Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sequencing Targeted Therapies
3. EGFR Inhibitors
4. Osimertinib
5. The Optimal Use of Osimertinib
6. Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O’Brien, S.G.; Gathmann, I.; Kantarjian, H.; Gattermann, N.; Deininger, M.W.; Silver, R.T.; Goldman, J.M.; Stone, R.M.; et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhot, F.; Druker, B.; Larson, R.A.; Gathmann, I.; So, C.; Waltzman, R.; O’Brien, S.G. High rates of durable response are achieved with imatinib after treatment with interferon alpha plus cytarabine: Results from the International Randomized Study of Interferon and STI571 (IRIS) trial. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lavallade, H.; Apperley, J.F.; Khorashad, J.S.; Milojkovic, D.; Reid, A.G.; Bua, M.; Szydlo, R.; Olavarria, E.; Kaeda, J.; Goldman, J.M.; et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: Incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.M.; Wang, L.; Austin, G.M.; Knight, K.; Watmough, S.J.; Shwe, K.H.; Dasgupta, R.; Butt, N.M.; Galvani, D.; Hoyle, C.F.; et al. A population study of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia demonstrates lower efficacy than in clinical trials. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1963–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, F.J.; le Coutre, P.D.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Larson, R.A.; Gattermann, N.; Ottmann, O.G.; Hochhaus, A.; Radich, J.P.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 48-month follow-up results of a phase II study. Leukemia 2013, 27, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Giles, F.J.; Bhalla, K.N.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Larson, R.A.; Gattermann, N.; Ottmann, O.G.; Hochhaus, A.; Radich, J.P.; Saglio, G.; et al. Nilotinib is effective in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase after imatinib resistance or intolerance: 24-month follow-up results. Blood 2011, 117, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Coutre, P.D.; Giles, F.J.; Hochhaus, A.; Apperley, J.F.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Blakesley, R.; Shou, Y.; Gallagher, N.J.; Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; et al. Nilotinib in patients with Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase following imatinib resistance or intolerance: 24-month follow-up results. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Gandhi, L.; Gadgeel, S.; Riely, G.J.; Cetnar, J.; West, H.; Camidge, D.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Chiappori, A.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; et al. Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.J.; Chiappori, A.A.; West, H.L.; Azada, M.C.; Morcos, P.N.; Lee, R.M.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.D.; Etienne, G.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglio, G.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Lobo, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Perol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crino, L.; Ahn, M.J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Bang, Y.J.; Kwak, E.L.; Iafrate, A.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Fox, S.B.; Riely, G.J.; Solomon, B.; Ou, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated results from a phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lu, Y.; Kim, S.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Primary results of ALESIA: A randomised, phase III, open-label study of alectinib vs crizotinib in Asian patients with treatment-naïve ALK+ Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. In Proceedings of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2018 Congress, Munich, Germany, 22 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Gainor, J.F.; Bergqvist, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Deng, Y.L.; Liu, W.; Dardaei, L.; et al. Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isozaki, H.; Ichihara, E.; Takigawa, N.; Sendo, T.; Tanimoto, M.; Kiura, K. Crizotinib to overcome alectinib-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, e19140. [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki, H.; Ichihara, E.; Takigawa, N.; Ohashi, K.; Ochi, N.; Yasugi, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Yamane, H.; Hotta, K.; Sakai, K.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Acquire Resistance to the ALK Inhibitor Alectinib by Activating Alternative Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, D.W.; Tiseo, M.; Langer, C.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Shaw, A.T.; Huber, R.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, D.H.; Bazhenova, L.A.; et al. Exploratory Analysis of Brigatinib Activity in Patients With Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases in Two Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Lee, K.H.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Osimertinib vs standard of care (SoC) EGFR-TKI as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA. In Proceedings of the ESMO 2017 Congress, Madrid, Spain, 9 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Riely, G.J.; Politi, K.A.; Miller, V.A.; Pao, W. Update on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7232–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, M.; O’Brien, S.G.; Guilhot, F.; Goldman, J.M.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.P.; Radich, J.P.; Hatfield, A.K.; Mone, M.; Filian, J.; et al. International Randomized Study of Interferon Vs STI571 (IRIS) 8-Year Follow up: Sustained Survival and Low Risk for Progression or Events in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase (CML-CP) Treated with Imatinib. Blood 2009, 114, 1126. [Google Scholar]
- Camidge, D.R.; Pao, W.; Sequist, L.V. Acquired resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: Learning from lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, N.; Iwama, E.; Kubo, N.; Harada, T.; Miyawaki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, I.; Baba, E.; Akashi, K.; Sasaki, H.; et al. Most T790M mutations are present on the same EGFR allele as activating mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin-Heymann, N.; Ulkus, L.; Brannigan, B.W.; McDermott, U.; Lamb, J.; Maheswaran, S.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. The T790M “gatekeeper” mutation in EGFR mediates resistance to low concentrations of an irreversible EGFR inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sos, M.L.; Rode, H.B.; Heynck, S.; Peifer, M.; Fischer, F.; Kluter, S.; Pawar, V.G.; Reuter, C.; Heuckmann, J.M.; Weiss, J.; et al. Chemogenomic profiling provides insights into the limited activity of irreversible EGFR Inhibitors in tumor cells expressing the T790M EGFR resistance mutation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westover, D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Cho, B.C.; Lovly, C.M.; Paz-Ares, L. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i10–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heon, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Britt, G.J.; Costa, D.B.; Rabin, M.S.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E. Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5873–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Spicer, J. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer metastatic to the brain. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeling, A.E.; Guy, S.P.; Woodburn, J.R.; Ashton, S.E.; Curry, B.J.; Barker, A.J.; Gibson, K.H. ZD1839 (Iressa): An orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5749–5754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Winterdahl, M.; Memon, A.; Sorensen, B.S.; Keiding, S.; Sorensen, L.; Nexo, E.; Meldgaard, P. Erlotinib accumulation in brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: Visualization by positron emission tomography in a patient harboring a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Katakami, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Takeshita, J.; Tanaka, K.; Nanjo, S.; Fujita, S.; Kaji, R.; Imai, Y.; Monden, K.; et al. Rebiopsy of non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Comparison between T790M mutation-positive and mutation-negative populations. Cancer 2013, 119, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Lee, M.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Improvement in Overall Survival in a Randomized Study That Compared Dacomitinib With Gefitinib in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.C.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J.; Chen, Y.M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.W.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.C.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Felip, E.; Cobo, M.; Lu, S.; Syrigos, K.; Lee, K.H.; Goker, E.; Georgoulias, V.; Li, W.; Isla, D.; et al. Afatinib versus erlotinib as second-line treatment of patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the lung (LUX-Lung 8): An open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.D.; Barbacci, E.G.; Iwata, K.K.; Arnold, L.; Boman, B.; Cunningham, A.; DiOrio, C.; Doty, J.; Morin, M.J.; Moyer, M.P.; et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Yasuda, H.; Tani, T.; Hamamoto, J.; Oashi, A.; Ishioka, K.; Arai, D.; Nukaga, S.; Miyawaki, M.; Kawada, I.; et al. In vitro modeling to determine mutation specificity of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors against clinically relevant EGFR mutants in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38789–38803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ambrogio, L.; Shimamura, T.; Kubo, S.; Takahashi, M.; Chirieac, L.R.; Padera, R.F.; Shapiro, G.I.; Baum, A.; Himmelsbach, F.; et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4702–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.W.; Yang, J.C.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of Osimertinib with Other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastases Models, and Early Evidence of Clinical Brain Metastases Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Thress, K.S.; Alden, R.S.; Lawrance, R.; Paweletz, C.P.; Cantarini, M.; Yang, J.C.; Barrett, J.C.; Janne, P.A. Association Between Plasma Genotyping and Outcomes of Treatment With Osimertinib (AZD9291) in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib As First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, J.L.; Heideman, D.A.; Thunnissen, E.; Paul, M.A.; van Wijk, A.W.; Postmus, P.E.; Smit, E.F. Incidence of T790M mutation in (sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Collins, B.; Chmielecki, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; et al. Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Rukazenkov, Y.; Todd, A.; Markovets, A.; Chmielecki, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Gray, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulananda, S.; Do, H.; Musafer, A.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Combination Osimertinib and Gefitinib in C797S and T790M EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thress, K.S.; Paweletz, C.P.; Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Stetson, D.; Dougherty, B.; Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Vivancos, A.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Tian, S.K.; Drilon, A.E.; Borsu, L.; Riely, G.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M. Acquired Resistance of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer to a T790M-Specific EGFR Inhibitor: Emergence of a Third Mutation (C797S) in the EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Domain. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersanelli, M.; Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Gnetti, L.; Bozzetti, C.; Squadrilli, A.; Lagrasta, C.A.; Bottarelli, L.; Osipova, G.; Capelletto, E.; et al. L718Q Mutation as New Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, e121–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Azuma, K.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Togashi, Y.; Sesumi, Y.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Sato, K.; Tomizawa, K.; et al. Characterization of EGFR T790M, L792F, and C797S Mutations as Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Afatinib in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. EAI045: The fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Loriot, Y.; Andre, F.; Gobert, A.; Auger, N.; Lacroix, L.; Soria, J.C. EGFR-independent mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC patients. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Scheffler, M.; Plenker, D.; Dahmen, L.; Scheel, A.H.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Persigehl, T.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; et al. Heterogeneous Mechanisms of Primary and Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4837–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Niederst, M.J.; Karlovich, C.A.; Wakelee, H.A.; Neal, J.W.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fulton, L.; Hata, A.N.; Lockerman, E.L.; Kalsy, A.; et al. Heterogeneity Underlies the Emergence of EGFRT790 Wild-Type Clones Following Treatment of T790M-Positive Cancers with a Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Fu, W.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Z.; Liang, G. Recent progress of small-molecule epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors against C797S resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4290–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knebel, F.H.; Bettoni, F.; Shimada, A.K.; Cruz, M.; Alessi, J.V.; Negrao, M.V.; Reis, L.F.L.; Katz, A.; Camargo, A.A. Sequential liquid biopsies reveal dynamic alterations of EGFR driver mutations and indicate EGFR amplification as a new mechanism of resistance to osimertinib in NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.I.; Cui, J.; Schrock, A.B.; Goldberg, M.E.; Zhu, V.W.; Albacker, L.; Stephens, P.J.; Miller, V.A.; Ali, S.M. Emergence of novel and dominant acquired EGFR solvent-front mutations at Gly796 (G796S/R) together with C797S/R and L792F/H mutations in one EGFR (L858R/T790M) NSCLC patient who progressed on osimertinib. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Hu, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ni, J.; et al. EGFR G796D mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49671–49679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.M.; Song, A.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Keam, B.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to AZD9291: A Mutation-Selective, Irreversible EGFR Inhibitor. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Ercan, D.; Chen, L.; Yun, C.H.; Li, D.; Capelletti, M.; Cortot, A.B.; Chirieac, L.; Iacob, R.E.; Padera, R.; et al. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Nature 2009, 462, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Tu, H.Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.L. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S Responds to Combination Therapy of First- and Third-Generation EGFR TKIs and Shifts Allelic Configuration at Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu Koyyala, V.P.; Batra, U.; Jain, P.; Sharma, M.; Goyal, P.; Domadia, K.; Botra, S. Good response to erlotinib in a patient after progression on osimertinib: A rare case of spatiotemporal T790M heterogeneity in a patient with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer. South Asian J Cancer 2017, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

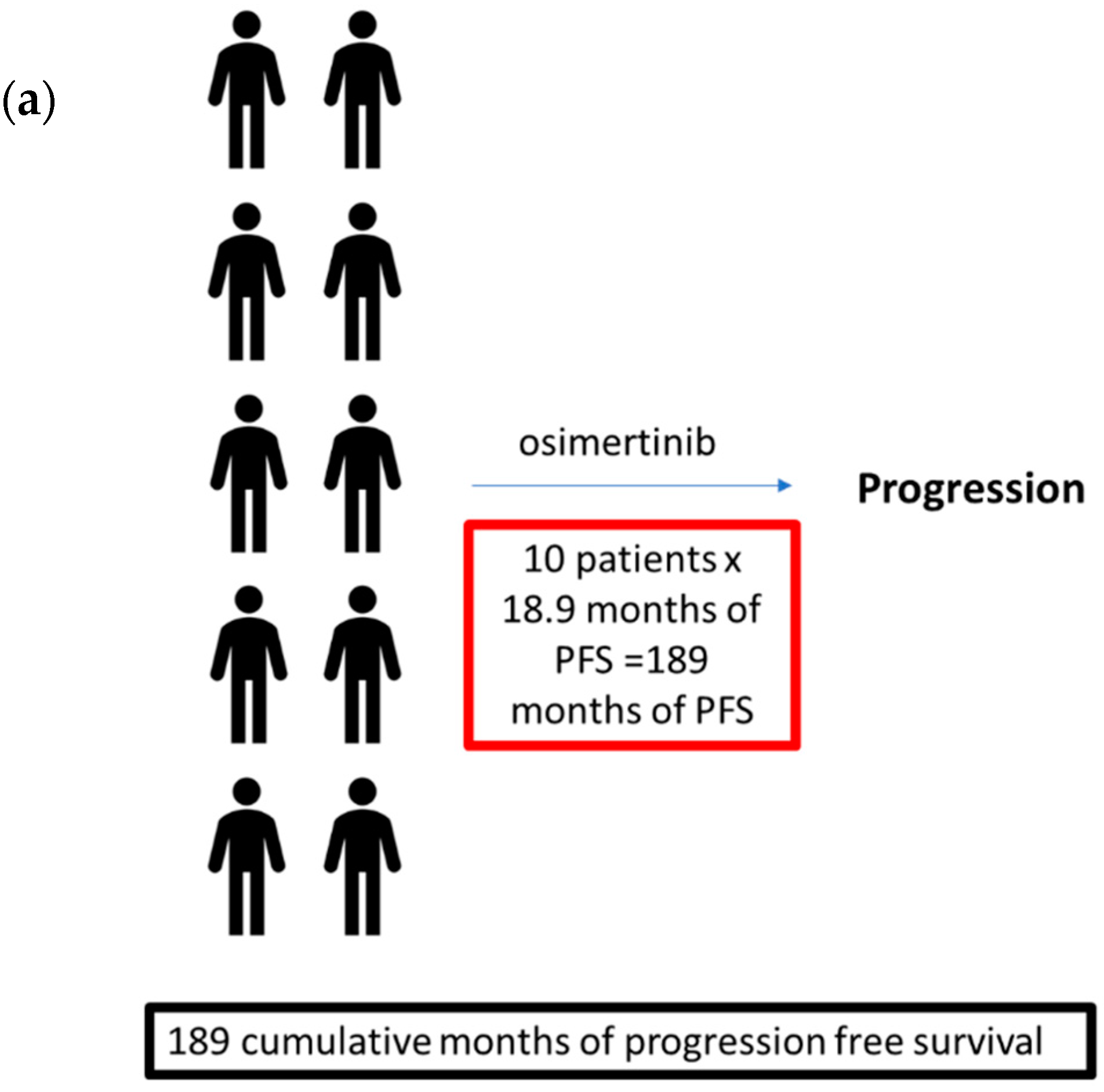
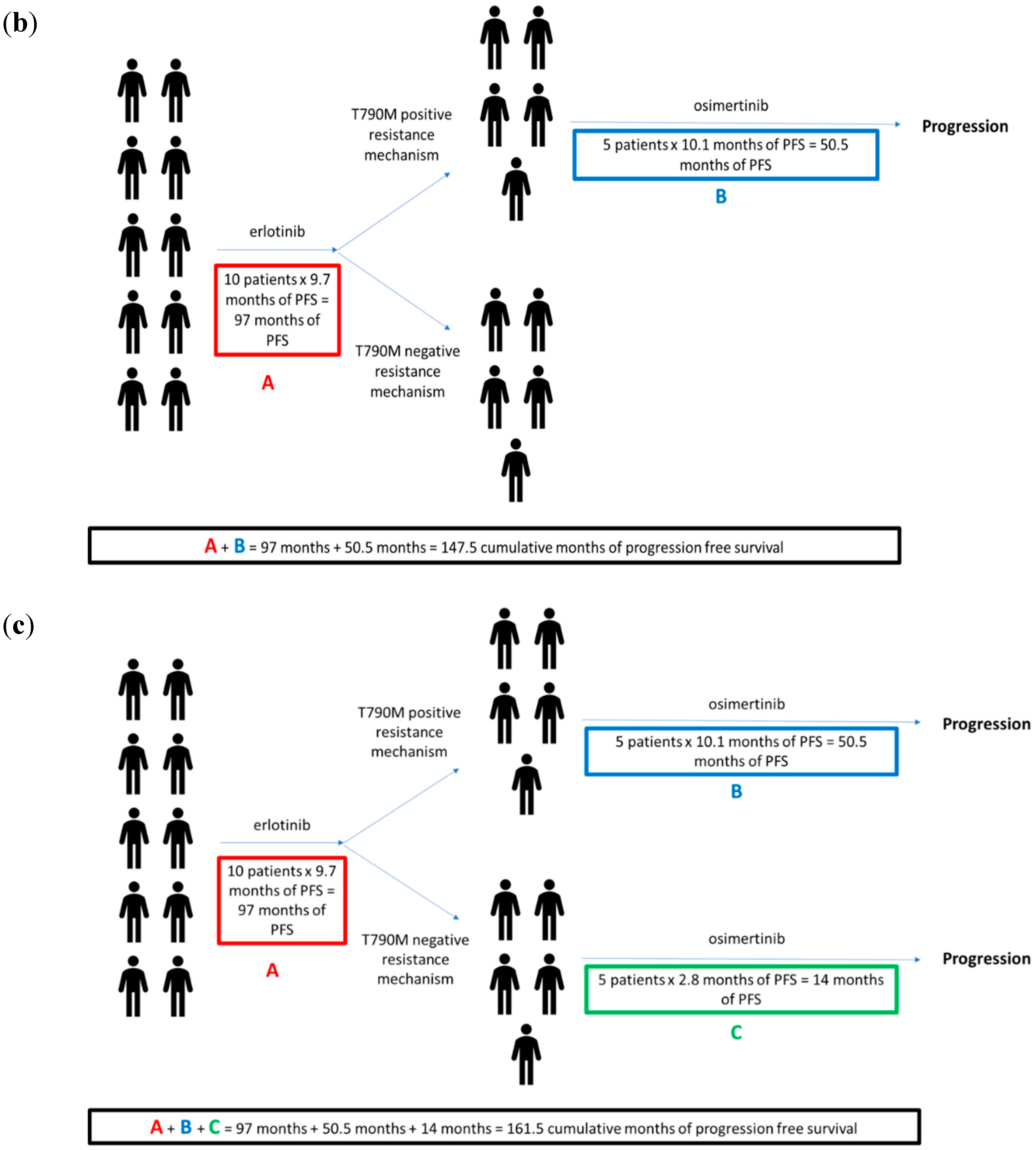
| Category | Example TKI | Wt EGFR (IC50 in nM) | Exon 19del (IC50 in nM) | L858R (IC50 in nM) | Exon 19del + T790M EGFRm (IC50 in nM) | L858R + T790M (IC50 in nM) | Dosing Schedule | Common Toxicities (% with Grades 3–4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-generation EGFR TKI | erlotinib | 20 [51] | 23 [52] | 39 [52] | 1600 [52] | >10000 [52] | 150 mg once daily | diarrhea (5), rash (12), paronychia (0), stomatitis (1) [16] |
| Second-generation EGFR TKI | afatinib | 0.5 [53] | 0.2 [52] | 0.2 [52] | 141 [52] | 196 [52] | 40 mg once daily | diarrhea (14), rash (16), paronychia (11), stomatitis (8) [18] |
| Third-generation EGFR TKI | osimertinib | 938 [52] | 12 [52] | 9 [52] | 3 [52] | 13 [52] | 80 mg once daily | diarrhea (2), rash (3), paronychia (1), stomatitis (5) [29] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.; Gerber, D.E. Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used? Cancers 2019, 11, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030366
Le T, Gerber DE. Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used? Cancers. 2019; 11(3):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Tri, and David E. Gerber. 2019. "Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used?" Cancers 11, no. 3: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030366
APA StyleLe, T., & Gerber, D. E. (2019). Newer-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: How Are They Best Used? Cancers, 11(3), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030366





