The Phylogeographic Diversity of EBV and Admixed Ancestry in the Americas–Another Model of Disrupted Human-Pathogen Co-Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
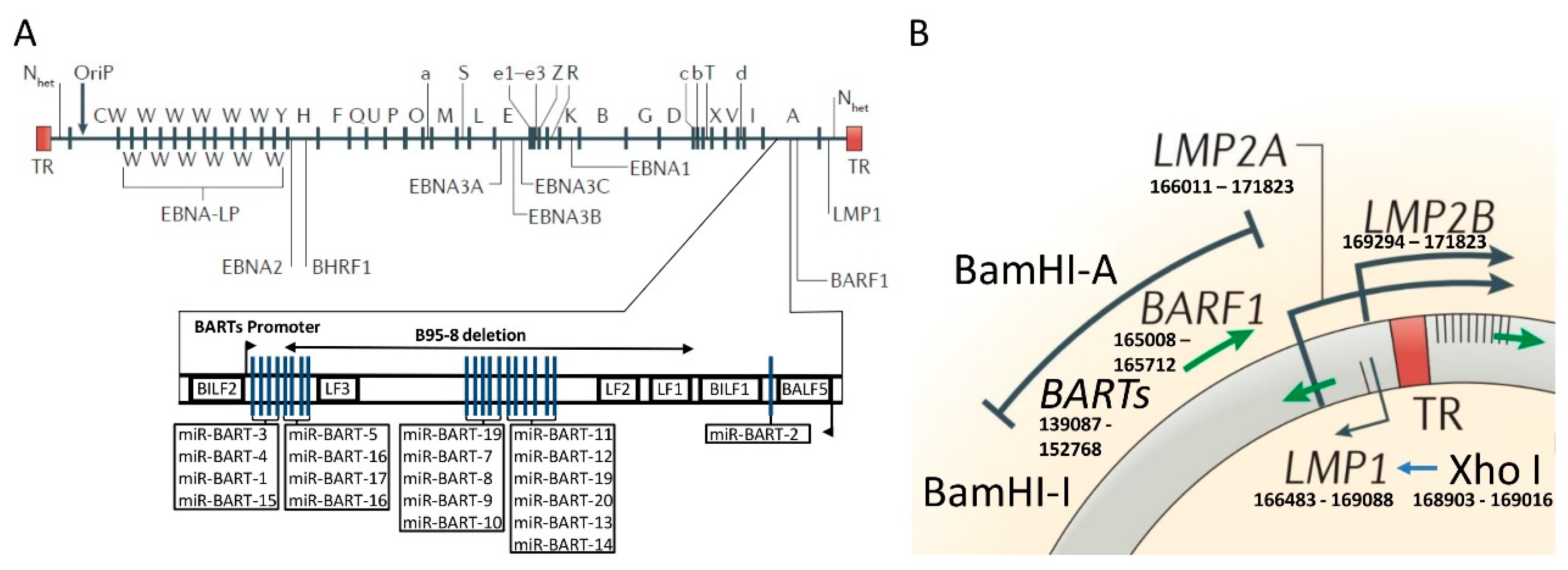
2. Phylogenetic Classification of EBV
3. The Molecular Structure of the Cosegregated BamHI–I Fragment and XhoI Region of the EBV
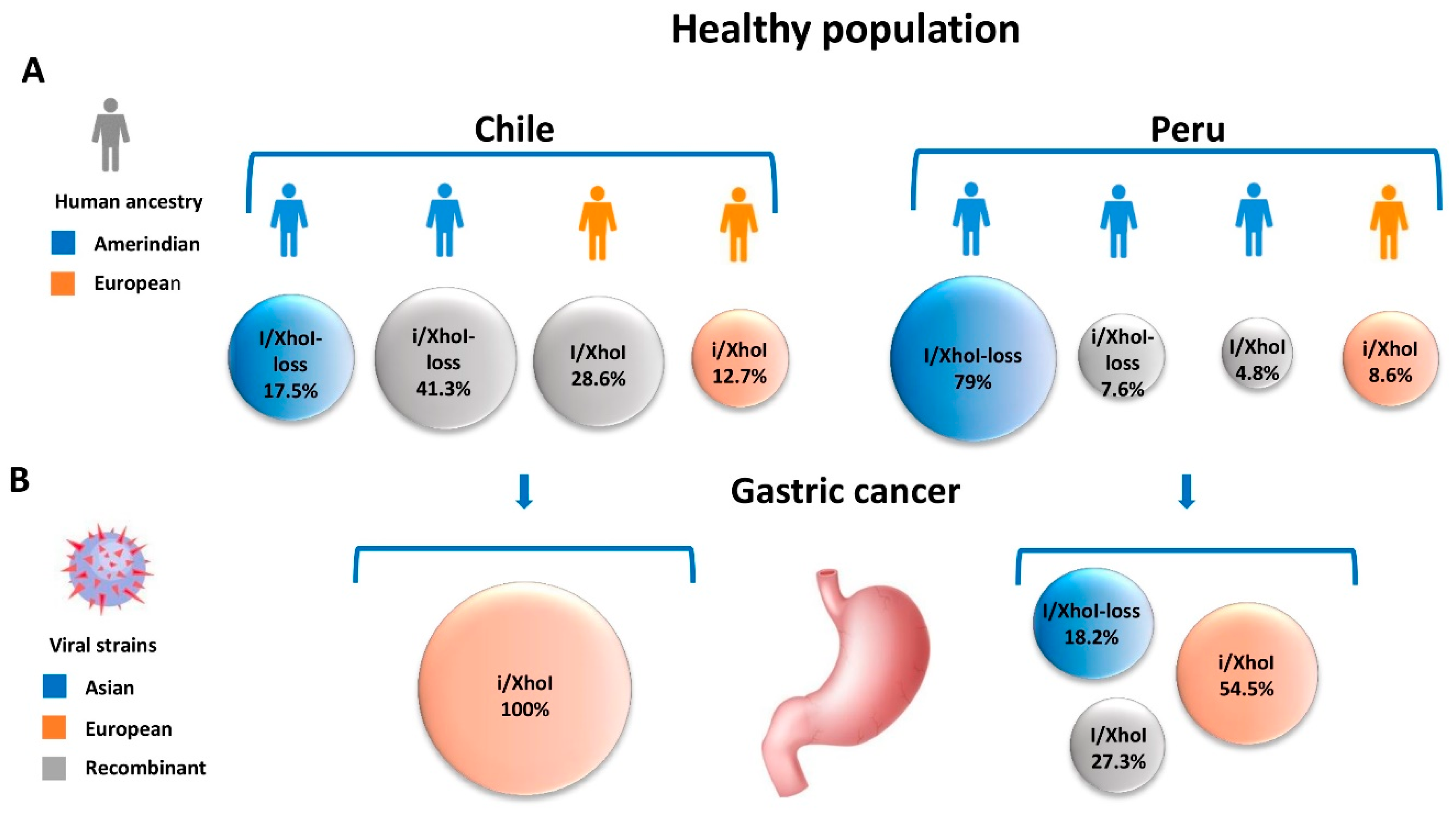
4. Human Ancestry in the Americas and EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma
5. Other Examples of “Disrupted Co-Evolution” in Cancer-Related Infectious Agents
6. Are Phylogeographic Variations of Epstein–Barr Virus Relevant to Other EBV-Associated Diseases?
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Consortium. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, J.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Shimokuri, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yanai, H.; Sakai, K.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. Clinical Importance of Epstein(-)Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, H.; Pinto-Correia, A.L.; Medeiros, R.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M. Epstein-Barr virus is associated with gastric carcinoma: The question is what is the significance? World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 4347–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, S.H.; An, J.S.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, Y.S. Clinicopathological and molecular characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: A meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.; Pfeiffer, R.; Camargo, M.C.; Rabkin, C.S. Meta-analysis shows that prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer differs based on sex and anatomic location. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Y. Meta-analysis of the relationship between Epstein-Barr virus infection and clinicopathological features of patients with gastric carcinoma. Science China. Life Sci. 2010, 53, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, M.C.; Murphy, G.; Koriyama, C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Kim, W.H.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Corvalan, A.H.; Carrascal, E.; Abdirad, A.; Anwar, M.; et al. Determinants of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer: An international pooled analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S.; Iriya, K.; Yamaguti, T.; Hamada, G.S.; Itoh, T.; Eizuru, Y.; Aikou, T.; Watanabe, S.; Tsugane, S.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma in Japanese Brazilians and non-Japanese Brazilians in Sao Paulo. Jpn. J. Cancer res. 2001, 92, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulley, M.L.; Pulitzer, D.R.; Eagan, P.A.; Schneider, B.G. Epstein-Barr virus infection is an early event in gastric carcinogenesis and is independent of bcl-2 expression and p53 accumulation. Hum. Pathol. 1996, 27, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, Q.N.; Geradts, J.; Gulley, M.L.; Boudreau, D.A.; Bravo, J.C.; Schneider, B.G. Epstein-Barr virus in gastric adenocarcinomas: Association with ethnicity and CDKN2A promoter methylation. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, A.; Figueroa, U.; Espinoza, B.; Sandoval, A.; Carrasco-Aviño, G.; Aguayo, F.R.; Corvalan, A.H. Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Gastric Carcinoma: The Americas’ Perspective; Lunet, N., Ed.; Intech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R.; Bankier, A.T.; Biggin, M.D.; Deininger, P.L.; Farrell, P.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Hatfull, G.; Hudson, G.S.; Satchwell, S.C.; Seguin, C.; et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 1984, 310, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, O.; Smith, P.R.; Spender, L.C.; Elgueta Karstegl, C.; Niller, H.H.; Huang, D.; Farrell, P.J. Updated Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA sequence and analysis of a promoter for the BART (CST, BARF0) RNAs of EBV. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Li, T.; Hung, G.C.; Li, B.; Tsai, S.; Lo, S.C. Identification and characterization of EBV genomes in spontaneously immortalized human peripheral blood B lymphocytes by NGS technology. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Pan, Y.; Ji, J.; Lu, Z.; Ke, Y. Genome-wide analysis of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isolated from EBV-associated gastric carcinoma (EBVaGC). Oncotarget 2015, 7, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santpere, G.; Darre, F.; Blanco, S.; Alcami, A.; Villoslada, P.; Mar Alba, M.; Navarro, A. Genome-wide analysis of wild-type Epstein-Barr virus genomes derived from healthy individuals of the 1,000 Genomes Project. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.; Marinho-Dias, J.; Ribeiro, J.; Sousa, H. Epstein-Barr virus strains and variations: Geographic or disease-specific variants? J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample, J.; Young, L.; Martin, B.; Chatman, T.; Kieff, E.; Rickinson, A.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar]
- Zimber, U.; Adldinger, H.K.; Lenoir, G.M.; Vuillaume, M.; Knebel-Doeberitz, M.V.; Laux, G.; Desgranges, C.; Wittmann, P.; Freese, U.K.; Schneider, U.; et al. Geographical prevalence of two types of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology 1986, 154, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yao, Q.Y.; Rooney, C.M.; Sculley, T.B.; Moss, D.J.; Rupani, H.; Laux, G.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Rickinson, A.B. New type B isolates of Epstein-Barr virus from Burkitt’s lymphoma and from normal individuals in endemic areas. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68 Pt 11, 2853–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: From latent genes to tumours. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5108–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, G.S.; Gibson, T.J.; Barrell, B.G. The BamHI F region of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Virology 1985, 147, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvalan, A.H.; Ding, S.; Koriyama, C.; Carrascal, E.; Carrasquilla, G.; Backhouse, C.; Urzua, L.; Argandona, J.; Palma, M.; Eizuru, Y.; et al. Association of a distinctive strain of Epstein-Barr virus with gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, M.L.; Lam, W.P.; Sham, J.; Choy, D.; Yong-Sheng, Z.; Guo, H.Y.; Ng, M.H. Detection and prevalence of the “f” variant of Epstein-Barr virus in southern China. Virology 1991, 185, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, M.L.; Chang, R.S.; Huang, M.L.; Guo, H.Y.; Choy, D.; Sham, J.; Tsao, S.Y.; Cheng, P.; Ng, M.H. Epstein-Barr virus genotypes associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in southern China. Virology 1990, 177, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.N.; Ding, Y.G.; Feng, Z.Y.; Li, H.G.; He, D.; Du, H.; Wu, B.; Shao, C.K. Association of distinctive Epstein-Barr virus variants with gastric carcinoma in Guangzhou, southern China. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chao, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, B. Genotypic analysis of Epstein-Barr virus isolates associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Northern China. Intervirology 2011, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, M.L.; Chang, G.C. Detection of distinct Epstein-Barr virus genotypes in NPC biopsies from southern Chinese and Caucasians. Int. J. Cancer 1992, 52, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, M.L.; Chang, R.S.; Jones, J.H. Genetic polymorphism of natural Epstein-Barr virus isolates from infectious mononucleosis patients and healthy carriers. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3862–3866. [Google Scholar]
- Sidagis, J.; Ueno, K.; Tokunaga, M.; Ohyama, M.; Eizuru, Y. Molecular epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in EBV-related malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, M.; Chen, J.J.; Constantine, N.; Massoud, M.; Raab-Traub, N. EBV strain variation: Geographical distribution and relation to disease state. Virology 1992, 190, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.F.; Zabarovsky, E.R.; Chen, F.; Cao, S.L.; Ernberg, I.; Klein, G.; Winberg, G. Isolation and sequencing of the Epstein-Barr virus BNLF-1 gene (LMP1) from a Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72 Pt 10, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanim, F.; Yao, Q.Y.; Niedobitek, G.; Sihota, S.; Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in normal donors and in virus-associated tumors from different geographic locations. Blood 1996, 88, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.; Chacon-Duque, J.C.; Mendoza-Revilla, J.; Fuentes-Guajardo, M.; Ruiz-Linares, A. The Genetic Diversity of the Americas. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2017, 18, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordonez, P.; Koriyama, C.; Ding, S.; Yoshiwara, E.; Corvalan, A.H.; Takano, J.; Chirinos, J.L.; Watanabe, J.; Miyagui, J.; Hidalgo, H.; et al. Identification of the distinctive type i/XhoI+ strain of Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinoma in Peru. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3607–3613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sans, M. Admixture studies in Latin America: From the 20th to the 21st century. Hum. Boil. 2000, 72, 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Eyheramendy, S.; Martinez, F.I.; Manevy, F.; Vial, C.; Repetto, G.M. Genetic structure characterization of Chileans reflects historical immigration patterns. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliburton, I.W. Intertypic recombinants of herpes simplex viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1980, 48, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nature reviews. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, S.; Pfuhl, T.; Mamiani, A.; Ehses, C.; Roemer, K.; Kremmer, E.; Jaker, C.; Hock, J.; Meister, G.; Grasser, F.A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, M.; Liang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, R.; Feng, Q.; Feng, L.; Luo, B.; Zeng, Y.X. Genome-wide analysis of Epstein-Barr virus identifies variants and genes associated with gastric carcinoma and population structure. Tumour Boil. 2017, 39, 1010428317714195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.M.; Luftig, M.A. To be or not IIb: A multi-step process for Epstein-Barr virus latency establishment and consequences for B cell tumorigenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, K.; Sato, H.; Rajadurai, P.; Busson, P.; Young, L.; Rickinson, A.; Tursz, T.; Raab-Traub, N. Novel transcription from the Epstein-Barr virus terminal EcoRI fragment, DIJhet, in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4948–4956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadler, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Structural analyses of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI A transcripts. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.P.; Brink, A.A.; Vervoort, M.B.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Meijer, C.J.; van den Brule, A.J. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcripts encoding homologues to important human proteins in diverse EBV associated diseases. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 52, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- zur Hausen, A.; Brink, A.A.; Craanen, M.E.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Meijer, C.J.; van den Brule, A.J. Unique transcription pattern of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in EBV-carrying gastric adenocarcinomas: Expression of the transforming BARF1 gene. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2745–2748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Roh, J.K.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, B.L.; Kim, W.H.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BARF1 promotes proliferation of gastric carcinoma cells through regulation of NF-kappaB. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10515–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, A.A.; Vervoort, M.B.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Meijer, C.J.; van den Brule, A.J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification, a new method for analysis of spliced and unspliced Epstein-Barr virus latent transcripts, and its comparison with reverse transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbial. 1998, 36, 3164–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.X.; Ooka, T. A transforming function of the BARF1 gene encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2897–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K. Role of EBER and BARF1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.X.; Moulin, J.C.; Decaussin, G.; Berger, F.; Ooka, T. Expression and tumorigenicity of the Epstein-Barr virus BARF1 gene in human Louckes B-lymphocyte cell line. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, W.; Decaussin, G.; Ligout, A.; Takada, K.; Ooka, T. Malignant transformation of Epstein-Barr virus-negative Akata cells by introduction of the BARF1 gene carried by Epstein-Barr virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3859–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Tsao, S.W.; Ooka, T.; Nicholls, J.M.; Cheung, H.W.; Fu, S.; Wong, Y.C.; Wang, X. Anti-apoptotic role of BARF1 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 238, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sall, A.; Caserta, S.; Jolicoeur, P.; Franqueville, L.; de Turenne-Tessier, M.; Ooka, T. Mitogenic activity of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BARF1 protein. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4938–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiech, T.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Lassman, S.; Heidt, T.; Schopflin, A.; Sarbia, M.; Werner, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Sakka, E.; Ooka, T.; et al. Cyclin D1 expression is induced by viral BARF1 and is overexpressed in EBV-associated gastric cancer. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strockbine, L.D.; Cohen, J.I.; Farrah, T.; Lyman, S.D.; Wagener, F.; DuBose, R.F.; Armitage, R.J.; Spriggs, M.K. The Epstein-Barr virus BARF1 gene encodes a novel, soluble colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4015–4021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sapi, E.; Flick, M.B.; Gilmore-Hebert, M.; Rodov, S.; Kacinski, B.M. Transcriptional regulation of the c-fms (CSF-1R) proto-oncogene in human breast carcinoma cells by glucocorticoids. Oncogene 1995, 10, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.Y.; Nguyen, A.V.; Russell, R.G.; Pollard, J.W. Colony-stimulating factor 1 promotes progression of mammary tumors to malignancy. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebe, E.K.; Le Large, T.Y.; Tarbouriech, N.; Oosterhoff, D.; De Gruijl, T.D.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Greijer, A.E. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BARF1 protein is a decoy receptor for macrophage colony stimulating factor and interferes with macrophage differentiation and activation. Viral Immunol. 2012, 25, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebe, E.K.; Le Large, T.Y.; Greijer, A.E.; Middeldorp, J.M. BamHI-A rightward frame 1, an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded oncogene and immune modulator. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohidin, T.B.; Ng, C.C. BARF1 gene silencing triggers caspase-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis in Epstein-Barr virus-positive malignant cells. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Schafer, A.; Lu, S.; Bilello, J.P.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Edwards, R.; Raab-Traub, N.; Cullen, B.R. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differentially expressed. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundhoff, A.; Sullivan, C.S.; Ganem, D. A combined computational and microarray-based approach identifies novel microRNAs encoded by human gamma-herpesviruses. RNA 2006, 12, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Pfuhl, T.; Motsch, N.; Barth, S.; Nicholls, J.; Grasser, F.; Meister, G. Identification of novel Epstein-Barr virus microRNA genes from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Pegtel, M.; Hopmans, E.; Murray, P.; Middeldorp, J.; Shapiro, M.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. A novel persistence associated EBV miRNA expression profile is disrupted in neoplasia. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Moosmann, A.; Gromminger, S.; Walz, N.; Grundhoff, A.; Hammerschmidt, W. Micro RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus promote cell cycle progression and prevent apoptosis of primary human B cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, M.; Tagawa, T. MicroRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus Control Innate and Adaptive Antiviral Immunity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01667-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakovicova, I.; Jerez, S.; Wichmann, I.A.; Sandoval-Borquez, A.; Carrasco-Veliz, N.; Corvalan, A.H. Role of microRNAs and Exosomes in Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Gastric Cancers. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburger, J.R.; Moreno-Estrada, A.; Gignoux, C.R.; Nelson, D.; Sanchez, E.; Ortiz-Tello, P.; Pons-Estel, B.A.; Acevedo-Vasquez, E.; Miranda, P.; Langefeld, C.D.; et al. Genomic Insights into the Ancestry and Demographic History of South America. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Estrada, A.; Gignoux, C.R.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.C.; Zakharia, F.; Sikora, M.; Contreras, A.V.; Acuna-Alonzo, V.; Sandoval, K.; Eng, C.; Romero-Hidalgo, S.; et al. Human genetics. The genetics of Mexico recapitulates Native American substructure and affects biomedical traits. Science 2014, 344, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriner, D. Overview of Admixture Mapping. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2017, 94, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mayar, J.V.; Vinner, L.; de Barros Damgaard, P.; de la Fuente, C.; Chan, J.; Spence, J.P.; Allentoft, M.E.; Vimala, T.; Racimo, F.; Pinotti, T.; et al. Early human dispersals within the Americas. Science 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryc, K.; Velez, C.; Karafet, T.; Moreno-Estrada, A.; Reynolds, A.; Auton, A.; Hammer, M.; Bustamante, C.D.; Ostrer, H. Colloquium paper: Genome-wide patterns of population structure and admixture among Hispanic/Latino populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107 (Suppl. 2), 8954–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashktorab, H.; Kupfer, S.S.; Brim, H.; Carethers, J.M. Racial Disparity in Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, E.; Duan, L.; Wu, B.U. Racial and Ethnic Minorities at Increased Risk for Gastric Cancer in a Regional US Population Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Moore, S.P.; Hassler, S.; Ellison-Loschmann, L.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. The burden of stomach cancer in indigenous populations: A systematic review and global assessment. Gut 2014, 63, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friborg, J.T.; Melbye, M. Cancer patterns in Inuit populations. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circumpolar Inuit Cancer Review Working Group; Kelly, J.; Lanier, A.; Santos, M.; Healey, S.; Louchini, R.; Friborg, J.; Young, K.; Ng, C. Cancer among the circumpolar Inuit, 1989-2003. II. Patterns and trends. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2008, 67, 408–420. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.; Janssen, F.; Kunst, A.E. The decline in stomach cancer mortality: Exploration of future trends in seven European countries. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 26, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, R.A.; Taub, M.A.; Gignoux, C.R.; Fu, W.; Musharoff, S.; O’Connor, T.D.; Vergara, C.; Torgerson, D.G.; Pino-Yanes, M.; Shringarpure, S.S.; et al. A continuum of admixture in the Western Hemisphere revealed by the African Diaspora genome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.P.; Forman, D.; Pineros, M.; Fernandez, S.M.; de Oliveira Santos, M.; Bray, F. Cancer in indigenous people in Latin America and the Caribbean: A review. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineros, M.; Ferlay, J.; Murillo, R. Cancer incidence estimates at the national and district levels in Colombia. Salud Publica Mex. 2006, 48, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, E.M.; Fernandes, M.R.; de Carvalho, D.C.; Leitao, L.P.C.; Cavalcante, G.C.; Pereira, E.E.B.; Modesto, A.A.C.; Guerreiro, J.F.; de Assumpcao, P.P.; Dos Santos, S.E.B.; et al. Correction to: Effect of genetic ancestry to the risk of susceptibility to gastric cancer in a mixed population of the Brazilian Amazon. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodaman, N.; Sobota, R.S.; Mera, R.; Schneider, B.G.; Williams, S.M. Disrupted human–pathogen co-evolution: A model for disease. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, B.; Balloux, F.; Moodley, Y.; Manica, A.; Liu, H.; Roumagnac, P.; Falush, D.; Stamer, C.; Prugnolle, F.; van der Merwe, S.W.; et al. An African origin for the intimate association between humans and Helicobacter pylori. Nature 2007, 445, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorell, K.; Yahara, K.; Berthenet, E.; Lawson, D.J.; Mikhail, J.; Kato, I.; Mendez, A.; Rizzato, C.; Bravo, M.M.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Rapid evolution of distinct Helicobacter pylori subpopulations in the Americas. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Ramirez, Z.Y.; Mendez-Tenorio, A.; Kato, I.; Bravo, M.M.; Rizzato, C.; Thorell, K.; Torres, R.; Aviles-Jimenez, F.; Camorlinga, M.; Canzian, F.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis Show Helicobacter pylori Strains from Latin America Have Followed a Unique Evolution Pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sablet, T.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Shaffer, C.L.; Schneider, B.G.; Asim, M.; Chaturvedi, R.; Bravo, L.E.; Sicinschi, L.A.; Delgado, A.G.; Mera, R.M.; et al. Phylogeographic origin of Helicobacter pylori is a determinant of gastric cancer risk. Gut 2011, 60, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Chen, Z.; Bernard, H.U.; Chan, P.K.S.; DeSalle, R.; Dillner, J.; Forslund, O.; Haga, T.; McBride, A.A.; Villa, L.L.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Papillomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Chan, S.Y.; Burk, R.D.; Das, B.C.; Fujinaga, K.; Icenogle, J.P.; Kahn, T.; Kiviat, N.; Lancaster, W.; Mavromara-Nazos, P.; et al. The genetic drift of human papillomavirus type 16 is a means of reconstructing prehistoric viral spread and the movement of ancient human populations. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6413–6423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.K.; Chan, S.Y.; Campo, M.S.; Fujinaga, K.; Mavromara-Nazos, P.; Labropoulou, V.; Pfister, H.; Tay, S.K.; ter Meulen, J.; Villa, L.L.; et al. Evolution of human papillomavirus type 18: An ancient phylogenetic root in Africa and intratype diversity reflect coevolution with human ethnic groups. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6424–6431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, M.L.; Duraturo, M.L.; Salatiello, I.; Buonaguro, L.; Losito, S.; Botti, G.; Stellato, G.; Greggi, S.; Piccoli, R.; Pilotti, S.; et al. Analysis of human papillomavirus type-16 variants in Italian women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L.F.; Koutsky, L.A.; Galloway, D.A.; Kuypers, J.; Hughes, J.P.; Wheeler, C.M.; Holmes, K.K.; Kiviat, N.B. Genomic variation of human papillomavirus type 16 and risk for high grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, S.; Palser, A.; Elgueta Karstegl, C.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Ramayanti, O.; Cohen, J.I.; Hildesheim, A.; Fellner, M.D.; Wiels, J.; White, R.E.; et al. Natural Variation of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes, Proteins, and Primary MicroRNA. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.M.; Yu, K.J.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Hildesheim, A.; Bhatia, K. The extent of genetic diversity of Epstein-Barr virus and its geographic and disease patterns: A need for reappraisal. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.; Marinho-Dias, J.; Ribeiro, J.; Esteves, M.; Maltez, E.; Baldaque, I.; Breda, E.; Monteiro, E.; Medeiros, R.; Sousa, H. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus strains and LMP1-deletion variants in Portugal. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.T.; Leung, S.F.; Lo, K.W.; Chiu, K.W.; Tam, J.S.; Fok, T.F.; Johnson, P.J.; Lee, J.C.; Huang, D.P. Specific latent membrane protein 1 gene sequences in type 1 and type 2 Epstein-Barr virus from nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Hong Kong. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 76, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Lay, J.D.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Su, I.J. Genomic analysis of Epstein-Barr virus in nasal and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A comparison with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in an endemic area. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 50, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.X.; Zong, Y.S.; Zhang, M.; Han, A.J.; Zhong, B.L.; Liang, Y.J. Study of sequence variations of Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi = Chin. J. Pathol. 2005, 34, 791–795. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, E.L.; Peh, S.C.; Sam, C.K. Analyses of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in Malaysian nasopharyngeal carcinoma: High prevalence of 30-bp deletion, Xho1 polymorphism and evidence of dual infections. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.S.; Su, I.J.; Chung, P.J.; Shu, C.H.; Ng, C.K.; Wu, S.J.; Liu, S.T. Detection of an Epstein-Barr-virus variant in T-cell-lymphoma tissues identical to the distinct strain observed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Taiwanese population. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, W.; Feki, L.; Khabir, A.; Boudawara, T.; Ghorbel, A.; Charfeddine, I.; Daoud, J.; Frikha, M.; Hammami, A.; Karray-Hakim, H. Polymorphism analysis of Epstein-Barr virus isolates of nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies from Tunisian patients. Virus Genes 2007, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, V.G.; Marques-Silva, A.C.; Moreli, M.L. The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) 30-bp deletion and XhoI-polymorphism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.T.; Lo, K.W.; Leung, S.F.; Chan, W.Y.; Choi, P.H.; Johnson, P.J.; Lee, J.C.; Huang, D.P. Prevalence of LMP1 deletion variant of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and gastric tumors in Hong Kong. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.P.; Hao, S.P.; Lin, S.Y.; Ueng, S.H.; Pai, P.C.; Tseng, C.K.; Hsueh, C.; Hsieh, M.S.; Yu, J.S.; Tsang, N.M. The 30-bp deletion of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 gene has no effect in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; N.L., H.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; IARC: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ansell, S.M. Hodgkin Lymphoma: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, Y.S. Prevalence and prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus infection in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.G.; Sandvej, K.; Li, P.J.; Ji, X.L.; Yan, Q.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Da, J.P.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.J. Epstein--Barr virus gene polymorphisms in Chinese Hodgkin’s disease cases and healthy donors: Identification of three distinct virus variants. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cosio, M.; Santon, A.; Martin, P.; Reguero, M.E.; Cristobal, E.; Bellas, C. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus strains and variants in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma by laser microdissection. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Park, E.R.; Park, S.H.; Lin, Z.; Kim, Y.S. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus isolated from the malignant lymphomas in Korea. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 67, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvej, K.; Peh, S.C.; Andresen, B.S.; Pallesen, G. Identification of potential hot spots in the carboxy-terminal part of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BNLF-1 gene in both malignant and benign EBV-associated diseases: High frequency of a 30-bp deletion in Malaysian and Danish peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood 1994, 84, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyle, M.J.; Vasak, E.; Tschuchnigg, M.; Turner, J.J.; Sculley, T.; Penny, R.; Cooper, D.A.; Tindall, B.; Sewell, W.A. Subtypes of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Hodgkin’s disease: Association between B-type EBV and immunocompromise. Blood 1993, 81, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guiretti, D.M.; Chabay, P.A.; Valva, P.; Stefanoff, C.G.; Barros, M.H.; De Matteo, E.; Renault, I.Z.; Preciado, M.V.; Hassan, R. Structural variability of the carboxy-terminus of Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 gene in Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Chen, W.G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Murakami, I.; Chen, H.L.; Ohara, N.; Nose, S.; Hamaya, K.; Matsui, S.; Bacchi, M.M.; et al. Deletion of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 gene in Japanese and Brazilian gastric carcinomas, metastatic lesions, and reactive lymphocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corvalán, A.H.; Ruedlinger, J.; de Mayo, T.; Polakovicova, I.; Gonzalez-Hormazabal, P.; Aguayo, F. The Phylogeographic Diversity of EBV and Admixed Ancestry in the Americas–Another Model of Disrupted Human-Pathogen Co-Evolution. Cancers 2019, 11, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020217
Corvalán AH, Ruedlinger J, de Mayo T, Polakovicova I, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P, Aguayo F. The Phylogeographic Diversity of EBV and Admixed Ancestry in the Americas–Another Model of Disrupted Human-Pathogen Co-Evolution. Cancers. 2019; 11(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorvalán, Alejandro H., Jenny Ruedlinger, Tomas de Mayo, Iva Polakovicova, Patricio Gonzalez-Hormazabal, and Francisco Aguayo. 2019. "The Phylogeographic Diversity of EBV and Admixed Ancestry in the Americas–Another Model of Disrupted Human-Pathogen Co-Evolution" Cancers 11, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020217
APA StyleCorvalán, A. H., Ruedlinger, J., de Mayo, T., Polakovicova, I., Gonzalez-Hormazabal, P., & Aguayo, F. (2019). The Phylogeographic Diversity of EBV and Admixed Ancestry in the Americas–Another Model of Disrupted Human-Pathogen Co-Evolution. Cancers, 11(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020217





