In Vivo Lymphatic Circulating Tumor Cells and Progression of Metastatic Disease
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
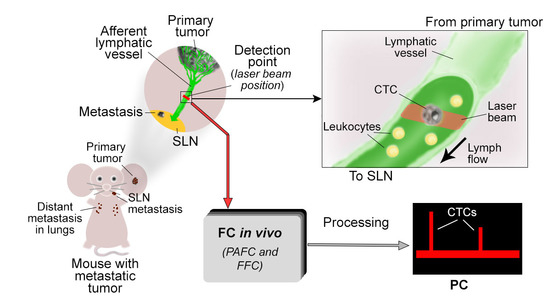
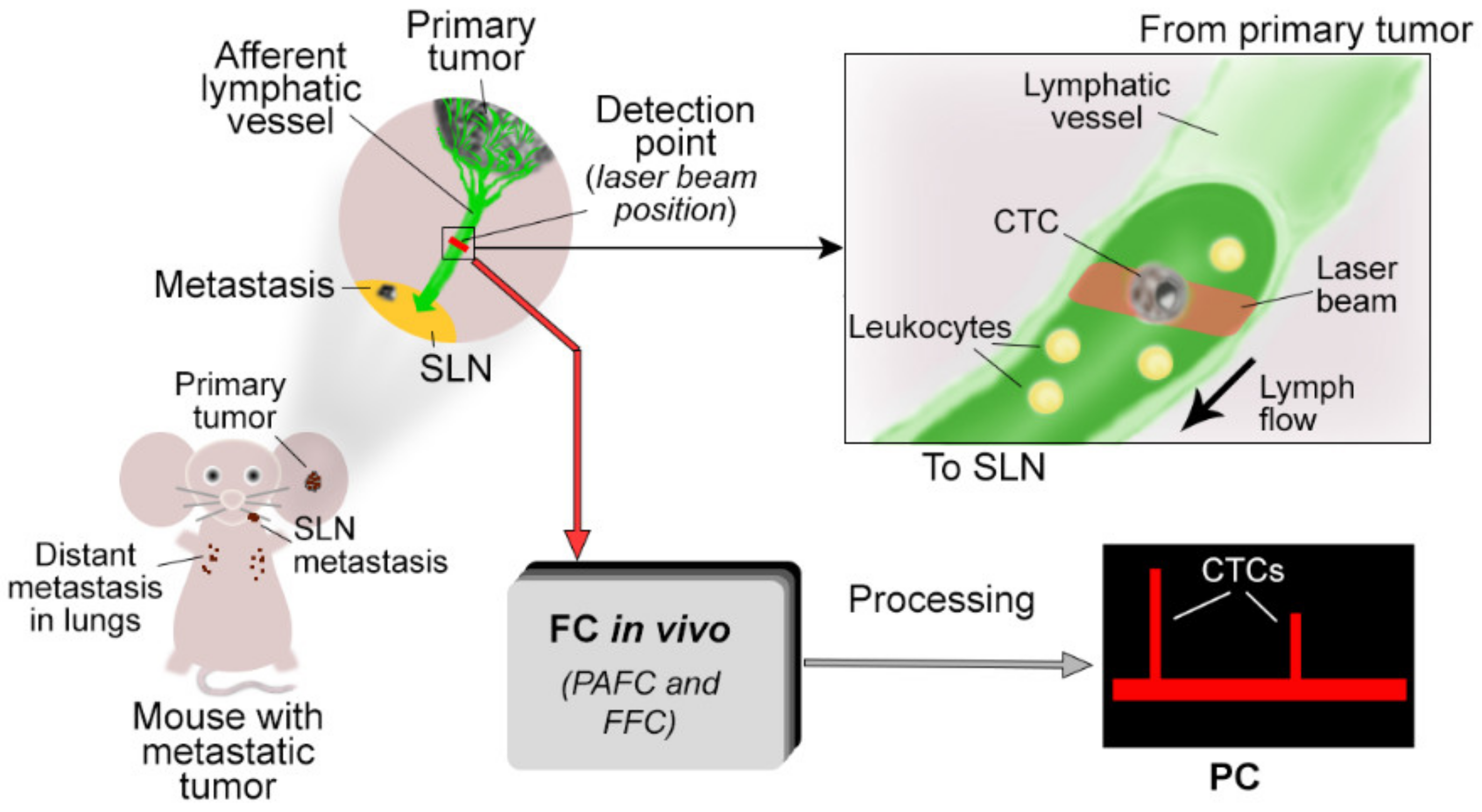
2.1. Optimization of PAFC and FFC Platforms for Detection of L-CTCs
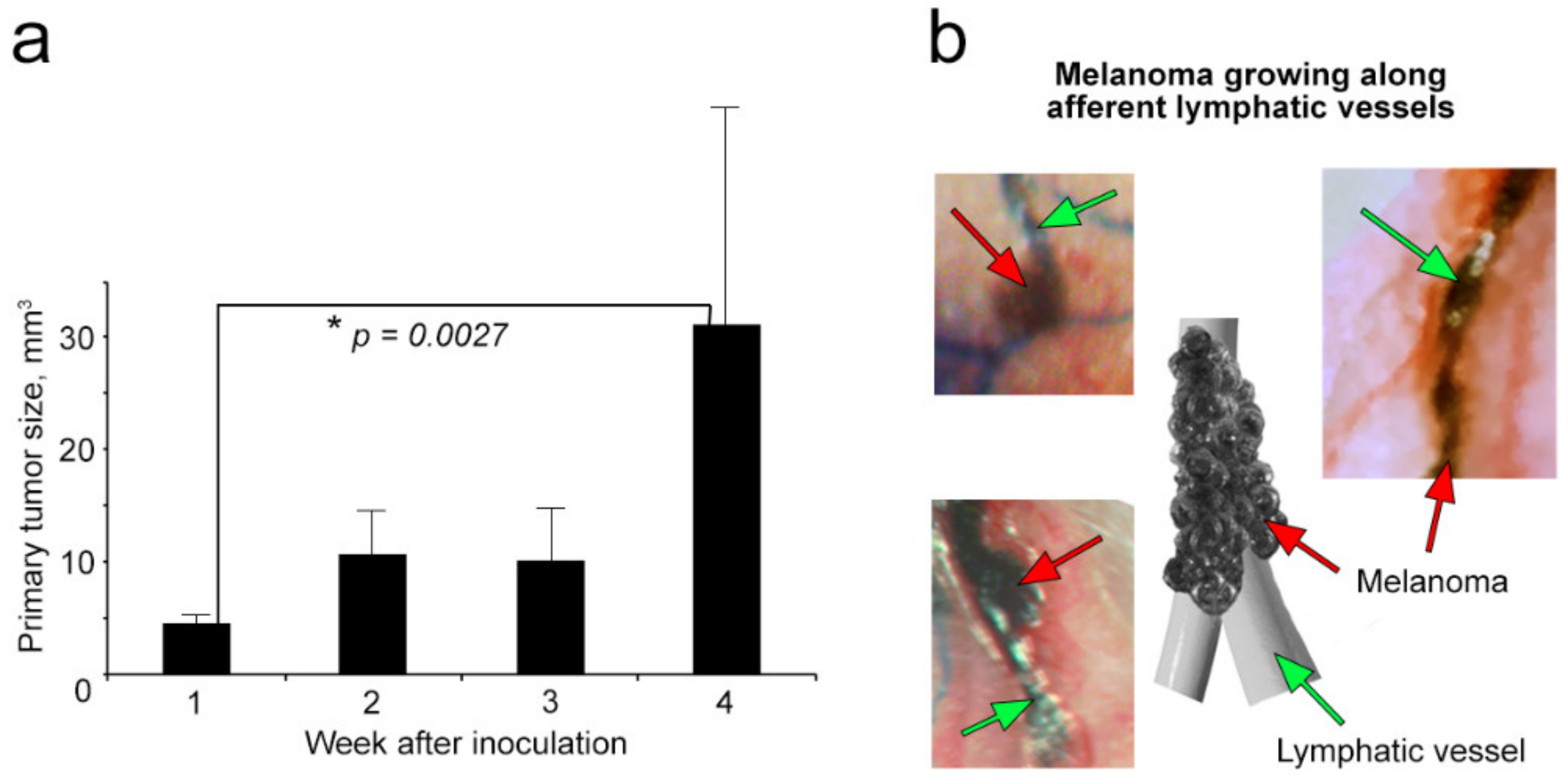
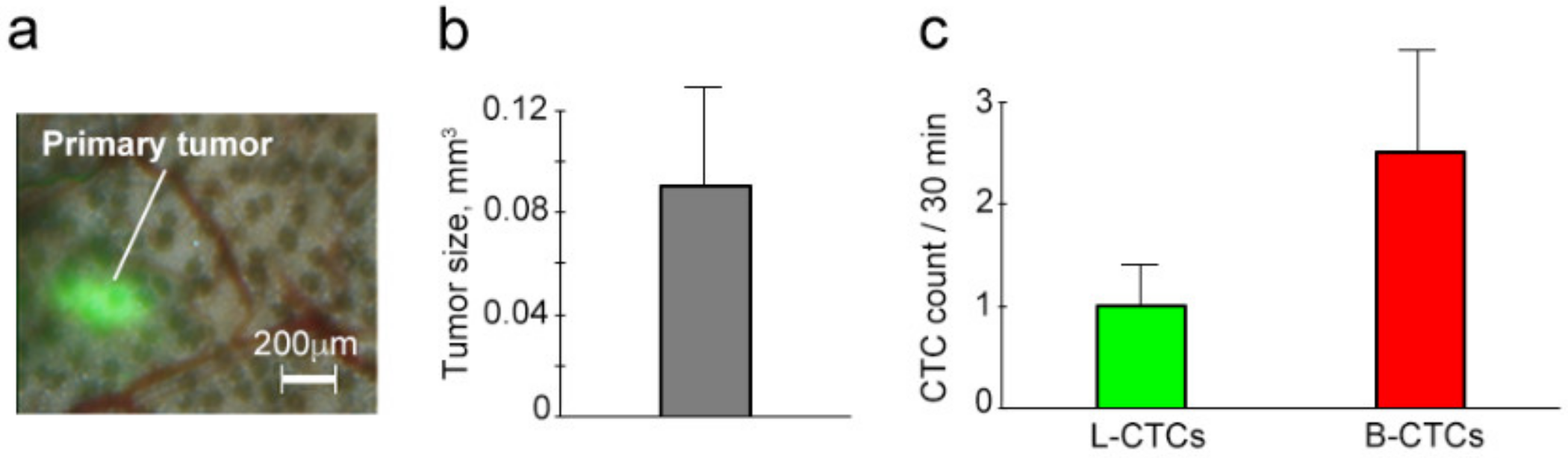
2.2. Growth of Primary Melanoma
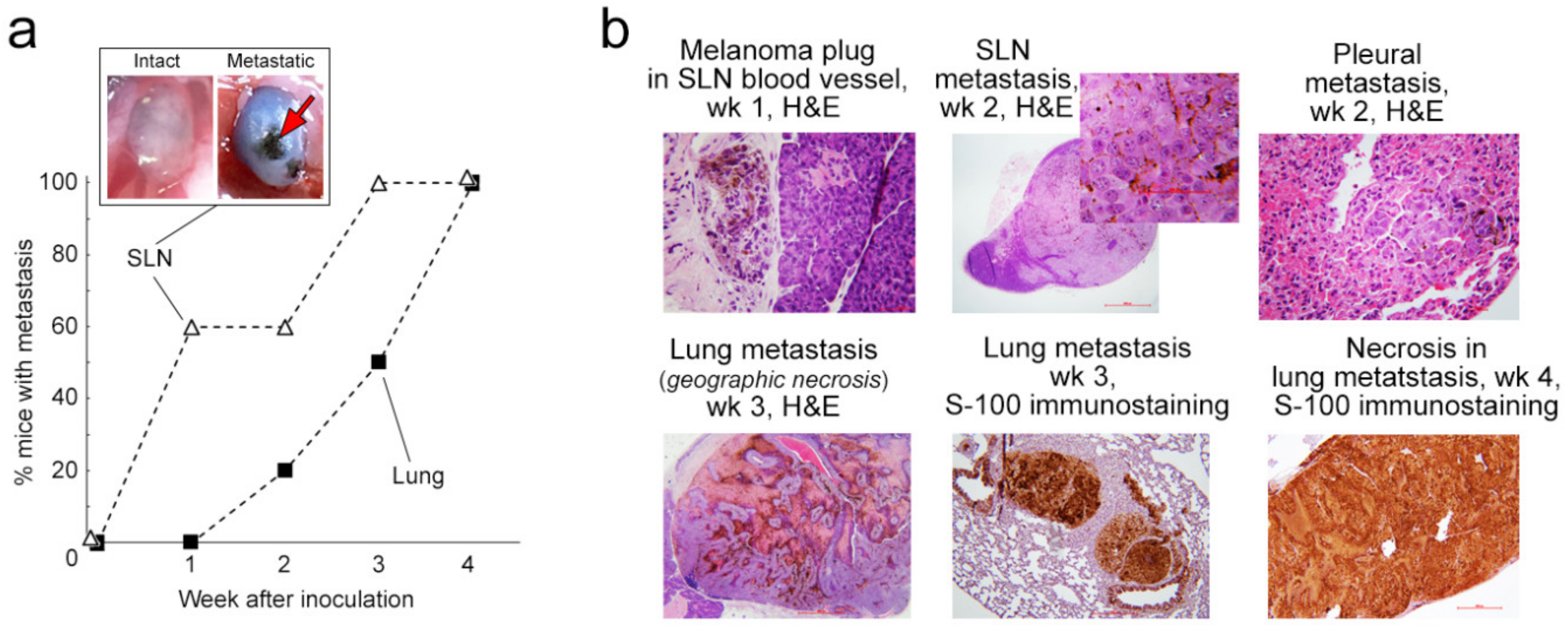
2.3. Progress of Metastasis: Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
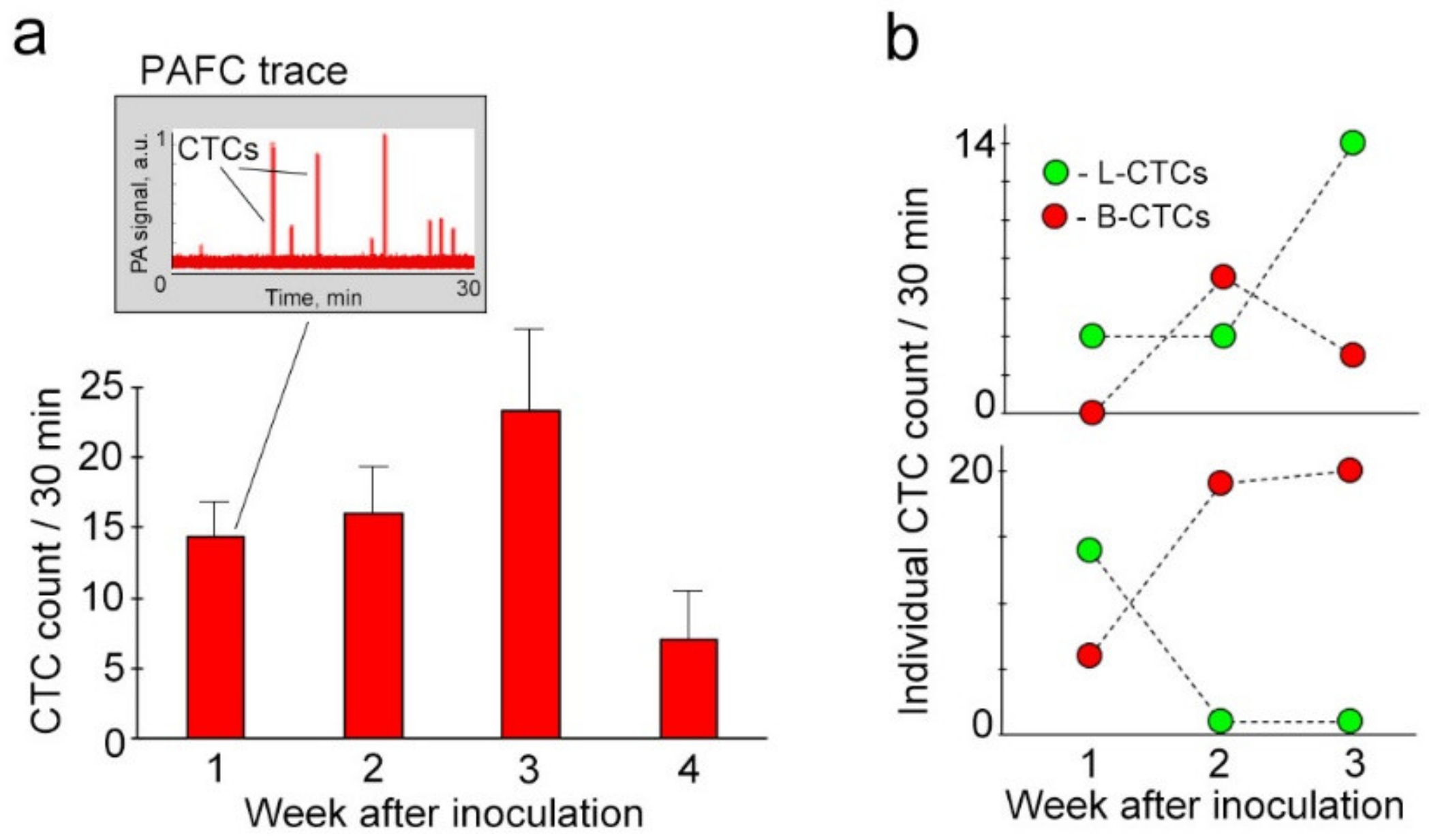
2.4. Real-Time Quantification and Individual Dynamic of Spontaneous L-CTCs over Melanoma Progression
2.5. Parallel Progression of L-CTCs and B-CTCs and Their Cross-Talk In Vivo
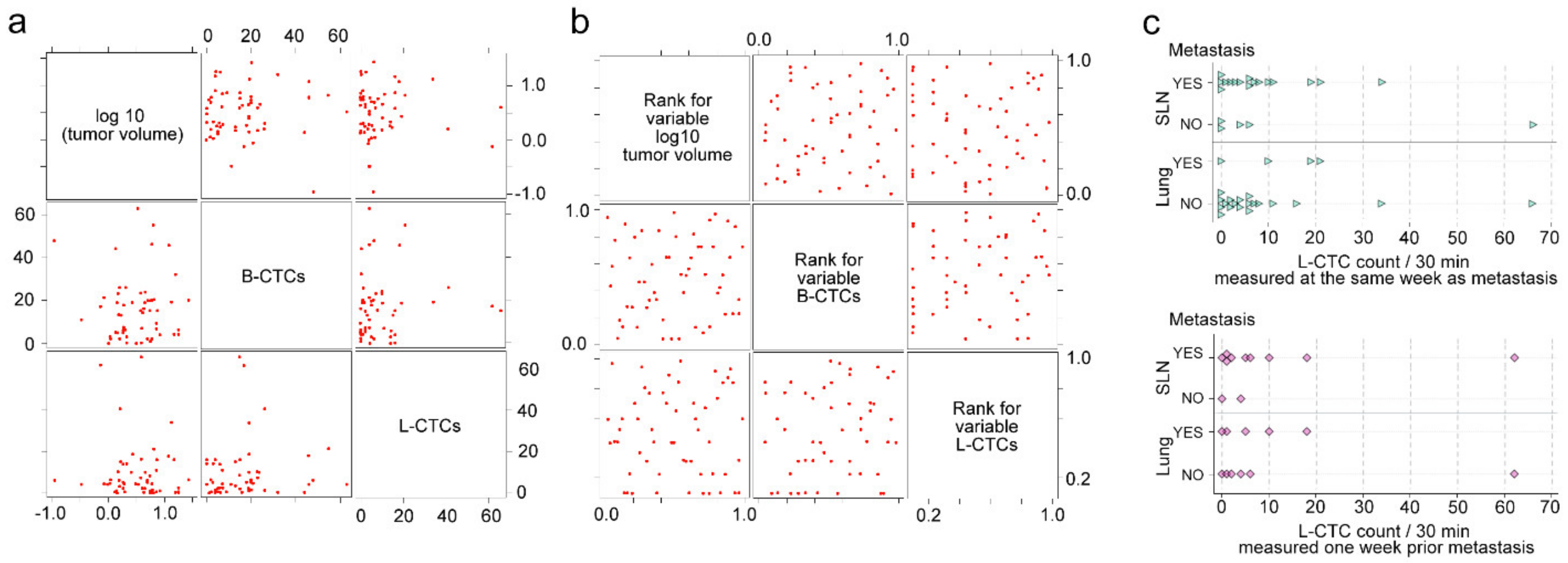
2.6. Correlations of L-CTCs Counts with Primary Tumor Size, Metastasis and B-CTCs
2.7. Detection of L-CTCs in Metastatic Breast Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tumor Cell Lines
4.2. Mouse Model
4.3. In Vivo PAFC and FFC
4.4. Mapping Afferent Lymphatic Vessels with Evans Blue (EB) Dye
4.5. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, S.C.P. Circulating tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, I.J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: The “seed and soil” hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.A. Parallel progression of primary tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicha, M.S.; Hayes, D.F. Circulating tumor cells: Not all detected cells are bad and not all bad cells are detected. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1508–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.K.; Cummins, A.G.; Price, T.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Hardingham, J.E. Circulating tumour cells: The evolving concept and the inadequacy of their enrichment by EPCAM-based methodology for baskc clinical cancer research. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Pantel, K. Unravelling tumour heterogeneity by single-cell profiling of circulating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Stott, S.L.; Smas, M.E.; Ting, D.T.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Wells, M.N.; Shah, A.M.; et al. Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science 2013, 339, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genna, A.; Vanwynsberghe, A.M.; Villard, A.V.; Pottier, C.; Ancel, J.; Polette, M.; Gilles, C. EMT-associated heterogeneity in circulating tumor cells: Sticky friends on the road to metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanzha, E.; Zharov, V. Circulating Tumor Cell Detection and Capture by Photoacoustic Flow Cytometry in Vivo and ex Vivo. Cancers 2013, 5, 1691–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Shashkov, E.V.; Spring, P.M.; Suen, J.Y.; Zharov, V.P. In vivo, noninvasive, label-free detection and eradication of circulating metastatic melanoma cells using two-color photoacoustic flow cytometry with a diode laser. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7926–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Shashkov, E.V.; Kelly, T.; Kim, J.W.; Yang, L.; Zharov, V.P. In vivo magnetic enrichment and multiplex photoacoustic detection of circulating tumour cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wang, H.; Hartmann, L.C.; Cheng, J.X.; Low, P.S. In vivo quantitation of rare circulating tumor cells by multiphoton intravital flow cytometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11760–11765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Yao, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Huang, C.H.; Zou, J.; Wang, L.V. In vivo label-free photoacoustic flow cytography and on-the-spot laser killing of single circulating melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Wei, X.; Prossin, A.; Lin, C.P. In vivo flow cytometer for real-time detection and quantification of circulating cells. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.C.; Yan, J.; Liu, G.D.; Tan, X.Y.; Weng, X.F.; Wu, W.Z.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.B. Real-time monitoring of rare circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells in an orthotopic model by in vivo flow cytometry assesses resection on metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Menyaev, Y.A.; Yadem, A.C.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Juratli, M.A.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Foster, S.R.; Jamshidi-Parsian, A.; Siegel, E.R.; Makhoul, I.; et al. In vivo liquid biopsy using Cytophone platform for photoacoustic detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with melanoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Zharov, V.P. Photoacoustic flow cytometry. Methods 2012, 57, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Galanzha, E.I.; Shashkov, E.V.; Moon, H.M.; Zharov, V.P. Golden carbon nanotubes as multimodal photoacoustic and photothermal high-contrast molecular agents. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Weingold, R.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Nolan, J.; Harrington, W.; Kuchyanov, A.S.; Parkhomenko, R.G.; Watanabe, F.; Nima, Z.; et al. Spaser as a biological probe. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashchenok, A.M.; Jose, J.; Trochet, P.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Gorin, D.A. Multifunctional polyelectrolyte microcapsules as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging in blood. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselova, M.V.; Bratashov, D.N.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Harrington, W.; Watts, A.; Han, M.; Khlebtsov, B.N.; Galanzha, E.I.; Gorin, D.A.; et al. Photoacoustic and fluorescent effects in multilayer plasmon-dye interfaces. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nima, Z.A.; Watanabe, F.; Jamshidi-Parsian, A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Han, M.; Watts, J.A.; Biris, A.S.; Zharov, V.P.; Galanzha, E.I. Bioinspired magnetic nanoparticles as multimodal photoacoustic, photothermal and photomechanical contrast agents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedosekin, D.A.; Juratli, M.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Moore, C.L.; Rusch, N.J.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Zharov, V.P.; Galanzha, E.I. Photoacoustic and photothermal detection of circulating tumor cells, bacteria and nanoparticles in cerebrospinal fluid in vivo and ex vivo. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, I.; McGinty, F. Lymphatic metastasis and its inhibition: An experimental model. J. Pathol. 1974, 113, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujam, F.J.A.; Going, J.J.; Edwards, J.; Mohammed, Z.M.A.; McMillan, D.C. The role of lymphatic and blood vessel invasion in predicting survival and methods of detection in patients with primary operable breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 89, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, M.H.; Jones, K.; Wilting, J.; Dictor, M.; Selg, M.; McHale, N.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Jackson, D.G. Structure function relationships in the lymphatic system and implications for cancer biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgrabinska, S.; Skobe, M. Role of lymphatic vasculature in regional and distant metastases. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 95, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Dieterich, L.C.; Ikenberg, K.; Bachmann, S.B.; Mangana, J.; Proulx, S.T.; Amann, V.C.; Levesque, M.P.; Dummer, R.; Baluk, P.; et al. Unexpected contribution of lymphatic vessels to promotion of distant metastatic tumor spread. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, F.L.; Page, D.L.; Fleming, I.D.; Fritz, A.G.; Balch, C.M.; Haller, D.G.; Morrow, M. AJCC: Cancer Staging Manual, 6th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Foldi, M.; Foldi, E.; Kubik, S. Foldi’s Textbook of Lymphology; Urban & Fishwer: Munich, Germany, 2003; p. 690. [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski, W.L. The lymphatic system in body homeostasis: Physiological conditions. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2003, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajita, H.; Kishi, K. High-resolution imaging of lymphatic vessels with photoacoustic lymphangiography. Radiology 2019, 292, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Kokoska, M.S.; Shashkov, E.V.; Kim, J.W.; Tuchin, V.V.; Zharov, V.P. In vivo fiber-based multicolor photoacoustic detection and photothermal purging of metastasis in sentinel lymph nodes targeted by nanoparticles. J. Biophotonics 2009, 2, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanzha, E.I.; Shashkov, E.V.; Tuchin, V.V.; Zharov, V.P. In vivo multispectral, multiparameter, photoacoustic lymph flow cytometry with natural cell focusing, label-free detection and multicolor nanoparticle probes. Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewski, W.L. Collection and physiological measurements of peripheral lymph and interstitial fluid in man. Lymphology 1977, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pucci, F.; Garris, C.; Lai, C.P.; Newton, A.; Pfirschke, C.; Engblom, C.; Alvarez, D.; Sprachman, M.; Evavold, C.; Magnuson, A.; et al. SCS macrophages suppress melanoma by restricting tumor-derived vesicle-B cell interactions. Science 2016, 352, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Jiang, P.; Yamauchi, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Tsuchiya, H.; Tomita, K.; Moossa, A.R.; Bouvet, M.; Hoffman, R.M. Real-time imaging of tumor-cell shedding and trafficking in lymphatic channels. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8223–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedosekin, D.A.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Melerzanov, A.V.; Zharov, V.P.; Galanzha, E.I. In vivo photoswitchable flow cytometry for direct tracking of single circulating Tumor Cells. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, R. Defining the highway of lymphatic patterns for melanoma. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Derakhshan, M.; Darabi, H.; Hedayat, P.; Momeni, M. Melanoma: Where we are and where we go. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juratli, M.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Melerzanov, A.V.; Zharov, V.P.; Galanzha, E.I. Dynamic fluctuation of circulating tumor cells during cancer progression. Cancers 2014, 6, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naxerova, K.; Reiter, J.G.; Brachtel, E.; Lennerz, J.K.; Van De Wetering, M.; Rowan, A.; Cai, T.; Clevers, H.; Swanton, C.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. Origins of lymphatic and distant metastases in human colorectal cancer. Science 2017, 357, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedrin, D.; Gligorijevic, B.; Wyckoff, J.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Condeelis, J.; Segall, J.E.; van Rheenen, J. Intravital imaging of metastatic behavior through a mammary imaging window. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schineis, P.; Runge, P.; Halin, C. Cellular traffic through afferent lymphatic vessels. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2019, 112, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, G.; Kipnis, J.; Randolph, G.J.; Harvey, N.L. The Lymphatic Vasculature in the 21st Century: Novel Functional Roles in Homeostasis and Disease. Cell 2020, 182, 270–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.T.; Alférez, D.G.; Amant, F.; Annibali, D.; Arribas, J.; Biankin, A.V.; Bruna, A.; Budinská, E.; Caldas, C.; Chang, D.K.; et al. Interrogating open issues in cancer precision medicine with patient-derived xenografts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. Metastatic colonization: Settlement, adaptation and propagation of tumor cells in a foreign tissue environment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammela, T.; Saaristo, A.; Holopainen, T.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Andersson, L.C.; Virolainen, S.; Immonen, I.; Alitalo, K. Photodynamic ablation of lymphatic vessels and intralymphatic cancer cells prevents metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, I.J. Biological heterogeneity of cancer. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 1141–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, E.; Shackleton, M.; Sabel, M.S.; Fullen, D.R.; Johnson, T.M.; Morrison, S.J. Efficient tumour formation by single human melanoma cells. Nature 2008, 456, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.R.; Fidler, I.J. Tumor cell-organ microenvironment interactions in the pathogenesis of cancer metastasis. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Heller, D.A.; Winslow, M.M.; Dahlman, J.E.; Pratt, G.W.; Langer, R.; Jacks, T.; Anderson, D.G. Treating metastatic cancer with nanotechnology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, R.; Clement, O.; Bittoun, J.; Carnot, F.; Frija, G. MR lymphography with superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles in rats: Pathologic basis for contrast enhancement. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 162, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Week(s) After Inoculation | Number of Mice | SNL Metastasis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastasis; % Mice | % SLN Involvement | Mitotic Activity; % Mice | Apoptosis | Necrosis | ||
| 1 | N = 12 | 60 | 9.95 ± 2.72 | No | No | No |
| 2 | N = 5 | 60 | 63.33 ± 6.67 | No | No | Yes |
| 3 | N = 10 | 100 | 100 | 11.8 ± 1.1/hpf * (100%) | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | N = 5 | 100 | 100 | 13.2 ± 1.3/hpf (100%) | Yes | Yes |
| Week(s) After Inoculation | Number of Mice | Distant Metastasis (Lung) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastasis; % Mice | Mitotic Activity; % Mice | Apoptosis | Necrosis | ||
| 1 | N = 12 | 0 | - | - | - |
| 2 | N = 5 | 20 | No | No | No |
| 3 | N = 10 | 50 | 11.7 ± 0.7 / hpf (20%) | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | N = 5 | 100 | 12.9 ± 0.8 / hpf (60%) | Yes | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Watts, J.A.; Jamshidi-Parsian, A.; Nadeem, U.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Siegel, E.R.; Zharov, V.P.; Galanzha, E.I. In Vivo Lymphatic Circulating Tumor Cells and Progression of Metastatic Disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102866
Han M, Watts JA, Jamshidi-Parsian A, Nadeem U, Sarimollaoglu M, Siegel ER, Zharov VP, Galanzha EI. In Vivo Lymphatic Circulating Tumor Cells and Progression of Metastatic Disease. Cancers. 2020; 12(10):2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102866
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Mikyung, Julia Alex Watts, Azemat Jamshidi-Parsian, Urooba Nadeem, Mustafa Sarimollaoglu, Eric R. Siegel, Vladimir P. Zharov, and Ekaterina I. Galanzha. 2020. "In Vivo Lymphatic Circulating Tumor Cells and Progression of Metastatic Disease" Cancers 12, no. 10: 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102866
APA StyleHan, M., Watts, J. A., Jamshidi-Parsian, A., Nadeem, U., Sarimollaoglu, M., Siegel, E. R., Zharov, V. P., & Galanzha, E. I. (2020). In Vivo Lymphatic Circulating Tumor Cells and Progression of Metastatic Disease. Cancers, 12(10), 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102866