Fundamental Study for a Graphite-Based Microelectromechanical System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Resonance Frequency of a Graphite Sheet
3. MEMS Fabrication Process Using HOPG
3.1. Fabrication Method
3.2. Fabrication Results
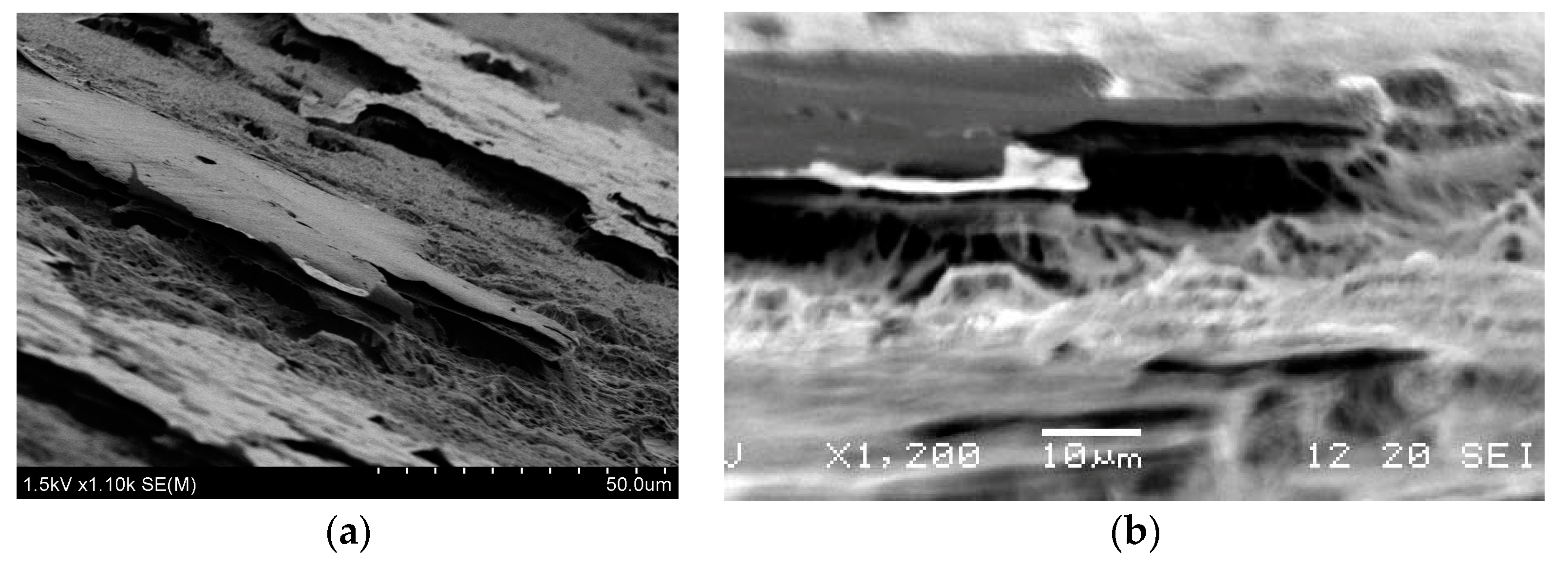
4. High-Precision Graphite Sheet
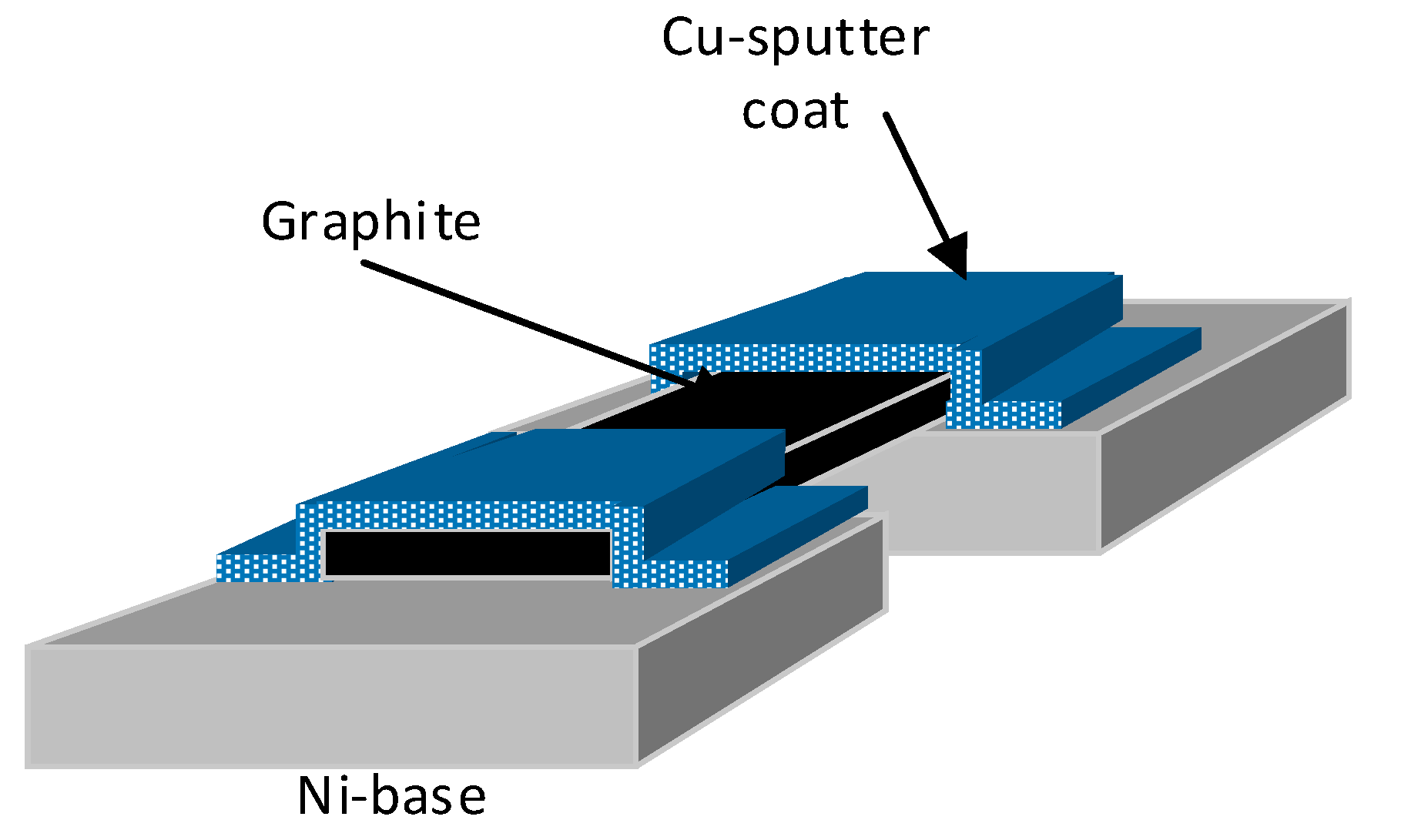
4.1. Over Coating the Metal for Adhesion
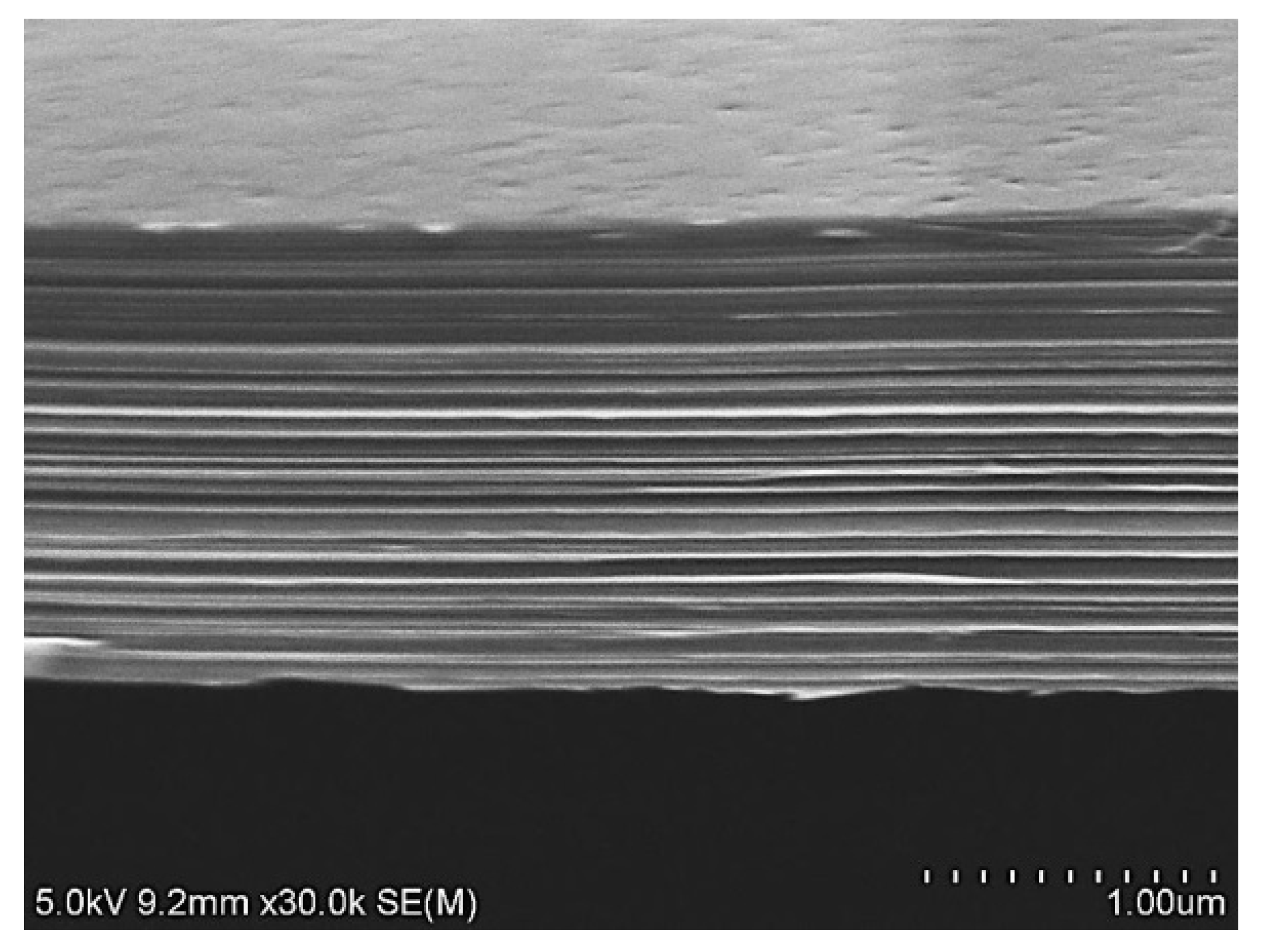
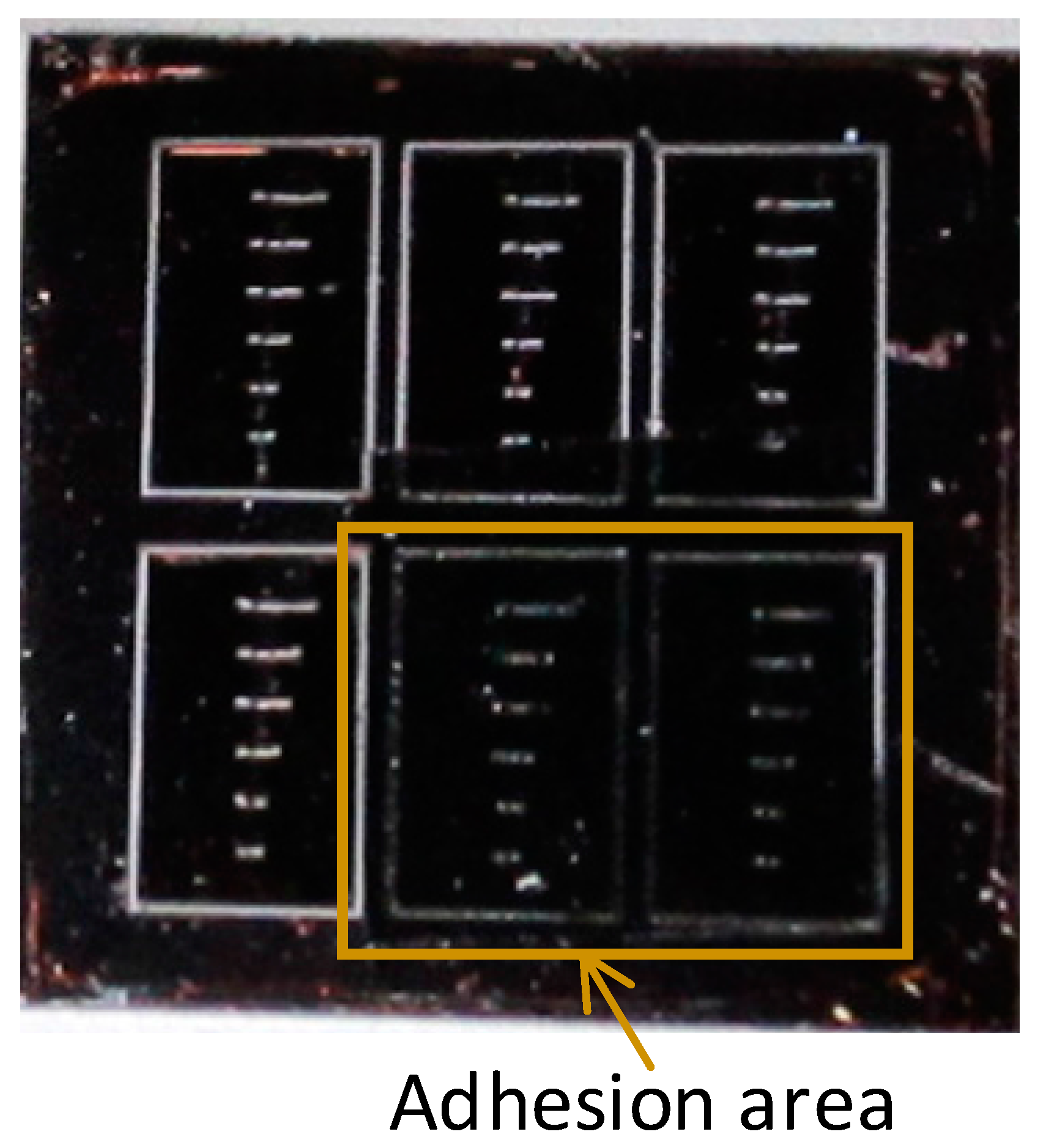
4.2. High-Precision Graphite and Area Adhesions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Nanocarbon Materials: Synthesis and Structure Characterization. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Nanoscience: Carbon-Related Systems and Nanomaterials, NCKU, Tainan, Taiwan, 4–7 July 2012; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, A.N. Foundations of Nanomechanics: From Solid-State Theory to Device Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 349–405. [Google Scholar]
- Schueller, J.A.O.; Brittain, T.S.; Whitesides, M.G. Fabrication of Glassy Carbon Microstructures by Soft Lithography. Sens. Actuators 1999, A72, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. A Novel Method for the Fabrication of High-Aspect Ratio C-MEMS Structures. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Phan, H.-P.; Qamar, A.; Nguyena, N.-T.; Dao, D.V. Flexible and multifunctional electronics fabricated by a solvent-free and user-friendly method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 77267–77274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Phan, H.-P.; Nguyen, T.-K.; Qamar, A.; Woodfield, P.; Zhu, Y.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Dao, D.V. Solvent-free fabrication of biodegradable hot-film flow sensor for noninvasive respiratory monitoring. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 215401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, F.; Debray, A.; Martin, P.; Fujita, H.; Kawakatsu, H. Suspended HOPG Nanosheets for HOPG Nanoresonator Engineering and New Carbon Nanostructure Synthesis. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Rosenblatt, S.; Bolotin, K.I.; Kalb, W.; Kim, P.; Kymissis, I.; Stormer, H.L.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J. Performance of Monolayer Graphene Nanomechanical Resonators with Electrical Readout. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, J.S. Electromechanical Resonators, from Graphene Sheets. Science 2007, 315, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. MEMS: Design and Fabrication; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 3-1–3-112. [Google Scholar]
- Esashi, M. Microsensors and Microactuators for Biomedical Applications, Nanofabrication and Biosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sone, J. Feasible Development of a Carbon-Based MEMS Using a MEMS Fabrication Process. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 8, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, B.T. Physics of Graphite. London; Applied Science: Englewood, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bunch, J.S. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Graphene Sheets. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Huang, H.; Nemchuk, N.; Ruoff, R.S. Patterning of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite by oxygen plasma etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, R.; Minami, K.; Esashi, M. Thin Beam Bulk Micromachining Based on RIE and Xenon Difluoride Silicon Etching. Sens. Actuators 1998, A66, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morassi, A.; Vestroni, F. Dynamic Methods for Damage Detection in Structures; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 83–193. [Google Scholar]
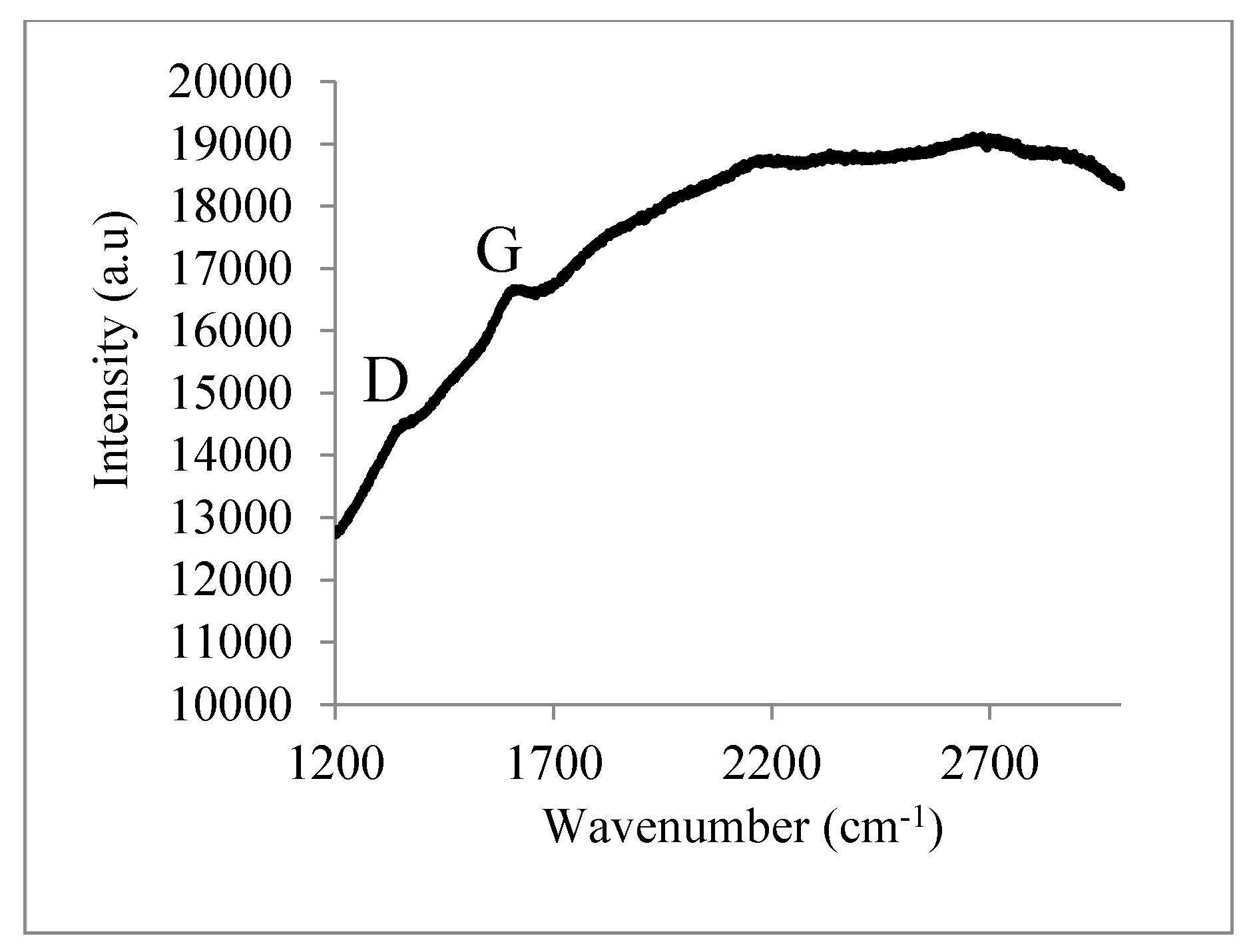
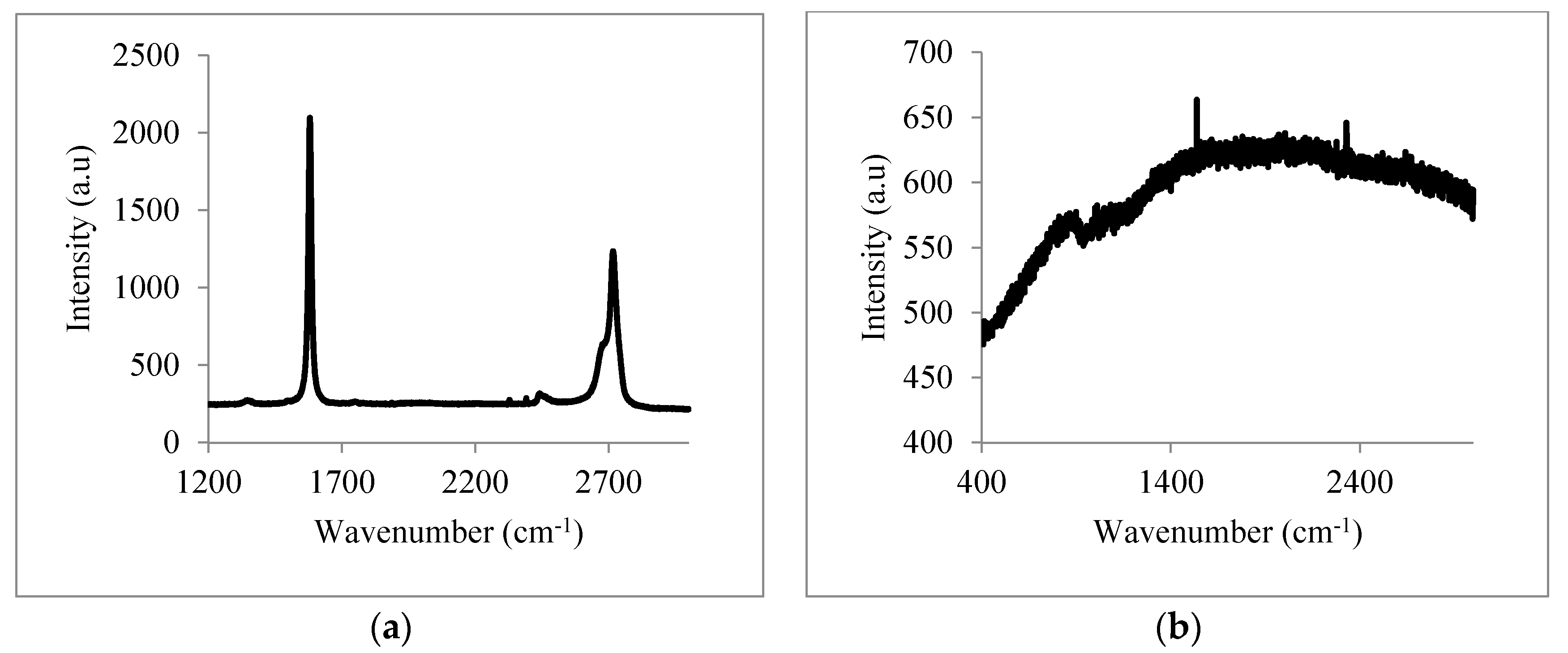
- Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Cancado, L.G.; Jorioa, A.; Saito, R. Studying disorder in graphite-based systems by Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
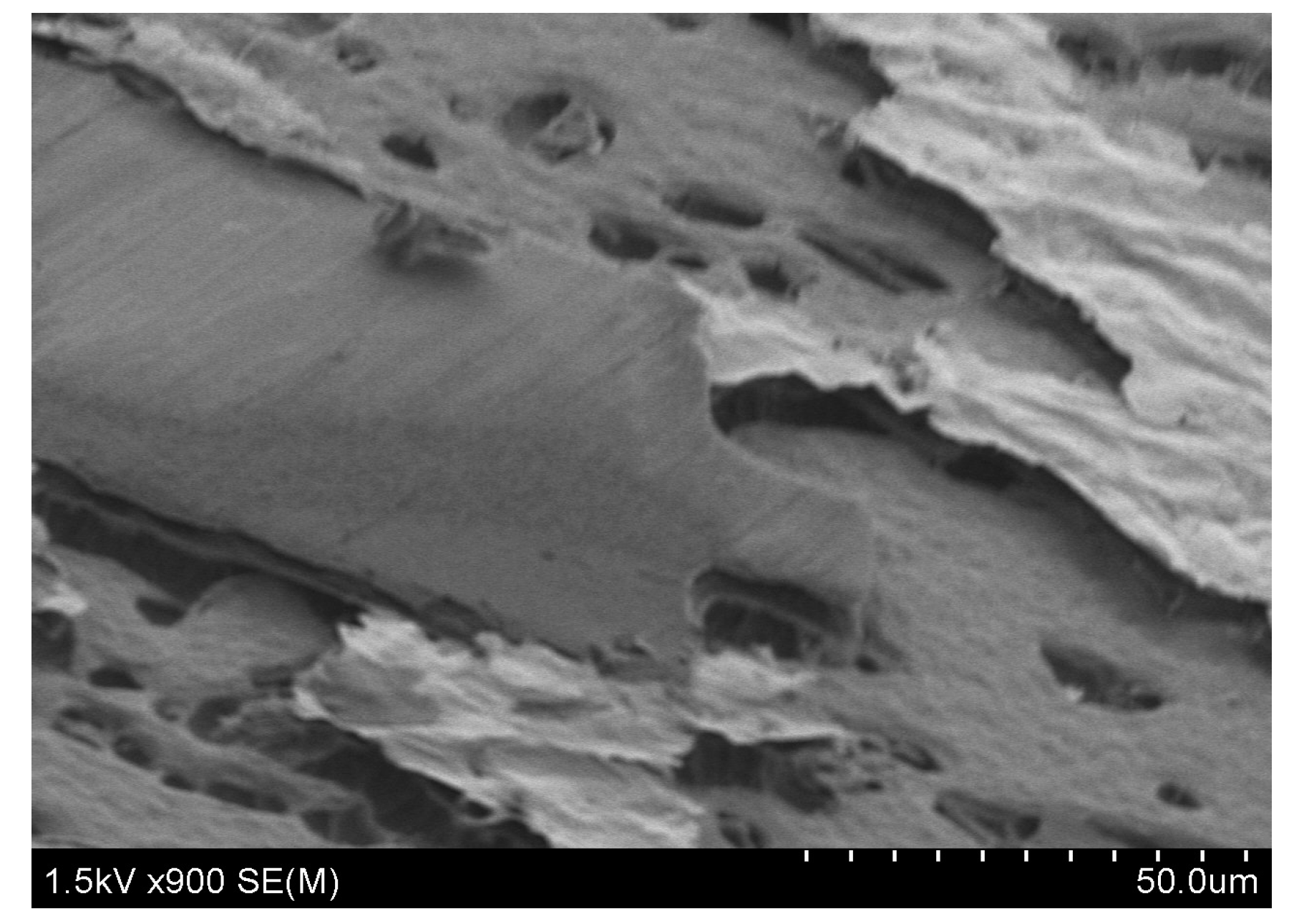
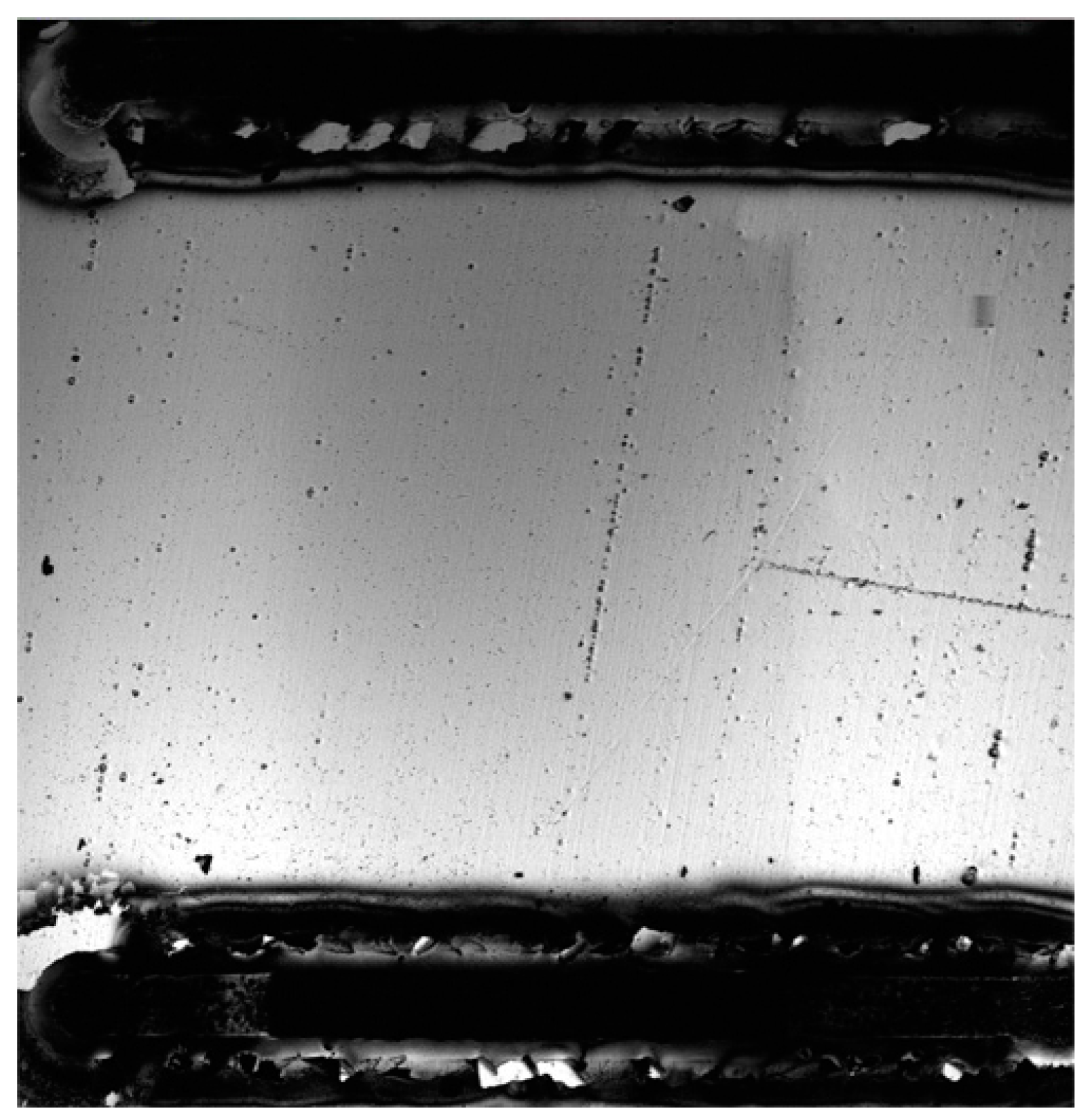



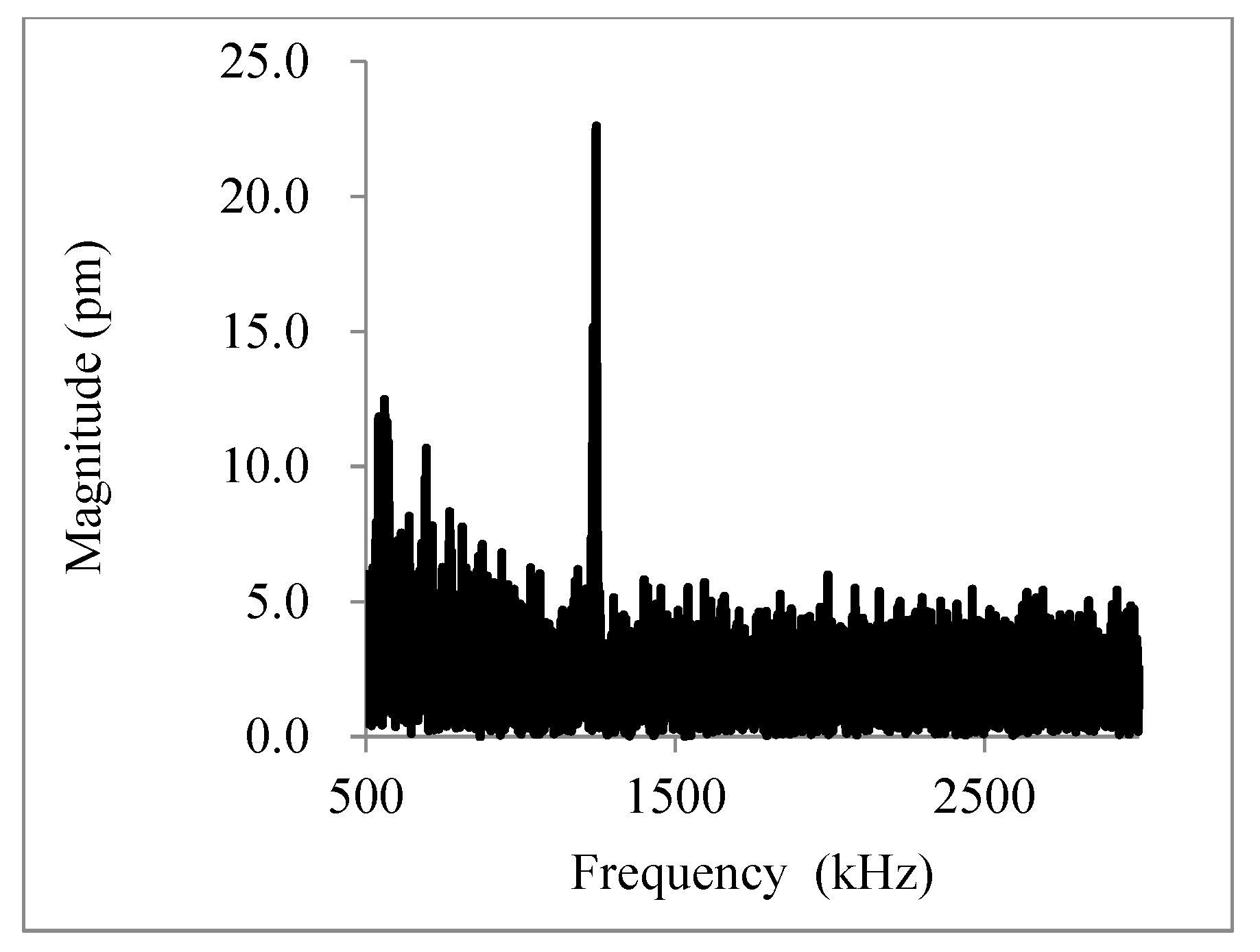


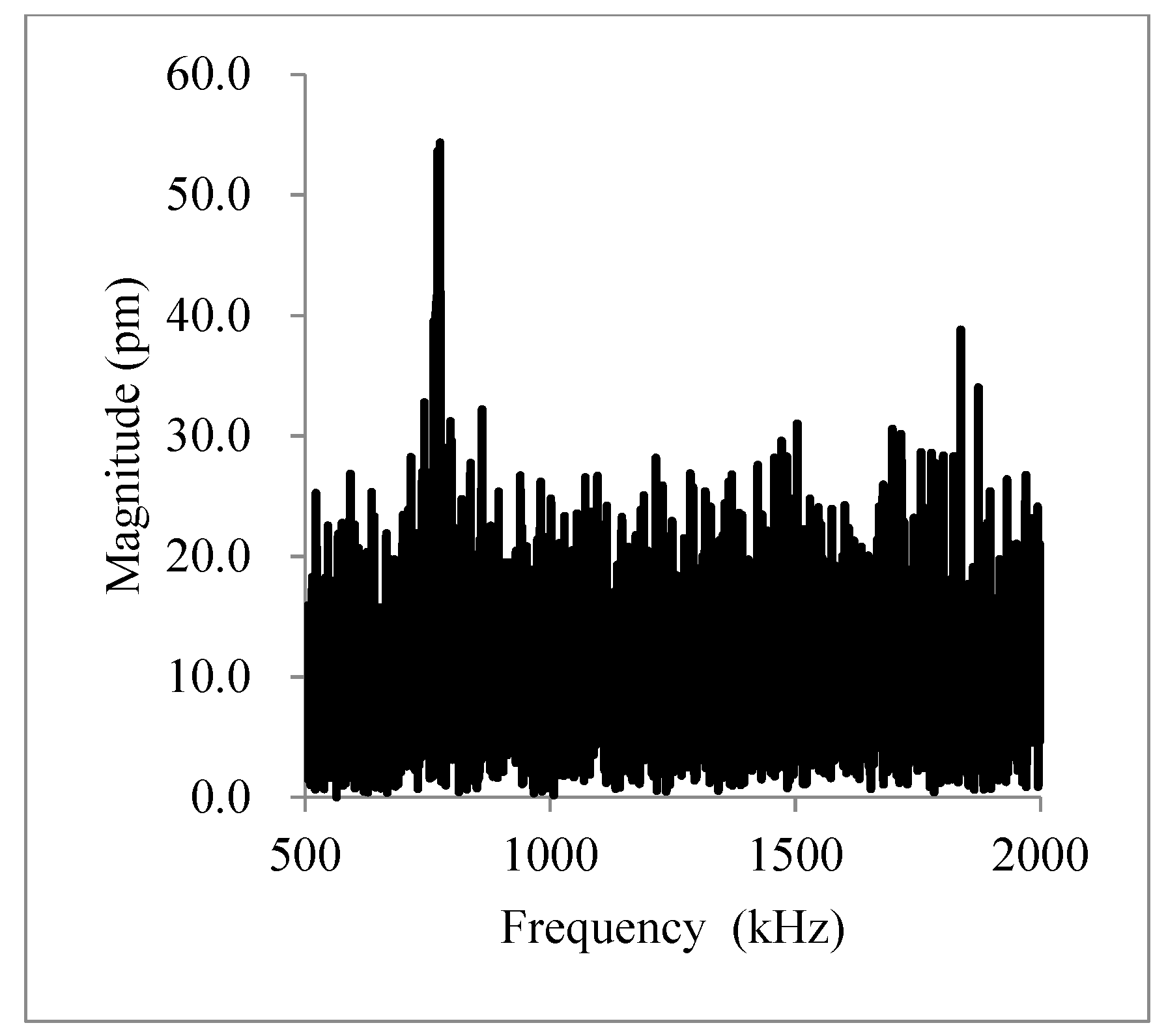
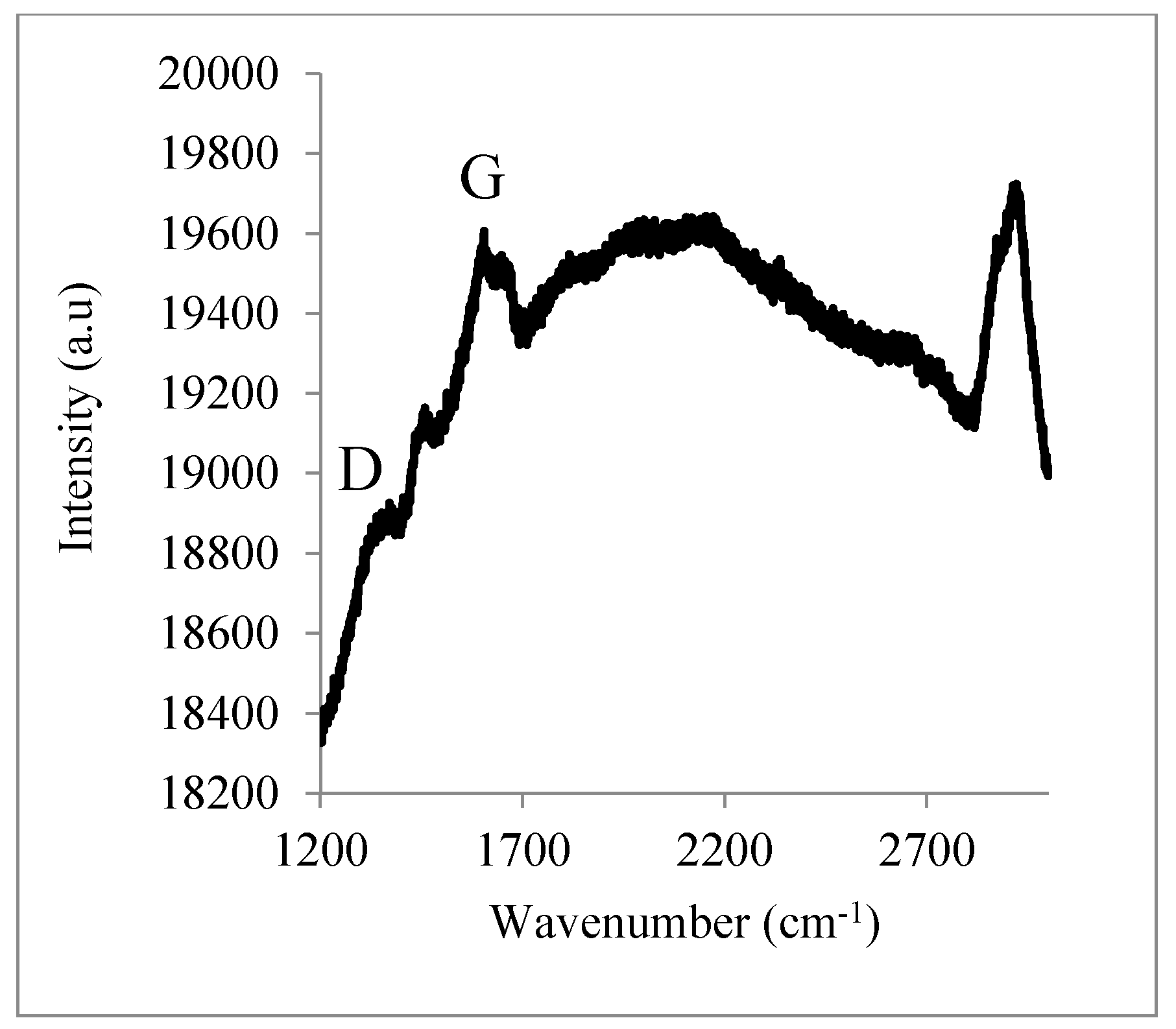
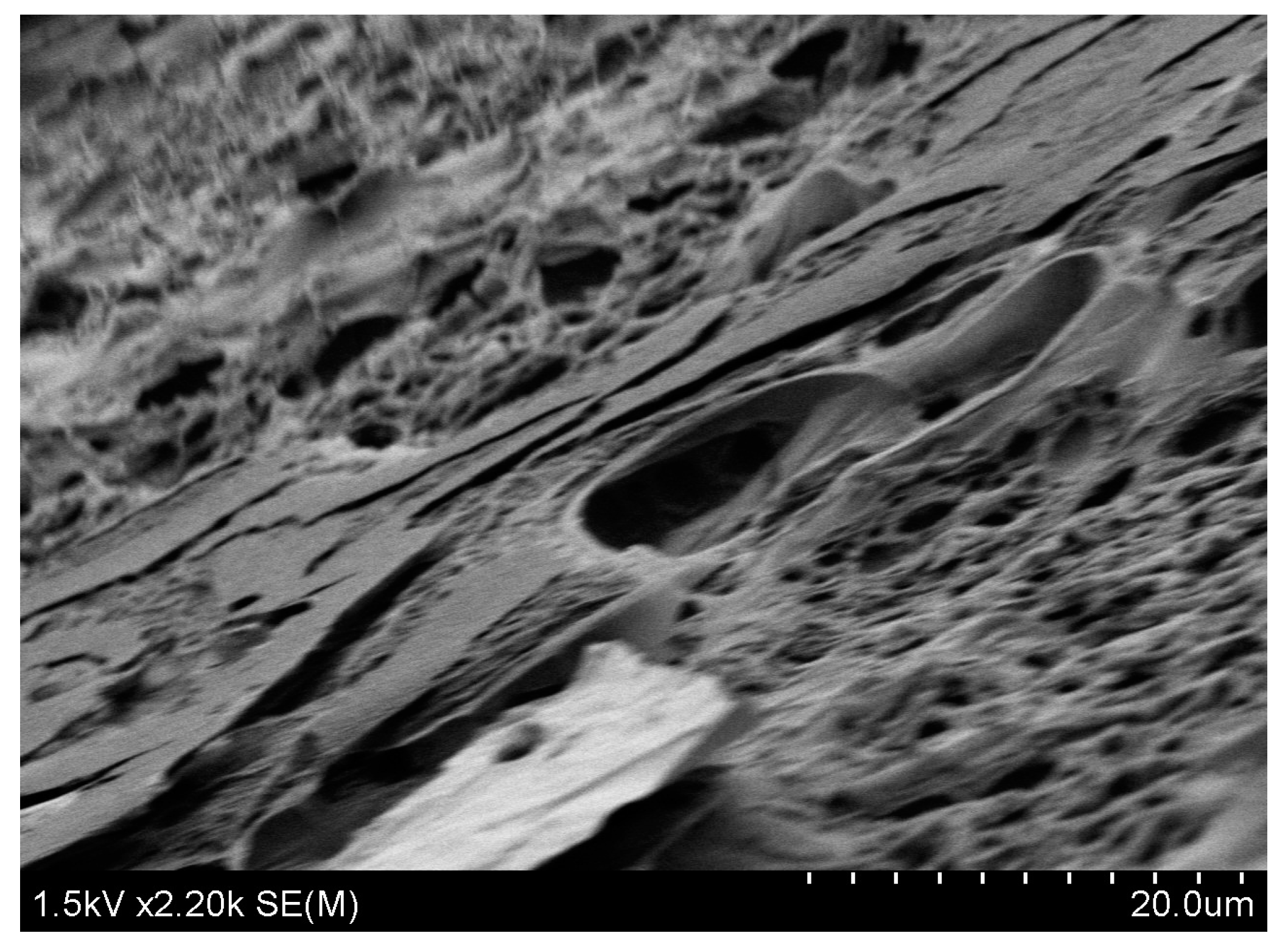
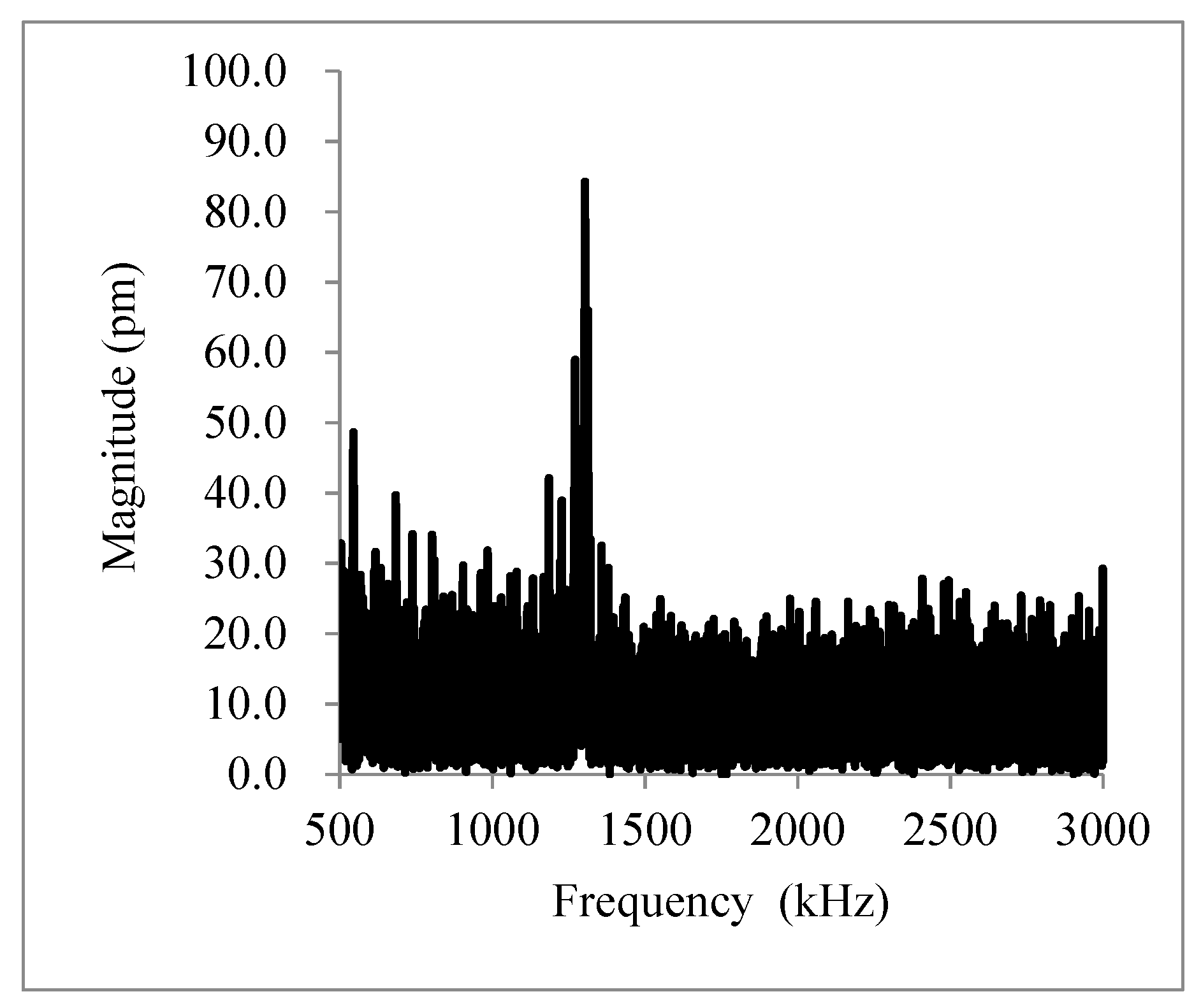







| Name | b (µm) | L (µm) | t (µm) | Calc. (kHz) | Meas. (kHz) | Ratio | Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5 | 7 | 32 | 0.5 | 923 | 720 | 0.773 | Smooth |
| C11 | 15 | 20 | 0.5 | 2364 | 1243 | 0.526 | Smooth |
| C13 | 6 | 44 | 0.5 | 488 | 497 | 1.018 | Rough |
| C19 | 12 | 15 | 0.5 | 4204 | 1195 | 0.284 | Rough |
| Name | b (µm) | L (µm) | t (µm) | Calc. (kHz) | Meas. (kHz) | Ratio | Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB501 | 10 | 56 | 0.5 | 1899 | 770 | 0.405 | Rough |
| DB115 | 5 | 16 | 0.5 | 23,264 | 545 | 0.023 | Rough |
| DB150 | 19 | 24 | 0.5 | 10,339 | 1303 | 0.126 | Rough |
| DB201 | 15 | 55 | 0.5 | 1969 | 780 | 0.396 | Rough |
| DB202 | 15 | 26 | 0.5 | 8810 | 1057 | 0.12 | Rough |
| DB310 | 8 | 57 | 1.0 | 3666 | 1313 | 0.358 | Rough |
| L (mm) | t (µm) | Calc. (Hz) | Meas. (Hz) | Ratio | Q Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 2.0 | 4832 | 4903 | 1.015 | 55 |
| 2.0 | 2.0 | 10,873 | 7813 | 0.719 | 40 |
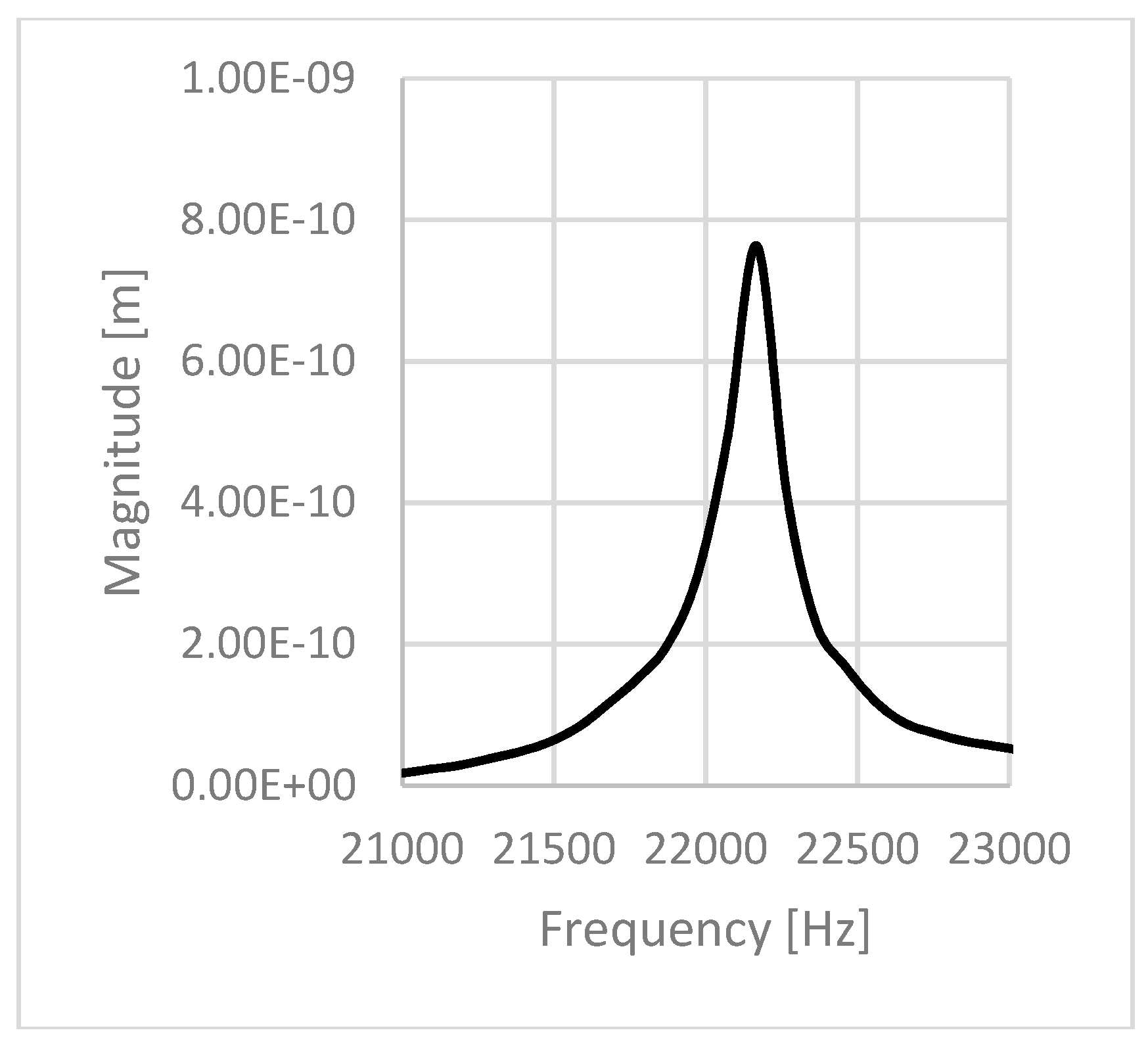
| 1.5 | 2.0 | 19,330 | 22,168 | 1.147 | 123 |
| 1.0 | 2.0 | 43,493 | 16,756 | 0.385 | 8.9 |
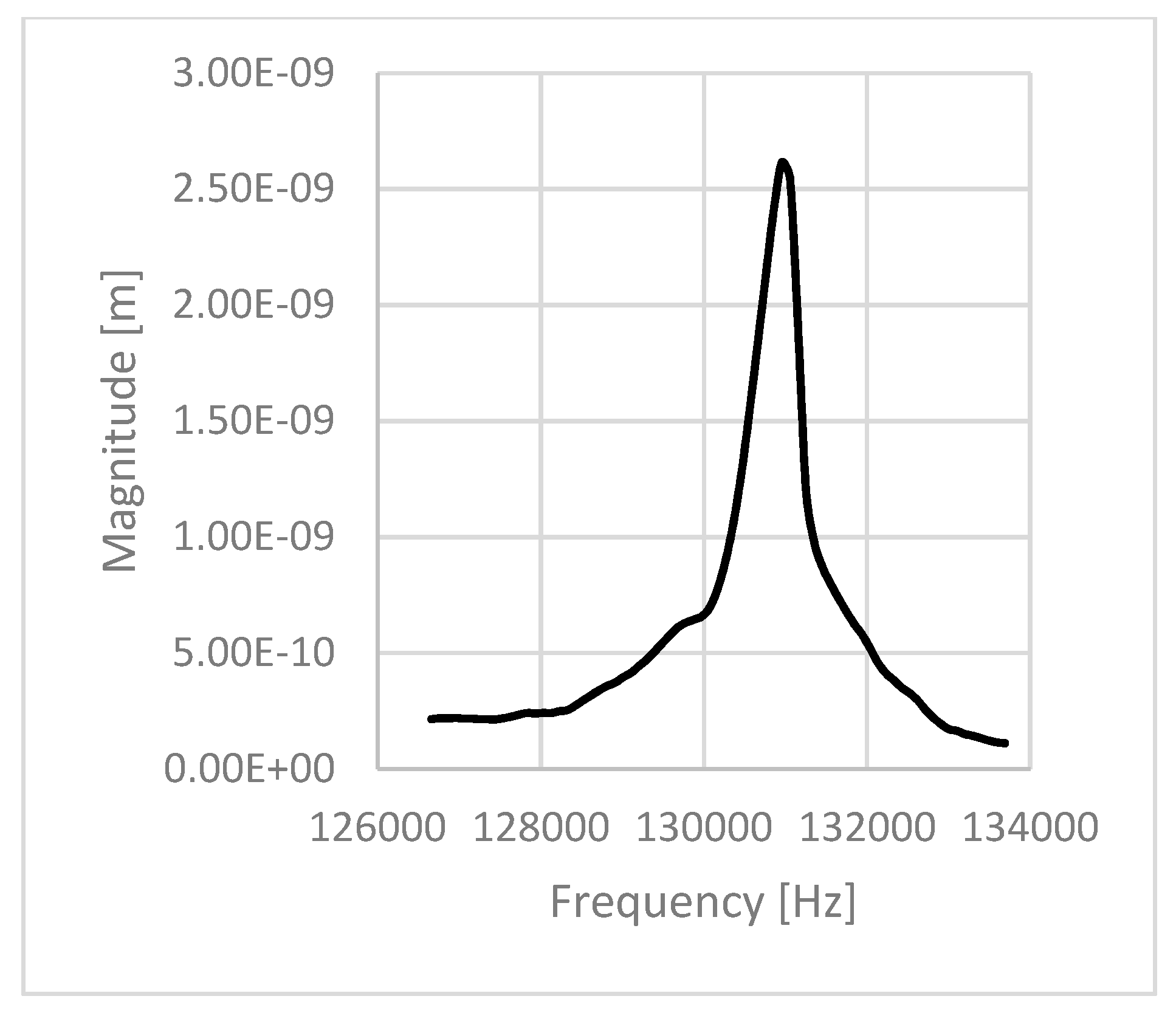
| 0.5 | 2.5 | 217,465 | 131,054 | 0.603 | 160 |
| L (mm) | t (µm) | Calc. (Hz) | Meas. (Hz) | Ratio | Q Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.03 | 1 | 20,498 | 23,696.6 | 1.156 | 98,700 |
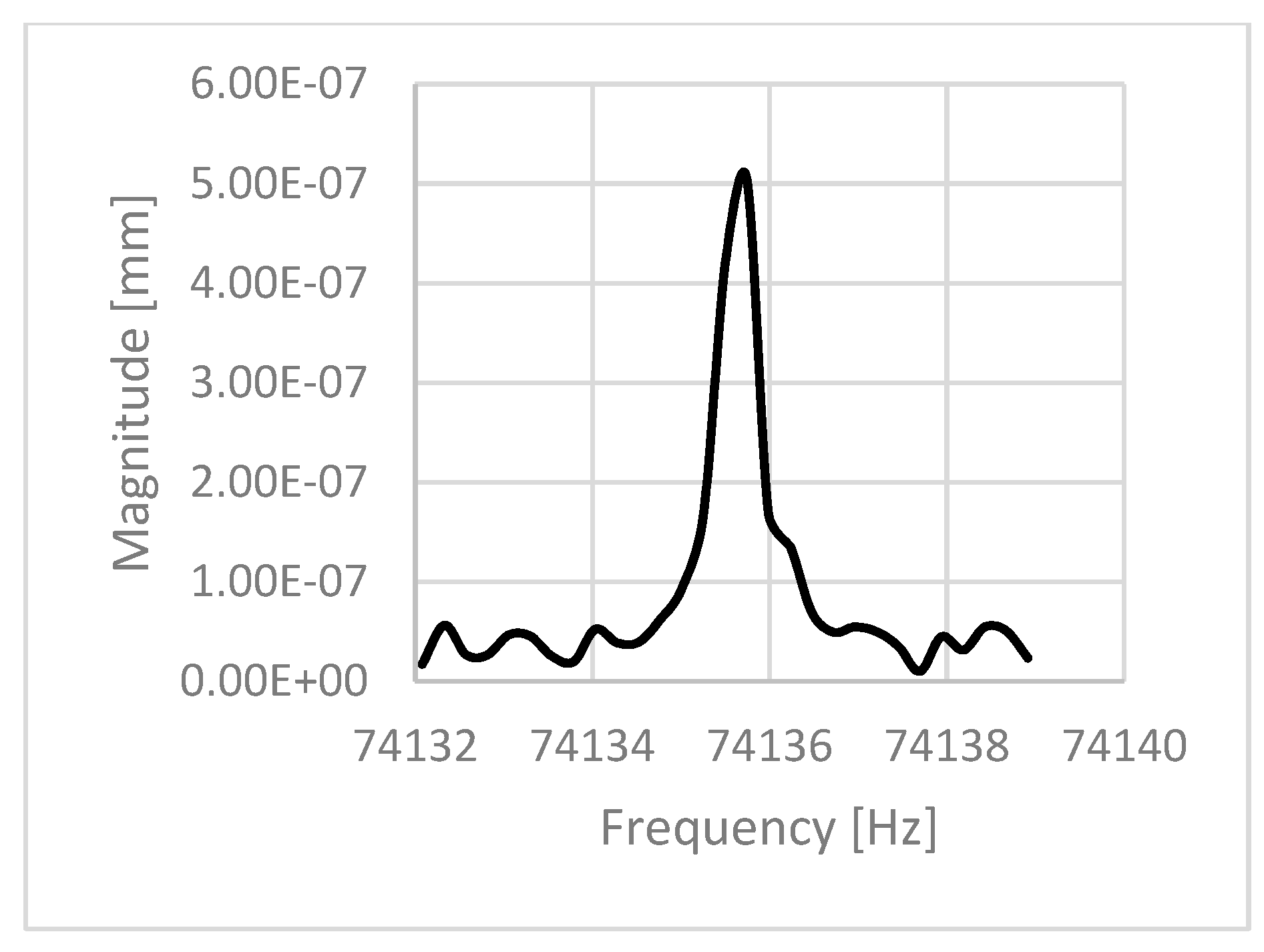
| 0.53 | 1 | 77,417 | 74,135.7 | 0.958 | 150,000 |
| 1.03 | 2.9 | 59,444 | 74,053.7 | 1.246 | 74,000 |
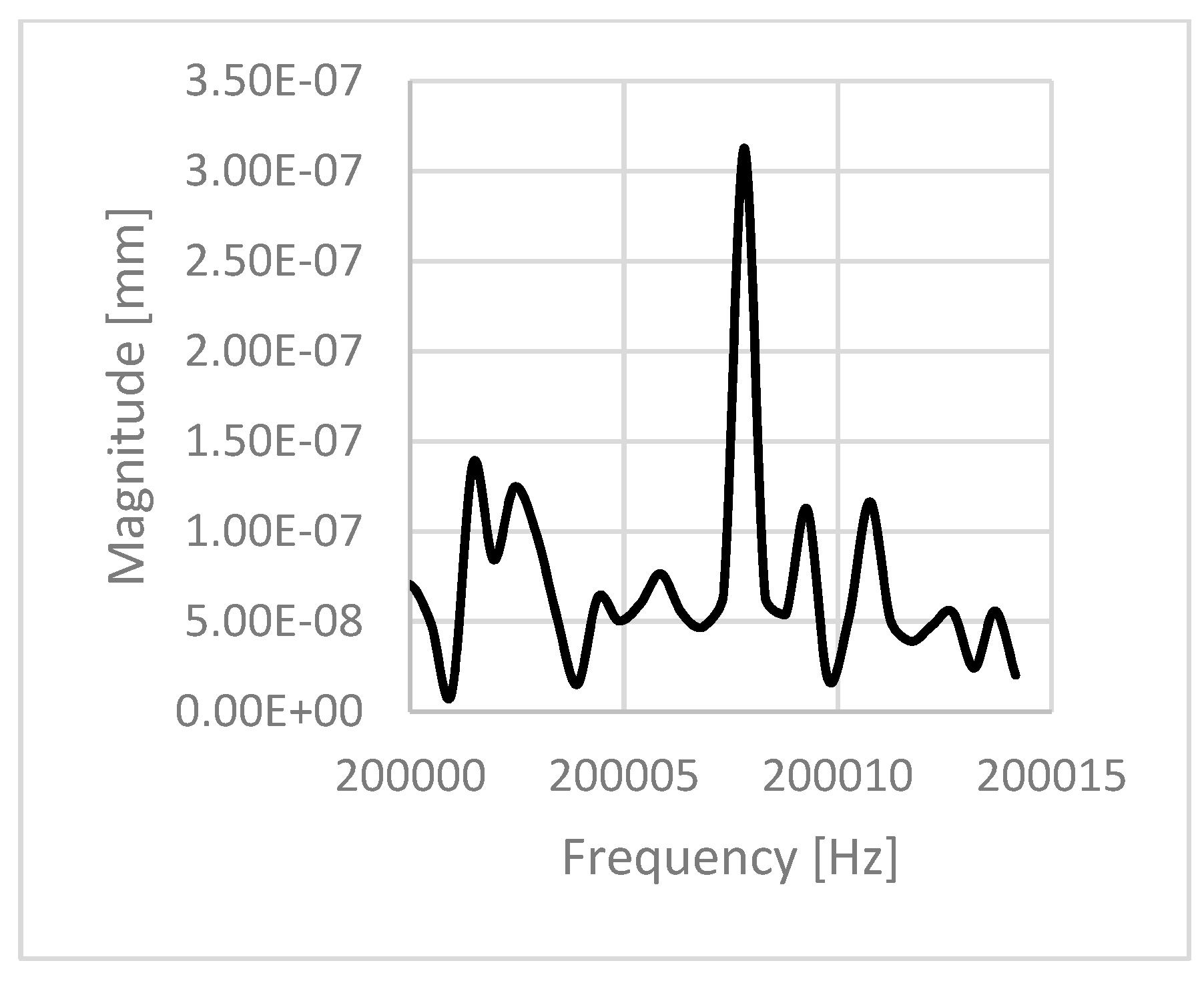
| 0.53 | 2.9 | 224,510 | 200,007.8 | 0.891 | 554,100 |
| 0.43 | 2.9 | 341,075 | 304,755.9 | 0.894 | 400,000 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sone, J.; Murakami, M.; Tatami, A. Fundamental Study for a Graphite-Based Microelectromechanical System. Micromachines 2018, 9, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020064
Sone J, Murakami M, Tatami A. Fundamental Study for a Graphite-Based Microelectromechanical System. Micromachines. 2018; 9(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020064
Chicago/Turabian StyleSone, Junji, Mutsuaki Murakami, and Atsushi Tatami. 2018. "Fundamental Study for a Graphite-Based Microelectromechanical System" Micromachines 9, no. 2: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020064
APA StyleSone, J., Murakami, M., & Tatami, A. (2018). Fundamental Study for a Graphite-Based Microelectromechanical System. Micromachines, 9(2), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020064





