Is the Proteome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles a Marker of Advanced Lung Cancer?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
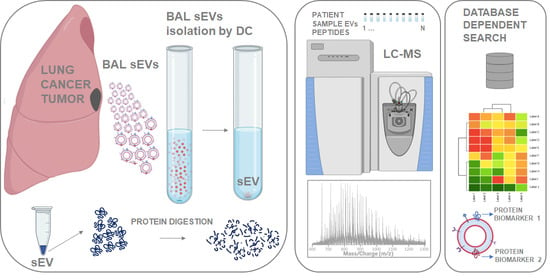
2.1. Outline of Study
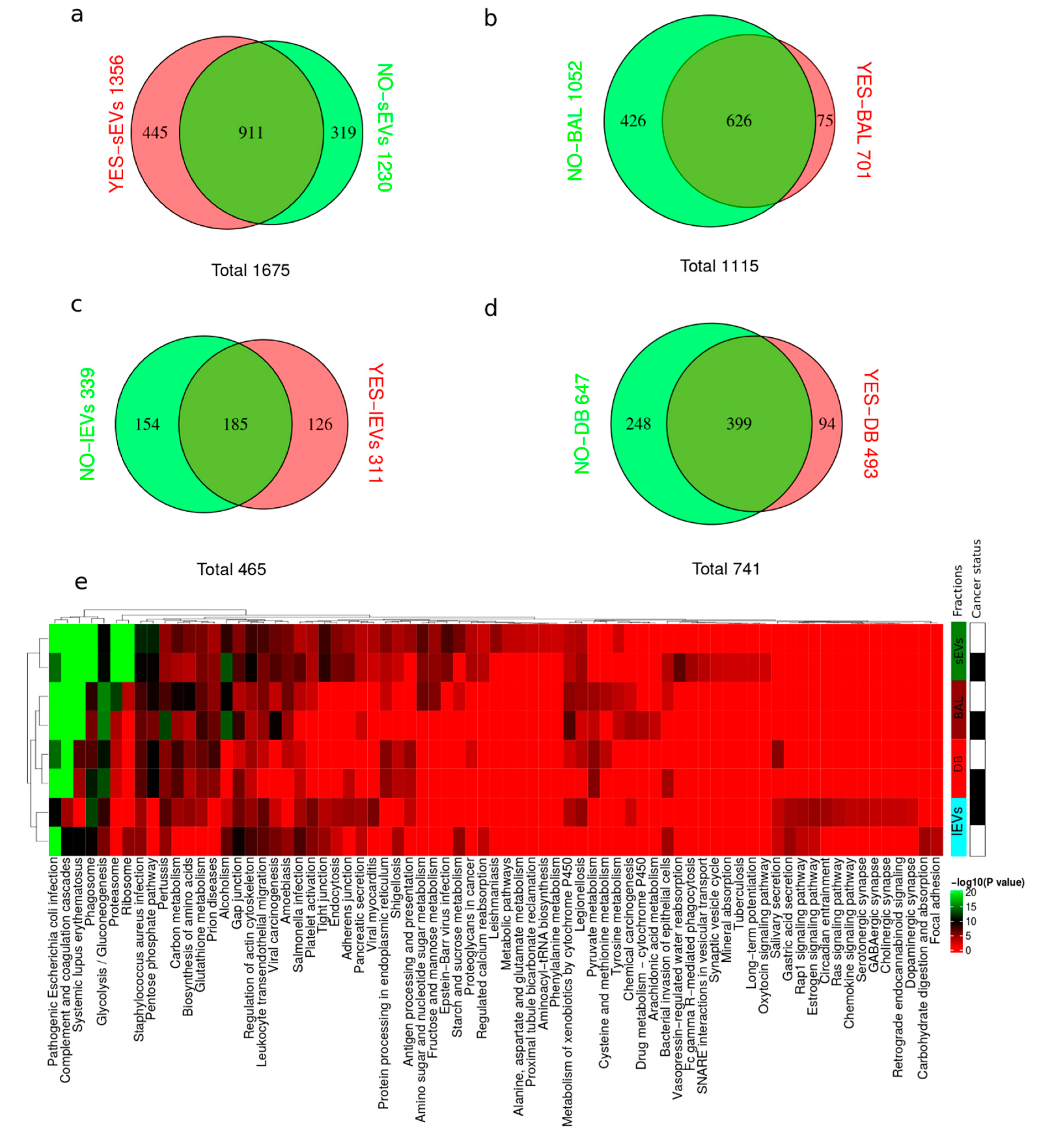
2.2. Proteome Content of lEVs, sEVs, Acellular BAL, and EV Depleted BAL (DB)
2.3. Baseline Characteristic of Clinical Samples for the Enrichment of sEVs
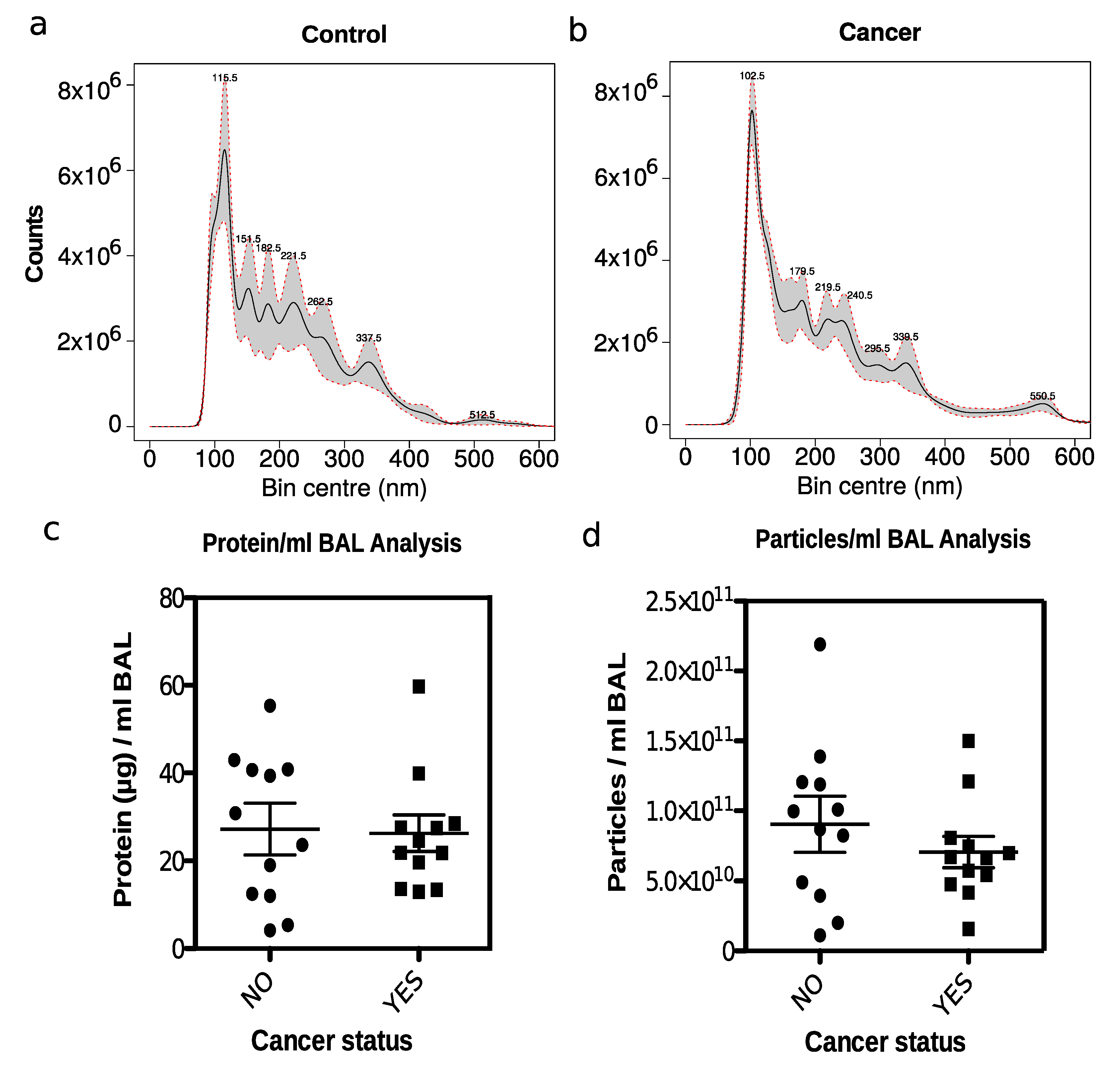
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis of Isolated EVs
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Overall Proteome of EVs
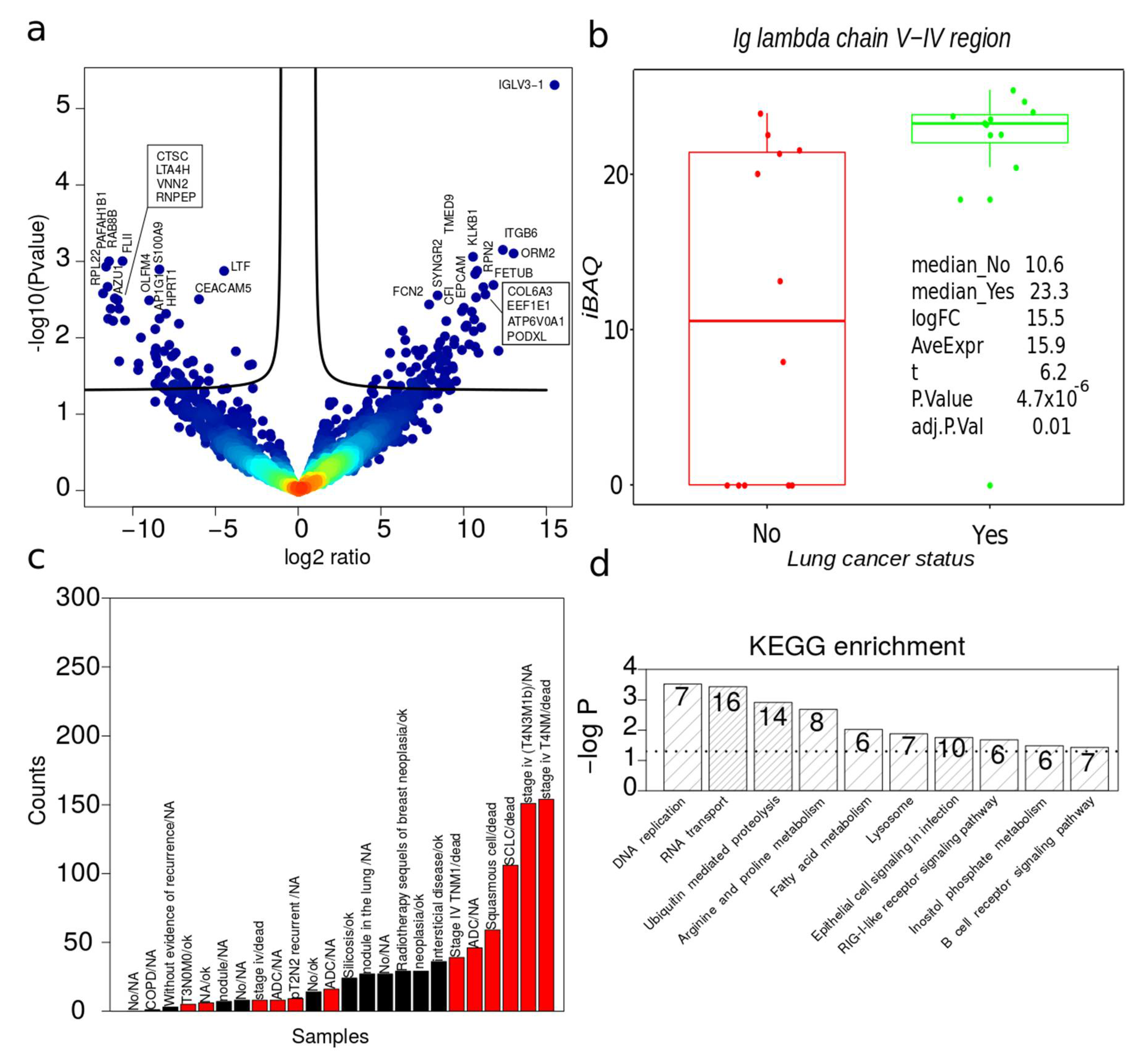
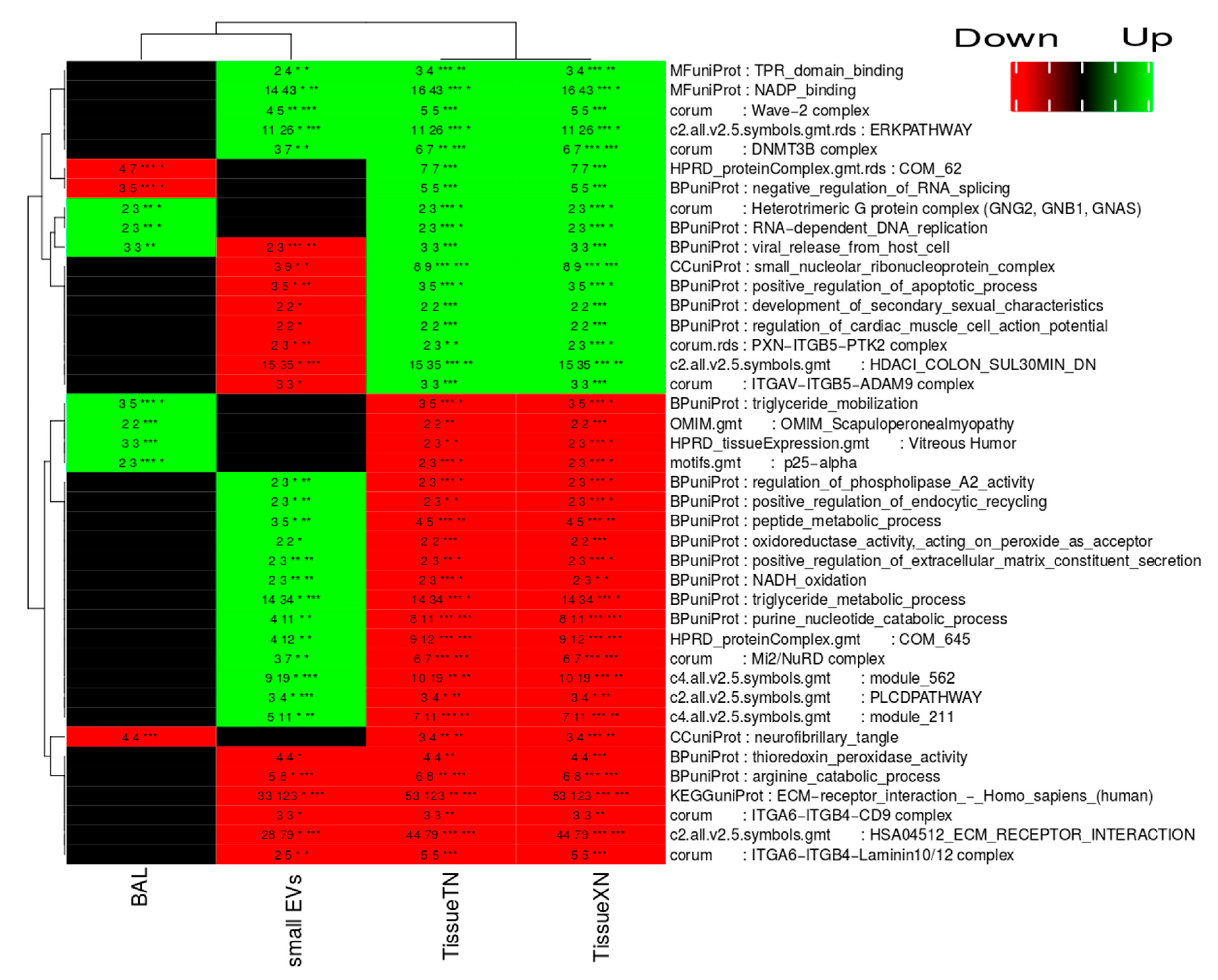
2.6. Dysregulated Proteins in BAL Exosomes
2.7. Complete Functional Regulation
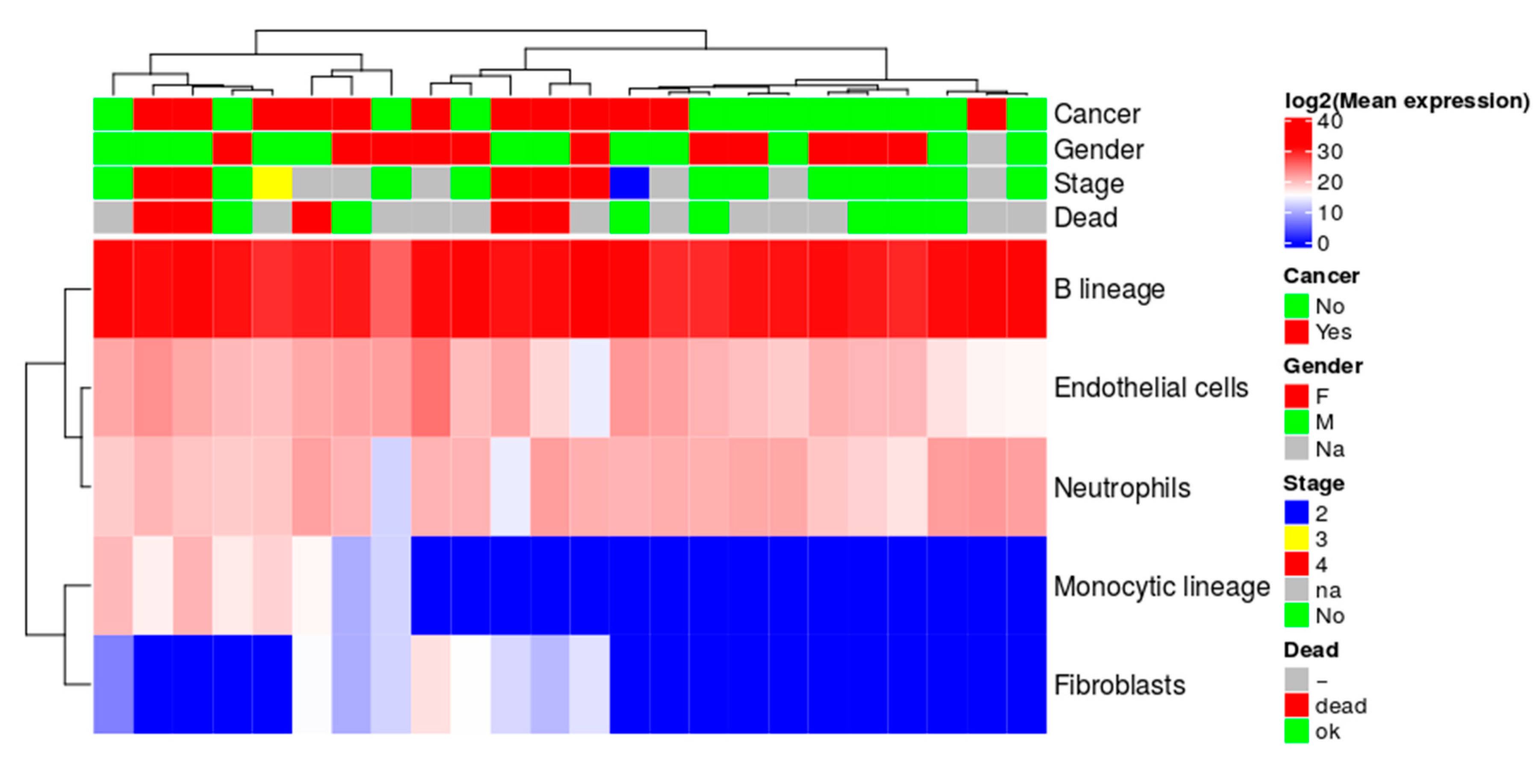
2.8. Quantitative Evaluation of Immune Cell Lineage Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Samples
4.2. BAL Processing
4.3. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Acellular BAL
4.4. Protein Measurements
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. Peptide Sample Preparation
4.8. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.9. Database Search
4.10. Functional Analysis of Identified Proteins in BAL Fractions
4.11. Quantitative Analysis
4.12. Complete Functional Regulation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fidler, M.M.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. The global cancer burden and human development: A review. Scand. J. Public Health 2018, 46, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.C.; Raben, D.; Formenti, S.C. The Integration of Radiotherapy with Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5792–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthiesen, R. MS-Based Biomarker Discovery in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Lung Cancer. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2020, 14, e1900077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Groot, M.; Pinilla-Vera, M.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; Jin, Y. Identification of miRNA-rich vesicles in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: Insights into the function and heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 294, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venosa, A.; Katzen, J.; Tomer, Y.; Kopp, M.; Jamil, S.; Russo, S.J.; Mulugeta, S.; Beers, M.F. Epithelial Expression of an Interstitial Lung Disease-Associated Mutation in Surfactant Protein-C Modulates Recruitment and Activation of Key Myeloid Cell Populations in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Q.; Lv, S.; Hu, X.; Lou, J. DNA Methylation Analysis of the SHOX2 and RASSF1A Panel in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3585–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, S.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Quinn, K.; Zhang, X.; Petrache, I.; Bowler, R.P.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N. A prototypic small molecule database for bronchoalveolar lavage-based metabolomics. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Cavadas, B.; Ferreira, J.C.; Marques, P.I.; Monteiro, C.; Sucena, M.; Sousa, C.; Vaz Rodrigues, L.; Teixeira, G.; Pinto, P.; et al. Profiling of lung microbiota discloses differences in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumeraci, T.; Schmidt, B.; Wolf, T.; Zapatka, M.; Pich, A.; Brors, B.; Eils, R.; Fleischhacker, M.; Schlegelberger, B.; von Neuhoff, N. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of lung cancer patients: Mapping the uncharted waters using proteomics technology. Lung Cancer 2011, 72, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, M.D.; Nogal, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Melendez, R.; Salinas, A.; Gonzalez De la Pena, M.; Martin-Juan, J.; Corral, J.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Carnero, A.; et al. Identification of proteomic signatures associated with lung cancer and COPD. J. Proteom. 2013, 89, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Cuco, C.M.; Lavareda, C.; Miguel, F.; Ventura, M.; Almeida, S.; Pinto, P.; de Abreu, T.T.; Rodrigues, L.V.; Seixas, S.; et al. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Proteomics in Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; McDonald, C.F.; Collins, A.L.; Darby, I.A.; Pouniotis, D.S. Quantitative proteomics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2015, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ortea, I.; Rodriguez-Ariza, A.; Chicano-Galvez, E.; Arenas Vacas, M.S.; Jurado Gamez, B. Discovery of potential protein biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by SWATH MS data-independent acquisition and targeted data extraction. J. Proteom. 2016, 138, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.Y.; Choi, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.S. In-Depth Proteomic Analysis of Human Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid toward the Biomarker Discovery for Lung Cancers. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, e1900028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Baeta, H.; Silva, B.C.; Moraes, M.C.S.; Bodo, C.; Beck, H.C.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Saraswat, M.; Pandey, A.; Matthiesen, R. Extra-cellular vesicles carry proteome of cancer hallmarks. Front. Biosci. 2020, 25, 398–436. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.; To, C.; Zhu, C.Q.; Tong, J.; Pham, N.A.; Taylor, P.; Ignatchenko, V.; Ignatchenko, A.; Zhang, W.; et al. Integrated omic analysis of lung cancer reveals metabolism proteome signatures with prognostic impact. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Rider, M.A.; Bundy, J.L.; Liu, X.; Singh, R.K.; Meckes, D.G., Jr. Proteomic profiling of NCI-60 extracellular vesicles uncovers common protein cargo and cancer type-specific biomarkers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86999–87015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Kim, H.S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K.E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle and Particle Biomarkers Define Multiple Human Cancers. Cell 2020, 182, 1044–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Molina, H.; Matthiesen, R. New insights into functional regulation in MS-based drug profiling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, K.; Albares, L.; Wendt, C.; Hubel, A. Isolation of fibroblasts and epithelial cells in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). Exp. Lung Res. 2013, 39, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Lacroix, L.; Buttard, B.; Elarouci, N.; Petitprez, F.; Selves, J.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, J.; Clayton, A. How pure are your vesicles? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, A.W.; Ramarathinam, S.H.; Ternette, N. Mass spectrometry-based identification of MHC-bound peptides for immunopeptidomics. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani-Sternberg, M.; Barnea, E.; Beer, I.; Avivi, I.; Katz, T.; Admon, A. Soluble plasma HLA peptidome as a potential source for cancer biomarkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18769–18776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetkovic, A.; Jang, S.C.; Konecna, B.; Hoog, J.L.; Sihlbom, C.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J. Detailed Analysis of Protein Topology of Extracellular Vesicles-Evidence of Unconventional Membrane Protein Orientation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.Y.; Hsin, I.L.; Yang, T.Y.; Sung, W.W.; Chi, J.Y.; Chang, J.T.; Ko, J.L.; Sheu, G.T. The ERK-ZEB1 pathway mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pemetrexed resistant lung cancer cells with suppression by vinca alkaloids. Oncogene 2017, 36, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Jan, Y.H.; Yang, C.J.; Huang, M.S.; Hsiao, M. Squalene synthase promotes the invasion of lung cancer cells via the osteopontin/ERK pathway. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.G.; Del Rio, I.B.; Sari, S.; Sekerim, A.; Young, L.C.; Hartig, N.; Areso Zubiaur, I.; El-Bahrawy, M.A.; Hynds, R.E.; Lei, W.; et al. SHOC2 phosphatase-dependent RAF dimerization mediates resistance to MEK inhibition in RAS-mutant cancers. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maacha, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Jimenez, L.; Raza, A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S.; Grivel, J.C. Extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication: Roles in the tumor microenvironment and anti-cancer drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Chapuy, B.; Vogel, D.; Wenzel, D.; Oppermann, M.; Lahmann, M.; Weinhage, T.; Menck, K.; Hupfeld, T.; Koch, R.; et al. Exosomal evasion of humoral immunotherapy in aggressive B-cell lymphoma modulated by ATP-binding cassette transporter A3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15336–15341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostler, K.R.; Davis, E.M.; Payne, S.L.; Gosalia, B.B.; Exposito-Cespedes, J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Godley, L.A. Cancer cells express aberrant DNMT3B transcripts encoding truncated proteins. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; He, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Mo, F.; Yang, S.; Han, J.; Wei, X. Targeting epigenetic regulators for cancer therapy: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.; Rivenbark, A.G.; Coleman, W.B. Enhancement of chemotherapeutic efficacy in hypermethylator breast cancer cells through targeted and pharmacologic inhibition of DNMT3b. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 131, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Guo, E.; Ming, J.; Sun, W.; Nie, X.; Sun, L.; Peng, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; et al. Radiation-Induced DNMT3B Promotes Radioresistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Methylation of p53 and p21. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 17, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Sun, H.; Xu, C.; Chen, T.; Zou, B.; Jiang, P.; Du, W. Evidence for a direct cross-talk between malic enzyme and the pentose phosphate pathway via structural interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17113–17120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, H.; Pietila, M.; Ivaska, J. The complexity of integrins in cancer and new scopes for therapeutic targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala-Kulawik, J.; Guzman, J.; Costabel, U. Immune cells in bronchoalveolar lavage in peripheral lung cancer—Analysis of 140 cases. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2003, 70, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, T.C.; Ebner, P.J.; Moore, B.L.; Squalls, O.G.; Waugh, K.A.; Eruslanov, E.B.; Singhal, S.; Mitchell, J.D.; Franklin, W.A.; Merrick, D.T.; et al. Antigen-Presenting Intratumoral B Cells Affect CD4(+) TIL Phenotypes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmi, Y.; Spitzer, M.H.; Linde, I.L.; Burt, B.M.; Prestwood, T.R.; Perlman, N.; Davidson, M.G.; Kenkel, J.A.; Segal, E.; Pusapati, G.V.; et al. Allogeneic IgG combined with dendritic cell stimuli induce antitumour T-cell immunity. Nature 2015, 521, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMahon, H.; Austin, J.H.; Gamsu, G.; Herold, C.J.; Jett, J.R.; Naidich, D.P.; Patz, E.F., Jr.; Swensen, S.J. Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: A statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2005, 237, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Ribeiro, H.; Voabil, P.; Penque, D.; Jensen, O.N.; Molina, H.; Matthiesen, R. Global mass spectrometry and transcriptomics array based drug profiling provides novel insight into glucosamine induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2014, 13, 3294–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiesen, R.; Prieto, G.; Amorim, A.; Aloria, K.; Fullaondo, A.; Carvalho, A.S.; Arizmendi, J.M. SIR: Deterministic protein inference from peptides assigned to MS data. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4176–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, M.; Matthiesen, R. Annotation-Modules: A tool for finding significant combinations of multisource annotations for gene lists. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology Resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.; Harsha, H.C.; Pandey, A.; Prasad, T.S. Human Protein Reference Database and Human Proteinpedia as resources for phosphoproteome analysis. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruepp, A.; Brauner, B.; Dunger-Kaltenbach, I.; Frishman, G.; Montrone, C.; Stransky, M.; Waegele, B.; Schmidt, T.; Doudieu, O.N.; Stumpflen, V.; et al. CORUM: The comprehensive resource of mammalian protein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D646–D650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NO (N = 12) | YES (N = 12) | Total (N = 24) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.355 | |||
| <55 | 4 (33.3%) | 1 (8.3%) | 5 (12.5%) | |
| >55 | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (8.3%) | 2 (8.3%) | |
| NA | 7 (58.3%) | 10 (83.3%) | 17 (70.8%) | |
| Smoking History | 0.370 | |||
| Current smoker | 4 (33.3%) | 3 (25.0%) | 7 (29.2%) | |
| Former smoker | 2 (16.7%) | 6 (50.0%) | 8 (33.3%) | |
| Nonsmoker | 2 (16.7%) | 1 (8.3%) | 3 (12.5%) | |
| Unknown | 4 (33.3%) | 2 (16.7%) | 6 (25.0%) | |
| Gender | 0.100 | |||
| NA | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| F | 8 (66.7%) | 3 (25.0%) | 11 (45.8%) | |
| M | 4 (33.3%) | 8 (66.7%) | 12 (50.0%) | |
| Batch | 0.390 | |||
| 1 | 2 (16.7%) | 5 (41.7%) | 7 (29.2%) | |
| 2 | 9 (75.0%) | 6 (50.0%) | 15 (62.5%) | |
| 3 | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (8.3%) | 2 (8.3%) | |
| Stage | <0.001 | |||
| 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| 3 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| 4 | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (41.7%) | 5 (20.8%) | |
| NA | 1 (8.3%) | 5 (41.7%) | 6 (25.0%) | |
| No | 11 (91.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 11 (45.8%) | |
| Status | 0.012 | |||
| Alive | 12 (100.0%) | 7 (58.3%) | 19 (79.2%) | |
| Dead | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (41.7%) | 5 (20.8%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, A.S.; Moraes, M.C.S.; Hyun Na, C.; Fierro-Monti, I.; Henriques, A.; Zahedi, S.; Bodo, C.; Tranfield, E.M.; Sousa, A.L.; Farinho, A.; et al. Is the Proteome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles a Marker of Advanced Lung Cancer? Cancers 2020, 12, 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113450
Carvalho AS, Moraes MCS, Hyun Na C, Fierro-Monti I, Henriques A, Zahedi S, Bodo C, Tranfield EM, Sousa AL, Farinho A, et al. Is the Proteome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles a Marker of Advanced Lung Cancer? Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113450
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Ana Sofia, Maria Carolina Strano Moraes, Chan Hyun Na, Ivo Fierro-Monti, Andreia Henriques, Sara Zahedi, Cristian Bodo, Erin M Tranfield, Ana Laura Sousa, Ana Farinho, and et al. 2020. "Is the Proteome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles a Marker of Advanced Lung Cancer?" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113450
APA StyleCarvalho, A. S., Moraes, M. C. S., Hyun Na, C., Fierro-Monti, I., Henriques, A., Zahedi, S., Bodo, C., Tranfield, E. M., Sousa, A. L., Farinho, A., Rodrigues, L. V., Pinto, P., Bárbara, C., Mota, L., Abreu, T. T. d., Semedo, J., Seixas, S., Kumar, P., Costa-Silva, B., ... Matthiesen, R. (2020). Is the Proteome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles a Marker of Advanced Lung Cancer? Cancers, 12(11), 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113450