Colorectal Cancer Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using an Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
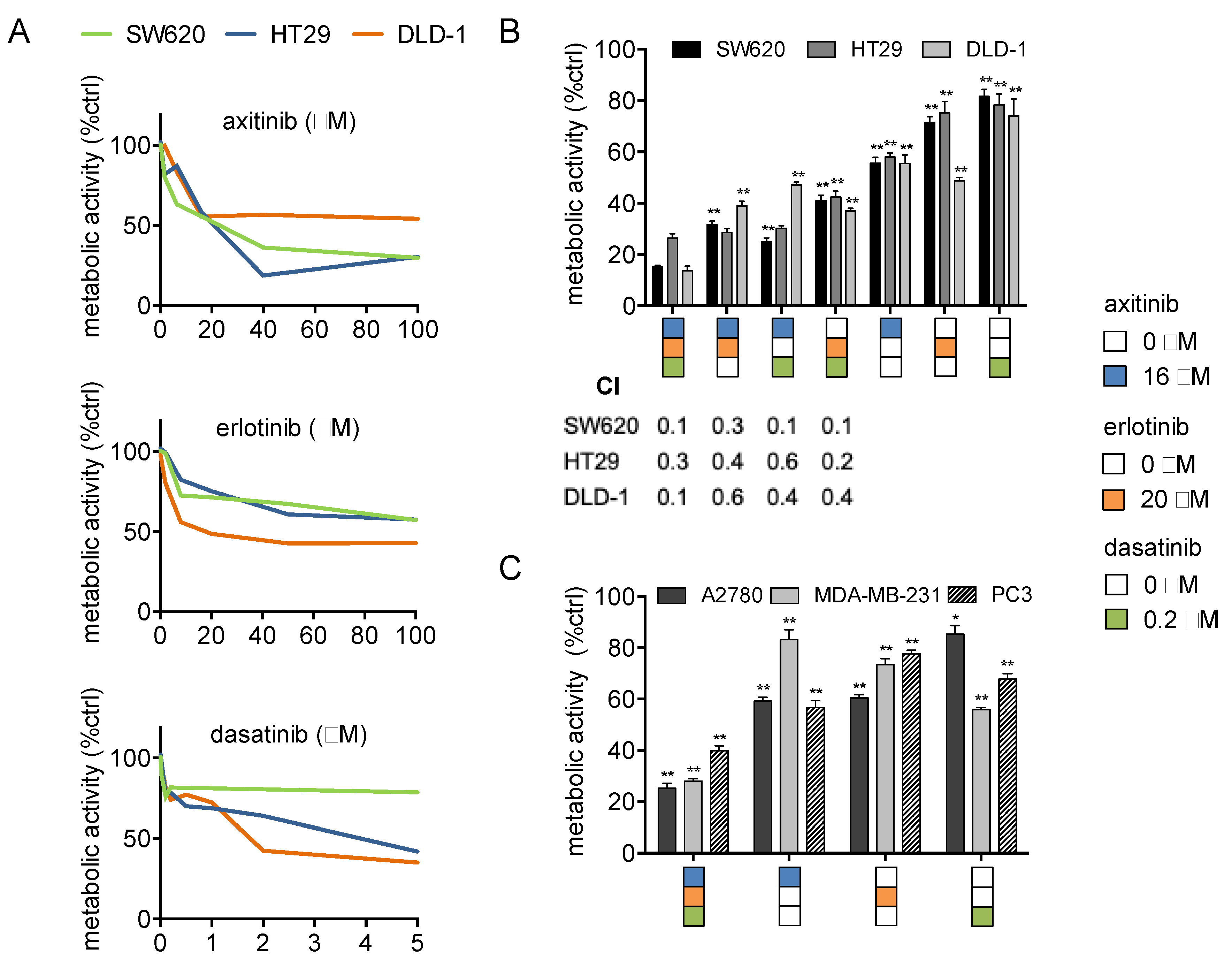
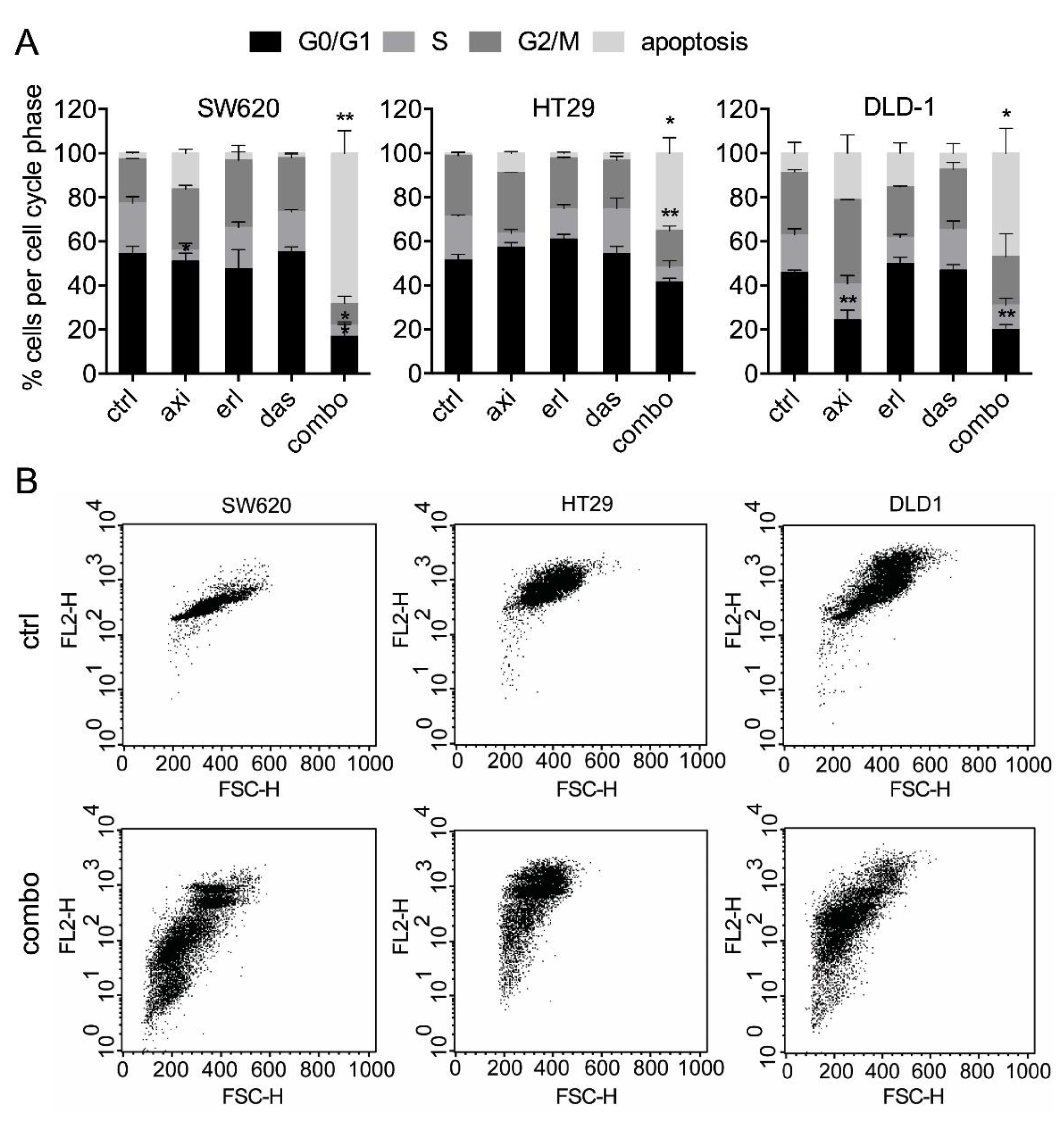
2.1. Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib Combination Synergistically Inhibits Cancer Cell Metabolic Activity and Induces Apoptosis
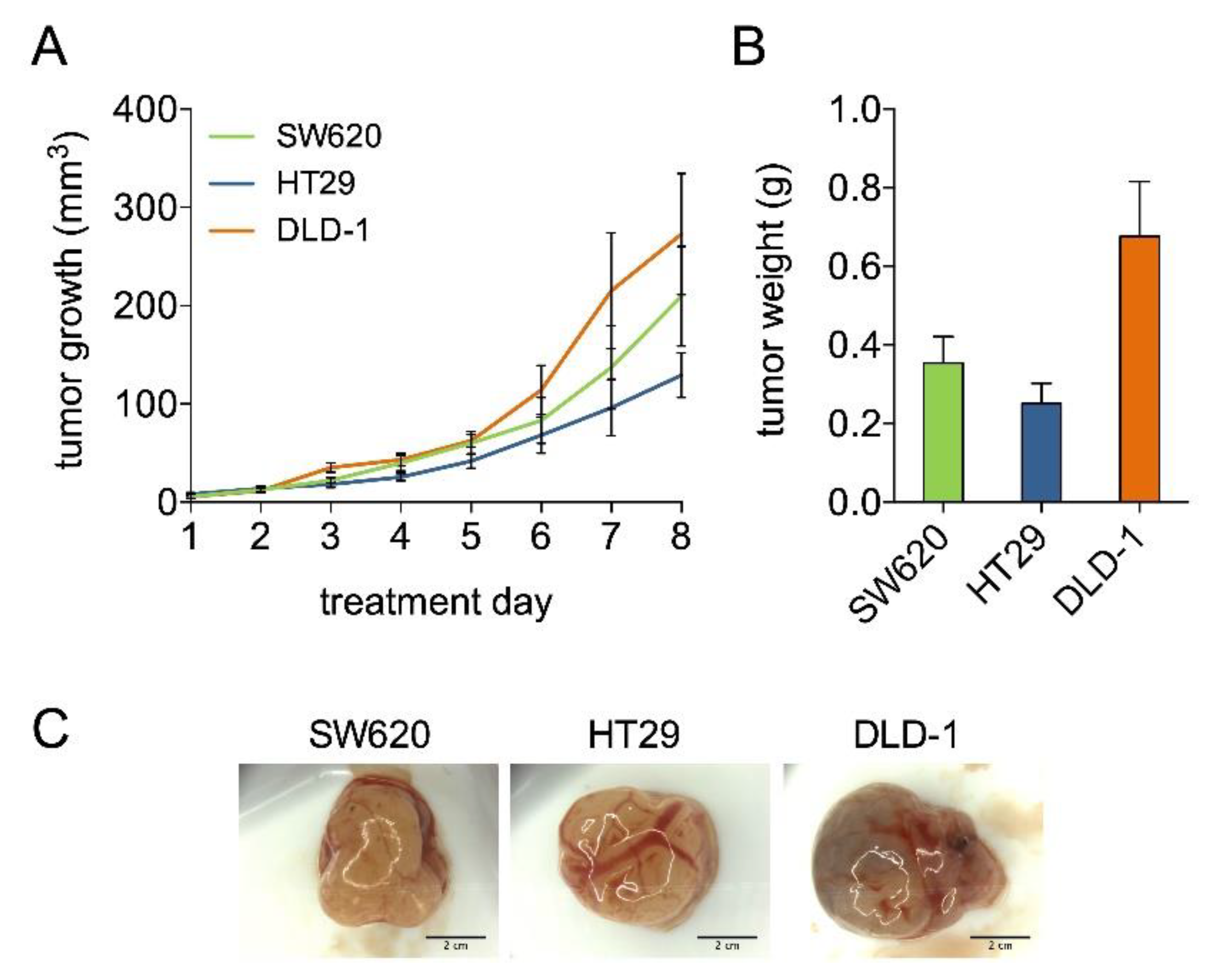
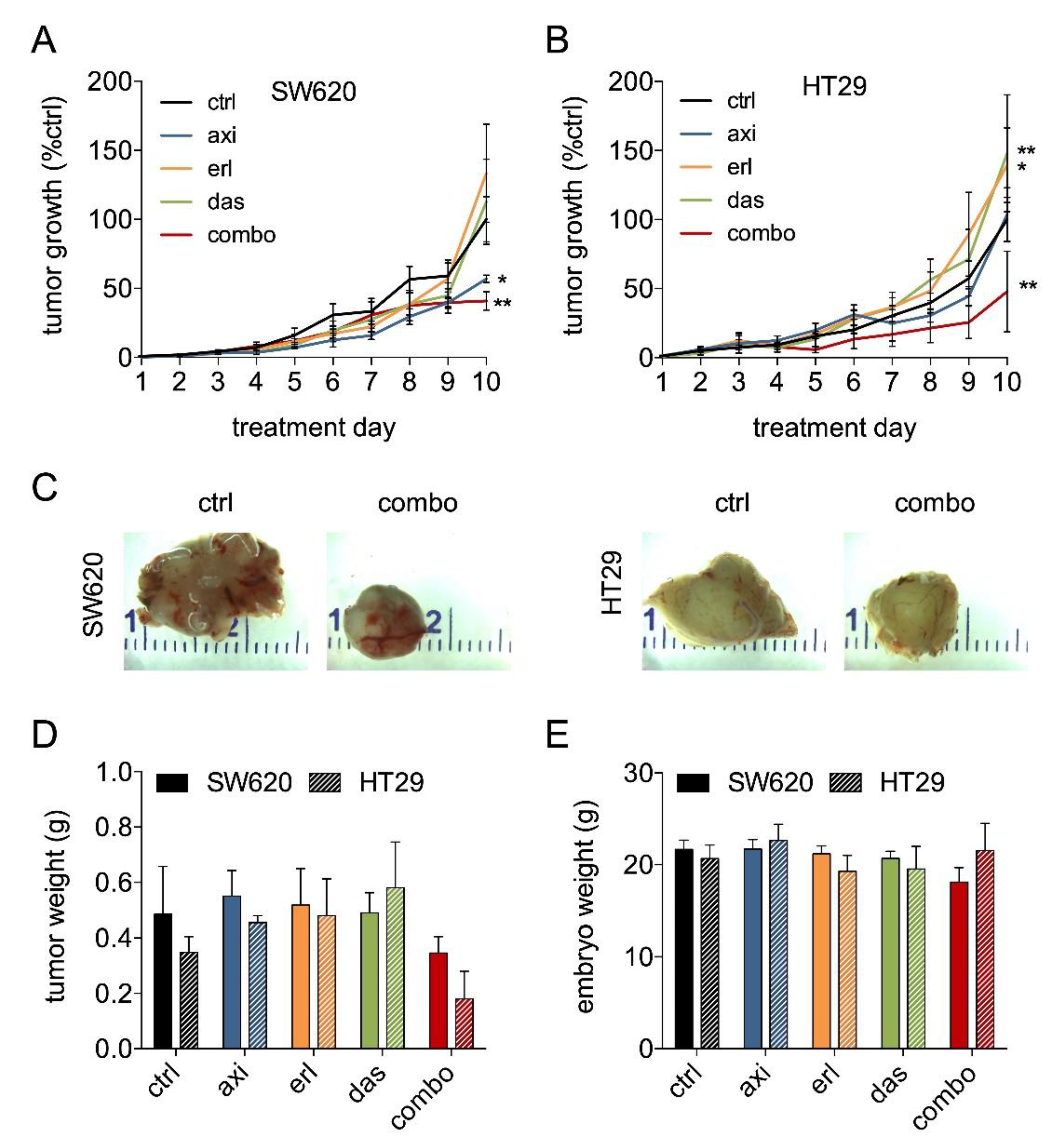
2.2. Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib Combination Therapy Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in the CAM Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Metabolic Activity Assay
4.4. Apoptosis Assay
4.5. Phosphoproteome and Transcriptome Analysis
4.6. Colorectal Cancer Tumors Grown on the Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM)
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Statistics and Data Correction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, H.; Kloor, M.; Pox, C.P. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, W.A.; Swaika, A.; Mody, K. Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Math, M.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Grönroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denlinger, C.S.; Barsevick, A.M. The challenges of colorectal cancer survivorship. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2009, 7, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarity, A.; O’Sullivan, J.; Kennedy, J.; Mehigan, B.; McCormick, P. Current targeted therapies in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Scapozza, L.; I Altaba, A.R. Drug repurposing in oncology: Compounds, pathways, phenotypes and computational approaches for colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenergy 2019, 1871, 434–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.S.; Banerji, U. Combine and conquer: Challenges for targeted therapy combinations in early phase trials. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Current trends in multidrug optimization. SLAS Technol. 2017, 22, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aranda, M.; Redondo, M. Targeting Receptor Kinases in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusk, T.; Grivas, N.; Bex, A. Antiangiogenic therapy combined with immune checkpoint blockade in renal cancer: A review. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani, M.; Decio, A.; Giavazzi, R.; Ghilardi, C. Contribution of tumor endothelial cells to drug resistance: Anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors act as p-glycoprotein antagonists. Angiogenesis 2017, 12, 217–241. [Google Scholar]
- Berndsen, R.H.; Abdul, U.K.; Weiss, A.; Zoetemelk, M.; Winkel, M.T.T.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Epigenetic approach for angiostatic therapy: Promising combinations for cancer treatment. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beijnum, J.R.; Giovannetti, E.; Poel, D.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Griffioen, A.W. miRNAs: Micro-managers of anti-cancer combination therapies. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Yaeger, R.; Wasan, H.; Yoshino, T.; Desai, J.; Ciardiello, F.; Gollerkeri, A.; Maharry, K.; et al. LBA-006BEACON CRC: A randomized, 3-Arm, phase 3 study of encorafenib and cetuximab with or without binimetinib vs. choice of either irinotecan or FOLFIRI plus cetuximab in BRAF V600E–mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.K.; Yu, F.; Shahangian, A.; Cheng, G.; Sun, R.; Ho, C.-M. Closed-loop control of cellular functions using combinatory drugs guided by a stochastic search algorithm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alaoui-Lasmaili, K.; Djermoune, E.-H.; Tylcz, J.-B.; Meng, D.; Plenat, F.; Thomas, N. A new algorithm for a better characterization and timing of the anti-VEGF vascular effect named “normalization”. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Ding, X.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Wong, I.; Wong, T.J.; Berndsen, R.H.; Dormond, O.; Dallinga, M.; Shen, L.; Schlingemann, R.O.; et al. Rapid optimization of drug combinations for the optimal angiostatic treatment of cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Weiss, A.; Ding, X.; Dyson, P.J.; Bergh, H.V.D.; Griffioen, A.W.; Ho, C.-M. Optimization of drug combinations using Feedback System Control. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Berndsen, R.H.; Ding, X.; Ho, C.-M.; Dyson, P.J.; Bergh, H.V.D.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. A streamlined search technology for identification of synergistic drug combinations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, W.; Weiss, A.; Li, Y.; Wong, I.; Griffioen, A.W.; Bergh, H.V.D.; Xu, H.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Ho, C.-M. Discovery of a low order drug-cell response surface for applications in personalized medicine. Phys. Boil. 2014, 11, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, S.; Igea, A.; Arroyo, R.; Alcalde, V.; Canovas, B.; Orozco, M. Quantification of Pathway Cross-talk Reveals Novel Synergistic Drug Combinations for Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienstmann, R.; Vermeulen, L.; Guinney, J.; Kopetz, S.; Tejpar, S.; Tabernero, J. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Segura, T.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. The chicken chorioallantoic membrane model in biology, medicine and bioengineering. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Alitalo, K.; Allen, E.; Anisimov, A.; Aplin, A.C.; Auerbach, R.; Augustin, H.G.; Bates, D.O.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Bender, R.H.F.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the use and interpretation of angiogenesis assays. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 425–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinska, M.; Murias, M.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Beyond mouse cancer models: Three-dimensional human-relevant in vitro and non-mammalian in vivo models for photodynamic therapy. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subauste, M.C.; Kupriyanova, T.A.; Conn, E.M.; Ardi, V.C.; Quigley, J.P.; Deryugina, E.I. Evaluation of metastatic and angiogenic potentials of human colon carcinoma cells in chick embryo model systems. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.; Danielsen, S.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.; Lothe, R. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovitz, A.; Stinson, J.C.; McCombs, W.B.; McCoy, C.; Mazur, K.C.; Mabry, N.D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 4562–4569. [Google Scholar]
- Brattain, M.G.; Brattain, D.; Fine, W.D.; Khaled, F.M.; Marks, M.; Kimball, P.M.; Arcolano, L.; Danbury, B.H. Initiation and characterization of cultures of human colonic carcinoma with different biological characteristics utilizing feeder layers of confluent fibroblasts. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 1981, 2, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fogh, J.; Trempe, G. New Human Tumor Cell Lines. In Human Tumor Cells In Vitro; Fogh, J., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 115–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Dorotinsky, C.; McGuire, L.; Macy, M.; Hay, R. DLD-1 and HCT-15 cell lines derived separately from colorectal carcinomas have totally different chromosome changes but the same genetic origin. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1995, 81, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Brummelen, E.M.J.; de Boer, A.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. BRAF Mutations as Predictive Biomarker for Response to Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies. Oncologist 2017, 22, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S.A.; Dixon, D.; Hailey, J.R.; Harada, T.; Herbert, R.A.; Maronpot, R.R.; Nolte, T.; Rehg, J.E.; Rittinghausen, S.; Rosol, T.J.; et al. Recommendations from the INHAND Apoptosis/Necrosis Working Group. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 44, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Rix, U.; Carlson, S.M.; Gleixner, K.V.; Grebien, F.; Gridling, M.; Müller, A.C.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Bilban, M.; Colinge, J.; et al. Systems-pharmacology dissection of a drug synergy in imatinib-resistant CML. Nat. Methods 2012, 8, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kleibeuker, E.A.; Hooven, M.A.T.; Castricum, K.C.; Honeywell, R.; Griffioen, A.W.; Verheul, H.M.; Slotman, B.J.; Thijssen, V.L. Optimal treatment scheduling of ionizing radiation and sunitinib improves the antitumor activity and allows dose reduction. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Bonvin, D.; Jichlinski, P.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Low-dose angiostatic tyrosine kinase inhibitors improve photodynamic therapy for cancer: Lack of vascular normalization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Samaras, P.; Frejno, M.; Gessulat, S.; Barnert, M.; Kienegger, H. ProteomicsDB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaeger, S.; Heinzlmeir, S.; Wilhelm, M.; Polzer, H.; Vick, B.; Koenig, P.-A.; Reinecke, M.; Ruprecht, B.; Petzoldt, S.; Meng, C.; et al. The target landscape of clinical kinase drugs. Science 2017, 358, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, R.H.; Castrogiovanni, C.; Weiss, A.; Rausch, M.; Dallinga, M.G.; Miljkovic-Licina, M.; Klaassen, I.; Meraldi, P.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Anti-angiogenic effects of crenolanib are mediated by mitotic modulation independently of PDGFR expression. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzaez, M.; Guevara, T.; Sancho, M.; Pérez-Payá, E. Intrinsic caspase-8 activation mediates sensitization of erlotinib-resistant tumor cells to erlotinib/cell-cycle inhibitors combination treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S.; Vitagliano, D.; Morgillo, F.; Capasso, A.; Sforza, V.; Nappi, A.; Ciardiello, D.; Ciardiello, F.; Martinelli, E. Primary and Acquired Resistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells to Anti-EGFR Antibodies Converge on MEK/ERK Pathway Activation and Can Be Overcome by Combined MEK/EGFR Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3775–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Huijbers, E.J.M.; Thijssen, V.L.; Griffioen, A.W. The Great Escape; the Hallmarks of Resistance to Antiangiogenic Therapy. Pharm. Rev. 2015, 67, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, E.J.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Thijssen, V.L.; Sabrkhany, S.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Griffioen, A.W. Role of the tumor stroma in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 25, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffioen, A.W.; Molema, G. Angiogenesis: Potentials for pharmacologic intervention in the treatment of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic inflammation. Pharm. Rev. 2000, 52, 237–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ramjiawan, R.R.; Griffioen, A.W.; Duda, D.G. Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: Is there a role for combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, A.W.; Mans, L.A.; De Graaf, A.M.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; De Hoog, C.L.; De Jong, T.A.; Vyth-Dreese, F.A.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Bex, A.; Jonasch, E. Rapid angiogenesis onset after discontinuation of sunitinib treatment of renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3961–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøyum, A. Isolation of Lymphocytes, Granulocytes and Macrophages. Scand. J. Immunol. 1976, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Mijn, J.C.; Broxterman, H.J.; Knol, J.C.; Piersma, S.R.; De Haas, R.R.; Dekker, H.; Pham, T.V.; Van Beusechem, V.W.; Halmos, B.; Mier, J.W.; et al. Sunitinib activates Axl signaling in renal cell cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Bonvin, D.; Berndsen, R.H.; Scherrer, E.; Wong, T.J.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Angiostatic treatment prior to chemo- or photodynamic therapy improves anti-tumor efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berndsen, R.H.; Swier, N.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Colorectal Cancer Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using an Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib. Cancers 2019, 11, 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121878
Berndsen RH, Swier N, van Beijnum JR, Nowak-Sliwinska P. Colorectal Cancer Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using an Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121878
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerndsen, Robert H., Nathalie Swier, Judy R. van Beijnum, and Patrycja Nowak-Sliwinska. 2019. "Colorectal Cancer Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using an Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121878
APA StyleBerndsen, R. H., Swier, N., van Beijnum, J. R., & Nowak-Sliwinska, P. (2019). Colorectal Cancer Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using an Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib, and Dasatinib. Cancers, 11(12), 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121878





