PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
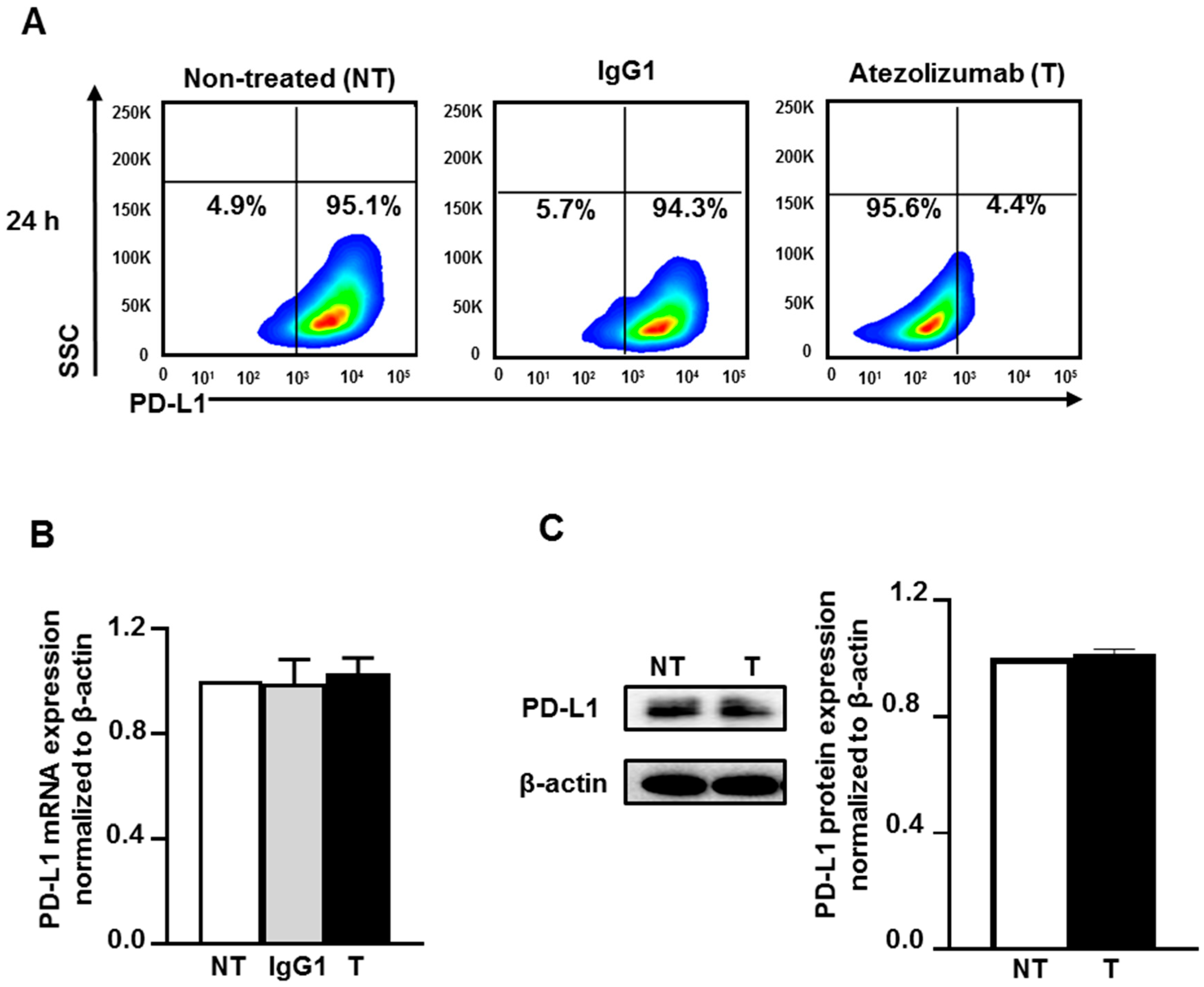
2.1. Atezolizumab Blocks the Epitope of PD-L1 and Does Not Alter PD-L1 mRNA and Protein Expression
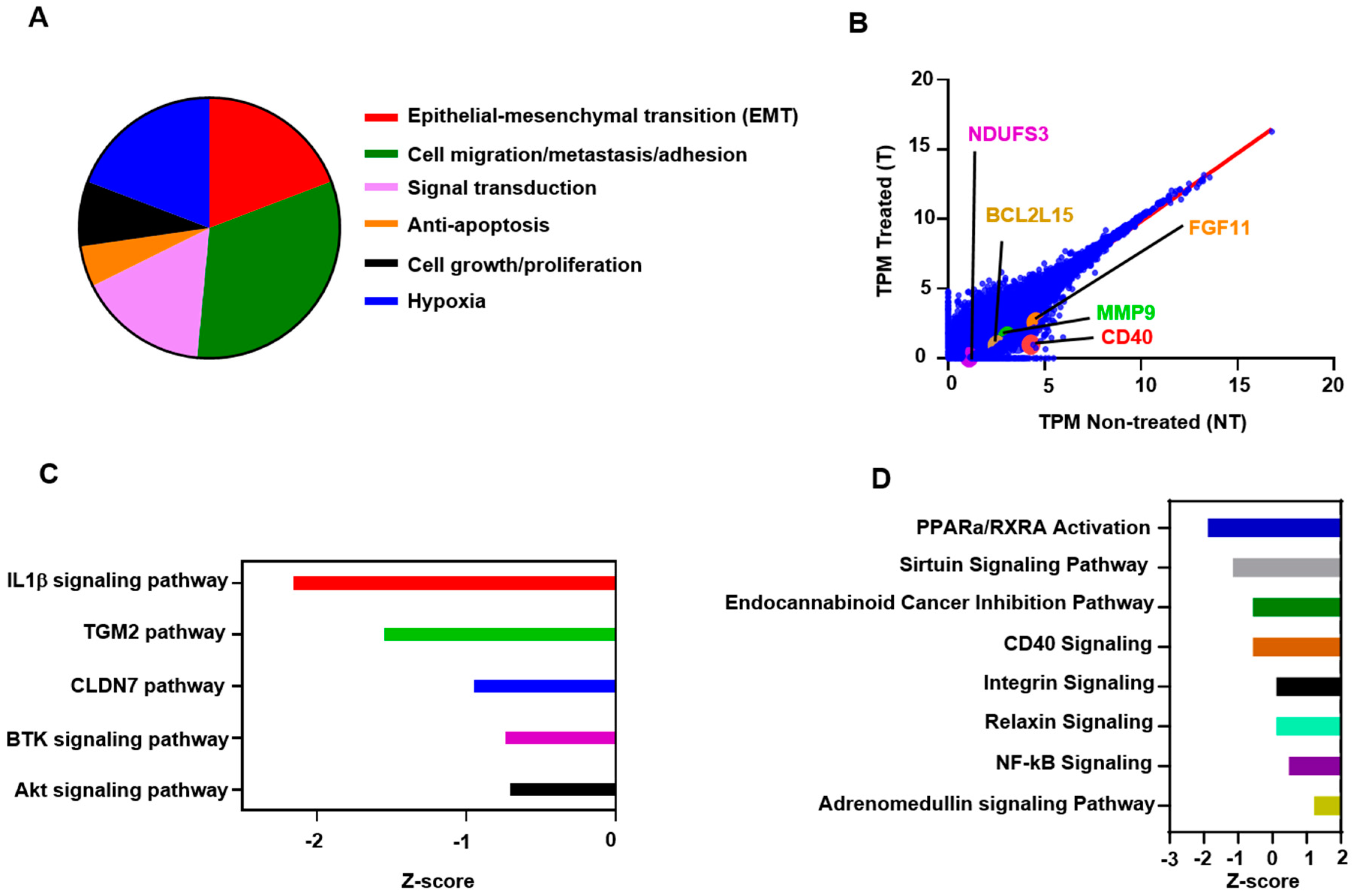
2.2. Atezolizumab Downregulates Genes Promoting Cell Migration/Metastasis and EMT
2.3. Atezolizumab Downregulates Anti-Apoptotic Genes, Upregulates Pro-Apoptotic Genes, and Downregulates Genes Involved in Cell Growth and Proliferation
2.4. Atezolizumab Upregulates DNA Repair Genes and Downregulates Genes Related to Hypoxia
2.5. Atezolizumab Downregulates NF-kB, Akt, and CD40 Signaling Pathways
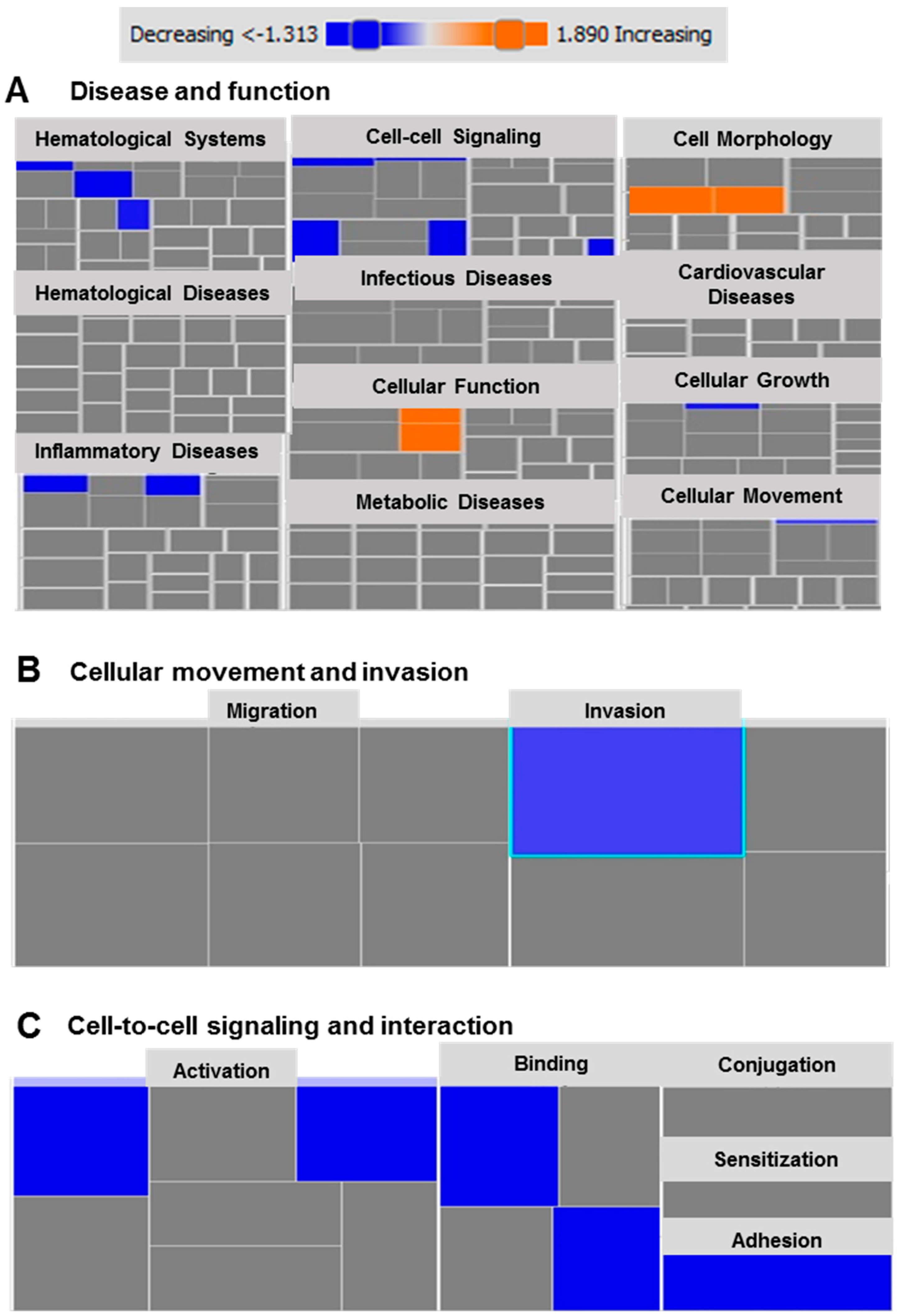
2.6. Functional and Network Analyses Identified Key Genes Associated with the Response of MDA-MB-231 to Atezolizumab
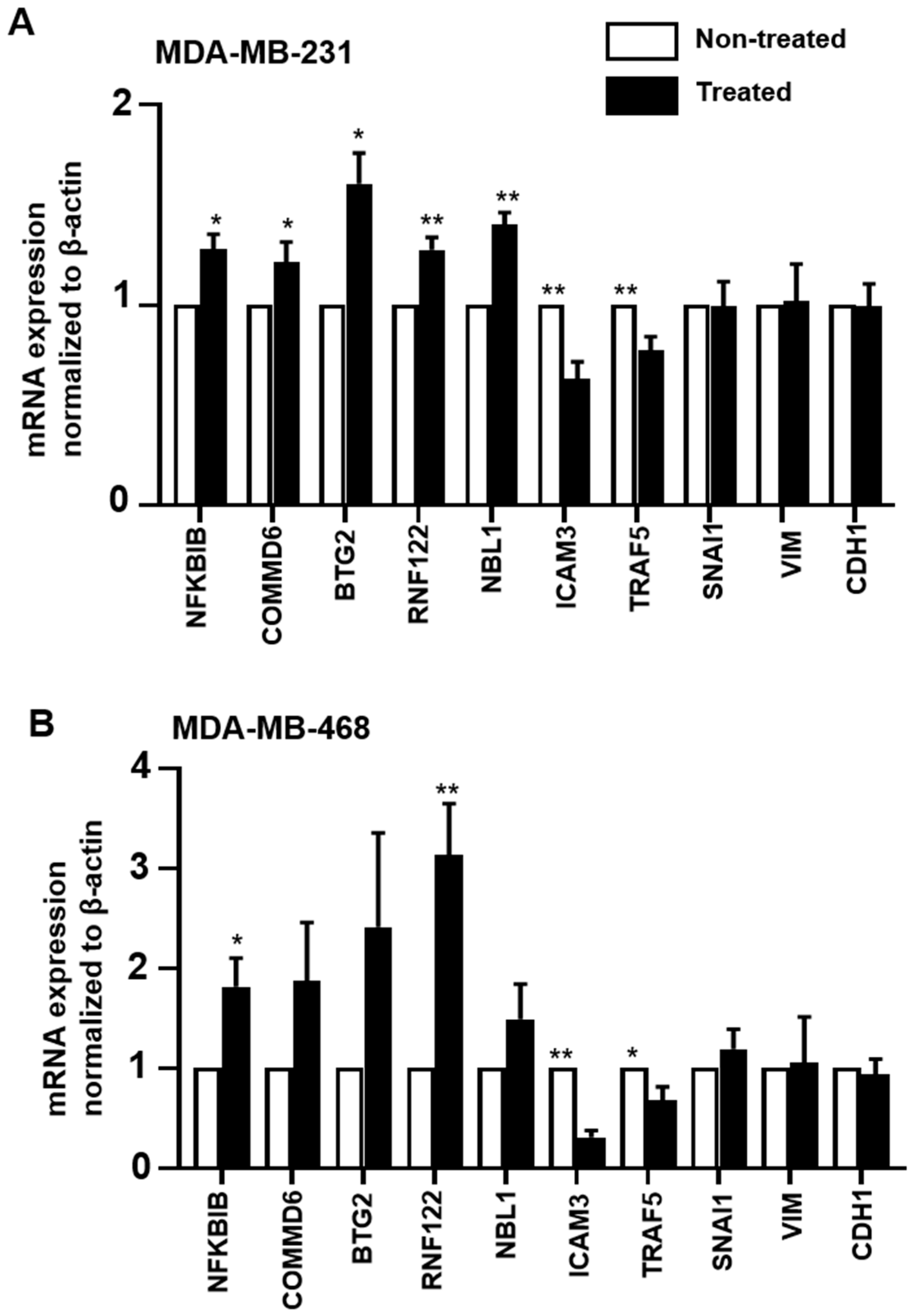
2.7. Validation of RNA-Seq Data by RT-qPCR
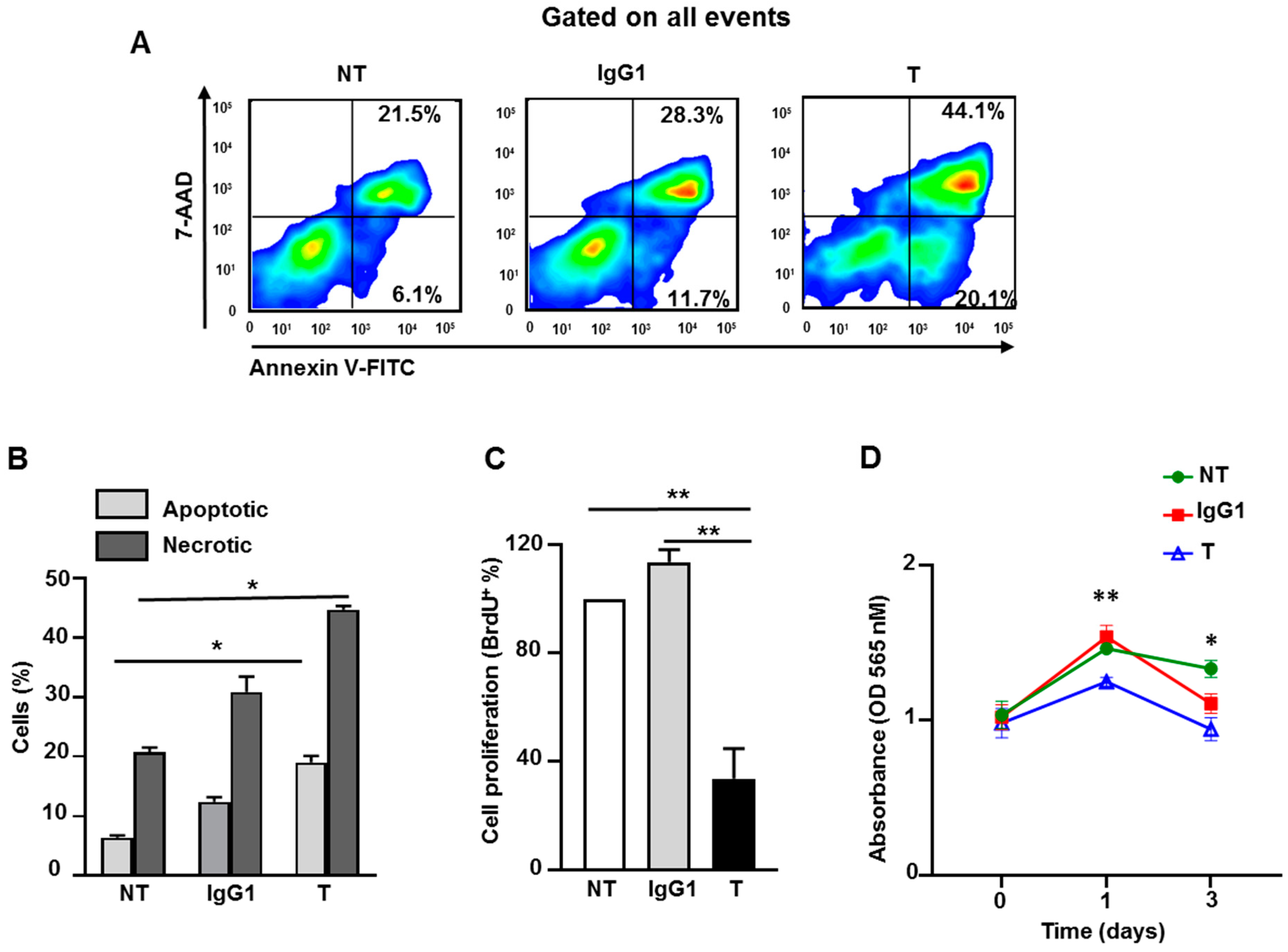
2.8. Atezolizumab Increases Necrosis/Apoptosis and Reduces Proliferation and Viability in MDA-MB-231 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Flow Cytometry
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
4.5. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.6. RNA Library Preparation and RNA-Seq
4.7. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.8. Gene Set Enrichment Analyses and Modeling of Gene Interaction
4.9. Death/Apoptosis Assay
4.10. BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay
4.11. MTT Cell Viability Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Fishman, M.N.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Drake, C.G.; Kluger, H.; Stadler, W.M.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; McNeel, D.G.; Curti, B.; et al. Immunomodulatory Activity of Nivolumab in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5461–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Cui, Y.; Guo, Y. Programmed Cell Death Protein-1 Predicts the Recurrence of Breast Cancer in Patients Subjected to Radiotherapy After Breast-Preserving Surgery. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818793425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lau, R.; Yu, D.; Zhu, W.; Korman, A.; Weber, J. PD1 blockade reverses the suppression of melanoma antigen-specific CTL by CD4+ CD25(Hi) regulatory T cells. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikas, P.; Borcherding, N.; Zhang, W. The clinical promise of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: A focus on T-regulatory cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, Y.; Ishida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T.; Minato, N. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12293–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, G.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; et al. The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapy versus docetaxel for pretreated advanced NSCLC: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4239–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothapalli, A.; Khattak, M.A. Safety and efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy for metastatic melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with viral hepatitis: A case series. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosset, M.; Vargas, T.R.; Lagrange, A.; Boidot, R.; Vegran, F.; Roussey, A.; Chalmin, F.; Dondaine, L.; Paul, C.; Lauret Marie-Joseph, E.; et al. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: An adaptive immune resistance mechanism to immunogenic chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1433981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Yao, S.; Zhu, G.; Flies, A.S.; Flies, S.J.; Chen, L. B7-H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood 2008, 111, 3635–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.; Barsoum, I.B.; Truesdell, P.; Cotechini, T.; Macdonald-Goodfellow, S.K.; Petroff, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M.; Craig, A.W.; Graham, C.H. Activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint confers tumor cell chemoresistance associated with increased metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10557–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Li, C.W.; Chen, M.K.; Shao, B.; Hsu, J.M.; Chan, L.C.; Yang, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Lai, Y.J.; et al. Inhibition of ATR downregulates PD-L1 and sensitizes tumor cells to T cell-mediated killing. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Darvin, P.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. PD-L1 Expression in Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells Is Epigenetically Regulated through Posttranslational Histone Modifications. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 3958908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Turner, A.; Wu, C.; Lu, B.; Jiang, J. PD-L1 Expression Promotes Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Human Esophageal Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Teng, F.; Kong, L.; Yu, J. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 5023–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenst, S.; Schaerli, A.R.; Gao, F.; Daster, S.; Trella, E.; Droeser, R.A.; Muraro, M.G.; Zajac, P.; Zanetti, R.; Gillanders, W.E.; et al. Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, M.T.; Lenkiewicz, E.; Malasi, S.; Basu, A.; Yearley, J.H.; Annamalai, L.; McCullough, A.E.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Narang, P.; Wilson Sayres, M.A.; et al. The association of genomic lesions and PD-1/PD-L1 expression in resected triple-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, E.A.; Gru, A.A.; Atkins, K.A.; Friedman, L.A.; Moore, M.E.; Bullock, T.N.; Cross, J.V.; Dillon, P.M.; Mills, A.M. PD-L1 Expression and Intratumoral Heterogeneity Across Breast Cancer Subtypes and Stages: An Assessment of 245 Primary and 40 Metastatic Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, C.; Gombos, A.; Latifyan, S.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Kok, M.; Buisseret, L. Targeting immune checkpoints in breast cancer: An update of early results. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan Nair, V.; Toor, S.M.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Dual inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 activation downregulates expression of PD-L1 in human breast cancer cells. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, H.; Khalil, F.; Antonia, S. PD-L1 expression is increased in a subset of basal type breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; Lin, W.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Meyerson, M. The menin tumor suppressor protein is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Lee, Y.; Wischnewski, H.; Brun, C.M.; Schwarz, T.; Azzalin, C.M. RNaseH1 regulates TERRA-telomeric DNA hybrids and telomere maintenance in ALT tumour cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Van De Venter, M.; Nitulescu, G.; Ungurianu, A.; Juzenas, P.; Peng, Q.; Olaru, O.T.; Gradinaru, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tsoukalas, D.; et al. The Akt pathway in oncology therapy and beyond (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Gajate, P.; Grande, E. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a promising target in solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 58, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, N.; Becker, K.G.; Wood, W.H.; Zhang, Y.; Morin, P.J. Claudin-7 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer and promotes invasion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated tissue transglutaminase overexpression couples acquired tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance and migration through c-FLIP and MMP-9 proteins in lung cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21164–21172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mon, N.N.; Senga, T.; Ito, S. Interleukin-1beta activates focal adhesion kinase and Src to induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and invasion of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulotta, C.; Ottewell, P. The role of IL-1B in breast cancer bone metastasis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thar Min, A.K.; Okayama, H.; Saito, M.; Ashizawa, M.; Aoto, K.; Nakajima, T.; Saito, K.; Hayase, S.; Sakamoto, W.; Tada, T.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-converted tumor cells can induce T-cell apoptosis through upregulation of programmed death ligand 1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, Y.J.; Pyo, H.J.; Ryu, S.E.; Shin, W.; Heo, Y.S. Molecular mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via anti-PD-L1 antibodies atezolizumab and durvalumab. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.M.; Toor, S.M.; Rakib, F.; Mall, R.; Mroue, K.; Ullah, E.; Al-Saad, K.; Kolatkar, P.R.; Elkord, E. Investigation of the effect of PD-L1 blockade on triple negative breast cancer cells using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. In Vaccines 2019. (under review). [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.A.; Gupta, H.B.; Sareddy, G.; Pandeswara, S.; Lao, S.; Yuan, B.; Drerup, J.M.; Padron, A.; Conejo-Garcia, J.; Murthy, K.; et al. Tumor-Intrinsic PD-L1 Signals Regulate Cell Growth, Pathogenesis, and Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer and Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6964–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.S.; Ostrowski, M.; Balderson, B.; Christian, N.; Crowe, S.M. Glucose metabolism regulates T cell activation, differentiation, and functions. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escors, D.; Gato-Canas, M.; Zuazo, M.; Arasanz, H.; Garcia-Granda, M.J.; Vera, R.; Kochan, G. The intracellular signalosome of PD-L1 in cancer cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, L.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wang, H. Knockdown of PD-L1 in Human Gastric Cancer Cells Inhibits Tumor Progression and Improves the Cytotoxic Sensitivity to CIK Therapy. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Falcone, I.; Pilotto, S.; Bria, E.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M.; Ciuffreda, L. Role of mTOR Signaling in Tumor Microenvironment: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Yamada, T.; Inoue, K.; Nabe, S.; Kuwahara, M.; Takemori, N.; Takemori, A.; Matsuda, S.; Kanoh, M.; Imai, Y.; et al. The tumor suppressor menin prevents effector CD8 T-cell dysfunction by targeting mTORC1-dependent metabolic activation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, S.; Faouzi Zaarour, R.; Hassan Venkatesh, G.; Francis, A.; El-Sayed, W.; Buart, S.; Bravo, P.; Thiery, J.; Chouaib, S. Role of Hypoxic Stress in Regulating Tumor Immunogenicity, Resistance and Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdin, E.; Hirschey, M.D.; Finley, L.W.; Haigis, M.C. Sirtuin regulation of mitochondria: Energy production, apoptosis, and signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonda, D.J.; Lee, H.G.; Camins, A.; Pallas, M.; Casadesus, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X. The sirtuin pathway in ageing and Alzheimer disease: Mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Bae, S.; Kong, J.M.; Choi, J.; Jang, M.; Choi, J.; Hong, J.M.; Hwang, Y.I.; Kang, J.S.; et al. Direct Interaction of CD40 on Tumor Cells with CD40L on T Cells Increases the Proliferation of Tumor Cells by Enhancing TGF-beta Production and Th17 Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Yuan, L.; Slakey, L.M.; Jones, F.E.; Burow, M.E.; Hill, S.M. Inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion by melatonin is mediated through regulation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, M.; Mei, L.; Ruan, J.; Hu, Q.; Peng, J.; Su, H.; Liao, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; et al. Key roles of necroptotic factors in promoting tumor growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22219–22233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, M. FOXO factors and breast cancer: Outfoxing endocrine resistance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R113–R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.R.; Ahmed, S.O.; Ahmed, M.; Khan, O.S.; Al Abdulmohsen, S.; Platanias, L.C.; Al-Kuraya, K.S.; Uddin, S. Cross-talk between NFkB and the PI3-kinase/AKT pathway can be targeted in primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell lines for efficient apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.Y.; Lai, M.; Shephard, J.; Xiao, C. Concurrent PI3K and NF-kappaB activation drives B-cell lymphomagenesis. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredel, M.; Scholtens, D.M.; Harsh, G.R.; Bredel, C.; Chandler, J.P.; Renfrow, J.J.; Yadav, A.K.; Vogel, H.; Scheck, A.C.; Tibshirani, R.; et al. A network model of a cooperative genetic landscape in brain tumors. JAMA 2009, 302, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| PD-L1 | Forward, 5′- TGGCATTTGCTGAACGCATTT -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- TGCAGCCAGGTCTAATTGTTTT -3′ | |
| NFKBIB | Forward, 5′- CGACACCTACCTCGCTCAG -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- GTCGGAATCGGGGTACAAGG -3′ | |
| COMMD6 | Forward, 5′- GGAAACTGGGTATGGCTGTGA -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- TGTGGAATCGTCATTTCAAAGCA -3′ | |
| BTG2 | Forward, 5′- ACGGGAAGGGAACCGACAT-3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- CAGTGGTGTTTGTAGTGCTCTG -3′ | |
| RNF122 | Forward, 5′- ATTCCAGTGGTGTAACGGGTG -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- CCTGTGCCGAAGATGACCATA -3′ | |
| NBL1 | Forward, 5′- CATGTGGGAGATTGTGACGCT-3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- CCTCGTGACTAGGCTCCTTG -3′ | |
| ICAM3 | Forward, 5′- GGAGTTCCTTTTGCGGGTG -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- TCAGAGCTGGGACAATCAGTA -3′ | |
| TRAF5 | Forward, 5′- CCACTCGGTGCTTCACAAC -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- GTACCGGCCCAGAATAACCT -3′ | |
| SNAI1 | Forward, 5′-TCGGAAGCCTAACTACAGCGA -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- AGATGAGCATTGGCAGCGAG -3′ | |
| VIM | Forward, 5′- GACGCCATCAACACCGAGTT-3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- CTTTGTCGTTGGTTAGCTGGT-3′ | |
| CDH1 | Forward, 5′- CGAGAGCTACACGTTCACGG -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- GGGTGTCGAGGGAAAAATAGG -3′ | |
| β-ACTIN | Forward, 5′- AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC -3′ |
| Reverse, 5′- AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG -3′ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, R.; Taha, R.Z.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Alajez, N.M.; Elkord, E. PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081050
Saleh R, Taha RZ, Sasidharan Nair V, Alajez NM, Elkord E. PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(8):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081050
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Reem, Rowaida Z. Taha, Varun Sasidharan Nair, Nehad M. Alajez, and Eyad Elkord. 2019. "PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 8: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081050
APA StyleSaleh, R., Taha, R. Z., Sasidharan Nair, V., Alajez, N. M., & Elkord, E. (2019). PD-L1 Blockade by Atezolizumab Downregulates Signaling Pathways Associated with Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Hypoxia in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers, 11(8), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081050






