Role of SOX Protein Groups F and H in Lung Cancer Progression
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Summary
2. Introduction—Lung Cancer Classification
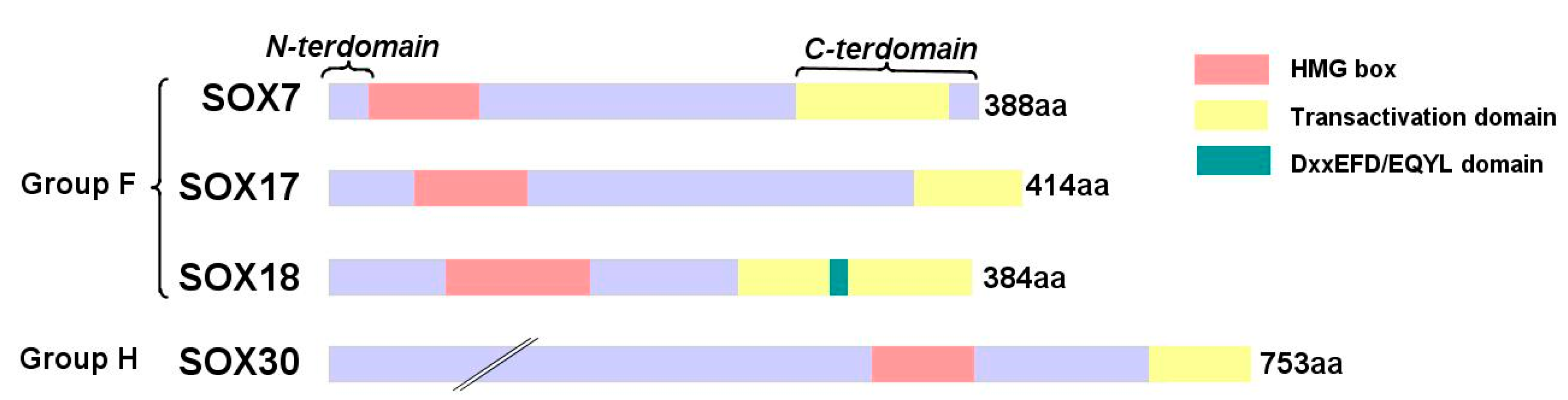
3. SOX Protein Family
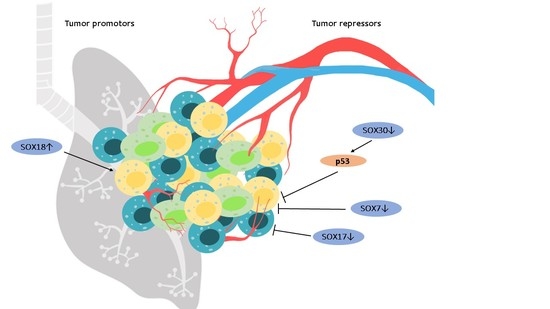
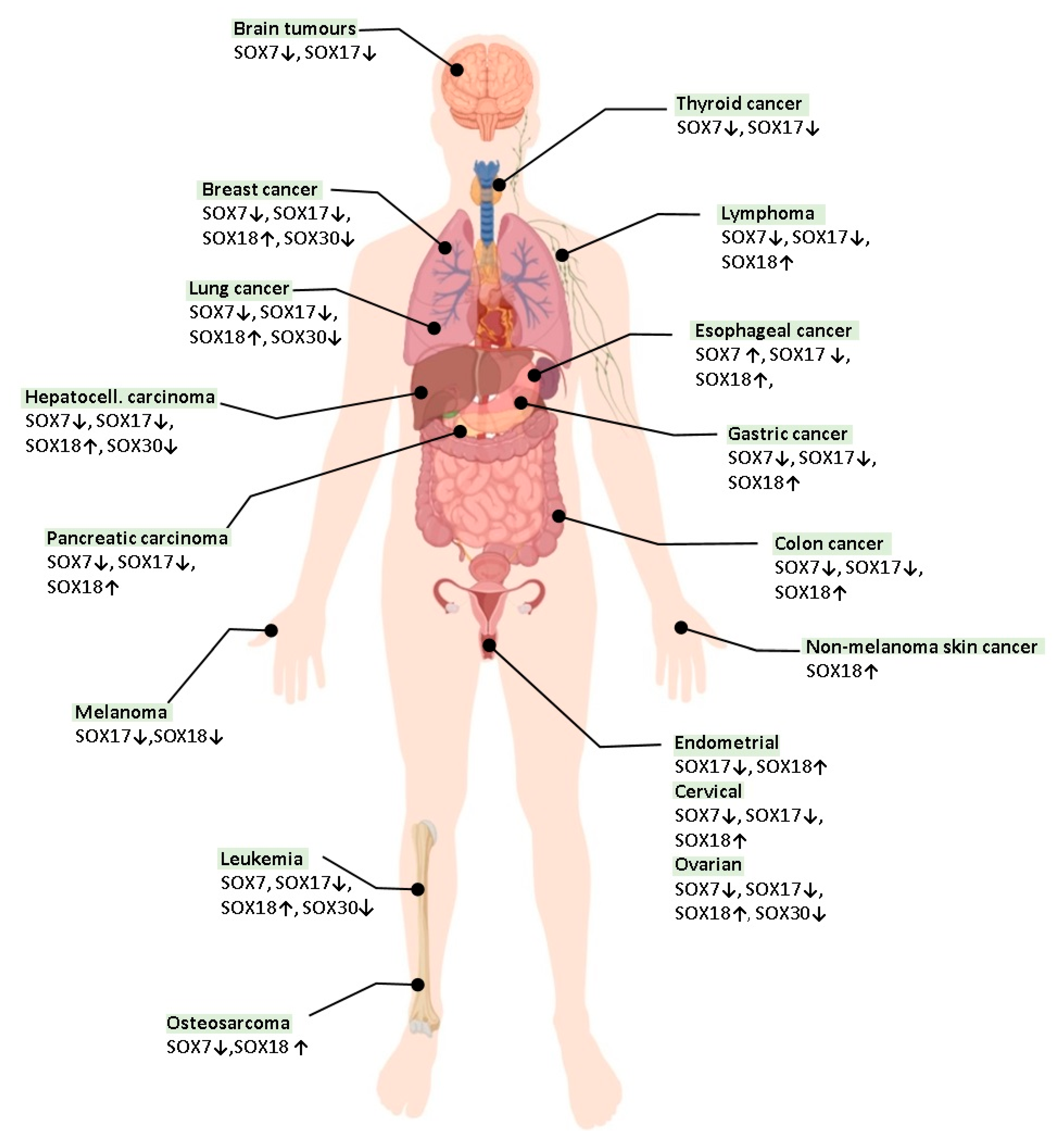
4. The Role of SOX Proteins in Lung Tumorigenesis
4.1. SOX7
4.2. SOX17
4.3. SOX18
4.4. SOX30
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz, C.S.D.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung Cancer Statistics. Lung Cancer Pers. Med. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamat, F.; Khandashpour, M.; Naeimi-Tabiei, M.; Ariannia, A.; Ashaari, M.; Sedaghat, S.; Ghasemi-Kebria, F.; Salamat, F.; Moghaddami, A.; Hasanpour-Heidari, S.; et al. Increasing trends of lung cancer in Golestan province, Northern Iran (2004–2016). Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 65, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Ferlay, J.; Rutherford, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bray, F. International trends in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype: Adenocarcinoma stabilizing in men but still increasing in women. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, M.M.; Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer incidence in young women vs. young men: A systematic analysis in 40 countries. Int. J. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuvdendorj, A.; Feenstra, T.; Tseveen, B.; Buskens, E. Smoking-attributable burden of lung cancer in Mongolia a data synthesis study on differences between men and women. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiam, K.; Touré, N.O.; Ndiaye, E.M.; Baddredine, H.; Ndiaye, M.; Diop, M. Epidemiology of primary lung cancer among non-smokers in Senegal. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2019, 36, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlík, F. Impact of smoking on metabolic changes and effectiveness of drugs used for lung cancer. Central Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 28, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbromski, M.; Rzechonek, A.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Glatzel-Plucinska, N.; Chachaj, A.; Werynska, B.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P. Influence of miR-7a and miR-24-3p on the SOX18 transcript in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; González-Marrón, A.; Lidón-Moyano, C.; Matilla-Santander, N.; Fu, M.; Vidal, C.; Martinez-Garcia, M.Á.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M. Smoking pattern and risk of lung cancer among women participating in cancer screening programmes. J. Public Health 2020, 42, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharairi, N.A. The Effects of Dietary Supplements on Asthma and Lung Cancer Risk in Smokers and Non-Smokers: A Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Chung, T.H.; Kim, B.; Deshmukh, A.A.; Salloum, R.G.; Bian, J. Provider-Patient Discussions About Smoking and the Impact of Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines: NHIS 2011–2015. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Publishing Production Team. Erratum: Epidemiology of lung cancer in Northern Greece: An 18-year hospital-based cohort study focused on the differences between smokers and non-smokers. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Domvri, K.; Porpodis, K.; Zisi, P.; Apostolopoulos, A.; Cheva, A.; Papamitsou, T.; Papakosta, D.; Kontakiotis, T. Epidemiology of lung cancer in Northern Greece: An 18-year hospital-based cohort study focused on the differences between smokers and non-smokers. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2020, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.T.; Lau, E.C.; Moolgavkar, S.H. Smoking, air pollution, and lung cancer risk in the Nurses’ Health Study cohort: Time-dependent confounding and effect modification. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Haro, A.; Shikada, Y.; Maruyama, R.; Maehara, Y. Non-small cell lung cancer in never smokers as a representative ‘non-smoking-associated lung cancer’: Epidemiology and clinical features. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 16, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couraud, S.; Zalcman, G.; Milleron, B.; Morin, F.; Souquet, P.-J. Lung cancer in never smokers—A review. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Tong, K.; Ramsden, K.; Ionescu, D.; Laskin, J. Histologic classification of non-small-cell lung cancer over time: Reducing the rates of not-otherwise-specified. Curr. Oncol. 2015, 22, e164–e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M. Classification and Pathology of Lung Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; He, J.; Li, T.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Xing, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Ma, Q.; Liu, B.; et al. Accurate Classification of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Pathology and Mapping of EGFR Mutation Spatial Distribution by Ambient Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Parra-Cuentas, E.; Wistuba, I.I. Diagnosis and Molecular Classification of Lung Cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2016, 170, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okami, J.; Shintani, Y.; Okumura, M.; Ito, H.; Ohtsuka, T.; Toyooka, S.; Mori, T.; Watanabe, S.-I.; Date, H.; Yokoi, K.; et al. Demographics, Safety and Quality, and Prognostic Information in Both the Seventh and Eighth Editions of the TNM Classification in 18,973 Surgical Cases of the Japanese Joint Committee of Lung Cancer Registry Database in 2010. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linning, E.; Lu, L.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zhao, B. Radiomics for Classification of Lung Cancer Histological Subtypes Based on Nonenhanced Computed Tomography. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, P.; Moreira, A.; Coudray, N.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Narula, N.; Snuderl, M.; Fenyö, D.; Razavian, N.; Tsirigos, A. Classification and Mutation Prediction from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology Images Using Deep Learning. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 24, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, U.; Kawa, B.; Siddique, M.; Mak, S.M.; Nair, A.; McLean, E.; Bille, A.; Goh, V.; Cook, G. Non-invasive classification of non-small cell lung cancer: A comparison between random forest models utilising radiomic and semantic features. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D. Pathology of Lung Cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadara, H.; Wistuba, I. Field Cancerization in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, H.; Shen, L.; Fujimoto, J.; Saintigny, P.; Chow, C.-W.; Lang, W.; Chu, Z.; Garcia, M.; Kabbout, M.; Fan, Y.-H.; et al. Characterizing the molecular spatial and temporal field of injury in early-stage smoker non-small cell lung cancer patients after definitive surgery by expression profiling. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gicking, J.; Aumann, M. Lung lobe torsion. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2011, 33, E4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harding, A.D.; Simmons, C.C. Lung cancer in the emergency department. Australas. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2012, 15, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, I.; Schnabel, P.A. What’s new in lung pathology: Minutes from the Pulmonary Pathology Working Group of the German Society of Pathology. Pathologe 2011, 32 (Suppl. 2), 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, T.J.; Kwon, D.M.; Riley, K.E.; Shen, M.J.; Hamann, H.A.; Ostroff, J.S. Lung Cancer Stigma: Does Smoking History Matter? Ann. Behav. Med. 2020, 54, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidkhori, G.; Narimani, Z.; Ashtiani, S.H.; Moeini, A.; Nowzari-Dalini, A.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Reconstruction of an Integrated Genome-Scale Co-Expression Network Reveals Key Modules Involved in Lung Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Weroha, S.J.; Molina, J.R. Oncogenic Pathways, Molecularly Targeted Therapies, and Highlighted Clinical Trials in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Molina, J.R.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Allen-Ziegler, K.; Rowland, K.M.; Reuter, N.F.; Luyun, R.F.; Dy, G.K.; Marks, R.S.; Schild, S.E.; et al. Brief Report: A Phase II “Window-of-Opportunity” Frontline Study of the mTOR Inhibitor, Temsirolimus Given as a Single Agent in Patients with Advanced NSCLC, an NCCTG Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, A.-P.; Martin, B.; Verdebout, J.M.; Feoli, F.; Mascaux, C.; Ninane, V.; Sculier, J.P. EGFR, c-erbB-2 and ki-67 in NSCLC and preneoplastic bronchial lesions. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carbonnaux, M.; Souquet, P.-J.; Meert, A.-P.; Scherpereel, A.; Peters, M.J.; Couraud, S. Inequalities in lung cancer: A world of EGFR. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbay, J.; Collignon, J.; Koopman, P.; Capel, B.; Economou, A.; Münsterberg, A.; Vivian, N.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nat. Cell Biol. 1990, 346, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.; Schepers, G.; Koopman, P. Phylogeny of the SOX Family of Developmental Transcription Factors Based on Sequence and Structural Indicators. Dev. Biol. 2000, 227, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell-Badge, R. The early history of the Sox genes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, S.D.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M. The SOX family of genes in cancer development: Biological relevance and opportunities for therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.W.J.; Liu, X. The Role of Sox Genes in Lung Morphogenesis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15767–15783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.M.; Diez-Valle, R.; Manterola, L.; Rubio, A.; Liu, D.; Cortes-Santiago, N.; Urquiza, L.; Jauregi, P.; De Munain, A.L.; Sampron, N.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Modifications of Sox2 Contribute to the Invasive Phenotype of Malignant Gliomas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Yanagihara, K.; Yuasa, Y. SOX2 is frequently downregulated in gastric cancers and inhibits cell growth through cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, N.; Liu, L.; Cao, D.; Gao, M.; Lin, C.; Jin, C. SOX9 overexpression plays a potential role in idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.-F.; Cong, Y.; Lin, D. SOX9 expression correlates with microvascular density, progress and prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2012, 41, 848–849. [Google Scholar]
- Passeron, T.; Valencia, J.C.; Namiki, T.; Vieira, W.D.; Passeron, H.; Miyamura, Y.; Hearing, V.J. Upregulation of SOX9 inhibits the growth of human and mouse melanomas and restores their sensitivity to retinoic acid. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, M. From head to toes: The multiple facets of Sox proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, M. All purpose Sox: The many roles of Sox proteins in gene expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.I.S.; Ma, A.C.H.; Fung, T.-K.; Leung, A.Y.H. Characterization of Sry-related HMG box group F genes in zebrafish hematopoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 2011, 39, 986–998.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Bauer, J.; Wise, P.; Krüger, M.; Simonsen, U.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Corydon, T.J. The role of SOX family members in solid tumours and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashimada, K.; Koopman, P. Sry: The master switch in mammalian sex determination. Development 2010, 137, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, S.; Kato, H.; Okuda, A. Role of SoxB1 transcription factors in development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3675–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, L.A.; Lee, T.I.; Cole, M.F.; Johnstone, S.E.; Levine, S.S.; Zucker, J.P.; Guenther, M.G.; Kumar, R.M.; Murray, H.L.; Jenner, R.G.; et al. Core Transcriptional Regulatory Circuitry in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell 2005, 122, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoser, M.; Potzner, M.R.; Koch, J.M.C.; Bösl, M.R.; Wegner, M.; Sock, E. Sox12 Deletion in the Mouse Reveals Nonreciprocal Redundancy with the Related Sox4 and Sox11 Transcription Factors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 4675–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, V.; Li, P.; De Crombrugghe, B. A new long form of Sox5 (L-Sox5), Sox6 and Sox9 are coexpressed in chondrogenesis and cooperatively activate the type II collagen gene. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5718–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Tang, P.; Liu, S.; Dewing, P.; Harley, V.R.; Vilain, E. Dimerization of SOX9 is required for chondrogenesis, but not for sex determination. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Hiraoka, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Sakai, Y.; Kido, S.; Aiso, S. Isolation and characterization of a mouse SRY-related cDNA, mSox7. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1445, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Kanai-Azuma, M.; Noce, T.; Saido, T.C.; Shiroishi, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Yazaki, K. Identification of two Sox17 messenger RNA isoforms, with and without the high mobility group box region, and their differential expression in mouse spermatogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 133, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, T.L.; Mynett-Johnson, L.; Wright, E.M.; Hosking, B.M.; Koopman, P.; Muscat, G.E. Sequence and expression of Sox-18 encoding a new HMG-box transcription factor. Gene 1995, 161, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Hara, K.; Kanai-Azuma, M.; Matsui, T.; Miura, Y.; Tsunekawa, N.; Kurohmaru, M.; Saijoh, Y.; Koopman, P.; Kanai, Y. Redundant roles of Sox17 and Sox18 in early cardiovascular development of mouse embryos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, M.; Caprini, A.; Hosking, B.; Orsenigo, F.; Wilhelm, D.; Browne, C.; Paavonen, K.; Karnezis, T.; Shayan, R.; Downes, M.; et al. Sox18 induces development of the lymphatic vasculature in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 456, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Harley, V. Acquisition of SOX transcription factor specificity through protein–protein interaction, modulation of Wnt signalling and post-translational modification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosking, B.M.; Muscat, G.E.; Koopman, P.; Dowhan, D.H.; Dunn, T.L. Trans-activation and DNA-binding properties of the transcription factor, Sox-18. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 2626–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M. Function and molecular evolution of mammalian Sox15, a singleton in the SoxG group of transcription factors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, D.; Lin, X.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Duo, S.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. The transcription factor SOX30 is a key regulator of mouse spermiogenesis. Development 2018, 145, dev164723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.-M.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, W.-M.; Liu, W.-B.; Mao, C.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Huang, C.-S.; et al. Epigenetic Inactivation of SOX30 Is Associated with Male Infertility and Offers a Therapy Target for Non-obstructive Azoospermia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, M.; Damont, A.; Blanco, M.; Lastrucci, E.; El Kennani, S.; Ialy-Radio, C.; El Khattabi, L.; Terrier, S.; Louwagie, M.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; et al. Multi-omic analysis of gametogenesis reveals a novel signature at the promoters and distal enhancers of active genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4115–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Fu, K.; Yin, H.; Cui, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, W.; Cheng, L.; Tan, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Sox30 initiates transcription of haploid genes during late meiosis and spermiogenesis in mouse testes. Development 2018, 145, dev164855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Liu, W.; Xiao, H.; Dong, Y.; Sun, L.; Mao, C.; Yin, L.; Jiang, X.; Ao, L.; Cui, Z.; et al. High expression of SOX30 is associated with favorable survival in human lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Shi, X.; Yin, L.; Ao, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Cao, J.; et al. SOX30, a novel epigenetic silenced tumor suppressor, promotes tumor cell apoptosis by transcriptional activating p53 in lung cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4391–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phochanukul, N.; Russell, S. No backbone but lots of Sox: Invertebrate Sox genes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takash, W. SOX7 transcription factor: Sequence, chromosomal localisation, expression, transactivation and interference with Wnt signalling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4274–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, M.; Koopman, P.; Beltrame, M. SoxF genes: Key players in the development of the cardio-vascular system. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futaki, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Emoto, T.; Weber, C.N.; Sekiguchi, K. Sox7 Plays Crucial Roles in Parietal Endoderm Differentiation in F9 Embryonal Carcinoma Cells through Regulating Gata-4 and Gata-6 Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10492–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Shen, H.; Ishida, S.; Dickson, C. SOX7 and GATA-4 Are Competitive Activators ofFgf-3Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28564–28573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.; Mazan, A.; Gandillet, A.; Pearson, S.; Lacaud, G.; Kouskoff, V. SOX7 regulates the expression of VE-cadherin in the haemogenic endothelium at the onset of haematopoietic development. Development 2012, 139, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovall, D.B.; Cao, P.; Sui, G. SOX7: From a developmental regulator to an emerging tumor suppressor. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Niimi, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Futaki, S.; Sekiguchi, K. SOX7 and SOX17 Regulate the Parietal Endoderm-specific Enhancer Activity of Mouse Laminin α1 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 38055–38061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandillet, A.; Serrano, A.G.; Pearson, S.; Lie-A-Ling, M.; Lacaud, G.; Kouskoff, V. Sox7-sustained expression alters the balance between proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors at the onset of blood specification. Blood 2009, 114, 4813–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Stovall, D.B.; Wan, M.; Zhang, Q.; Chou, J.; Li, D.; Sui, G. SOX7 Target Genes and Their Contribution to Its Tumor Suppressive Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovall, D.B.; Wan, M.; Miller, L.D.; Cao, P.; Maglic, D.; Zhang, Q.; Stampfer, M.R.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Sui, G. The regulation of SOX7 and its tumor suppressive role in breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Cui, G.; Ding, M.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Dai, D.; Chen, L. miR-935 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting SOX7. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 79, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Giri, V.; Cui, Y.; Yin, M.; Xian, Z.; Li, J. LncRNA FTX inhibits hippocampal neuron apoptosis by regulating miR-21-5p/SOX7 axis in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Xi, H.; Cai, A.; Bian, S.; Wei, B.; Chen, L. Decreased expression of Sox7 correlates with the upregulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and the poor survival of gastric cancer patients. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ge, Z.; Song, S.; Zhang, S.; Yan, H.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y. Decreased Expression of SOX7 is Correlated with Poor Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2012, 18, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, D.; Ma, H.; Li, Y. LncRNA MEG3 enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-21-5p/SOX7 axis. Onco. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 5137–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayano, T.; Garg, M.; Yin, D.; Sudo, M.; Kawamata, N.; Shi, S.; Chien, W.; Ding, L.-W.; Leong, G.; Mori, S.; et al. SOX7 is down-regulated in lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, Q.; Qu, M.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Di, S. MicroRNA-616 promotes the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting SOX7. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lv, Z.; He, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Ren, X.; Wang, F.; Zhu, X.; Ding, Y.; et al. The SOX17/miR-371-5p/SOX2 axis inhibits EMT, stem cell properties and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9099–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Han, T.; Zhao, X.-L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.-Q.; Lin, G.-W. Methylation of the CpG Island Near SOX7 Gene Promoter Is Correlated with the Poor Prognosis of Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2012, 227, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivnan, A.; Foley, N.H.; Tracey, L.; Davidoff, A.M.; Stallings, R.L. MicroRNA-184-mediated inhibition of tumour growth in an orthotopic murine model of neuroblastoma. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4391–4395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.-G.; Li, W.-H.; He, W.-G.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, G.-X.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.-F.; Liu, Q.-L.; Huang, Y.-N.; Zhang, L.; et al. Mir-184 Post-Transcriptionally Regulates SOX7 Expression and Promotes Cell Proliferation in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Dong, W.; Li, L.; Feng, Y.; Pan, L.; Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, G.; Su, D.; et al. SOX7, down-regulated in colorectal cancer, induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.W.; Mak, C.S.; Leung, T.H.; Chan, K.K.; Ngan, H.Y. Down-regulation of Sox7 is associated with aberrant activation of Wnt/b-catenin signaling in endometrial cancer. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.-Y.; Ding, L.-W.; Johnson, K.; Zhou, S.; Tyner, J.W.; Yang, H.; Doan, N.B.; Said, J.W.; Xiao, J.-F.; Loh, X.-Y.; et al. SOX7 regulates MAPK/ERK-BIM mediated apoptosis in cancer cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6196–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, W.; Ding, W.; Zhang, L. MiR-9 is involved in TGF-β1-induced lung cancer cell invasion and adhesion by targeting SOX7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhan, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, J. Ski prevents TGF-beta-induced EMT and cell invasion by repressing SMAD-dependent signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Minamiya, Y.; Goto, A.; Nanjo, H.; Saito, H.; Motoyama, S. Bronchioloalveolar invasion in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with expression of transforming growth factor-beta1. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Takanashi, S.; Kanehira, Y.; Tsushima, T.; Imai, T.; Okumura, K. Transforming growth factor-beta1 level correlates with angiogenesis, tumor progression, and prognosis in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2001, 91, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zan, J.; Wang, Z.; Ling, L.; Li, Q.; Lv, J.; Qi, S.; Cao, Y.; et al. miR-24-3p promotes cell migration and proliferation in lung cancer by targeting SOX7. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Li, C.; Cai, P.; Yu, L.; Zhao, B.; Chen, G. Knockdown of miR-935 increases paclitaxel sensitivity via regulation of SOX7 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3397–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, R.; Kan, Q. miR-935 Promotes Liver Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration by Targeting SOX7. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2017, 25, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E.; Jagannathan, S.; Driscoll, J.J. Correlation of long non-coding RNA expression with metastasis, drug resistance and clinical outcome in cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8027–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Dong, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Kang, L.; Lei, X.-P.; Zhai, X.-S. Silencing of Pin1 suppresses hyperoxia-induced apoptosis of A549 cells. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2015, 17, 496–501. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Li, L.I.; Xiaoxiang, W.U.; Shuying, D.; Xuhui, T. Influence of Berberine on Cisplatin Antineoplastic Effect in A549 Cells. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2015, 18, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z. Effect of microRNA-21 on multidrug resistance reversal in A549/DDP human lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Stainier, D.Y. A molecular pathway leading to endoderm formation in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.; Woodland, H.R. Changes in embryonic cell fate produced by expression of an endodermal transcription factor, Xsox17. Mech. Dev. 2000, 99, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai-Azuma, M.; Kanai, Y.; Gad, J.M.; Tajima, Y.; Taya, C.; Kurohmaru, M.; Sanai, Y.; Yonekawa, H.; Yazaki, K.; Tam, P.P.L.; et al. Depletion of definitive gut endoderm in Sox17-null mutant mice. Devolopment 2002, 129, 2367–2379. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, T.; Kanai-Azuma, M.; Hara, K.; Matoba, S.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kawakami, H.; Kurohmaru, M.; Koopman, P.; Kanai, Y. Redundant roles of Sox17 and Sox18 in postnatal angiogenesis in mice. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3513–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Saunders, T.L.; Morrison, S.J. Sox17 Dependence Distinguishes the Transcriptional Regulation of Fetal from Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Cell 2007, 130, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Molecular cloning and characterization of human SOX17. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 9, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, K.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Tong, H.; Wan, X. SOX17 is a tumor suppressor in endometrial cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76036–76046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Jia, Y.; Yu, Y.; Brock, M.V.; Herman, J.G.; Han, C.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M. SOX17 methylation inhibits its antagonism of Wnt signaling pathway in lung cancer. Discov. Med. 2012, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yu, X.-F.; Ouyang, N.; Luo, Q.-L.; Zhao, S.-Y.; Guan, X.-F.; Chen, T.; Li, J.-X. Multi-platform analysis of methylation-regulated genes in human lung adenocarcinoma. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2019, 82, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, I.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, J.-M.; Huang, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Yan, J.-J.; Sheu, B.-S.; Lu, P.-J.; Chang, W.-L.; Lai, W.-W.; et al. Low SOX17 expression is a prognostic factor and drives transcriptional dysregulation and esophageal cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.-; Wang, B.-L.; Shen, Z.-Z.; Huang, W.; Shao, Z.-M. Sox17, the canonical Wnt antagonist, is epigenetically inactivated by promoter methylation in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Brock, M.V.; Zheng, X.; Yu, Y.; Herman, J.G.; Guo, M. Inhibition of SOX17 by MicroRNA 141 and Methylation Activates the WNT Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Wang, C.-M.; Zhou, Y.; Du, C.-Y.; Zheng, B.-Q.; Cao, X.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Sun, M.-H.; Shi, Y.-Q. Sox17 regulates proliferation and cell cycle during gastric cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2011, 307, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betel, D.; Wilson, M.; Gabow, A.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C. The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D149–D153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Bao, W.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wan, X. SOX17 increases the cisplatin sensitivity of an endometrial cancer cell line. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Q.; He, Y. MicroRNA-21-5p promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting SRY-box 17 in endometrial cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.W.; Keiser, A.R.; Wells, J.M.; Zorn, A.M.; Whitsett, J.A. Sox17 Promotes Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits TGF-β/Smad3 Signaling to Initiate Progenitor Cell Behavior in the Respiratory Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Marsboom, G.; Jambusaria, A.; Xiong, S.; Toth, P.T.; Benevolenskaya, E.V.; Rehman, J.; Malik, A.B. Sox17 is required for endothelial regeneration following inflammation-induced vascular injury. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.S.; Holzner, M.; Weng, M.; Srivastava, Y.; Jauch, R. SOX17 in cellular reprogramming and cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Qu, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, Y. SOX17 Inhibits Tumor Metastasis Via Wnt Signaling In Endometrial Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 8275–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, H. E-cadherin mediated adhesion system in cancer cells. Cancer 1996, 77 (Suppl. 8), 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Teknos, T.N.; Pan, Q. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.H.; Tokheim, C.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Sengupta, S.; Bertrand, D.; Weerasinghe, A.; Colaprico, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Driver Genes and Mutations. Cell 2018, 174, 1034–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, Y.; Tan, D.S.; Malik, V.; Weng, M.; Javed, A.; Cojocaru, V.; Wu, G.; Veerapandian, V.; Cheung, L.W.T.; Jauch, R. Cancer-associated missense mutations enhance the pluripotency reprogramming activity of OCT4 and SOX17. FEBS J. 2019, 287, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgkouranidou, I.; Chimonidou, M.; Milaki, G.; Tsaroucha, E.; Kakolyris, S.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. SOX17 promoter methylation in plasma circulating tumor DNA of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Yin, W.; Peng, M.; Wu, F.; Wu, X.; Tang, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Hulbert, A.; et al. Ultrasensitive DNA hypermethylation detection using plasma for early detection of NSCLC: A study in Chinese patients with very small nodules. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinner, D.; Rankin, S.; Lee, M.; Zorn, A.M. Sox17 and beta-catenin cooperate to regulate the transcription of endodermal genes. Development 2004, 131, 3069–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, D.; Kordich, J.J.; Spence, J.R.; Opoka, R.; Rankin, S.A.; Lin, S.-C.J.; Jonatan, D.; Zorn, A.M.; Wells, J.M. Sox17 and Sox4 Differentially Regulate β-Catenin/T-Cell Factor Activity and Proliferation of Colon Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7802–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojčić, S.; Stevanovic, M. The human SOX18 gene: cDNA cloning and high resolution mapping. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1492, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M. SOX18 and the Transcriptional Regulation of Blood Vessel Development. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 11, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, D.J.; Bowles, J.; Nagy, A.; Muscat, G.E.; Koopman, P. Mice Null for Sox18 Are Viable and Display a Mild Coat Defect. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 9331–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I.A.; Bisucci, T.; Raghoenath, S.; Olsson, J.E.; Muscat, G.E.; Koopman, P. Sox18 Is Transiently Expressed during Angiogenesis in Granulation Tissue of Skin Wounds with an Identical Expression Pattern to Flk-1 mRNA. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrthum, A.; Devriendt, K.; Chitayat, D.; Matthijs, G.; Glade, C.; Steijlen, P.M.; Fryns, J.-P.; Van Steensel, M.A.M.; Vikkula, M. Mutations in the Transcription Factor Gene SOX18 Underlie Recessive and Dominant Forms of Hypotrichosis-Lymphedema-Telangiectasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Katoh, M. Expression of human SOX18 in normal tissues and tumors. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 10, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, T.; Koltowska, K.; Pichol-Thievend, C.; Le Guen, L.; Fontaine, F.; Smith, K.A.; Truong, V.; Skoczylas, R.; Stacker, S.A.; Achen, M.G.; et al. VEGFD regulates blood vascular development by modulating SOX18 activity. Blood 2014, 123, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pula, B.; Olbromski, M.; Wojnar, A.; Gomulkiewicz, A.; Witkiewicz, W.; Ugorski, M.; Dzięgiel, P.; Podhorska-Okolow, M. Impact of SOX18 expression in cancer cells and vessels on the outcome of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2013, 36, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pula, B.; Kobierzycki, C.; Solinski, D.; Olbromski, M.; Nowak-Markwitz, E.; Spaczyński, M.; Kędzia, W.; Zabel, M.; Dziegiel, P. SOX18 expression predicts response to platinum-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar]
- Ornat, M.; Kobierzycki, C.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Pula, B.; Zamirska, A.; Bieniek, A.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Dziegiel, P.; Podhorska-Okolow, M. SOX18 Expression in Non-melanoma Skin Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jethon, A.; Pula, B.; Olbromski, M.; Werynska, B.; Muszczynska-Bernhard, B.; Witkiewicz, W.; Dziegiel, P.; Podhorska-Okolow, M. Prognostic significance of SOX18 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.; Hahn, C.N.; Poh, A.; Dong, C.; Wilhelm, D.; Olsson, J.E.; Muscat, G.E.; Parsons, P.G.; Gamble, J.R.; Koopman, P. Effect of Disrupted SOX18 Transcription Factor Function on Tumor Growth, Vascularization, and Endothelial Development. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, B.M.; Wyeth, J.R.; Pennisi, D.J.; Wang, S.-C.M.; Koopman, P.; Muscat, G.E. Cloning and functional analysis of the Sry -related HMG box gene, Sox18. Gene 2001, 262, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeth, M.; Niederleithner, H.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Bilban, M.; Mayer, H.; Resch, U.; Lemberger, C.; Wagner, O.; Hofer, E.; Petzelbauer, P.; et al. The Transcription Factor SOX18 Regulates the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 and Guidance Molecules in Human Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, B.; Jo, M.J.; Kook, M.-C.; Ryu, K.W.; Choi, I.J.; Nam, B.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Lee, J.H. The lymphangiogenic factor SOX 18: A key indicator to stage gastric tumor progression. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammann, R.; Strunnikova, M.; Schagdarsurengin, U.; Rastetter, M.; Papritz, M.; Hattenhorst, U.E.; Hofmann, H.-S.; Silber, R.-E.; Burdach, S.; Hansen, G. CpG island methylation and expression of tumour-associated genes in lung carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhikina, T.L.; Kozlova, A.; Skvortsov, T.A.; Sverdlov, E. Heterogeneity and degree of TIMP4, GATA4, SOX18, and EGFL7 gene promoter methylation in non–small cell lung cancer and surrounding tissues. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, J.; Esteller, M. Cancer epigenomics: Beyond genomics. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, A.; Gaudet, F.; Waghmare, A.; Jaenisch, R. Chromosomal Instability and Tumors Promoted by DNA Hypomethylation. Science 2003, 300, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvisi, D.F.; Simile, M.M.; Ladu, S.; Pellegrino, R.; De Murtas, V.; Pinna, F.; Tomasi, M.L.; Frau, M.; Virdis, P.; De Miglio, M.R.; et al. Altered methionine metabolism and global DNA methylation in liver cancer: Relationship with genomic instability and prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.F. A Mouse Skin Multistage Carcinogenesis Model Reflects the Aberrant DNA Methylation Patterns of Human Tumors. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5527–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, B.-H.; Cho, N.-Y.; Yoo, E.J.; Choi, M.; Shin, S.-H.; Jang, J.J.; Suh, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kang, G.H. Prognostic Implications of and Relationship between CpG Island Hypermethylation and Repetitive DNA Hypomethylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, A.T. The promise and the problems of epigenetic biomarkers in cancer. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2011, 5, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzner, B.; Kemmler, G.; Greil, R.; Kopp, M.; Zeimet, A.; Raderer, M.; Hejna, M.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Krajnik, G.; Huber, H.; et al. The impact of hemoglobin levels on fatigue and quality of life in cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlodrop, I.J.H.; Niessen, H.E.C.; Derks, S.; Baldewijns, M.M.L.L.; Van Criekinge, W.; Herman, J.G.; Van Engeland, M. Analysis of Promoter CpG Island Hypermethylation in Cancer: Location, Location, Location! Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.-G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; et al. MicroRNA Gene Expression Deregulation in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairinger, F.D.; Ting, S.; Werner, R.; Walter, R.F.H.; Hager, T.; Vollbrecht, C.; Christoph, D.C.; Worm, K.; Mairinger, T.; Sheu-Grabellus, S.-Y.; et al. Different micro-RNA expression profiles distinguish subtypes of neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: Results of a profiling study. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L. Effect of smoking on the microRNAs expression in pneumoconiosis patients. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, W.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Guo, L. MicroRNA-155 modulates Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation and is associated with multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 266, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, C.; Yuan, X.; He, J.-T.; Pan, Q.-H.; Sun, F.-Y. microRNA-155 acts as an oncogene by targeting the tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Olbromski, M.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Jankowska-Konsur, A.; Witkiewicz, W.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P. MicroRNAs modulate the expression of the SOX18 transcript in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, X.; Leng, X. MiR-7-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting SOX18 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, Z.-H.; Huang, B.; Wang, D. Characterization, phylogeny, alternative splicing and expression of Sox30 gene. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, E.; Nishina, Y.; Inazawa, J.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Ohsugi, M.; Tezuka, T.; Yoshida, M.; Semba, K. Identification of a novel Sry-related gene and its germ cell-specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Dong, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, X.; Shi, R.; Chen, H.; Cui, Z.; Ao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Sox30 Is Associated with Testis Development in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y. SOX30 confers a tumor suppressive effect in acute myeloid leukemia through inactivation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 52, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.-J.; Wen, X.-M.; Zhou, J.-D.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Z.-J.; Guo, H.; Ma, J.-C.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Lin, J.; et al. SOX30 methylation correlates with disease progression in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 4789–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, W. Correlation of sex-determining region Y-box 30 with tumor characteristics and its prognostic value in breast cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birrer, M.J.; Johnson, M.E.; Hao, K.; Wong, K.-K.; Park, D.-C.; Bell, A.; Welch, W.R.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Mok, S.C. Whole Genome Oligonucleotide-Based Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis Identified Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 As a Prognostic Marker for Advanced-Stage Serous Ovarian Adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, W.-B.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, M.-Q.; Yang, J.-T.; Zhang, X.; Hao, X.-L.; Yin, L.; Mao, C.-Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. SOX30 is a prognostic biomarker and chemotherapeutic indicator for advanced-stage ovarian cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, X1–X2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q. SOX30, a target gene of miR-653-5p, represses the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells through inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhong, J.; Wu, C.; Yang, G.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, A. Decreased expression of SRY-box containing gene 30 is related to malignant phenotypes of human bladder cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.T.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, R.H.; Wang, F.H.; Li, X.Y.; Hondermarck, H.; Thorne, R.F.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. MicroRNA-645 is an oncogenic regulator in colon cancer. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, E.; Burek, M.; Foerster, C. Tight Junctions and the Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2016, 4, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-Q.; Gao, Y.-F.; Zhou, H.-H.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Jin, W.-L. Gap junction as an intercellular glue: Emerging roles in cancer EMT and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, T.; Mesnil, M.; Naus, C.C.; Lampe, P.D.; Laird, D.W. Gap junctions and cancer: Communicating for 50 years. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 16, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celentano, A.; Mignogna, M.D.; McCullough, M.; Cirillo, N. Pathophysiology of the Desmo-Adhesome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Palencia, A.; Gomez-Morales, M.; Gomez-Capilla, J.A.; Pedraza, V.; Boyero, L.; Rosell, R.; Fárez-Vidal, M.E. Gene expression profiling reveals novel biomarkers in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Morales, M.; Cámara-Pulido, M.; Miranda-León, M.T.; Sanchez-Palencia, A.; Boyero, L.; Gomez-Capilla, J.A.; Fárez-Vidal, M.E. Differential immunohistochemical localization of desmosomal plaque-related proteins in non-small-cell lung cancer. Histopathology 2013, 63, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, C.; Daigo, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Kato, T.; Ito, T.; Tsuchiya, E.; Sone, S.; Nakamura, Y. Plakophilin 3 Oncogene as Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target for Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7102–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Mireskandari, M.; Knösel, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kohler, L.H.; Kunze, A.; Presselt, N.; Petersen, I. Diagnostic and prognostic impact of desmocollins in human lung cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, M.-Q.; Liu, W.-B.; Sun, L.; Hao, X.-L.; Yin, L.; Jiang, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, J. SOX30 specially prevents Wnt-signaling to suppress metastasis and improve prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Lyons, J.P.; Mori-Akiyama, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Water-soluble extract of Saxifraga stolonifera has anti-tumor effects on Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4671–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, W.B.; Shi, X.Y.; Yang, J.T.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.M. SOX30 Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Attenuating Wnt-Signaling via Transcriptional and Posttranslational Regulation of beta-Catenin in Lung Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 31, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, H. SOX6 suppresses cyclin D1 promoter activity by interacting with beta-catenin and histone deacetylase 1, and its down-regulation induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19052–19061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansukhani, A.; Ambrosetti, D.; Holmes, G.; Cornivelli, L.; Basilico, C. Sox2 induction by FGF and FGFR2 activating mutations inhibits Wnt signaling and osteoblast differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olbromski, M.; Podhorska-Okołów, M.; Dzięgiel, P. Role of SOX Protein Groups F and H in Lung Cancer Progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113235
Olbromski M, Podhorska-Okołów M, Dzięgiel P. Role of SOX Protein Groups F and H in Lung Cancer Progression. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113235
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlbromski, Mateusz, Marzenna Podhorska-Okołów, and Piotr Dzięgiel. 2020. "Role of SOX Protein Groups F and H in Lung Cancer Progression" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113235
APA StyleOlbromski, M., Podhorska-Okołów, M., & Dzięgiel, P. (2020). Role of SOX Protein Groups F and H in Lung Cancer Progression. Cancers, 12(11), 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113235