Challenges and Inconsistencies in Using Lysophosphatidic Acid as a Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LC-MS Analysis of Lysophospholipids
2.2. Comparing Lysophospholipids in Control and Ovarian Cancer Plasma Samples
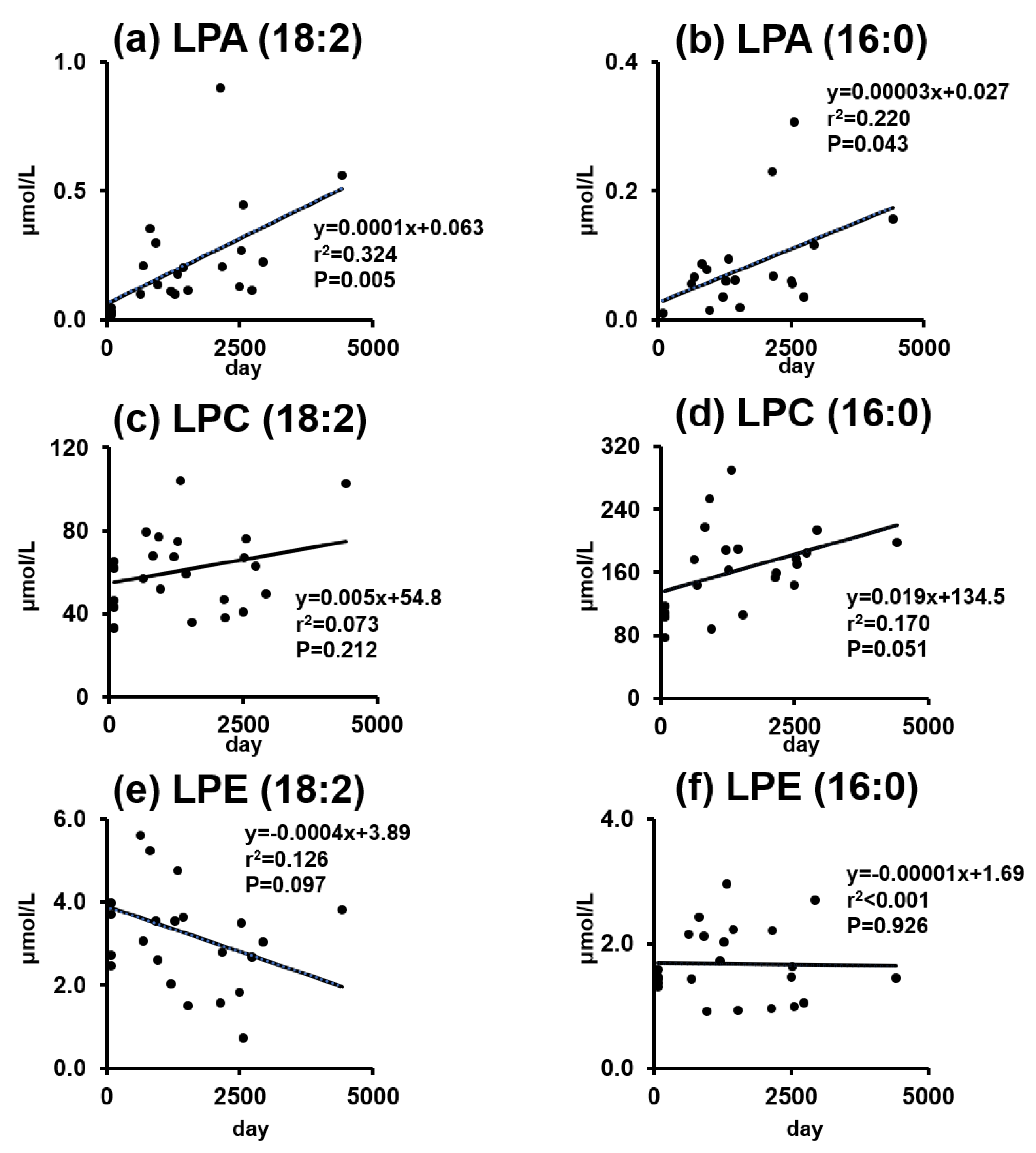
2.3. Phospholipids and Lysophospholipids Change over Time
2.4. Lysophospholipid Changes Depending on Incubation Time, EDTA Content, and Autotaxin Inhibitor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Plasma Samples
4.3. Blood Incubation Analysis
4.4. Extraction of Phospholipids
4.5. HPLC-MS Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasaroli, D.; Coukos, G.; Scholler, N. Beyond ca125: The coming of age of ovarian cancer biomarkers. Are we there yet? Biomark. Med. 2009, 3, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, R.; Sant, M.; Coleman, M.P.; Francisci, S.; Baili, P.; Pierannunzio, D.; Trama, A.; Visser, O.; Brenner, H.; Ardanaz, E.; et al. Cancer survival in europe 1999-2007 by country and age: Results of eurocare--5-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaballa, A.; Barretina, P.; Casado, A.; Garcia, Y.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Guerra, E.; Lainez, N.; Martinez, J.; Redondo, A.; Romero, I. Seom clinical guideline in ovarian cancer (2016). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, I.J.; Menon, U.; Ryan, A.; Gentry-Maharaj, A.; Burnell, M.; Kalsi, J.K.; Amso, N.N.; Apostolidou, S.; Benjamin, E.; Cruickshank, D.; et al. Ovarian cancer screening and mortality in the UK collaborative trial of ovarian cancer screening (ukctocs): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet (Lond.) 2016, 387, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomnytska, M.; Pinto, R.; Becker, S.; Engstrom, U.; Gustafsson, S.; Bjorklund, C.; Templin, M.; Bergstrand, J.; Xu, L.; Widengren, J.; et al. Platelet protein biomarker panel for ovarian cancer diagnosis. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, W.S.; Marks, S.T. Diagnosis and management of adnexal masses. Am. Fam. Phys. 2016, 93, 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, P.E.; Taylor, K.J. Is early detection of ovarian cancer possible? Ann. Med. 1995, 27, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wiper, D.W.; Wu, M.; Morton, R.E.; Elson, P.; Kennedy, A.W.; Belinson, J.; Markman, M.; Casey, G. Lysophosphatidic acid as a potential biomarker for ovarian and other gynecologic cancers. JAMA 1998, 280, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Jayaraman, M.; Yan, M.; Ward, J.D.; Fung, K.M.; Moxley, K.; Sood, A.K.; Isidoro, C.; Mukherjee, P.; et al. Lpa induces metabolic reprogramming in ovarian cancer via a pseudohypoxic response. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, U.; Roy Chowdhury, S.; Vasudevan, M.; Bankar, K.; Roychoudhury, S.; Roy, S.S. Gene regulatory networking reveals the molecular cue to lysophosphatidic acid-induced metabolic adaptations in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 491–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorato, J.M.; Shipkova, P.; Minnich, A.; Aubry, A.F.; Easter, J.; Tymiak, A. Challenges in accurate quantitation of lysophosphatidic acids in human biofluids. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1784–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y. An extremely simple method for extraction of lysophospholipids and phospholipids from blood samples. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.; Schmitz, G.; Liebisch, G. High-throughput analysis of sphingosine 1-phosphate, sphinganine 1-phosphate, and lysophosphatidic acid in plasma samples by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutphen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wilbanks, G.D.; Fiorica, J.; Grendys, E.C., Jr.; LaPolla, J.P.; Arango, H.; Hoffman, M.S.; Martino, M.; Wakeley, K.; et al. Lysophospholipids are potential biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2004, 13, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Dong, L.; Yang, S.; Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; et al. Diagnostic value of plasma lysophosphatidic acid levels in ovarian cancer patients: A case-control study and updated meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowska, A.; Cecerska, E.; Dolegowska, B. Methods for quantifying lysophosphatidic acid in body fluids: A review. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 453, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowska, A.; Cecerska-Heryc, E.; Matoszka, N.; Dolegowska, B. Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in ovarian cancer. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Qu, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cai, H. Roles of lpa receptor signaling in breast cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onallah, H.; Catane, L.J.; Trope, C.G.; Hetland Falkenthal, T.E.; Reich, R.; Davidson, B. Activity and clinical relevance of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid pathways in high-grade serous carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, H. Mechanisms of lysophosphatidic acid-mediated lymphangiogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hoppel, C.L. Comprehensive approach to the quantitative analysis of mitochondrial phospholipids by hplc-ms. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 912, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y. Measurement of endogenous lysophosphatidic acid by esi-ms/ms in plasma samples requires pre-separation of lysophosphatidylcholine. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 3739–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bese, T.; Barbaros, M.; Baykara, E.; Guralp, O.; Cengiz, S.; Demirkiran, F.; Sanioglu, C.; Arvas, M. Comparison of total plasma lysophosphatidic acid and serum ca-125 as a tumor marker in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 21, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kennedy, A.W.; Belinson, J.; Xu, Y. Evaluation of plasma lysophospholipids for diagnostic significance using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (esi-ms) analyses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 905, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlakova, I.; Vavrova, J.; Tosner, J.; Hanousek, L. Lysophosphatidic acid: An ovarian cancer marker. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2008, 29, 511–514. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlakova, I.; Vavrova, J.; Tosner, J.; Hanousek, L. Lysophosphatidic acid (lpa)-a perspective marker in ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 2011, 32, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.I.; Chen, L.X.; Liao, X.I.; Li, X.J.; Wu, Q.H. The relationship of lysophosphatidic acid and mmp-2 in diagnosing epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Proc. Clin. Med. 2013, 22, 403–405. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.-R.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.-H. Quantitative analysis of acyl-lysophosphatidic acid in plasma using negative ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 788, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y. The applicable value of conbined detection of lpa, ca125 and afp in the early diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Lab. Med. Clin. 2008, 5, 1430–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Meleh, M.; Pozlep, B.; Mlakar, A.; Meden-Vrtovec, H.; Zupancic-Kralj, L. Determination of serum lysophosphatidic acid as a potential biomarker for ovarian cancer. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 858, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozlep, B.; Meleh, M.; Kobal, B.; Verdenik, I.; Osredkar, J.; Kralj, L.Z.; Meden-Vrtovec, H. Use of lysophosphatidic acid in the management of benign and malignant ovarian tumors. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2007, 28, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.L.; Morrison, P.; Miller, B.; Riely, C.A.; Tolley, B.; Westermann, A.M.; Bonfrer, J.M.; Bais, E.; Moolenaar, W.H.; Tigyi, G. Plasma lysophosphatidic acid concentration and ovarian cancer. JAMA 2002, 287, 3081–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murph, M.; Tanaka, T.; Pang, J.; Felix, E.; Liu, S.; Trost, R.; Godwin, A.K.; Newman, R.; Mills, G. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for quantifying plasma lysophospholipids: Potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 433, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, J.; Taira, A.; Takanezawa, Y.; Kishi, Y.; Hama, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Mizuno, K.; Saku, K.; Taguchi, R.; Arai, H. Serum lysophosphatidic acid is produced through diverse phospholipase pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48737–48744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Ohkawa, R.; Okubo, S.; Tozuka, M.; Yokota, H.; Ikeda, H.; Ohshima, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yatomi, Y. Suppression of lysophosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidylcholine formation in the plasma in vitro: Proposal of a plasma sample preparation method for laboratory testing of these lipids. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 367, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Kurano, M.; Ikeda, H.; Igarashi, K.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Lysophospholipids in laboratory medicine. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2018, 94, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, T.; Koh, E.; Ptaszynska, M.; Bandle, R.W.; Liotta, L.A.; Schiffmann, E.; Stracke, M.L. L-histidine inhibits production of lysophosphatidic acid by the tumor-associated cytokine, autotaxin. Lipids Health Dis. 2005, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yin, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Lampe, J.W.; Becker, L.B. Potential of lysophosphatidylinositol as a prognostic indicator of cardiac arrest using a rat model. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yin, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Lampe, J.W.; Stevens, J.F.; Becker, L.B.; Kim, J. Comprehensive analysis of phospholipids in the brain, heart, kidney, and liver: Brain phospholipids are least enriched with polyunsaturated fatty acids. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 442, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lampe, J.W.; Yin, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Becker, L.B. Phospholipid alterations in the brain and heart in a rat model of asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary bypass resuscitation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 408, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
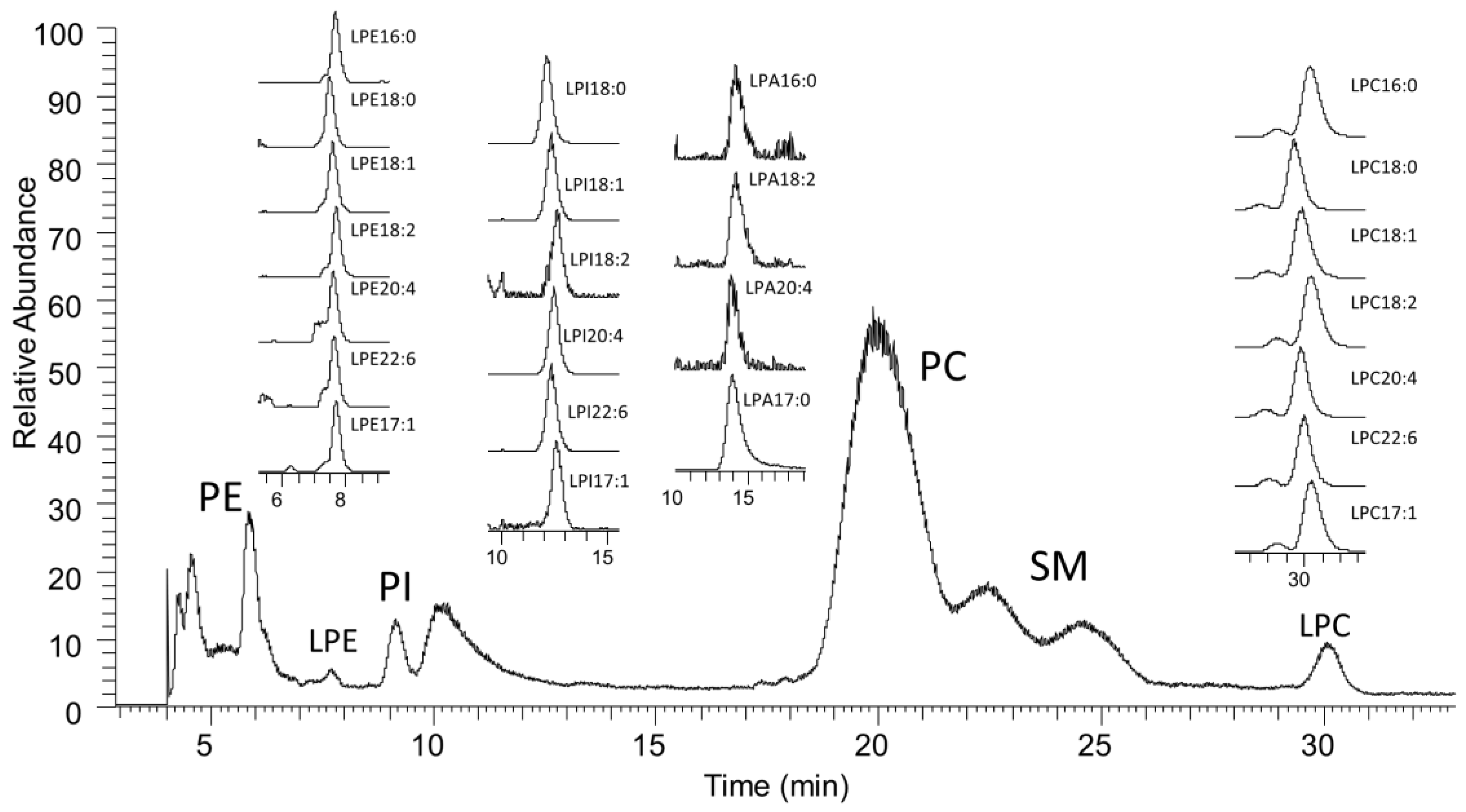


| LPPL Species | Control (mean ± SD) | Benign (mean ± SD) | Cancer (mean ± SD) | p Value (Control vs. Benign) | p Value (Control vs. Cancer) | p Value (Benign vs. Cancer) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPA(18:2) | 0.26 ± 0.20 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.197 |
| LPA(16:0) | 0.09 ± 0.07 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| LPI(18:0) | 10.4 ± 6.63 | 4.79 ± 5.25 | 3.19 ± 2.13 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.992 |
| LPI(20:4) | 2.28 ± 1.09 | 3.38 ± 1.97 | 3.69 ± 2.38 | 0.046 | 0.038 | 0.846 |
| LPC(16:0) | 178.8 ± 47.6 | 143.4 ± 45.2 | 121.4 ± 44.2 | 0.036 | 0.001 | 0.108 |
| LPC(18:0) | 83.0 ± 31.2 | 60.5 ± 23.4 | 51.0 ± 19.0 | 0.026 | 0.001 | 0.158 |
| LPC(18:2) | 64.4 ± 19.6 | 70.2 ± 39.2 | 66.7 ± 37.1 | 0.937 | 0.682 | 0.808 |
| LPC(20:4) | 17.0 ± 7.36 | 27.6 ± 18.1 | 30.5 ± 19.1 | 0.052 | 0.007 | 0.527 |
| LPC(22:6) | 4.11 ± 2.38 | 6.78 ± 4.50 | 9.20 ± 6.36 | 0.049 | 0.001 | 0.181 |
| LPE(16:0) | 1.74 ± 0.64 | 1.55 ± 0.62 | 1.57 ± 0.76 | 0.344 | 0.320 | 0.981 |
| LPE(18:0) | 2.70 ± 1.20 | 2.06 ± 0.95 | 2.11 ± 0.96 | 0.043 | 0.054 | 0.770 |
| LPE(18:2) | 3.08 ± 1.30 | 2.45 ± 0.96 | 2.12 ± 1.13 | 0.078 | 0.014 | 0.233 |
| LPE(20:4) | 1.48 ± 0.70 | 1.73 ± 0.49 | 1.78 ± 0.70 | 0.055 | 0.121 | 0.981 |
| LPE(22:6) | 0.99 ± 0.45 | 1.51 ± 0.42 | 1.86 ± 0.97 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.436 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yagi, T.; Shoaib, M.; Kuschner, C.E.; Nishikimi, M.; Becker, L.B.; Lee, A.T.; Kim, J. Challenges and Inconsistencies in Using Lysophosphatidic Acid as a Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040520
Yagi T, Shoaib M, Kuschner CE, Nishikimi M, Becker LB, Lee AT, Kim J. Challenges and Inconsistencies in Using Lysophosphatidic Acid as a Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(4):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040520
Chicago/Turabian StyleYagi, Tsukasa, Muhammad Shoaib, Cyrus E. Kuschner, Mitsuaki Nishikimi, Lance B. Becker, Annette T. Lee, and Junhwan Kim. 2019. "Challenges and Inconsistencies in Using Lysophosphatidic Acid as a Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 4: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040520
APA StyleYagi, T., Shoaib, M., Kuschner, C. E., Nishikimi, M., Becker, L. B., Lee, A. T., & Kim, J. (2019). Challenges and Inconsistencies in Using Lysophosphatidic Acid as a Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer. Cancers, 11(4), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040520





