Oncobox Bioinformatical Platform for Selecting Potentially Effective Combinations of Target Cancer Drugs Using High-Throughput Gene Expression Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Signaling Pathway Activation in Drug-Resistant Cell Lines
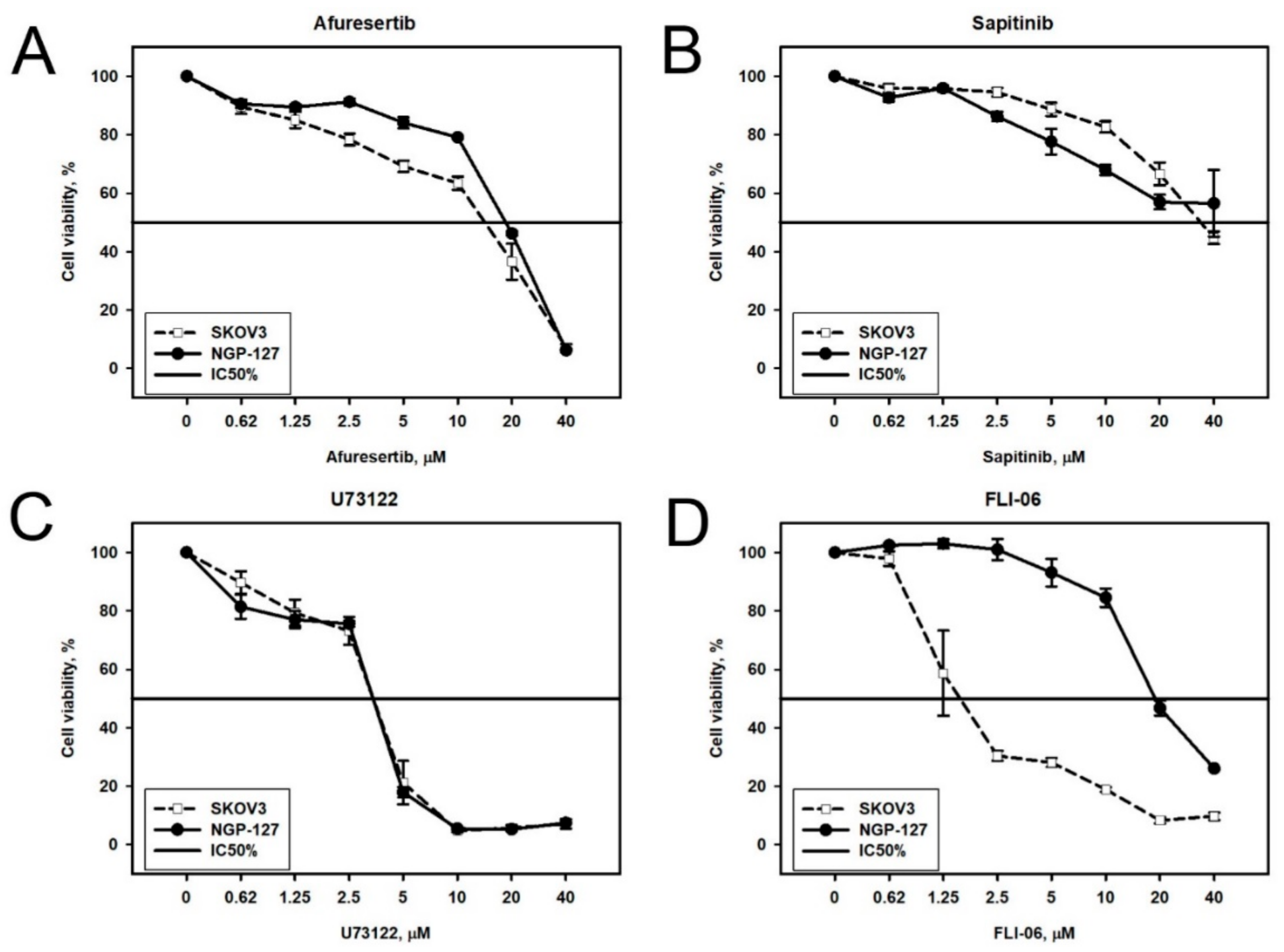
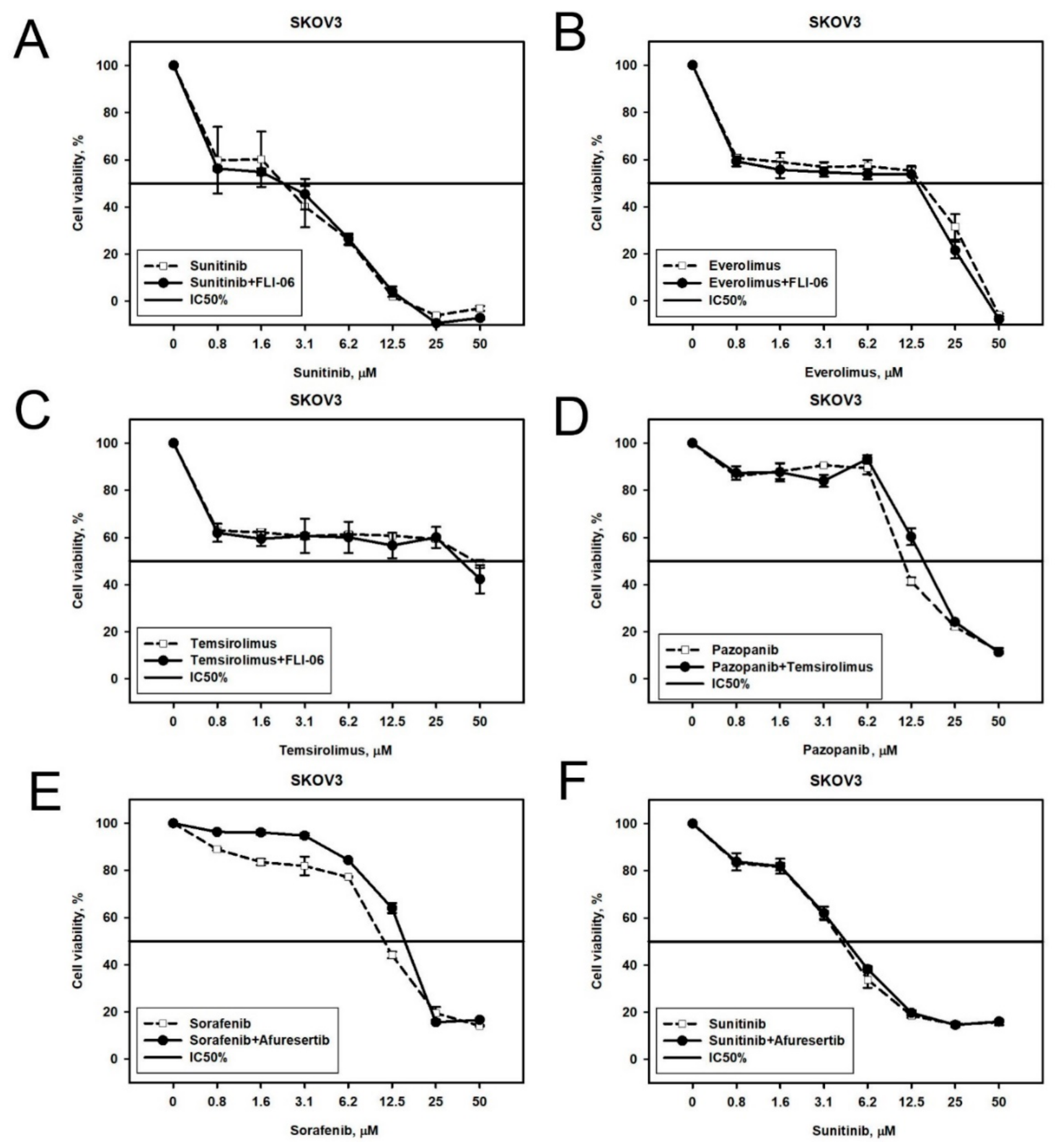
2.2. Prediction and Experimental Testing of Drugs Combinations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biosamples
4.2. Cell Culturing and Viability Assay
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorff, T.B.; Goldkorn, A.; Quinn, D.I. Targeted therapy in renal cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2009, 1, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Bois, A.; Floquet, A.; Kim, J.-W.; Rau, J.; del Campo, J.M.; Friedlander, M.; Pignata, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Vergote, I.; Colombo, N.; et al. Incorporation of pazopanib in maintenance therapy of ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3374–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Mazzi, V.; Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. Personalization of targeted therapy in advanced thyroid cancer. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.N.; Schaap, N.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Tiu, R.V.; Zachee, P.; Jourdan, E.; Winton, E.; Silver, R.T.; Schouten, H.C.; et al. Janus kinase-2 inhibitor fedratinib in patients with myelofibrosis previously treated with ruxolitinib (JAKARTA-2): A single-arm, open-label, non-randomised, phase 2, multicentre study. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e317–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Cazzato, E.; Ladewig, E.; Frattini, V.; Rosenbloom, D.I.S.; Zairis, S.; Abate, F.; Liu, Z.; Elliott, O.; Shin, Y.-J.; et al. Clonal evolution of glioblastoma under therapy. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hata, A.N.; Niederst, M.J.; Archibald, H.L.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mulvey, H.E.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Ji, F.; Bhang, H.C.; Krishnamurthy Radhakrishna, V.; et al. Tumor cells can follow distinct evolutionary paths to become resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorokin, M.; Kholodenko, R.; Grekhova, A.; Suntsova, M.; Pustovalova, M.; Vorobyeva, N.; Kholodenko, I.; Malakhova, G.; Garazha, A.; Nedoluzhko, A.; et al. Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be linked with the decreased sensitivity to X-ray irradiation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5111–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliper, A.M.; Korzinkin, M.B.; Kuzmina, N.B.; Zenin, A.A.; Venkova, L.S.; Smirnov, P.Y.; Zhavoronkov, A.A.; Buzdin, A.A.; Borisov, N.M. Mathematical Justification of Expression-Based Pathway Activation Scoring (PAS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1613, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzdin, A.A.; Prassolov, V.; Zhavoronkov, A.A.; Borisov, N.M. Bioinformatics Meets Biomedicine: OncoFinder, a Quantitative Approach for Interrogating Molecular Pathways Using Gene Expression Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1613, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, N.; Suntsova, M.; Sorokin, M.; Garazha, A.; Kovalchuk, O.; Aliper, A.; Ilnitskaya, E.; Lezhnina, K.; Korzinkin, M.; Tkachev, V.; et al. Data aggregation at the level of molecular pathways improves stability of experimental transcriptomic and proteomic data. Cell Cycle 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzdin, A.A.; Zhavoronkov, A.A.; Korzinkin, M.B.; Venkova, L.S.; Zenin, A.A.; Smirnov, P.Y.; Borisov, N.M. Oncofinder, a new method for the analysis of intracellular signaling pathway activation using transcriptomic data. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirin, P.V.; Lebedev, T.D.; Orlova, N.N.; Gornostaeva, A.S.; Prokofijeva, M.M.; Nikitenko, N.A.; Dmitriev, S.E.; Buzdin, A.A.; Borisov, N.M.; Aliper, A.M.; et al. Silencing AML1-ETO gene expression leads to simultaneous activation of both pro-apoptotic and proliferation signaling. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldoni, M.; Johansson, C. A mathematical approach to study combined effects of toxicants in vitro: Evaluation of the Bliss independence criterion and the Loewe additivity model. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepelin, D.; Korzinkin, M.; Vanyushina, A.; Aliper, A.; Borisov, N.; Vasilov, R.; Zhukov, N.; Sokov, D.; Prassolov, V.; Gaifullin, N.; et al. Molecular pathway activation features linked with transition from normal skin to primary and metastatic melanomas in human. Oncotarget 2016, 1, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, I.; Suntsova, M.; Ilnitskaya, E.; Roumiantsev, S.; Sorokin, M.; Garazha, A.; Spirin, P.; Lebedev, T.; Gaifullin, N.; Larin, S.; et al. Gene expression and molecular pathway activation signatures of MYCN-amplified neuroblastomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83768–83780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, B.; Ilyukha, V.; Sorokin, M.; Buzdin, A.; Vannier, E.; Poltorak, A. Cutting edge: Activation of STING in T cells induces type I IFN responses and cell death. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirin, P.; Lebedev, T.; Orlova, N.; Morozov, A.; Poymenova, N.; Dmitriev, S.E.; Buzdin, A.; Stocking, C.; Kovalchuk, O.; Prassolov, V. Synergistic suppression of t(8;21)-positive leukemia cell growth by combining oridonin and MAPK1/ERK2 inhibitors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56991–57002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicolantonio, F.; Mercer, S.J.; Knight, L.A.; Gabriel, F.G.; Whitehouse, P.A.; Sharma, S.; Fernando, A.; Glaysher, S.; Di Palma, S.; Johnson, P.; et al. Cancer cell adaptation to chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Palafox, M.; Asghar, U.; Rivas, M.A.; Cutts, R.J.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Pearson, A.; Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, O.; Grueso, J.; et al. Early adaptation and acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in Estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, N.; Jiang, T.; Rosen, D.M.; Nelkin, B.D.; Ball, D.W. Dual inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin in differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Ashihara, E.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kimura, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Yao, H.; Nagao, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Hirai, H.; et al. Rakicidin A effectively induces apoptosis in hypoxia adapted Bcr-Abl positive leukemic cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Tang, J.; Andersson, E.I.; Timonen, S.; Koschmieder, S.; Wennerberg, K.; Mustjoki, S.; Aittokallio, T. Patient-customized drug combination prediction and testing for t-cell prolymphocytic leukemia patients. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhong, R.; Wang, T.; Wong, S.; Xiao, G.; Xie, Y. DIGRE: Drug-induced genomic residual effect model for successful prediction of multidrug effects. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2015, 4, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Ma, C.; Tang, K.; Zhu, R.; Wu, Z.; Shen, R.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Huang, D.; et al. Combining genomic and network characteristics for extended capability in predicting synergistic drugs for cancer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Fei, T.; Zheng, X.; Brown, M.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.S.; Wang, H. An integrative pharmacogenomic approach identifies two-drug combination therapies for personalized cancer medicine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Yang, J.; Karan, C.; Menden, M.P.; Costello, J.C.; Tang, H.; Xiao, G.; Li, Y.; Allen, J.; Zhong, R.; et al. A community computational challenge to predict the activity of pairs of compounds. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tjulandin, S.; Moiseyenko, V.; Semiglazov, V.; Manikhas, G.; Learoyd, M.; Saunders, A.; Stuart, M.; Keilholz, U. Phase I, dose-finding study of AZD8931, an inhibitor of EGFR (erbB1), HER2 (erbB2) and HER3 (erbB3) signaling, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; He, L.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. SynergyFinder: A web application for analyzing drug combination dose-response matrix data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2413–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolstad, B. PreprocessCore: A Collection of Pre-Processing Functions. Available online: https://rdrr.io/bioc/preprocessCore/ (accessed on 26 September 2018).
- Pathway Central—Qiagen. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/shop/genes-and-pathways/ pathway-central/ (accessed on 26 September 2018).
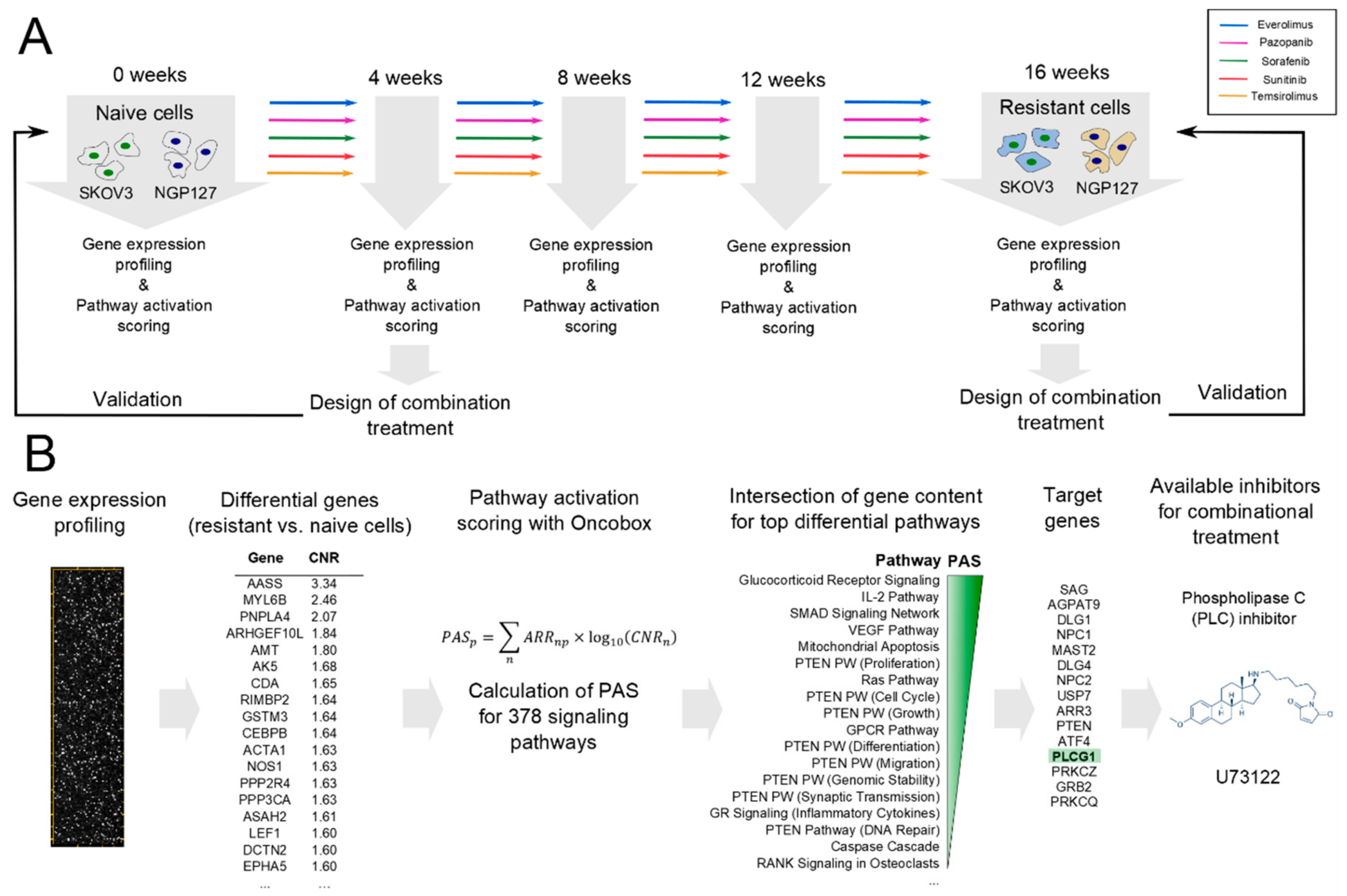
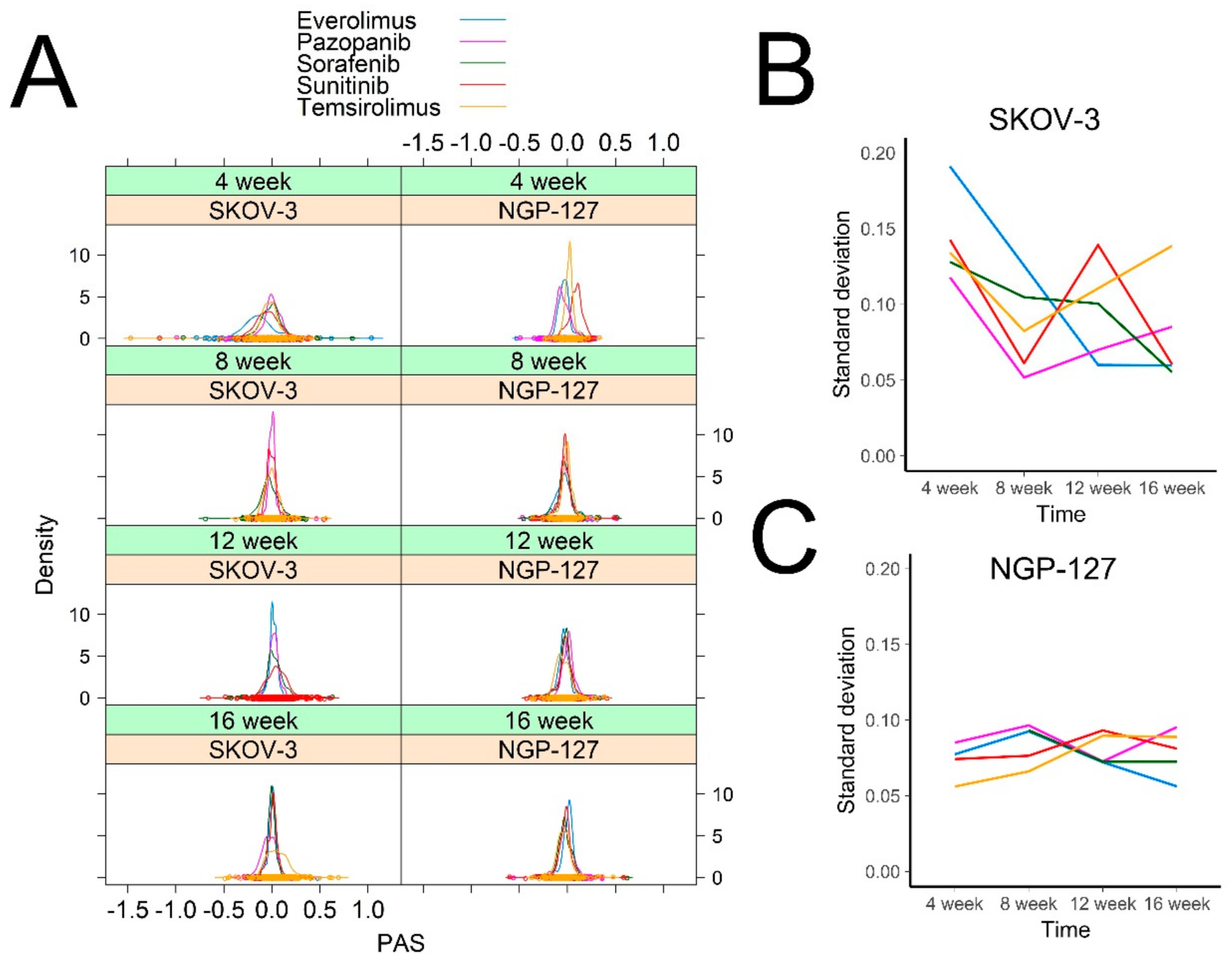

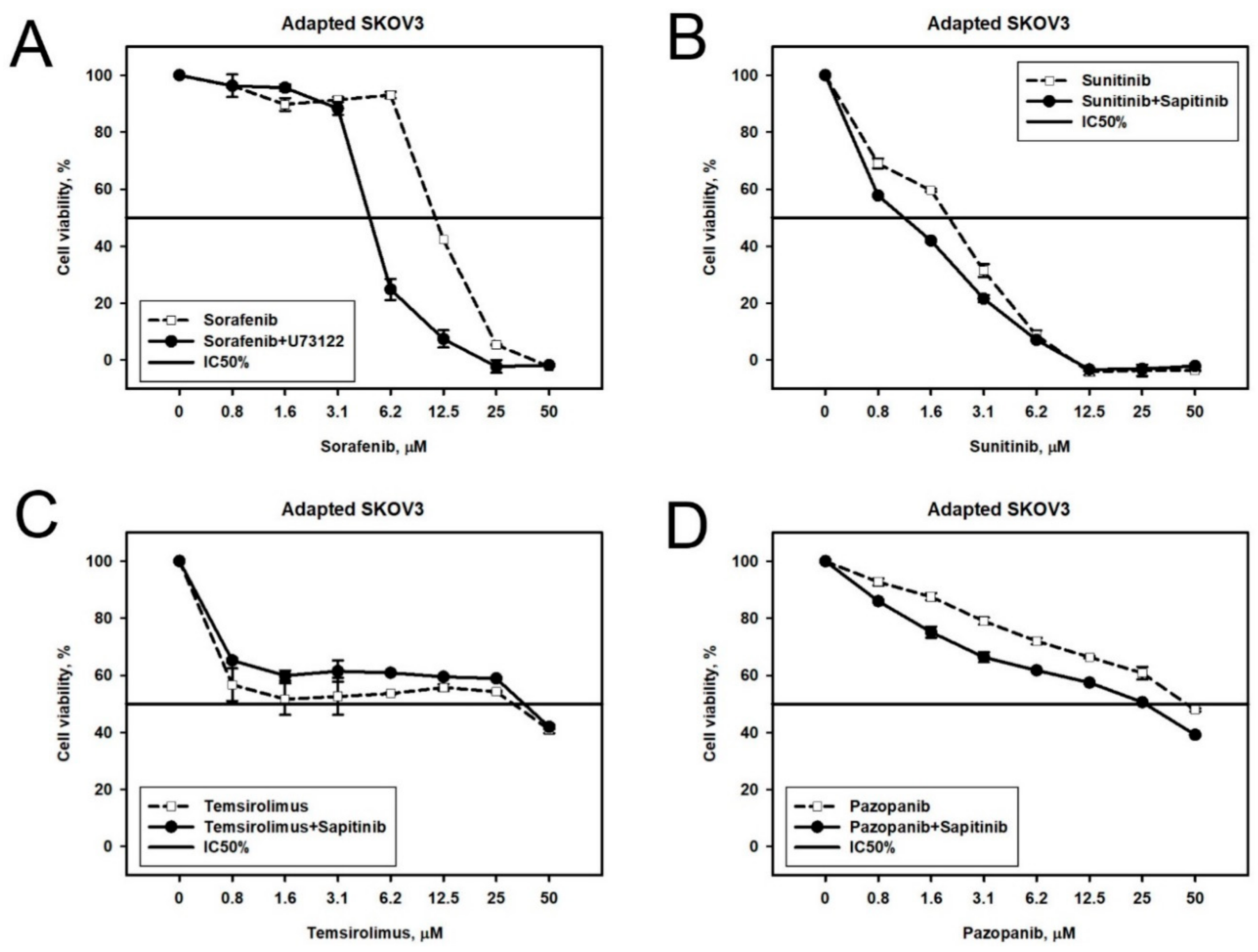
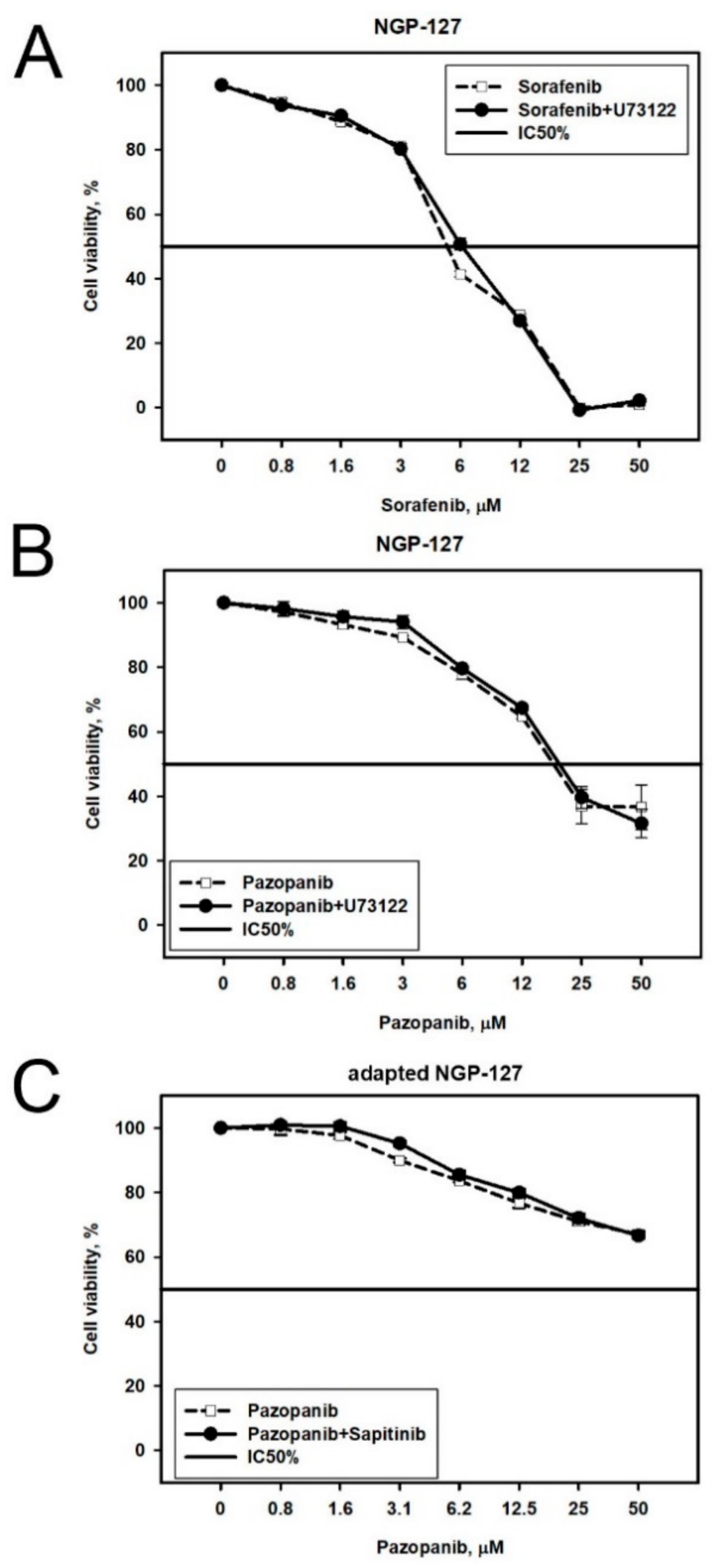
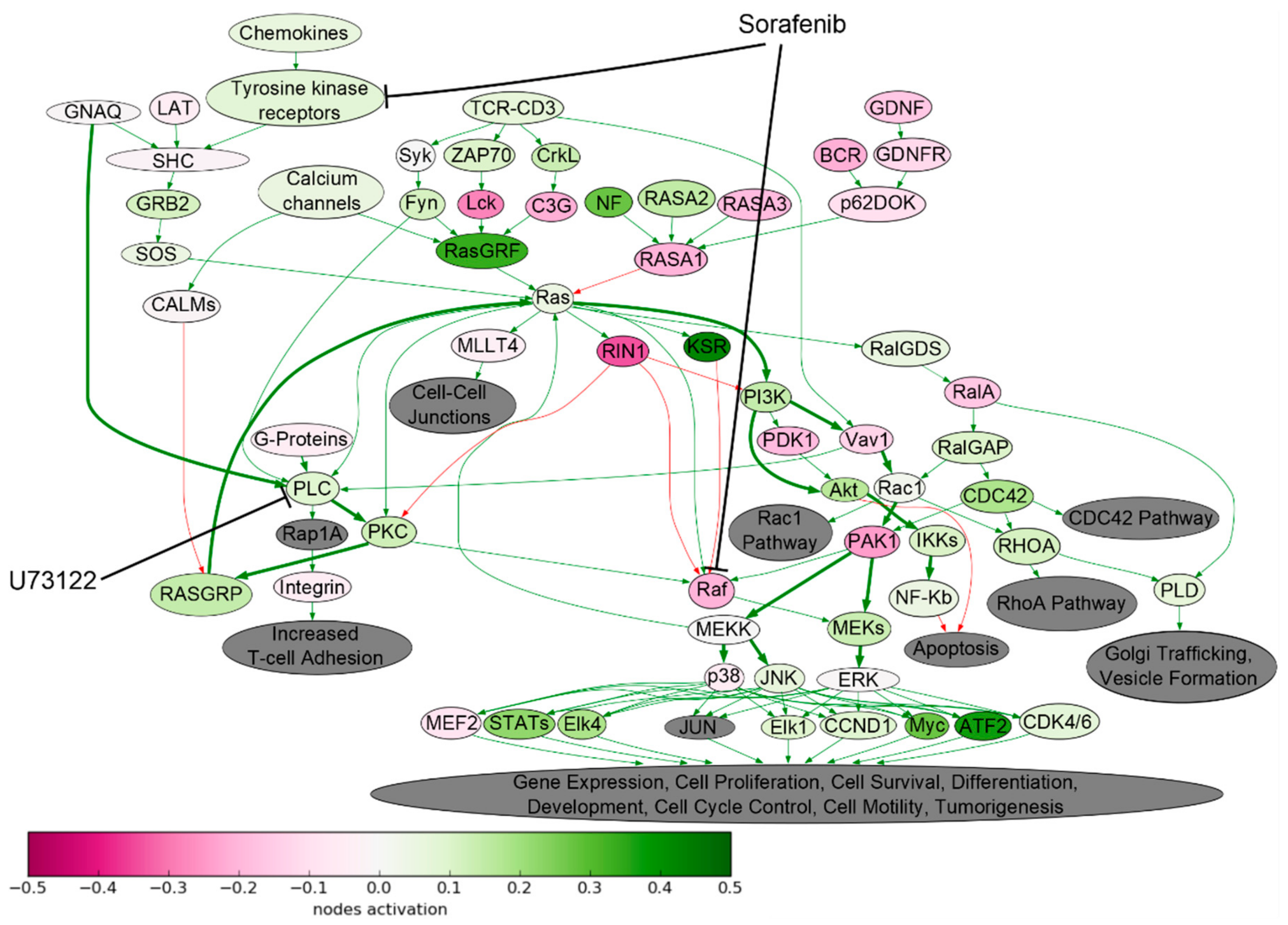
| Cell Line | Drug | 4–8 Week | 16 Weeks |
|---|---|---|---|
| NGP-127 | Sorafenib | Phospholipase C, JNK1-2-3/MAP2K4-7 | JAK1, JAK3 |
| Sunitinib | JNK1-2-3/MAP2K4-7 | RAS, PI3K | |
| Pazopanib | Phospholipase C, Adenylate cyclase | EGFR | |
| Temsirolimus | JNK1-2-3/MAP2K4-7 | RAS | |
| Everolimus | PRKACA | PI3K | |
| SKOV-3 | Sorafenib | Akt | Phospholipase C |
| Sunitinib | Notch, Akt | EGFR, ErbB2, ADCYs | |
| Pazopanib | mTOR | ErbB3 | |
| Temsirolimus | Notch | EGFR-ErbB2 | |
| Everolimus | Notch | MAP2K6-MAP2K3 |
| Drug/Inhibitor | Molecular Target |
|---|---|
| Temsirolimus | mTOR, FKBP12 |
| Everolimus | mTOR, FKBP12 |
| Sunitinib | VEGFR2 (Flk-1) and PDGFRβ |
| Sorafenib | Raf-1, B-Raf and VEGFR-2 |
| Pazopanib | VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFR, FGFR, c-Kit and c-Fms |
| Afuresertib (GSK2110183) | Akt |
| Sapitinib (AZD8931) | EGFR, ErbB2 and ErbB3 |
| FLI-06 | Notch |
| U73122 | Phospholipase C (PLC) |
| Drug | SKOV-3 | NGP-127 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC20 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | IC20 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | |
| Afuresertib | 2.7 | 17 | 8 | 19 |
| FLI-06 | 1.5 | 2 | 11 | 20 |
| U73122 | 3 | 3.2 | 1 | 3.5 |
| Sapitinib | 11 | 37 | 4.2 | ≥40 |
| Sorafenib * | 9.6 | 5.5 | ||
| Pazopanib * | ≥50 | 12 | ||
| Sunitinib * | 3 | 3.1 | ||
| Temsirolimus * | 17 | 11.8 | ||
| Everolimus * | 17.6 | 15.5 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorokin, M.; Kholodenko, R.; Suntsova, M.; Malakhova, G.; Garazha, A.; Kholodenko, I.; Poddubskaya, E.; Lantsov, D.; Stilidi, I.; Arhiri, P.; et al. Oncobox Bioinformatical Platform for Selecting Potentially Effective Combinations of Target Cancer Drugs Using High-Throughput Gene Expression Data. Cancers 2018, 10, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100365
Sorokin M, Kholodenko R, Suntsova M, Malakhova G, Garazha A, Kholodenko I, Poddubskaya E, Lantsov D, Stilidi I, Arhiri P, et al. Oncobox Bioinformatical Platform for Selecting Potentially Effective Combinations of Target Cancer Drugs Using High-Throughput Gene Expression Data. Cancers. 2018; 10(10):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorokin, Maxim, Roman Kholodenko, Maria Suntsova, Galina Malakhova, Andrew Garazha, Irina Kholodenko, Elena Poddubskaya, Dmitriy Lantsov, Ivan Stilidi, Petr Arhiri, and et al. 2018. "Oncobox Bioinformatical Platform for Selecting Potentially Effective Combinations of Target Cancer Drugs Using High-Throughput Gene Expression Data" Cancers 10, no. 10: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100365
APA StyleSorokin, M., Kholodenko, R., Suntsova, M., Malakhova, G., Garazha, A., Kholodenko, I., Poddubskaya, E., Lantsov, D., Stilidi, I., Arhiri, P., Osipov, A., & Buzdin, A. (2018). Oncobox Bioinformatical Platform for Selecting Potentially Effective Combinations of Target Cancer Drugs Using High-Throughput Gene Expression Data. Cancers, 10(10), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100365







