CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker
Abstract
:1. Introduction
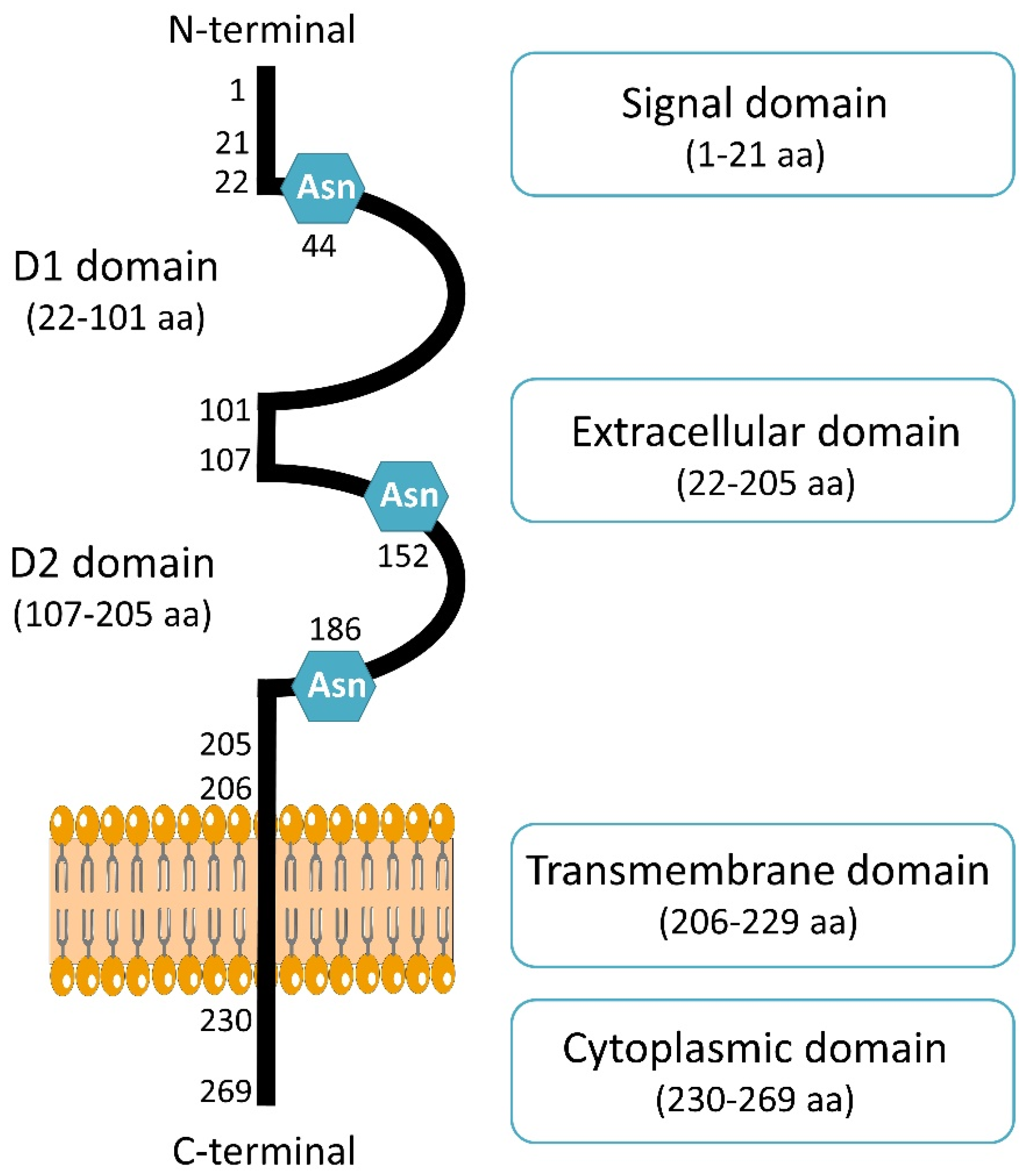
2. CD147 Biological Functions in Cancer: Structure and Partners
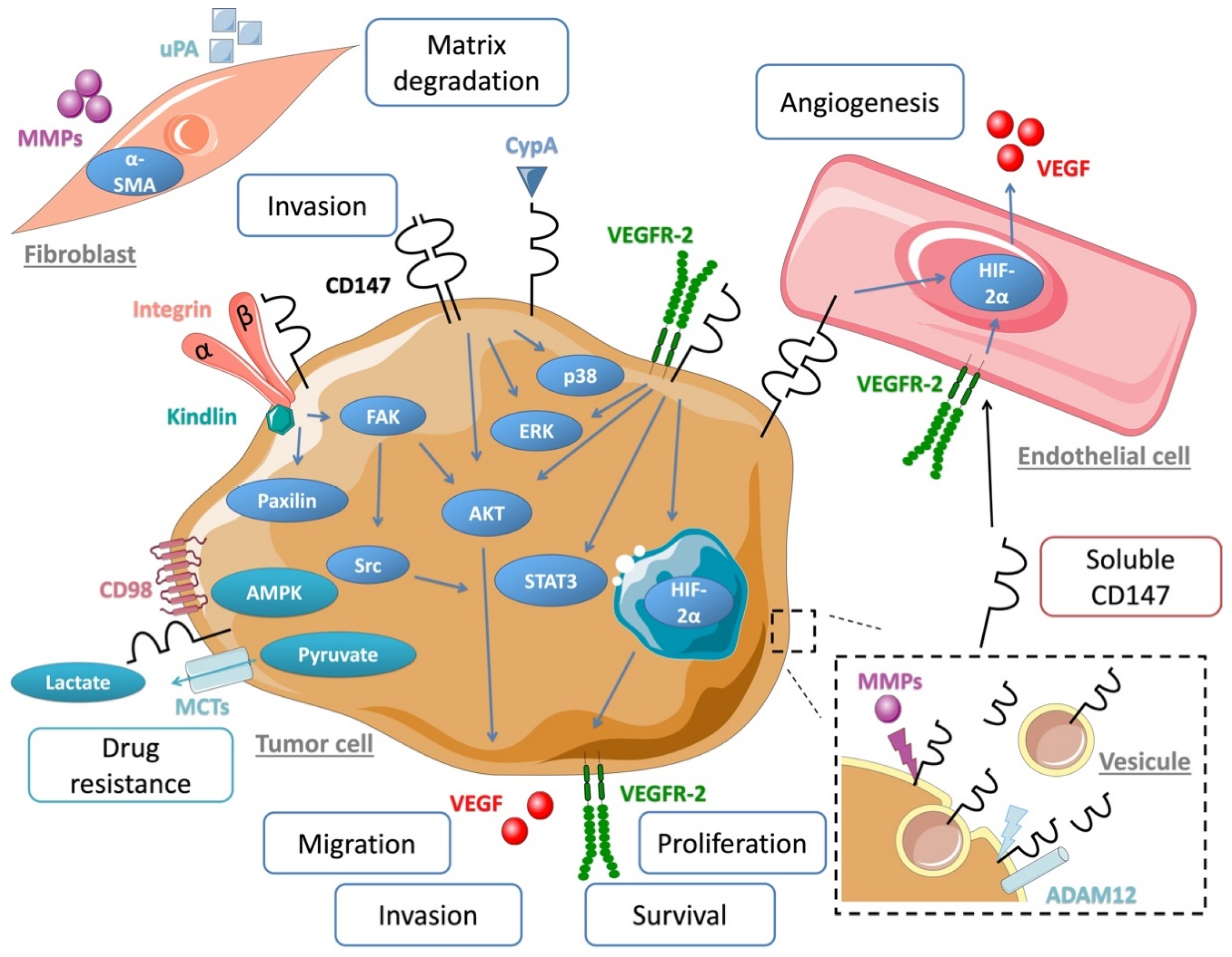
3. CD147 Regulates Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis
4. CD147 Regulates Tumors Cells Adhesion
5. CD147 Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis
6. CD147 Therapeutic Targeting Strategies
7. CD147 as a Prognostic Biomarker
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grzywa, T.M.; Paskal, W.; Włodarski, P.K. Intratumor and Intertumor Heterogeneity in Melanoma. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 956–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dang, H.; Wang, X.W. The significance of intertumor and intratumor heterogeneity in liver cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, V.; Teti, G.; Focaroli, S.; Mazzotti, M.C.; Mazzotti, A.; Falconi, M. The tumor microenvironment promotes cancer progression and cell migration. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 9608–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-N.; Xin, T.; Chen, M.; Gao, P. Chemoresistance in mesenchymal lung cancer cells is correlated to high regulatory T cell presence in the tumor microenvironment. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, D.; Von Hoff, D.D. Tumor-stroma interactions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunen, S.P.; Tatti-Bugaeva, O.; Lehti, K. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteases as diverse effectors of cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1974–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabison, E.E.; Huet, E.; Baudouin, C.; Menashi, S. Direct epithelial–stromal interaction in corneal wound healing: Role of EMMPRIN/CD147 in MMPs induction and beyond. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, G.D.; Toole, B.P. How, with whom and when: An overview of CD147-mediated regulatory networks influencing matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 36, e00283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, T. Basigin (CD147), a multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein with various binding partners. J. Biochem. 2016, 159, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, F.; Quemener, C.; Kellouche, S.; Naimi, B.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Millot, G.; Gabison, E.E.; Calvo, F.; Dosquet, C.; Lebbe, C.; et al. EMMPRIN promotes angiogenesis through hypoxia-inducible factor-2 -mediated regulation of soluble VEGF isoforms and their receptor VEGFR-2. Blood 2009, 114, 5547–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, C.F.; Zhao, Y.; Zavaglia, K.; Jin, P.; Panelli, M.C.; Voiculescu, S.; Mandruzzato, S.; Lee, H.M.; Seliger, B.; Freedman, R.S.; et al. Common cancer biomarkers. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Yi, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. The clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of EMMPRIN overexpression in cancers: Evidence from 39 cohort studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82643–82660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Zucker, S.; Toole, B.P. Roles of the multifunctional glycoprotein, emmprin (basigin; CD147), in tumour progression. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, C.; Zhang, Y.; DeCastro, R.; Guo, H.; Nakamura, T.; Kataoka, H.; Nabeshima, K. The Human Tumor Cell-derived Collagenase Stimulatory Factor (Renamed EMMPRIN) Is a Member of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Kaname, T.; Miyauchi, T.; Kuwano, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Muramatsu, T.; Kajii, T. Mapping basigin (BSG), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, to 19p13.3. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1993, 64, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-G.; Kong, L.-M.; Song, F.; Xing, J.-L.; Wang, L.-X.; Sun, Z.-J.; Tang, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Characterization of Basigin Isoforms and the Inhibitory Function of Basigin-3 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 2591–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.M.; Kirk, P.; Holt, O.J.; Puklavec, M.J.; Brown, M.H.; Barclay, A.N. A novel form of the membrane protein CD147 that contains an extra Ig-like domain and interacts homophilically. BMC Biochem. 2003, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, R.J.; Chen, L.; Mesquita, F.S.; Nowak, R.A. Basigin-2 Is a Cell Surface Receptor for Soluble Basigin Ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17805–17814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, T.; Miyauchi, T. Basigin (CD147): A multifunctional transmembrane protein involved in reproduction, neural function, inflammation and tumor invasion. Histol. Histopathol. 2003, 18, 981–987. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.-L.; Hu, T.; Du, J.-M.; Ding, J.-P.; Yang, X.-M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, W.-D.; et al. Crystal structure of HAb18G/CD147: Implications for immunoglobulin superfamily homophilic adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18056–18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadool, J.M.; Linser, P.J. Evidence for the formation of multimeric forms of the 5A11/HT7 antigen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 229, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Shibata, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Hagihara, M.; Asai, N.; Takahashi, M.; Mizutani, S.; Muramatsu, T.; Kadomatsu, K. Homo-oligomer formation by basigin, an immunoglobulin superfamily member, via its N-terminal immunoglobulin domain. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Bültmann, A.; Fischel, S.; Gillitzer, A.; Cullen, P.; Walch, A.; Jost, P.; Ungerer, M.; Tolley, N.D.; Lindemann, S.; et al. Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (CD147) Is a Novel Receptor on Platelets, Activates Platelets, and Augments Nuclear Factor κB–Dependent Inflammation in Monocytes. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutti, N.; Kuepper, M.; Friedrich, K. Soluble extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN, EMN) regulates cancer-related cellular functions by homotypic interactions with surface CD147. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 4187–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.-Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhao, P.; Dong, Z.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.-L.; Chen, Z.-N.; Yu, X.-L. Dimerization is essential for HAb18G/CD147 promoting tumor invasion via MAPK pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Koga, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Hamasaki, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Oyama, M.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Seiki, M.; Toole, B.P.; Nabeshima, K. CD73 complexes with emmprin to regulate MMP-2 production from co-cultured sarcoma cells and fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Chen, Z.-N.; Fan, Z. A novel role of EMMPRIN/CD147 in transformation of quiescent fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts by breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chang, S.B.; Hemler, M.E. Links between CD147 Function, Glycosylation, and Caveolin-1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 4043–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, N.; Koshikawa, N.; Tomari, T.; Nabeshima, K.; Isobe, T.; Seiki, M. Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP/MMP-14) Cleaves and Releases a 22-kDa Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN) Fragment from Tumor Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37576–37585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, S.S.; Mengistab, A.T.; Tauscher, A.N.; LaVail, J.; Basbaum, C. The microvesicle as a vehicle for EMMPRIN in tumor–stromal interactions. Oncogene 2004, 23, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtsen, R.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Gnosa, S.; Schwarz, J.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Kveiborg, M. Identification of ADAM12 as a Novel Basigin Sheddase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Tang, L.L.; Wang, S.M.; Yan, G.J.; Liao, L.Q. Plasma soluble cluster of differentiation 147 levels are increased in breast cancer patients and associated with lymph node metastasis and chemoresistance. Hong Kong Med. J. 2018, 24, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Rode, A.; Nicoll, A.; Maczurek, A.E.; Lim, L.; Lim, S.; Angus, P.; Kronborg, I.; Arachchi, N.; Gorelik, A.; et al. Circulating CD147 predicts mortality in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, P.; Wilson, M.C.; Heddle, C.; Brown, M.H.; Barclay, A.N.; Halestrap, A.P. CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Hemler, M.E. Caveolin-1 regulates matrix metalloproteinases-1 induction and CD147/EMMPRIN cell surface clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11112–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.Y.; Fox, D.A.; Horejsi, V.; Sagawa, K.; Skubitz, K.M.; Katz, D.R.; Chain, B. The functional interactions between CD98, β1-integrins, and CD147 in the induction of U937 homotypic aggregation. Blood 2001, 98, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Song, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, S.-J.; Yu, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-N.; Jiang, J.-L. Extracellular Membrane-proximal Domain of HAb18G/CD147 Binds to Metal Ion-dependent Adhesion Site (MIDAS) Motif of Integrin β1 to Modulate Malignant Properties of Hepatoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4759–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Floch, R.; Chiche, J.; Marchiq, I.; Naiken, T.; Ilc, K.; Murray, C.M.; Critchlow, S.E.; Roux, D.; Simon, M.-P.; Pouysségur, J. CD147 subunit of lactate/H+ symporters MCT1 and hypoxia-inducible MCT4 is critical for energetics and growth of glycolytic tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16663–16668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchiq, I.; Albrengues, J.; Granja, S.; Gaggioli, C.; Pouysségur, J.; Simon, M.-P. Knock out of the BASIGIN/CD147 chaperone of lactate/H+ symporters disproves its pro-tumour action via extracellular matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) induction. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24636–24648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granja, S.; Marchiq, I.; Floch, R.L.; Moura, C.S.; Baltazar, F.; Pouysségur, J. Disruption of BASIGIN decreases lactic acid export and sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to biguanides independently of the LKB1 status. Oncotarget 2014, 6, 6708–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chang, S.; Jiang, X.; Su, J.; Dong, C.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, H. RNA interference targeting CD147 inhibits the proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic activity of thyroid carcinoma cells by down-regulating glycolysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walters, D.K.; Arendt, B.K.; Jelinek, D.F. CD147 regulates the expression of MCT1 and lactate export in multiple myeloma cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3175–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Cao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Caveolin-1 up-regulates CD147 glycosylation and the invasive capability of murine hepatocarcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hemler, M.E. Metabolic activation-related CD147-CD98 complex. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Chen, Z.-N.; Jiang, J. CD147 promotes Src-dependent activation of Rac1 signaling through STAT3/DOCK8 during the motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Nakada, M.T.; Rafferty, P.; Laraio, J.; McCabe, F.L.; Millar, H.; Cunningham, M.; Snyder, L.A.; Bugelski, P.; Yan, L. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by EMMPRIN via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doyle, L.A.; Yang, W.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Krogmann, T.; Gao, Y.; Rishi, A.K.; Ross, D.D. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15665–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allikmets, R.; Schriml, L.M.; Hutchinson, A.; Romano-Spica, V.; Dean, M. A Human Placenta-specific ATP-Binding Cassette Gene (ABCP) on Chromosome 4q22 That Is Involved in Multidrug Resistance. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5337–5339. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, O.M.; Köttgen, A.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Guggino, W.B.; Köttgen, M. Identification of a urate transporter, ABCG2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10338–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Liao, L.; Chen, C.; Zeng, W.; Liu, S.; Su, J.; Zhao, S.; Chen, M.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. CD147 mediates chemoresistance in breast cancer via ABCG2 by affecting its cellular localization and dimerization. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Zeng, W.; Su, J.; Wu, L.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. CD147 promotes MTX resistance by immune cells through up-regulating ABCG2 expression and function. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 70, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, S.; Yu, L. Cyclophilin A is upregulated in small cell lung cancer and activates ERK1/2 signal. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Fan, C.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W. Association of increased ligand cyclophilin A and receptor CD147 with hypoxia, angiogenesis, metastasis and prognosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2012, 60, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, V.; Pushkarsky, T.; Li, J.-H.; Dai, W.W.; Sherry, B.; Bukrinsky, M. Regulation of CD147 cell surface expression: Involvement of the proline residue in the CD147 transmembrane domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17013–17019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Zucker, S.; Gordon, M.K.; Toole, B.P.; Biswas, C. Stimulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Production by Recombinant Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer from Transfected Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Li, R.; Zucker, S.; Toole, B.P. EMMPRIN (CD147), an inducer of matrix metalloproteinase synthesis, also binds interstitial collagenase to the tumor cell surface. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 888–891. [Google Scholar]
- Kanekura, T.; Chen, X.; Kanzaki, T. Basigin (cd147) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucci, N.; Millimaggi, D.; Mari, M.; Del Fattore, A.; Bologna, M.; Teti, A.; Angelucci, A.; Dolo, V. Receptor Activator of NF- B Ligand Enhances Breast Cancer-Induced Osteolytic Lesions through Upregulation of Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer/CD147. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6150–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudroy, S.; Polette, M.; Nawrocki-Raby, B.; Cao, J.; Toole, B.P.; Zucker, S.; Birembaut, P. EMMPRIN-mediated MMP regulation in tumor and endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2002, 19, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, T.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, D.; Shen, W.; Li, L.; Lv, Y.; Jin, Y.; Song, X.; Teng, C. CD147, MMP9 expression and clinical significance of basal-like breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Ye, C.; Yang, Y.; Guan, X.; Dong, B.; Zhao, M.; Hao, C. Expression of CD147 and matrix metalloproteinase-11 in colorectal cancer and their relationship to clinicopathological features. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-M.; O’Neill, P.; Jin, W.; Foty, R.; Medina, D.J.; Xu, Z.; Lomas, M.; Arndt, G.M.; Tang, Y.; Nakada, M.; et al. Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (CD147) Confers Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Anoikis through Inhibition of Bim. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9719–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, X.; LI, L.; Dong, H.-L.; Chen, Z.-N. Acquisition of anoikis resistance through CD147 upregulation: A new mechanism underlying metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemener, C.; Gabison, E.E.; Naïmi, B.; Lescaille, G.; Bougatef, F.; Podgorniak, M.P.; Labarchède, G.; Lebbé, C.; Calvo, F.; Menashi, S.; et al. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer up-regulates the urokinase-type plasminogen activator system promoting tumor cell invasion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucker, S.; Hymowitz, M.; Rollo, E.E.; Mann, R.; Conner, C.E.; Cao, J.; Foda, H.D.; Tompkins, D.C.; Toole, B.P. Tumorigenic potential of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, C.A.; Seidl, S.; Petat-Dutter, K.; Offner, S.; Geigl, J.B.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Wendler, N.; Passlick, B.; Huber, R.M.; Schlimok, G.; et al. Combined transcriptome and genome analysis of single micrometastatic cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menashi, S.; Serova, M.; Ma, L.; Vignot, S.; Mourah, S.; Calvo, F. Regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer and matrix metalloproteinase expression by amphiregulin in transformed human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7575–7580. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Yan, M. CD147 promotes progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via NF-kappa B signaling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berditchevski, F.; Chang, S.; Bodorova, J.; Hemler, M.E. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin-associated proteins. Evidence that alpha3beta1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29174–29180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Dong, X.; Peng, F.; Shen, L. Integrin β1 regulates the invasion and radioresistance of laryngeal cancer cells by targeting CD147. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yang, X.-M.; Wei, D.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.-X.; Feng, F.; Nan, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.-N.; et al. A chimeric antibody targeting CD147 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility via FAK-PI3K-Akt-Girdin signaling pathway. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Y.-M.; Zhao, P.; Yang, X.-M.; Jiang, J.-L.; Chen, Z.-N. Overexpression of HAb18G/CD147 promotes invasion and metastasis via α3β1 integrin mediated FAK-paxillin and FAK-PI3K-Ca2+ pathways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Dou, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, P.; Lau, W.B.; Tao, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z. The interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with integrin α6β1 and its implications for the invasion potential of human hepatoma cells. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, D.M.; Dang, D. EMMPRIN Expression in Oral SCC Is Regulated by FYN Kinase. Anticancer. Res. 2011, 31, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Grass, G.D.; Bratoeva, M.; Toole, B.P. Regulation of invadopodia formation and activity by CD147. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Collazo, J.; Gal, J.; Shi, P.; Liu, L.; Ström, A.-L.; Lu, X.; McCann, R.O.; et al. EMMPRIN Regulates Cytoskeleton Reorganization and Cell Adhesion in Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2012, 72, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delyon, J.; Khayati, F.; Djaafri, I.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Sadoux, A.; Setterblad, N.; Boutalbi, Z.; Maouche, K.; Maskos, U.; Menashi, S.; et al. EMMPRIN regulates β1 integrin-mediated adhesion through Kindlin-3 in human melanoma cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.; Legate, K.R.; Zent, R.; Fässler, R. The Tail of Integrins, Talin, and Kindlins. Science 2009, 324, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.; Bauer, M.; Schmid, S.; Ruppert, R.; Schmidt, S.; Sixt, M.; Wang, H.-V.; Sperandio, M.; Fässler, R. Kindlin-3 is required for beta2 integrin-mediated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagerholm, S.C.; Guenther, C.; Llort Asens, M.; Savinko, T.; Uotila, L.M. Beta2-Integrins and Interacting Proteins in Leukocyte Trafficking, Immune Suppression, and Immunodeficiency Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djaafri, I.; Khayati, F.; Menashi, S.; Tost, J.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Sadoux, A.; Daunay, A.; Teixeira, L.; Soulier, J.; Idbaih, A.; et al. A novel tumor suppressor function of Kindlin-3 in solid cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8970–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Nakada, M.T.; Kesavan, P.; McCabe, F.; Millar, H.; Rafferty, P.; Bugelski, P.; Yan, L. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer stimulates tumor angiogenesis by elevating vascular endothelial cell growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, F.; Menashi, S.; Khayati, F.; Naïmi, B.; Porcher, R.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Millot, G.; Janin, A.; Calvo, F.; Lebbé, C.; et al. EMMPRIN Promotes Melanoma Cells Malignant Properties through a HIF-2alpha Mediated Up-Regulation of VEGF-Receptor-2. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khayati, F.; Pérez-Cano, L.; Maouche, K.; Sadoux, A.; Boutalbi, Z.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Maskos, U.; Setterblad, N.; Janin, A.; Calvo, F.; et al. EMMPRIN/CD147 is a novel coreceptor of VEGFR-2 mediating its activation by VEGF. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9766–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S.M.; Castorino, J.J.; Wang, D.; Philp, N.J. Monocarboxylate transporter 4 regulates maturation and trafficking of CD147 to the plasma membrane in the metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zou, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Xin, X. Bridge linkage role played by CD98hc of anti-tumor drug resistance and cancer metastasis on cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 942–947. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, S.; Ghatak, S.; Zoltan-Jones, A.; Toole, B.P. Regulation of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells by Hyaluronan. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25285–25288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.J.; Bourguignon, L.Y.W. Hyaluronan and the Interaction Between CD44 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Oncogenic Signaling and Chemotherapy Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, R.; Takahashi, F.; Cui, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Gu, T.; Sasaki, S.; Tominaga, S.; Nishio, K.; Tanabe, K.K.; Takahashi, K. Interaction between CD44 and hyaluronate induces chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, R.I.C.; García, M.G.; Alaniz, L.; Blanco, G.; Alvarez, E.; Hajos, S.E. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides sensitize lymphoma resistant cell lines to vincristine by modulating P-glycoprotein activity and PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Dai, L.; Bratoeva, M.; Slomiany, M.G.; Toole, B.P.; Parsons, C. Cooperative roles for emmprin and LYVE-1 in the regulation of chemoresistance for primary effusion lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baba, M.; Inoue, M.; Itoh, K.; Nishizawa, Y. Blocking CD147 induces cell death in cancer cells through impairment of glycolytic energy metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, D.M.; Spina, R.; Carter, D.L.; Lim, K.S.; Jeffery, C.J.; Bar, E.E. Disruption of the monocarboxylate transporter-4-basigin interaction inhibits the hypoxic response, proliferation, and tumor progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Simanovich, E.; Brod, V.; Lahat, N.; Bitterman, H.; Rahat, M.A. An epitope-specific novel anti-EMMPRIN polyclonal antibody inhibits tumor progression. Oncoimmunology 2015, 5, e1078056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugyo, A.; Tsuji, A.B.; Sudo, H.; Koizumi, M.; Ukai, Y.; Kurosawa, G.; Kurosawa, Y.; Saga, T.; Higashi, T. Efficacy Evaluation of Combination Treatment Using Gemcitabine and Radioimmunotherapy with 90Y-Labeled Fully Human Anti-CD147 Monoclonal Antibody 059-053 in a BxPC-3 Xenograft Mouse Model of Refractory Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, N.R.; Knowles, J.A.; Helman, E.E.; Aldridge, J.C.; Carroll, W.R.; Magnuson, J.S.; Clemons, L.; Ziober, B.; Rosenthal, E.L. Anti-EMMPRIN antibody treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in an ex-vivo model. Anticancer. Drugs 2010, 21, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Ishikawa, K. Combined inhibition of EMMPRIN and epidermal growth factor receptor prevents the growth and migration of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ku, X.-M.; Li, Y.; Bian, H.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Ye, H.; Yao, X.-Y.; Li, B.-H.; Yang, X.-M.; Liao, C.-G.; et al. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase production and tumor cell invasion by four monoclonal antibodies against different epitopes of HAb18G/CD147 extracellular domain. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 2006, 25, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, X.-M.; Liao, C.-G.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.-M.; Yang, B.; Yao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.-M.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Z.-N. Epitope Mapping of Series of Monoclonal Antibodies Against the Hepatocellular Carcinoma-associated Antigen HAb18G/CD147. Scand. J. Immunol. 2007, 65, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xing, J.; Zhang, S. Anti-Human Hepatoma Monoclonal Antibody Hab18 Light/Heavy Chain Variable Region Gene, and Use Thereof. EP Patent 20030711796, 29 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-N.; Mi, L.; Xu, J.; Song, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.-L.; Bian, H.-J.; Jiang, J.-L.; Wang, X.-H.; et al. Targeting radioimmunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma with iodine (131I) metuximab injection: Clinical Phase I/II trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, Q.; Bian, H.-J.; Zhu, P.; Xu, H.-Y.; Song, F.; Yang, X.-M.; Mi, L.; et al. A randomized controlled trial of Licartin for preventing hepatoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Hepatology 2007, 45, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-Y.; He, D.; Sheng, C.-B.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.-J.; Wu, X.-Q.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.-L.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.-N. Therapeutic anti-CD147 antibody sensitizes cells to chemoradiotherapy via targeting pancreatic cancer stem cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3543–3554. [Google Scholar]
- Huhe, M.; Lou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.-N. A novel antibody-drug conjugate, HcHAb18-DM1, has potent anti-tumor activity against human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, H.; Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Geng, J.; Liu, J.; Feng, F.; Song, F.; Li, L.; et al. A novel small-molecule compound targeting CD147 inhibits the motility and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9429–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinello, I.; Saulle, E.; Quaranta, M.T.; Pasquini, L.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Ottone, T.; Voso, M.T.; Testa, U.; Labbaye, C. The small-molecule compound AC-73 targeting CD147 inhibits leukemic cell proliferation, induces autophagy and increases the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Haematologica 2019, 104, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Nakai, Y.; Nakata, W.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, K.; Kawashima, A.; Fujita, K.; Uemura, M.; Takayama, H.; Nonomura, N. EMMPRIN promotes angiogenesis, proliferation, invasion and resistance to sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma, and its level predicts patient outcome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhong, W.-D.; Zhang, Z.; Mi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, C.-G.; Bian, H.-J.; Jiang, J.-L.; et al. HAb18G (CD147), a cancer-associated biomarker and its role in cancer detection. Histopathology 2009, 54, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudron, A.; Battistella, M.; Feugeas, J.-P.; Pages, C.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Dorval, S.M.; Brentano, E.F.; Sadoux, A.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Menashi, S.; et al. EMMPRIN/CD147 is an independent prognostic biomarker in cutaneous melanoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, A.I.C.; Huang, L.; Xu, J.; Kumta, S.-M.; Wood, D.; Zheng, M.H. Expression and localization of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer in giant cell tumor of bone. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 89, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Mane, D.R. Immunohistochemical expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) in normal oral mucosa, oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2018, 22, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lescaille, G.; Menashi, S.; Cavelier-Balloy, B.; Khayati, F.; Quemener, C.; Podgorniak, M.P.; Naïmi, B.; Calvo, F.; Lebbe, C.; Mourah, S. EMMPRIN/CD147 up-regulates urokinase-type plasminogen activator: Implications in oral tumor progression. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, N.; Beckers, S.; Waigel, S.; Mensah, J.; Wu, J.; Mo, J.; Fleisher, K.E.; Bouquot, J.; Sacks, P.G.; Zacharias, W. Increased EMMPRIN (CD 147) expression during oral carcinogenesis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 80, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienel, W.; Polzer, B.; Elshawi, K.; Lindner, M.; Morresi-Hauf, A.; Vay, C.; Eder, F.; Passlick, B.; Klein, C.A. Cellular localization of EMMPRIN predicts prognosis of patients with operable lung adenocarcinoma independent from MMP-2 and MMP-9. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Wan, Z.; Sheng, B.; Lin, Y.; Fu, T.; Zeng, Q.; Qi, C. Overexpression of EMMPRIN is associated with lymph node metastasis and advanced stage of non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimers, N.; Zafrakas, K.; Assmann, V.; Egen, C.; Riethdorf, L.; Riethdorf, S.; Berger, J.; Ebel, S.; Jänicke, F.; Sauter, G.; et al. Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteases inducer on micrometastatic and primary mammary carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3422–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tsang, J.Y.S.; Lee, M.; Ni, Y.-B.; Chan, S.-K.; Cheung, S.-Y.; Hu, J.; Hu, H.; Tse, G.M.K. CD147 expression is associated with poor overall survival in chemotherapy treated triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.; Goldberg, I.; Berner, A.; Kristensen, G.B.; Reich, R. EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, M.; Wang, S.; Feng, F.; Ji, P.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, G.; et al. Prognostic significance of CD147 in patients with glioblastoma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 115, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.-X.; He, H.-C.; Han, Z.; Bi, X.-C.; Dai, Q.-S.; Ye, Y.-K.; Qin, W.-J.; Zeng, G.-H.; Zhu, G.; Xu, C.-L.; et al. CD147 and VEGF Expression in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Their Prognostic Value. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabien, A.; Stephan, C.; Kilic, E.; Weichert, W.; Kristiansen, G.; Miller, K.; Jung, K.; Erbersdobler, A. Renal cell neoplasias: Reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs discriminates tumor subtypes, while extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer indicates prognosis. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madigan, M.C.; Kingsley, E.A.; Cozzi, P.J.; Delprado, W.J.; Russell, P.J.; Li, Y. The role of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer protein in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Liang, Y.; Lin, S.X.; Li, L.; He, H.; Bi, X.; Han, Z.; Dai, Q.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Expression of CD147 is associated with prostate cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Als, A.B.; Dyrskjøt, L.; von der Maase, H.; Koed, K.; Mansilla, F.; Toldbod, H.E.; Jensen, J.L.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Sengeløv, L.; Jensen, K.M.E.; et al. Emmprin and survivin predict response and survival following cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemdan, T.; Malmström, P.-U.; Jahnson, S.; Segersten, U. Emmprin Expression Predicts Response and Survival following Cisplatin Containing Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer: A Validation Study. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-C.; Takahashi, H.; Murai, Y.; Cui, Z.-G.; Nomoto, K.; Miwa, S.; Tsuneyama, K.; Takano, Y. Upregulated EMMPRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: A good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, C.; Wu, D.; Shi, S.; Liao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z. The prognostic and clinicopathologic characteristics of CD147 and esophagus cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenzinger, A.; Wittschieber, D.; von Winterfeld, M.; Goeppert, B.; Kamphues, C.; Weichert, W.; Dietel, M.; Rabien, A.; Klauschen, F. High extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147 expression is strongly and independently associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Bai, Y. CD147 and VEGF co-expression predicts prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 40, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Reference | First Author | Year | Type of Cancer | Sample Size | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [113] | Si et al. | 2003 | Bone cancer | 19 | CD147 expression associated with progression and aggressiveness |
| [121] | Davidson et al. | 2003 | Ovarian cancer | 130 | CD147 is expressed in all sites (effusions, primary tumor and solid metastases) and predict poor prognosis |
| [119] | Reimers et al. | 2004 | Breast cancer | 2222 | CD147 expression in primary tumor predicts a poor prognosis |
| [116] | Vigneswaran et al. | 2006 | Oral cancer | 140 | CD147 overexpress in advanced primary and metastatic tumors |
| [129] | Zheng et al. | 2006 | Gastric carcinoma | 319 | CD147 expression linked to tumor size |
| [127] | Als et al. | 2007 | Bladder cancer | 124 | CD147 expression predict response to Cisplatin-containing chemotherapy |
| [117] | Sienel et al. | 2008 | Lung cancer | 150 | Membrane localization of CD147 was associated with poor survival independently of MMP-2 and MMP-9 |
| [125] | Madigan et al. | 2008 | Prostate cancer | 120 | Higher expression of CD147 in high grades |
| [123] | Liang et al. | 2009 | Renal cancer | 53 | CD147 expression correlated with VEGF expression and played a role in progression |
| [132] | Fu et al. | 2010 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 62 | Co-expression of CD147 and VEGF promote unfavorable prognosis |
| [131] | Stenzinger et al. | 2011 | Colorectal cancer | 285 | CD147 expression decreased survival |
| [115] | Lescaille et al. | 2012 | Oral cancer | 20 | CD147 expression increased with invasive stage |
| [126] | Zhong et al. | 2012 | Prostate cancer | 240 | CD147 expression can serve as a significant marker for progression |
| [122] | Yang et al. | 2013 | Glioblastoma | 206 | High CD147 expression mediated poor overall survival |
| [124] | Rabien et al. | 2013 | Renal cancer | 395 | CD147 expression increased only with progression |
| [128] | Hemdan et al. | 2015 | Bladder cancer | 250 | Strong expression of CD147 promoted worse response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| [112] | Caudron et al. | 2016 | Melanoma | 196 | High CD147 expression associated with metastatic potential and short survival |
| [118] | Liu et al. | 2017 | Lung cancer | 72 | High CD147 in serum-mediated metastasis and advanced stage |
| [130] | Li et al. | 2017 | Esophagus cancer | 17 studies (1140 samples) | Worse survival and poor prognosis with CD147 strong expression |
| [114] | Arora et al. | 2018 | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | 100 | CD147 intensity associated with different grades |
| [120] | Liu et al. | 2018 | Breast cancer | 1174 | CD147 expression mediated survival in chemotherapy-treated patients |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landras, A.; Reger de Moura, C.; Jouenne, F.; Lebbe, C.; Menashi, S.; Mourah, S. CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker. Cancers 2019, 11, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111803
Landras A, Reger de Moura C, Jouenne F, Lebbe C, Menashi S, Mourah S. CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandras, Alexandra, Coralie Reger de Moura, Fanelie Jouenne, Celeste Lebbe, Suzanne Menashi, and Samia Mourah. 2019. "CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111803
APA StyleLandras, A., Reger de Moura, C., Jouenne, F., Lebbe, C., Menashi, S., & Mourah, S. (2019). CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker. Cancers, 11(11), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111803






