The Clinicopathological Features and Genetic Alterations in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinicopathologic Characteristics
2.2. Initial Recurrence Patterns
2.3. Survival Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Sample Collection
4.2. Follow-Up
4.3. Identification of HP Infection
4.4. EBV Detection
4.5. Mutation Analysis of GC-Related Genes Based on MassARRAY
4.6. Microsatellite Instability Analysis
4.7. IHC Staining of PD-L1
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CPS | combined positive score |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| EBER | EBV-encoded small RNAs |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| GC | Gastric cancer |
| HP | Helicobacter pylori |
| IHC | Immunohistochemical |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| MSI | Microsatellite instability |
| MSI-H | Microsatellite instability-high |
| MSS | Microsatellite stable |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TNM | tumor, node, metastasis |
| UICC | Union for International Cancer Control |
References
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, H.; Kaneda, A.; Fukayama, M. Epstein-Barr Virus-associated gastric carcinoma: Use of host cell machineries and somatic gene mutations. Pathobiology 2015, 82, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizasa, H.; Nanbo, A.; Nishikawa, J.; Jinushi, M.; Yoshiyama, H. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-associated Gastric Carcinoma. Viruses 2012, 4, 3420–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, J.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Shimokuri, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yanai, H.; Sakai, K.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. Clinical importance of Epstein–Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, B.H.; Hwang, J.E.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, S.C.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, E.H.; Yim, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Clinical Significance of Four Molecular Subtypes of Gastric Cancer Identified by The Cancer Genome Atlas Project. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, J.; zur Hausen, A.; Klein Kranenbarg, E.; van de Velde, C.J.; Middeldorp, J.M.; van den Brule, A.J.; Meijer, C.J.; Bloemena, E. EBV-positive gastric adenocarcinomas: A distinct clinicopathologic entity with a low frequency of lymph node involvement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, C.; Mota, M.; Gradiz, R.; Cipriano, M.A.; Caramelo, F.; Cruz, H.; Alarcão, A.; E Sousa, F.C.; Oliveira, F.; Martinho, F.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas in Portugal. Infect. Agents Cancer 2017, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, A.; Abe, H.; Kunita, A.; Kanda, T.; Yamashita, H.; Seto, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fukayama, M. Viral loads correlate with upregulation of PD-L1 and worse patient prognosis in Epstein-Barr Virus-associated gastric carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S.; Itoh, T.; Kijima, Y.; Sueyoshi, K.; Corvalan, A.; Herrera-Goepfer, R.; Eizuru, Y. Prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus involvement in gastric carcinoma in Japan. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 10, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, A.P.; Yen, T.S.; Shekitka, K.M.; Sobin, L.H. Lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the stomach with Epstein-Barr virus demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction. Mod. Pathol. 1990, 3, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, M.; Land, C.E.; Uemura, Y.; Tokudome, T.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, E. Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibata, D.; Weiss, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 140, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Truong, C.D.; Feng, W.; Li, W.; Khoury, T.; Li, Q.; Alrawi, S.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K.; Yao, J.; Tan, D. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: A study of 235 cases at a comprehensive cancer center in U.S.A. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, D.C.; Ito, M.; Mangham, D.C.; Reynolds, G.; Herbst, H.; Hallissey, M.T.; Fielding, J.W.; Newbold, K.M.; Jones, E.L.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus and carcinomas: Rare association of the virus with gastric adenocarcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ott, G.; Kirchner, T.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K. Monoclonal Epstein-Barr virus genomes but lack of EBV-related protein expression in different types of gastric carcinoma. Histopathology 1994, 25, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoncini, L.; Vindigni, C.; Megha, T.; Funto, I.; Pacenti, L.; Musaro, M.; Renieri, A.; Seri, M.; Anagnostopoulos, J.; Tosi, P. Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer: Data and unanswered questions. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 53, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J.; Qi, C.; Li, J.; Shen, L.; Peng, Z. Positive Status of Epstein-Barr Virus as a Biomarker for Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Sakai, K.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Yanagihara, M.; Shuto, T.; Shimokuri, K.; Kanda, T.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. EBV-associated gastric cancer evades T-cell immunity by PD-1/PD-L1 interactions. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Abe, H.; Kunita, A.; Yamashita, H.; Seto, Y.; Fukayama, M. Overexpression and gene amplification of PD-L1 in cancer cells and PD-L1+ immune cells in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: The prognostic implications. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, S.H.; An, J.S.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, Y.S. Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, A.N.; Kang, B.W.; Bae, H.I.; Kwon, O.K.; Park, K.B.; Lee, S.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, W.; Jeon, S.W.; Kang, H.; et al. Exon 9 mutation of PIK3CA associated with poor survival in patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.L.; Huang, K.H.; Chang, S.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, M.H.; Chao, Y.; Lo, S.S.; Li, A.F.; Wu, C.W.; Shyr, Y.M. Comparison of the Clinicopathological Characteristics and Genetic Alterations Between Patients with Gastric Cancer with or Without Helicobacter pylori Infection. Oncol. 2019, 24, e845–e853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; McMillan, N.A. Molecular basis of pathogenesis, prognosis and therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, N.J.; Kulwichit, W.; Edwards, R.H.; Shair, K.H.; Bendt, K.M.; Raab-Traub, N. LMP1 signaling and activation of NFkappaB in LMP1 transgenic mice. Oncogene 2006, 25, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X.F. The signal pathways in azoxymethaneinduced colon cancer and preventive implications. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falasca, M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway specific inhibitors: A novel strategy to sensitize cancer cells to anti-cancer drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. The Src/PI3K/Akt signal pathway may play a key role in decreased drug efficacy in obesity-associated cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, S.K.; Chae, H.S.; Kang, J.H. LY294002 may overcome 5-FU resistance via down-regulation of activated p-AKT in Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.M.; Kim, E.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Gastric Cancer Risk: A Meta-analysis With Meta-regression of Case-control Studies. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2016, 49, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnoni, A.; Brunetti, O.; Longo, V.; Calabrese, A.; Argentiero, A.L.; Calbi, R.; Antonio, G.S.; Licchetta, A. Immune System and Bone Microenvironment: Rationale for Targeted Cancer Therapies. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ribas, A.; Hu-Lieskovan, S. What does PD-L1 positive or negative mean? J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2835–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Doi, T.; Jang, R.W.; Muro, K.; Satoh, T.; Machado, M.; Sun, W.; Jalal, S.I.; Shah, M.A.; Metges, J.P. Safety and Efficacy of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer: Phase 2 Clinical KEYNOTE-059 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e180013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, P.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F.; Racanelli, V. Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Gastric Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.J.; Du, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, L.Y.; Cao, G.W. Inflammation-related factors predicting prognosis of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4586–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, P.; Lernia, G.D.; Solimando, A.G.; Cicco, S.; Saltarella, I.; Lamanuzzi, A.; Ria, R.; Frassanito, M.A.; Ponzoni, M.; Ditonno, P.; et al. Bone marrow endothelial cells sustain a tumorspecific CD8+ T cell subset with suppressive function in myeloma patients. Oncoimmunology. 2019, 8, e1486949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouthon, L.; Lortholary, O. Intravenous immunoglobulins in infectious diseases: Where do we stand? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, A.; Marasco, C.; Melaccio, A.; Sportelli, A.; Saltarella, I.; Solimando, A.; Dammacco, F.; Ria, R. Subcutaneous immunoglobulins in patients with multiple myeloma and secondary hypogammaglobulinemia. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 191, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, O. Immune Checkpoints Aberrations and Gastric Cancer; Assessment of Prognostic Value and Evaluation of Therapeutic Potentials. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 97, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.; Brunetti, O.; Gnoni, A.; Antonella Licchetta, A.; Delcuratolo, S.; Memeo, R.; Solimando, A.G.; Argentiero, A. Emerging Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Medicina 2019, 55, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Helicobacter pylori in gastric carcinogenesis: Mechanisms. Gastroenterol. Clin. 2013, 42, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meimarakis, G.; Winter, H.; Assmann, I.; Kopp, R.; Lehn, N.; Kist, M.; Stolte, M.; Jauch, K.W.; Hatz, R.A. Helicobacter pylori as a prognostic indicator after curative resection of gastric carcinoma: A prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.B.; Zhang, L.Y.; Keshari, R.P.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, Z.W.; Xu, D.Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Li, W. Relationship between H. pylori infection and clinicopathological features and prognosis of gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyżek, P.; Gościniak, G. Immunomodulatory influence of HIV and EBV on Helicobacter pylori infections—A review. Ann. Parasitol. 2019, 65, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuramoto, S.; Sasako, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Fujii, M.; Nashimoto, A.; Furukawa, H.; Nakajima, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Imamura, H.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.; Oliveira, A.; Malta, M.; Oliveira, C.; Silva, F.; Galaghar, A.; Afonso, L.P.; Neves, M.C.; Medeiros, R.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; et al. Clinical and pathological chaterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma in Portugal. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7292–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Soung, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Park, W.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, Y.G.; Kim, C.J.; et al. BRAF and KRAS mutations in stomach cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6942–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.L.; Chang, S.C.; Lan, Y.T.; Huang, K.H.; Chen, J.H.; Lo, S.S.; Hsieh, M.C.; Li, A.F.; Wu, C.W.; Chiou, S.H. Microsatellite instability is associated with a better prognosis for gastric cancer patients after curative surgery. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaab, H.O.; Sau, S.; Alzhrani, R.; Tatiparti, K.; Bhise, K.; Kashaw, S.K.; Iyer, A.K. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: Mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
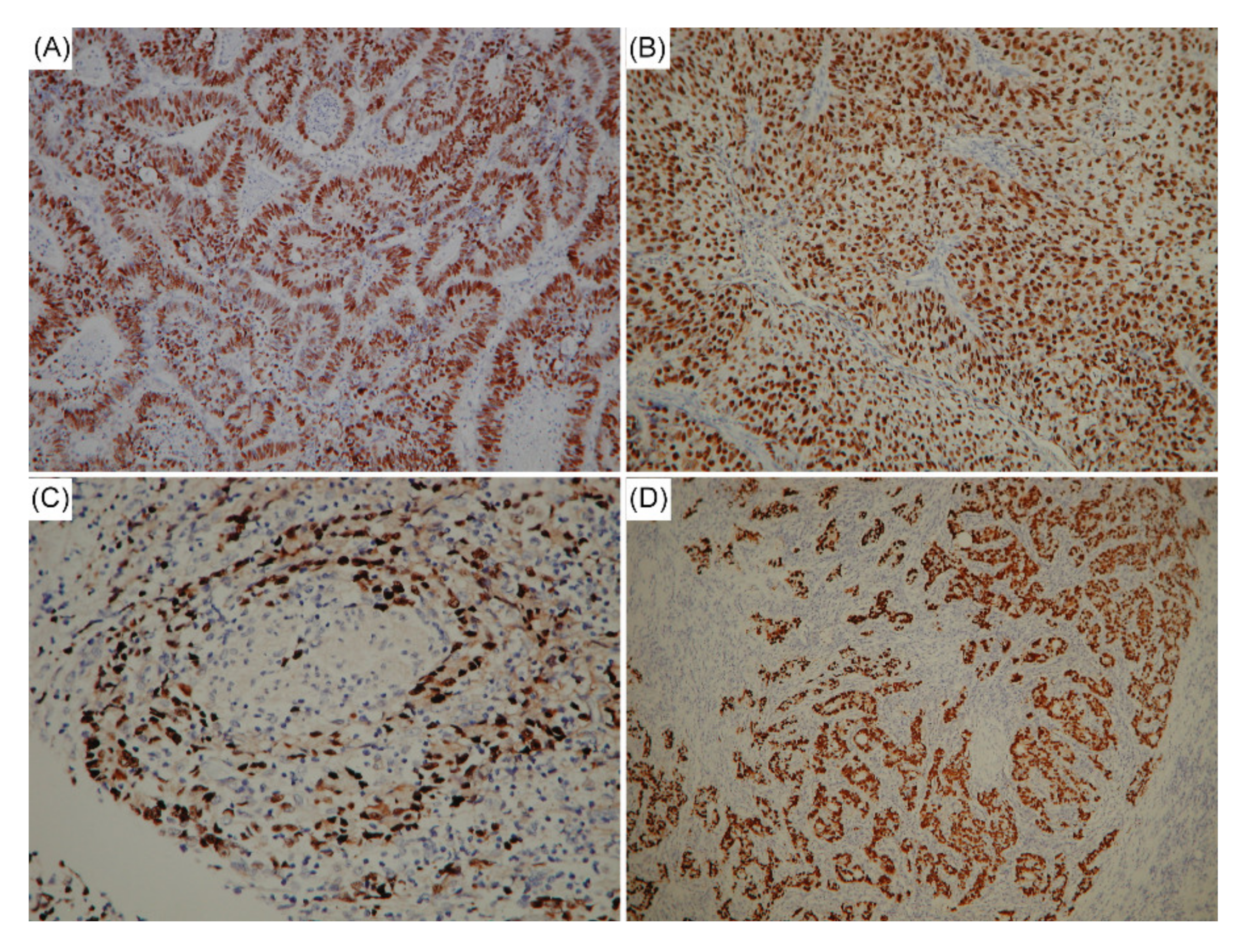
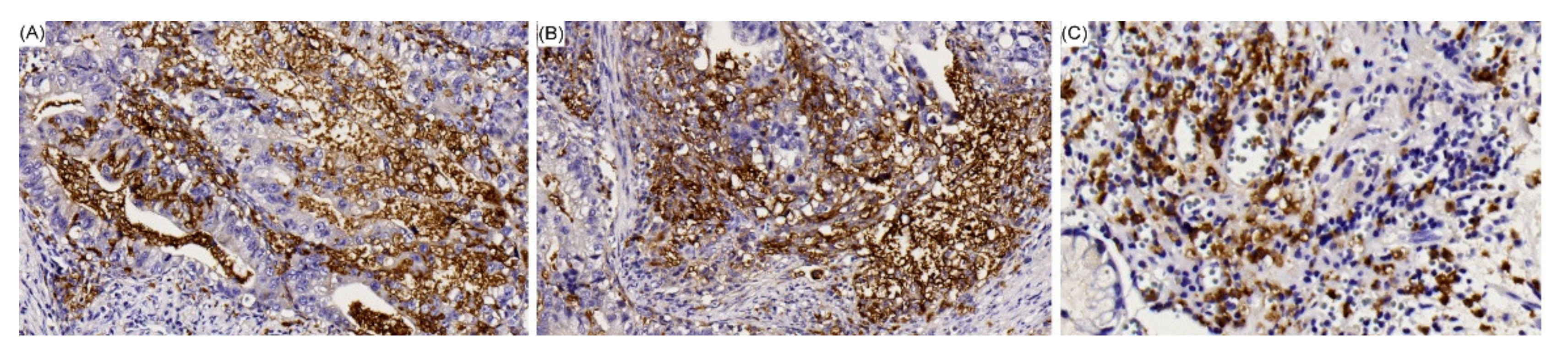
| Variables | EBV-Negative n = 417 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 43 n (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 0.794 | ||
| <65 | 166 (39.8) | 18 (41.9) | |
| ≥65 | 251 (60.2) | 25 (58.1) | |
| Gender (M/F) | 294/123 | 35/8 | 0.132 |
| Tumor size (<5/≥ 5 cm) | 163/254 | 16/27 | 0.810 |
| Tumor location | <0.001 | ||
| Upper stomach | 67 (16.1) | 17 (39.5) | |
| Middle stomach | 136 (32.6) | 18 (41.9) | |
| Lower stomach | 201 (48.2) | 9 (18.6) | |
| Whole stomach | 13 (3.1) | 0 | |
| Cell differentiation | 0.540 | ||
| Poor | 225 (54.0) | 26 (60.5) | |
| Moderate | 185 (44.4) | 17 (39.5) | |
| Well | 7 (1.6) | 0 | |
| Histological type | <0.001 | ||
| Intestinal/solid type | 201 (48.2) | 17 (39.5) | |
| Diffuse (poor cohesive) type | 197 (47.2) | 15 (34.9) | |
| Lymphoepithelioma-like | 19 (4.6) | 11 (25.6) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 295 (70.7) | 29 (67.4) | 0.651 |
| Lymphoid stroma | 49 (11.8) | 18 (41.9) | <0.001 |
| MSI status | 0.640 | ||
| MSI-L/S | 379 (90.9) | 40 (93.0) | |
| MSI-H | 38 (9.1) | 3 (7.0) | |
| HP infection | 151 (36.2) | 6 (14.0) | 0.003 |
| PIK3CA amplification | 191 (45.8) | 15 (34.9) | 0.117 |
| PD-L1 expression | 120 (28.8) | 20 (46.5) | 0.016 |
| Genetic mutation | |||
| PI3K/AKT pathway | 59 (14.1) | 11 (25.9) | 0.047 |
| ARID1A | 50 (12.0) | 3 (7.0) | 0.327 |
| TP53 | 56 (13.4) | 3 (7.0) | 0.228 |
| KRAS | 10 (2.4) | 0 | 0.305 |
| BRAF | 3 (0.7) | 0 | 0.577 |
| Pathological T category | 0.995 | ||
| T1/2/3/4 | 63/71/142/141 | 7/7/15/14 | |
| Pathological N category | 0.670 | ||
| N0/1/2/3 | 134/68/106/109 | 14/10/9/10 | |
| Pathological TNM Stage | 0.996 | ||
| I/II/III | 87/119/211 | 9/12/22 |
| Variables | Intestinal/Solid Type GC | Diffuse (Poorly Cohesive) Type GC | Lymphoepithelioma-Like GC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV-Negative n = 201 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 17 n (%) | p Value | EBV-Negative n = 197 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 15 n (%) | p Value | EBV-Negative n = 19 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 11 n (%) | p Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.671 | 0.818 | 0.643 | ||||||
| <65 | 61 (30.3) | 6 (35.3) | 98 (49.7) | 7 (46.7) | 7 (36.8) | 5 (45.5) | |||
| ≥65 | 140 (69.7) | 11 (64.7) | 99 (50.3) | 8 (53.3) | 12 (63.2) | 6 (54.5) | |||
| Gender (M/F) | 163/38 | 15/2 | 0.465 | 116/81 | 12/3 | 0.107 | 15/4 | 8/3 | 0.698 |
| Tumor size (<5/≥5 cm) | 82/119 | 7/10 | 0.976 | 75/122 | 6/9 | 0.882 | 6/13 | 3/8 | 0.804 |
| Tumor location | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.082 | ||||||
| Upper stomach | 38 (18.9) | 6 (35.3) | 25 (12.7) | 7 (46.7) | 4 (21.1) | 4 (36.4) | |||
| Middle stomach | 55 (27.4) | 7 (41.2) | 77 (39.1) | 6 (40.0) | 4 (21.1) | 5 (45.5) | |||
| Lower stomach | 106 (52.7) | 4 (23.5) | 84 (42.6) | 2 (13.3) | 11 (57.8) | 2 (18.1) | |||
| Whole stomach | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 11 (5.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Cell differentiation | 0.721 | 0.608 | 0.685 | ||||||
| Poor | 37 (18.4) | 4 (23.5) | 170 (86.3) | 12 (80.0) | 18 (94.7) | 10 (90.9) | |||
| Moderate | 159 (79.1) | 13 (76.5) | 25 (12.7) | 3 (20.0) | 1 (5.3) | 1 (9.1) | |||
| Well | 5 (2.5) | 0 | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Lymphovascular invasion | 144 (71.6) | 10 (58.8) | 0.265 | 137 (69.5) | 10 (66.4) | 0.816 | 14 (73.7) | 9 (81.8) | 0.612 |
| Lymphoid stroma | 27 (13.4) | 6 (35.3) | 0.016 | 5 (2.5) | 2 (13.3) | 0.024 | 19 (100) | 11 (100) | |
| MSI status | 0.917 | 0.841 | - | ||||||
| MSI-L/S | 179 (89.1) | 15 (88.2) | 181 (91.9) | 14 (93.3) | 19 (100) | 11 (100) | |||
| MSI-H | 22 (10.9) | 2 (11.8) | 16 (8.1) | 1 (6.7) | 0 | 0 | |||
| HP infection | 59 (29.4) | 0 | 0.009 | 88 (44.7) | 3 (20.0) | 0.063 | 4 (21.1) | 3 (27.3) | 0.698 |
| PIK3CA amplification | 80 (39.8) | 3 (17.6) | 0.071 | 103 (52.3) | 7 (46.7) | 0.675 | 8 (42.1) | 5 (45.5) | 0.858 |
| PD-L1 expression | 51 (25.4) | 9 (52.9) | 0.019 | 62 (31.5) | 5 (33.3) | 0.881 | 7 (36.8) | 6 (54.5) | 0.346 |
| Genetic mutation | |||||||||
| PI3K/AKT pathway | 40 (19.9) | 6 (35.3) | 0.135 | 19 (9.6) | 2 (13.3) | 0.645 | 0 | 3 (27.3) | 0.016 |
| ARID1A | 32 (15.9) | 3 (17.6) | 0.852 | 18 (9.1) | 0 | 0.221 | 0 | 0 | - |
| TP53 | 20 (10.0) | 1 (5.9) | 0.585 | 31 (15.7) | 1 (6.7) | 0.344 | 5 (26.3) | 1 (9.1) | 0.256 |
| KRAS | 9 (4.5) | 0 | 0.373 | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0.782 | 0 | 0 | - |
| BRAF | 3 (1.5) | 0 | 0.612 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - |
| Pathological T category | 0.311 | 0.554 | 0.636 | ||||||
| T1/2/3/4 | 27/44/63/67 | 5/2/5/5 | 34/22/71/70 | 1/2/7/5 | 2/5/8/4 | 1/3/3/4 | |||
| Pathological N category | 0.300 | 0.584 | 0.991 | ||||||
| N0/1/2/3 | 75/36/54/36 | 8/4/1/4 | 56/26/47/68 | 4/3/5/3 | 3/6/5/5 | 2/3/3/3 | |||
| Pathological TNM Stage | 0.474 | 0.717 | 0.610 | ||||||
| I/II/III | 47/66/88 | 6/4/7 | 37/46/114 | 2/4/9 | 3/7/9 | 1/4/6 | |||
| Initial Recurrence Pattern | Intestinal/Solid Type GC | Diffuse (Poorly Cohesive) Type GC | Lymphoepithelioma-Like GC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV-Negative n = 201 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 17 n (%) | p Value | EBV-Negative n = 197 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 15 n (%) | p Value | EBV-Negative n = 19 n (%) | EBV-Positive n = 11 n (%) | p Value | |
| Total patients with recurrence | 66 (32.8) | 9 (52.9) | 0.094 | 71 (36.0) | 4 (26.7) | 0.464 | 5 (26.3) | 4 (36.4) | 0.563 |
| Locoregional recurrence | 32 (15.9) | 2 (11.8) | 0.650 | 26 (13.2) | 2 (13.3) | 0.988 | 3 (15.8) | 1 (9.1) | 0.603 |
| Distant metastasis | 56 (27.9) | 9 (52.9) | 0.030 | 61 (31.0) | 3 (20.0) | 0.373 | 4 (21.1) | 3 (27.3) | 0.698 |
| Peritoneal dissemination | 21 (10.4) | 2 (11.8) | 0.865 | 35 (17.8) | 2 (13.3) | 0.663 | 2 (10.5) | 1 (9.1) | 0.900 |
| Hematogenous metastasis | 31 (15.4) | 7 (41.2) | 0.007 | 26 (13.2) | 1 (6.7) | 0.465 | 2 (10.5) | 2 (18.2) | 0.552 |
| Liver | 24 (11.9) | 6 (35.3) | 0.001 | 13 (6.6) | 1 (6.7) | 0.992 | 2 (10.5) | 0 | 0.265 |
| Lung | 3 (1.5) | 1 (5.9) | 0.195 | 5 (2.5) | 0 | 0.532 | 1 (5.3) | 1 (9.1) | 0.685 |
| Bone | 6 (3.0) | 1 (5.9) | 0.515 | 5 (2.5) | 0 | 0.532 | 0 | 1 (9.1) | 0.181 |
| Brain | 0 | 0 | - | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0.782 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Adrenal | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0.771 | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 0.695 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Skin | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0.771 | 3 (1.5) | 0 | 0.630 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Distant lymphatic recurrence | 17 (8.5) | 1 (5.9) | 0.711 | 16 (8.1) | 1 (6.7) | 0.841 | 2 (10.5) | 0 | 0.265 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age (year) | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| <65 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| ≥65 | 1.62 | 1.263–2.074 | 1.56 | 1.204–2.030 | ||
| Gender | <0.001 | |||||
| Male | 1.00 | |||||
| Female | 0.59 | 0.449–0.784 | ||||
| Tumor size (cm) | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||||
| <5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| ≥5 | 2.21 | 1.705–2.855 | 1.54 | 1.172–2.019 | ||
| Cell differentiation | 0.318 | |||||
| Poor | 1.00 | |||||
| Moderate | 0.85 | 0.671–1.070 | ||||
| Well | 0.68 | 0.255–1.856 | ||||
| Pathological TNM stage | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| I | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| II | 1.38 | 0.932–2.052 | 1.17 | 0.784–1.759 | ||
| III | 3.61 | 2.546–5.115 | 2.94 | 2.032–4.252 | ||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | 1.166 | |||||
| Yes | 1.00 | |||||
| No | 1.17 | 0.830–1.636 | ||||
| MSI status | 0.944 | |||||
| MSI/L/S | 1.00 | |||||
| MSI-H | 0.99 | 1.654–1.485 | ||||
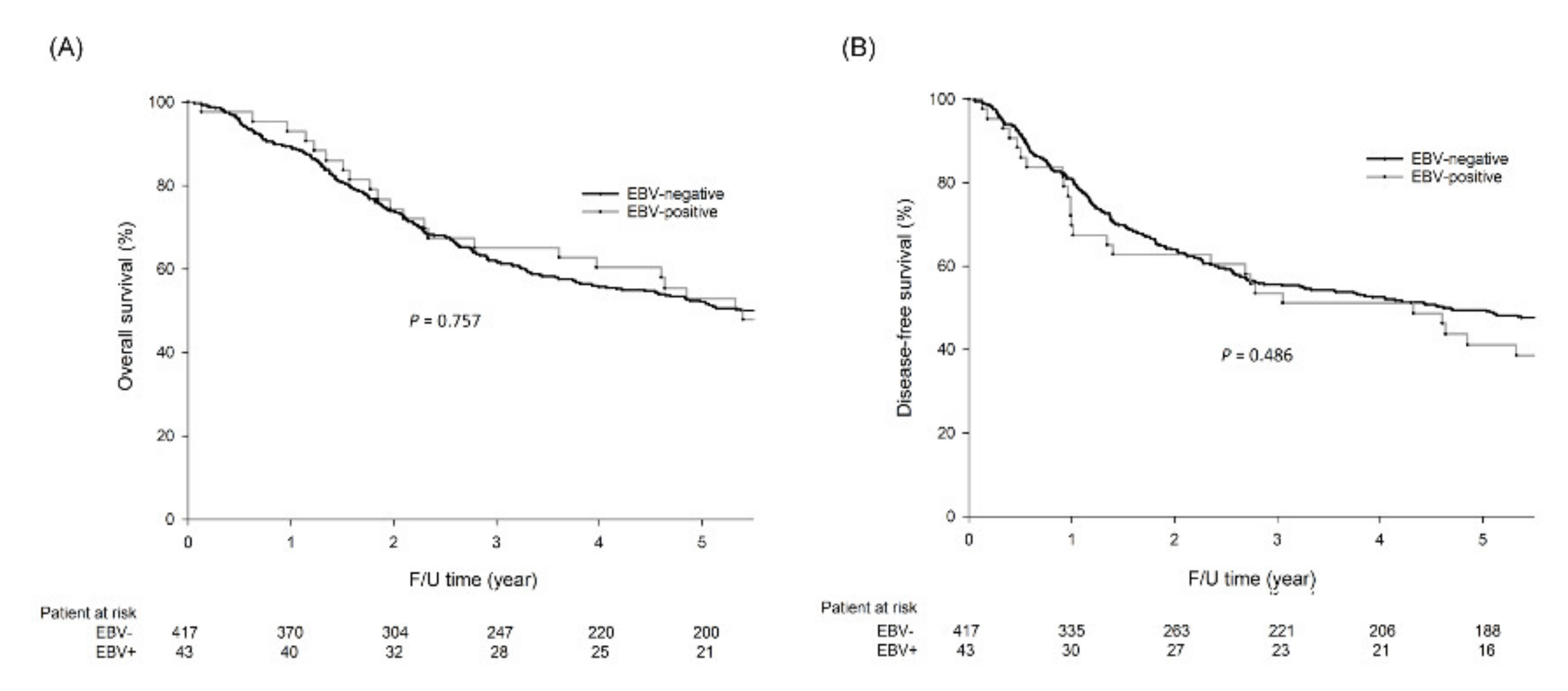
| EBV | 0.985 | |||||
| Negative | 1.00 | |||||
| Positive | 0.99 | 0.555–1.749 | ||||
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| <65 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| ≥65 | 1.51 | 1.185–1.925 | 1.51 | 1.185–1.925 | ||
| Gender | <0.001 | |||||
| Male | 1.00 | |||||
| Female | 0.58 | 0.436–0.759 | ||||
| Tumor size (cm) | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| <5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| ≥5 | 2.21 | 1.713–2.846 | 1.55 | 1.187–2.031 | ||
| Cell Differentiation | 0.271 | |||||
| Poor | 1.00 | |||||
| Moderate | 0.84 | 0.668–1.060 | ||||
| Well | 0.66 | 0.243–1.769 | ||||
| Pathological TNM stage | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| I | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| II | 1.37 | 0.930–2.016 | 1.16 | 0.778–1.716 | ||
| III | 3.46 | 2.459–4.861 | 2.74 | 1.910–3.936 | ||
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy | 0.351 | |||||
| Yes | 1.00 | |||||
| No | 1.17 | 0.841–1.630 | ||||
| MSI status | 0.975 | |||||
| MSI/L/S | 1.00 | |||||
| MSI-H | 1.01 | 0.668–1.516 | ||||
| EBV | 0.967 | |||||
| Negative | 1.00 | |||||
| Positive | 0.99 | 0.557–1.752 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, W.-L.; Chen, M.-H.; Huang, K.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Chao, Y.; Lo, S.-S.; Li, A.F.-Y.; Wu, C.-W.; Shyr, Y.-M. The Clinicopathological Features and Genetic Alterations in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Surgery. Cancers 2020, 12, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061517
Fang W-L, Chen M-H, Huang K-H, Lin C-H, Chao Y, Lo S-S, Li AF-Y, Wu C-W, Shyr Y-M. The Clinicopathological Features and Genetic Alterations in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Surgery. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061517
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Wen-Liang, Ming-Huang Chen, Kuo-Hung Huang, Chien-Hsing Lin, Yee Chao, Su-Shun Lo, Anna Fen-Yau Li, Chew-Wun Wu, and Yi-Ming Shyr. 2020. "The Clinicopathological Features and Genetic Alterations in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Surgery" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061517
APA StyleFang, W.-L., Chen, M.-H., Huang, K.-H., Lin, C.-H., Chao, Y., Lo, S.-S., Li, A. F.-Y., Wu, C.-W., & Shyr, Y.-M. (2020). The Clinicopathological Features and Genetic Alterations in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Surgery. Cancers, 12(6), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061517





