Anti-Proliferative Effect of Statins Is Mediated by DNMT1 Inhibition and p21 Expression in OSCC Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
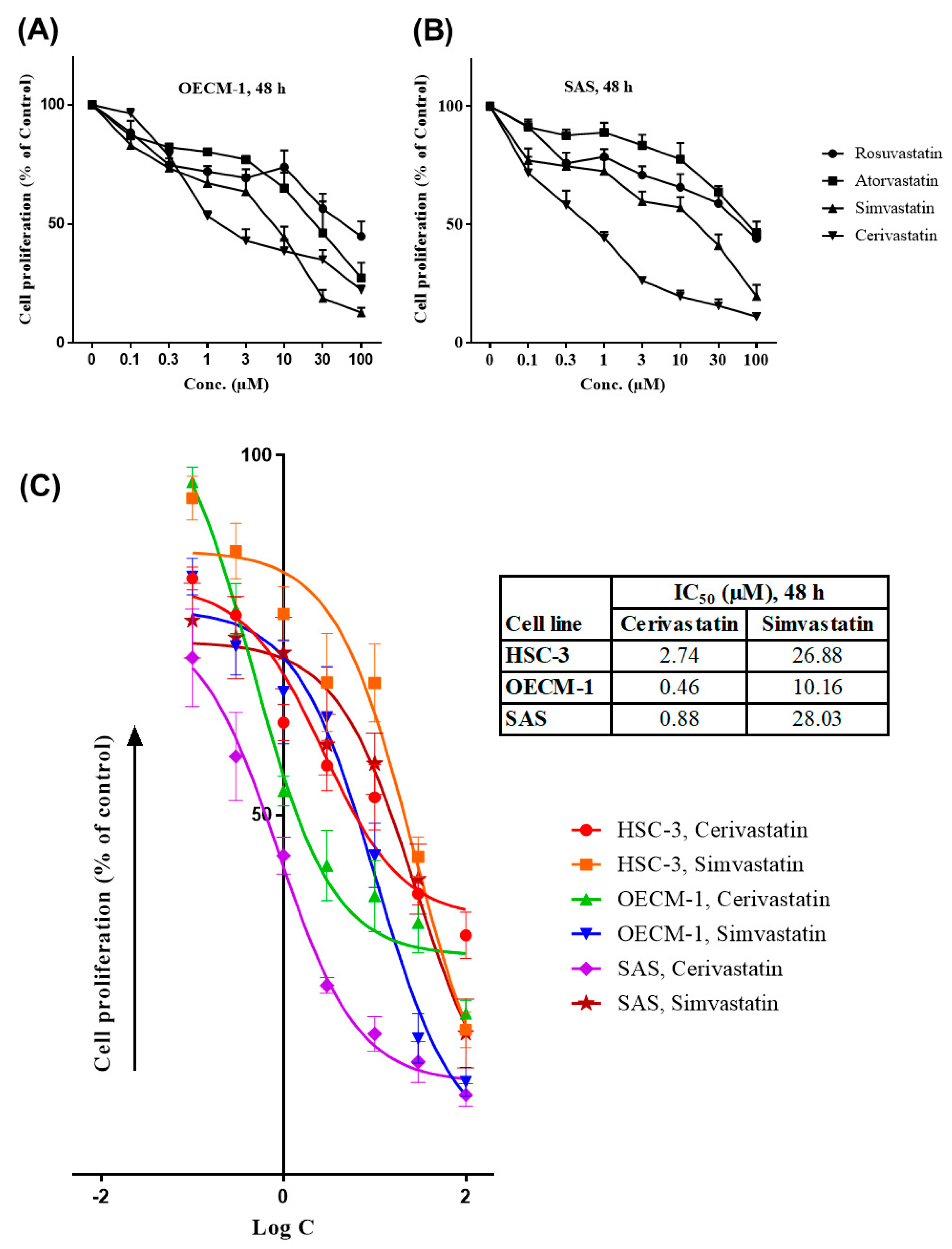
2.1. Statins Inhibited the Proliferation of OSCC Cells
2.2. Statins Induced G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Increased Sub G1 Cell Population
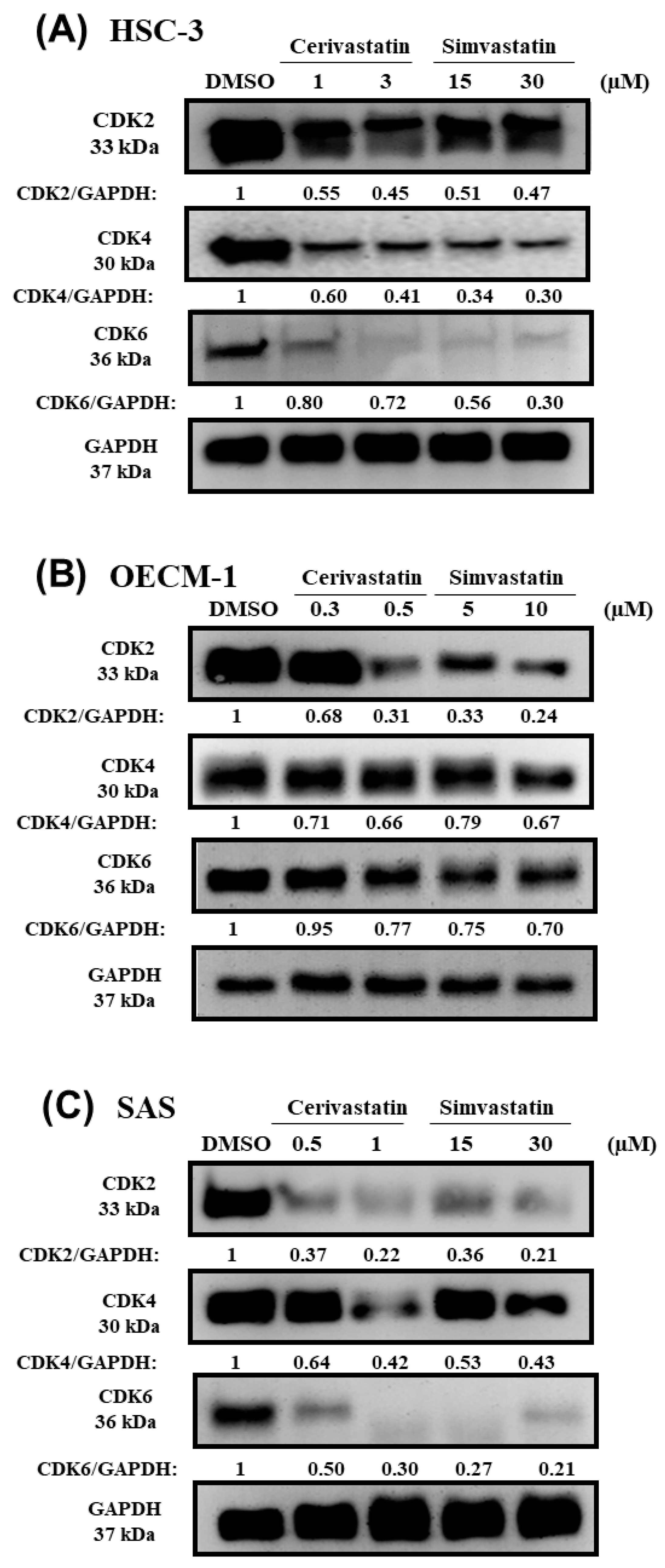
2.3. Statins Modulated the Expression of p21 and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
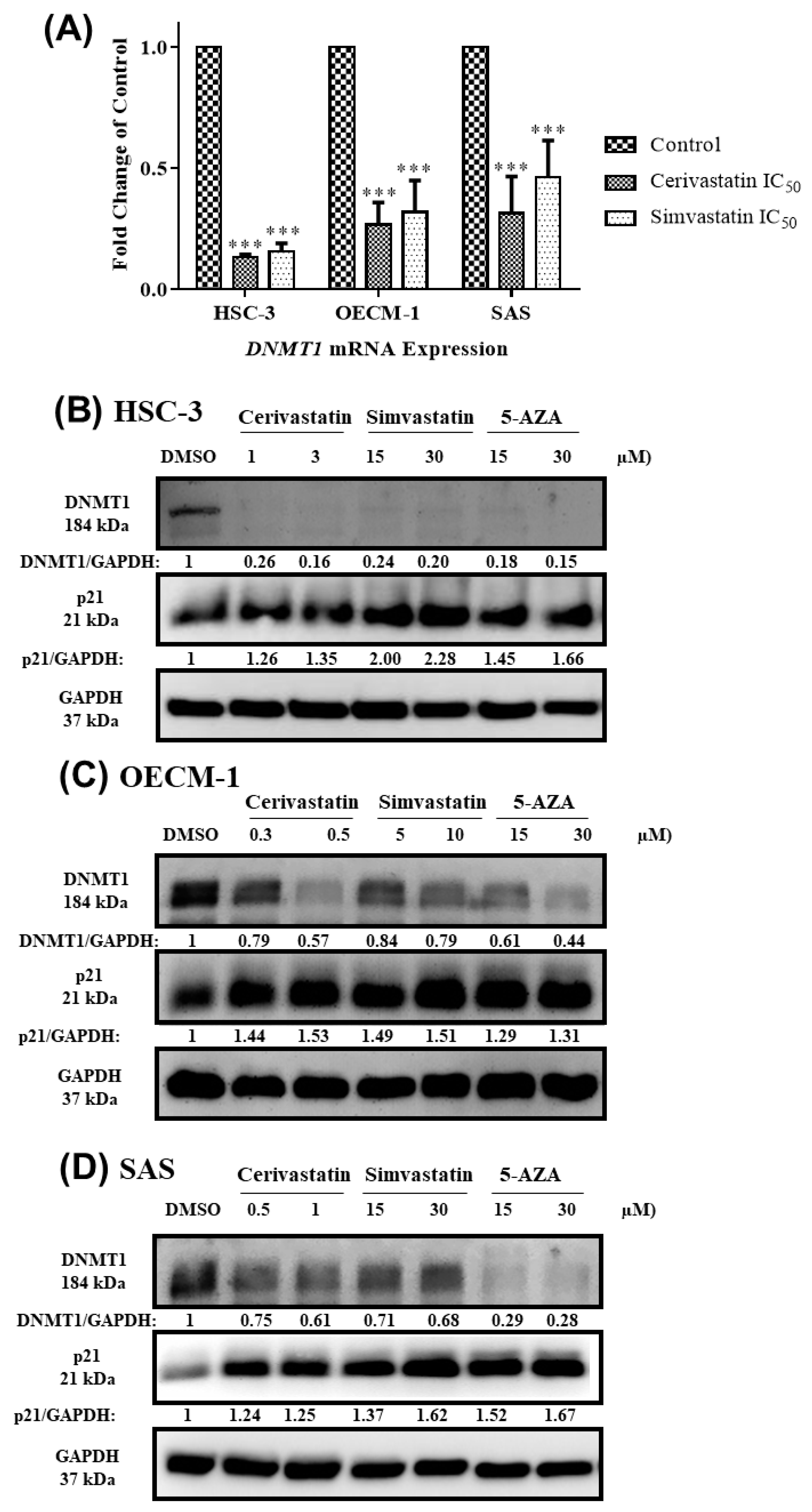
2.4. Statins Inhibited DNMT1 to Promote p21 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Growth Condition
4.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
4.6. Western Blotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzmaurice, C. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 2006 to 2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 4, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, S.; Masood, M.; Scully, C. The magnitude of tobacco smoking-betel quid chewing-alcohol drinking interaction effect on oral cancer in South-East Asia. A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, A.C.; Day, T.A.; Neville, B.W. Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an update. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartner, L. Chemotherapy for oral cancer. Dent. Clin. North Am. 2018, 62, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Mirshahidi, S.; Simental, A.; Lee, S.C.; De Andrade Filho, P.A.; Peterson, N.R.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.; Yuan, X. Cancer stem cell self-renewal as a therapeutic target in human oral cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5440–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimie, A.I.; Ciocan, C.; Gulei, D.; Mehterov, N.; Atanasov, A.G.; Dudea, D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Current insights into oral cancer epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sébert, M.; Renneville, A.; Bally, C.; Peterlin, P.; Beyne-Rauzy, O.; Legros, L.; Gourin, M.; Sanhes, L.; Wattel, E.; Gyan, E.; et al. A phase II study of guadecitabine in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and low blast count acute myeloid leukemia after azacitidine failure. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabry’s, D.; Dörfler, A.; Yaromina, A.; Hessel, F.; Krause, M.; Oertel, R.; Baumann, M. Effects of lovastatin alone or combined with irradiation on tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2008, 184, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.B.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chin, L.H.; Tseng, J.H.; Tang, L.W.; Horng, S.; Fan, Y.C.; Hsu, S.P. A synergistic anti-cancer effect of troglitazone and lovastatin in a human anaplastic thyroid cancer cell line and in a mouse xenograft model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.T.; Ho, H.J.; Lin, J.T.; Shieh, J.J.; Wu, C.Y. Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21 accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, G.; Dan, H.C.; Jiang, W.; Ju, L.; Wu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. Simvastatin induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer cells via PPARγ signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosper, J.; Masuccio, A.; Kullmann, M.; Ploner, C.; Geley, S.; Hengst, L. Statin-induced depletion of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate inhibits cell proliferation by a novel pathway of Skp2 degradation. Oncotarget 2014, 6, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, M.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Tseng, J.H.; Liou, J.J.; Horng, S.; Wen, H.C.; Fan, Y.C.; Zhong, W.B.; Hsu, S.P. Simvastatin inhibits cell proliferation and migration in human anaplastic thyroid cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, M.; Ying, L.; Zhu, L. Inhibitory effect of simvastatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, A.P.; Maaser, K.; Höpfner, M.; Huether, A.; Schuppan, D.; Scherübl, H. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Synergistic antiproliferative action with ligands of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukomadu, C.; Dutta, A. P21-dependent inhibition of colon cancer cell growth by mevastatin is independent of inhibition of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43586–43594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingersol, M.A.; Miller, D.R.; Martinez, O.; Wakefield, C.B.; Hsieh, K.C.; Simha, M.V.; Kao, C.L.; Chen, H.T.; Batra, S.K.; Lin, M.F. Statin derivates as therapeutic agents for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, K.; Tsubaki, M.; Yamazoe, Y.; Nishiura, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ogaki, M.; Nishinobo, M.; Shimamoto, K.; Moriyama, K.; Nishida, S. Fluvastatin induces apoptosis on human tongue carcinoma cell line HSC-3. Yakugaku Zasshi 2008, 128, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, J.; Zeki, A.A.; Mirzaei, N.; Tewary, S.; Rezaei Moghadam, A.; Glogowska, A.; Nagakannan, P.; Eftekharpour, E.; Wiechec, E.; Gordon, J.W.; et al. Mevalonate cascade inhibition by simvastatin induces the intrinsic apoptosis pathway via depletion of isoprenoids in tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e44841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, C.; Miller, D.H.; Lynch, K.; Brodsky, A.S. Oxysterols synergize with statins by inhibiting SREBP-2 in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Mukthavaram, R.; Chao, Y.; Nomura, N.; Bharati, I.S.; Fogal, V.; Pastorino, S.; Teng, D.; Cong, X.; Pingle, S.C.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anticancer effects of mevalonate pathway modulation on human cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Ning, J.; Wang, J.; Lang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; et al. Simvastatin suppresses proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer via pyroptosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezquita, B.; Mezquita, P.; Pau, M.; Gasa, L.; Navarro, L.; Samitier, M.; Pons, M.; Mezquita, C. All-trans-retinoic acid activates the pro-invasive Src-YAP-Interleukin 6 axis in triple-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells while cerivastatin reverses this action. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, L.; Bauer, N.; Nwaeburu, C.C.; Gladkich, J.; Gross, W.; Hackert, T.; Sticht, C.; et al. Simvastatin inhibits sonic hedgehog signaling and stemness features of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 426, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhaescu, I.; Izzedine, H. Mevalonate pathway: A review of clinical and therapeutical implications. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, P.J.; Yu, R.; Longo, J.; Archer, M.C.; Penn, L.Z. The interplay between cell signaling and the mevalonate pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, F.; Lombardi, R.; Milone, M.R.; Pucci, B.; De Rienzo, S.; Budillon, A.; Bruzzese, F. Targeting mevalonate pathway in cancer treatment: Repurposing of statins. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, I.; Maruya, S.; Shirasaki, T.; Mizukami, H.; Takahata, T.; Myers, J.N.; Kakehata, S.; Yagihashi, S.; Shinkawa, H. Simvastatin inactivates β1-integrin and extracellular signal-related kinase signaling and inhibits cell proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Obata, N.; Kawashima, K.; Tabata, M.; Imano, M.; Satou, T.; Nishida, S. Combination therapy with dacarbazine and statins improved the survival rate in mice with metastatic melanoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. P21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Gong, Y.; Yan, G.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Hou, J.; Liu, B.; Tang, C. Atorvastatin treatment modulates p16 promoter methylation to regulate p16 expression. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1868–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Han, Y.K.; Song, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, K.; Yi, J.M.; Park, H.R. Aberrantly hypermethylated tumor suppressor genes were identified in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chou, J.L.; Chan, M.W.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Tsou, Y.A.; Tsai, M.H.; et al. DNA methylation profiles and biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Epigenetics 2005, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jithesh, P.V.; Risk, J.M.; Schache, A.G.; Dhanda, J.; Lane, B.; Lloglou, T.; Shou, R.J. The epigenetic landscape of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaździcka, J.; Gołąbek, K.; Strzelczyk, J.K.; Ostrowska, Z. Epigenetic modifications in head and neck cancer. Biochem. Genet. 2020, 58, 213–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, E.; Nakamura, M.; Ikuta, M.; Shimada, K.; Matsuyoshi, S.; Kirita, T.; Konishi, N. Promotor hypermethylation of p14ARF is a key alteration for progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2005, 41, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, M.; Saitoh, M.; Kusano, K.; Nagayasu, H.; Kurashige, Y.; Malsantha, M.; Arakawa, T.; Takuma, T.; Chiba, I.; Kaku, T.; et al. High frequency of hypermethylation of p14, p15 and p16 in oral pre-cancerous lesions associated with betel-quid chewing in Sri Lanka. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2008, 37, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Toyota, M.; Suzuki, H.; Akino, K.; Ogi, K.; Sogabe, Y.; Kashima, L.; Maruyama, R.; Nojima, M.; Mita, H.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of RASSF2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, R.M.; Squarize, C.H.; Almeida, L.O. Epigenetic modifications and head and neck cancer: Implications for tumor progression and resistance to therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin toxicity mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W. Statins in therapy: Understanding their hydrophilicity, lipophilicity, binding to 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, ability to cross the blood brain barrier and metabolic stability based on electrostatic molecular orbital studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; McKinstry, R.; Gupta, S.; Gilfor, D.; Windle, J.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Grant, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Dent, P. Cyclin kinase inhibitor p21 potentiates bile acid–induced apoptosis in hepatocytes that is dependent on p53. Hepatology 2002, 36, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartel, A.L. The conflicting roles of the cdk inhibitor p21(CIP1/WAF1) in apoptosis. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.H.; Kim, W.H.; Choi, K.H. P21 promotes ceramide-induced apoptosis and antagonizes the antideath effect of bcl-2 in human hepatocarcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, L.; Steinman, R. A proapoptotic function of p21 in differentiating granulocytes. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiah, S.G.; Chang, L.C.; Tai, K.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Wu, C.W.; Shieh, Y.S. The involvement of promoter methylation and DNA methyltransferase-1 in the regulation of EpCAM expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supic, G.; Kozomara, R.; Zeljic, K.; Jovic, N.; Magic, Z. Prognostic value of the DNMTs mRNA expression and genetic polymorphisms on the clinical outcome in oral cancer patients. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 21, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoosi, F.; Sanaei, M. Effect of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in comparison to valproic acid and trichostatin a on histone deacetylase 1, DNA methyltransferase 1, and cip/Kip family (p21, p27, and p57) genes expression, cell growth inhibition, and apoptosis induction in colon cancer sw480 cell line. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, J.H.; Hsu, T.W.; Su, K.; Li, A.F.; Hsu, H.S.; Hung, S.C. IL-6 enriched lung cancer stem-like cell population by inhibition of cell cycle regulators via DNMT1 upregulation. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hu, B.; Ni, J.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wan, R.; Hu, G.; et al. Transcriptional repression of SOCS3 mediated by IL-6/STAT3 signaling via DNMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Gomez, J.; Castillejo, J.A.; Jimenez, A.; Gonzalez, M.G.; Moreno, F.; Rodriguez, M.D.; Barrios, M.; Maldonado, J.; Torres, A. 5′ CpG island hypermethylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the p21CIP1/WAF1/SDI1 gene and confers poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, N.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ahmad, M.M.; Haque, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Hasan, S.I.; Shukla, N.K.; Husain, S.A. Association of mutation and hypermethylation of p21 gene with susceptibility to breast cancer: A study from North India. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Nikbakht, M.; Jain, V.; Sehgal, A.; Capalash, N.; Kaur, J. Promoter hypermethylation of p73 and p53 genes in cervical cancer patients among north Indian population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 9145–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlic, H.; Thaler, R.; Gerner, C.; Grunt, T.; Proestling, K.; Haider, F.; Varga, F. Inhibition of the mevalonate pathway affects epigenetic regulation in cancer cells. Cancer Genet. 2015, 208, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodach, L.L.; Jacobs, R.J.; Voorneveld, P.W.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Verspaget, H.W.; Van Wezel, T.; Morreau, H.; Hommes, D.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Van den Brink, G.R.; et al. Statins augment the chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells inducing epigenetic reprogramming and reducing colorectal cancer cell ’stemness’ via the bone morphogenetic protein pathway. Gut 2011, 60, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazin, C.; Wajapeyee, N.; Gobeil, S.; Virbasius, C.M.; Green, M.R. An elaborate pathway required for ras-mediated epigenetic silencing. Nature 2007, 449, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karreth, F.A.; Tuveson, D.A. Modelling oncogenic ras/RAF signalling in the mouse. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, R.; Karlic, H.; Spitzer, S.; Klaushofer, K.; Varga, F. Extra-cellular matrix suppresses expression of the apoptosis mediator Fas by epigenetic DNA methylation. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Lyons, J.; Miller, A.L.; Phan, V.T.; Alarcón, I.R.; McCormick, F. Chapter 1 ras signaling and therapies. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 102, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márton, I.J.; Horváth, J.; Lábiscsák, P.; Márkus, B.; Dezső, B.; Szabó, A.; Tar, I.; Piffkó, J.; Jakus, P.; Barabás, J.; et al. Salivary IL-6 mRNA is a robust biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jougasaki, M.; Ichiki, T.; Takenoshita, Y.; Setoguchi, M. Statins suppress interleukin-6-induced monocyte chemo-attractant protein-1 by inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription pathways in human vascular endothelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, A.; Shirai, R.; Ishii, H.; Kushima, H.; Otani, S.; Hashinaga, K.; Umeki, K.; Kishi, K.; Tokimatsu, I.; Hiramatsu, K.; et al. Inhibitory effect of statins on inflammatory cytokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 168, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, C.; Burger, F.; Steffens, S.; Veillard, N.R.; Nguyen, T.H.; Trono, D.; Mach, F. Statins reduce interleukin-6–induced C-reactive protein in human hepatocytes. New evidence for direct anti-inflammatory effects of statins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, B.N.; Nör, J.E.; Min, K.S.; Choi, C.H.; Koh, J.T.; Lee, K.J.; Hwang, Y.C. Simvastatin inhibits the expression of inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules induced by LPS in human dental pulp cells. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kitajima, I. Pitavastatin inactivates NF-κb and decreases IL-6 production through Rho kinase pathway in MCF-7 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Trial Using Simvastatin. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/clinical-trials/intervention/simvastatin (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Gnyszka, A.; Jastrzebski, Z.; Flis, S. DNA methyltransferase Inhibitors and Their Emerging Role in Epigenetic Therapy of Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Astex Pharmaceuticals and Otsuka Announce Results of the Phase 3 ASTRAL-1 Study of Guadecitabine (SGI-110) in Treatment-Naïve AML Patients Ineligible to Receive Intense Induction Chemotherapy. Available online: https://astx.com/astex-pharmaceuticals-and-otsuka-announce-results-of-the-phase-3-astral-1-study-of-guadecitabine-sgi-110-in-treatment-naive-aml-patients-ineligible-to-receive-intense-induction-chemotherapy/ (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Chen, C.Y.; Chiou, S.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Jan, C.I.; Lin, S.C.; Hu, W.Y.; Chou, S.H.; Liu, C.J.; Lo, J.F. Tid1 functions as a tumour suppressor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2009, 219, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dongoran, R.A.; Wang, K.-H.; Lin, T.-J.; Yuan, T.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Anti-Proliferative Effect of Statins Is Mediated by DNMT1 Inhibition and p21 Expression in OSCC Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2084. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082084
Dongoran RA, Wang K-H, Lin T-J, Yuan T-C, Liu C-H. Anti-Proliferative Effect of Statins Is Mediated by DNMT1 Inhibition and p21 Expression in OSCC Cells. Cancers. 2020; 12(8):2084. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082084
Chicago/Turabian StyleDongoran, Rachmad Anres, Kai-Hung Wang, Tsung-Jen Lin, Ta-Chun Yuan, and Chin-Hung Liu. 2020. "Anti-Proliferative Effect of Statins Is Mediated by DNMT1 Inhibition and p21 Expression in OSCC Cells" Cancers 12, no. 8: 2084. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082084
APA StyleDongoran, R. A., Wang, K.-H., Lin, T.-J., Yuan, T.-C., & Liu, C.-H. (2020). Anti-Proliferative Effect of Statins Is Mediated by DNMT1 Inhibition and p21 Expression in OSCC Cells. Cancers, 12(8), 2084. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082084





