Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Expression and Plasma Levels of FAP According to Gender and Age of RCC Patients
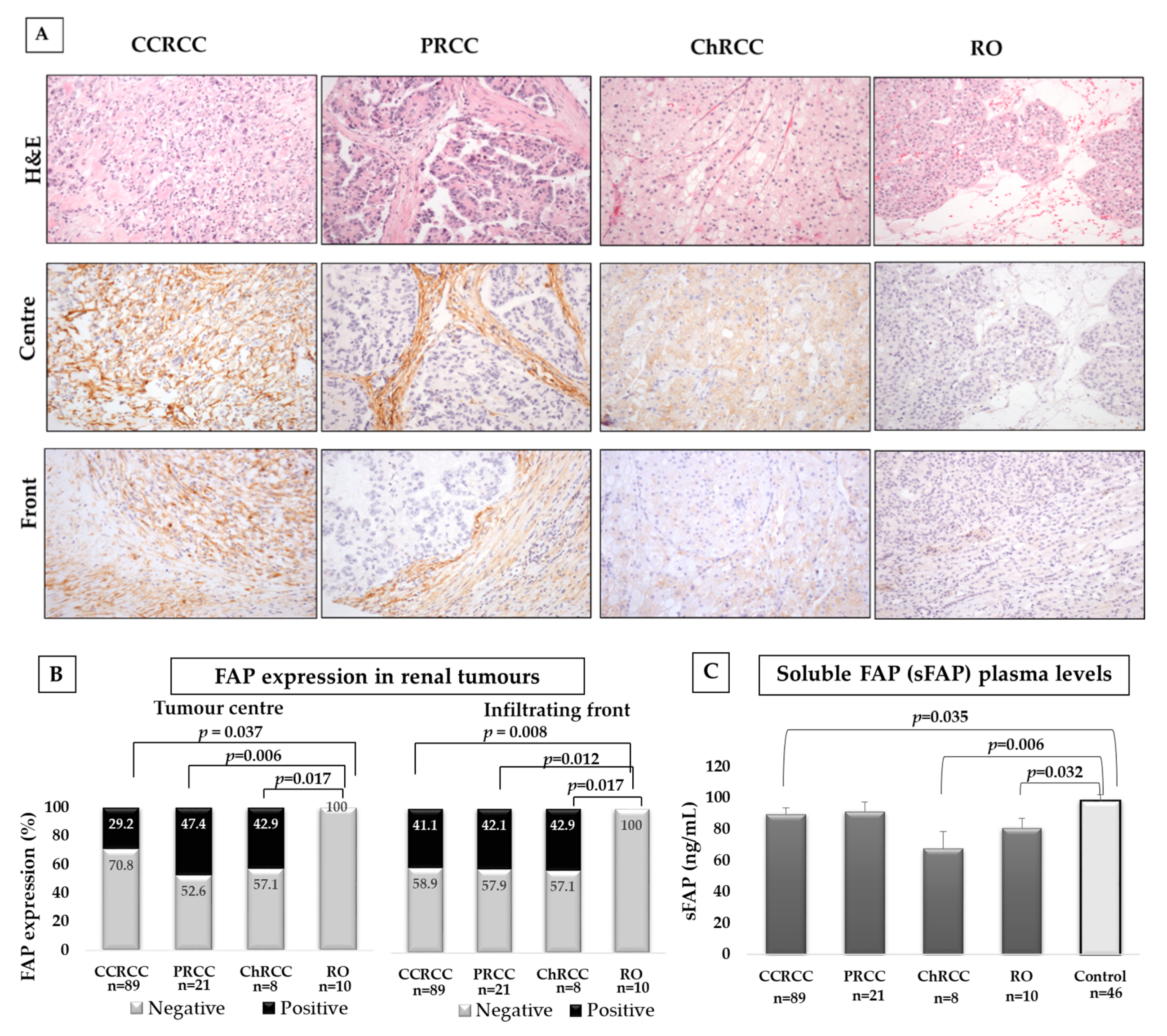
2.2. FAP Expression in Different Histological Subtypes of RCC and in Plasma Samples of Renal Tumour Patients and Control Subjects
2.3. Tissue FAP Expression and sFAP Levels in Terms of CCRCC Aggressiveness
2.3.1. FAP and Fuhrman Grade
2.3.2. FAP and Tumour Size
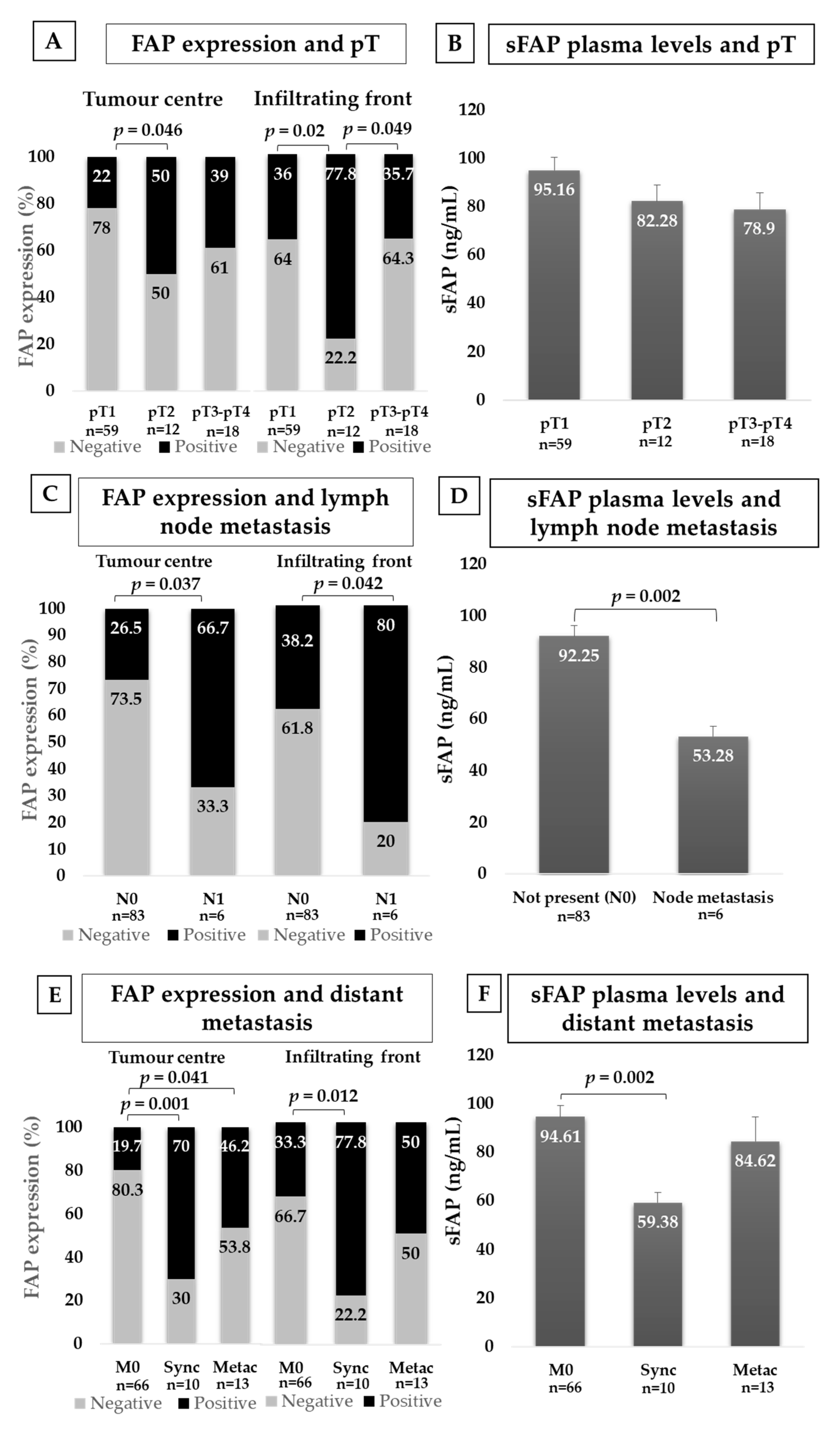
2.3.3. FAP and Local Invasion (pT)
2.3.4. FAP and Lymph Node Invasion (N)
2.3.5. FAP and Distant Metastasis (M)
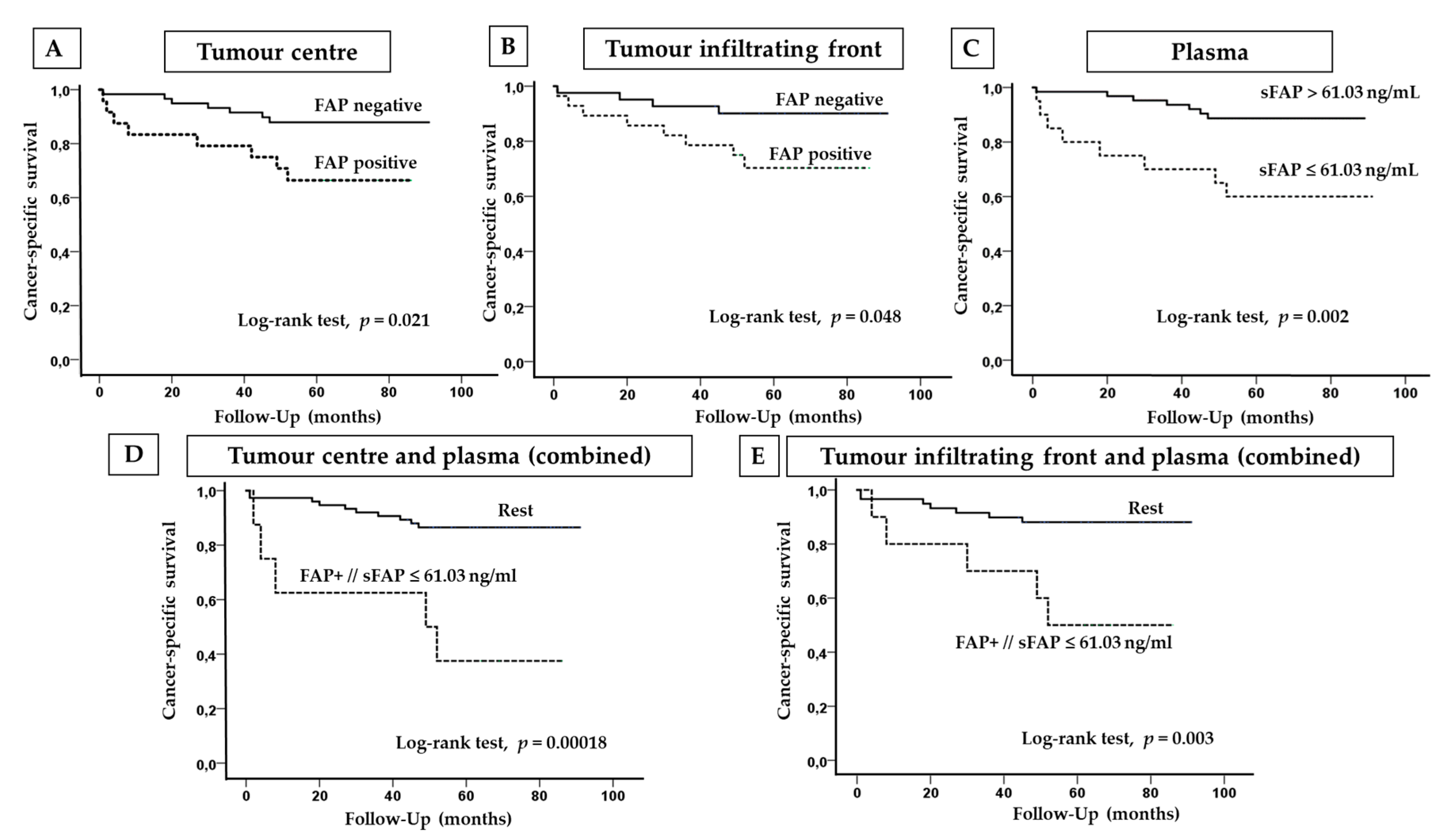
2.4. FAP Expression and Plasma Levels in Terms of the Cancer-Specific Survival (CSS) of CCRCC Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. ELISA Assays
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, G.T.; Cheng, L. Neoplasms of the kidney. In Urologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd ed.; Bostwick, D.G., Cheng, L., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 76–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.; Christie, A.; Rajaram, S.; Zhou, Q.; Araj, E.; Chintalapati, S.; Cadeddu, J.; Margulis, V.; Pedrosa, I.; Rakheja, D.; et al. Ontological analyses reveal clinically-significant clear cell renal cell carcinoma subtypes with convergent evolutionary trajectories into an aggressive type. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.J.; De Cubas, A.A.; Fan, H.; Smith, C.C.; Lang, M.; Reznik, E.; Bowlby, R.; Gibb, E.A.; Akbani, R.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 313–326.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Templeton, A.J.; Duran, I.; Ocana, A.; de Gouveia, P.; Aneja, P.; Knox, J.J.; Tannock, I.F.; Escudier, B.; Amir, E. Systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk-Wojtas, A.; Stec, R.; Szczylik, C. Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer? In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 34, pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Turajlic, S.; Swanton, C.; Boshoff, C. Kidney cancer: The next decade. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2477–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, T.; Pietras, K.; McAllister, S. Fibroblasts as architects of cancer pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1832, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBleu, V.; Kalluri, R. A peek into cancer-associated fibroblasts: Origin, functions and translational impact. Dis. Model Mech. 2018, 11. pii: dmm029447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errarte, P.; Larrinaga, G.; López, J.I. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in renal cell carcinoma. An example of tumour modulation through tumour/non-tumour cell interactions. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 21, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K.; Majidpoor, J. Stromal reprogramming: A target for tumour therapy. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calais, J. FAP: The Next Billion Dollar Nuclear Theranostics Target? J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, F.; He, J.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Cai, Z. Fibroblast activation protein-α in tumour microenvironment: Recent progression and implications. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3203–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidroozi, M.; Zucker, S.; Chen, W.T. Plasma Seprase and DPP4 Levels as Markers of Disease and Prognosis in Cancer. Dis. Markers 2012, 32, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Xing, S.; Xu, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Evaluation of the circulating level of fibroblast activation protein α for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30050–30062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qi, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Che, D. Fibroblast activation protein overexpression and clinical implications in solid tumours: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Beitia, M.; Errarte, P.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Etxezarraga, M.C.; Loizate, A.; Echevarria, E.; Badiola, I.; Larrinaga, G. Altered expression of fibroblast activation protein-α (FAP) in colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and in lymph node and liver metastases. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 10337–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errarte, P.; Guarch, R.; Pulido, R.; Blanco, L.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Beitia, M.; Gil, J.; Angulo, J.C.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. The Expression of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas Is Associated with Synchronous Lymph Node Metastases. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.I.; Errarte, P.; Erramuzpe, A.; Guarch, R.; Cortés, J.M.; Angulo, J.C.; Pulido, R.; Irazusta, J.; Llarena, R.; Larrinaga, G. Fibroblast activation protein predicts prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Frank, I.; Leibovich, B.C.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M.L. Impact of tumour size on the predictive ability of the pT3a primary tumour classification for renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2006, 177, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenocchio, E.; Colombi, F.; Calella, M.G.; Filippi, R.; Depetris, I.; Chilà, G.; Lombardi, P.; Marino, D.; Cagnazzo, C.; Ferraris, R.; et al. Improvement of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patient Survival: Single Institution Experience. Cancers 2019, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Peng, C.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Yutaka, Y.; Xiong, B.; Yang, X. Stromal fibroblast activation protein alpha promotes gastric cancer progression via epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Wnt/ β-catenin pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.M.; Xu, W.; Du, J.; Zhang, K.S.; Zhang, Q.G.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, Z.G.; Liu, S.Q.; Xie, W.Y.; Liu, H.F.; et al. The application of the fibroblast activation protein α-targeted immunotherapy strategy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33472–33482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, N.; Andres, H.; Rollinger, W.; Krause, F.; Dilba, P.; Tacke, M.; Karl, J. A combination of serum markers for the early detection of colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6111–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazbeck, R.; Jaenisch, S.E.; Abbott, C.A. Potential disease biomarkers: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 and fibroblast activation protein. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, R.R.; Vu, P.; Albiges, L.K.; Lin, X.; Simantov, R.; Temel, J.S.; Choueiri, T.K. The Effect of Weight Change During Treatment With Targeted Therapy in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, 443–450.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baak, M.A.; Vink, R.G.; Roumans, N.J.T.; Cheng, C.C.; Adams, A.C.; Mariman, E.C.M. Adipose tissue contribution to plasma fibroblast growth factor 21 and fibroblast activation protein in obesity. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2020, 44, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkova, A.; Busek, P.; Sedo, A.; Konvalinka, J. Molecular recognition of fibroblast activation protein for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.A.; Vennin, C.; Papanicolaou, M.; Chambers, C.R.; Herrmann, D.; Morton, J.P.; Cox, T.R.; Timpson, P. CAF Subpopulations: A New Reservoir of Stromal Targets in Pancreatic Cancer. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. PNAS 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Byrd, D.R.; Compton, C.C.; Fritz, A.G.; Greene, F.L.; Trotti, A. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman, S.A.; Lasky, L.C.; Limas, C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1982, 6, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.; Larrinaga, G.; Errarte, P.; Martín, A.; Dotor, A.; Esquinas, C.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Pulido, R.; López, J.I.; Angulo, J.C. The coexpression of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) and basal-type markers (CK 5/6 and CD44) predicts prognosis in high-grade invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 91, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, T.; Stuart, M.; Osting, J.; Tollenaar, R.; Sier, C.; Mesker, W. Increased expression of cancer-associated fibroblast markers at the invasive front and its association with tumour-stroma ratio in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitte De Willige, S.; Malfliet, J.J.; Deckers, J.W.; Dippel, D.W.; Leebeek, F.W.; Rijken, D.C. Plasma levels of soluble fibroblast activation protein in arterial thrombosis; determinants and cleavage of its substrate alpha-2-antiplasmin. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 178, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, T.W.; Dunshee, D.R.; Kljavin, N.M.; Skelton, N.J.; Sonoda, J.; Ernst, J.A. Selective Homogeneous Assay for Circulating Endopeptidase Fibroblast Activation Protein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| FAP at the Tumour Centre | FAP at the Infiltrating Front | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma sFAP (ng/mL) | Negative | Positive | p= | Negative | Positive | p= |
| CCRCC | 89.1 ± 4.4 | 90.5 ± 8.6 | 0.69 | 90.4 ± 5.5 | 90.9 ± 8.4 | 0.64 |
| PRCC | 95.9 ± 11.2 | 94.1 ± 4.9 | 0.87 | 89.9 ± 11.1 | 92.9 ± 4.4 | 0.51 |
| ChRCC | 57.3 ± 11.8 | 86.74 ± 23.8 | 0.29 | 53.4 ± 9.3 | 92.1 ± 22.1 | 0.16 |
| A | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumour Centre | Infiltrating Front | ||||||||
| 5-Year CSS | Variables | p= | ExpB | Inf | Sup | p= | ExpB | Inf | Sup |
| Multiple Cox Regression | FAP | 0.26 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 1.65 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 2.35 |
| Grade | 0.2 | 2.92 | 0.57 | 15 | 0.56 | 1.93 | 0.21 | 18.17 | |
| pT | 0.03 | 2.12 | 1.08 | 4.17 | 0.08 | 2.01 | 0.92 | 4.4 | |
| N | 0.11 | 2.75 | 0.8 | 9.41 | 0.11 | 3.23 | 0.76 | 13.66 | |
| M | 0.001 | 35.76 | 4.3 | 297.7 | 0.004 | 29.58 | 2.97 | 294.8 | |
| Final Step of Wald Method | pT | 0.052 | 1.95 | 0.99 | 3.81 | 0.039 | 2.15 | 1.04 | 4.46 |
| N | 0.07 | 3.04 | 0.91 | 10.1 | - | ||||
| M | 0.001 | 33.24 | 4.21 | 262.4 | 0.001 | 29.94 | 3.78 | 237.4 | |
| B | |||||||||
| Plasma | |||||||||
| 5-Year CSS | Variables | p= | ExpB | Inf | Sup | ||||
| Multiple Cox Regression | sFAP | 0.079 | 4.67 | 0.83 | 26.18 | ||||
| Grade | 0.5 | 1.75 | 0.34 | 9 | |||||
| pT | 0.01 | 2.71 | 1.22 | 6.01 | |||||
| N | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.11 | 4.45 | |||||
| M | 0.002 | 28.47 | 3.39 | 238.8 | |||||
| Final Step of Wald Method | sFAP | 0.011 | 4.24 | 1.39 | 12.95 | ||||
| pT | 0.007 | 2.51 | 1.29 | 4.89 | |||||
| M | 0.001 | 32.5 | 4.13 | 256.2 | |||||
| C | |||||||||
| Tumour Centre | Infiltrating Front | ||||||||
| 5-Year CSS | p = | ExpB | Inf | Sup | p = | ExpB | Inf | Sup | |
| Multiple Cox Regression | FAP/sFAP | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.2 | 4.87 | 0.83 | 1.28 | 0.13 | 12.1 |
| Grade | 0.32 | 2.24 | 0.46 | 10.98 | 0.6 | 1.84 | 0.19 | 18.1 | |
| pT | 0.048 | 1.97 | 1.01 | 3.85 | 0.12 | 1.96 | 0.84 | 4.61 | |
| N | 0.27 | 2.55 | 0.48 | 13.43 | 0.55 | 2.08 | 0.19 | 22.6 | |
| M | 0.002 | 27.46 | 3.37 | 223.5 | 0.007 | 20.81 | 2.34 | 185.3 | |
| Final Step of Wald Method | pT | 0.52 | 1.95 | 0.99 | 3.81 | 0.039 | 2.15 | 1.04 | 4.45 |
| N | 0.07 | 3.04 | 0.91 | 10.1 | - | ||||
| M | 0.001 | 33.24 | 4.21 | 262.4 | 0.001 | 29.9 | 3.78 | 237.4 | |
| Tumour Subtype | CCRCC (n = 89) | PRCC (n = 21) | ChRCC (n = 8) | RO (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (range) | 61.4 (36–82) | 54.0 (26–80) | 64.6 (47–74) | 63.5 (40–84) |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 60/29 | 17/4 | 7/1 | 3/7 |
| Follow-up (months) | 59.9 (1–91) | |||
| Survival | ||||
| Alive | 68 | |||
| Dead of disease | 15 | |||
| Dead by other causes | 6 | |||
| Diameter | ||||
| ≤4 cm | 28 | |||
| >4 to 7cm | 39 | |||
| >7 cm | 22 | |||
| Fuhrman grade | ||||
| G1 | 3 | |||
| G2 | 46 | |||
| G3 | 30 | |||
| G4 | 10 | |||
| Local invasion (pT) | ||||
| pT1 | 59 | |||
| pT2 | 12 | |||
| pT3 | 16 | |||
| pT4 | 2 | |||
| Lymph node invasion (N) | ||||
| No | 83 | |||
| Yes | 6 | |||
| Distant metastasis (M) | ||||
| No | 66 | |||
| Synchronous | 10 | |||
| Metachronous | 13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Errarte, P.; Etxezarraga, M.C.; Echevarria, E.; Angulo, J.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours. Cancers 2020, 12, 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113393
Solano-Iturri JD, Errarte P, Etxezarraga MC, Echevarria E, Angulo J, López JI, Larrinaga G. Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113393
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolano-Iturri, Jon Danel, Peio Errarte, María C. Etxezarraga, Enrique Echevarria, Javier Angulo, José I. López, and Gorka Larrinaga. 2020. "Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113393
APA StyleSolano-Iturri, J. D., Errarte, P., Etxezarraga, M. C., Echevarria, E., Angulo, J., López, J. I., & Larrinaga, G. (2020). Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours. Cancers, 12(11), 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113393








