Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
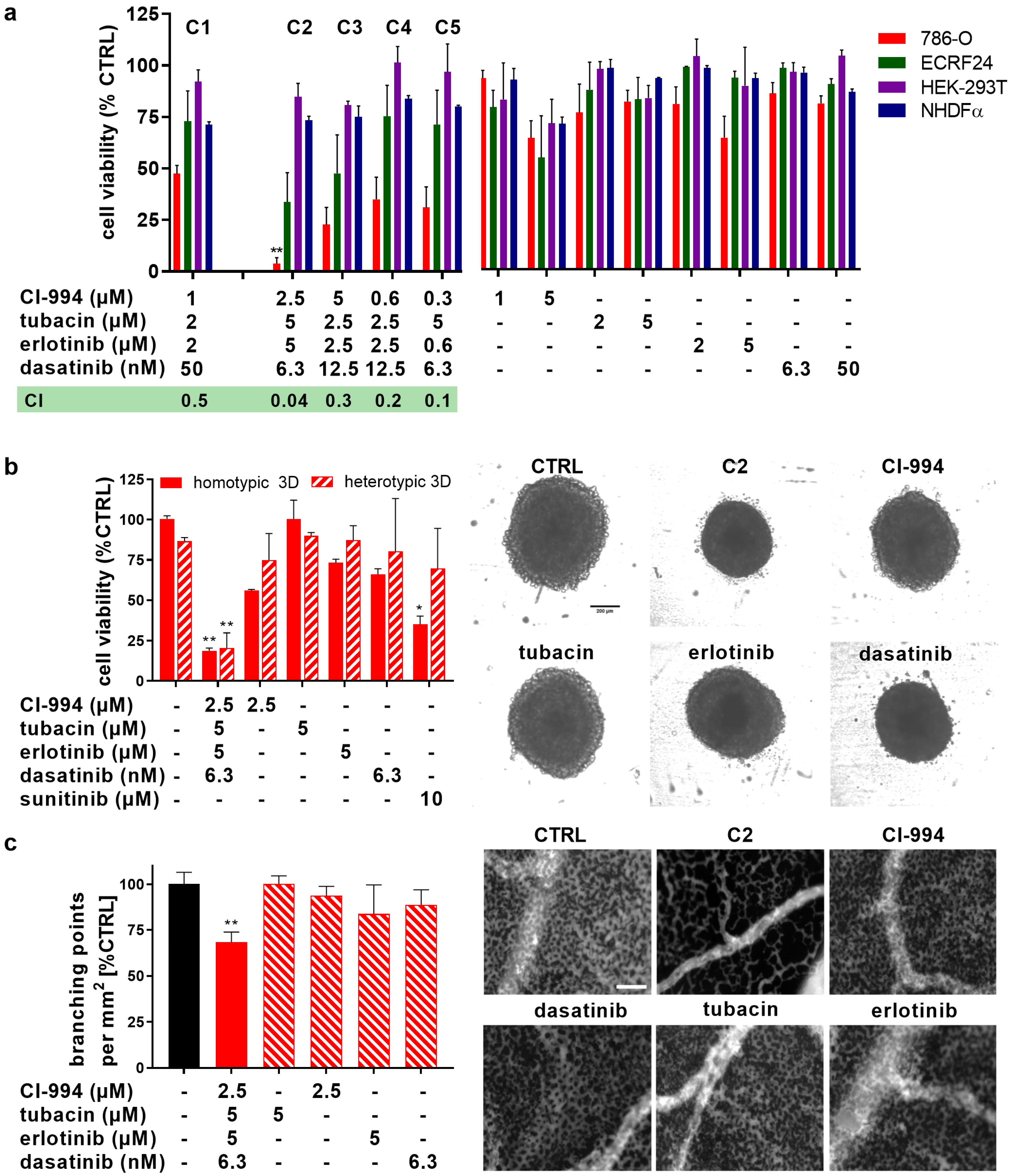
2.1. Therapeutically Guided Multidrug Optimization Screen Identifies Synergistic Low-Dose Drug Combinations Consisting of HDAC and Kinase Inhibitors
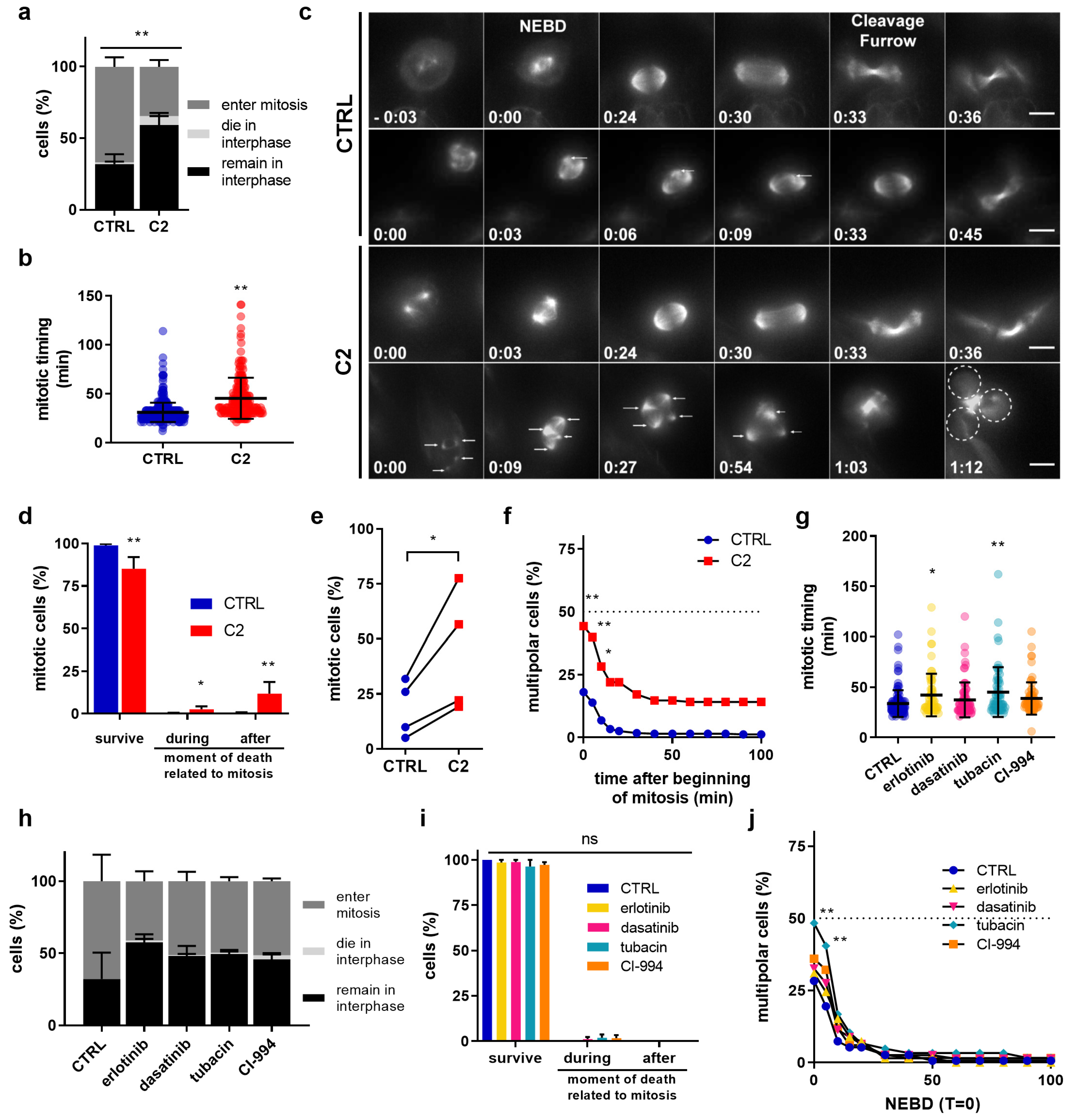
2.2. C2 Activity on Cell Cycle Regulation, Actin Cytoskeleton Reorganization, and Nuclear Structures
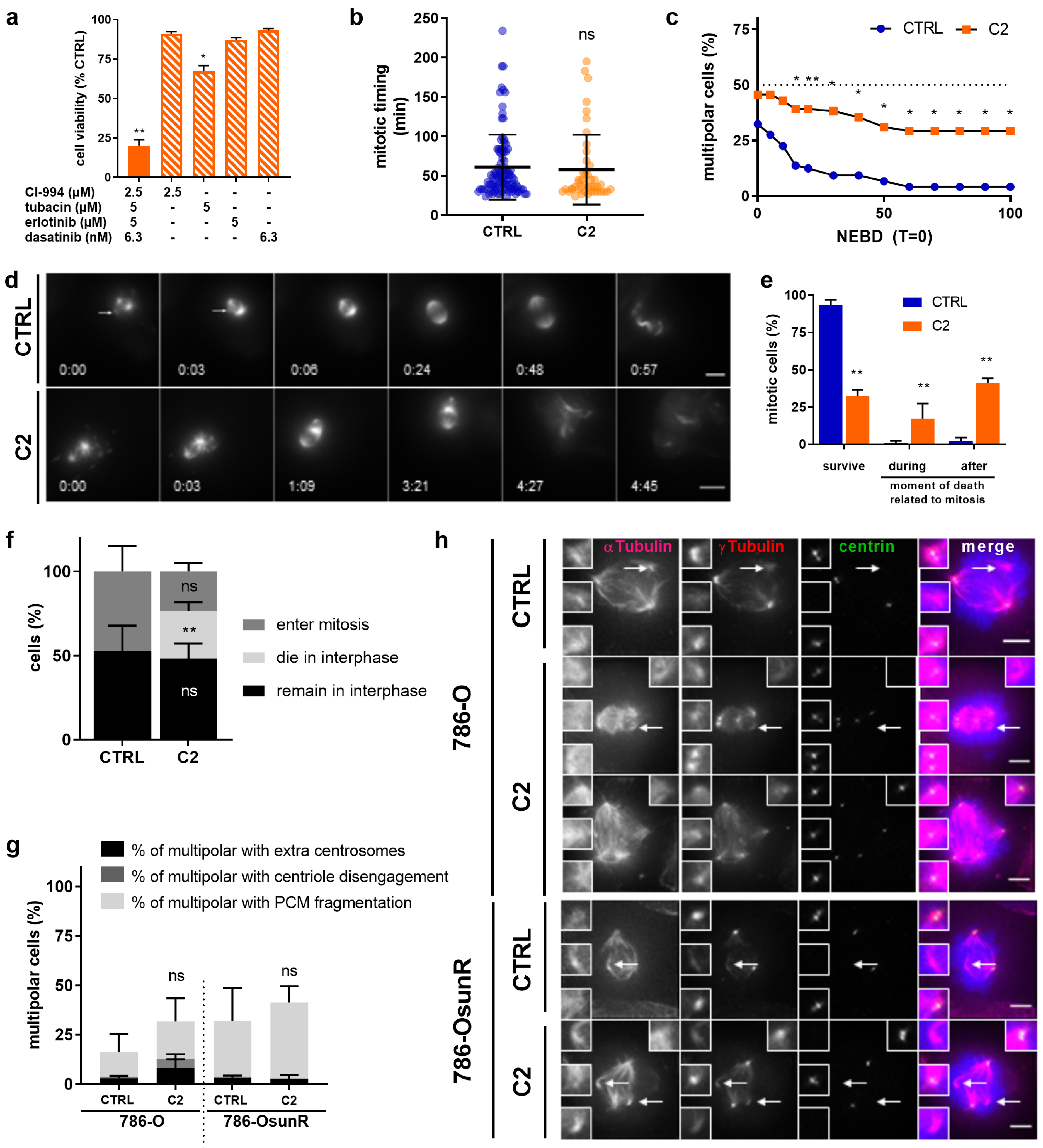
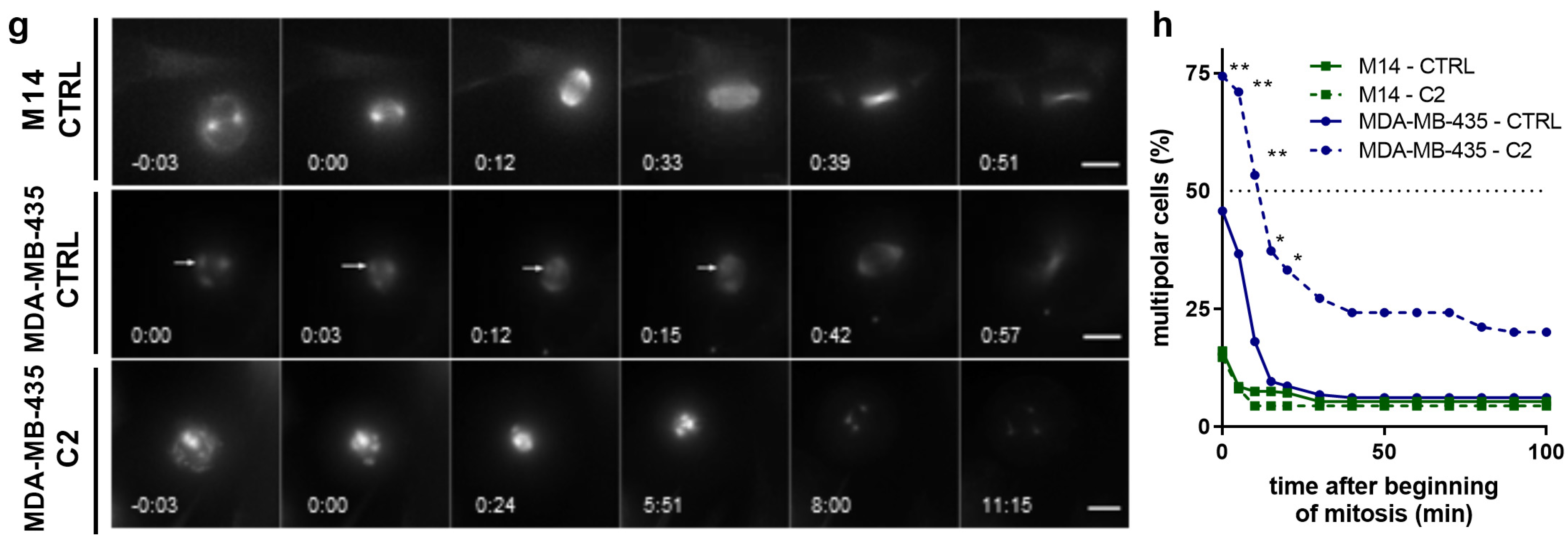
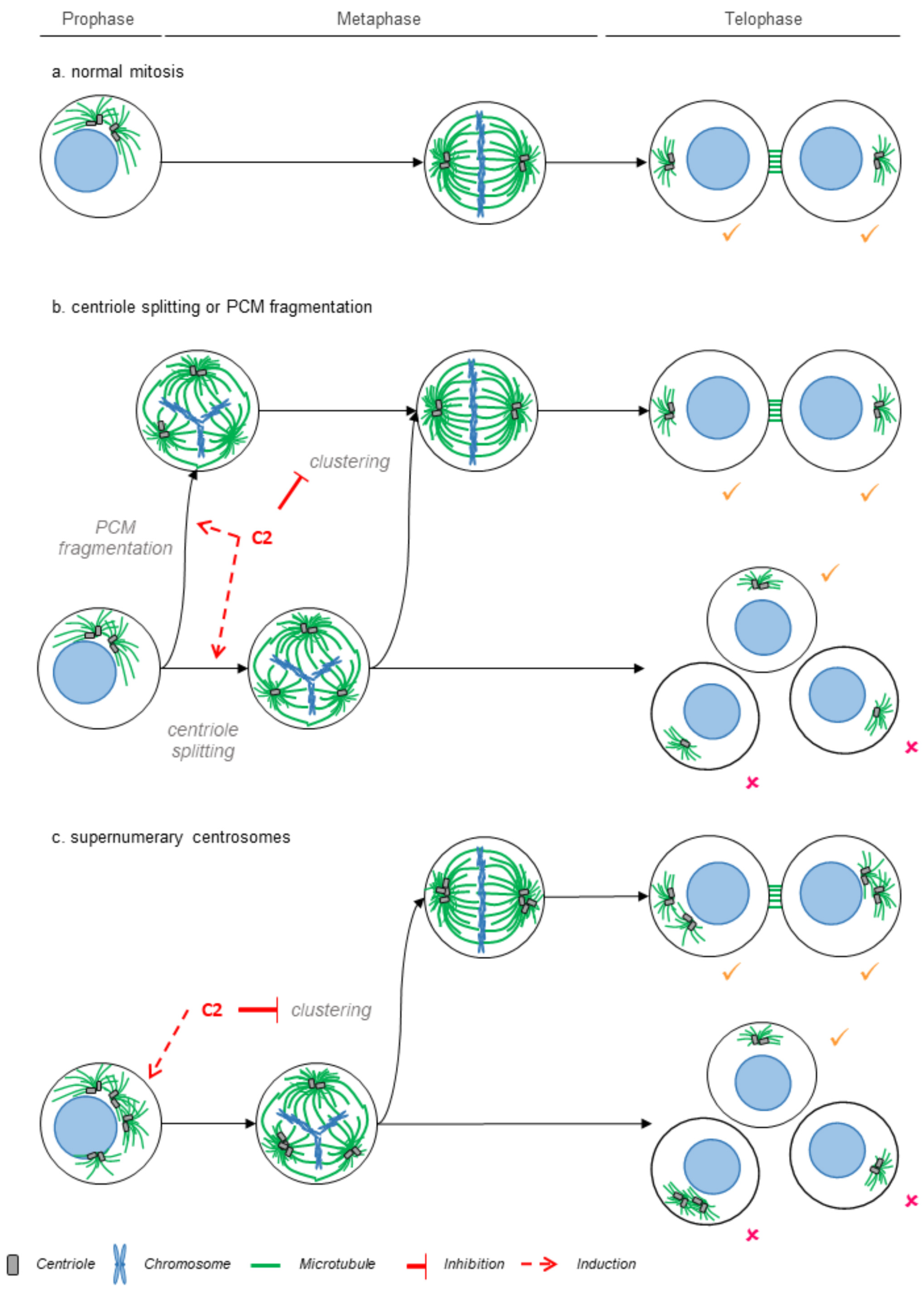
2.3. C2 Prevents the Clustering of Multipolar Spindles in 786-O Cells
2.4. C2 Activity Prevents Spindle Pole Clustering in Sunitinib-Resistant 786-O Cells
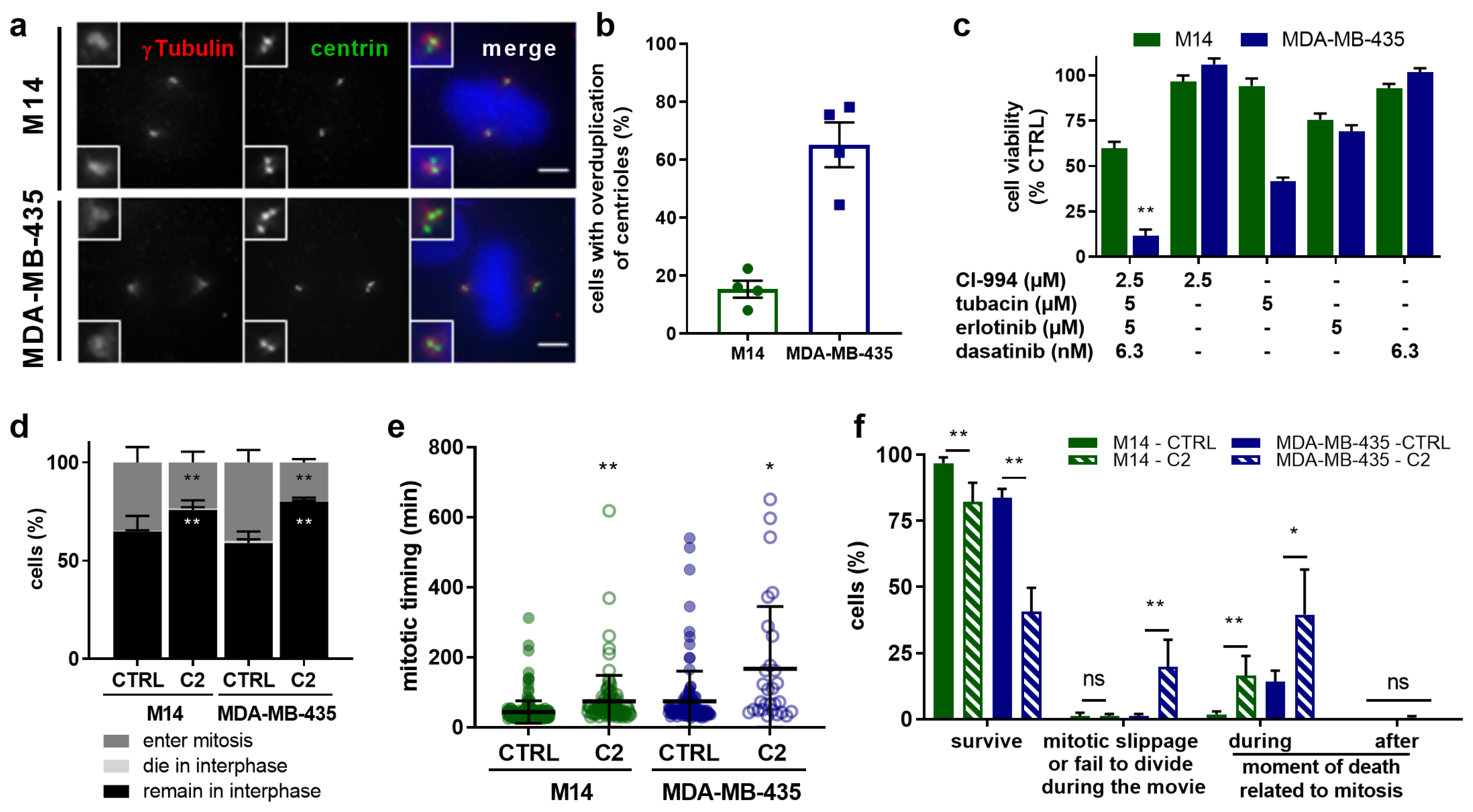
2.5. C2 Treatment Shows Greater Efficacy in the Cells with Abnormal Centrosome Numbers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Cells
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Data Modeling and Analysis for Combinatorial Drug Screening
4.5. Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures
4.6. Two-Dimensional Cell Migration Assay
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Mitosis Live Cell Imaging
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Allen, B.; Antal, T.; Chatterjee, K.; Shah, P.; Moon, Y.S.; Yaqubie, A.; Kelly, N.; Le, D.T.; et al. Evolutionary Dynamics of Cancer in Response to Targeted Combination Therapy. Elife 2013, 2, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehar, J.; Krueger, A.S.; Avery, W.; Heilbut, A.M.; Johansen, L.M.; Price, E.R.; Rickles, R.J.; Short, G.F., 3rd; Staunton, J.E.; Jin, X.; et al. Synergistic Drug Combinations Tend to Improve Therapeutically Relevant Selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, C.T.; Borisy, A.A.; Stockwell, B.R. Multicomponent Therapeutics for Networked Systems. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, H. A Robustness-Based Approach to Systems-Oriented Drug Design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehár, J.; Krueger, A.; Zimmermann, G.; Borisy, A. High-Order Combination Effects and Biological Robustness. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, J.R.; Patel, C.; McCabe, K.E.; Lu, D.; Davis, M.A.; Tancioni, I.; von Schalscha, T.; Bartakova, A.; Haft, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; et al. A Strategy to Combine Pathway-Targeted Low Toxicity Drugs in Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31104–31118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Nikanjam, M.; Kurzrock, R. Dosing de Novo Combinations of Two Targeted Drugs: Towards A Customized Precision Medicine Approach to Advanced Cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11310–11320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Berndsen, R.H.; Ding, X.; Ho, C.M.; Dyson, P.J.; van den Bergh, H.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. A Streamlined Search Technology for Identification of Synergistic Drug Combinations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Current Trends in Multidrug Optimization: An Alley of Future Successful Treatment of Complex Disorders. SLAS Technol. 2017, 22, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Weiss, A.; Ding, X.; Dyson, P.J.; van den Bergh, H.; Griffioen, A.W.; Ho, C.M. Optimization of Drug Combinations Using Feedback System Control. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, W.; Weiss, A.; Li, Y.; Wong, I.; Griffioen, A.W.; van den Bergh, H.; Xu, H.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Ho, C.M.; et al. Discovery of A Low Order Drug-Cell Response Surface for Applications in Personalized Medicine. Phys. Biol. 2014, 11, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Jaynes, J.; Ding, X. Combinig Two-Level and Three-Level Orthogonal Arrays for Factor Screening and Response Surface Exploration. Stat. Sin. 2014, 24, 269–289. [Google Scholar]
- Baldewijns, M.M.; van Vlodrop, I.J.; Schouten, L.J.; Soetekouw, P.M.; de Bruïne, A.P.; van Engeland, M. Genetics and Epigenetics of Renal Cell Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1785, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, A.I.; Zhou, J.; O’Brate, A.; Hamel, E.; Wong, J.; Nivens, M.; El-Naggar, A.; Yao, T.P.; Khuri, F.R.; Giannakakou, P. The Synergistic Combination of the Farnesyl Transferase Inhibitor Lonafarnib and Paclitaxel Enhances Tubulin Acetylation and Requires a Functional Tubulin Deacetylase. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3883–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBonte, M.J.; Wilson, P.M.; Fazzone, W.; Russell, J.; Louie, S.G.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Lenz, H.J.; Ladner, R.D. The Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitor Lapatinib Synergistically Enhances the Antitumor Activity of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Panobinostat in Colorectal Cancer Models. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3635–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, J.C.; Tsai, A.C.; Liou, J.P.; Pan, S.L.; Teng, C.M. The HDAC Inhibitor, MPT0E028, Enhances Erlotinib-Induced Cell Death in EGFR-TKI-Resistant NSCLC Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurn, K.T.; Thomas, S.; Moore, A.; Munster, P.N. Rational Therapeutic Combinations with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, R.H.; Abdul, U.K.; Weiss, A.; Zoetemelk, M.; Te Winkel, M.T.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Epigenetic Approach for Angiostatic Therapy: Promising Combinations for Cancer Treatment. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the chou-talalay method. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Alitalo, K.; Allen, E.; Anisimov, A.; Aplin, A.C.; Auerbach, R.; Augustin, H.G.; Bates, D.O.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Bender, R.H.F.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Angiogenesis Assays. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 425–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Segura, T.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. The Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane Model in Biology, Medicine and Bioengineering. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibowitz, M.L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Pellman, D. Chromothripsis: A New Mechanism for Rapid Karyotype Evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normand, G.; King, R.W. Understanding Cytokinesis Failure. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 676, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Hagan, I.M.; Glover, D.M. The Centrosome and its Duplication Cycle. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, 15800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, E.A. Centrosome Aberrations: Cause or Consequence of Cancer Progression? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, S.A.; Pellman, D. Causes and Consequences of Centrosome Abnormalities in Cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adar, Y.; Stark, M.; Bram, E.E.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; van den Bergh, H.; Szewczyk, G.; Sarna, T.; Skladanowski, A.; Griffioen, A.W.; Assaraf, Y.G. Imidazoacridinone-Dependent Lysosomal Photodestruction: A Pharmacological Trojan Horse Approach to Eradicate Multidrug-Resistant Cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, E.A.; Stearns, T. The Centrosome Cycle: Centriole Biogenesis, Duplication and Inherent Asymmetries. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyss, D.; Gergely, F. Centrosome Function in Cancer: Guilty or Innocent? Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteil, G.; Guerrero, A.; Vieira, A.F.; de Almeida, B.P.; Machado, P.; Mendonça, S.; Mesquita, M.; Villarreal, B.; Fonseca, I.; Francia, M.E.; et al. Over-Elongation of Centrioles in Cancer Promotes Centriole Amplification and Chromosome Missegregation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusz, S.M.; Tang, Y.Z.; Sarker, S.J.; Prevoo, W.; Kiyani, I.; Beltran, L.; Peters, J.; Sahdev, A.; Bex, A.; Powles, T.; et al. Heterogeneous Response and Progression Patterns Reveal Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Response in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashif, M.; Andersson, C.; Hassan, S.; Karlsson, H.; Senkowski, W.; Fryknäs, M.; Nygren, P.; Larsson, R.; Gustafsson, M.G. In Vitro Discovery of Promising Anti-Cancer Drug Combinations Using Iterative Maximisation of a Therapeutic Index. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Fan, L.X.; Zhou, X.; Sweeney, W.E., Jr.; Avner, E.D.; Li, X. HDAC6 Regulates Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Endocytic Trafficking and Degradation in Renal Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 49418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Roche, O.; Yan, M.S.; Finak, G.; Evans, A.J.; Metcalf, J.L.; Hast, B.E.; Hanna, S.C.; Wondergem, B.; Furge, K.A.; et al. Regulation of Endocytosis via the Oxygen-Sensing Pathway. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, A.M.; Lin, X.; Korytowsky, B.; Matczak, E.; Lechuga, M.J.; Wiltshire, R.; Motzer, R.J. Sunitinib Objective Response in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Analysis of 1059 Patients Treated on Clinical Trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, S.C.; Hamming, L.; Soetekouw, P.M.; Aarts, M.J.; Veeck, J.; van Engeland, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C. Resistance to Sunitinib in Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Molecular Mechanisms to Predictive Markers and Future Perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, T.; Ferretti, S.; Ebel, N.; Tam, A.; Ho, S.; Harbinski, F.; Farsidjani, A.; Zubrowski, M.; Sellers, W.R.; Schlegel, R.; et al. High Order Drug Combinations are Required to Effectively Kill Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6950–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraldi, P. Centrosomes in Spindle Organization and Chromosome Segregation: A Mechanistic View. Chromosome Res. 2016, 24, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Godinho, S.A.; Chandhok, N.S.; Ganem, N.J.; Azioune, A.; Thery, M.; Pellman, D. Mechanisms to Suppress Multipolar Divisions in Cancer Cells with Extra Centrosomes. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, P.L.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Barr, A.R.; Tátrai, P.; Taylor, C.; Papachristou, E.K.; Woods, C.G.; Chavali, S.; Gergely, F. A CEP215–HSET Complex Links Centrosomes with Spindle Poles and Drives Centrosome Clustering in Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleylein-Sohn, J.; Pöllinger, B.; Ohmer, M.; Hofmann, F.; Nigg, E.A.; Hemmings, B.A.; Wartmann, M. Acentrosomal Spindle Organization Renders Cancer Cells Dependent on the Kinesin HSET. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5391–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Mikule, K.; Wang, W.; Su, N.; Petteruti, P.; Gharahdaghi, F.; Code, E.; Zhu, X.; Jacques, K.; Lai, Z.; et al. Discovery and Mechanistic Study of A Small Molecule Inhibitor for Motor Protein KIFC1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhai, L.; Wang, Y.; Boohaker, R.J.; Lu, W.; Gupta, V.V.; Padmalayam, I.; Bostwick, R.J.; White, E.L.; Ross, L.J.; et al. Discovery of A Novel Inhibitor of Kinesin-Like Protein KIFC1. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, C.A.; Richards, F.M.; Bender, A.; Bond, P.J.; Korb, O.; Kern, O.; Riddick, M.; Owen, P.; Myers, R.M.; Raff, J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of An Allosteric Inhibitor of HSET that Targets Cancer Cells with Supernumerary Centrosomes. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganem, N.J.; Godinho, S.A.; Pellman, D. A Mechanism Linking Extra Centrosomes to Chromosomal Instability. Nature 2009, 460, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silkworth, W.T.; Nardi, I.K.; Scholl, L.M.; Cimini, D. Multipolar Spindle Pole Coalescence is A Major Source of Kinetochore Mis-Attachment and Chromosome Mis-Segregation in Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sercin, O.; Larsimont, J.C.; Karambelas, A.E.; Marthiens, V.; Moers, V.; Boeckx, B.; Le Mercier, M.; Lambrechts, D.; Basto, R.; Blanpain, C. Transient PLK4 Overexpression Accelerates Tumorigenesis in p53-Deficient Epidermis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.S.; Bakker, B.; Boeckx, B.; Moyett, J.; Lu, J.; Vitre, B.; Spierings, D.C.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Cleveland, D.W.; Lambrechts, D.; et al. Centrosome Amplification Is Sufficient to Promote Spontaneous Tumorigenesis in Mammals. Dev. cell 2017, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasadil, L.M.; Andersen, K.A.; Yeum, D.; Rocque, G.B.; Wilke, L.G.; Tevaarwerk, A.J.; Raines, R.T.; Burkard, M.E.; Weaver, B.A. Cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel in Breast Cancer is Due to Chromosome Missegregation on Multipolar Spindles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 229ra43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crasta, K.; Ganem, N.J.; Dagher, R.; Lantermann, A.B.; Ivanova, E.V.; Pan, Y.; Nezi, L.; Protopopov, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Pellman, D. DNA Breaks and Chromosome Pulverization from Errors in Mitosis. Nature 2012, 482, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, V.; Rida, P.C.; Celik, B.; Turaga, R.C.; Ogden, A.; Cantuaria, G.; Gopalakrishnan, J.; Aneja, R. Centrosome-Declustering Drugs Mediate A Two-Pronged Attack on Interphase and Mitosis in Supercentrosomal Cancer Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J. Deacetylation of Alpha-Tubulin and Cortactin is Required for HDAC6 to Trigger Ciliary Disassembly. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, E.P.; Di Filippo, M.; Galbiati, F. Failure to Reabsorb the Primary Cilium Induces Cellular Senescence. FASEB J. 2018, 33, 4866–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontijn, R.; Hop, C.; Brinkman, H.J.; Slater, R.; Westerveld, A.; van Mourik, J.A.; Pannekoek, H. Maintenance of Vascular Endothelial Cell-Specific Properties after Immortalization with An Amphotrophic Replication-Deficient Retrovirus Containing Human Papilloma Virus 16 E6/E7 DNA. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 216, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndsen, R.H.; Swier, N.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Colorectal Carcinoma Growth Retardation through Induction of Apoptosis, Using An Optimized Synergistic Cocktail of Axitinib, Erlotinib and Dasatinib. Cancers 2019. under revisions. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, K.; Nishida, S.; Sontag, E.D.; Cluzel, P. Mechanism-Independent Method for Predicting Response to Multidrug Combinations in Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12254–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; van Berkel, M.; Wong, T.J.; Griffioen, A.W. A Genomic Screen for Angiosuppressor Genes in the Tumor Endothelium Identifies A Multifaceted Angiostatic Role for Bromodomain Containing 7 (BRD7). Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; van den Boezem, E.; Hautvast, P.; Buurman, W.A.; Griffioen, A.W. Tumor Angiogenesis is Enforced by Autocrine Regulation of High-Mobility Group Box 1. Oncogene 2013, 17, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
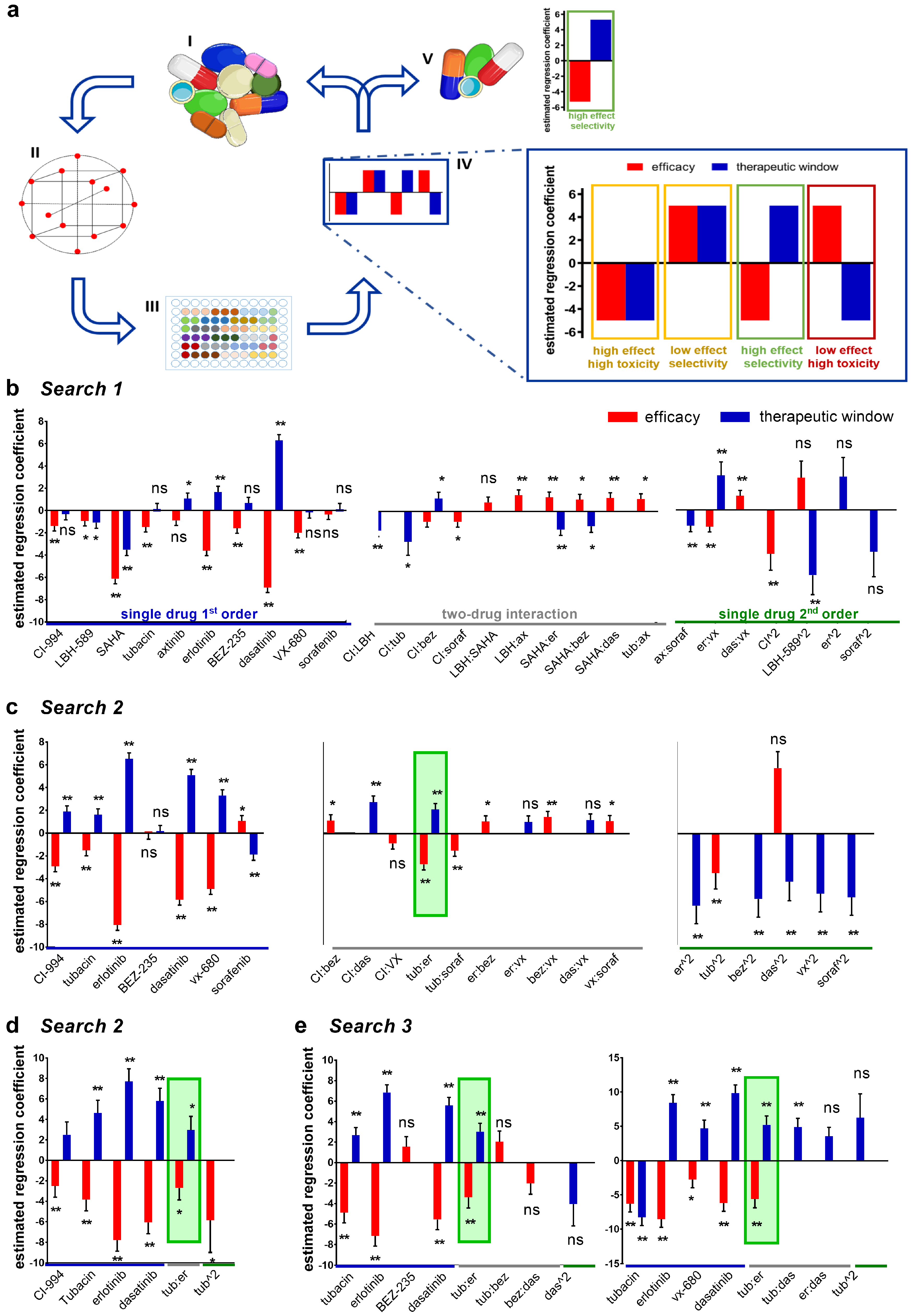
| Drug | 786-O | Target | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ED50 (μM) | ED20 (μM) | ||
| CI-994 | 11.5 | 1 | Class I HDACs |
| LBH-589 | 0.01 | 0.002 | Class I and II HDACs |
| SAHA | 3.7 | 1 | Class I and II HDACs |
| tubacin | 6 | 2 | HDAC6 |
| axitinib | 11.5 | 0.2 | VEGFRs, PDGFR |
| erlotinib | 6.6 | 2 | EGFR |
| BEZ-235 | 0.09 | 0.02 | mTOR |
| dasatinib | 0.1 | 0.05 | SRC |
| VX-680 | 33 | 0.65 | pan-Aurora Kinases |
| sorafenib | 2.1 | 0.01 | VEGFRs, PDGFR |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiss, A.; Le Roux-Bourdieu, M.; Zoetemelk, M.; Ramzy, G.M.; Rausch, M.; Harry, D.; Miljkovic-Licina, M.; Falamaki, K.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Meraldi, P.; et al. Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering. Cancers 2019, 11, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101612
Weiss A, Le Roux-Bourdieu M, Zoetemelk M, Ramzy GM, Rausch M, Harry D, Miljkovic-Licina M, Falamaki K, Wehrle-Haller B, Meraldi P, et al. Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101612
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiss, Andrea, Morgan Le Roux-Bourdieu, Marloes Zoetemelk, George M. Ramzy, Magdalena Rausch, Daniela Harry, Marijana Miljkovic-Licina, Katayoun Falamaki, Bernard Wehrle-Haller, Patrick Meraldi, and et al. 2019. "Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101612
APA StyleWeiss, A., Le Roux-Bourdieu, M., Zoetemelk, M., Ramzy, G. M., Rausch, M., Harry, D., Miljkovic-Licina, M., Falamaki, K., Wehrle-Haller, B., Meraldi, P., & Nowak-Sliwinska, P. (2019). Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering. Cancers, 11(10), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101612






