Cannabidiol Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of TRAIL by Upregulating DR5 in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.9. ROS Measurement (DCFH-DA Assay)
2.10. Tumor Xenograft Experiment
2.11. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining and Scoring
2.12. Terminal Deoxyribonucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Staining
2.13. Combination Index and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
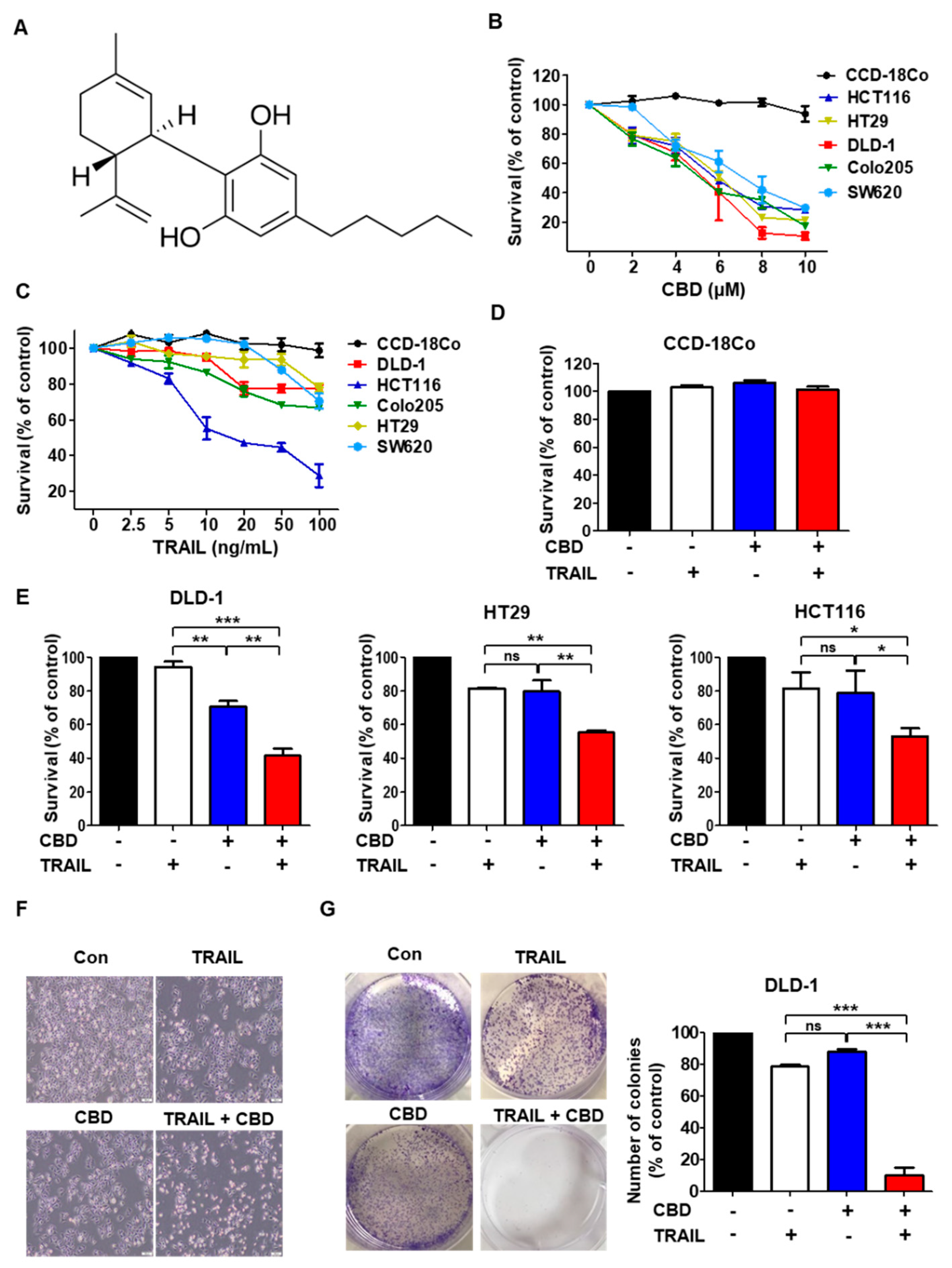
3.1. Cannabidiol Enhances TRAIL-Induced Cell Death in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
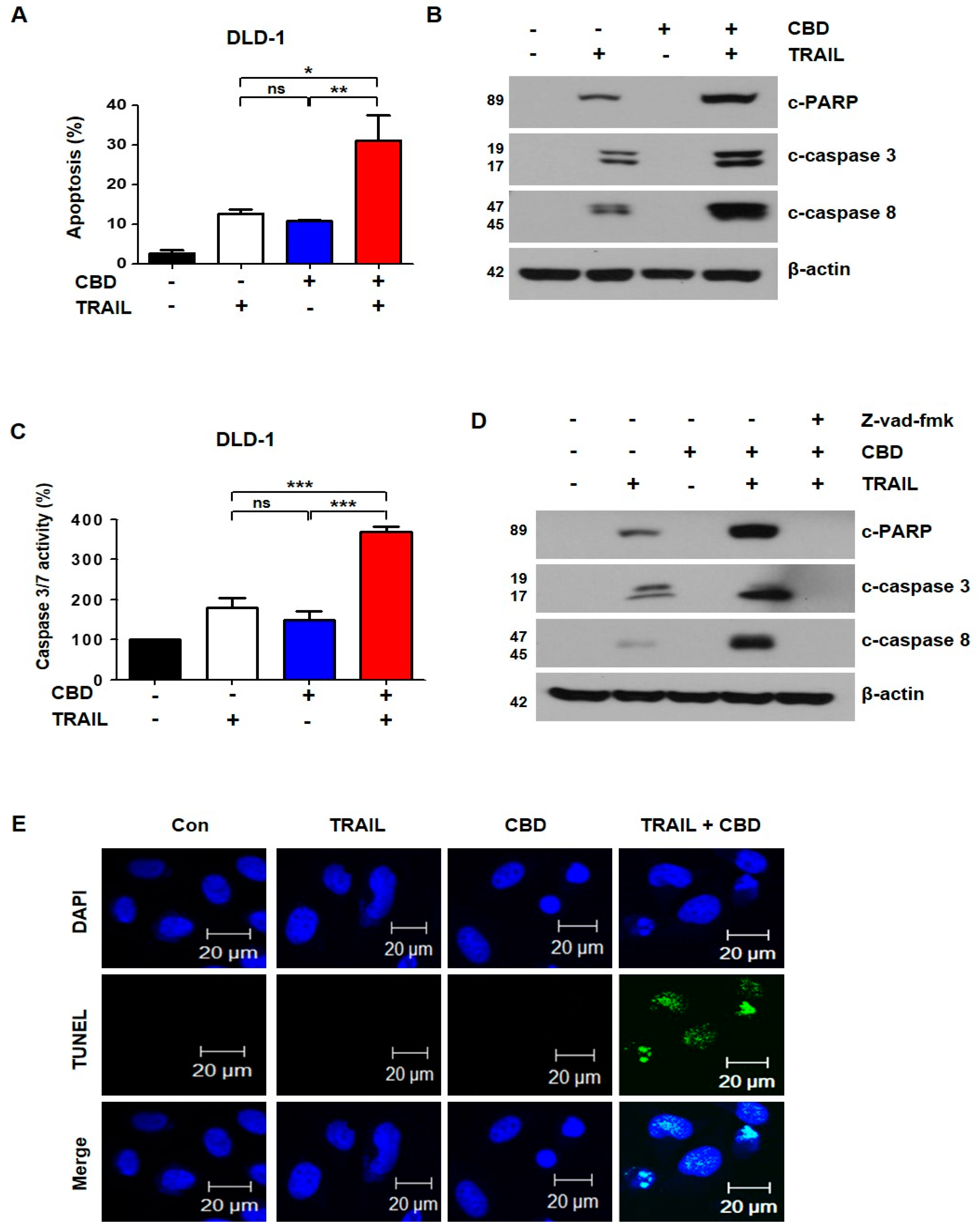
3.2. Combination of TRAIL and Cannabidiol Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells
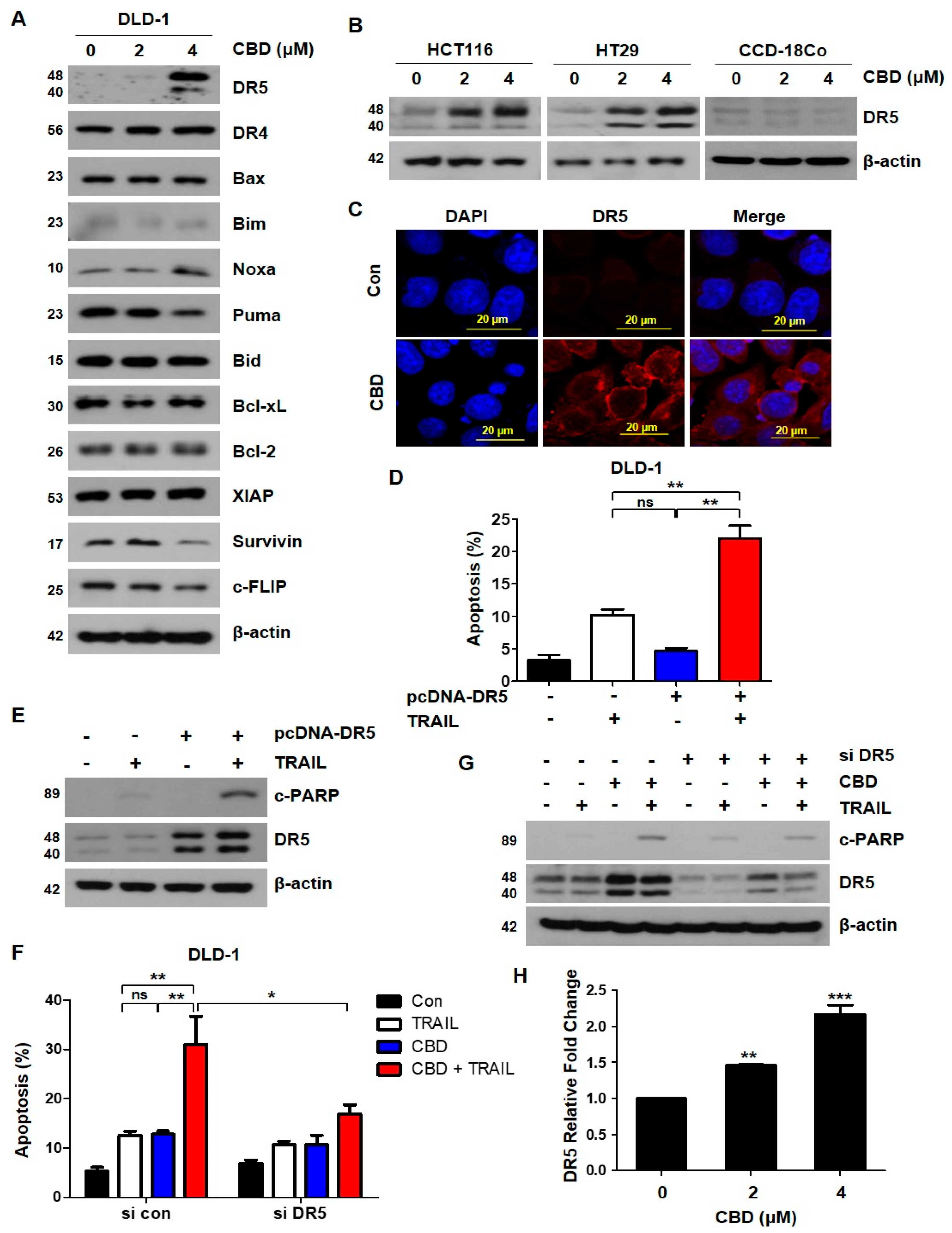
3.3. Cannabidiol Increases TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis by Upregulating DR5
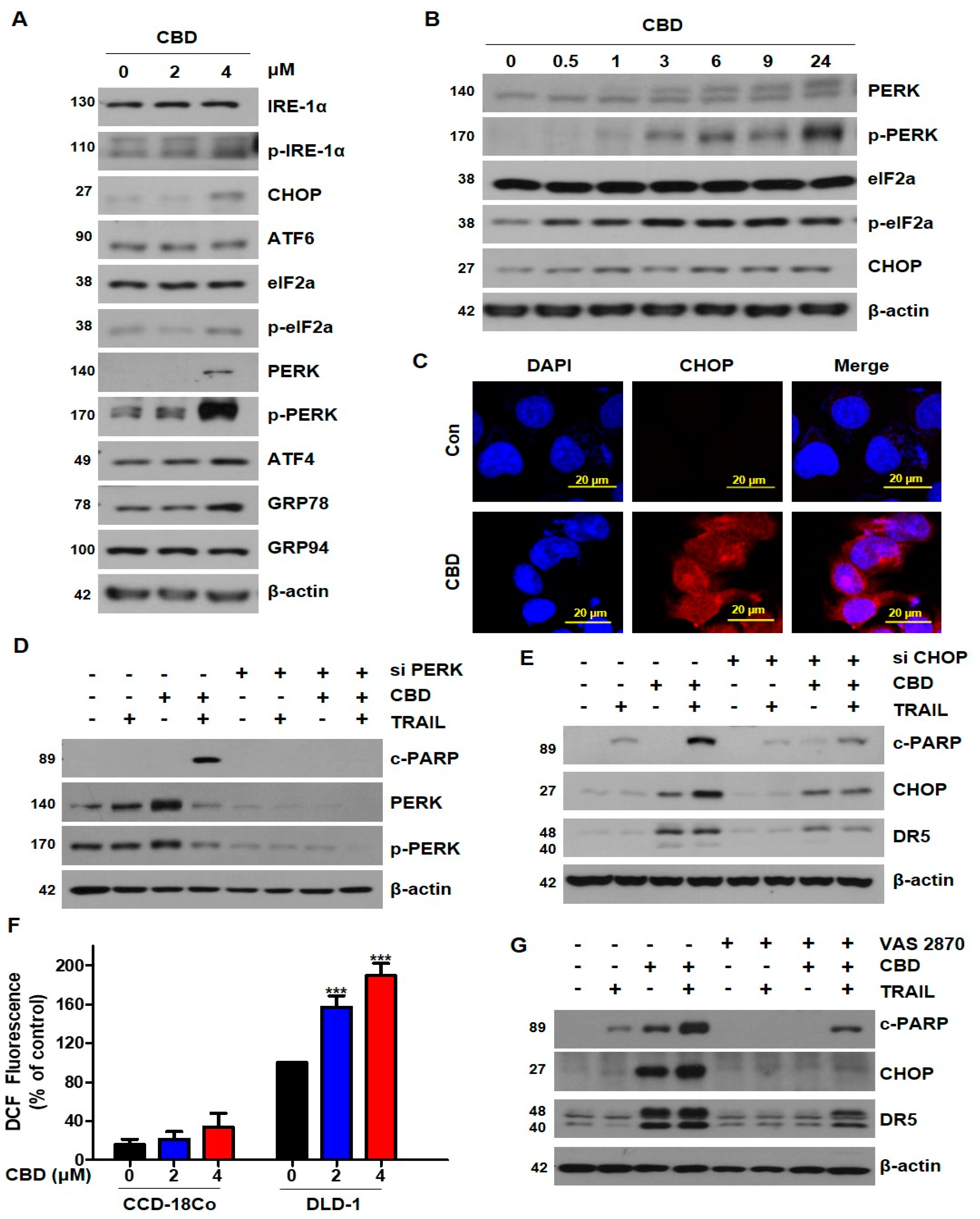
3.4. Cannabidiol Induces Activation of the ER Stress-CHOP Pathway
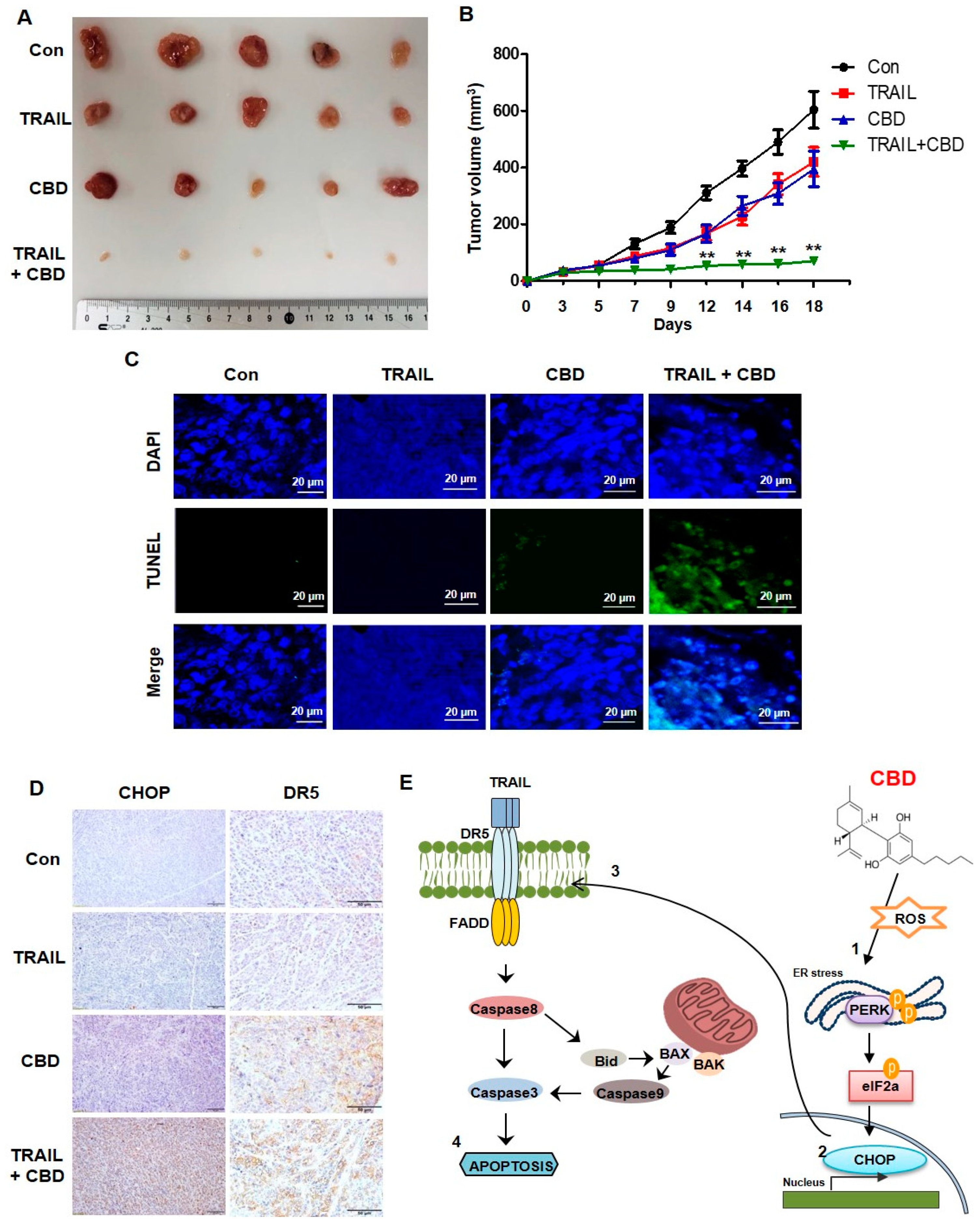
3.5. Cannabidiol Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérino, D.; Lalaoui, N.; Morizot, A.; Solary, E.; Micheau, O. TRAIL in cancer therapy: Present and future challenges. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaat, A.; Abd-Rabou, A.; Reda, A. TRAIL combinations: The new ‘trail’ for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S. Safety and tolerability of TRAIL receptor agonists in cancer treatment. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckey, D.W.; Shah, K. TRAIL on trial: Preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Mishra, D.P. Trailing TRAIL Resistance: Novel Targets for TRAIL Sensitization in Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.V.; Zhang, X.D.; Van Berkel, E.; Sanders, J.E.; Zhang, X.Y.; Thomas, W.D.; Nguyen, T.; Hersey, P. The role of NF-kappa B in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5337–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, K.; Srivastava, R.K. Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/PTEN/Akt kinase pathway in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K.W.; Punnoose, E.A.; Januario, T.; Lawrence, D.A.; Pitti, R.M.; Lancaster, K.; Lee, D.; von Goetz, M.; Yee, S.F.; Totpal, K.; et al. Death-receptor O-glycosylation controls tumor-cell sensitivity to the proapoptotic ligand Apo2L/TRAIL. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.; Golan, H.; Schiby, G.; PriChen, S.; Smoum, R.; Moshe, I.; Peshes-Yaloz, N.; Castiel, A.; Waldman, D.; Gallily, R.; et al. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of non-psychoactive cannabidiol in neuroblastoma. Curr. Oncol. 2016, 23, S15-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.A.; Dennis, J.L.; Dalgleish, A.G.; Liu, W.M. Inhibiting Heat Shock Proteins Can Potentiate the Cytotoxic Effect of Cannabidiol in Human Glioma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 5827–5837. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, A.S.; Marie, M.A.; Sheweita, S.A. Novel mechanism of cannabidiol-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines. Breast 2018, 41, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreevalsan, S.; Joseph, S.; Jutooru, I.; Chadalapaka, G.; Safe, S.H. Induction of apoptosis by cannabinoids in prostate and colon cancer cells is phosphatase dependent. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3799–3807. [Google Scholar]
- Aviello, G.; Romano, B.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Gallo, L.; Piscitelli, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Izzo, A.A. Chemopreventive effect of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol on experimental colon cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, C.C.; Jan, T.R. Cannabidiol induced apoptosis in human monocytes through mitochondrial permeability transition pore-mediated ROS production. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, S.; Morizot, A.; Micheau, O. Regulating TRAIL receptor-induced cell death at the membrane: A deadly discussion. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledzinski, P.; Zeyland, J.; Slomski, R.; Nowak, A. The current state and future perspectives of cannabinoids in cancer biology. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Ramer, R. Anti-tumour actions of cannabinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramer, R.; Heinemann, K.; Merkord, J.; Rohde, H.; Salamon, A.; Linnebacher, M.; Hinz, B. COX-2 and PPAR-gamma confer cannabidiol-induced apoptosis of human lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Wu, J.; Hei, T.K. Regulation of human glioblastoma cell death by combined treatment of cannabidiol, gamma-radiation and small molecule inhibitors of cell signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74068–74095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wang, H.G. CHOP is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5 expression in human carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45495–45502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glab, J.A.; Doerflinger, M.; Nedeva, C.; Jose, I.; Mbogo, G.W.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W.; Kueh, A.J.; Herold, M.J.; Huang, D.C.; et al. DR5 and caspase-8 are dispensable in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.P.; Devi, L.A.; Rozenfeld, R. Cannabidiol causes activated hepatic stellate cell death through a mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecha, M.; Torrao, A.S.; Mestre, L.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Mechoulam, R.; Guaza, C. Cannabidiol protects oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from inflammation-induced apoptosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibody | Source | Catalog Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR5 | Abcam | Ab8416 | 1:80 |
| CHOP | novus | NB600 | 1:100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.L.; Kim, B.R.; Kim, D.Y.; Jeong, Y.A.; Jeong, S.; Na, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Yun, H.K.; Jo, M.J.; Kim, B.G.; et al. Cannabidiol Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of TRAIL by Upregulating DR5 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050642
Kim JL, Kim BR, Kim DY, Jeong YA, Jeong S, Na YJ, Park SH, Yun HK, Jo MJ, Kim BG, et al. Cannabidiol Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of TRAIL by Upregulating DR5 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(5):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050642
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jung Lim, Bo Ram Kim, Dae Yeong Kim, Yoon A. Jeong, Soyeon Jeong, Yoo Jin Na, Seong Hye Park, Hye Kyeong Yun, Min Jee Jo, Bu Gyeom Kim, and et al. 2019. "Cannabidiol Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of TRAIL by Upregulating DR5 in Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 5: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050642
APA StyleKim, J. L., Kim, B. R., Kim, D. Y., Jeong, Y. A., Jeong, S., Na, Y. J., Park, S. H., Yun, H. K., Jo, M. J., Kim, B. G., Kim, H. D., Kim, D. H., Oh, S. C., Lee, S. I., & Lee, D.-H. (2019). Cannabidiol Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of TRAIL by Upregulating DR5 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 11(5), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050642





