Tailored Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer Cells Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Functionalization of MF66
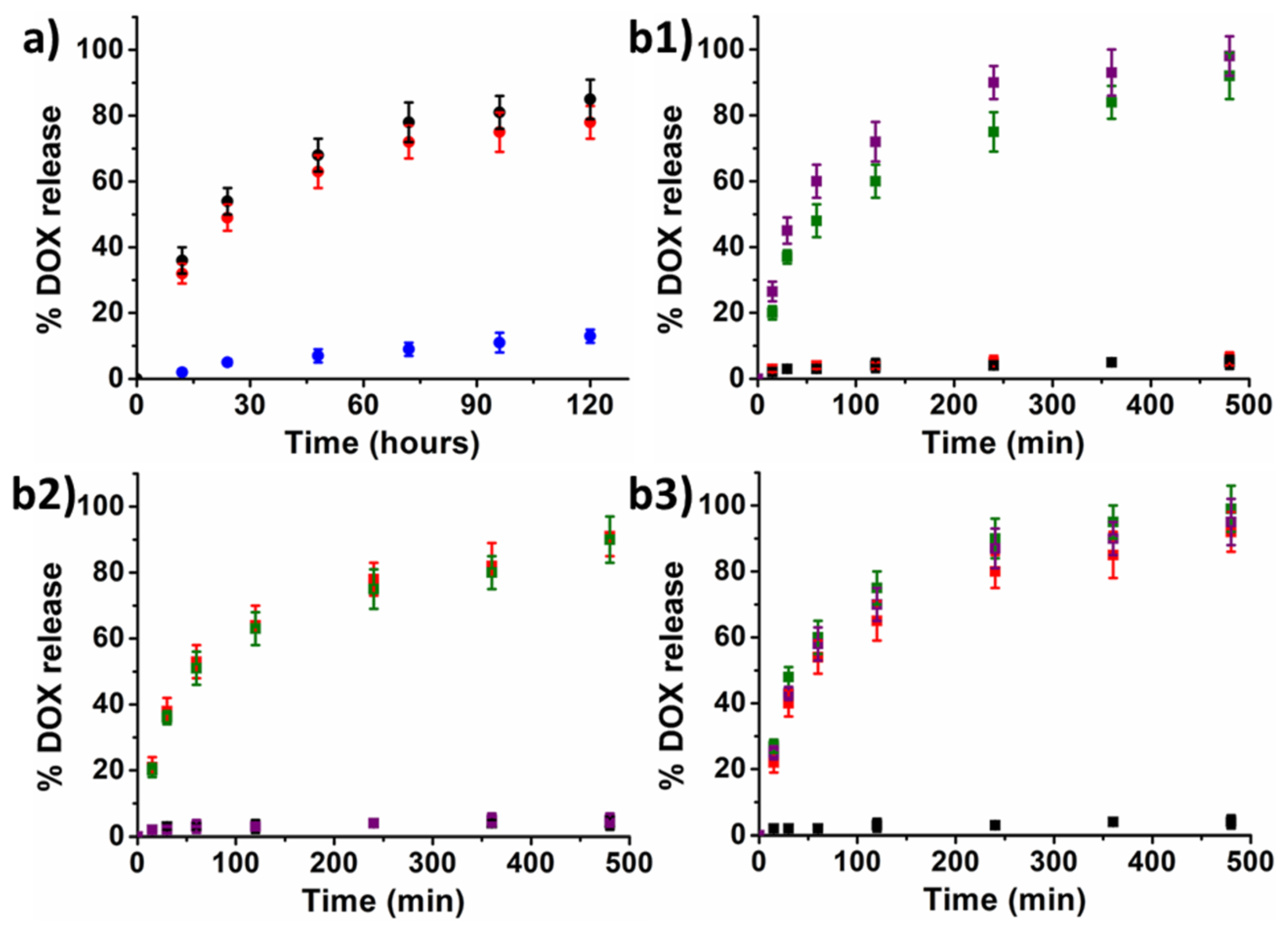
2.2. Drugs Release Studies
2.2.1. Drug Release Studies from Electrostatic Functionalized MF66
2.2.2. Drug Release Studies from Covalent Functionalized MF66-MNPs
2.3. Effects of Electrostatic Formulation in Cell Culture
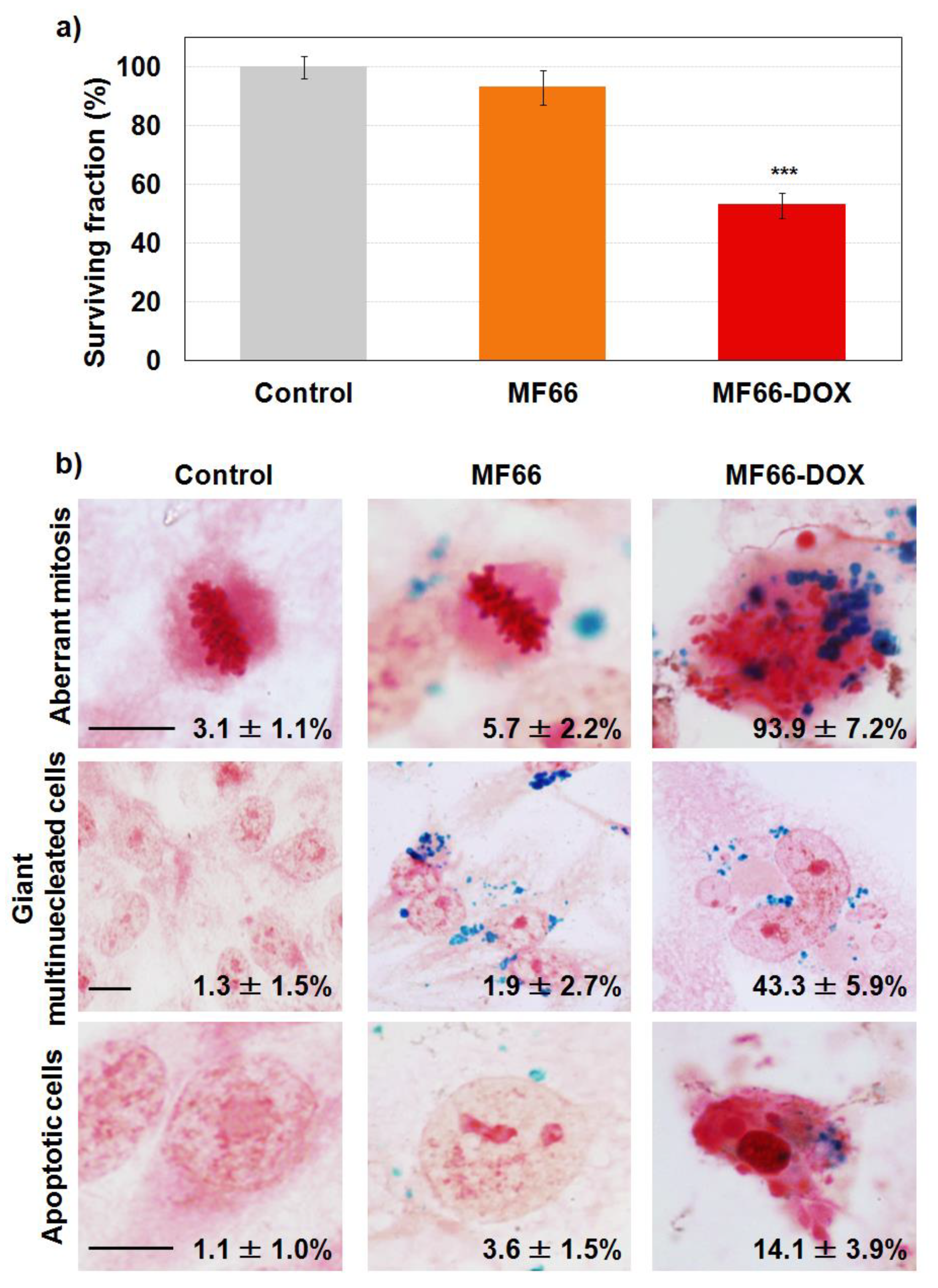
2.3.1. Cell Viability Reduction with Functionalized MF66 with DOX
2.3.2. Labelling Efficacy and Morphological Alterations
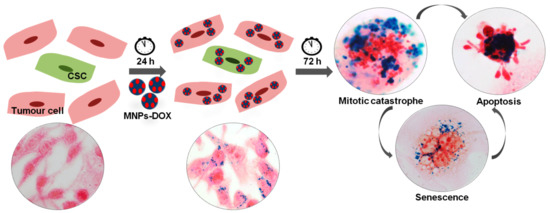
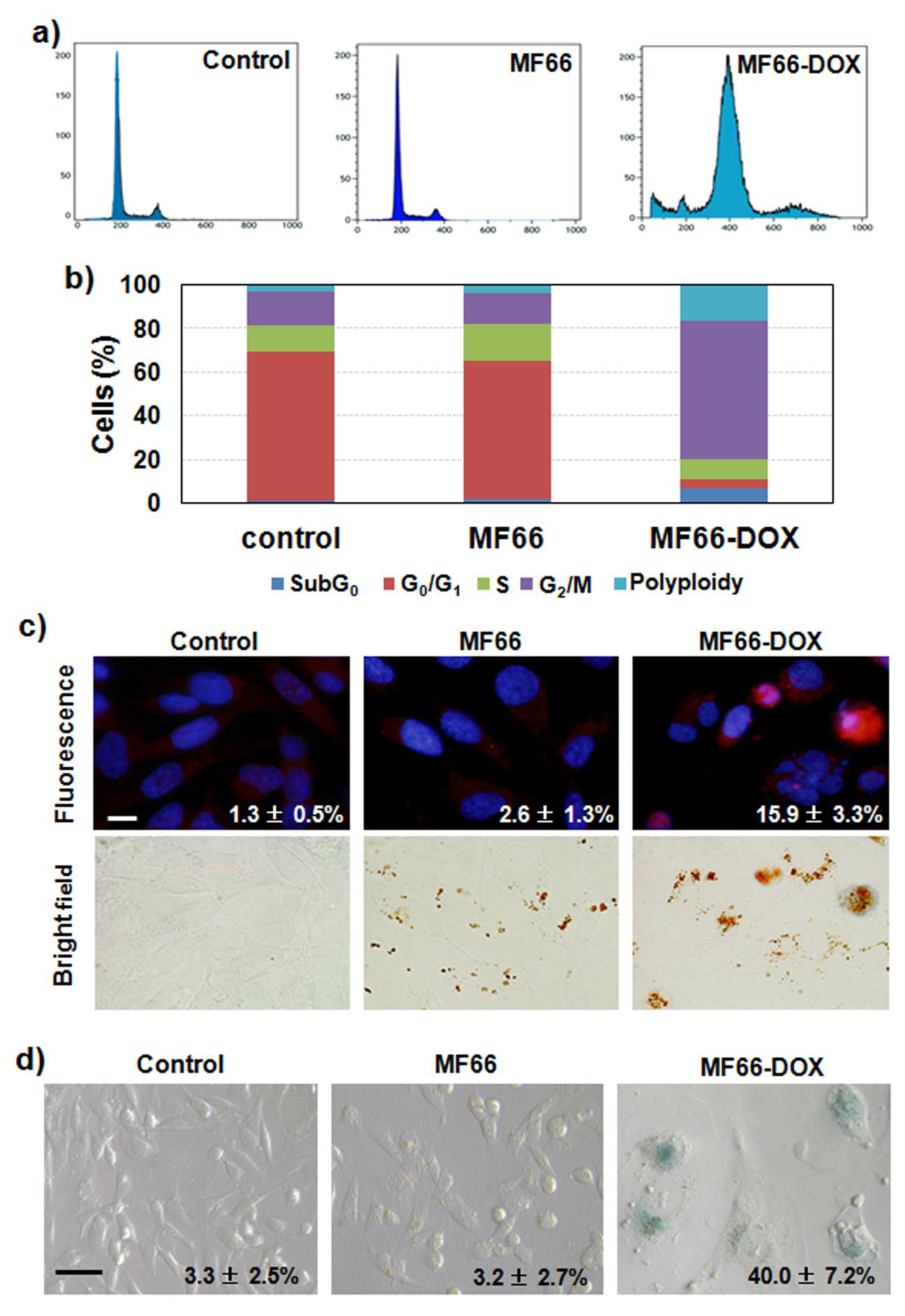
2.3.3. MF66 Formulation with DOX Triggered Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Senescence
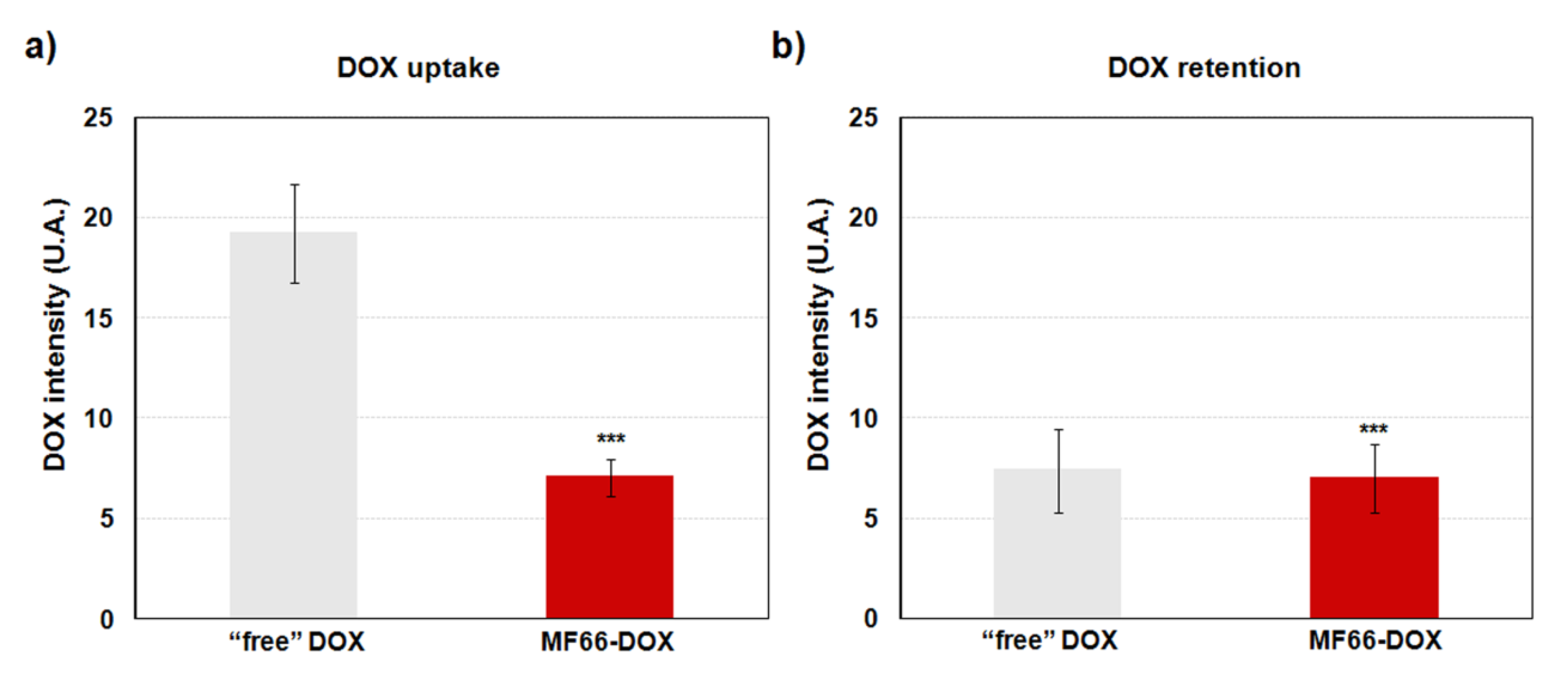
2.3.4. Increase in DOX Retention with the Nanoformulation
2.4. Effect of Covalent Formulations in Cell Culture
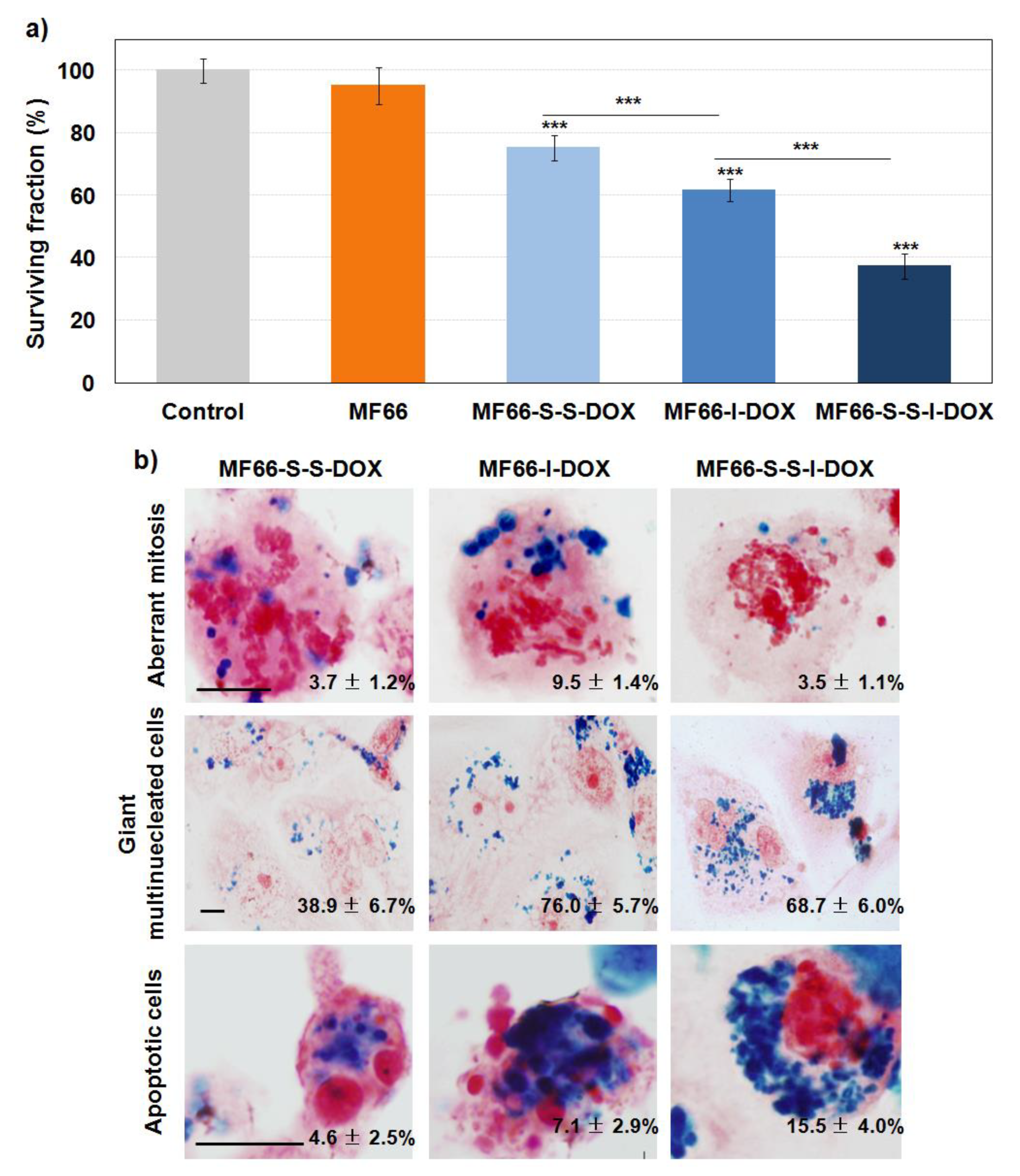
2.4.1. Cell Viability Reduction with the Three Covalent MF66 Formulations with DOX
2.4.2. DOX Covalent Formulations Have Similar Behaviour than the Electrostatic Formulation
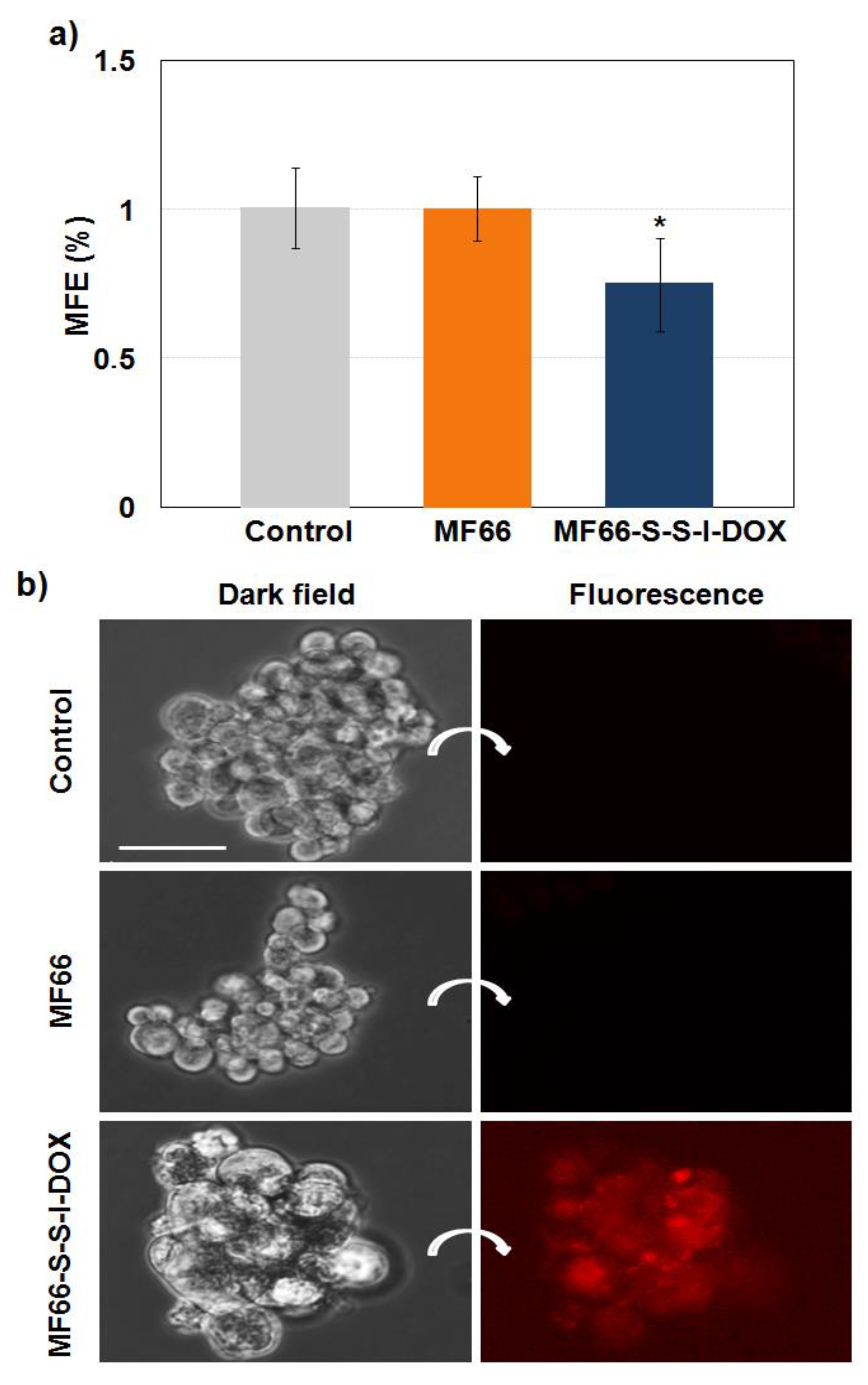
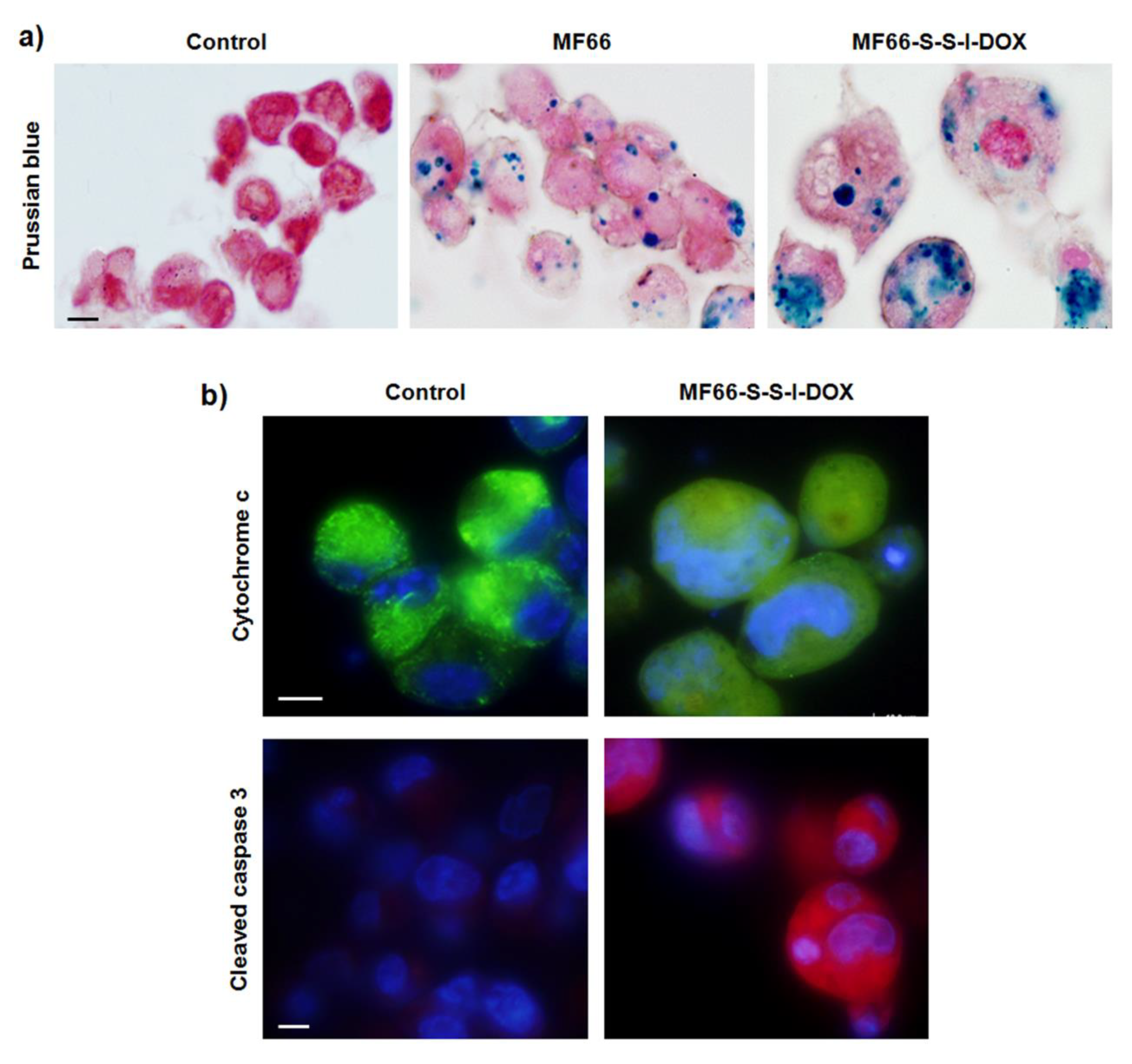
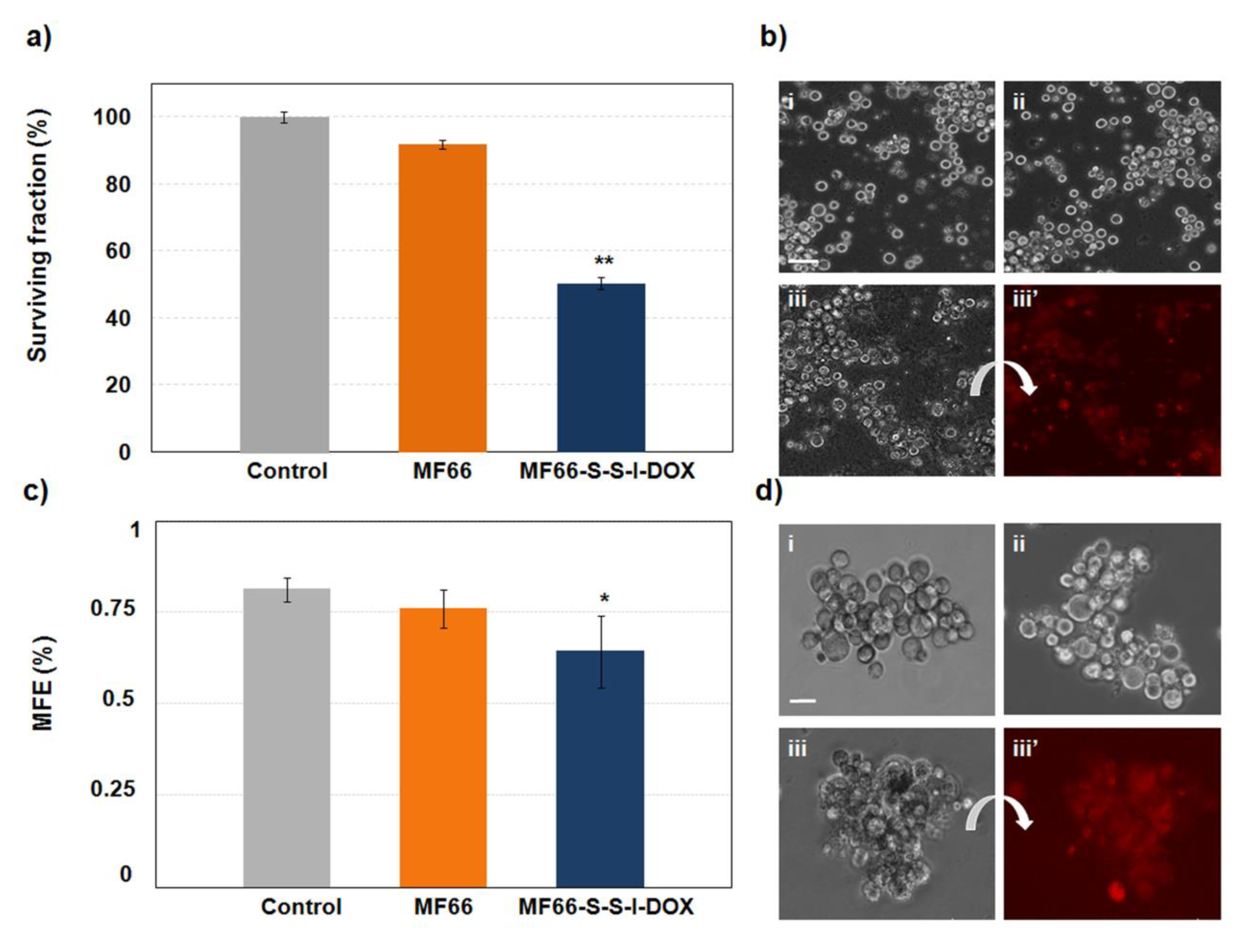
2.4.3. MF66-S-S-I-DOX Are Able to Target Breast Cancer Stem Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
4.2. Synthesis of Doxorubicin Derivatives
4.3. Electrostatic and Covalent Functionalization of MNPs
4.4. DOX Release Studies
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Nanoparticles Preparation
4.7. Cytotoxicity Analysis
4.8. Nanoparticles Internalization and Cancer Cell Morphology
4.9. Analysis of Internalized DOX into Cells
4.10. Analysis of Cellular Inactivation Mechanisms
4.10.1. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.10.2. Indirect Immunofluorescence for Cleaved Caspase-3 and Cytochrome c
4.10.3. Cellular Senescence Assessment
4.10.4. Videomicroscopy
4.11. Mammosphere Forming Efficiency
4.12. Mammosphere Morphology and Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lage, H. An overview of cancer multidrug resistance: A still unsolved problem. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3145–3167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caley, A.; Jones, R. The principles of cancer treatment by chemotherapy. Surgery 2012, 30, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G., Jr. Timeline: Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Bikadi, Z.; Rosenberg, M.F.; Mao, Q. Structure and function of the human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugde, P.; Biswas, R.; Merien, F.; Lu, J.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y. The therapeutic potential of targeting ABC transporters to combat multi-drug resistance. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 511–530. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Xie, Y. Nanodrug delivery systems for targeting the endogenous tumor microenvironment and simultaneously overcoming multidrug resistance properties. J. Control. Release 2017, 251, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Pattni, B.S.; Abouzeid, A.H.; Torchilin, V.P. Nanopreparations to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1748–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Escribano, E.; Queralt, J.; Busquets, M.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetically-guided and magnetically-responsive drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8070–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Carregal-Romero, S.; Casula, M.F.; Gutiérrez, L.; Morales, M.P.; Böhm, I.B.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Prosperi, D.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4306–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gautier, J.; Allard-Vannier, E.; Munnier, E.; Souce, M.; Chourpa, I. Recent advances in theranostic nanocarriers of doxorubicin based on iron oxide and gold nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cagel, M.; Grotz, E.; Bernabeu, E.; Moretton, M.A.; Chiappetta, D.A. Doxorubicin: Nanotechnological overviews from bench to bedside. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Kievit, F.M.; Veiseh, O.; Stephen, Z.R.; Wang, T.; Lee, D.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Zhang, M. Fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles with controllable drug loading and release through a simple assembly approach. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saito, G.; Swanson, J.A.; Lee, K.D. Drug delivery strategy utilizing conjugation via reversible disulfide linkages: Role and site of cellular reducing activities. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.Y.; Qian, W.P.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.A.; Staley, C.A. Theranostic nanoparticles with controlled release of gemcitabine for targeted therapy and MRI of pancreatic cancer. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionigi, C.; Piñeiro, Y.; Riminucci, A.; Bañobre, M.; Rivas, J.; Dediu, V. Regulating the thermal response of PNIPAM hydrogels by controlling the adsorption of magnetite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 114, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Teves, S.S.; Kemp, C.J.; Henikoff, S. Doxorubicin, DNA torsion, and chromatin dynamics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, A.S.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanooncology: The future of cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Ting, C.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Wang, C.H.; Liu, H.L.; Yen, T.C.; Yeh, C.K. SPIO-conjugated, doxorubicin-loaded microbubbles for concurrent MRI and focused-ultrasound enhanced brain-tumor drug delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomankova, K.; Polakova, K.; Pizova, K.; Binder, S.; Havrdova, M.; Kolarova, M.; Kriegova, E.; Zapletalova, J.; Malina, L.; Horakova, J.; et al. In vitro cytotoxicity analysis of doxorubicin-loaded/superparamagnetic iron oxide colloidal nanoassemblies on MCF7 and NIH3T3 cell lines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.G.; Janicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, J.A.; Desotelle, J.A.; Wilding, G.; Jarrard, D.F. Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayans, R.; Andrais, B.; Murray, D. Roles of Polyploid/Multinucleated Giant Cancer Cells in Metastasis and Disease Relapse Following Anticancer Treatment. Cancers 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, M. Senescent cells: New target for an old treatment? Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 4, e1299666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, M.P.; Brandt, R.M.; Putavet, D.A.; Klein, J.D.; Derks, K.W.; Bourgeois, B.R.; Stryeck, S.; Rijksen, Y.; Van Willigenburg, H.; Feijtel, D.A.; et al. Targeted Apoptosis of Senescent Cells Restores Tissue Homeostasis in Response to Chemotoxicity and Aging. Cell 2017, 169, 132–147.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, G.; Alakhova, D.Y.; Kabanov, A.V. Endocytosis of nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.C. The molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59950–59964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilapong, C.; Keereeta, Y.; Munkhetkorn, S.; Thongtem, S.; Thongtem, T. Enhanced doxorubicin delivery and cytotoxicity in multidrug resistant cancer cells using multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Yin, M.; Hu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhang, Z. A safe, simple and efficient doxorubicin prodrug hybrid micelle for overcoming tumor multidrug resistance and targeting delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossatz, S.; Grandke, J.; Couleaud, P.; Latorre, A.; Aires, A.; Crosbie-Staunton, K.; Ludwig, R.; Dähring, H.; Ettelt, V.; Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; et al. Efficient treatment of breast cancer xenografts with multifunctionalized iron oxide nanoparticles combining magnetic hyperthermia and anti-cancer drug delivery. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Latorre, A.; Somoza, A. Glutathione-triggered drug release from nanostructures. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2662–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Latorre, A.; Posch, C.; Garcimartín, Y.; Celli, A.; Sanlorenzo, M.; Vujic, I.; Ma, J.; Zekhtser, M.; Rappersberger, K.; Ortiz-Urda, S.; et al. DNA and aptamer stabilized gold nanoparticles for targeted delivery of anticancer therapeutics. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7436–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, K.; Hola, K.; Subr, V.; Bakandritsos, A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Targeted Drug Delivery with Polymers and Magnetic Nanoparticles: Covalent and Noncovalent Approaches, Release Control, and Clinical Studies. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5338–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; Shao, X.; Zhong, W.; Liao, W.; Xing, M.M. Theranostic, pH-Responsive, Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticles Inducing Active Targeting and Apoptosis for Advanced Gastric Cancer. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, E.; Czubek, B.; Nowicka, A.M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Stojek, Z.; Mazerska, Z. Improved cytotoxicity and preserved level of cell death induced in colon cancer cells by doxorubicin after its conjugation with iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 33, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Jang, Y.; Maharjan, S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, S.; Gankhuyag, N.; Yang, M.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, M.H.; et al. Combination therapy with doxorubicin-loaded galactosylated poly(ethyleneglycol)-lithocholic acid to suppress the tumor growth in an orthotopic mouse model of liver cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 116, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello-Varona, S.; Herrero-Martin, D.; Lopez-Alemany, R.; Munoz-Pinedo, C.; Tirado, O.M. “(Not) all (dead) things share the same breath”: Identification of cell death mechanisms in anticancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, F.L.; Harrison, H.; Spence, K.; Ablett, M.P.; Simões, B.M.; Farnie, G.; Clarke, R.B. A detailed mammosphere assay protocol for the quantification of breast stem cell activity. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2012, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Q.; Tang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X. Direct inhibition of ACTN4 by ellagic acid limits breast cancer metastasis via regulation of beta-catenin stabilization in cancer stem cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farahmand, L.; Darvishi, B.; Salehi, M.; Samadi Kouchaksaraei, S.; Majidzadeh-A, K. Functionalised nanomaterials for eradication of CSCs, a promising approach for overcoming tumour heterogeneity. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Ge, H.L.; Zhao, G.P.; Xu, Y.C.; Wang, Y. CD44hiCD24lo mammosphere-forming cells from primary breast cancer display resistance to multiple chemotherapeutic drugs. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3293–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, D.S.; Tevis, K.M.; Blessing, W.A.; Colson, Y.L.; Zaman, M.H.; Grinstaff, M.W. Breast Cancer Spheroids Reveal a Differential Cancer Stem Cell Response to Chemotherapeutic Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10382. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, G.W.; Khalafalla, S.E. Preparing Magnetic Fluids by a Peptizing Method; Bureau of Mines Innovative Processes in Extractive Metallurgy Programme, TPR 59; U.S. Department of the Interior: Lakewood, CO, USA, 1972.
- Salas, G.; Casado, C.; Teran, F.J.; Miranda, R.; Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Controlled synthesis of uniform magnetite nanocrystals with high-quality properties for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21065–21075. [Google Scholar]
- Latorre, A.; Couleaud, P.; Aires, A.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Somoza, A. Multifunctionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for controlled drug release: A general approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 82, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Banderas, A.I.; Aires, A.; Teran, F.J.; Perez, J.E.; Cadenas, J.F.; Alsharif, N.; Ravasi, T.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Kosel, J. Functionalized magnetic nanowires for chemical and magneto-mechanical induction of cancer cell death. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, R.S.; Kaneko, T.; Daues, A.; Edson, M.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Olech, L.J.; Grattan, J.A.; Spitalny, G.L.; Braslawsky, G.R. Evaluation in vitro of adriamycin immunoconjugates synthesized using an acid-sensitive hydrazone linker. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6600–6607. [Google Scholar]
- Furgeson, D.Y.; Dreher, M.R.; Chilkoti, A. Structural optimization of a “smart” doxorubicin-polypeptide conjugate for thermally targeted delivery to solid tumors. J. Control. Release 2006, 110, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shmidt, M.S.; Vior, M.C.G.; Riega, S.D.E.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.M.; Abasolo, M.I.; Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; Tabero, A.; Villanueva, A.; Moglioni, A.G.; Blanco, M.M.; et al. 3-Hydroxykynurenic acid: Physicochemical properties and fluorescence labeling. Dyes and Pigments 2019, 162, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; Filice, M.; Guillén, M.J.; Amaro, R.; Viñambres, M.; Tabero, A.; Paredes, K.O.; Villanueva, A.; Calvo, P.; Del Puerto Morales, M.; et al. Tailor-made PEG coated iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents for long lasting magnetic resonance molecular imaging of solid cancers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 107, 110262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Sampedro, G.; Epelde-Elezcano, N.; Martínez-Martínez, V.; Esnal, I.; Bañuelos, J.; García-Moreno, I.; Agarrabeitia, A.R.; De La Moya, S.; Tabero, A.; Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; et al. A versatile fluorescent molecular probe endowed with singlet oxygen generation under white-light photosensitization. Dyes and Pigments 2017, 142, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; Calero, M.; Aires, A.; L. Cortajarena, A.; Simões, B.M.; Latorre, A.; Somoza, Á.; Clarke, R.B.; Miranda, R.; Villanueva, A. Tailored Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer Cells Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061397
Lazaro-Carrillo A, Calero M, Aires A, L. Cortajarena A, Simões BM, Latorre A, Somoza Á, Clarke RB, Miranda R, Villanueva A. Tailored Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer Cells Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061397
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazaro-Carrillo, Ana, Macarena Calero, Antonio Aires, Aitziber L. Cortajarena, Bruno M. Simões, Alfonso Latorre, Álvaro Somoza, Robert B. Clarke, Rodolfo Miranda, and Angeles Villanueva. 2020. "Tailored Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer Cells Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061397
APA StyleLazaro-Carrillo, A., Calero, M., Aires, A., L. Cortajarena, A., Simões, B. M., Latorre, A., Somoza, Á., Clarke, R. B., Miranda, R., & Villanueva, A. (2020). Tailored Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer Cells Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells. Cancers, 12(6), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061397