Current Concepts of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
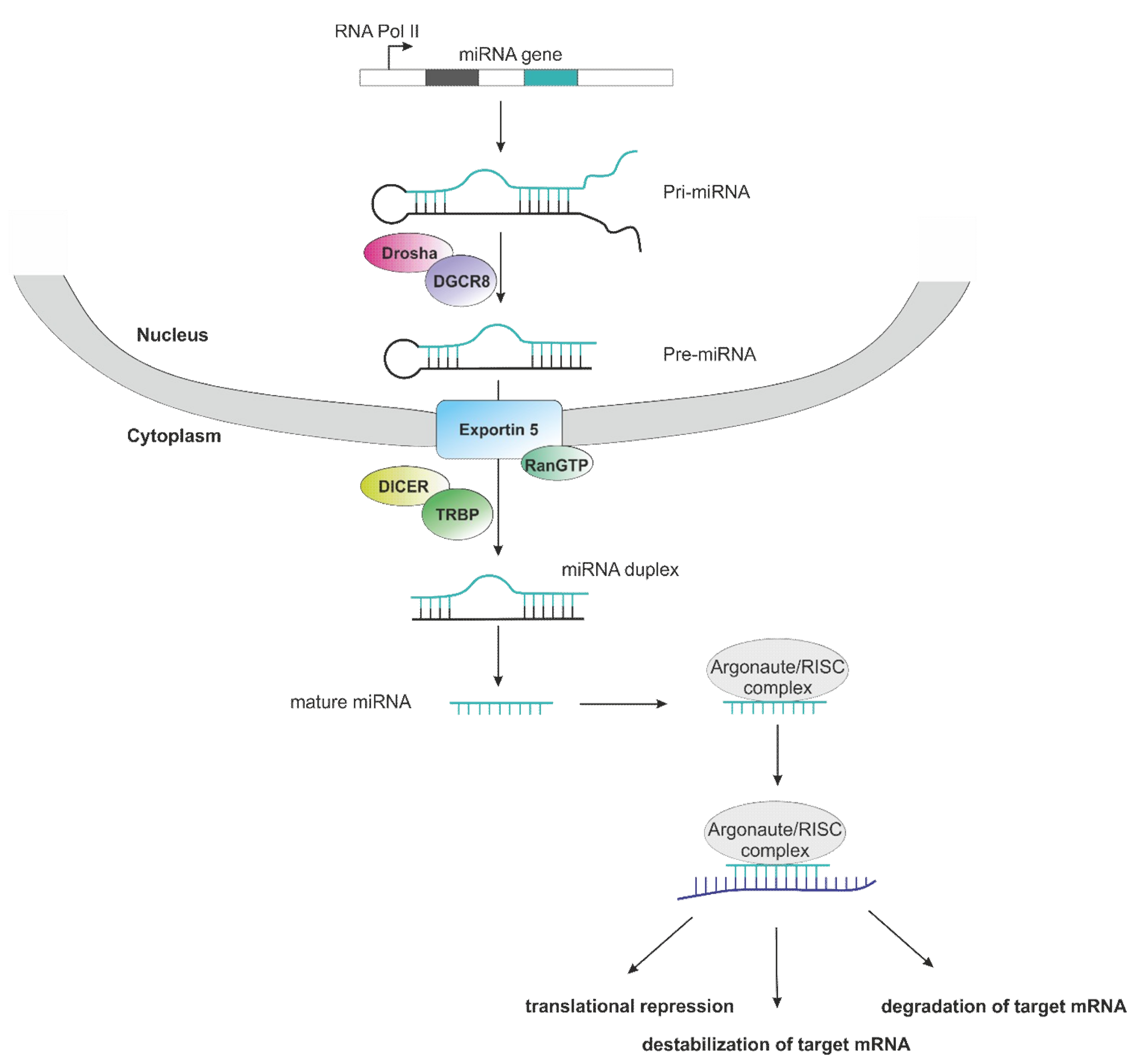
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Role of microRNAs in Non-Clear Cell RCC
3.1.1. Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Diagnostic Potential of miRNAs in pRCC
Prognostic Potential of miRNAs in pRCC
3.1.2. Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
Diagnostic Potential of miRNAs in chRCC
Prognostic Potential of miRNAs in chRCC
3.1.3. Tubulocystic Renal Cell Carcinoma
miRNA Expression in tcRCC
3.1.4. Clear-cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
miRNA Expression in ccpRCC
3.1.5. Xp11 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma
miRNA Expression in Xp11 RCC
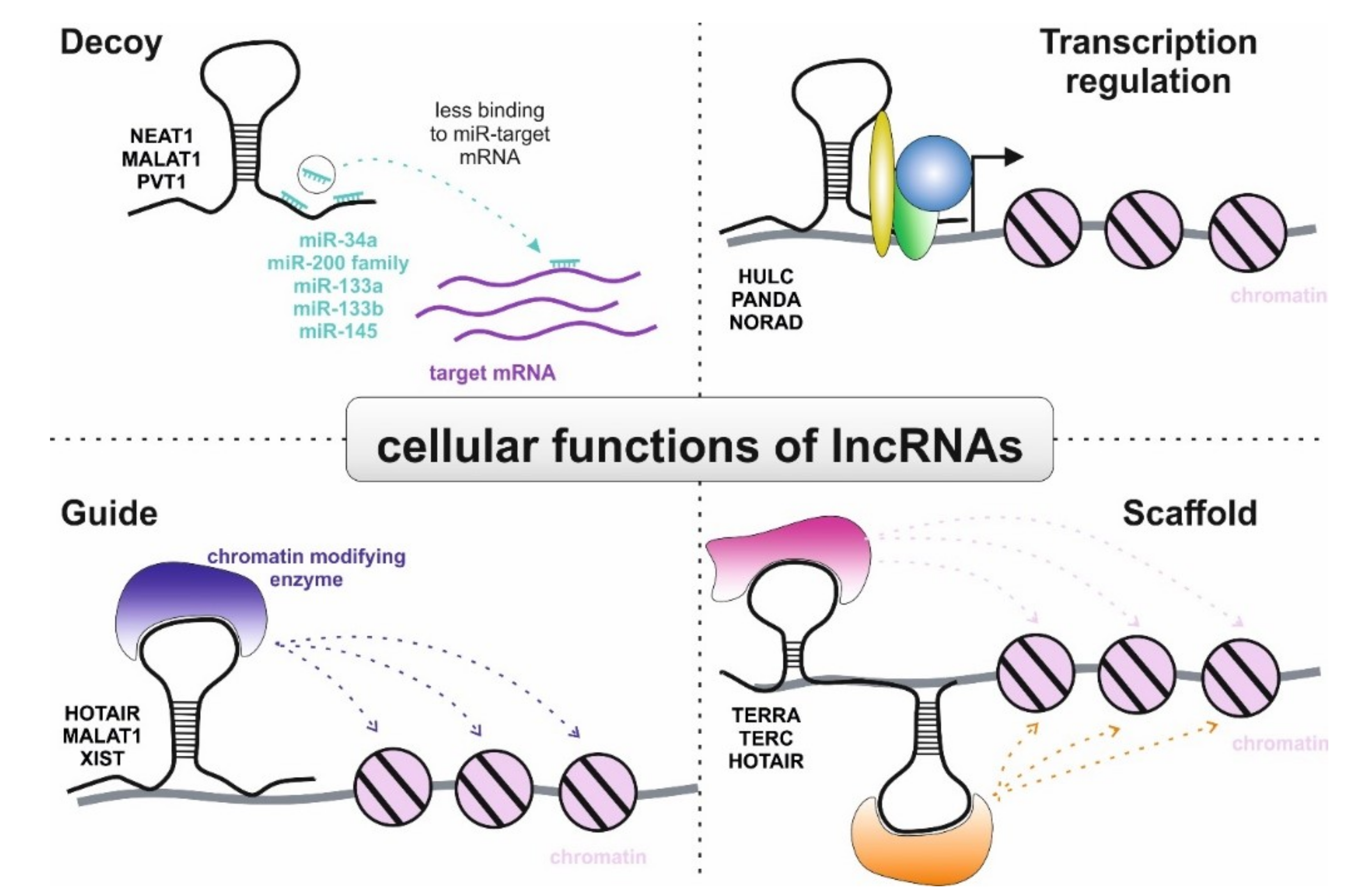
3.2. Role of lncRNAs in Non-Clear Cell RCC
3.2.1. Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
3.2.2. Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, M.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znaor, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Laversanne, M.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. International Variations and Trends in Renal Cell Carcinoma Incidence and Mortality. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Jesche, J.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. Renal cell carcinoma stage migration in a single European centre over 25 years: Effects on 5- and 10-year metastasis-free survival. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2012, 44, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Campbell, S.C.; Escudier, B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 2009, 373, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Stojakovic, T.; Mannweiler, S.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. High plasma fibrinogen level represents an independent negative prognostic factor regarding cancer-specific, metastasis-free, as well as overall survival in a European cohort of non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Stoeckigt, C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Stojakovic, T.; Golbeck, S.; Eberhard, K.; Gerger, A.; Mannweiler, S.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. Validation of the pre-treatment neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in a large European cohort of renal cell carcinoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Pummer, K.; Mannweiler, S.; Zigeuner, R. Presence and extent of histological tumour necrosis is an adverse prognostic factor in papillary type 1 but not in papillary type 2 renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2013, 62, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Jesche, J.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Rehak, P.; Pummer, K.; Pichler, M.; Zigeuner, R. Histologic Tumor Necrosis Is an Independent Prognostic Indicator for Clear Cell and Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Jesche, J.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. Predictive ability of the 2002 and 2010 versions of the Tumour-Node-Metastasis classification system regarding metastasis-free, cancer-specific and overall survival in a European renal cell carcinoma single-centre series. BJU Int. 2013, 111, E191–E195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Jesche, J.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. Prognostic Value of the Leibovich Prognosis Score Supplemented by Vascular Invasion for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Chromecki, T.F.; Jesche, J.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Rehak, P.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. External Validation of the Leibovich Prognosis Score for Nonmetastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma at a Single European Center Applying Routine Pathology. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieder, A.; Guenzel, T.; Lebentrau, S.; Schneider, C.; Franzen, A. Diagnostic relevance of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the head and neck: An evaluation of 22 cases in 671 patients. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.C.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; MacKenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.-H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Albiges, L.; Staehler, M.; Bensalah, K.; Dabestani, S.; Giles, R.H. Updated European Association of Urology Guidelines Recommendations for the Treatment of First-line Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 73, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, D.; Grunwald, V.; Escudier, B.; Hammers, H.J.; George, S.; Nathan, P. Patient-reported outcomes of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib (CheckMate 214): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 116–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, J.; Stärk, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Boil. 2005, 3, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Winter, E.; Ress, A.L.; Bauernhofer, T.; Gerger, A.; Kiesslich, T. miR-181a is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer treated with EGFR inhibitor. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strubberg, A.M.; Madison, B.B. MicroRNAs in the etiology of colorectal cancer: Pathways and clinical implications. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Ivan, C.; Ling, H.; Winter, E. Genome-Wide miRNA Analysis Identifies miR-188-3p as a Novel Prognostic Marker and Molecular Factor Involved in Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckmann, K.-P.; Radtke, A.; Geczi, L.; Matthies, C.; Anheuser, P.; Eckardt, U.; Sommer, J.; Zengerling, F.; Trenti, E.; Pichler, R.; et al. Serum Levels of MicroRNA-371a-3p (M371 Test) as a New Biomarker of Testicular Germ Cell Tumors: Results of a Prospective Multicentric Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbuch, A.; Adiprasito, J.B.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Seles, M.; Klec, C.; Pichler, G.P.; Resel, M.; Posch, F.; Lembeck, A.L.; Stöger, H.; et al. MiR-371a-3p Serum Levels Are Increased in Recurrence of Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troppan, K.; Wenzl, K.; Pichler, M.; Pursche, B.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; Feichtinger, J.; Thallinger, G.G.; Beham-Schmid, C.; Neumeister, P.; Deutsch, A. miR-199a and miR-497 Are Associated with Better Overall Survival due to Increased Chemosensitivity in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18077–18095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbacher, D.; Klec, C.; Pasculli, B.; Cerk, S.; Rinner, B.; Karbiener, M.; Ivan, C.; Barbano, R.; Ling, H.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; et al. MiR-1287-5p inhibits triple negative breast cancer growth by interaction with phosphoinositide 3-kinase CB, thereby sensitizing cells for PI3Kinase inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, Q. Identification of microRNAs associated with glioma diagnosis and prognosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26394–26403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Che, S.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q. miR-155 contributes to the progression of glioma by enhancing Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 5323–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Pang, B.; Xin, T.; Guo, H.; Xing, Y.; Xu, S.; Feng, B.; Liu, B.; Pang, Q. Plasma miR-221/222 Family as Novel Descriptive and Prognostic Biomarkers for Glioma. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, K.; Koch, K.; Zandl, M.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Guertl, B.; Pichler, M.; Leuschner, I.; Hoefler, G. Nephroblastomas Show Low Expression of MicroR-204 and High Expression of its Target, the Oncogenic Transcription Factor MEIS1. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2014, 17, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonemori, K.; Kurahara, H.; Maemura, K.; Natsugoe, S. MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebisch, A.; Hatzl, S.; Pichler, M.; Wölfler, A.; Sill, H. Therapeutic Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Role of Non-Coding RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzl, S.; Geiger, O.; Kuepper, M.K.; Caraffini, V.; Seime, T.; Furlan, T.; Nussbaumer, E.; Wieser, R.; Pichler, M.; Scheideler, M.; et al. Increased Expression of miR-23a Mediates a Loss of Expression in the RAF Kinase Inhibitor Protein RKIP. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3644–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cancer Hallmarks and MicroRNAs: The Therapeutic Connection. Adv. Cancer. Res. 2017, 135, 119–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Boil. 2013, 10, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A. Cellular localization of long non-coding RNAs affects silencing by RNAi more than by antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martianov, I.; Ramadass, A.; Barros, A.S.; Chow, N.; Akoulitchev, A. Repression of the human dihydrofolate reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript. Nature 2007, 445, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.T. Lessons from X-chromosome inactivation: Long ncRNA as guides and tethers to the epigenome. Genome Res. 2009, 23, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoutsos, I.; Kil Lee, S.; Nam, S.Y.; Anfossi, S.; Pasculli, B.; Pichler, M.; Jing, Y.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Telonis, A.G.; Rossi, S.; et al. N-BLR, a primate-specific non-coding transcript leads to colorectal cancer invasion and migration. Genome Boil. 2017, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, M.; Ling, H.; Ivan, C.; Pichler, M.; Matsushita, D.; Goblirsch, M.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Shigeyasu, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; et al. H19 Noncoding RNA, an Independent Prognostic Factor, Regulates Essential Rb-E2F and CDK8-beta-Catenin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. EBioMedicine 2016, 13, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storkel, S.; Berg, E.V.D. Morphological classification of renal cancer. World J. Urol. 1995, 13, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, G.C.; Pichler, M.; Chromecki, T.F.; Strini, K.A.; Klatte, T.; Pummer, K.; Remzi, M.; Mannweiler, S.; Zigeuner, R. Tumour-associated macrophages might represent a favourable prognostic indicator in patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2013, 63, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B.; Eble, J.N. Papillary renal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 105 tumors. Mod. Pathol. 1997, 10, 537. [Google Scholar]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Linehan, W.M.; Spellman, P.T.; Ricketts, C.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Fei, S.S.; Davis, C.; Wheeler, D.A.; Murray, B.A.; Schmidt, L.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Papillary Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Steffens, S.; Janssen, M.; Roos, F.C.; Becker, F.; Schumacher, S.; Seidel, C.; Wegener, G.; Thüroff, J.W.; Hofmann, R.; Stöckle, M.; et al. Incidence and long-term prognosis of papillary compared to clear cell renal cell carcinoma – A multicentre study. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2347–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignot, G.; Elie, C.; Conquy, S.; Vieillefond, A.; Flam, T.; Zerbib, M.; Debre, B.; Amsellem-Ouazana, D. Survival Analysis of 130 Patients with Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: Prognostic Utility of Type 1 and Type 2 Subclassification. Urology 2007, 69, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faragalla, H.; Youssef, Y.M.; Scorilas, A.; Khalil, B.; White, N.M.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Khella, H.; Jewett, M.A.; Evans, A.; Lichner, Z.; et al. The Clinical Utility of miR-21 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker for Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Santos, R.M.; Costa-Pinheiro, P.; Luis, A.; Antunes, L.; Lobo, F.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jeronimo, C. MicroRNA profile: A promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour diagnosis. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2646–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.M.; Fatoohi, E.; Metias, M.; Jung, K.; Stephan, C.; Yousef, G.M. Metastamirs: A stepping stone towards improved cancer management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, M.P.; Alvarez, K.; Kim, H.-J.; Monzon, F.A. Molecular Classification of Adult Renal Epithelial Neoplasms Using MicroRNA Expression and Virtual Karyotyping. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 20, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, A.; Saleeb, R.; Wala, S.J.; Khella, H.W.; Ding, Q.; Zhai, H.; Krishan, K.; Krizova, A.; Gabril, M.; Evans, A.; et al. A miRNA-based classification of renal cell carcinoma subtypes by PCR and in situ hybridization. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Peng, X.-C.; Zheng, X.-L.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.-W. MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, L. miR-126 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation by targeting EGFL7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wu, J.; Deng, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Liang, W.-Y.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Yu, Q.-H.; Li, J. MicroRNA-126 affects rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PIK3R2 and regulating PI3K-AKT signal pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74217–74226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wach, S.; Nolte, E.; Theil, A.; Stöhr, C.; Rau, T.T.; Hartmann, A.; Ekici, A.; Keck, B.; Taubert, H.; Wullich, B. MicroRNA profiles classify papillary renal cell carcinoma subtypes. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelloni, A.; Ramazzotti, G.; Poli, A.; Piazzi, M.; Focaccia, E.; Blalock, W.; Faenza, I. MiRNA-210: A Current Overview. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6511–6521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Park, M.-S.; Maeng, L.-S.; Yoon, C.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Hwang, K.-C.; Chung, Y.-A. Survival of hypoxic human mesenchymal stem cells is enhanced by a positive feedback loop involving miR-210 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Veter Sci. 2013, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.S.; Michael, M.Z.; Rawlings, L.H.; Van Der Hoek, M.B.; Gleadle, J.M. The VHL-dependent regulation of microRNAs in renal cancer. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, D.; Alexe, G.; Antes, T.; Liu, H.; Madabhushi, A.; DeLisi, C.; Ganesan, S.; Bhanot, G.; Liou, L.S. Identification of a MicroRNA Panel for Clear-cell Kidney Cancer. Urology 2010, 75, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, A.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Circulating miR-210 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrozza, V.; Pastore, A.L.; Palleschi, G.; Tito, C.; Porta, N.; Ricci, S.; Marigliano, C.; Costantini, M.; Simone, G.; Di Carlo, A.; et al. Secreted miR-210-3p as non-invasive biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69551–69558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furge, K.A.; Chen, J.; Koeman, J.; Swiatek, P.; Dykema, K.; Lucin, K.; Kahnoski, R.; Yang, X.J.; Teh, B.T. Detection of DNA Copy Number Changes and Oncogenic Signaling Abnormalities from Gene Expression Data Reveals MYC Activation in High-Grade Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3171–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellut, J.; Bertz, S.; Nolte, E.; Stöhr, C.; Polifka, I.; Lieb, V.; Herrmann, E.; Jung, R.; Hartmann, A.; Wullich, B.; et al. Differential prognostic value of MYC immunohistochemistry in subtypes of papillary renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, C. MiR-155 Promotes Uveal Melanoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Regulating NDFIP1 Expression. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.-C.; Qiu, H.-Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M.-B.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y. PTEN in kidney cancer: A review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wen, H.; Jing, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Nan, K.; Yao, Y.; Tian, T. MicroRNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, W.; Lin, T.-X.; Zhong, G.-Z.; Liao, B.; Wang, B.; Gu, P.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Lu, F.-D.; et al. MicroRNA-155 promotes bladder cancer growth by repressing the tumor suppressor DMTF1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16043–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Mao, X.; Shi, P.; He, B.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; et al. MicroRNAs in the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova-Salas, I.; Rubio-Briones, J.; Calatrava, A.; Mancarella, C.; Masiá, E.; Casanova, J.; Fernandez-Serra, A.; Rubio, L.; Ramírez-Backhaus, M.; Armiñán, A.; et al. Identification of miR-187 and miR-182 as Biomarkers of Early Diagnosis and Prognosis in Patients with Prostate Cancer Treated with Radical Prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Radova, L.; Sachlova, M.; Kosarova, Z.; Slaba, K.; Fabian, P.; Grolich, T.; Prochazka, V.; Kala, Z.; Svoboda, M.; et al. Serum-based microRNA signatures in early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekari, N.; Baradaran, B.; Shanehbandi, D.; Kazemi, T. Circulating MicroRNAs: Valuable Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.Z.; Xu, L.W.; Xu, Z.; Wu, R.; Xin, H.; Zhu, M.; Lu, T.Z.; Genf, L.-G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, C.-C.; et al. Expression Profiles and Clinical Significance of MicroRNAs in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, H.-T.; Wang, X.-X. hsa-mir-3199-2 and hsa-mir-1293 as Novel Prognostic Biomarkers of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma by COX Ratio Risk Regression Model Screening. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 3488–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yuan, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Song, P.; Li, F.; Xu, C.; Zhao, X. An integrated analysis for long noncoding RNAs and microRNAs with the mediated competing endogenous RNA network in papillary renal cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4037–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-Z.; Xin, H.; Lu, T.-Z.; Xu, Z.; Yu, P.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Li, M.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, B.; Xu, X.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes and prognosis in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fillmore, R.; Xi, Y. MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 344, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Hussein, M.H.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.M.; Shaalan, A.A.M. MicroRNA-34a: A Key Regulator in the Hallmarks of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Luo, A.; CHhen, H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Song, Z.; Yan, D.; Kong, X. Expression Profiles of microRNAs in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines Using microRNA Sequencing. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, A.; Brunson, A.; Brown, M.; Pan, C.-X.; Lara, P.N. Evolving Epidemiologic Trends in Nonclear Cell Renal Cell Cancer: An Analysis of the California Cancer Registry. Urology 2013, 82, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, T.; Han, K.-R.; Said, J.W.; Böhm, M.; Allhoff, E.P.; Kabbinavar, F.F.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Pantuck, A.J. Pathobiology and prognosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2008, 26, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, N.A.; Tamboli, P. Oncocytic renal neoplasms: Diagnostic considerations. Clin. Lab. Med. 2005, 25, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petillo Kort, E.J.; Anema, J.; Petillo, D.; Furge, K.A.; Yang, X.J.; Teh, B.T. MicroRNA profiling of human kidney cancer subtypes. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, Y.M.; White, N.M.; Grigull, J.; Krizova, A.; Samy, C.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Evans, A.; Yousef, G.M. Accurate Molecular Classification of Kidney Cancer Subtypes Using MicroRNA Signature. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, E.; Dotan, Z.; Barshack, I.; Ben David, M.; Dov, A.; Tabak, S.; Zion, O.; Benjamin, S.; Benjamin, H.; Kuker, H.; et al. Accurate Molecular Classification of Renal Tumors Using MicroRNA Expression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, C.; Matsuura, K.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Tanigawa, M.; Yoshimoto, T.; Narimatsu, T.; Nguyen, L.; Hijiya, N.; Uchida, T.; Sato, F.; et al. Genome-wide microRNA expression profiling in renal cell carcinoma: Significant down-regulation of miR-141 and miR-200c. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, M.; Hazama, S.; Tsunedomi, R.; Tanaka, H.; Takenouchi, H.; Kanekiyo, S.; Tokumitsu, Y.; Tomochika, S.; Tokuhisa, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; et al. Overexpression of miR-221 and miR-222 in the cancer stroma is associated with malignant potential in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Deng, T.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Bai, M.; et al. miR-221 and miR-222 synergistically regulate hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 to promote cell proliferation and migration in gastric cancer. Tumor Boil. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Fan, S.; Yu, X.; et al. miR-221/222 enhance the tumorigenicity of human breast cancer stem cells via modulation of PTEN/Akt pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 79, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Kojima, S.; Nishikawa, R.; Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Enokida, H.; Matsushita, R.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. MicroRNA expression signature of castration-resistant prostate cancer: The microRNA-221/222 cluster functions as a tumour suppressor and disease progression marker. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.-J.; Dong, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Di, W.-Y.; Jiao, L.-Y.; Gao, Q.-Z.; Zhang, C.-G. miRNA-221 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting TIMP2 in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5224–5229. [Google Scholar]
- Khella, H.W.Z.; Butz, H.; Ding, Q.; Rotondo, F.; Evans, K.R.; Kupchak, P.; Dharsee, M.; Latif, A.; Pasic, M.D.; Lianidou, E.; et al. miR-221/222 Are Involved in Response to Sunitinib Treatment in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gu, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Da, J. miR-203 inhibition of renal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting of FGF2. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Itesako, T.; Tatarano, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Fuse, M.; Kojima, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Seki, N. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition-related microRNA-200s regulate molecular targets and pathways in renal cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaan, S.; Khella, H.W.; Girgis, A.; Scorilas, A.; Lianidou, E.; Gabril, M.; Krylov, S.N.; Jewett, M.; Bjarnason, G.A.; El-Said, H.; et al. miR-210 Is a Prognostic Marker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Yadav, S.S.; Tomar, V.; Yadav, S.; Talreja, S. Tubulocystic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Great Imitator. Rev. Urol. 2016, 18, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; MacLennan, G.T.; Gupta, R.; Grignon, D.; Paraf, F.; Vieillefond, A.; Paner, G.; Stovsky, M.; MBA, F.; Young, A.N.; et al. Tubulocystic carcinoma of the kidney: Clinicopathologic analysis of 31 cases of a distinctive rare subtype of renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, J.S.; Bindroo, S.; Varshney, N.; Mittal, V. Tubulocystic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Renal Tumor. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2014, 1, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Armesto, M.; Fernandez-Mercado, M.; Arestín, M.; Manterola, L.; Goicoechea, I.; Larrea, E.; Caffarel, M.M.; Araujo, A.M.; Sole, C.; et al. Noncoding RNA Expression and Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Distinguish Tubulocystic Renal Cell Carcinoma (TC-RCC) from Other Renal Neoplasms. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E.; Culig, Z.; Remšík, J.; Souček, K. Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Hirata, H.; Ueno, K.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Gupta, A.; Dahiya, R. MicroRNA-34a suppresses malignant transformation by targeting c-Myc transcriptional complexes in human renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Stoudemire, J.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; et al. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, S.; Truong, L.D.; Ro, J.Y.; Ayala, A.G.; Shen, S.S. Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma is the fourth most common histologic type of renal cell carcinoma in 290 consecutive nephrectomies for renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zarzour, J.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Gordetsky, J. Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: New Clinical and Imaging Characteristics. Urology 2017, 103, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Larrea, E.; Larrinaga, G.; Goicoechea, I.; Arestin, M.; Fernandez-Mercado, M.; Hes, O.; Cacers, F.; Manterola, L.; Lorpze, J.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing and non-coding RNA expression analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma suggests distinct pathological mechanisms from other renal tumour subtypes. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munari, E.; Marchionni, L.; Chitre, A.; Hayashi, M.; Martignoni, G.; Brunelli, M.; Gobbo, S.; Argani, P.; Allaf, M.; Hoque, M.O.; et al. Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Micro-RNA expression profiling and comparison with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongroo, P.S.; Rustgi, A.K. The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Boil. Ther. 2010, 10, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, S.M.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dudas, M.E.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Fine, S.W.; Gopalan, A.; Reuter, V.E.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Russo, P.; et al. Clear-cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Molecular and immunohistochemical analysis with emphasis on the von Hippel–Lindau gene and hypoxia-inducible factor pathway-related proteins. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. Integrated Profiling of MicroRNAs and mRNAs: MicroRNAs Located on Xq27.3 Associate with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Ni, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X. [Corrigendum] miR-122 promotes proliferation and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by suppressing Forkhead box O3. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, C.; Tan, R.; Wang, Z.; Qin, C.; Zhang, J.; Tao, J.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Z.; et al. MiR-122 promotes renal cancer cell proliferation by targeting Sprouty2. Tumor Boil. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, X.; Du, Q.; Luo, G.; Liu, K.; et al. miR-122 promotes metastasis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating Dicer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.; Edelman, M.; Argani, P. Xp11 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Case Rev. 2010, 15, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchionni, L.; Hayashi, M.; Guida, E.; Ooki, A.; Munari, E.; Jabboure, F.J.; Dinalankara, W.; Raza, A.; Netto, G.J.; Hoque, M.O.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of Xp11 renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 67, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shuch, B.M.; Gerstein, M.B. Whole-genome analysis of papillary kidney cancer finds significant noncoding alterations. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, 1006685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klec, C.; Prinz, F.; Pichler, M. Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, N.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, R.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance via the miR-34a/c-Met axis in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62927–62938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Yang, F.Q.; Chen, S.J.; Che, J.; Zheng, J.H. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Tang, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, K.; Hu, J.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, W.; Yu, G.; Yao, W.; Zhou, H.; et al. LncRNA MALAT1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ZEB2 expression by sponging miR-200s in clear cell kidney carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38005–38015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Cui, M.; Deng, Q.; Liu, J. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed profiles and reconstruction of a competing endogenous RNA network in papillary renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4685–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, M.; Zhan, Q.; Shen, B.; Peng, C. lncRNA MEG3 had anti-cancer effects to suppress pancreatic cancer activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Yu, M.-S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.-R.; Yan, B. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA MEG3 suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis through AKT pathway. Tumor Boil. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, A.; Liu, S.; Lu, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, F.; Shi, Y.; Shen, S.; Liang, J.; et al. Aberrant Methylation-mediated Silencing of lncRNA MEG3 Functions as a ceRNA in Esophageal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-H.; Wang, X. lncRNA MEG3 inhibit proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via p53 signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3850–3856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Dai, J.; Zhuo, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, F.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, D. Study on the mechanism behind lncRNA MEG3 affecting clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-7/RASL11B signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9503–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Zeng, J.; Chen, G.; Huang, H. Survival prediction of kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma by comprehensive LncRNA characterization. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110811–110829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Dai, G. Identification of a universal 6-lncRNA prognostic signature for three pathologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 120, 7375–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.-T.; Xu, M.; Kuang, Y.; Han, X.-Y.; Wang, M.-Q.; Yang, Q. Biomarker and competing endogenous RNA potential of tumor-specific long noncoding RNA in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6399–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | miRNA | Expression Level | Endpoint | Outcome | Independent in Multivariate Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| papillary RCC | |||||
| Ge et al., 2015 [78] | miR-200c | ↓ | OS | good | no |
| miR-127 | ↓ | OS | good | no | |
| miR-34a | ↑ | OS | good | yes | |
| Luo et al., 2017 [79] | hsa-miR-1293 | ↑ | PFS | poor | N/E |
| hsa-miR-3199-2 | ↑ | PFS | poor | N/E | |
| Huang et al., 2017 [80] | miR-133a | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E |
| miR-133b | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E | |
| miR-145 | ↑ | OS | poor | no | |
| miR-216a | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E | |
| miR-217 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E | |
| miR-1297 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E | |
| miR-211 | ↑ | OS | good | N/E | |
| chromophobe RCC | |||||
| Ge et al., 2015 [81] | miR-191 | ↑ | RFS, OS | poor | no |
| miR-19a | ↑ | RFS, OS | poor | no | |
| miR-210 | ↑ | RFS, OS | poor | yes (RFS) | |
| miR-425 | ↑ | RFS, OS | poor | no | |
| miR-186 | ↑ | OS | poor | no |
| Reference | lncRNA | Expression Level | Endpoint | Outcome | Independent in Multivariate Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PapillaryRCC | |||||
| Lan et al., 2017 [134] | AFAP1-AS1 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * |
| GAS6-AS1 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| RP11-1C8.7 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| RP11-21L19.1 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| RP11-503C24.1 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| RP11536I6.2 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| RP11-63A11.1 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| Zuo et al., 2018 [135] | AC003092.1 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * |
| AC079160.1 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| COL18A1-AS1 | ↓ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| LINC00520 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| LINC02154 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| SLC7A11-AS1 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E * | |
| chromophobe RCC | |||||
| He et al., 2016 [136] | COL18A1-AS1 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E |
| BRE-AS1 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E | |
| SNHG7 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E | |
| TMEM51-AS1 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E | |
| C21orf62-AS1 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E | |
| LINC00336 | ↓ | OS | Poor | N/E | |
| LINC00882 | ↑ | OS | poor | N/E |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barth, D.A.; Slaby, O.; Klec, C.; Juracek, J.; Drula, R.; Calin, G.A.; Pichler, M. Current Concepts of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101580
Barth DA, Slaby O, Klec C, Juracek J, Drula R, Calin GA, Pichler M. Current Concepts of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101580
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarth, Dominik A., Ondrej Slaby, Christiane Klec, Jaroslav Juracek, Rares Drula, George A. Calin, and Martin Pichler. 2019. "Current Concepts of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101580
APA StyleBarth, D. A., Slaby, O., Klec, C., Juracek, J., Drula, R., Calin, G. A., & Pichler, M. (2019). Current Concepts of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 11(10), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101580







