Complex: Structural Basis for GTPase Activation and Its Loss in Oncogenic Ras Mutants. Science 1997, 277, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Hood, F.E.; Hartley, J.L. The Frequency of Ras Mutations in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.D.; Fesik, S.W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Luo, J.; Der, C.J. Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission Possible? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fang, G.; Rudolph, J. Ras inhibition via direct Ras binding—Is there a path forward? Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5766–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, C.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Forster, M.; Blackhall, F. KRAS: Reasons for optimism in lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 99, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahearn, I.M.; Haigis, K.M.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Philips, M.R. Regulating the regulator: Post-translational modification of RAS. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, T.B.; Hahn, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Muschel, R.J.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: An overview of the results of preclinical and clinical investigations. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 14522880. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, N.E.; Omer, C.A.; Conner, M.W.; Anthony, N.J.; Davide, J.P.; Desolms, S.J.; Giuliani, E.A.; Gomez, R.P.; Graham, S.L.; Hamilton, K.; et al. Inhibition of farnesyltransferase induces regression of mammary and salivary carcinomas in ras transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjei, A.A.; Mauer, A.; Bruzek, L.; Marks, R.S.; Hillman, S.; Geyer, S.; Hanson, L.J.; Wright, J.J.; Erlichman, C.; Kaufmann, S.H.; et al. Phase II Study of the Farnesyl Transferase Inhibitor R115777 in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymach, J.V.; Johnson, D.H.; Khuri, F.R.; Safran, H.; Schlabach, L.L.; Yunus, F.; Devore, R.F.; De Porre, P.M.; Richards, H.M.; Jia, X.; et al. Phase II study of the farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777 in patients with sensitive relapse small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Chau, N.; Bauman, J.; Bible, K.; Chintakuntlawar, A.; Cabanillas, M.; Wong, D.; Garcia, I.B.; Brose, M.; Boni, V.; et al. Preliminary results from a phase II trial of tipifarnib in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) with HRAS mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, F.; Shivani, M.; Wang, Z.; Chan, S.; Gilardi, M.; Gutkind, S. Antitumor activity of tipifarnib and PI3K pathway inhibitors in HRAS-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, S43–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Xue, J.Y.; Lito, P. Targeting KRAS(G12C): From Inhibitory Mechanism to Modulation of Antitumor Effects in Patients. Cell 2020, 183, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Rosen, N.; Solit, D.B. Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- My Cancer Genome. Biomarkers. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/alteration/kras-g12c/#ref-4 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Lindsay, C.R.; Blackhall, F.H. Direct Ras G12C inhibitors: Crossing the rubicon. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, A.M.; Der, C.J. KRAS: The Critical Driver and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnett-Kane, V.; Burkitt-Wright, E.; Blackhall, F.; Malliri, A.; Evans, D.; Lindsay, C.R. Germline and sporadic cancers driven by the RAS pathway: Parallels and contrasts. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, M.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Peters, U.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Babbar, A.; Firdaus, S.J.; Darjania, L.; et al. Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers with a Covalent G12C-Specific Inhibitor. Cell 2018, 172, 578–589.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, J.; Engstrom, L.D.; Hargis, L.; Calinisan, A.; Aranda, R.; Briere, D.M.; Sudhakar, N.; Bowcut, V.; Baer, B.R.; Ballard, J.A.; et al. The KRASG12C Inhibitor MRTX849 Provides Insight toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS-Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrem, J.M.; Peters, U.; Sos, M.L.; Wells, J.A.; Shokat, K.M. K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 503, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Solomon, M.; Li, L.-S.; Hansen, R.; Rosen, N. Allele-specific inhibitors inactivate mutant KRAS G12C by a trapping mechanism. Science 2016, 351, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.C.; Manandhar, A.; Carrasco, M.A.; Gurbani, D.; Gondi, S.; Westover, K.D. Biochemical and Structural Analysis of Common Cancer-Associated KRAS Mutations. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Byers, L.A.; Diao, L.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Tong, P.; Izzo, J.G.; Behrens, C.; Kadara, H.; Parra, E.R.; Canales, J.R.; et al. Co-occurring Genomic Alterations Define Major Subsets of KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma with Distinct Biology, Immune Profiles, and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Hartmaier, R.J.; Trabucco, S.E.; Gay, L.; et al. STK11/LKB1 Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, N.J.; Klein, A.B.; Golozar, A.; Collins, J.M.; Fraeman, K.H.; Nordstrom, B.L.; McEwen, R.; Hembrough, T.; Rizvi, N.A. STK11 (LKB1) mutations in metastatic NSCLC: Prognostic value in the real world. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janne, P.; Papadopoulos, K.; Ou, I.; Rybkin, I.; Johnson, M. A Phase 1 Clinical Trial Evaluating the Pharmacokinetics (PK), Safety, and Clinical Activity of MRTX849, a Mutant-Selective Small Molecule KRAS G12C Inhibitors, in Advanced Solid Tumours. Available online: https://www.mirati.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/AACR-NCI-EORTC-Clinical-Data-Presentation_Janne_October-2019-1-1.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Hong, D.S.; Fakih, M.G.; Strickler, J.H.; Desai, J.; Durm, G.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Falchook, G.S.; Price, T.J.; Sacher, A.; Denlinger, C.S.; et al. KRASG12C Inhibition with Sotorasib in Advanced Solid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Okamoto, I.; Taguri, M.; Morita, S.; Nakagawa, K. Postprogression Survival in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Who Receive Second-Line or Third-Line Chemotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janne, P.; Rybkin, I.; Spira, A.; Riely, G.; Papadopolous, K.; Sabari, J.K.; Johnson, M.L.; Heist, R.S.; Bazhenova, L.; Barve, M.; et al. KRYSTAL-1: Activity and Safety of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring KRAS G12C mutation. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Ou, S.H.I.; Barve, M.; Rybkin, I.I.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Leal, T.A.; Velastegui, K.; Christensen, J.G.; Kheoh, T.; Weiss, J.; et al. KRYSTAL-1: Activity and Safety of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Har-boring KRAS G12C mutation. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Yang, S. Overcoming Resistance to Drugs Targeting KRAS Mutation. Innovation 2020, 1, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.F. PI3K/Akt: Getting it right matters. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6473–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Greninger, P.; Rhodes, D.; Koopman, L.; Violette, S.; Bardeesy, N.; Settleman, J. A Gene Expression Signature Associated with “K-Ras Addiction” Reveals Regulators of EMT and Tumor Cell Survival. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzumdar, M.D.; Chen, P.-Y.; Dorans, K.J.; Chung, K.M.; Bhutkar, A.; Hong, E.; Noll, E.M.; Sprick, M.; Trumpp, A.; Jacks, T. Survival of pancreatic cancer cells lacking KRAS function. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Yao, W.; Ying, H.; Hua, S.; Liewen, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.-J.; Sadanandam, A.; Hu, B.; et al. Yap1 Activation Enables Bypass of Oncogenic Kras Addiction in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2014, 158, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.D.; Xue, W.; Krall, E.B.; Bhutkar, A.; Piccioni, F.; Wang, X.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sood, S.; Rosenbluh, J.; Kim, J.W.; et al. KRAS and YAP1 Converge to Regulate EMT and Tumor Survival. Cell 2014, 158, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román, M.; Baraibar, I.; López, I.; Nadal, E.; Rolfo, C.; Vicent, S.; Gil-Bazo, I. KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, J.R.; A Fecher, L.; Falchook, G.S.; Nallapareddy, S.; Gordon, M.S.; Becerra, C.; DeMarini, D.J.; Cox, D.S.; Xu, Y.; Morris, S.R.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and efficacy data for the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Heuvel, M.M.V.D.; Barlesi, F.; Cobo, M.; Mazieres, J.; Crinò, L.; Orlov, S.; Blackhall, F.; Wolf, J.; Garrido, P.; et al. Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared with Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients with KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA 2017, 317, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenschein, G.; Smit, E.F.; Planchard, D.; Kim, D.-W.; Cadranel, J.; De Pas, T.; Dunphy, F.; Udud, K.; Ahn, M.-J.; Hanna, N.H.; et al. A randomized phase II study of the MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor trametinib (GSK1120212) compared with docetaxel in KRAS-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.S.; Balmanno, K.; Sale, M.J.; Newman, S.; Dry, J.R.; Hampson, M.; Edwards, P.A.W.; Smith, P.D.; Cook, S.J. Amplification of the Driving Oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, Underpins Acquired Resistance to MEK1/2 Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitai, H.; Ebi, H.; Tomida, S.; Floros, K.V.; Kotani, H.; Adachi, Y.; Oizumi, S.; Nishimura, M.; Faber, A.C.; Yano, S. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Defines Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Induced by MEK Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahallad, A.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Salazar, R.; Zecchin, D.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bardelli, A.; Bernards, R. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 483, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Turke, A.B.; Coffee, E.M.; Nishino, M.; Cogdill, A.P.; Brown, R.D.; Della Pelle, P.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Hung, K.E.; et al. EGFR-Mediated Reactivation of MAPK Signaling Contributes to Insensitivity of BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancers to RAF Inhibition with Vemurafenib. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, M.R.; Hwang, E.; Mroue, R.; Bielski, C.M.; Wandler, A.M.; Huang, B.J.; Firestone, A.J.; Young, A.; Lacap, J.A.; Crocker, L.; et al. KRAS Allelic Imbalance Enhances Fitness and Modulates MAP Kinase Dependence in Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 817–829.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrogio, C.; Köhler, J.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Wang, H.; Paranal, R.; Li, J.; Capelletti, M.; Caffarra, C.; Li, S.; Lv, Q.; et al. KRAS Dimerization Impacts MEK Inhibitor Sensitivity and Oncogenic Activity of Mutant KRAS. Cell 2018, 172, 857–868.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misale, S.; Fatherree, J.P.; Cortez, E.; Li, C.; Bilton, S.J.; Timonina, D.; Myers, D.T.; Lee, D.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Greenberg, M.; et al. KRAS G12C NSCLC Models Are Sensitive to Direct Targeting of KRAS in Combination with PI3K Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 25, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Aronowitz, J.; Mai, T.T.; Vides, A.; Qeriqi, B.; Kim, D.; Li, C.; De Stanchina, E.; Mazutis, L.; et al. Rapid non-uniform adaptation to conformation-specific KRAS(G12C) inhibition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 577, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.B.; De La Cruz, F.F.; Phat, S.; Myers, D.T.; Wong, E.; Shahzade, H.A.; Hong, C.B.; Corcoran, R.B. Vertical Pathway Inhibition Overcomes Adaptive Feedback Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 26, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dance, M.; Montagner, A.; Salles, J.-P.; Yart, A.; Raynal, P. The molecular functions of Shp2 in the Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2) pathway. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, C.; Ran, H.; Diskin, B.; Wei, W.; Jen, J.; Geer, M.J.; Araki, K.; Ozerdem, U.; Simeone, D.M.; Miller, G.; et al. SHP2 Inhibition Prevents Adaptive Resistance to MEK Inhibitors in Multiple Cancer Models. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, C.; Velazquez, R.; Wang, H.; Dunkl, L.M.; Kazic-Legueux, M.; Haberkorn, A.; Billy, E.; Manchado, E.; Brachmann, S.M.; et al. SHP2 Inhibition Overcomes RTK-Mediated Pathway Reactivation in KRAS-Mutant Tumors Treated with MEK Inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.J.; Haderk, F.; Stahlhut, C.; Schulze, C.J.; Hemmati, G.; Wildes, D.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Mordec, K.; Marquez, A.; Romero, J.; et al. RAS nucleotide cycling underlies the SHP2 phosphatase dependence of mutant BRAF-, NF1- and RAS-driven cancers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Koczywas, M.; Ulahannan, S.; Janne, P.; Pacheco, J.; Burris, H.; McCoach, C.; Wang, J.; Gordon, M.; Haura, E.; et al. A12 The SHP2 Inhibitor RMC-4630 in Patients with KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Preliminary Evaluation of a First-in-Man Phase 1 Clinical Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, S15–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.; Ulahannan, S.; Koczywas, M.; Brahmer, J.; Capasso, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Gordon, M.; McCoach, C.; Nagasaka, M.; Ng, K.; et al. Intermittent dosing of RMC-4630, a potent, selective inhibitor of SHP2, combined with the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, in a phase 1b/2 clinical trial for advanced solid tumors with activating mutations of RAS signaling. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, S8–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, C.; Li, S.; Teng, K.W.; Foster, C.J.; Peng, D.H.; Ran, H.; Mita, P.; Geer, M.J.; Hattori, T.; Koide, A.; et al. SHP2 inhibition diminishes KRASG12C cycling and promotes tumor microenvironment remodeling. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Loo, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Kowal, C.; Delach, S.; Wang, Y.; Goldoni, S.; et al. Combinations with Allosteric SHP2 Inhibitor TNO155 to Block Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.N.; Shaw, A.T. Resistance looms for KRASG12C inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, V.; Yaeger, R.; Arcella, P.; Cancelliere, C.; Lamba, S.; Lorenzato, A.; Arena, S.; Montone, M.; Mussolin, B.; Bian, Y.; et al. EGFR Blockade Reverts Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Chen, L.; Tan, X.; Crosby, K.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Upadhyay, R.; Maira, M.; McNamara, K.; Perera, S.A.; Song, Y.; et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, B.; Contino, G.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Corcoran, R.B.; Deshpande, V.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Hezel, A.F.; Wong, K.-K.; Loda, M.; Weissleder, R.; et al. Combined MEK and PI3K Inhibition in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Beeram, M.; Rasco, D.W.; Smith, L.S.; Gunn, S.; Smetzer, L.; Mays, T.A.; Kaiser, B.; et al. The Clinical Effect of the Dual-Targeting Strategy Involving PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/MEK/ERK Pathways in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, D.; Soria, J.-C.; Sharma, S.; Banerji, U.; Azaro, A.; Desai, J.; Ringeisen, F.P.; Kaag, A.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hourcade-Potelleret, F.; et al. A phase 1b dose-escalation study of BYL719 plus binimetinib (MEK162) in patients with selected advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Arcas, M.; Moore, C.; Rana, S.; Van Maldegem, F.; Mugarza, E.; Romero-Clavijo, P.; Herbert, E.; Horswell, S.; Li, L.-S.; Janes, M.R.; et al. Development of combination therapies to maximize the impact of KRAS-G12C inhibitors in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, K.; Steri, V.; Ge, A.Y.; Hwang, Y.C.; Yogodzinski, C.H.; Shkedi, A.R.; Choi, A.L.M.; Mitchell, D.C.; Swaney, D.L.; Hann, B.C.; et al. KRASG12C inhibition produces a driver-limited state revealing collateral dependencies. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqcena, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hosney, C.; Alhamed, A.; Chatterjeem, A.; Foster, D. Blocking anaplerotic entry of glu-tamine into the TCA cycle sensitizes K-Ras mutant cancer cells to cytotoxic drugs. Oncogene 2014, 34, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.A. Metabolic vulnerability of KRAS-driven cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e963445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Goswami, D.; Adiseshaiah, P.P.; Burgan, W.; Yi, M.; Guerin, T.M.; Kozlov, S.V.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F. Undermining Glutaminolysis Bolsters Chemotherapy While NRF2 Promotes Chemoresistance in KRAS-Driven Pancreatic Cancers. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1630–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, S.J.; Hata, A.N. Can the Help Match the Hype? KRASG12C-Specific Inhibitors and Beyond. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinicaltrials.gov Reference | Drug Name | Target | Stage of Development | Estimated Enrolment | Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03600883 CodeBreak 100 | Sotorasib (AMG 510) +/− anti PD-1/L1 (Amgen) | KRASG12C | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 533 | AMG 510 monotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumours + KRASG12C mutation and AMG 510 combination therapy (anti-PD1/L1) in patients with advanced NSCLC + KRAS p.G12C mutation |
| NCT04185883 CodeBreak 101 | Sotorasib (AMG 510) (Amgen) | KRASG12C | Phase 1b recruiting | 456 | AMG 510 monotherapy and in combination with other anti-cancer therapies in patients with advanced KRASG12C mutant solid tumours |
| NCT04380753 CodeBreak 105 | Sotorasib (AMG 510) (Amgen) | KRASG12C | Phase 1 recruiting | 12 | AMG 510 in patients of Chinese descent with advanced/metastatic solid tumours with KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04303780 CodeBreak 200 | Sotorasib (AMG 510) (Amgen) vs. docetaxel | KRASG12C | Phase 3 recruiting | 650 | AMG 510 vs docetaxel in pre-treated locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic NSCLC patients with KRAS.G12C mutation |
| NCT03785249 | Adagrasib (MRTX849) +/− pembolizumab/ cetuximab/ afatinib (mirati therapeutics) | KRASG12C (+/− anti-PD-1, EGFR) | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 391 | MRTX849 in patients with advanced solid tumours with a KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04330664 | Adagrasib (MRTX849), TNO155 (Mirati therapeutics and Novaratis) | KRASG12C, SHP2 | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 148 | Combination of MRTX849 with TN0155 in patients with advanced solid tumours and KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04449874 | GDC-6036 (Roche) | KRASG12C | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 108 | GDC-6036 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumours with a KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04165031 | LY3499446 (Eli Lilly) +/− Abemaciclib /cetuximab/erlotinib vs docetaxel | KRASG12C (+/− CDK4/6, EGFR) | Phase 1: terminated due to toxicity | 230 | LY3499446 in patients with advanced solid tumours and KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04006301 | JNJ-74699157 (Wellspring biosciences and Janssen) | KRASG12C | Phase 1: terminated due to toxicity | 10 (actual) | Complete: JNJ-74699157 in patients with advanced solid tumours (including NSCLC, CRC) with a KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT04585035 | D-1553 (InventisBio) | KRASG12C | Phase 1/2 not yet recruiting | 200 | D-1553 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumours with KRASG12C mutation |
| NCT03114319 | TNO155 +/− EGF816 (Novaratis) | SHP2 (+/−EGFR) | Phase 1 recruiting | 255 | TNO155 alone or in combination with EGF816 in patients with advanced selected solid tumours (EGFR or KRASG12C mutant NSCLC, oesophageal SCC, HNSCC, melanoma) |
| NCT04000529 | TNO155 + spartalizumab/ribociclib (Novaratis) | SHP2 (+ anti-PD-1/ CDK4/6) | Phase 1b recruiting | 126 | TNO155 in combination with spartalizumab or ribociclib in selected malignancies (NSCLC, CRC, HNSCC, GIST, oesophageal SCC) |
| NCT03565003 | JAB-3068 (Jacobio Pharmaceuticals) | SHP2 | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 120 | JAB-3068 in patients with advanced solid tumours in China |
| NCT03518554 | JAB-3068 (Jacobio Pharmaceuticals) | SHP2 | Phase 1 recruiting | 45 | JAB-3068 in patients with advanced solid tumours |
| NCT04121286 | JAB-3312 (Jacobio Pharmaceuticals) | SHP2 | Phase 1 recruiting | 24 | JAB-3312 in patients with advanced solid tumours in China |
| NCT04045496 | JAB-3312 (Jacobio Pharmaceuticals) | SHP2 | Phase 1 recruiting | 24 | JAB-3312 in adult patients with advanced solid tumours |
| NCT03989115 | RMC-4630 + cobimetinib/osimertinib (Revolution Medicines and Sanofi) | SHP2 (+ MEK/EGFR) | Phase 1/2 recruiting | 168 | RMC-4630 + cobimetinib in patients with relapsed/refractory solid tumours and RMC-4630 + osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutant, locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC |
| NCT03634982 | RMC-4630 (Revolution Medicines and Sanofi) | SHP2 | Phase 1 recruiting | 210 | RMC-4630 monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory solid tumours |
| NCT04252339 | RLY-1971 (Relay Therapeutics) | SHP2 | Phase 1 recruiting | 52 | RLY-1971 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumours |
| NCT04528836 | BBP-398 (Navire Pharma) | SHP2 | Phase 1 not yet recruiting | 60 | BBP-398 in patients with MAPK pathway- or RTK-driven advanced solid tumours |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dunnett-Kane, V.; Nicola, P.; Blackhall, F.; Lindsay, C. Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors. Cancers 2021, 13, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010151
Dunnett-Kane V, Nicola P, Blackhall F, Lindsay C. Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors. Cancers. 2021; 13(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleDunnett-Kane, Victoria, Pantelis Nicola, Fiona Blackhall, and Colin Lindsay. 2021. "Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors" Cancers 13, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010151
APA StyleDunnett-Kane, V., Nicola, P., Blackhall, F., & Lindsay, C. (2021). Mechanisms of Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors. Cancers, 13(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010151





