The Genetic Architecture of Gliomagenesis–Genetic Risk Variants Linked to Specific Molecular Subtypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Characteristics of Datasets
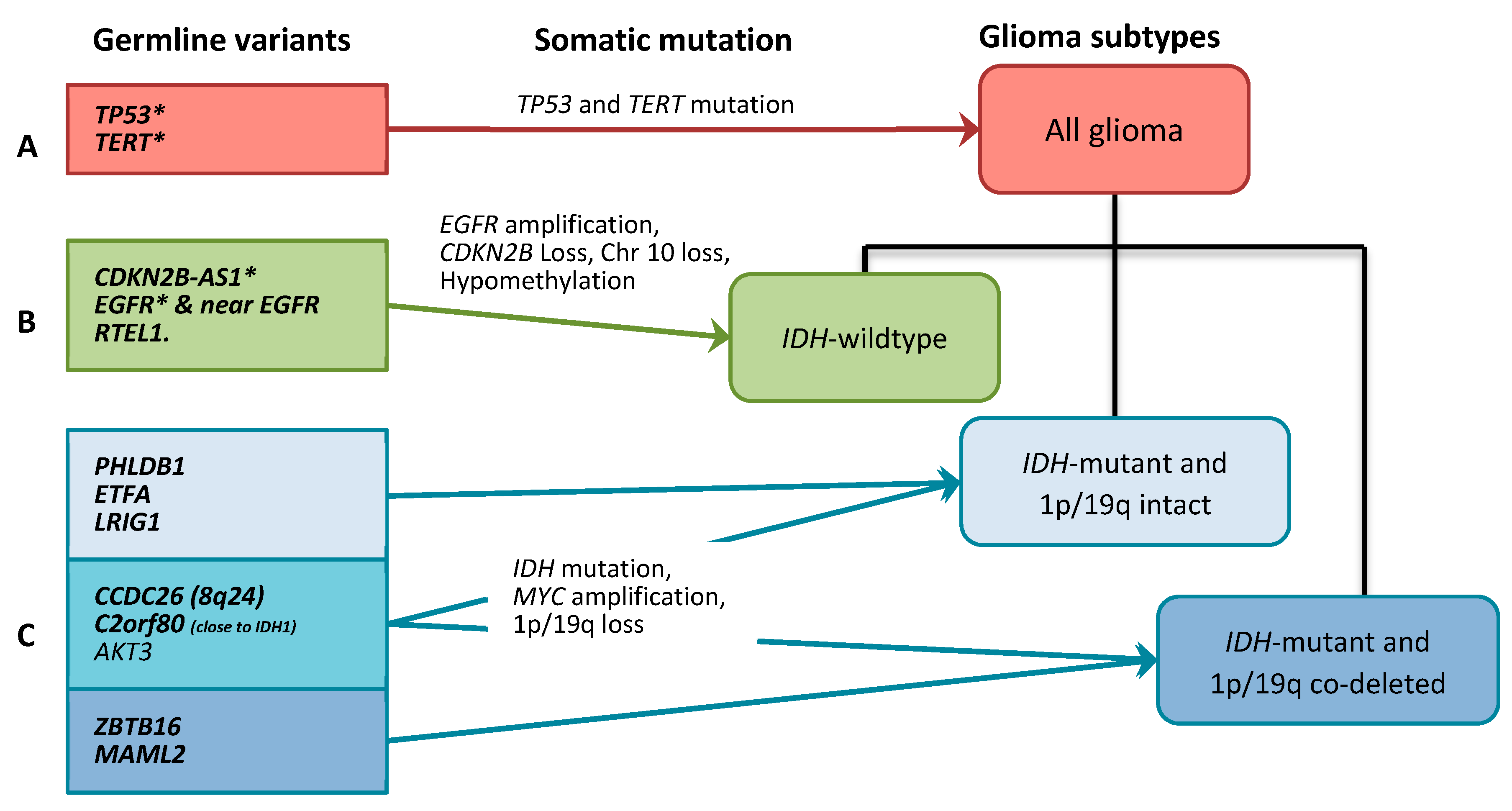
2.2. Gliomagenesis Models
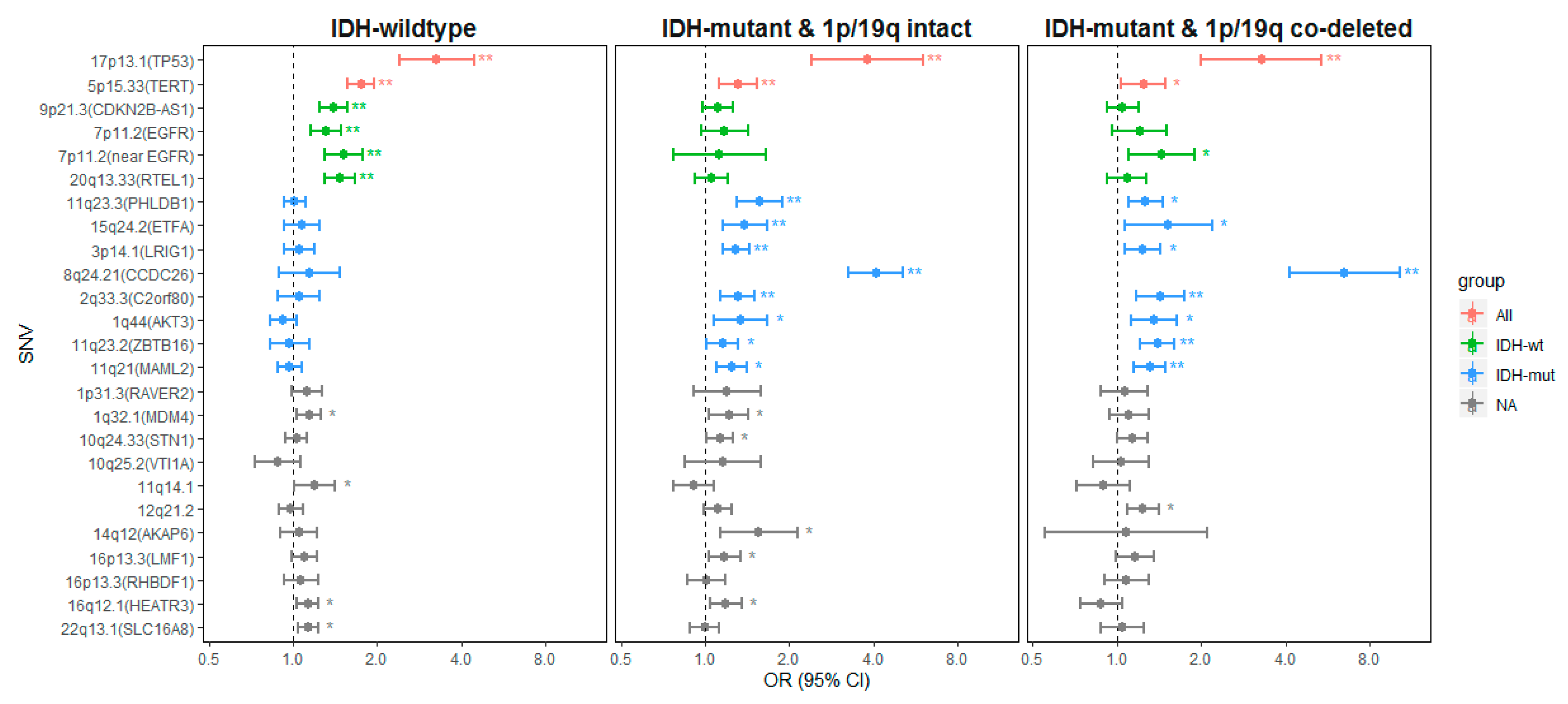
2.2.1. Genetic Variants Associated with all Glioma
2.2.2. Genetic Variants Associated with IDH-wt Glioma
2.2.3. Genetic Variants Associated with IDH-Mutant Glioma
2.3. Genetic Effects on the Gene Expression Levels
3. Discussion
3.1. All Glioma Risk Genes
3.2. IDH-wildtype Glioma Risk Variants
3.3. IDH-Mutant Glioma Risk Variants
3.4. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Swedish GICC Study Population
4.2. Genotyping and Imputation in Swedish GICC Study
4.3. Immunohistochemistry in Swedish GICC Study
4.4. Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) in Swedish GICC Study
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Expression Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnersley, B.; Labussiere, M.; Holroyd, A.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Broderick, P.; Vijayakrishnan, J.; Mokhtari, K.; Delattre, J.Y.; Gousias, K.; Schramm, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for glioma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, S.; Hosking, F.J.; Robertson, L.B.; Dobbins, S.E.; Sanson, M.; Malmer, B.; Simon, M.; Marie, Y.; Boisselier, B.; Delattre, J.Y.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies five susceptibility loci for glioma. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melin, B.S.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Wrensch, M.R.; Johansen, C.; Il’yasova, D.; Kinnersley, B.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Labreche, K.; Chen, Y.; Armstrong, G.; et al. Genome-wide association study of glioma subtypes identifies specific differences in genetic susceptibility to glioblastoma and non-glioblastoma tumors. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrensch, M.; Jenkins, R.B.; Chang, J.S.; Yeh, R.F.; Xiao, Y.; Decker, P.A.; Ballman, K.V.; Berger, M.; Buckner, J.C.; Chang, S.; et al. Variants in the CDKN2B and RTEL1 regions are associated with high-grade glioma susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Schwartzbaum, J.; Wiklund, F.; Sjostrom, S.; Liu, Y.; Tsavachidis, S.; Ahlbom, A.; Auvinen, A.; Collatz-Laier, H.; Feychting, M.; et al. A comprehensive study of the association between the EGFR and ERBB2 genes and glioma risk. Acta Oncol. 2010, 49, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, P.; Melin, B.S.; Wang, Z.; McKean-Cowdin, R.; Michaud, D.S.; Wang, S.S.; Bondy, M.; Houlston, R.; Jenkins, R.B.; Wrensch, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study of glioma and meta-analysis. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labreche, K.; Kinnersley, B.; Berzero, G.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Rahimian, A.; Detrait, I.; Marie, Y.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Delattre, J.Y.; et al. Diffuse gliomas classified by 1p/19q co-deletion, TERT promoter and IDH mutation status are associated with specific genetic risk loci. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel-Passow, J.E.; Decker, P.A.; Kosel, M.L.; Kollmeyer, T.M.; Molinaro, A.M.; Rice, T.; Caron, A.A.; Drucker, K.L.; Praska, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; et al. Using germline variants to estimate glioma and subtype risks. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, G.T. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronberg, H.; Adolfsson, J.; Aly, M.; Nordstrom, T.; Wiklund, P.; Brandberg, Y.; Thompson, J.; Wiklund, F.; Lindberg, J.; Clements, M.; et al. Prostate cancer screening in men aged 50–69 years (STHLM3): A prospective population-based diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Antonanzas, A.; Auzmendi-Iriarte, J.; Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Moreno-Cugnon, L.; Ruiz, I.; Villanua, J.; Egana, L.; Otaegui, D.; Sampron, N.; Matheu, A. Liquid Biopsy in Glioblastoma: Opportunities, Applications and Challenges. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, S.N.; Sulem, P.; Jonasdottir, A.; Masson, G.; Gudmundsson, J.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Magnusson, O.T.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; Sigurgeirsson, B.; Thorisdottir, K.; et al. A germline variant in the TP53 polyadenylation signal confers cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Rajaraman, P.; Melin, B.S.; Chung, C.C.; Zhang, W.; McKean-Cowdin, R.; Michaud, D.; Yeager, M.; Ahlbom, A.; Albanes, D.; et al. Further Confirmation of Germline Glioma Risk Variant rs78378222 in TP53 and Its Implication in Tumor Tissues via Integrative Analysis of TCGA Data. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.B.; Armstrong, G.N.; Olver, B.D.; Lloyd, A.L.; Shete, S.; Lau, C.; Claus, E.B.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.; Lai, R.; Il’yasova, D.; et al. Survey of familial glioma and role of germline p16INK4A/p14ARF and p53 mutation. Fam. Cancer 2010, 9, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.N.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goldkorn, A. Telomere and Telomerase Therapeutics in Cancer. Genes (Basel) 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, B.S.; Nordfjall, K.; Andersson, U.; Roos, G. hTERT cancer risk genotypes are associated with telomere length. Genet. Epidemiol. 2012, 36, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, V.; Nelson, C.P.; Albrecht, E.; Mangino, M.; Deelen, J.; Buxton, J.L.; Hottenga, J.J.; Fischer, K.; Esko, T.; Surakka, I.; et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Degerman, S.; Dahlin, A.M.; Wibom, C.; Johansson, G.; Bondy, M.L.; Melin, B.S. The association between longer relative leukocyte telomere length and risk of glioma is independent of the potentially confounding factors allergy, BMI, and smoking. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2019, 30, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, K.M.; Codd, V.; Rice, T.; Nelson, C.P.; Smirnov, I.V.; McCoy, L.S.; Hansen, H.M.; Elhauge, E.; Ojha, J.; Francis, S.S.; et al. Longer genotypically-estimated leukocyte telomere length is associated with increased adult glioma risk. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42468–42477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, I.; Kinnersley, B.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Labreche, K.; Il’yasova, D.; Armstrong, G.N.; Eckel-Passow, J.E.; Schoemaker, M.J.; Nothen, M.M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Identifies New Candidate Susceptibility Genes for Glioma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, A.M.; Wibom, C.; Ghasimi, S.; Brannstrom, T.; Andersson, U.; Melin, B. Relation between Established Glioma Risk Variants and DNA Methylation in the Tumor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojesen, S.E.; Pooley, K.A.; Johnatty, S.E.; Beesley, J.; Michailidou, K.; Tyrer, J.P.; Edwards, S.L.; Pickett, H.A.; Shen, H.C.; Smart, C.E.; et al. Multiple independent variants at the TERT locus are associated with telomere length and risks of breast and ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killedar, A.; Stutz, M.D.; Sobinoff, A.P.; Tomlinson, C.G.; Bryan, T.M.; Beesley, J.; Chenevix-Trench, G.; Reddel, R.R.; Pickett, H.A. A Common Cancer Risk-Associated Allele in the hTERT Locus Encodes a Dominant Negative Inhibitor of Telomerase. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.; Parikh, H.; Jia, J.; Chung, C.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Hoskins, J.W.; Hutchinson, A.; Burdette, L.; et al. Imputation and subset-based association analysis across different cancer types identifies multiple independent risk loci in the TERT-CLPTM1L region on chromosome 5p15.33. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6616–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Brat, D.J.; Verhaak, R.G.; Aldape, K.D.; Yung, W.K.; Salama, S.R.; Cooper, L.A.; Rheinbay, E.; Miller, C.R.; Vitucci, M.; et al. Comprehensive, Integrative Genomic Analysis of Diffuse Lower-Grade Gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Bafna, V.; Mischel, P.S. Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification in tumour pathogenesis and evolution. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, J.; Jun, H.J.; Lessard, J.; Ruiz, R.; Zhu, H.; Donovan, M.; Woolfenden, S.; Boskovitz, A.; Raval, A.; Bronson, R.T.; et al. Chronic activation of wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor and loss of Cdkn2a cause mouse glioblastoma formation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7198–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spath, F.; Andersson, U.; Dahlin, A.M.; Langseth, H.; Hovig, E.; Johannesen, T.B.; Grankvist, K.; Bjorkblom, B.; Wibom, C.; Melin, B. Pre-diagnostic serum levels of EGFR and ErbB2 and genetic glioma risk variants: A nested case-control study. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11065–11072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibom, C.; Ghasimi, S.; Van Loo, P.; Brannstrom, T.; Trygg, J.; Lau, C.; Henriksson, R.; Bergenheim, T.; Andersson, U.; Ryden, P.; et al. EGFR gene variants are associated with specific somatic aberrations in glioma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasimi, S.; Wibom, C.; Dahlin, A.M.; Brannstrom, T.; Golovleva, I.; Andersson, U.; Melin, B. Genetic risk variants in the CDKN2A/B, RTEL1 and EGFR genes are associated with somatic biomarkers in glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 127, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.K.; Han, S.J.; Choy, W.; Beleford, D.; Aghi, M.K.; Berger, M.S.; Shieh, J.T.; Bollen, A.W.; Perry, A.; Phillips, J.J.; et al. Familial melanoma-astrocytoma syndrome: Synchronous diffuse astrocytoma and pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma in a patient with germline CDKN2A/B deletion and a significant family history. Clin. Neuropathol. 2017, 36, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Wibom, C.; Cederquist, K.; Aradottir, S.; Borg, A.; Armstrong, G.N.; Shete, S.; Lau, C.C.; Bainbridge, M.N.; Claus, E.B.; et al. Germline rearrangements in families with strong family history of glioma and malignant melanoma, colon, and breast cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnington, M.S.; Santibanez Koref, M.; Mayosi, B.M.; Burn, J.; Keavney, B. Chromosome 9p21 SNPs Associated with Multiple Disease Phenotypes Correlate with ANRIL Expression. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Kim, S.T.; Liu, W.; Kim, J.W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Berens, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, J. An integrated analysis of germline and somatic, genetic and epigenetic alterations at 9p21.3 in glioblastoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottoriva, A.; Spiteri, I.; Piccirillo, S.G.; Touloumis, A.; Collins, V.P.; Marioni, J.C.; Curtis, C.; Watts, C.; Tavare, S. Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4009–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Chu, D.C.; Weng, S.J.; Chu, H.C.; Wu, A.T.H.; Lee, J.F.; Ali, A.A.A.; Chen, T.C.; Huang, H.S.; et al. Identification and preclinical evaluation of the small molecule, NSC745887, for treating glioblastomas via suppressing DcR3-associated signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 11922–11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Roth, W.; Isenmann, S.; Nakamura, M.; Platten, M.; Wick, W.; Kleihues, P.; Bahr, M.; Ohgaki, H.; Ashkenazi, A.; Weller, M. Soluble decoy receptor 3 is expressed by malignant gliomas and suppresses CD95 ligand-induced apoptosis and chemotaxis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.B.; Xiao, Y.; Sicotte, H.; Decker, P.A.; Kollmeyer, T.M.; Hansen, H.M.; Kosel, M.L.; Zheng, S.; Walsh, K.M.; Rice, T.; et al. A low-frequency variant at 8q24.21 is strongly associated with risk of oligodendroglial tumors and astrocytomas with IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, K.M.; Codd, V.; Smirnov, I.V.; Rice, T.; Decker, P.A.; Hansen, H.M.; Kollmeyer, T.; Kosel, M.L.; Molinaro, A.M.; McCoy, L.S.; et al. Variants near TERT and TERC influencing telomere length are associated with high-grade glioma risk. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, C.; von Paleske, L.; Uslu, V.V.; Remeseiro, S.; Takayama, N.; Ng, S.W.; Murison, A.; Langenfeld, K.; Petretich, M.; Scognamiglio, R.; et al. A Myc enhancer cluster regulates normal and leukaemic haematopoietic stem cell hierarchies. Nature 2018, 553, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktay, Y.; Ulgen, E.; Can, O.; Akyerli, C.B.; Yuksel, S.; Erdemgil, Y.; Durasi, I.M.; Henegariu, O.I.; Nanni, E.P.; Selevsek, N.; et al. IDH-mutant glioma specific association of rs55705857 located at 8q24.21 involves MYC deregulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, D.; Iyengar, N.; Dogra, S.; Wong, T.; Bready, D.; Tang, K.; Modrek, A.S.; Placantonakis, D.G. Mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapeutics. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, A.; Kapoor, M.; Georges, J.; Butler, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.; Crouch, A.; Smirnov, I.; Nakada, M.; Hepler, J.; et al. The role of AKT isoforms in glioblastoma: AKT3 delays tumor progression. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 130, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Holmlund, C.; Faraz, M.; Wang, W.; Bergenheim, T.; Kvarnbrink, S.; Johansson, M.; Henriksson, R.; Hedman, H. Lrig1 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene in malignant glioma. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, R.; Woods, N.T.; Mendoza-Fandino, G.; Forsyth, P.; Egan, K.M.; Monteiro, A.N. Functional analysis of the 11q23.3 glioma susceptibility locus implicates PHLDB1 and DDX6 in glioma susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Ren, X.; Zhang, C.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Wu, A. Bioinformatic profiling identifies an immune-related risk signature for glioblastoma. Neurology 2016, 86, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirian, E.S.; Armstrong, G.N.; Zhou, R.; Lau, C.C.; Claus, E.B.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Il’yasova, D.; Schildkraut, J.; Ali-Osman, F.; Sadetzki, S.; et al. The Glioma International Case-Control Study: A Report From the Genetic Epidemiology of Glioma International Consortium. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Reich, D. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Current Study | Labreche et al., 2018 [9] | Eckel-Passow et al., 2019 [10] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCGA | French GWAS | French Sequencing | Subtotal Subjects | Mayo Clinic | UCSF | Subtotal Subjects | ||
| Controls, N | 876 | 2648 | 1190 | 5527 | 9365 | 443 | 231 | 674 |
| Male, N (%) | 516 (58.9) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 250 (56.4) | 121 (54.4) | 371 (55.0) |
| Age, median (range) | 59 (21–82) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 56 (22–84) | 54 (18–89) | NA (18–89) |
| Cases, N | 330 | 521 | 1423 | 704 | 2648 | 1273 | 852 | 2125 |
| Male, N (%) | 135 (40.9) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 748 (58.8) | 495 (48.1) | 1243 (58.5) |
| Age, median (range) | 59 (22–81) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 48 (18–84) | 51 (19–87) | NA (18–87) |
| GBM, N (%) | 207 (62.7) | 183 (35.12) | 430 (30.2) | 181 (25.7) | 795 (30.0) | 481 (37.8) | 410 (48.1) | 891 (41.9) |
| Molecular subtypes | ||||||||
| IDH-wildtype, N | 258 | 55 | 450 | 277 | 782 | 165 | 335 | 500 |
| IDH-mutant and 1p/19q intact, N | 29 | 104 | 215 | 209 | 528 | 141 | 133 | 274 |
| IDH-mutant and 1p/19q co-deleted, N | 19 | 65 | 85 | 199 | 349 | 96 | 92 | 188 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.Y.-Y.; Johansson, G.; Wibom, C.; Brännström, T.; Malmström, A.; Henriksson, R.; Golovleva, I.; Bondy, M.L.; Andersson, U.; Dahlin, A.M.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Gliomagenesis–Genetic Risk Variants Linked to Specific Molecular Subtypes. Cancers 2019, 11, 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11122001
Wu WY-Y, Johansson G, Wibom C, Brännström T, Malmström A, Henriksson R, Golovleva I, Bondy ML, Andersson U, Dahlin AM, et al. The Genetic Architecture of Gliomagenesis–Genetic Risk Variants Linked to Specific Molecular Subtypes. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11122001
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wendy Yi-Ying, Gunnar Johansson, Carl Wibom, Thomas Brännström, Annika Malmström, Roger Henriksson, Irina Golovleva, Melissa L. Bondy, Ulrika Andersson, Anna M. Dahlin, and et al. 2019. "The Genetic Architecture of Gliomagenesis–Genetic Risk Variants Linked to Specific Molecular Subtypes" Cancers 11, no. 12: 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11122001
APA StyleWu, W. Y.-Y., Johansson, G., Wibom, C., Brännström, T., Malmström, A., Henriksson, R., Golovleva, I., Bondy, M. L., Andersson, U., Dahlin, A. M., & Melin, B. (2019). The Genetic Architecture of Gliomagenesis–Genetic Risk Variants Linked to Specific Molecular Subtypes. Cancers, 11(12), 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11122001






