GAS2L1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pancreatic CTC Heterogeneity Leads to Distinct Clustering
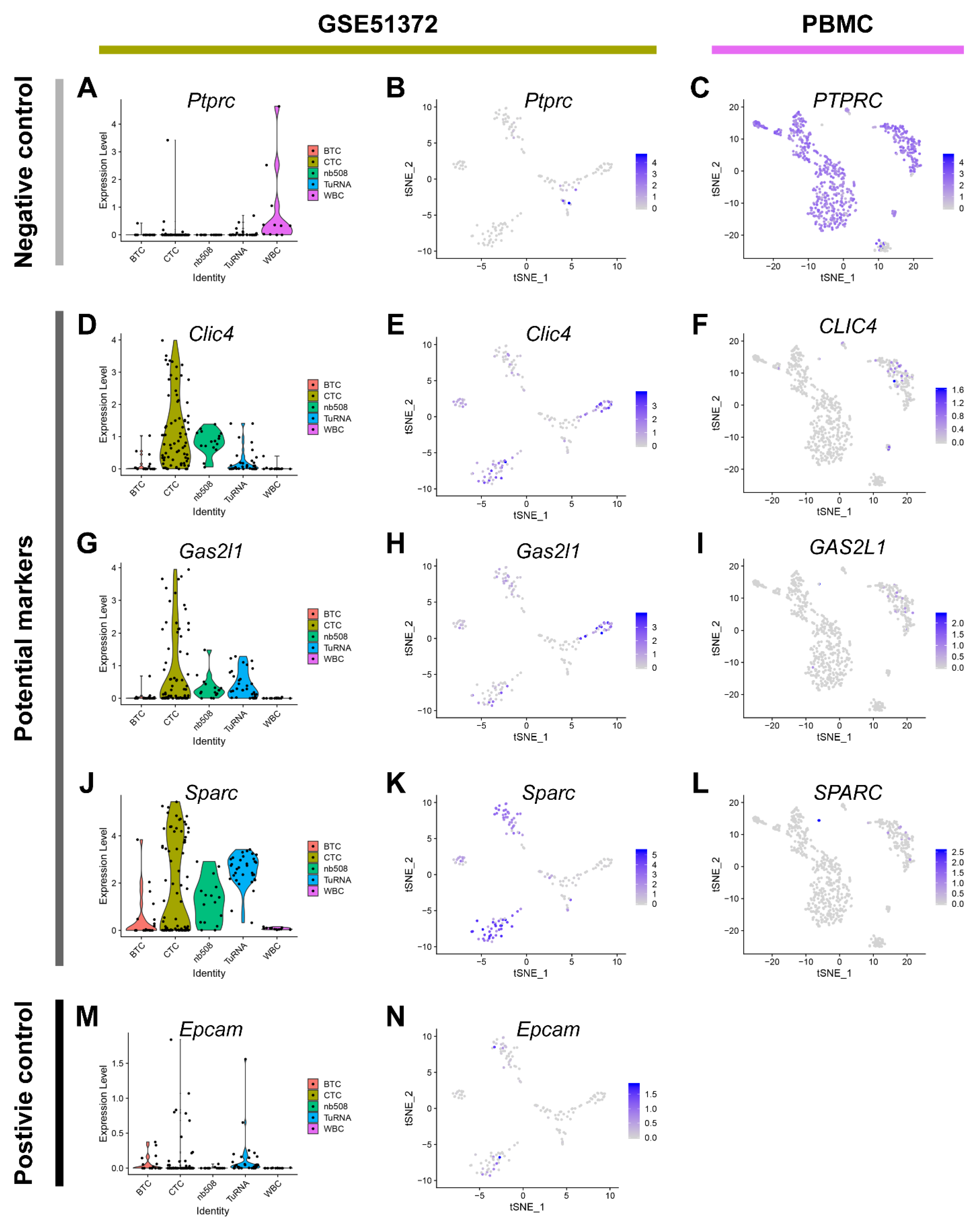
2.2. Clic4 and Gas2l1 Are Overexpressed in Pancreatic CTCs
2.3. Gas2l1 and Epcam Expression Identify Distinct CTCs Subpopulations and Synergize in CTC Identification
2.4. Intratumoral GAS2L1 Negatively Correlates with Recurrence-Free Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
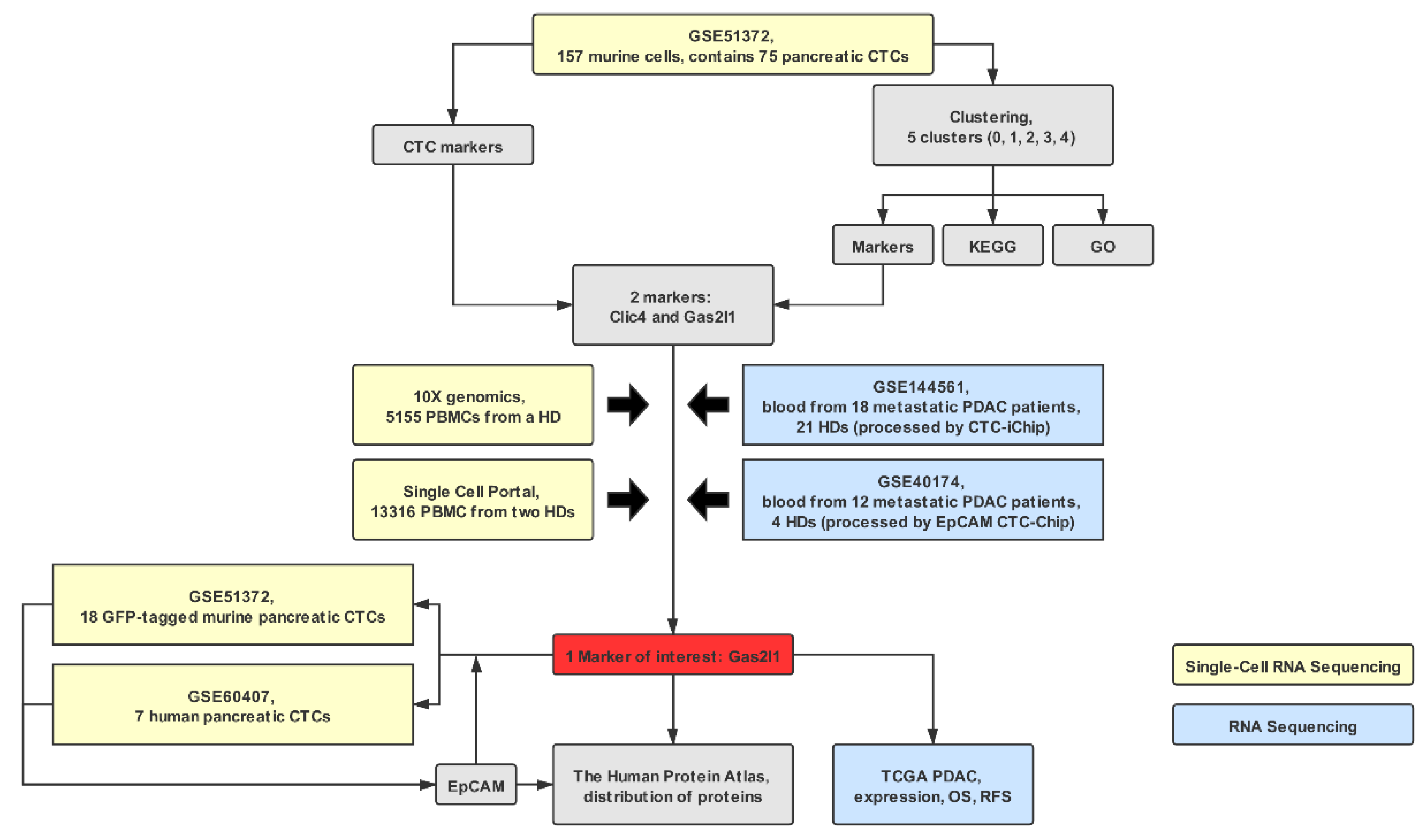
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Data Quality Check, Pre-Processing, and Clustering
4.3. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.-Y.; Kim, E.K.; Park, M.H.; Kim, H.M. Perspective on Cancer Therapeutics Utilizing Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Cancer therapy. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klotz, R.; Thomas, A.; Teng, T.; Han, S.M.; Iriondo, O.; Li, L.; Restrepo-Vassalli, S.; Wang, A.; Izadian, N.; MacKay, M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells Exhibit Metastatic Tropism and Reveal Brain Metastasis Drivers. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martini, V.; Timme-Bronsert, S.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Hoeppner, J.; Kulemann, B. Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Perspectives. Cancers 2019, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Zhuang, R.; Long, M.; Pavlovic, M.; Kang, Y.; Ilyas, A.; Asghar, W. Circulating tumor cell isolation, culture, and downstream molecular analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustberg, M.B.; Balasubramanian, P.; Miller, B.; Garcia-Villa, A.; Deighan, C.; Wu, Y.; Carothers, S.; Berger, M.; Ramaswamy, B.; Macrae, E.R.; et al. Heterogeneous atypical cell populations are present in blood of metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertolini, G.; D’Amico, L.; Moro, M.; Landoni, E.; Perego, P.; Miceli, R.; Gatti, L.; Andriani, F.; Wong, D.; Caserini, R.; et al. Microenvironment-Modulated Metastatic CD133+/CXCR4+/EpCAM- Lung Cancer-Initiating Cells Sustain Tumor Dissemination and Correlate with Poor Prognosis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3636–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, K.-C.; Sung, P.-L.; Chou, Y.-T.; Pan, C.-M.; Wang, P.-H.; Lee, O.K.-S.; Wu, C.-W. The role of EpCAM in tumor progression and the clinical prognosis of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 148, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudineh, M.; Aldridge, P.M.; Ahmed, S.; Green, B.J.; Kermanshah, L.; Nguyen, V.; Tu, C.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Nam, R.K.; Hansen, A.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of circulating tumour cell phenotypes using nanoparticle-mediated magnetic ranking. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestrin, M.; Salvianti, F.; Galardi, F.; De Luca, F.; Turner, N.; Malorni, L.; Pazzagli, M.; Di Leo, A.; Pinzani, P. Heterogeneity of PIK3CA mutational status at the single cell level in circulating tumor cells from metastatic breast cancer patients. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeinali, M.; Lee, M.; Nadhan, A.; Mathur, A.; Hedman, C.; Lin, E.; Harouaka, R.; Wicha, M.S.; Zhao, L.; Palanisamy, N.; et al. High-Throughput Label-Free Isolation of Heterogeneous Circulating Tumor Cells and CTC Clusters from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanduri, L.K.; Hissa, B.; Weitz, J.; Schölch, S.; Bork, U. The prognostic role of circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecot, C.V.; Bischoff, F.Z.; Mayer, J.A.; Wong, K.L.; Pham, T.; Bottsford-Miller, J.; Stone, R.L.; Lin, Y.G.; Jaladurgam, P.; Roh, J.W.; et al. A novel platform for detection of CK+ and CK− CTCs. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bäuerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.T.; Wittner, B.S.; Ligorio, M.; Vincent Jordan, N.; Shah, A.M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Brannigan, B.W.; Xega, K.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies extracellular matrix gene expression by pancreatic circulating tumor cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Stott, S.; Toner, M.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. Circulating tumor cells: Approaches to isolation and characterization. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachin, F.; Spuhler, P.; Martel-Foley, J.M.; Edd, J.F.; Barber, T.A.; Walsh, J.; Karabacak, M.; Pai, V.; Yu, M.; Smith, K.; et al. Monolithic Chip for High-throughput Blood Cell Depletion to Sort Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.U.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Taftaf, R.; Kawaguchi, M.; Chang, Y.-F.; Chen, W.; Entenberg, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gerratana, L.; Huang, S.; Patel, D.B.; et al. Homophilic CD44 Interactions Mediate Tumor Cell Aggregation and Polyclonal Metastasis in Patient-Derived Breast Cancer Models. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulemann, B.; Pitman, M.B.; Liss, A.S.; Valsangkar, N.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Hoeppner, J.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P. Circulating tumor cells found in patients with localized and advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Z. Clinical significance of pancreatic circulating tumor cells using combined negative enrichment and immunostaining-fluorescence in situ hybridization. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhim, A.D.; Thege, F.I.; Santana, S.M.; Lannin, T.B.; Saha, T.N.; Tsai, S.; Maggs, L.R.; Kochman, M.L.; Ginsberg, G.G.; Lieb, J.G.; et al. Detection of circulating pancreas epithelial cells in patients with pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Court, C.M.; Ankeny, J.S.; Sho, S.; Winograd, P.; Hou, S.; Song, M.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Girgis, M.D.; Graeber, T.G.; Agopian, V.G.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells Predict Occult Metastatic Disease and Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, A.D.; Mirek, E.T.; Aiello, N.M.; Maitra, A.; Bailey, J.M.; McAllister, F.; Reichert, M.; Beatty, G.L.; Rustgi, A.K.; Vonderheide, R.H.; et al. EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell 2012, 148, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, T.; Itoi, T.; Sofuni, A.; Itokawa, F.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tsuji, S.; Ishii, K.; Ikeuchi, N.; Tsuchida, A.; Kasuya, K.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with pancreatic cancer: A preliminary result. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2008, 15, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Huguet, F.; Louvet, C.; Mineur, L.; Bouché, O.; Chibaudel, B.; Artru, P.; Desseigne, F.; Bachet, J.B.; Mathiot, C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: The ancillary CirCe 07 study to the LAP 07 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2057–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, J.-Y.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Yang, C.-Y.; Tien, Y.-W.; Yang, S.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Liang, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; et al. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Microemboli as a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-S.; Park, S.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Norton, J.A.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Current status of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1623–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, E.; Zamarchi, R. Single-Cell Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells: How Far Have We Come in the -Omics Era? Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsavellas, G.; Huang, A.; McCullough, T.; Patel, H.; Araia, R.; Allen-Mersh, T.G. Flow cytometry correlates with RT-PCR for detection of spiked but not circulating colorectal cancer cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2002, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, F.K.C.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, K.; Grigoriev, I.; Hau, B.K.T.; Shen, Y.; Du, S.; Akhmanova, A.; Qi, R.Z. GAS2L1 Is a Centriole-Associated Protein Required for Centrosome Dynamics and Disjunction. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stroud, M.J.; Nazgiewicz, A.; McKenzie, E.A.; Wang, Y.; Kammerer, R.A.; Ballestrem, C. GAS2-like proteins mediate communication between microtubules and actin through interactions with end-binding proteins. J. Cell. Sci. 2014, 127, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van de Willige, D.; Hummel, J.J.; Alkemade, C.; Kahn, O.I.; Au, F.K.; Qi, R.Z.; Dogterom, M.; Koenderink, G.H.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Akhmanova, A. Cytolinker Gas2L1 regulates axon morphology through microtubule-modulated actin stabilization. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, R.; Piao, H.-Z. UCHL1 enhances the malignant development of glioma via targeting GAS2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Lee, C.-L.; Yang, S.-H.; Chien, C.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Yang, R.-N.; Chang, C.-C. Upregulation of the growth arrest-specific-2 in recurrent colorectal cancers, and its susceptibility to chemotherapy in a model cell system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Yang, S.-H.; Chien, C.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Huang, C.-J. Data on clinical significance of GAS2 in colorectal cancer cells. Data Brief 2016, 8, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, R.; Mok, M.T.S.; Kang, W.; Lau, S.S.K.; Yip, W.-K.; Chen, Y.; Lai, P.B.S.; Wong, V.W.S.; To, K.-F.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Truncated HBx-dependent silencing of GAS2 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through deregulation of cell cycle, senescence and p53-mediated apoptosis. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.-X.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Yang, D.-Y.; Seto, W.-K. Growth arrest-specific gene 2 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by intervention of cell cycle and p53-dependent apoptosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikenwalder, M.; Lorentzen, A. The role of polarisation of circulating tumour cells in cancer metastasis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3765–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luxton, G.W.G.; Gundersen, G.G. Orientation and Function of the Nuclear-Centrosomal Axis During Cell Migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Etienne-Manneville, S. Microtubules in cell migration. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 471–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killilea, A.N.; Csencsits, R.; Le, E.; Patel, A.M.; Kenny, S.J.; Xu, K.; Downing, K.H. Cytoskeletal Organization in Microtentacles. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 357, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, M.A.; Whipple, R.A.; Balzer, E.M.; Martin, S.S. Microtentacles tip the balance of cytoskeletal forces in circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7737–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lonsdorf, A.S.; Krämer, B.F.; Fahrleitner, M.; Schönberger, T.; Gnerlich, S.; Ring, S.; Gehring, S.; Schneider, S.W.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Engagement of αIIbβ3 (GPIIb/IIIa) with ανβ3 integrin mediates interaction of melanoma cells with platelets: A connection to hematogenous metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uppal, A.; Wightman, S.C.; Ganai, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; An, G. Investigation of the essential role of platelet-tumor cell interactions in metastasis progression using an agent-based model. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2014, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Gross, S.; O’Hara, S.M.; Smirnov, D.A.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Allard, W.J.; Bilbee, M.; Cheng, J.D.; Hoffman, J.P.; et al. Isolation and characterization of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2006, 6, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurr, N.K.; Durbin, H.; Sheer, D.; Parkar, M.; Bobrow, L.; Bodmer, W.F. Characterization and chromosomal assignment of a human cell surface antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody AUAI. Int. J. Cancer 1986, 38, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datar, R.H.; Zheng, A.; Cote, R.J. Significance of Studying Circulating Tumor Cells. In Circulating Tumor Cells; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, M.G.; Metcalf, R.L.; Carter, L.; Brady, G.; Blackhall, F.H.; Dive, C. Molecular analysis of circulating tumour cells—biology and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.G.; Chianese, D.; Doyle, G.V.; Miller, M.C.; Russell, T.; Sanders, R.A.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule in carcinoma cells present in blood and primary and metastatic tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinert, G.; Schölch, S.; Niemietz, T.; Iwata, N.; García, S.A.; Behrens, B.; Voigt, A.; Kloor, M.; Benner, A.; Bork, U.; et al. Immune escape and survival mechanisms in circulating tumor cells of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Hissa, B.; Győrffy, B.; Jann, J.-C.; Yang, C.; Reissfelder, C.; Schölch, S. Characterization of Stem-like Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolazzo, C.; Gradilone, A.; Loreni, F.; Raimondi, C.; Gazzaniga, P. EpCAMlow Circulating Tumor Cells: Gold in the Waste. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 1718920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schölch, S.; García, S.A.; Iwata, N.; Niemietz, T.; Betzler, A.M.; Nanduri1, L.K.; Bork, U.; Kahlert, C.; Thepkaysone, M.-L.; Swiersy, A.; et al. Circulating tumor cells exhibit stem cell characteristics in an orthotopic mouse model of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27232–27242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ridgway, L.D.; Wetzel, M.D.; Ngo, J.; Yin, W.; Kumar, D.; Goodman, J.C.; Groves, M.D.; Marchetti, D. The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 180ra48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 185–203.e13. [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ting, D.T.; Stott, S.L.; Wittner, B.S.; Ozsolak, F.; Paul, S.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Smas, M.E.; Winokur, D.; Gilman, A.J.; et al. RNA sequencing of pancreatic circulating tumour cells implicates WNT signaling in metastasis. Nature 2012, 487, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franses, J.W.; Philipp, J.; Missios, P.; Bhan, I.; Liu, A.; Yashaswini, C.; Tai, E.; Zhu, H.; Ligorio, M.; Nicholson, B.; et al. Pancreatic circulating tumor cell profiling identifies LIN28B as a metastasis driver and drug target. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Dataset–Sample Size | Gas2l1+ 1 | Epcam+ | Gas2l1+ and/or Epcam+ | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE51372-75 | 70 (93.3%) | 30 (40.0%) | 73 (97.3%) | 75 |
| GSE51372-18 | 15 (83.3%) | 2 (11.1%) | 15 (83.3%) | 18 |
| GSE60407-7 | 3 (42.9%) | 6 (85.7%) | 7 (100.0%) | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Kan, K.-J.; Grün, J.L.; Hissa, B.; Yang, C.; Győrffy, B.; Loges, S.; Reißfelder, C.; Schölch, S. GAS2L1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123774
Zhu L, Kan K-J, Grün JL, Hissa B, Yang C, Győrffy B, Loges S, Reißfelder C, Schölch S. GAS2L1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123774
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lei, Ke-Jia Kan, Johanna L. Grün, Barbara Hissa, Cui Yang, Balázs Győrffy, Sonja Loges, Christoph Reißfelder, and Sebastian Schölch. 2020. "GAS2L1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123774
APA StyleZhu, L., Kan, K.-J., Grün, J. L., Hissa, B., Yang, C., Győrffy, B., Loges, S., Reißfelder, C., & Schölch, S. (2020). GAS2L1 Is a Potential Biomarker of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 12(12), 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123774










