Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
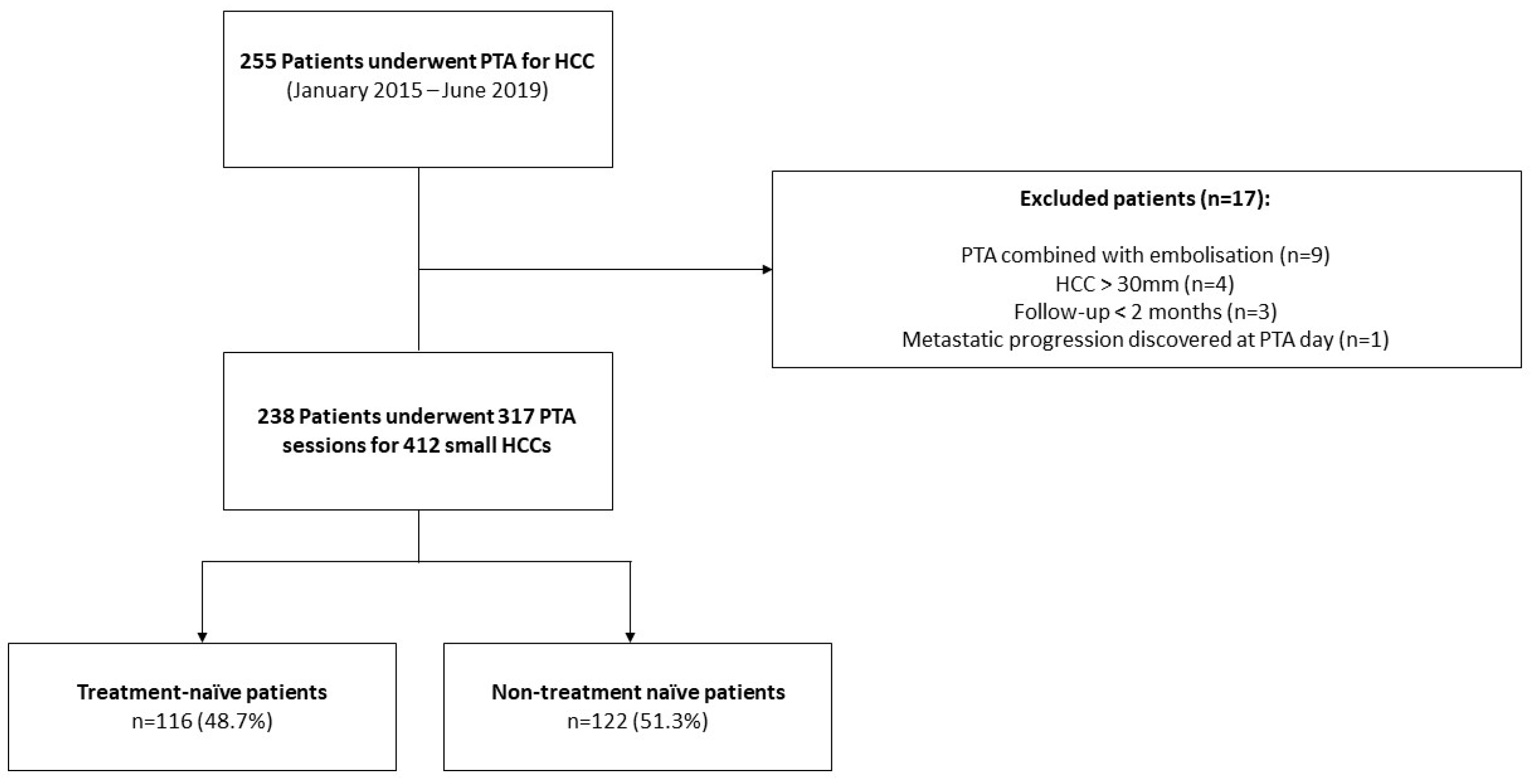
2.1. Patients
Patient and Tumor Data
2.2. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation
Guidance and Ablation
2.3. Complications
2.4. Follow-Up and Outcome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Technical/Treatment Success
3.3. Complications and Follow-Up
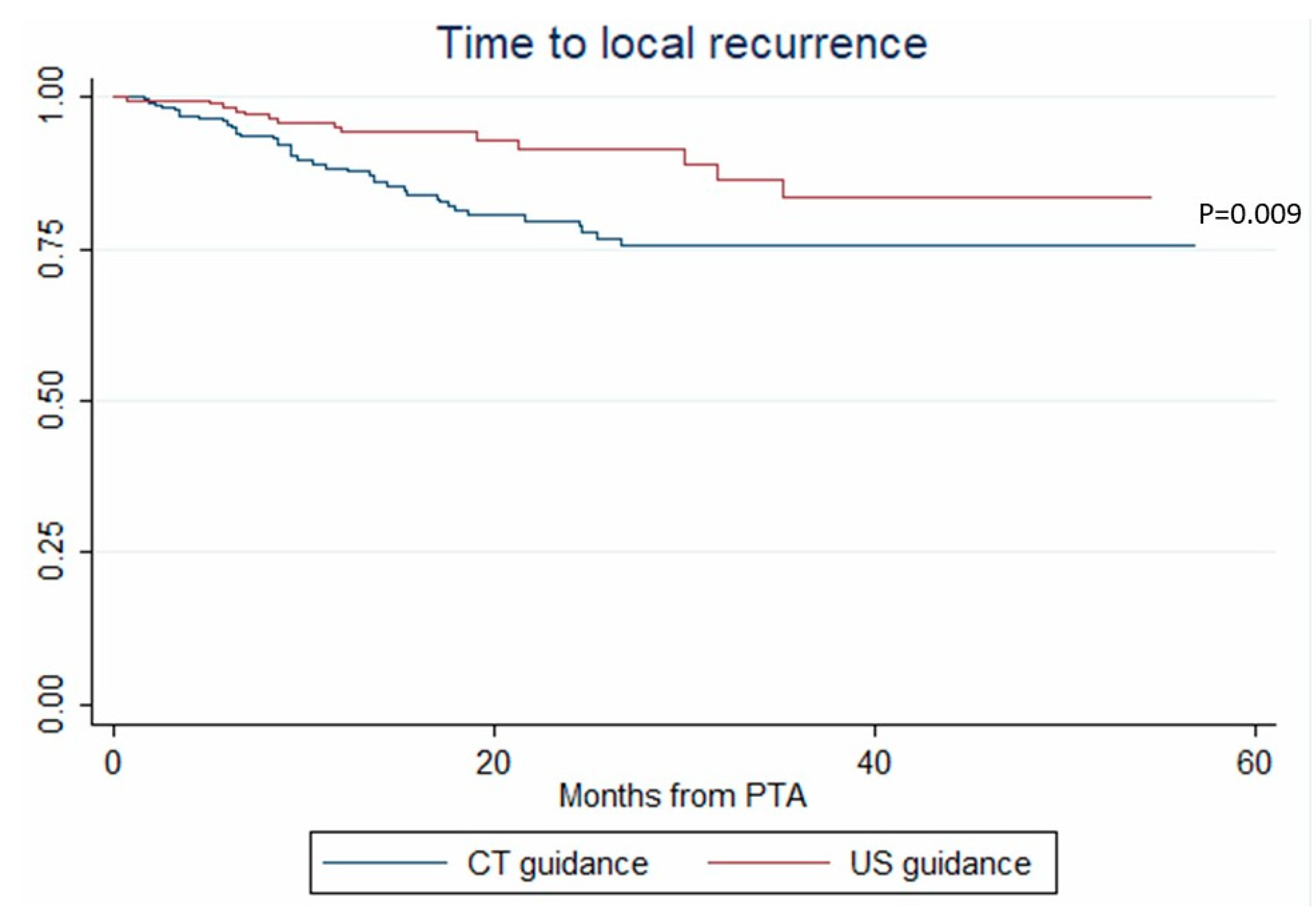
3.4. Local Tumor Progression
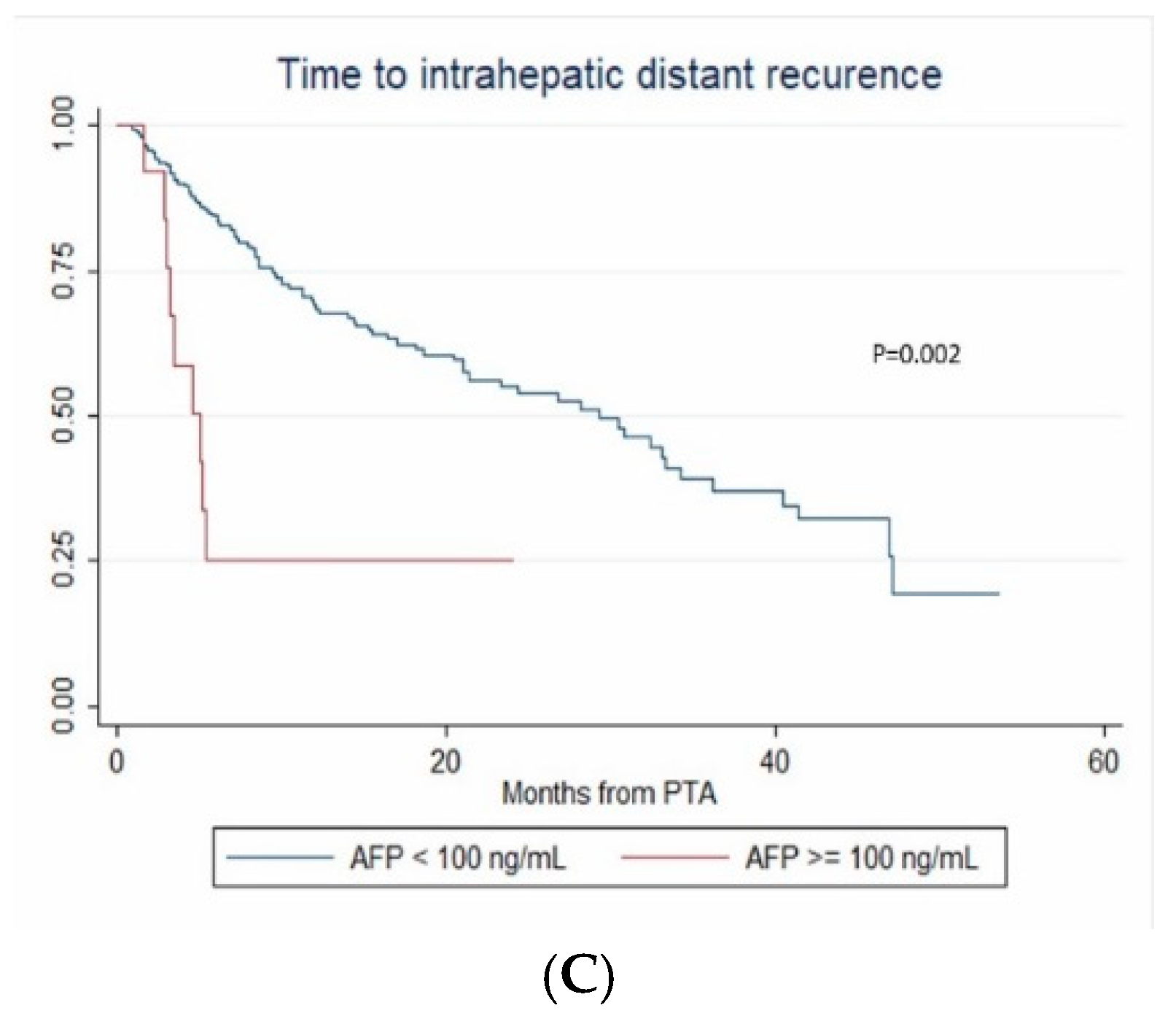
3.5. Intrahepatic Distant Recurrence
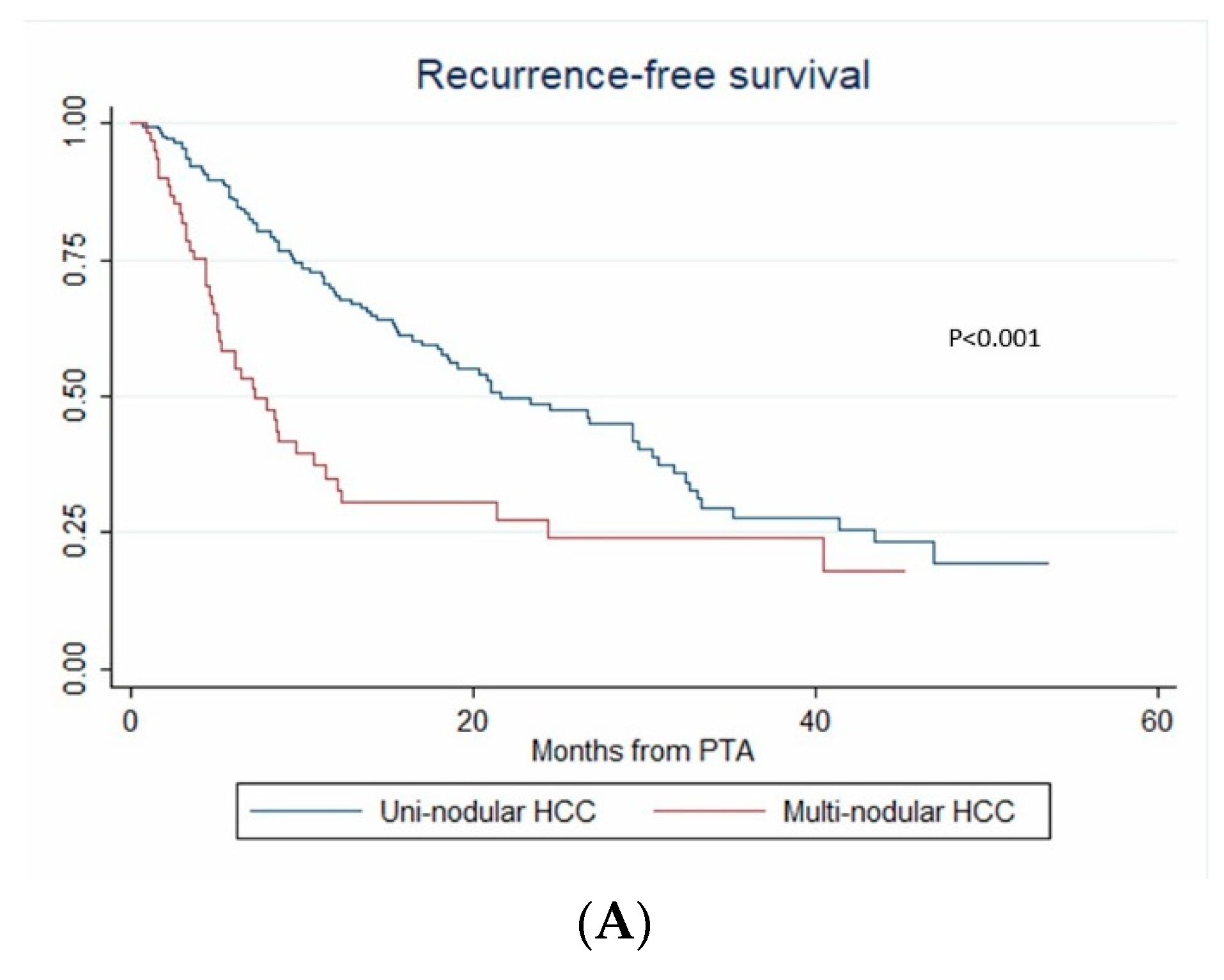
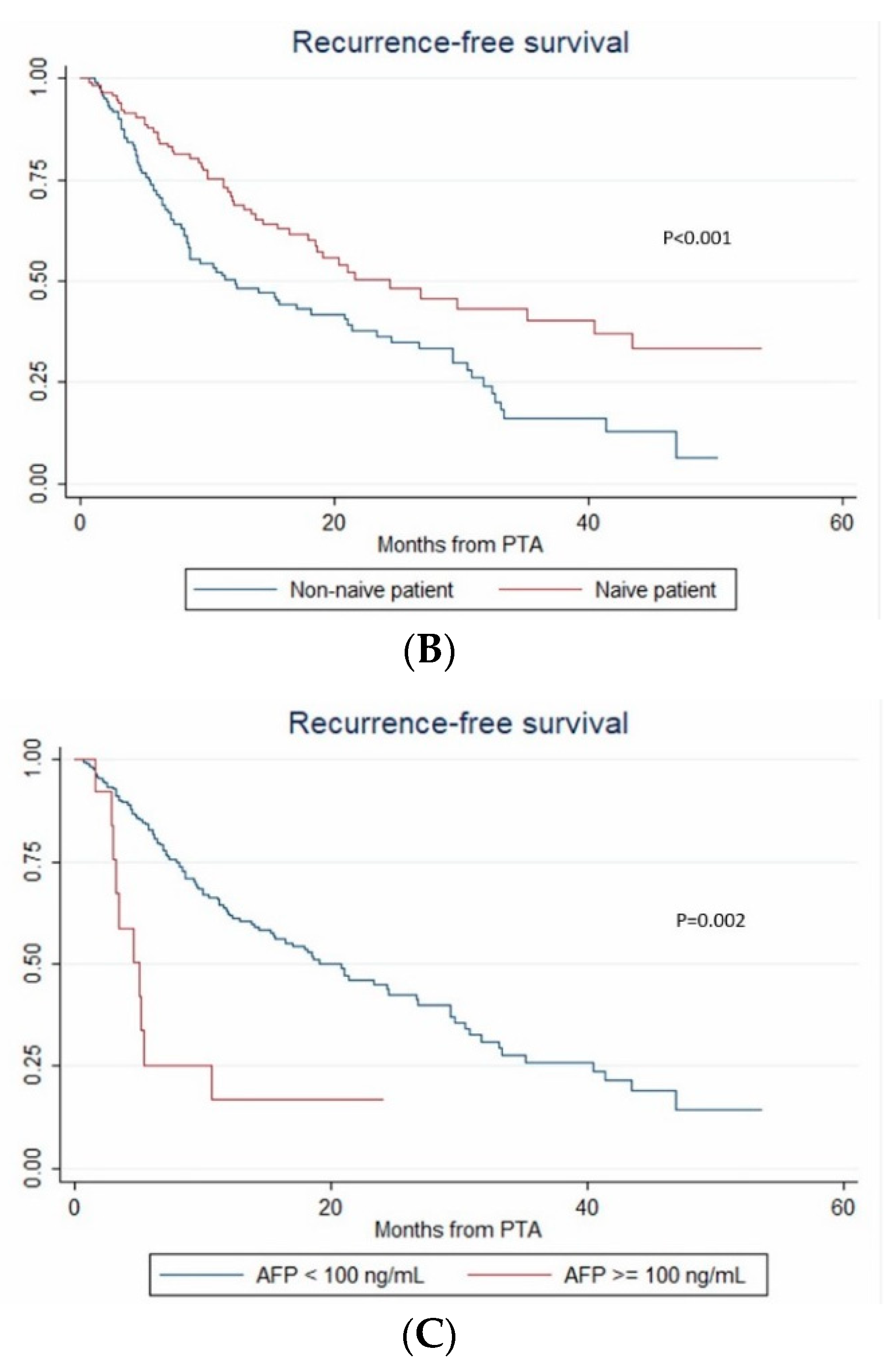
3.6. Recurrence-Free Survival
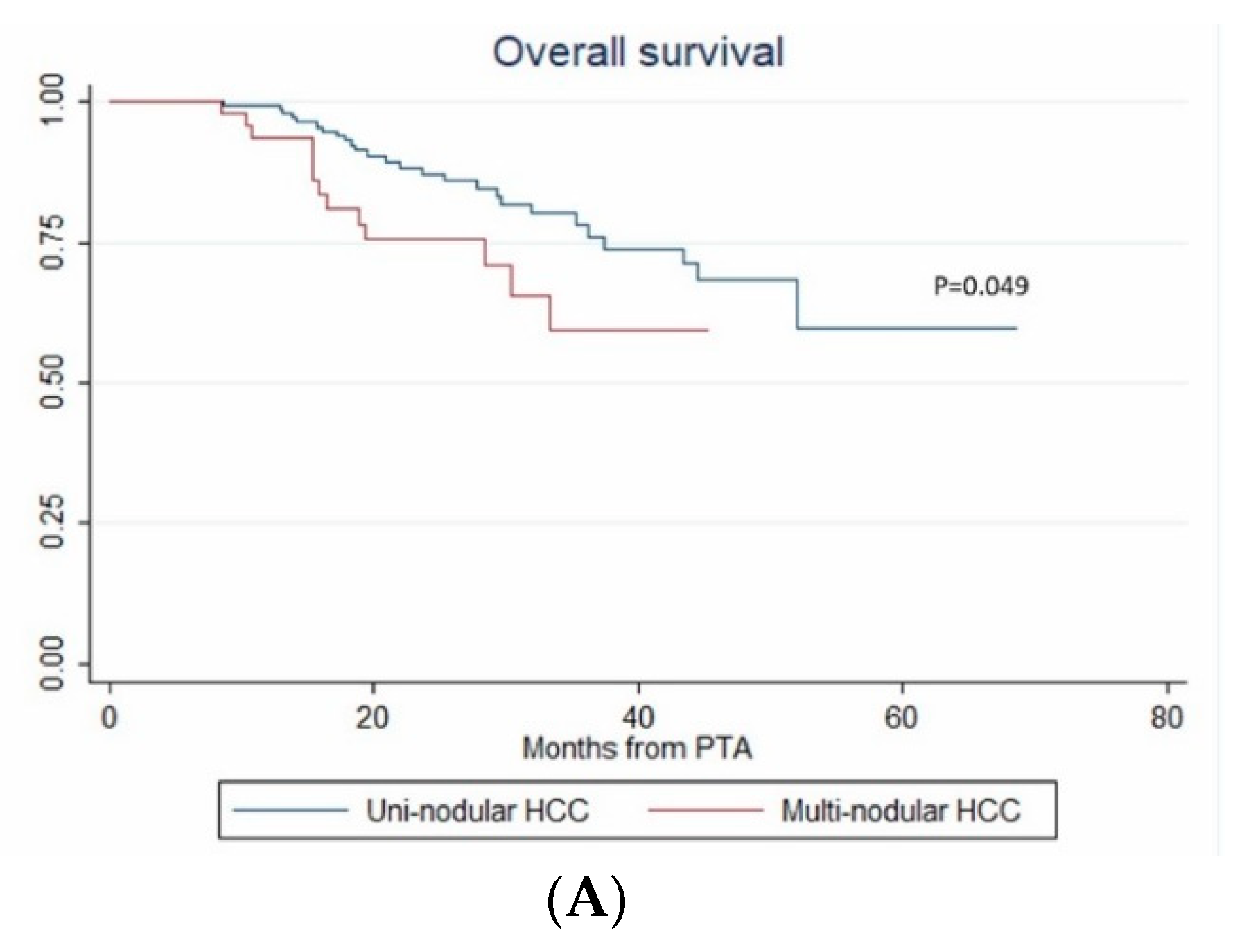
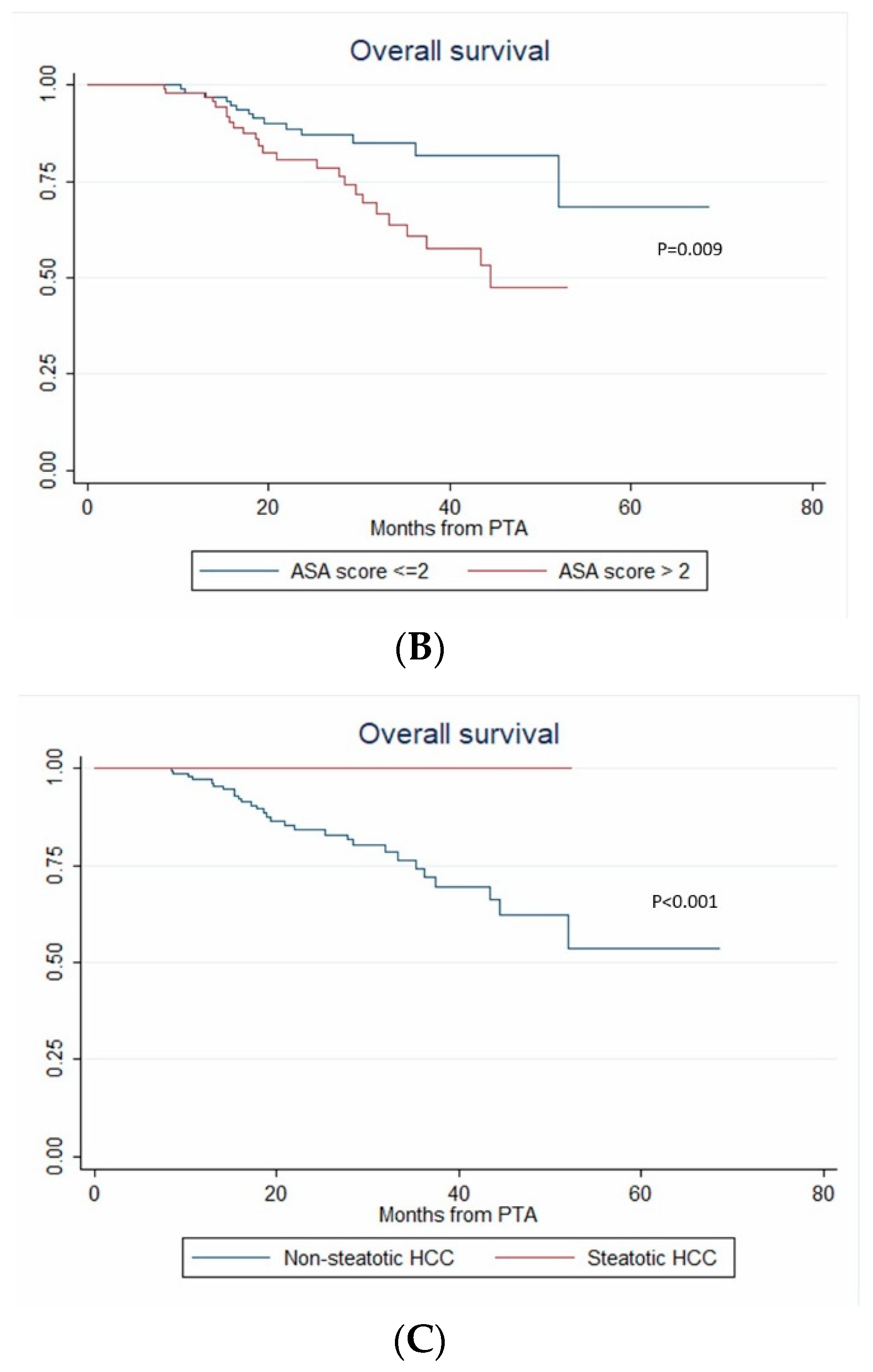
3.7. Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer, C.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Abate, D.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lim, H.K.; Rhim, H.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, D.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, S.W.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, M.S.; et al. Ten-year outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy of early hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of prognostic factors. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Arano, T.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Asaoka, Y.; Sato, T.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.W.; Kim, J.M.; Rhim, H.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Lim, H.K.; Choi, D.; Song, K.D.; Kwon, C.H.; Joh, J.W.; et al. Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiofrequency Ablation versus Nonanatomic Resection--Propensity Score Analyses of Long-term Outcomes. Radiology 2015, 275, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocquelet, A.; Balageas, P.; Laurent, C.; Blanc, J.F.; Frulio, N.; Salut, C.; Cassinotto, C.; Saric, J.; Possenti, L.; Bernard, P.H.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: A study of 281 Western patients. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2015, 31, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Kontchou, G.; Mahamoudi, A.; Aout, M.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Grando, V.; Coderc, E.; Vicaut, E.; Trinchet, J.C.; Sellier, N.; Beaugrand, M.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocquelet, A.; Aubé, C.; Rode, A.; Cartier, V.; Sutter, O.; Manichon, A.F.; Boursier, J.; N’kontchou, G.; Merle, P.; Blanc, J.-F.; et al. Comparison of no-touch multi-bipolar vs. monopolar radiofrequency ablation for small HCC. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; de Klerk, N.; Abramson, M.; Del Monaco, A.; Benke, G.; Dennekamp, M.; Musk, A.W.; Sim, M. Fractional polynomials and model selection in generalized estimating equations analysis, with an application to a longitudinal epidemiologic study in Australia. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; Sutter, O.; Nahon, P.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; Seror, O. Percutaneous treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: State of the art and innovations. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teratani, T.; Yoshida, H.; Shiina, S.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Tateishi, R.; Mine, N.; Kondo, Y.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-E.; Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, D.; Shin, S.W.; Cho, S.K. Outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma referred for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation at a tertiary center: Analysis focused on the feasibility with the use of ultrasonography guidance. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, e80–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.; Gorgen, A.; Muaddi, H.; Aravinthan, A.D.; Issachar, A.; Mironov, O.; Zhang, W.; Kachura, J.; Beecroft, R.; Cleary, S.P.; et al. Outcomes of radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma less than 3cm in potentially transplantable patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livraghi, T.; Meloni, F.; Di Stasi, M.; Rolle, E.; Solbiati, L.; Tinelli, C.; Rossi, S. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology 2008, 47, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Ohkubo, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Minagawa, M.; Takayama, T.; Kawasaki, S.; et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwaki, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Kokubu, S.; Hidaka, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Takada, J.; Watanabe, M.; Shibuya, A.; Minamino, T.; Saigenji, K. Repeat radiofrequency ablation provides survival benefit in patients with intrahepatic distant recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, M.; Cassinotto, C.; Piron, L.; Assenat, E.; Pageaux, G.P.; Escal, L.; Pierredon-Foulongne, M.A.; Verzilli, D.; Jaber, S.; Guiu, B. Percutaneous thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas located in the hepatic dome using artificial carbon dioxide pneumothorax: Retrospective evaluation of safety and efficacy. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2018, 35, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baère, T.; Dromain, C.; Lapeyre, M.; Briggs, P.; Duret, J.S.; Hakime, A.; Boige, V.; Ducreux, M. Artificially induced pneumothorax for percutaneous transthoracic radiofrequency ablation of tumors in the hepatic dome: Initial experience. Radiology 2005, 236, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, S.; Tanigawa, N.; Kojima, H.; Komemushi, A.; Shomura, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Shiraishi, T.; Sawada, S. Radiofrequency ablation combined with CO2 injection for treatment of retroperitoneal tumor: Protecting surrounding organs against thermal injury. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Deschamps, F.; Briggs, P.; Dromain, C.; Boige, V.; Hechelhammer, L.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Aupérin, A.; Goere, D.; Elias, D. Hepatic malignancies: Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation during percutaneous portal or hepatic vein occlusion. Radiology 2008, 248, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardella, J.F.; Kundu, S.; Miller, D.L.; Millward, S.F.; Sacks, D.; Radiology, S.O.I. Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J. Vasc. Interven. Radiol. 2009, 20, S189–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; de Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D.; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update. J. Vasc. Interven. Radiol. 2014, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W. Akaike’s information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 2001, 57, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.N.; Choi, D.; Rhim, H.; Rha, S.E.; Hong, H.P.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, J.W.; Seo, J.W.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Planning ultrasound for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation to treat small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas detected on computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: A multicenter prospective study to assess factors affecting ultrasound visibility. J. Vasc. Interven. Radiol. 2012, 23, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasugai, H.; Osaki, Y.; Oka, H.; Kudo, M.; Seki, T.; Osaka Liver Cancer Study, G. Severe complications of radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of 3,891 ablations in 2,614 patients. Oncology 2007, 72 (Suppl. 1), 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, J.H. Long-term Therapeutic Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Subcapsular versus Nonsubcapsular Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matched Study. Radiology 2016, 280, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Saviano, A.; de Matthaeis, N.; Cucchetti, A.; Ardito, F.; Federico, B.; Brunello, F.; Pinna, A.D.; Giorgio, A.; Giulini, S.M.; et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Ravetta, V.; Rosa, L.; Ghittoni, G.; Viera, F.T.; Garbagnati, F.; Silini, E.M.; Dionigi, P.; Calliada, F.; Quaretti, P.; et al. Repeated radiofrequency ablation for management of patients with cirrhosis with small hepatocellular carcinomas: A long-term cohort study. Hepatology 2011, 53, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, R.; Shiina, S.; Teratani, T.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Koike, Y.; Fujishima, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer 2005, 103, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwaki, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Shibuya, A.; Ono, K.; Hidaka, H.; Watanabe, M.; Kokubu, S.; Saigenji, K. Intrahepatic distant recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for a single small hepatocellular carcinoma: Risk factors and patterns. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Luo, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Bu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Identification of prognostic biomarkers in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and stratification by integrative multi-omics analysis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xia, C.Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Dong, H.; Yu, W.L.; Jin, G.Z.; Cong, W.M.; Wu, M.C. Determination of clonal origin of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma for personalized therapy and outcomes evaluation: A new strategy for hepatic surgery. J. Am. Coll Surg. 2013, 217, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lim, H.K.; Rhim, H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, S.W.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, M.S.; Yoo, B.C. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma as a first-line treatment: Long-term results and prognostic factors in a large single-institution series. European Radiol. 2007, 17, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as first-line treatment: Long-term results and prognostic factors in 162 patients with cirrhosis. Radiology 2014, 270, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Cho, O.K.; Koh, B.H.; Kim, Y. Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of the pattern and risk factors. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 59, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutami, R.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Shiota, K.; Kojiro, M. Pathomorphologic study on the mechanism of fatty change in small hepatocellular carcinoma of humans. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.H.; Yu, S.; Yu, Y.-H.; Tong, J.H.M.; Wang, L.; Tin, E.K.Y.; Chong, C.C.N.; Chan, S.L.; Wong, G.L.H.; Wong, V.W.S.; et al. Steatotic hepatocellular carcinoma: A variant associated with metabolic factors and late tumour relapse. Histopathology 2016, 69, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomao, M.; Yu, W.M.; Brown, R.S.; Emond, J.C.; Lefkowitch, J.H. Steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma (SH-HCC): A distinctive histological variant of HCC in hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis with associated NAFLD/NASH. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, J.; Ziol, M.; Paradis, V.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Molecular and histological correlations in liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Petit, J.M.; Loffroy, R.; Ben Salem, D.; Aho, S.; Masson, D.; Hillon, P.; Krause, D.; Cercueil, J.P. Quantification of liver fat content: Comparison of triple-echo chemical shift gradient-echo imaging and in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2009, 250, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Lim, S.; Jeong, W.K.; Choi, D.; Lee, W.J. Prediction of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinomas with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging: Impact of intra-tumoral fat detected on chemical-shift images. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; Martin, Y.; Caruso, S.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Bayard, Q.; Calderaro, J. Clinical Impact of Genomic Diversity From Early to Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap (Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability); Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Patients | |
| Age (mean ± SD, years) | 64.9 ± 9.9 |
| Sex (n, %) | |
| Male | 190 (79.8) |
| Female | 48 (20.29) |
| ASA score (n, %) | |
| 1-2 | 120 (50.4) |
| 3-4 | 118 (49.6) |
| Diabetes (n, %) | |
| No | 147 (61.8) |
| Yes | 91 (38.2) |
| Metformin treatment | 35 (14.7) |
| Prior treatment for HCC (n, %) | |
| No | 116 (48.7) |
| Yes | 122 (51.3) |
| Resection | 33 (27) |
| PTA | 55 (45) |
| TACE | 34 (28) |
| Liver disease | |
| Cirrhosis (n, %) | |
| No | 20 (8.4) |
| Yes | 218 (91.6 |
| Causes for liver disease (n, %) | |
| Alcohol (with or without viral hepatitis) | 135 (56.7) |
| Viral hepatitis B or C | 61 (25.6) |
| Hemochromatosis | 12 (5) |
| Other causes, including NASH | 30 (12.6) |
| Steatosis (n, %) | |
| No | 153 (65.7) |
| Yes | 80 (34.3) |
| Child-Pugh class | |
| A | 231 (97.1) |
| B | 7 (2.9) |
| MELD score (mean ± SD) | 8.8 ± 2.2 |
| Laboratory data (mean ± SD) | |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 36.1 ± 163.7 |
| Total bilirubin (µmol/L) | 13.5 ± 8.7 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 40.2 ± 4.9 |
| Prothrombin activity (%) | 84.6 ± 13.2 |
| Platelet count (× 10/mm3) | 139 ± 72 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 83.7 ± 31.1 |
| ALBI score | |
| 1 | 151 (66.8) |
| 2 | 75 (33.2) |
| HCC | |
| Method for diagnosis (n, %) | |
| Biopsy | 62 (15) |
| Imaging | 350 (85) |
| Tumor size (mean ± SD) | 15.1 ± 5 |
| <20 mm | 358 (86.9) |
| >20 mm | 54 (13.1) |
| No. of tumors (n, %) | |
| 1 | 242 (72.9) |
| 2 | 56 (21.4) |
| 3 | 18 (5.4) |
| 4 | 1 (0.3) |
| Steatotic HCC (n, %) | |
| Yes | 66 (16) |
| No | 317 (77) |
| Unknown | 29 (7) |
| Dome (n, %) | 93 (22.6) |
| Subcapsular location (n, %) | 150 (36.4) |
| Near large vessel (n, %) | 71 (17.2) |
| Near surrounding organ (n, %) | 36 (8.7) |
| PTA | |
| PTA modality (n, %) | |
| Radiofrequency | 174 (42.2) |
| Microwave | 238 (57.8) |
| Imaging guidance (n, %) | |
| US | 182 (44.2) |
| CT | 230 (55.8) |
| Artificial CO2 pneumothorax (n, %) | 47 (11.4) |
| Hydrodissection-CO2 dissection (n, %) | 36 (8.7) |
| Tumor tagging (n, %) | 208 (50.5) |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Bootstrapping (400 Replications) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Patients | ||||||
| Age | 0.968 (0.939–0.999) | 0.04 | 0.969 (0.938–1.001) | 0.054 | 0.969 (0.938–1.001) | 0.058 |
| Sex female vs male | 0.487 (0.189–1.252) | 0.136 | ||||
| ASA (>2 vs. ≤2) | 1.021 (0.565–1.845) | 0.944 | ||||
| Diabetes | 1.665 (0.904–3.066) | 0.102 | ||||
| Metformin treatment | 1.58 (0.6–4.19) | 0.36 | ||||
| Treatment-naïve patient | 1.309 (0.724–2.367) | 0.372 | ||||
| Liver diseases | ||||||
| Cirrhosis | 4.785 (0.574–39.91) | 0.148 | ||||
| Child-Pugh (B vs. A) | 1.559 (0.285–8.528) | 0.609 | ||||
| Cause of liver disease (vs. alcohol) | ||||||
| Viral hepatitis B or C | 0.624 (0.279–1.392) | 0.249 | ||||
| Hemochromatosis | 0.92 (0.273–3.097) | 0.893 | ||||
| Others (including NASH) | 0.859 (0.325–2.268) | 0.758 | ||||
| Steatosis | 1.12 (0.607–2.064) | 0.717 | ||||
| AFP ≥100 vs <100 ng/mL | 1.113 (0.298–4.162) | 0.873 | ||||
| AFP (per unit) | 0.999 (0.995–1.003) | 0.55 | ||||
| Bilirubin | 1.008 (0.977–1.04) | 0.616 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.969 (0.909–1.032) | 0.33 | ||||
| Prothrombin time | 1.001 (0.979–1.024) | 0.922 | ||||
| Platelet count (per 1,000/mm3) | 1 (0.996–1.005) | 0.836 | ||||
| Creatinine | 0.997 (0.985–1.008) | 0.552 | ||||
| MELD (>9 vs. ≤9) | 1.263 (0.69–2.312) | 0.449 | ||||
| ALBI score 2 vs. 1 | 1.241 (0.65–2.37) | 0.512 | ||||
| HCC | ||||||
| Tumor size (per mm) | 1.096 (1.04–1.154) | 0.001 | 1.108 (1.05–1.169) | <0.001 | 1.108 (1.051–1.168) | <0.001 |
| Tumor size <20 mm | 0.359 (0.181–0.709) | 0.003 | ||||
| Steatotic HCC | 0.487 (0.188–1.266) | 0.14 | ||||
| Dome tumor | 1.747 (0.942–3.24) | .077 | ||||
| Subcapsular | 0.932 (0.516–1.682) | 0.814 | ||||
| Near large vessel | 1.6096 (0.809–3.202) | 0.175 | ||||
| Near surrounding organ | 1.043 (0.387–2.809) | 0.934 | ||||
| PTA | ||||||
| PTA modality: MWA vs RF | 1.48 (0.81–2.703) | 0.202 | ||||
| US vs CT guidance | 0.394 (0.208–0.749) | 0.004 | 0.294 (0.107–0.803) | 0.017 | 0.294 (0.102–0.841) | 0.023 |
| Artificial pneumothorax | 1.301 (0.569–2.977) | 0.533 | ||||
| Tumor tagging | 1.82 (1.01–3.28) | 0.046 | 0.827 (0.325–2.103) | 0.689 | 0.827 (0.362–1.887) | 0.651 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Bootstrapping (400 Replications) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Patients | ||||||
| Age | 0.98 (0.957–1.005) | 0.112 | ||||
| Sex female vs male | 0.953 (0.526–1.727) | 0.874 | ||||
| ASA (>2 vs. ≤2) | 0.711 (0.475–1.065) | 0.098 | ||||
| Diabetes | 0.668 (0.394–1.131) | 0.133 | ||||
| Metformin treatment | 0.557 (0.275–1.127) | 0.104 | ||||
| Treatment-naïve patient | 0.999 (0.681–1.465) | 0.994 | ||||
| Liver diseases | ||||||
| Cirrhosis | 1.129 (0.464–2.748) | 0.798 | ||||
| Child-Pugh (B vs. A) | 2.514 (0.668–9.459) | 0.173 | ||||
| Cause of liver disease (vs. alcohol) | ||||||
| Viral hepatitis B or C | 1.067 (0.605–1.88) | 0.823 | ||||
| Hemochromatosis | 0.955 (0.321–2.847) | 0.934 | ||||
| Others (including NASH) | 0.753 (0.351–1.618) | 0.468 | ||||
| Steatosis | 1.205 (0.76–1.91) | 0.428 | ||||
| AFP ≥ 100 vs < 100 ng/mL | 3.576 (1.224–10.441) | 0.02 | 3.027 (1.068–8.576) | 0.037 | 3.027 (1.032–8.876) | 0.044 |
| AFP (per unit) | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 0.396 | ||||
| Bilirubin | 0.993 (0.968–1.018) | 0.581 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.955 (0.914–0.998) | 0.04 | 0.966 (0.923–1.011) | 0.139 | 0.966 (0.896–1.042) | 0.37 |
| Prothrombin time | 0.996 (0.98–1.012) | 0.668 | ||||
| Platelet count (per 1000/mm3) | 1 (0.997–1.003) | 0.952 | ||||
| Creatinine | 0.992 (0.984–1.002) | 0.087 | ||||
| MELD (>9 vs. ≤9) | 0.756 (0.493–1.161) | 0.202 | ||||
| ALBI score 2 vs. 1 | 1.406 (0.909–2.175) | 0.125 | ||||
| HCC | ||||||
| Tumor size (per mm) | 1.053 (1.02–1.087) | 0.002 | 1.06 (1.025–1.097) | 0.001 | 1.06 (1.014–1.108) | 0.01 |
| Tumor size < 20 mm | 0.615 (0.388–0.975) | 0.039 | ||||
| Steatotic HCC | 0.714 (0.431–1.184) | 0.192 | ||||
| Dome tumor | 0.736 (0.502–1.082) | 0.12 | ||||
| Subcapsular | 0.991 (0.713–1.376) | 0.955 | ||||
| Near large vessel | 0.973 (0.613–1.544) | 0.908 | ||||
| Near surrounding organ | 1.22 (0.696–2.138) | 0.488 | ||||
| PTA | ||||||
| PTA modality: MWA vs RF | 1.363 (0.956–1.943) | 0.087 | ||||
| US vs CT guidance | 1.006 (0.712–1.423) | 0.973 | ||||
| Artificial pneumothorax | 1.301 (0.569–2.977) | 0.533 | ||||
| Tumor tagging | 0.864 (.616–1.212) | 0.399 | ||||
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Bootstrapping (200 Replications) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95%CI) | p Value | |
| Patients | ||||||
| Age | 1.012 (0.978–1.046) | 0.496 | ||||
| Sex female vs. male | 0.431 (0.150–1.238) | 0.118 | ||||
| ASA (>2 vs. ≤2) | 2.404 (1.248–4.628) | 0.009 | 4.273 (1.386–13.171) | 0.011 | 4.273 (1.097–16.646) | 0.036 |
| Diabetes | 1.563 (0.839–2.912) | 0.16 | ||||
| Metformin treatment | 1.092 (0.434–2.752) | 0.851 | ||||
| Treatment-naïve patient | 0.692 (0.361–1.326) | 0.267 | ||||
| Local recurrence | 1.016 (0.515–2.004) | 0.964 | ||||
| IDR | 1.97 (0.988–3.931) | 0.054 | ||||
| Liver diseases | ||||||
| Cirrhosis | 1.397 (0.312–6.258) | 0.662 | ||||
| Child-Pugh (B vs. A) | 1.003 (0.094–10.707) | 0.998 | ||||
| Cause of liver disease (vs. alcohol) | ||||||
| Viral hepatitis B or C | 0.994 (0.493–2.005) | 0.986 | ||||
| Hemochromatosis | 0.407 (0.062–2.671) | 0.349 | ||||
| Others (including NASH) | 0.537 (0.177–1.631) | 0.273 | ||||
| Steatosis | 1.255 (0.654–2.406) | 0.495 | ||||
| AFP ≥ 100 vs < 100 ng/mL | 4.435 (1.456–13.513) | 0.009 | ||||
| AFP (per unit) | 1.0012 (1.001–1.003) | <0.001 | 1.002 (1.001–1.003) | <0.001 | 1.002 (0.998–1.006) | 0.293 |
| Bilirubin | 1.039 (1.002–1.077) | 0.038 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.915 (0.86–0.978) | 0.009 | ||||
| Prothrombin time | 0.973 (0.949–0.998) | 0.031 | ||||
| Platelet count (per 1,000/mm3) | 0.999 (0.994–1.003) | 0.615 | ||||
| Creatinine | 1.007 (1.002–1.011) | 0.003 | ||||
| MELD (>9 vs. ≤9) | 2.361 (1.253–4.448) | 0.008 | 2.014 (0.772–5.255) | 0.153 | 2.014 (0.669–6.063) | 0.213 |
| ALBI score 2 vs. 1 | 1.675 (0.869–3.23) | 0.123 | ||||
| HCC | ||||||
| Tumor size (per mm) | 1.023 (0.975–1.074) | 0.35 | ||||
| Tumor size < 20 mm | 1.159 (0.498–2.697) | 0.731 | ||||
| Nb. of HCC (1 vs. >1) | 1.979 (1.003–3.903) | 0.049 | 3.939 (1.601–9.69) | 0.003 | 3.939 (1.198–12.947) | 0.024 |
| Steatotic HCC | 4.15x10-16 (2.44 × 10-16–7.07 × 10-16) | <0.001 | 1.81 × 10-16 (7.96 × 10-17–4.13 × 10-16) | <0.001 | 1.81x10-16 (5.47 × 10-20–6.02 × 10-13) | <0.001 |
| Dome tumor | 1.152 (0.575–2.307) | 0.691 | ||||
| Subcapsular | 0.813 (0.41–1.609) | 0.552 | ||||
| Near large vessel | 1.334 (0.683–2.605) | 0.399 | ||||
| Near surrounding organ | 0.404 (0.09–1.822) | 0.238 | ||||
| PTA | ||||||
| PTA modality: MWA vs RF | 1.19 (0.845–1.69) | 0.08 | ||||
| US vs CT guidance | 0.797 (0.418–1.517) | 0.489 | ||||
| Artificial pneumothorax | 1.301 (0.569–2.977) | 0.533 | ||||
| Tumor tagging | 0.774 (0.4–1.499) | 0.448 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermida, M.; Cassinotto, C.; Piron, L.; Aho-Glélé, S.; Guillot, C.; Schembri, V.; Allimant, C.; Jaber, S.; Pageaux, G.-P.; Assenat, E.; et al. Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020313
Hermida M, Cassinotto C, Piron L, Aho-Glélé S, Guillot C, Schembri V, Allimant C, Jaber S, Pageaux G-P, Assenat E, et al. Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020313
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermida, Margaux, Christophe Cassinotto, Lauranne Piron, Serge Aho-Glélé, Chloé Guillot, Valentina Schembri, Carole Allimant, Samir Jaber, Georges-Philippe Pageaux, Eric Assenat, and et al. 2020. "Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients" Cancers 12, no. 2: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020313
APA StyleHermida, M., Cassinotto, C., Piron, L., Aho-Glélé, S., Guillot, C., Schembri, V., Allimant, C., Jaber, S., Pageaux, G.-P., Assenat, E., & Guiu, B. (2020). Multimodal Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predictive Factors of Recurrence and Survival in Western Patients. Cancers, 12(2), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020313






