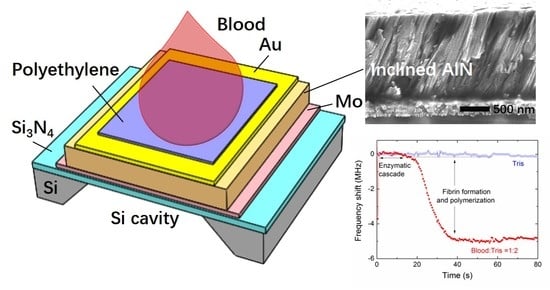
Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Resonator Based on Inclined c-Axis AlN Film for Monitoring of Human Hemostatic Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Studies
2.1. Device Structure
2.2. Device Fabrication
2.3. Measurement Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the AlN Film with Inclined c-Axis
3.2. Electro-Acoustic Response in Air, Water and Blood
3.3. Viscosity Characterization of Shear Resonance
3.4. Blood Coagulation Monitoring
3.5. Comparison of the FBAR Sensor and a Standard Coagulometer
3.6. Application for Warfarin Therapy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cuker, A.; Siegal, D.M.; Crowther, M.A.; Garcia, D.A. Laboratory measurement of the anticoagulant activity of the non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, P.M.; Martins, M.A.P.; Castilho, R.O. Review on mechanisms and interactions in concomitant use of herbs and warfarin therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganter, M.T.; Hofer, C.K. Coagulation monitoring: Current techniques and clinical use of viscoelastic point-of-care coagulation devices. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.; Al, M.; Westwood, M.; Ramos, I.C.; Ryder, S.; Armstrong, N.; Misso, K.; Ross, J.; Severens, J.; Kleijnen, J. Viscoelastic point-of-care testing to assist with the diagnosis, management and monitoring of haemostasis: A systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, M.A.; Smith, S.A. Viscoelastic coagulation testing: Technology, applications, and limitations. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 40, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Penn, L.S.; Xi, J. Quartz crystal microbalance: Sensing cell-substrate adhesion and beyond. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, K.; Shiratori, S. Viscosity sensing by adjusting the interface of a small liquid droplet/silica composite layer on quartz crystal microbalance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38475–38480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, N.G.; Pandey, S.N.; Sahay, P.P. Sn-doped in2O3 nanocrystalline thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis: Microstructural, optical, electrical, and formaldehyde-sensing characteristics. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, R.S.; Efremov, V.; Cullen, S.M.; Killard, A.J. Measurement of the evolution of rigid and viscoelastic mass contributions from fibrin network formation during plasma coagulation using quartz crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 192, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, V.; Killard, A.J.; Byrne, B.; Lakshmanan, R.S. The modelling of blood coagulation using the quartz crystal microbalance. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Sinn, S.; Drechsel, H.; Ziegler, C.; Wendel, H.P.; Northoff, H.; Gehring, F.K. Investigation of prothrombin time in human whole-blood samples with a quartz crystal biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Wendel, H.P.; Schmidt, K.; Langer, E.; Körber, M.K.; Faul, O.; Northoff, H.; von Heymann, C.; Gehring, F.K. QCM-D surpassing clinical standard for the dose administration of new oral anticoagulant in the patient of coagulation disorders. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.J.; Li, D.H.; Xu, Y. Hydrogen sensor based on Pd-functionalized film bulk acoustic resonator. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 159, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, F.; Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Functionalized nanoporous TiO2 fibers on quartz crystal microbalance platform for formaldehyde sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 171–172, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, Q.X.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.H.; Liu, Y.J. Highly sensitive ZnO thin film bulk acoustic resonator for hydrogen detection. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingjing, W.; Da, Z.; Ke, W.; Weiwei, H. The detection of formaldehyde using microelectromechanical acoustic resonator with multiwalled carbon nanotubes-polyethyleneimine composite coating. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 015003. [Google Scholar]
- Flewitt, A.J.; Luo, J.K.; Fu, Y.Q.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Du, X.Y.; Lu, J.R.; Zhao, X.B.; Iborra, E.; Ramos, M.; Milne, W.I. ZnO based SAW and FBAR devices for bio-sensing applications. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 2015, 222, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Kong, E.S.-W.; Zhang, Y. High Potential Columnar Nanocrystalline AlN Films Deposited by RF Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Nano-Micro Lett. 2012, 4, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W. Label-free immunosensor based on micromachined bulk acoustic resonator for the detection of trace pesticide residues. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 190, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, P. Film bulk acoustic biosensor for detection of trace pesticide residues in agricultural products. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ashley, G.M.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Jin, H.; Luo, J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Lu, J.R. Protein functionalized ZnO thin film bulk acoustic resonator as an odorant biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 163, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Zhao, H.; Kim, E.S.; Zhang, H.; Yuc, H.; Hu, X. Piezoelectric microelectromechanical resonant sensors for chemical and biological detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Yu, W. Film bulk acoustic formaldehyde sensor with polyethyleneimine-modified single-wall carbon nanotubes as sensitive layer. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 266, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingqvist, G.; Bjurstroöm, J.; Liljeholm, L.; Yantchev, V.; Katardjiev, I. Shear mode AlN thin film electro-acoustic resonant sensor operation in viscous media. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 123, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J. Lateral field excited film bulk acoustic resonator for detection of protein–ligand interactions. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. A pure shear mode ZnO film resonator for the detection of organophosphorous pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 171, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiji Kanazawa, K.; Gordon Ii, J.G. The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with liquid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1985, 175, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Gan, Y.; Sun, X.; Jin, Y. High sensitive self-assembled monolayer modified solid mounted resonator for organophosphate vapor detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4365–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Albers, W.M.; Tuppurainen, J.; Link, M.; Gabl, R.; Wersing, W.; Schreiter, M. Shear mode FBARs as highly sensitive liquid biosensors. Sens. Actuators A 2006, 128, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirschl, M.; Rantala, A.; Tukkiniemi, K.; Auer, S.; Hellgren, A.C.; Pitzer, D.; Schreiter, M.; Vikholm-Lundin, I. CMOS-integrated film bulk acoustic resonators for label-free biosensing. Sensors 2010, 10, 4180–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingqvist, G.; Bjurstroöm, J.; Hellgren, A.C.; Katardjiev, I. Immunosensor utilizing a shear mode thin film bulk acoustic sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 127, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Highly sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides by acetylcholinesterase-coated thin film bulk acoustic resonator mass-loading sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.C.; Appel, J.; Chae, J. Real-Time Monitoring of Whole Blood Coagulation Using a Microfabricated Contour-Mode Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2012, 21, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.-F.; Wang, Q.-M. Viscosity sensor using ZnO and AlN thin film bulk acoustic resonators with tilted polar c-axis orientations. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 094511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, W. ZnO Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator for the Kinetics Study of Human Blood Coagulation. Sensors 2017, 17, 1015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. Real-time monitoring of human blood clotting using a lateral excited film bulk acoustic resonator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q. Micro-electromechanical film bulk acoustic sensor for plasma and whole blood coagulation monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katardjiev, I.; Yantchev, V. Recent developments in thin film electro-acoustic technology for biosensor applications. Vacuum 2012, 86, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.; Weber, J.; Schreiter, M.; Wersing, W.; Elmazria, O.; Alnot, P. Sensing characteristics of high-frequency shear mode resonators in glycerol solutions. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 121, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chen, D.; Hongfei, W.; Guo, Q.; Yu, W. Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Viscosity Sensor for Blood Coagulation Monitoring in Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8099–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.M.; Lien, W.C.; Felmetsger, V.V.; Hopcroft, M.A.; Senesky, D.G.; Pisano, A.P. AlN thin films grown on epitaxial 3C-SiC (100) for piezoelectric resonant devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 141907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.; Schreiter, M.; Weber, J.; Gabl, R.; Pitzer, D.; Primig, R.; Wersing, W.; Assouar, M.B.; Elmazria, O. C-axis inclined ZnO films for shear-wave transducers deposited by reactive sputtering using an additional blind. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2006, 24, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Northoff, H.; Gehring, F.K. QCM-D providing new horizon in the domain of sensitivity range and information for haemostasis of human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Andersson, J.; Sellborn, A.; Berglin, M.; Nilsson, B.; Elwing, H. Quartz crystal microbalance-with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) for real time measurements of blood coagulation density and immune complement activation on artificial surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandey, H.L.; Cernosek, R.W.; Lee, W.E.; Ondrovic, L.E. Blood rheological characterization using the thickness-shear mode resonator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Stephanou, P.J.; Pisano, A.P. Piezoelectric aluminum nitride vibrating contour-mode MEMS resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Yantchev, V.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Pisano, A.P. Micromachined one-port aluminum nitride lamb wave resonators utilizing the lowest-order symmetric mode. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J.; Frye, G.C.; Ricco, A.J.; Senturia, S.D. Effect of surface roughness on the response of thickness-shear mode resonators in liquids. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 2910–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poller, L.; Keown, M.; Chauhan, N.; van den Besselaar, A.M.H.P.; Tripodi, A.; Shiach, C.; Jespersen, J. European Concerted Action on Anticoagulation. A multicentre calibration study of WHO international reference preparations for thromboplastin, rabbit (RBT/90) and human (rTF/95). J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, O.; Ermek, E.; Kilinc, N.; Bulut, S.; Baris, I.; Kavakli, I.H.; Yaralioglu, G.G.; Urey, H. A cartridge based sensor array platform for multiple coagulation measurements from plasma. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpelini, S.; Rhind, S.G.; Nascimento, B.; Tien, H.; Shek, P.N.; Peng, H.T.; Huang, H.; Pinto, R.; Speers, V.; Reis, M.; et al. Normal range values for thromboelastography in healthy adult volunteers. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsma, G.A. Hematology: Clinical Principles and Applications; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk, W.P.M.; Van Den Besselaar, A.M.H.P. International multicenter international sensitivity index (ISI) calibration of a new human tissue factor thromboplastin reagent derived from cultured human cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Electrode Geometry | Crystal Orientation | Field Intensity (V/m) * | Electromechanical Coupling | Mean Allan Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coplanar(lateral excited) | Normal c-axis | 1.73 | 0.32% | 5.39 × 10−8 |
| Sandwiched(thickness excited) | Inclined c-axis | 6.67 | 0.68% | 1.61 × 10−8 |
| Resonant Frequency (MHz) | Q Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare | Polyethylene-Coated | Bare | Polyethylene-Coated | |
| Shear mode | 1876.4 | 1868.3 | 276 | 263 |
| Longitudinal mode | 3163.3 | 3150.4 | 169 | 176 |
| Resonant Frequency (MHz) | Q Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Water | Blood | Air | Water | Blood | |
| Shear mode | 1868.3 | 1865.4 | 1863.1 | 263 | 203 | 129 |
| Longitudinal mode | 3150.4 | 3134.2 | -- | 176 | 21 | -- |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q. Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Resonator Based on Inclined c-Axis AlN Film for Monitoring of Human Hemostatic Parameters. Micromachines 2018, 9, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100501
Song S, Chen D, Wang H, Li C, Wang W, Yu W, Wang Y, Guo Q. Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Resonator Based on Inclined c-Axis AlN Film for Monitoring of Human Hemostatic Parameters. Micromachines. 2018; 9(10):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100501
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Shuren, Da Chen, Hongfei Wang, Chaohui Li, Wei Wang, Wangli Yu, Yanyan Wang, and Qiuquan Guo. 2018. "Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Resonator Based on Inclined c-Axis AlN Film for Monitoring of Human Hemostatic Parameters" Micromachines 9, no. 10: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100501
APA StyleSong, S., Chen, D., Wang, H., Li, C., Wang, W., Yu, W., Wang, Y., & Guo, Q. (2018). Shear Mode Bulk Acoustic Resonator Based on Inclined c-Axis AlN Film for Monitoring of Human Hemostatic Parameters. Micromachines, 9(10), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100501