JNK Pathway Mediates Low Oxygen Level Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
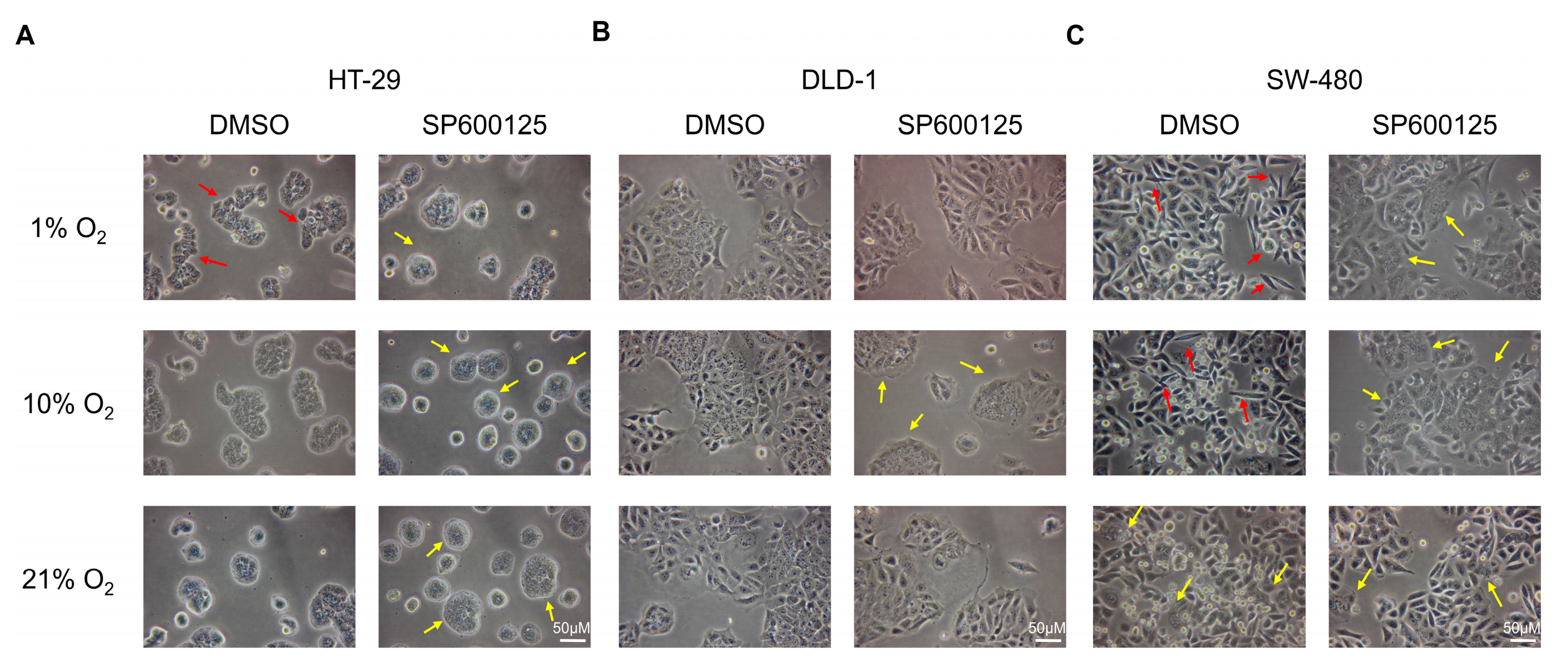
2.1. Low Oxygen Levels Induced Morphological Signs of EMT, Which Was Reversed by JNK Inhibition
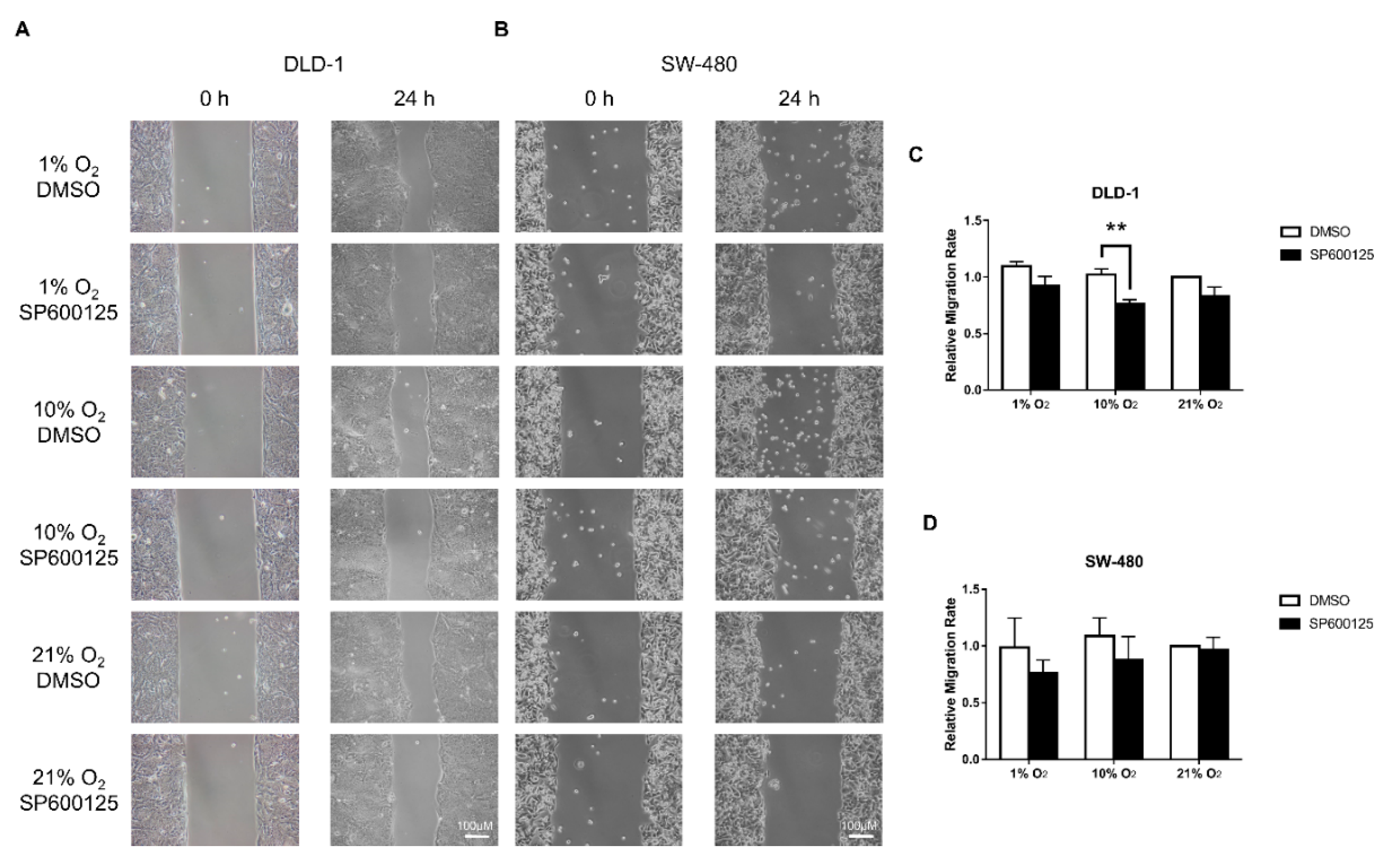
2.2. Cell Migration Was Reduced by JNK Inhibition
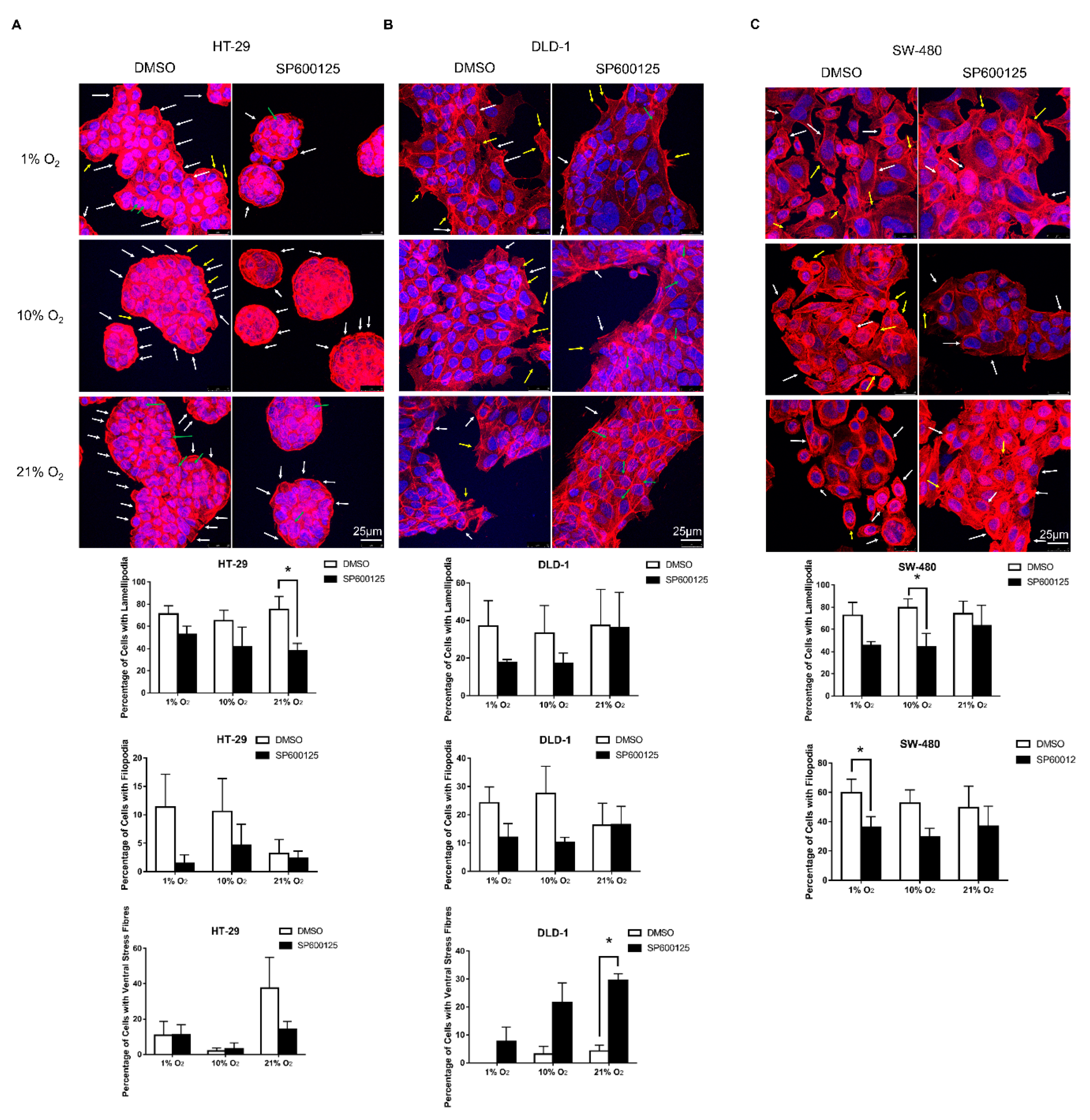
2.3. JNK Inhibition Reduced Lamellipodia and Filopodia Formation
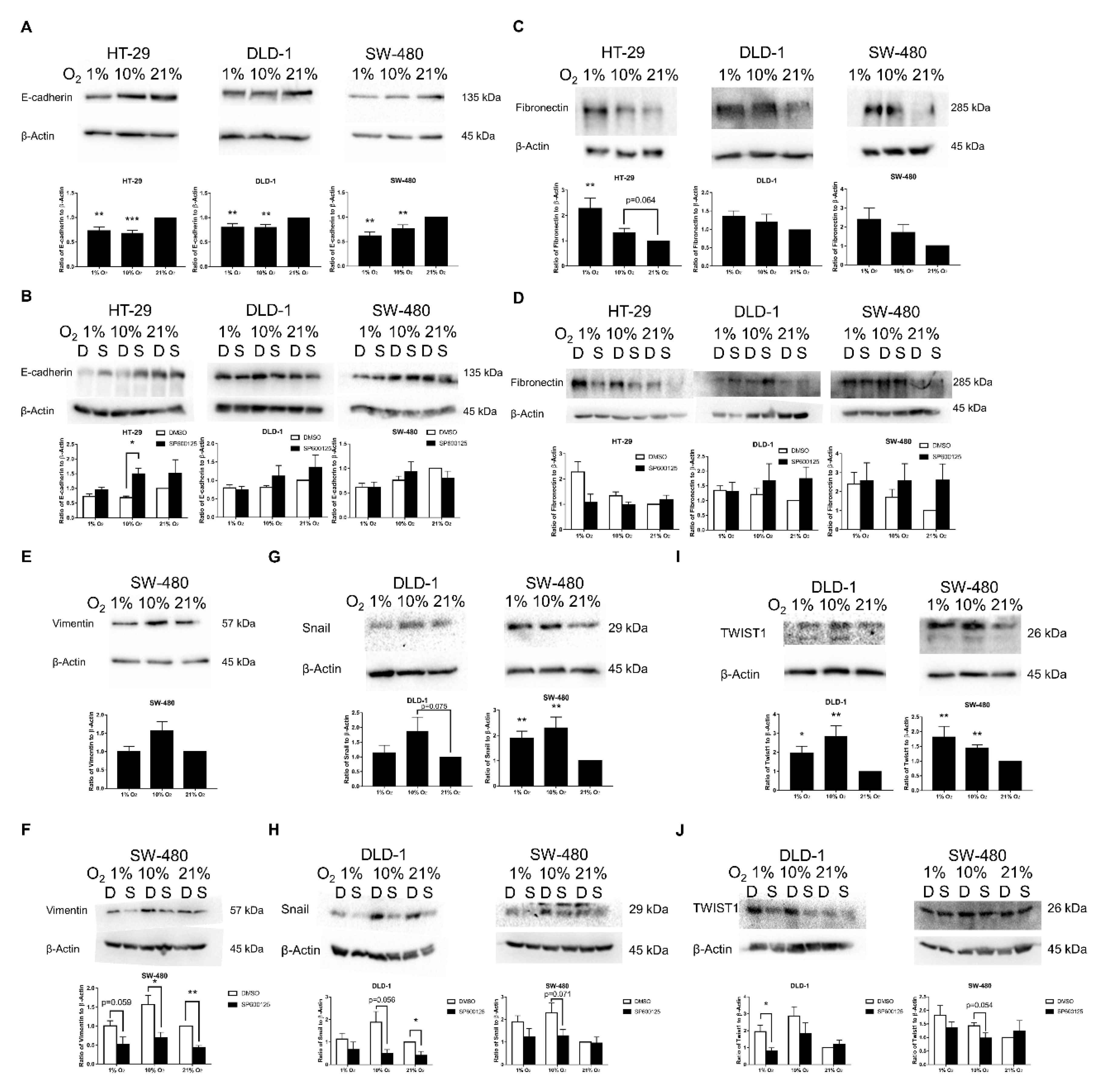
2.4. EMT Induced by Low Oxygen Levels via JNK Pathway Was Confirmed by EMT Markers and Transcription Factors
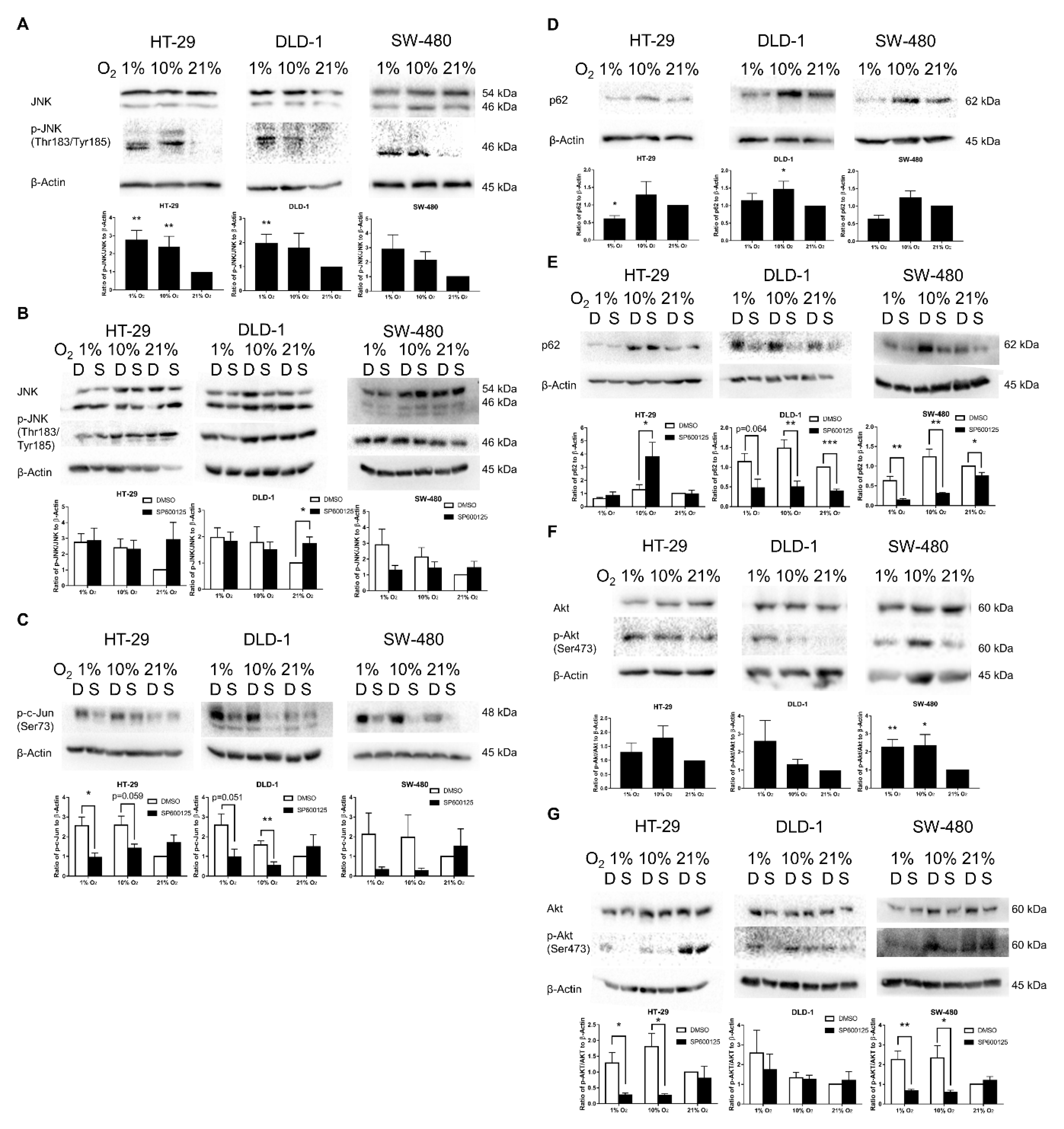
2.5. Confirmation of JNK and Akt Pathway Activation in Low Oxygen Levels
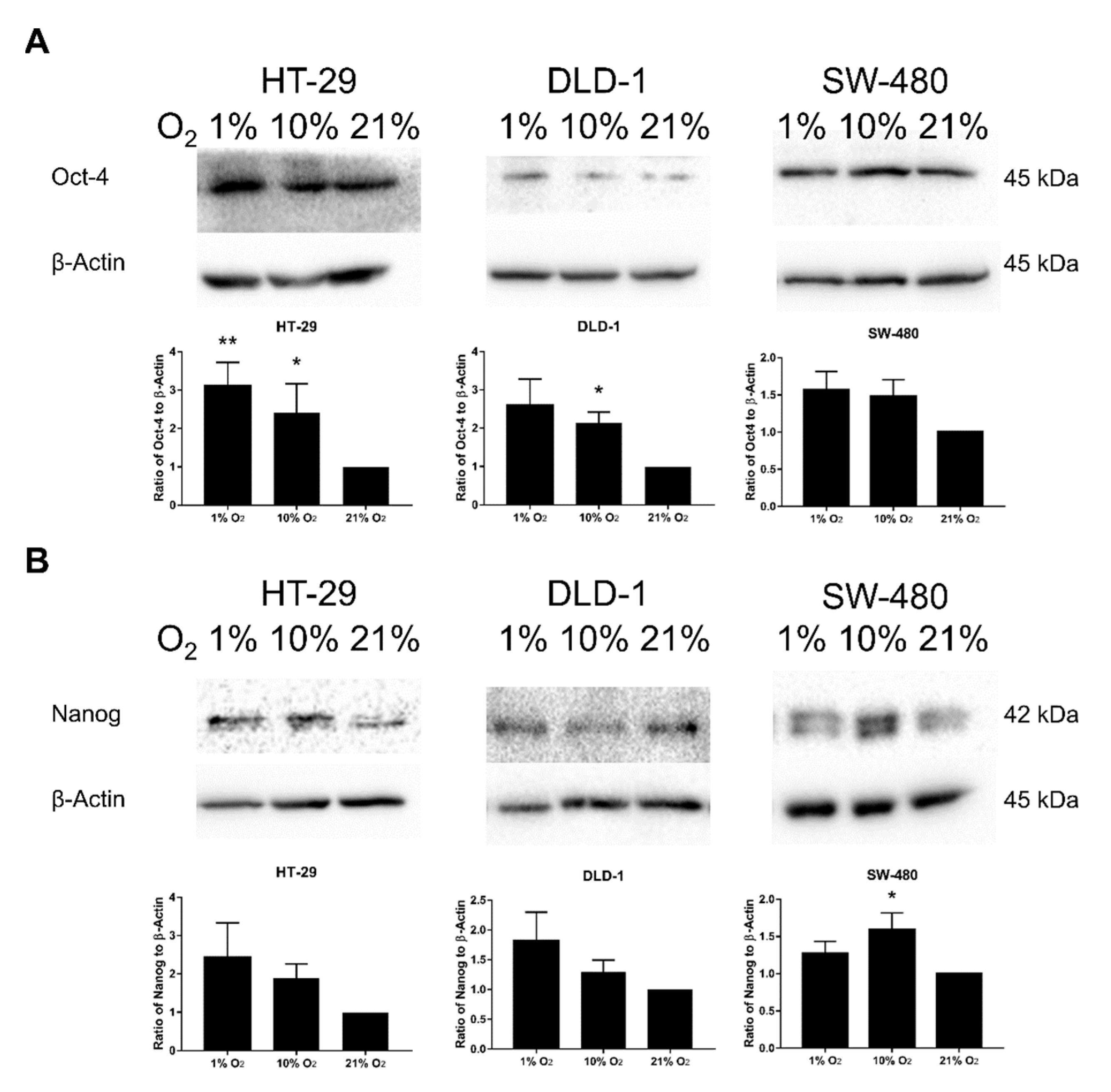
2.6. Promotion of SM under Low Oxygen Levels Was Partially Reversed by JNK Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Hypoxic Condition and JNK Inhibition
4.3. Cell Morphological Analysis
4.4. Cell Migration Assay
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guglielmo, A.; Staropoli, N.; Giancotti, M.; Mauro, M. Personalized medicine in colorectal cancer diagnosis and treatment: A systematic review of health economic evaluations. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2018, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Dai, C.; Peng, S. Mechanism of the mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its relationship with metastatic tumor formation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1608–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, J.; Srivastava, J.; Madson, N.; Wittmann, T.; Barber, D.L. Dynamic actin remodeling during epithelial-mesenchymal transition depends on increased moesin expression. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 4750–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.O.; Fang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, J. Role of cellular cytoskeleton in epithelial-mesenchymal transition process during cancer progression. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.F.; Sahai, E. The actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell motility. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jang, Y.S.; Min, S.Y.; Song, J.Y. Overexpression of MMP-9 and HIF-1α in Breast Cancer Cells under Hypoxic Conditions. J. Breast Cancer 2011, 14, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-J.; Park, S.-A.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.-J. Hypoxia induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells through ubiquitin-specific protease 47-mediated stabilization of Snail: A potential role of Sox9. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.; Kwon, C.I.; Kim, J.W.; Park, P.W.; Hahm, K.B. TWIST1 and SNAI1 as markers of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer are associated with the expression of ALDH1 and TGF-β1. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, Y.; Nie, B.; Pienta, K.J.; Morgan, T.M.; Taichman, R.S. Cancer Stem Cells and their Role in Metastasis. Pharmacel. Ther. 2013, 138, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Du, F.; Luo, Y.; Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Xu, B. The emerging role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 involved in chemo/radioresistance in solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, T.B.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Grosse-Gehling, P.; Baumann, M. Cancer Stem Cells as a Predictive Factor in Radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 22, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadde, R.; Vemula, S.; Jinka, R.; Merchant, N.; Bramhachari, P.V.; Nagaraju, G.P. Role of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) in the maintenance of stemness and malignancy of colorectal cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, S.Y.; Wu, V.W.C.; Law, H.K.W. Dynamics of oxygen level-driven regulators in modulating autophagy in colorectal cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. JNK-Induced Apoptosis, Compensatory Growth, and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sarkissyan, M.; Vadgama, J.V. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Herreros, A. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells as consequence of phenotypic instability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, L.; Fitzner, I.C.; Ahrens, T.; Geißler, A.-L.; Makowiec, F.; Hopt, U.T.; Bogatyreva, L.; Hauschke, D.; Werner, M.; Lassmann, S. Histone modifiers and marks define heterogeneous groups of colorectal carcinomas and affect responses to HDAC inhibitors in vitro. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 664–676. [Google Scholar]
- Spurling, C.C.; Godman, C.A.; Noonan, E.J.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Rosenberg, D.W.; Giardina, C. HDAC3 overexpression and colon cancer cell proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, C.P.; Fedele, A.O.; Linke, S.; Balrak, W.; Lisy, K.; Whitelaw, M.L.; Peet, D.J. Cell-specific regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1α and HIF-2α stabilization and transactivation in a graded oxygen environment. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22575–22585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocevar, B.A.; Brown, T.L.; Howe, P.H. TGF-β induces fibronectin synthesis through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent, Smad4-independent pathway. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocevar, B.A.; Prunier, C.; Howe, P.H. Disabled-2 (Dab2) mediates transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-stimulated fibronectin synthesis through TGFbeta-activated kinase 1 and activation of the JNK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25920–25927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibanez, J.F. JNK mediates TGF-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation of mouse transformed keratinocytes. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5385–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espada, J.; Peinado, H.; Lopez-Serra, L.; Setién, F.; Lopez-Serra, P.; Portela, A.; Renart, J.; Carrasco, E.; Calvo, M.; Juarranz, A.; et al. Regulation of SNAIL1 and E-cadherin function by DNMT1 in a DNA methylation-independent context. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 9194–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiland, D.H.; Ferrarese, R.; Claus, R.; Dai, F.; Masilamani, A.P.; Kling, E.; Weyerbrock, A.; Kling, T.; Nelander, S.; Carro, M.S. c-Jun-N-terminal phosphorylation regulates DNMT1 expression and genome wide methylation in gliomas. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 6940–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.L.; Li, H.P.; Lu, Y.J.; Hsueh, C.; Liang, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Tse, K.P.; Yu, J.S.; Chang, Y.S. Activation of DNA methyltransferase 1 by EBV LMP1 Involves c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase signaling. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11668–11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Feng, X.; Kong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tan, W. JNK signaling maintains the mesenchymal properties of multi-drug resistant human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells through snail and twist1. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.-J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Ye, Z.; Deng, S.-C.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, M.-L.; Huang, K.; Zhong, J.-X.; et al. Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5811–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, M.; Petit, V.; Jain, A.; Amsellem, R.; Johansen, T.; Larue, L.; Codogno, P.; Beau, I. SQSTM1/p62 regulates the expression of junctional proteins through epithelial-mesenchymal transition factors. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Yang, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, F.; Hong, D.-Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.-C.; Chen, Y. Fibronectin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via activation of calpain. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Ichimura, Y. Physiological significance of selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Sasaki, D.T.; Murray, B.W.; O’Leary, E.C.; Sakata, S.T.; Xu, W.; Leisten, J.C.; Motiwala, A.; Pierce, S.; Satoh, Y.; et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ko, Y.S.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Pyo, J.-S.; Jang, B.G.; Hwang, D.H.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, B.L. HER2-induced metastasis is mediated by AKT/JNK/EMT signaling pathway in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9141–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N. A new role for the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, D.N.; Sinha, N.; Naik, P.P.; Bhutia, S.K. Mechanism of autophagic regulation in carcinogenesis and cancer therapeutics. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 39, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, C.J.; Gray, A.; Dive, C. Comparison of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signalling within a panel of human colorectal cancer cell lines with mutant or wild-type PIK3CA. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5123–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjimichael, C.; Chanoumidou, K.; Papadopoulou, N.; Arampatzi, P.; Papamatheakis, J.; Kretsovali, A. Common stemness regulators of embryonic and cancer stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 1150–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, M.J.; Wickremesekera, S.K.; Peng, L.; Tan, S.T.; Itinteang, T. Cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer: A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeineddine, D.; Hammoud, A.A.; Mortada, M.; Boeuf, H. The Oct4 protein: More than a magic stemness marker. Am. J. Stem Cells 2014, 3, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shiou, S.R.; Singh, A.B.; Moorthy, K.; Datta, P.K.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Dhawan, P. Smad4 Regulates Claudin-1 Expression in a Transforming Growth Factor-β–Independent Manner in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford-Richens, K.L.; Rowan, A.J.; Gorman, P.; Halford, S.; Bicknell, D.C.; Wasan, H.S.; Roylance, R.R.; Bodmer, W.F.; Tomlinson, I.P. SMAD4 mutations in colorectal cancer probably occur before chromosomal instability, but after divergence of the microsatellite instability pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9719–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tam, S.Y.; Wu, V.W.C.; Law, H.K.W. JNK Pathway Mediates Low Oxygen Level Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010224
Tam SY, Wu VWC, Law HKW. JNK Pathway Mediates Low Oxygen Level Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010224
Chicago/Turabian StyleTam, Shing Yau, Vincent W.C. Wu, and Helen K.W. Law. 2020. "JNK Pathway Mediates Low Oxygen Level Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 12, no. 1: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010224
APA StyleTam, S. Y., Wu, V. W. C., & Law, H. K. W. (2020). JNK Pathway Mediates Low Oxygen Level Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 12(1), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010224




