Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-Cell Lymphoma in Asia Frequently Shows SETD2 Alterations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Summary of Clinicopathological and Immunohistochemical Profiles
2.2. Targeted NGS
2.3. Immunohistochemistry of H3K36me3
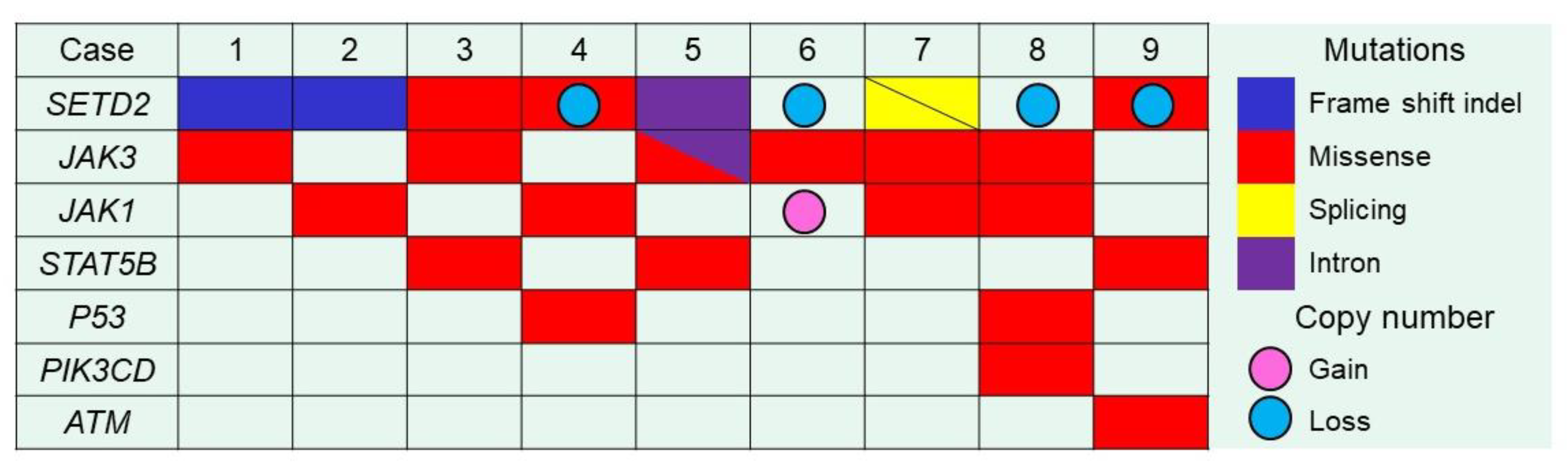
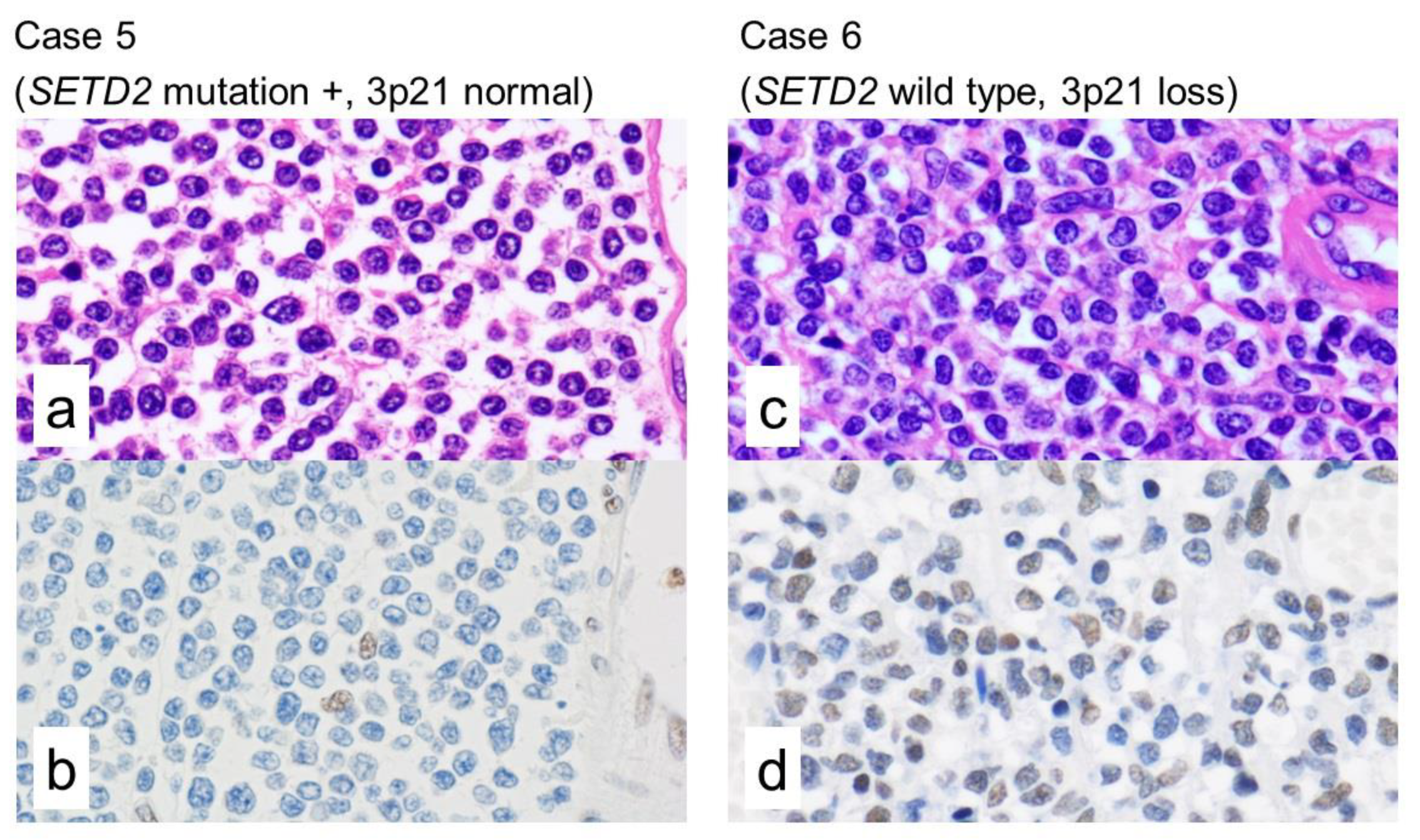
2.4. Integrated Analysis of Targeted NGS, a Whole-Genome Copy Number Microarray-Based Assay and Immunohistochemistry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cases and Materials
4.2. Targeted NGS
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Ethics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; et al. WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; IARC Press: Lyon, France; Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chott, A.; Haedicke, W.; Mosberger, I.; Födinger, M.; Winkler, K.; Mannhalter, C.; Müller-Hermelink, H.-K. Most CD56+ Intestinal Lymphomas Are CD8+CD5− T-Cell Lymphomas of Monomorphic Small to Medium Size Histology. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delabie, J.; Holte, H.; Vose, J.M.; Ullrich, F.; Jaffe, E.S.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Rimsza, L.; Harris, N.L.; Müller-Hermelink, K.; et al. Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma: Clinical and histological findings from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 2011, 118, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Biagi, F.; Gobbi, P.G.; McColl, K.E.L. How I treat enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Zinzani, P.L.; Govi, S.; Pileri, S.A. Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2011, 79, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.R. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: An Overview. Crit. Values 2009, 2, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.K.; Chan, A.C.; Cheuk, W.; Wan, S.K.; Lee, W.K.; Lui, Y.H.; Chan, W.K. Type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma: A distinct aggressive lymphoma with frequent γδ T-cell receptor expression. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, D.; Chen, J. Primary intestinal T-cell and NK-cell lymphomas: A clinicopathological and molecular study from China focused on type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma and primary intestinal NK-cell lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attygalle, A.; Cabeçadas, J.; Gaulard, P.; Jaffe, E.S.; De Jong, D.; Ko, Y.H.; Said, J.; Klapper, W. Peripheral T-cell and NK-cell lymphomas and their mimics; taking a step forward - report on the lymphoma workshop of the XVIth meeting of the European Association for Haematopathology and the Society for Hematopathology. Histopathology 2013, 64, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-Y.; Chuang, S.-S.; Tang, T.; Tan, L.; Ko, Y.-H.; Chuah, K.-L.; Ng, S.-B.; Chng, W.-J.; Gatter, K.; Loong, F.; et al. Type II EATL (epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma): A neoplasm of intra-epithelial T-cells with predominant CD8αα phenotype. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, S.-Y.; Ooi, A.-S.; Ang, M.-K.; Koh, M.; Wong, J.-C.; Dykema, K.; Ngeow, J.; Loong, S.L.E.; Gatter, K.C.; Tan, L.; et al. Nuclear expression of MATK is a novel marker of type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberti, A.; Dobay, M.P.; Bisig, B.; Vallois, D.; Boéchat, C.; Lanitis, E.; Bouchindhomme, B.; Parrens, M.-C.; Bossard, C.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; et al. Type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma features a unique genomic profile with highly recurrent SETD2 alterations. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeeuw, R.J.; Zettl, A.; Klinker, E.; Haralambieva, E.; Trottier, M.; Chari, R.; Ge, Y.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Chott, A.; Müller-Hermelink, H.; et al. Whole-Genome Analysis and HLA Genotyping of Enteropathy-Type T-Cell Lymphoma Reveals 2 Distinct Lymphoma Subtypes. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.H.; Karnan, S.; Kim, K.M.; Park, C.K.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, W.K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, W.Y.; et al. Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma—A clinicopathologic and array comparative genomic hybridization study. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Kojima, M.; Ando, K.; Takasaki, H.; Sakai, R.; Takata, K.; Yoshino, T.; Bea, S.; et al. Genomic and immunohistochemical profiles of enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma in Japan. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 10, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nairismägi, M.-L.; Tan, J.; Lim, J.Q.; Nagarajan, S.; Ng, C.C.Y.; Rajasegaran, V.; Huang, D.; Lim, W.K.; Laurensia, Y.; Wijaya, G.C.; et al. JAK-STAT and G-protein-coupled receptor signaling pathways are frequently altered in epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moffitt, A.B.; Ondrejka, S.L.; McKinney, M.; Rempel, R.E.; Goodlad, J.R.; Teh, C.H.; Leppa, S.; Mannisto, S.; Kovanen, P.E.; Tse, E.; et al. Enteropathy-associated T cell lymphoma subtypes are characterized by loss of function of SETD2. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Nakamura, N. Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma with T-cell receptor (TCR) of silent phenotype shows rearrangement of TCRβ or TCRγ gene. Pathol. Int. 2018, 69, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küçük, C.; Jiang, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chan, J.K.C.; Xiao, W.; Lack, N.; Alkan, C.; Williams, J.; Avery, K.N.; et al. Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from γδ-T or NK cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edmunds, J.W.; Mahadevan, L.C.; Clayton, A.L. Dynamic histone H3 methylation during gene induction: HYPB/Setd2 mediates all H3K36 trimethylation. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, I.Y.; Powell, R.T.; Tripathi, D.N.; Dere, R.; Ho, T.H.; Blasius, T.L.; Chiang, Y.C.; Davis, I.J.; Fahey, C.C.; Hacker, K.E.; et al. Dual chromatin and cytoskeletal remodeling by SETD2. Cell 2016, 166, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Mao, G.; Tong, D.; Huang, J.; Gu, L.; Yang, W.; Li, G.M. The histone mark H3K36me3 regulates human DNA mismatch repair through its interaction with MutSα. Cell 2013, 153, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfister, S.X.; Ahrabi, S.; Zalmas, L.P.; Sarkar, S.; Aymard, F.; Bachrati, C.Z.; Helleday, T.; Legube, G.; La Thangue, N.B.; Porter, A.C.; et al. SETD2-dependent histone H3K36 trimethylation is required for homologous recombination repair and genome stability. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skucha, A.; Ebner, J.; Grebien, F. Roles of SETD2 in leukemia-transcription, DNA-damage, and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mar, B.G.; Bullinger, L.B.; McLean, K.M.; Grauman, P.V.; Harris, M.H.; Stevenson, K.; Neuberg, N.S.; Sinha, A.U.; Sallan, S.E.; Silverman, L.B.; et al. Mutations in epigenetic regulators including SETD2 are gained during relapse in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viaene, A.N.; Santi, M.; Rosenbaum, J.; Li, M.M.; Surrey, L.F.; Nasrallah, M.L.P. SETD2 mutations in primary central nervous system tumors. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D.M.; Venancio, O.S.; Buza, E.L.; Tobias, J.W.; Deshpande, C.; Gudiel, A.A.; Kim-Kiselak, C.; Cicchini, M.; Yates, T.J.; Feldser, D.M. Systematic In Vivo Inactivation of Chromatin-Regulating Enzymes Identifies Setd2 as a Potent Tumor Suppressor in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalgliesh, G.L.; Furge, K.; Greenman, C.; Chen, L.; Bignell, G.; Butler, A.; Davies, H.; Edkins, S.; Hardy, C.; Latimer, C.; et al. Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes. Nature 2010, 463, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinney, M.; Moffitt, A.B.; Gaulard, P.; Travert, M.; De Leval, L.; Nicolae, A.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pittaluga, S.; Xi, L.; et al. The Genetic Basis of Hepatosplenic T-cell Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; He, F.; Zeng, H.; Ling, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wei, W.; Pang, Y.; Cheng, H.; et al. Identification of functional cooperative mutations of SETD2 in human acute leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontebasso, A.M.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Liu, X.-Y.; Sturm, D.; Korshunov, A.; Jones, D.T.W.; Witt, H.; Kool, M.; Albrecht, S.; et al. Mutations in SETD2 and genes affecting histone H3K36 methylation target hemispheric high-grade gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.K.; McPherson, J.R.; Tay, S.T.; Das, K.; Tan, I.B.; Ng, C.C.Y.; Chia, N.-Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Myint, S.S.; Hu, L.; et al. SETD2histone modifier loss in aggressive GI stromal tumours. Gut 2015, 65, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.H.; Park, I.Y.; Zhao, H.; Tong, P.; Champion, M.; Yan, H.; Monzon, F.A.; Hoang, A.; Tamboli, P.; Parker, A.S.; et al. High-resolution profiling of histone h3 lysine 36 trimethylation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoaib, M.; Sørensen, C.S. Epigenetic Deficiencies and Replicative Stress: Driving Cancer Cells to an Early Grave. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiel, M.J.; Velusamy, T.; Rolland, D.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Chung, F.; Bailey, N.G.; Schrader, A.; Li, B.; Li, J.Z.; Ozel, A.B.; et al. Integrated genomic sequencing reveals mutational landscape of T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crescenzo, R.; Abate, F.; Lasorsa, E.; Tabbo’, F.; Gaudiano, M.; Chiesa, N.; Di Giacomo, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Barbarossa, L.; Ercole, E.; et al. Convergent Mutations and Kinase Fusions Lead to Oncogenic STAT3 Activation in Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koskela, H.L.; Eldfors, S.; Ellonen, P.; van Adrichem, A.J.; Kuusanmäki, H.; Andersson, E.I.; Lagström, S.; Clemente, M.J.; Olson, T.; Jalkanen, S.E.; et al. Somatic STAT3 mutations in large granular lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerez, A.; Clemente, M.J.; Makishima, H.; Koskela, H.; Leblanc, F.; Ng, K.P.; Olson, T.; Przychodzen, B.; Afable, M.; Gomez-Segui, I.; et al. STAT3 mutations unify the pathogenesis of chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells and T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 3048–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT Pathway: Impact on Human Disease and Therapeutic Intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meresse, B.; Korneychuk, N.; Malamut, G.; Cerf-Bensussan, N. Interleukin-15, a Master Piece in the Immunological Jigsaw of Celiac Disease. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, S.; Hara, T.; Liang, B.; Wagatsuma, K.; Zuklys, S.; Holländer, G.A.; Nakase, H.; Chiba, T.; Tani-Ichi, S.; Ikuta, K.; et al. IL-7 Produced by Thymic Epithelial Cells Plays a Major Role in the Development of Thymocytes and TCRγδ+ Intraepithelial Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6173–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Nam, S.J.; Ahn, Y.-O.; Keam, B.; Park, H.H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Novel JAK3-Activating Mutations in Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchekioua, A.; Scourzic, L.; De Wever, O.; Zhang, Y.; Cervera, P.; Aline-Fardin, A.; Mercher, T.; Gaulard, P.; Nyga, R.; Jeziorowska, D.; et al. JAK3 deregulation by activating mutations confers invasive growth advantage in extranodal nasal-type natural killer cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, G.C.; Tan, S.Y.; Tang, T.; Poon, S.L.; Allen, G.E.; Tan, L.; Chong, S.C.; Ong, W.S.; Tay, K.; Tao, M.; et al. Janus Kinase 3—Activating Mutations Identified in Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGirt, L.Y.; Jia, P.; Baerenwald, D.A.; Duszynski, R.J.; Dahlman, K.B.; Zic, J.A.; Zwerner, J.P.; Hucks, D.; Dave, U.P.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing reveals oncogenic mutations in mycosis fungoides. Blood 2015, 126, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letourneau, A.; Maerevoet, M.; Milowich, D.; DeWind, R.; Bisig, B.; Missiaglia, E.; De Leval, L. Dual JAK1 and STAT3 mutations in a breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Case | Age | Sex | Celiac Disease | Location | Treatment | Prognosis (Survival Time) | TCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 66 | Female | No | Small and Large intestine | Operation | Unknown | γδ |
| 2 | 64 | Male | No | Small intestine | Operation, DeVIC | Dead (Unknown) | γδ |
| 3 | 58 | Male | No | Small intestine | Operation | (Unknown) | γδ |
| 4 | 74 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation, CHOP | Unknown | γδ |
| 5 | 49 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation, CHO, GEM | Dead (6 months) | γδ |
| 6 | 70 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation | Alive (4 months) | γδ |
| 7 | 62 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation, CHOP | Dead (7 months) | γδ |
| 8 | 61 | Female | No | Large intestine | Operation, DeVIC | Alive (50 months) | γδ |
| 9 | 81 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation, THP-COP, CDE-11 | Dead (8 months) | αβ |
| 10 | 64 | Female | No | Small intestine | Operation, EPOCH | Unknown | γδ |
| 11 | 75 | Male | No | Small intestine | Operation, CHO | Dead (3 months) | αβ |
| Case | Gene | Mutation Type | CNV | Exon | AA Changes | SIFT Prediction | H3K36me3 IHC | COSMIC ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SETD2 | Inflame indel | NA | exon 20 | p.Phe2481-Gln2484del | Probably damaging | Negative | None |
| JAK3 | Missense | NA | exon 13 | p.Ala573Val | Damaging | - | COSM34215(17) | |
| 2 | SETD2 | Frameshift indel | Normal | exon 20 | p.Tyr2489Trpfs*6 | Probably damaging | Negative | None |
| JAK1 | Missense | Normal | exon 22 | p.Lys1026Glu | Probably damaging | - | None | |
| 3 | SETD2 | Missense | Normal | exon 7 | p.Cys1631Phe | Incertain | Negative | None |
| JAK3 | Missense | Normal | exon 13 | p.Ala573Val | Damaging | - | COSM34215(17) | |
| STAT5B | Missense | Normal | exon 18 | p.Val712Glu | Damaging | - | COSM5414165(1) | |
| 4 | SETD2 | Missense | Loss | exon 20 | p.Leu2486Arg | Probably damaging | Negative | None |
| JAK1 | Missense | Normal | exon 15 | p.Ser703Ile | Damaging | - | COSM305942(10) | |
| TP53 | Missense | Normal | exon 7 | p.Gly244Asp | Damaging | - | COSM10735(43) | |
| 5 | SETD2 | Substitution (intron) | Normal | exon 5 | - | Probably damaging | Negative | None |
| JAK3 | Splicing | Normal | exon 20 | - | Incertain | - | None | |
| Missense | exon 13 | p.Ala573Val | Damaging | - | None | |||
| STAT5B | Missense | Normal | exon 16 | p.Asn642His | Damaging | - | COSM1716590(29) | |
| 6 | SETD2 | WT | Loss | - | - | - | Positive | None |
| JAK3 | Missense | Normal | exon 11 | p.Met511Ile | Probably damaging | - | COSM51374(29) | |
| 7 | SETD2 | Splicing | NA | exon 1 | - | Probably damaging | Negative | None |
| Splicing | exon 6 | - | Probably damaging | None | ||||
| JAK1 | Missense | NA | exon 17 | p.Leu783Phe | Probably damaging | - | COSM41758(5) | |
| JAK3 | Missense | NA | exon 15 | p.Val674Ala | Probably damaging | - | COSM327317(7) | |
| 8 | SETD2 | WT | Loss | - | - | - | Negative | None |
| JAK1 | Missense | Normal | exon 15 | p.Ser703Cys | Incertain | - | None | |
| JAK3 | Missense | Normal | exon 15 | p.Val674Ala | Probably damaging | - | COSM327317(7) | |
| PIK3CD | Missense | Normal | exon 8 | p.Met339Lys | Incertain | - | None | |
| TP53 | Missense | Normal | exon 10 | p.Arg337His | Probably damaging | - | None | |
| 9 | SETD2 | Missense | Loss | exon 11 | p.Ser1769Tyr | Incertain | Negative | None |
| STAT5B | Missense | Normal | exon 16 | p.Asn642His | Damaging | - | COSM1716590(29) | |
| ATM | Missense | Normal | exon 19 | p.Pro960His | Incertain | - | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomita, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Sakai, R.; Takata, K.; Yoshino, T.; Bea, S.; Campo, E.; Missiaglia, E.; Bouilly, J.; et al. Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-Cell Lymphoma in Asia Frequently Shows SETD2 Alterations. Cancers 2020, 12, 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123539
Tomita S, Kikuti YY, Carreras J, Sakai R, Takata K, Yoshino T, Bea S, Campo E, Missiaglia E, Bouilly J, et al. Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-Cell Lymphoma in Asia Frequently Shows SETD2 Alterations. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123539
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomita, Sakura, Yara Yukie Kikuti, Joaquim Carreras, Rika Sakai, Katsuyoshi Takata, Tadashi Yoshino, Silvia Bea, Elias Campo, Edoardo Missiaglia, Justine Bouilly, and et al. 2020. "Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-Cell Lymphoma in Asia Frequently Shows SETD2 Alterations" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123539
APA StyleTomita, S., Kikuti, Y. Y., Carreras, J., Sakai, R., Takata, K., Yoshino, T., Bea, S., Campo, E., Missiaglia, E., Bouilly, J., Letourneau, A., de Leval, L., & Nakamura, N. (2020). Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-Cell Lymphoma in Asia Frequently Shows SETD2 Alterations. Cancers, 12(12), 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123539







