Does Risk-Adapted Proton Beam Therapy Have a Role as a Complementary or Alternative Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Abstract
1. Introduction
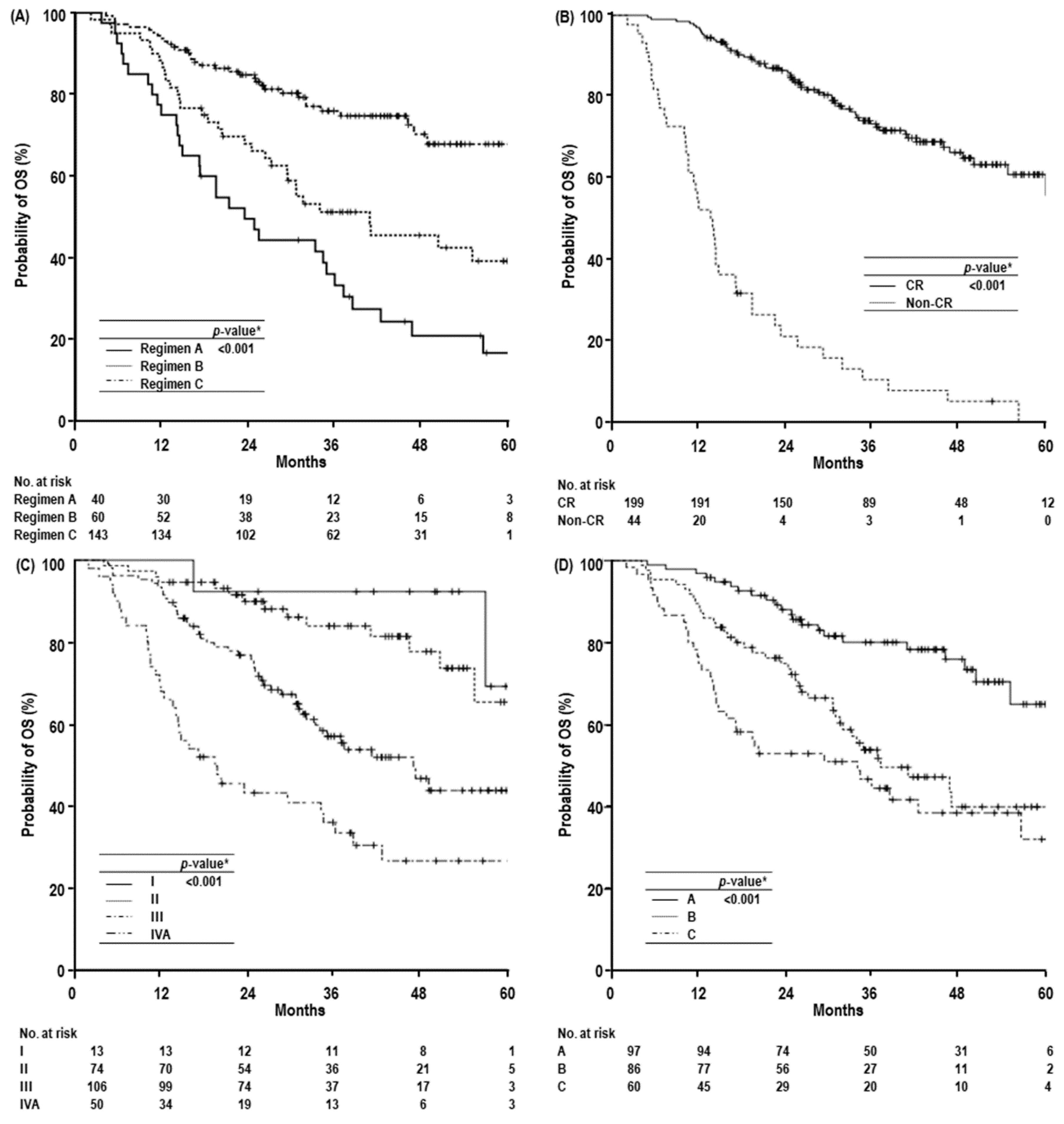
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Treatment
4.3. Evaluation and Statistical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. Aasld guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Study Group; National Cancer Center. Practice guidelines for management of hepatocellular carcinoma 2009. Korean J. Hepatol. 2009, 15, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Study Group; National Cancer Center. 2014 KLCSG-NCC Korea practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut Liver 2015, 9, 267–317. [Google Scholar]
- Bujold, A.; Massey, C.A.; Kim, J.J.; Brierley, J.; Cho, C.; Wong, R.K.; Dinniwell, R.E.; Kassam, Z.; Ringash, J.; Cummings, B.; et al. Sequential phase i and ii trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, D.A.; Kayali, Z.; Grove, R.; Slater, J.D. The safety and efficacy of high-dose proton beam radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase 2 prospective trial. Cancer 2011, 117, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Okumura, T.; Abei, M.; Fukumitsu, N.; Ishige, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Numajiri, H.; Ohnishi, K.; Ishikawa, H.; et al. Long-term outcomes of proton beam therapy in patients with previously untreated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumitsu, N.; Sugahara, S.; Nakayama, H.; Fukuda, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Abei, M.; Shoda, J.; Thono, E.; Tsuboi, K.; Tokuuye, K. A prospective study of hypofractionated proton beam therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.S.; Wo, J.Y.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ben-Josef, E.; McDonnell, E.I.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; Goyal, L.; et al. Multi-institutional phase ii study of high-dose hypofractionated proton beam therapy in patients with localized, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, M.; Furuse, J.; Nishio, T.; Konishi, M.; Ishii, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Nagase, M.; Nihei, K.; Ogino, T. Phase ii study of radiotherapy employing proton beam for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, B.H.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Woo, S.M.; Koh, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, C.M. Risk-adapted simultaneous integrated boost-proton beam therapy (sib-pbt) for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumour vascular thrombosis. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, W.J.; Park, S.J.; Hong, E.K.; Kim, C.M. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients for whom transcatheter arterial chemoembolization was ineffective or unsuitable. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 29, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Woo, S.M.; Koh, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; et al. Optimal time of tumour response evaluation and effectiveness of hypofractionated proton beam therapy for inoperable or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4034–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.H.; Woo, S.M.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Koh, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; Park, S.J.; et al. Phase i dose-escalation study of proton beam therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.H.; Woo, S.M.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, C.M. Simultaneous integrated boost-intensity modulated radiation therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Dawson, L.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma radiation therapy: Review of evidence and future opportunities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.U.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Woo, S.M.; Koh, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, C.M. Effectiveness and safety of proton beam therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, C.H.; Seong, J. Application of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in current clinical practice guidelines. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2016, 34, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, F.; Widesott, L.; Lorentini, S.; Amichetti, M. Is there a role for proton therapy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma? A systematic review. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuhata, M.; Takamatsu, S.; Shibata, S.; Bou, S.; Sato, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Asahi, S.; Tameshige, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Respiratory-gated proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract without fiducial markers. Cancers 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Takamatsu, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Mizuhata, M.; Bou, S.; Sato, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Asahi, S.; Tameshige, Y.; Maeda, Y.; et al. Proton beam therapy without fiducial markers using four-dimensional ct planning for large hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancers 2018, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Sugahara, S.; Fukuda, K.; Abei, M.; Shoda, J.; Sakurai, H.; Tsuboi, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Tokuuye, K. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma located adjacent to the alimentary tract. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, T.H.; Cho, K.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, S.B.; et al. Normal liver sparing by proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with helical intensity modulated radiotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.X.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.M. Charged particle therapy versus photon therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bru, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The bclc staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Llovet, J.M. Major achievements in hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2009, 373, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Park, J.W.; Nam, B.H.; Yu, A.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.B.; Park, S.J.; et al. Clinical outcomes of a cohort series of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis b virus-endemic area. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.F. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Kudo, M.; Ye, S.L.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Chen, X.P.; Dagher, L.; Furuse, J.; Geschwind, J.F.; de Guevara, L.L.; Papandreou, C.; et al. Gideon (global investigation of therapeutic decisions in hepatocellular carcinoma and of its treatment with sorafenib): Second interim analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, S.; Tanabe, G.; Nuruki, K.; Hamanoue, M.; Komorizono, Y.; Oketani, M.; Hokotate, H.; Inoue, H.; Baba, Y.; Imamura, Y.; et al. Prognostic performance of the new classification of primary liver cancer of japan (4th edition) for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A validation analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2002, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Oku, Y.; Sanuki, N.; Kunieda, E.; Koike, N.; Aoki, Y.; Ohashi, T.; Iwabuchi, S.; Takatsuka, K.; Takeda, T.; et al. Dose volume histogram analysis of focal liver reaction in follow-up multiphasic ct following stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 104, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, M.C.; Bentzen, S.M. Time-dose relationships: The linear-quadrantic approach. In Basic Clinical Radiobiology, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, W.J.; Park, S.J.; Hong, E.K.; Kim, C.M. Dose-volumetric parameters predicting radiation-induced hepatic toxicity in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 67, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified recist (mrecist) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Total | Dose-Fx Regimen A | Dose-Fx Regimen B | Dose-Fx Regimen C | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Gender | Male | 211 (86.8) | 34 (85.0) | 53 (88.3) | 124 (86.7) | 0.888 * |
| Female | 32 (13.2) | 6 (15.0) | 7 (11.7) | 19 (13.3) | ||
| Age, years | Median (range) | 61 (24–92) | 59 (24–81) | 62.5 (39–80) | 62 (34–92) | 0.133 † |
| <60 | 100 (41.2) | 22 (55.0) | 24 (40.0) | 54 (37.8) | 0.144 * | |
| ≥60 | 143 (58.8) | 18 (45.0) | 36 (60.0) | 89 (62.2) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0 | 237 (97.5) | 38 (95.0) | 59 (98.3) | 140 (97.9) | 0.520 * |
| 1 | 6 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | 1 (1.7) | 3 (2.1) | ||
| Etiology of LC | HBV | 188 (77.4) | 33 (82.5) | 45 (75.0) | 110 (76.9) | 0.799 * |
| HCV | 20 (8.2) | 3 (7.5) | 6 (10.0) | 11 (7.7) | ||
| Alcoholic | 17 (7.0) | 1 (2.5) | 6 (10.0) | 10 (7.0) | ||
| Unknown | 18 (7.4) | 3 (7.5) | 3 (5.0) | 12 (8.4) | ||
| Child-Pugh | A | 228 (93.8) | 36 (90.0) | 54 (90.0) | 138 (96.5) | 0.117 * |
| Classification | B7 | 15 (6.2) | 4 (10.0) | 6 (10.0) | 5 (3.5) | |
| AFP, ng/mL | Median (range) | 10.2 (1.2–38,396.4) | 25.3 (1.9–31,466.3) | 10.9 (2.2–38,396.4) | 9.3 (1.2–16,788.3) | 0.062 † |
| <10 | 120 (49.4) | 14 (35.0) | 30 (50.0) | 76 (53.1) | 0.127 * | |
| ≥10 | 123 (50.6) | 26 (65.0) | 30 (50.0) | 67 (46.9) | ||
| Tumor size, cm | Median (range) | 2.2 (1.0–17) | 6.0 (1.3–17) | 3.6 (1.0–12) | 1.5 (1.0–12.7) | <0.001 † |
| ≤2 | 115 (47.3) | 1 (2.5) | 16 (26.7) | 98 (68.5) | <0.001 * | |
| >2 | 128 (52.7) | 39 (97.5) | 44 (73.3) | 45 (31.5) | ||
| TVT | No | 184(75.7) | 11 (27.5) | 40 (66.7) | 133 (93.0) | <0.001 * |
| Branch | 29 (11.9) | 7 (17.5) | 15 (25.0) | 7 (4.9) | ||
| Main | 30 (12.3) | 22 (55.0) | 5 (8.3) | 3 (2.1) | ||
| mUICC stage | I | 13 (5.3) | 1 (2.5) | 2 (3.3) | 10 (7.0) | <0.001 * |
| II | 74 (30.5) | 1 (2.5) | 13 (21.7) | 60 (42.0) | ||
| III | 106 (43.6) | 12 (30.0) | 31 (51.7) | 63 (44.1) | ||
| IVA | 50 (20.6) | 26 (65.0) | 14 (23.3) | 10 (7.0) | ||
| BCLC stage | A | 97 (39.9) | 0 (0) | 17 (28.3) | 80 (55.9) | <0.001 * |
| B | 86 (35.4) | 11 (27.5) | 22 (36.7) | 53 (37.1) | ||
| C | 60 (24.7) | 29 (72.5) | 21 (35.0) | 10 (7.0) | ||
| Diagnosis at PBT | Primary | 10 (4.1) | 5 (12.5) | 2 (3.3) | 3 (2.1) | 0.021 |
| Recurrence | 233 (95.9) | 35 (87.5) | 58 (96.7) | 140 (95.9) | ||
| Pre-Tx to PBT site | No | 52 (21.4) | 7 (17.5) | 4 (6.7) | 41 (28.7) | 0.002 * |
| Yes | 191 (78.6) | 33 (82.5) | 56 (93.3) | 102 (71.3) | ||
| LRT | 186 (97.4) | 27 (81.8) | 54 (96.4) | 102 (97.4) | ||
| LRT + sorafenib | 5 (2.6) | 3 (9.1) | 2 (3.6) | 0 (0) | ||
| Sorafenib ± chemo | 3 (1.6) | 3 (9.1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Pre-Tx to other site | No | 70 (28.8) | 22 (55.0) | 23 (38.3) | 25 (17.5) | <0.001 * |
| Yes | 173 (43.9) | 18 (45.0) | 37 (61.7) | 118 (82.5) | ||
| LRT | 171 (98.3) | 18 (100) | 36 (97.3) | 117 (98.3) | ||
| LRT + sorafenib | 3 (1.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.7) | 2 (1.7) | ||
| Concurrent Tx | No | 236 (97.1) | 34 (85.0) | 59 (98.3) | 143 (100) | <0.001 * |
| Sorafenib | 7 (2.9) | 6 (15.0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) | ||
| Post-Tx to PBT site | No | 195 (80.2) | 12 (30.0) | 48 (80.0) | 135 (94.4) | <0.001 * |
| Yes | 48 (19.8) | 28 (70.0) | 12 (20.0) | 8 (5.6) | ||
| LRT | 16 (33.3) | 7 (25.0) | 7 (58.3) | 2 (25.0) | ||
| LRT ± sorafenib ± chemo | 7 (14.6) | 6 (21.4) | 0 (0) | 1 (12.5) | ||
| Sorafenib ± chemo | 25 (52.1) | 15 (53.6) | 5 (41.7) | 5 (62.5) | ||
| Post-Tx to other site | No | 66 (27.2) | 8 (20.0) | 18 (30.0) | 40 (28.0) | 0.515 * |
| Yes | 177 (72.8) | 32 (80.0) | 42 (70.0) | 103 (72.0) | ||
| LRT | 91 (51.7) | 4 (12.5) | 19 (45.2) | 68 (66.0) | ||
| LRT ± sorafenib ± chemo | 57 (32.4) | 17 (51.1) | 15 (35.7) | 26 (25.2) | ||
| Sorafenib ± chemo | 28 (15.9) | 11 (34.4) | 8 (19.0) | 9 (8.7) | ||
| Response | Dose-Fractionation Regimen, n (%) | p Value * | Pre-Tx to PBT Site, n (%) | p Value * | Post-Tx to PBT Site, n (%) | p Value * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regimen A | Regimen B | Regimen C | No | Yes | No | Yes | |||||
| Primary tumor | CR | 16 (40.0) | 51 (85.0) | 132 (92.3) | <0.001 | 47 (90.4) | 152 (79.6) | 0.405 | 174 (89.2) | 25 (53.1) | <0.001 |
| (n = 243) | PR | 18 (45.0) | 6 (10.0) | 6 (4.2) | 4 (7.7) | 26 (13.6) | 16 (8.2) | 14 (29.2) | |||
| SD | 6 (15.02) | 2 (3.3) | 5 (3.5) | 1 (1.9) | 12 (6.3) | 5 (2.6) | 1 (2.1) | ||||
| PD | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.1) | ||||
| TVT | CR | 9 (31.0) | 15 (75.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0.021 | 3 (42.9) | 27 (51.9) | 0.877 | 15 (60.0) | 15 (44.1) | 0.610 |
| (n = 59) | PR | 12 (41.4) | 3 (15.0) | 3 (30.0) | 3 (42.9) | 15 (28.9) | 7 (28.0) | 11 (32.4) | |||
| SD | 8 (27.6) | 1 (5.0) | 1 (10.0) | 1 (14.2) | 9 (17.3) | 3 (12.0) | 7 (20.6) | ||||
| PD | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) | ||||
| Characteristics | Univariate † | Multivariate ‡ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-yr OS, % (95% CI) | 3-yr OS, % (95% CI) | 5-yr OS, % (95% CI) | Median OS, Months (95% CI) | p Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | ||
| Gender | Male | 87.7 (83.2–92.2) | 62.2 (55.1–69.3) | 48.3 (38.5–58.1) | 56.5 (45.5–67.2) | 0.964 | - | NS |
| Female | 96.9 (90.8–100) | 60.2 (42.6–77.8) | 49.3 (29.3–69.3) | 46.6 (-) | - | |||
| Age, years | <60 | 88.0 (81.7–94.3) | 63.3 (53.3–73.3) | 45.0 (29.1–60.9) | 56.5 (35.1–77.9) | 0.945 | - | NS |
| ≥60 | 89.5 (84.4–94.6) | 60.8 (52.0–69.6) | 49.5 (38.3–60.7) | 55.0 (44.5–65.5) | - | |||
| ECOG PS | 0 | 88.6 (84.5–92.7) | 62.8 (56.1–69.5) | 48.6 (39.4–57.8) | 56.5 (44.9–68.0) | 0.175 | - | NS |
| 1 | 100 (-) | 25.0 (0–65.0) | - (-) | 21.2 (4.1–38.4) | - | |||
| Etiology of LC | HBV | 88.8 (84.3–93.3) | 62.4 (55.0–69.8) | 49.4 (39.2–59.6) | 56.5 (-) | 0.784 | - | NS |
| Others | 89.1 (80.9–97.3) | 60.0 (45.5–74.5) | 44.9 (26.1–63.7) | 55.0 (32.0–78.0) | - | |||
| Child-Pugh Classification | A | 90.4 (86.5–94.3) | 65.3 (58.6–72.0) | 50.5 (41.1–59.9) | 60.3 (-) | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.016 |
| B7 | 66.7 (42.8–90.6) | 0.91 (0–26.0) | 0.91 (0–26.0) | 17.1 (1.6–32.6) | 2.221 (1.162–4.246) | |||
| AFP, ng/mL | <10 | 92.5 (87.8–97.2) | 74.3 (65.7–82.9) | 56.3 (41.6–71.0) | NR | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.008 |
| ≥10 | 85.4 (79.1–91.7) | 49.9 (40.5–59.3) | 39.6 (28.6–50.6) | 34.3 (24.4–44.2) | 1.773 (1.158–2.713) | |||
| Tumor size, cm | ≤2 | 94.8 (90.7–98.9) | 79.5 (71.5–87.5) | 64.4 (49.3–7.5) | NR | <0.001 | - | NS |
| >2 | 83.6 (77.1–90.1) | 46.5 (37.1–55.9) | 34.0 (23.6–44.4) | 33.9 (28.4–39.5) | - | |||
| TVT | No | 93.5 (90.0–97.0) | 67.8 (60.4–75.3) | 54.1 (43.9–64.3) | 60.3 (-) | <0.001 | – | NS |
| Branch | 79.3 (60.4–91.4) | 49.0 (29.8–68.2) | 49.0 (29.8–68.2) | 34.3 (-) | ||||
| Main | 73.3 (57.4–89.2) | 38.8 (21.0–56.6) | 18.9 (0–38.1) | 19.4 (6.1–32.8) | - | |||
| mUICC stage | I | 100 (-) | 92.3 (77.8–100) | 69.2 (28.6–100) | NR | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| II | 94.6 (89.5–99.7) | 83.9 (74.5–93.3) | 65.4 (45.8–85) | NR | 3.186 (0.699–14.525) | 0.134 | ||
| III | 93.4 (88.7–98.1) | 57.0 (46.8–67.2) | 43.8 (31.3–56.3) | 46.6 (34.9–58.4) | 6.563 (1.557–27.669) | 0.010 | ||
| IVA | 68.0 (55.1–80.9) | 33.4 (19.7–47.1) | 26.6 (12.7–40.5) | 19.4 (10.0–28.8) | 7.119 (1.673–30.288) | 0.008 | ||
| BCLC stage | A | 96.9 (93.4–100) | 80.1 (71.5–88.7) | 65.1 (50.2–80.0) | NR | <0.001 | - | NS |
| B | 89.5 (83.0–96.0) | 53.9 (42.3–65.5) | 40.0 (26.1–53.9) | 37.1 (24.2–50.1) | - | |||
| C | 75.0 (64.0–86.0) | 44.6 (31.5–57.7) | 32.2 (16.0–48.6) | 33.9 (16.2–51.7) | - | |||
| Diagnosis at PBT | Primary | 90.0 (71.4–100) | 56.0 (22.5–89.5) | 42.0 (7.5–76.5) | 38.4 (8.5–68.2) | 0.578 | - | NS |
| Recurrence | 88.8 (83.8–92.1) | 62.0 (55.3–68.7) | 48.2 (38.8–57.6) | 56.5 (45.3–67.7) | - | |||
| Pre-Tx to PBT site | No | 98.1 (94.4–100) | 82.3 (71.1–93.5) | 78.4 (65.3–91.5) | NR | <0.001 | - | NS |
| Yes | 86.4 (81.5–91.3) | 56.8 (49.4–64.2) | 41.7 (32.1–51.3) | 46.9 (33.7–60.1) | - | |||
| Pre-Tx to other site | No | 87.1 (79.3–94.9) | 54.0 (41.3–66.7) | 41.4 (26.3–56.5) | 38.4 (19.7–57.1) | 0.130 | - | NS |
| Yes | 89.6 (85.1–94.1) | 64.9 (57.3–72.5) | 51.2 (39.8–62.5) | NR | - | |||
| Concurrent Tx | No | 89.8 (85.9–93.7) | 62.8 (56.1–69.5) | 49.4 (38.0–60.8) | 56.5 (-) | 0.001 | - | NS |
| Sorafenib | 57.1 (20.4–93.8) | 28.6 (0–62.1) | 0 (-) | 19.4 (0–40.3) | - | |||
| Post-Tx to PBT site | No | 93.8 (90.5–97.1) | 67.5 (60.2–74.8) | 53.8 (42.6–65.0) | 60.3 (-) | <0.001 | - | NS |
| Yes | 68.7 (55.6–81.8) | 40.2 (25.9–54.5) | 26.2 (12.5–39.9) | 25.4 (7.1–43.7) | - | |||
| Post-Tx to other sites | No | 81.8 (72.6–91.0) | 68.8 (56.8–80.8) | 61.9 (45.2–78.6) | NR | 0.294 | - | NS |
| Yes | 91.5 (87.3–95.6) | 59.8 (52.2–67.4) | 44.3 (34.1–54.5) | 48.7 (36.3–61.1) | - | |||
| Dose-fractionation | Regimen A | 75.0 (61.7–88.3) | 33.3 (18.4–48.2) | 16.7 (3.6–29.8) | 23.4 (15.3–31.5) | <0.001 | 2.045 (1.244–3.362) | 0.005 |
| Regimen B | 86.7 (78.1–95.3) | 51.2 (38.1–64.3) | 39.2 (24.9–53.5) | 40.8 (19.7–61.9) | 1.298 (0.740–2.277) | 0.363 | ||
| Regimen C | 93.7 (89.8–97.6) | 76.0 (68.4–83.6) | 67.9 (57.5–78.3) | NR | 1.000 | |||
| Primary tumor response | CR | 97.0 (94.6–99.4) | 73.3 (66.6–80.0) | 60.9 (51.5–70.3) | NR | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| Non-CR | 52.3 (37.6–67.0) | 10.6 (1.0–20.2) | 0 (-) | 13.7 (10.8–16.6) | 7.012 (4.324–11.370) | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.H.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, H.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Woo, S.M.; Koh, Y.-H.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Does Risk-Adapted Proton Beam Therapy Have a Role as a Complementary or Alternative Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Cancers 2019, 11, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020230
Kim TH, Park J-W, Kim BH, Kim H, Moon SH, Kim SS, Woo SM, Koh Y-H, Lee WJ, Kim DY, et al. Does Risk-Adapted Proton Beam Therapy Have a Role as a Complementary or Alternative Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Cancers. 2019; 11(2):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020230
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Hyun, Joong-Won Park, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyunjung Kim, Sung Ho Moon, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Myung Woo, Young-Hwan Koh, Woo Jin Lee, Dae Yong Kim, and et al. 2019. "Does Risk-Adapted Proton Beam Therapy Have a Role as a Complementary or Alternative Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma?" Cancers 11, no. 2: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020230
APA StyleKim, T. H., Park, J.-W., Kim, B. H., Kim, H., Moon, S. H., Kim, S. S., Woo, S. M., Koh, Y.-H., Lee, W. J., Kim, D. Y., & Kim, C.-M. (2019). Does Risk-Adapted Proton Beam Therapy Have a Role as a Complementary or Alternative Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Cancers, 11(2), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020230





