Analysis of Liquid–Liquid Droplets Fission and Encapsulation in Single/Two Layer Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by Xurographic Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
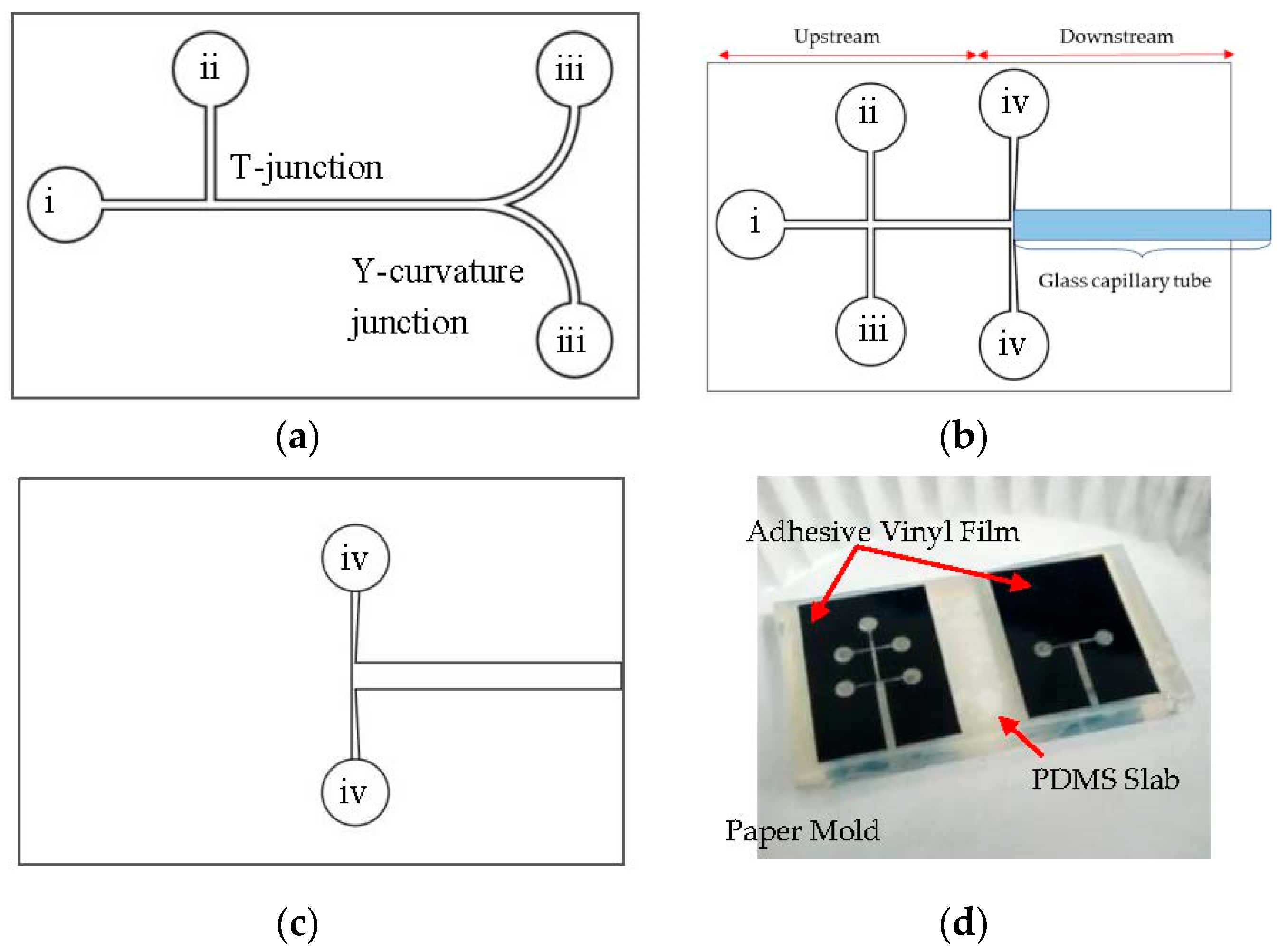
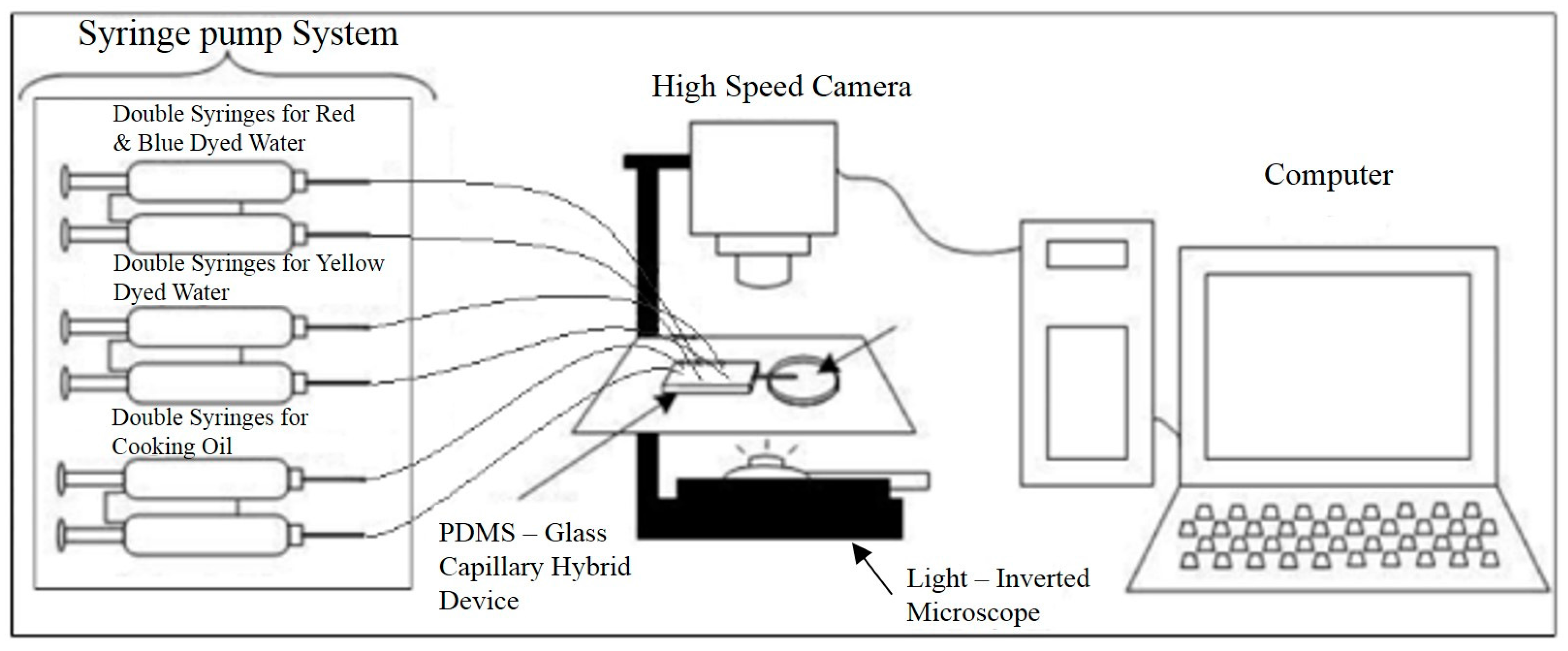
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication Analysis
3.1.1. Cutter Plotter Optimization
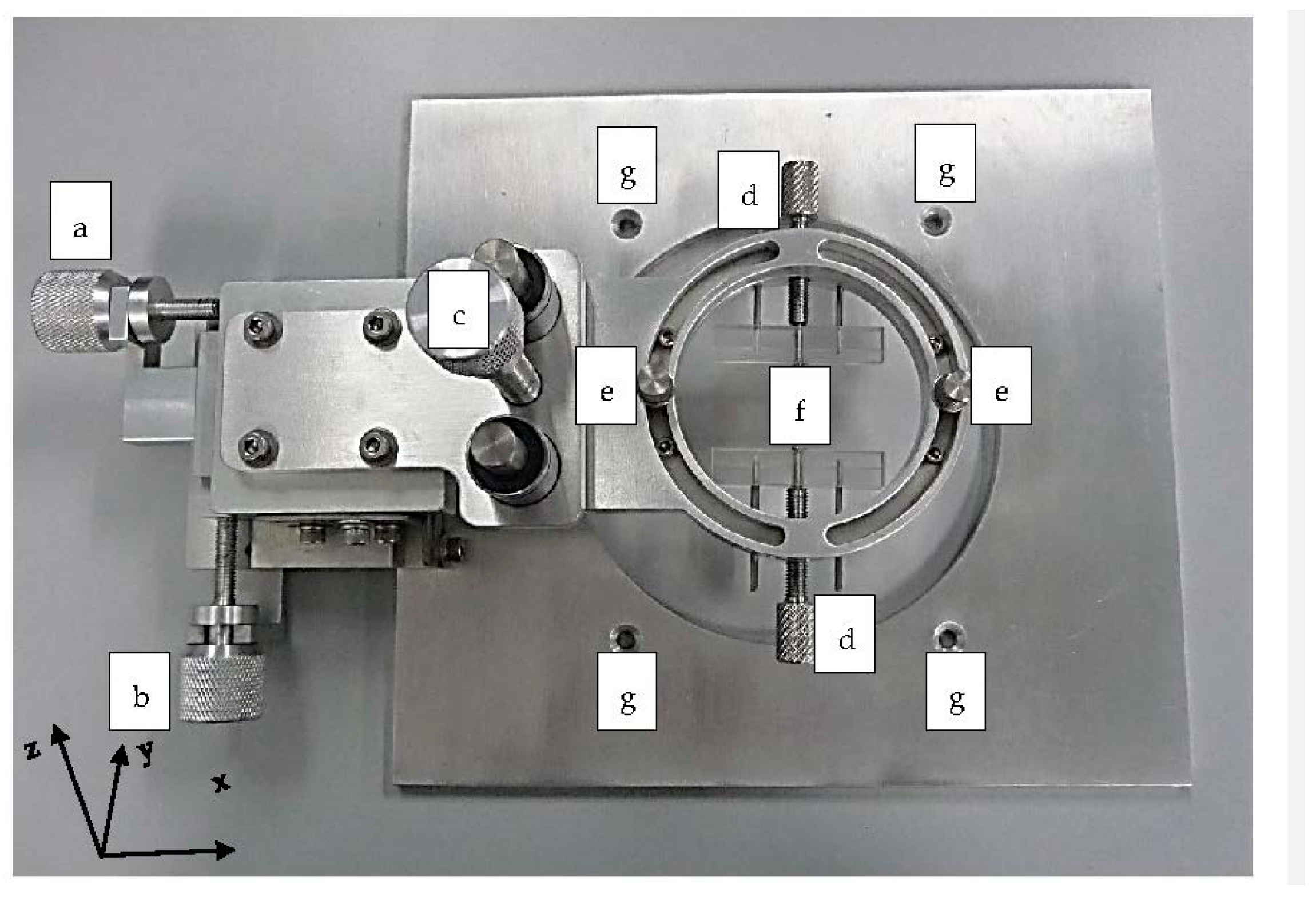
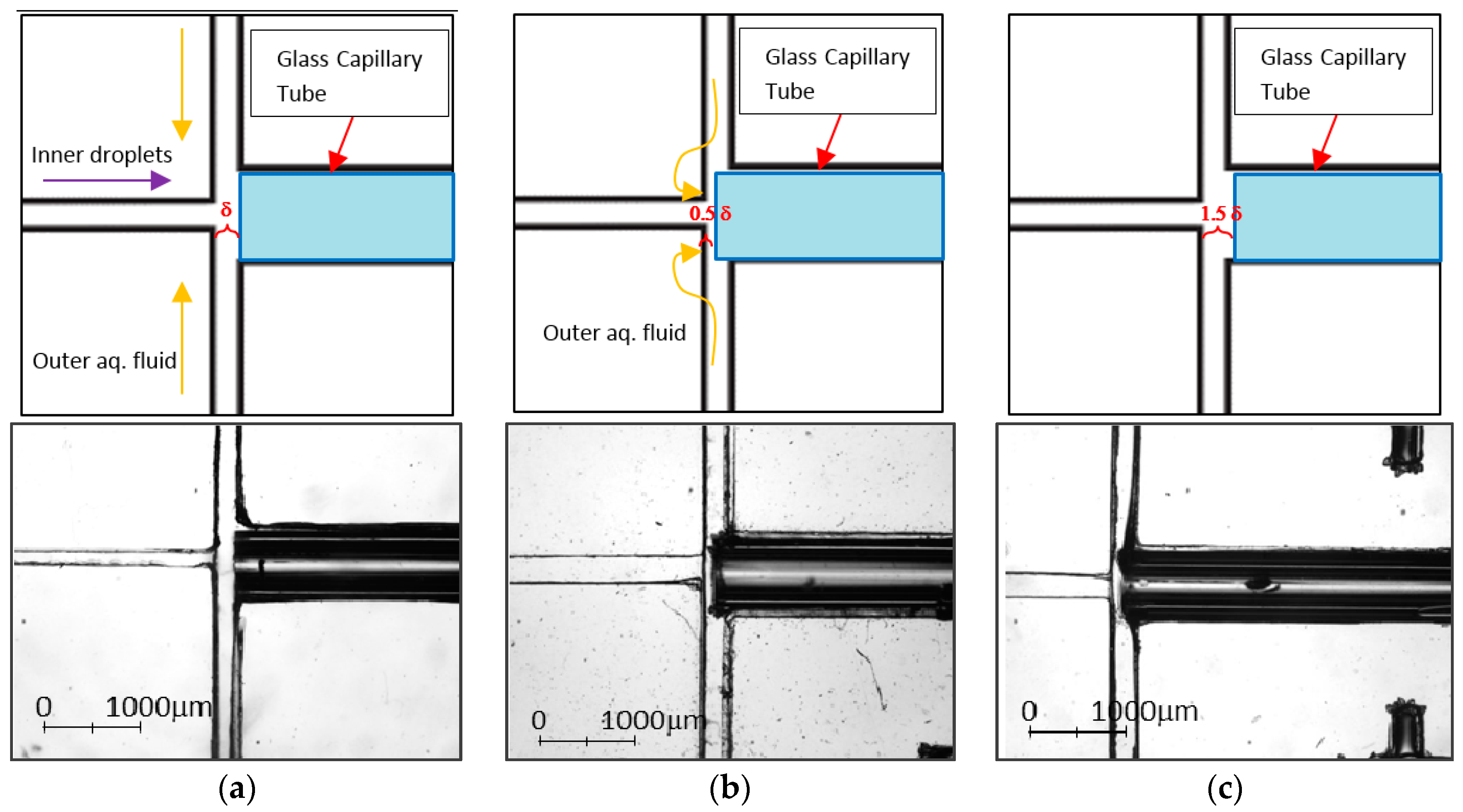
3.1.2. PDMS Aligner and Delta Analysis Results
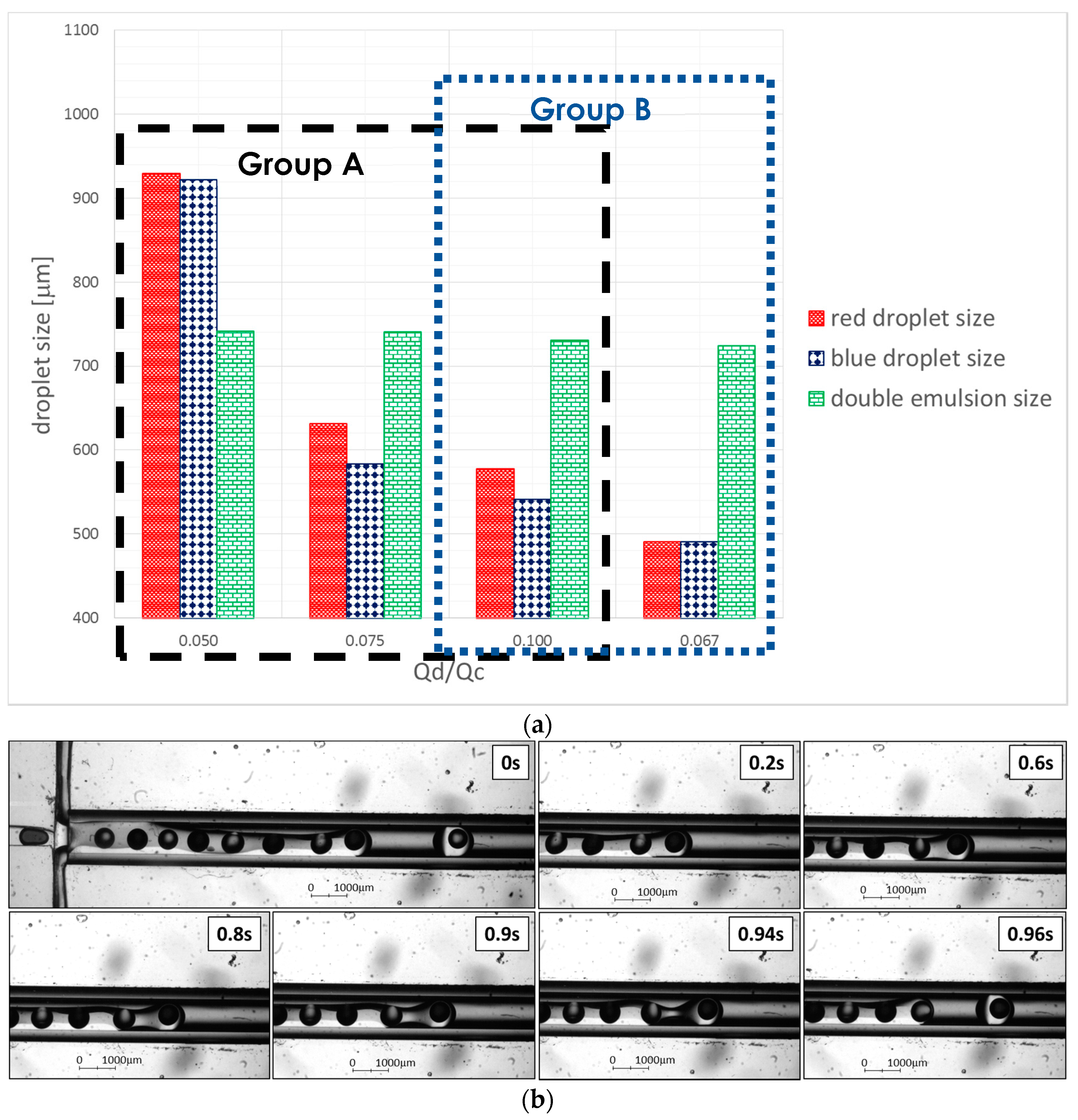
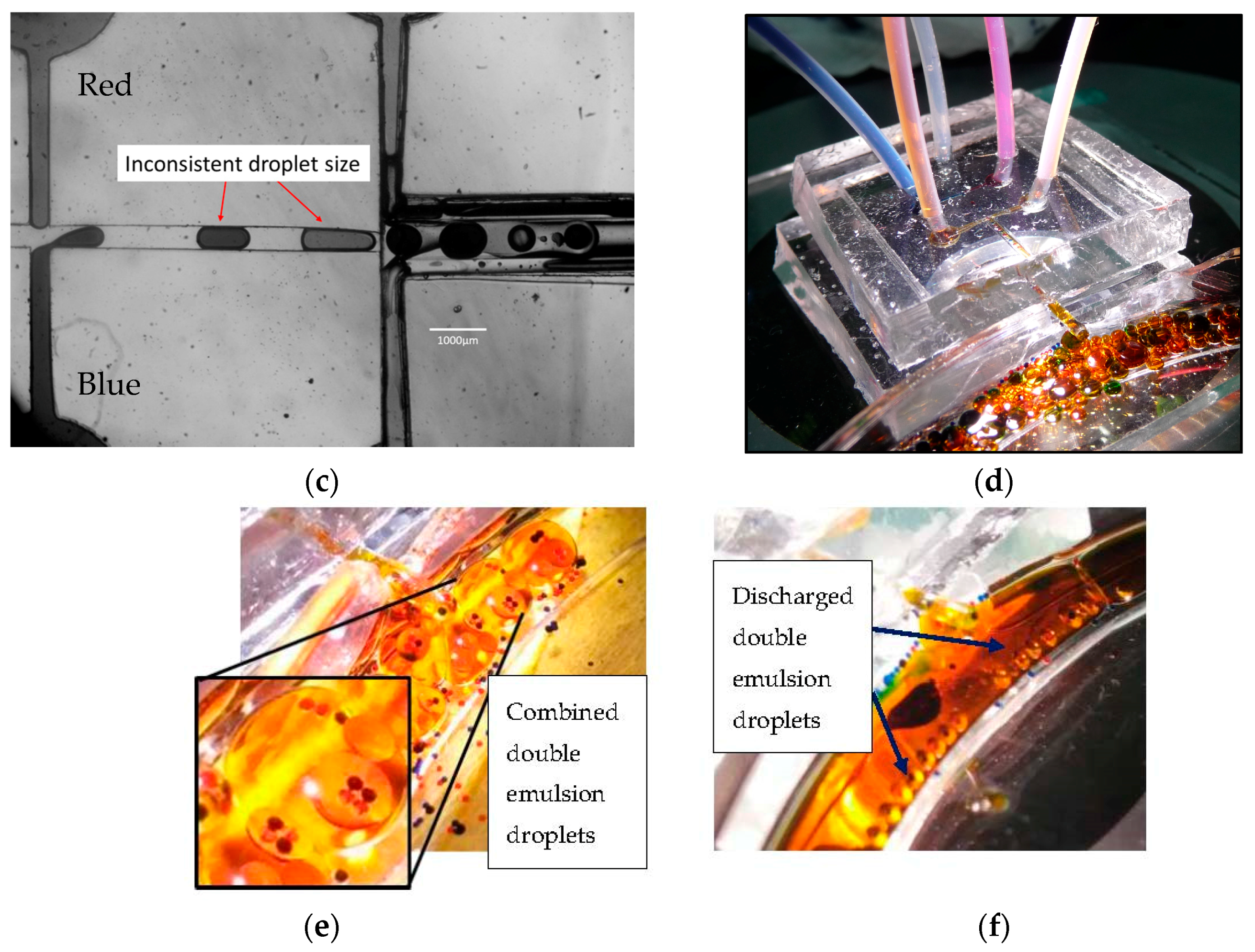
3.2. Experimental Results—Droplet Encapsulation
Relationship of Droplet Size with Flow Ratio, Qdisperse/Qcontinuous
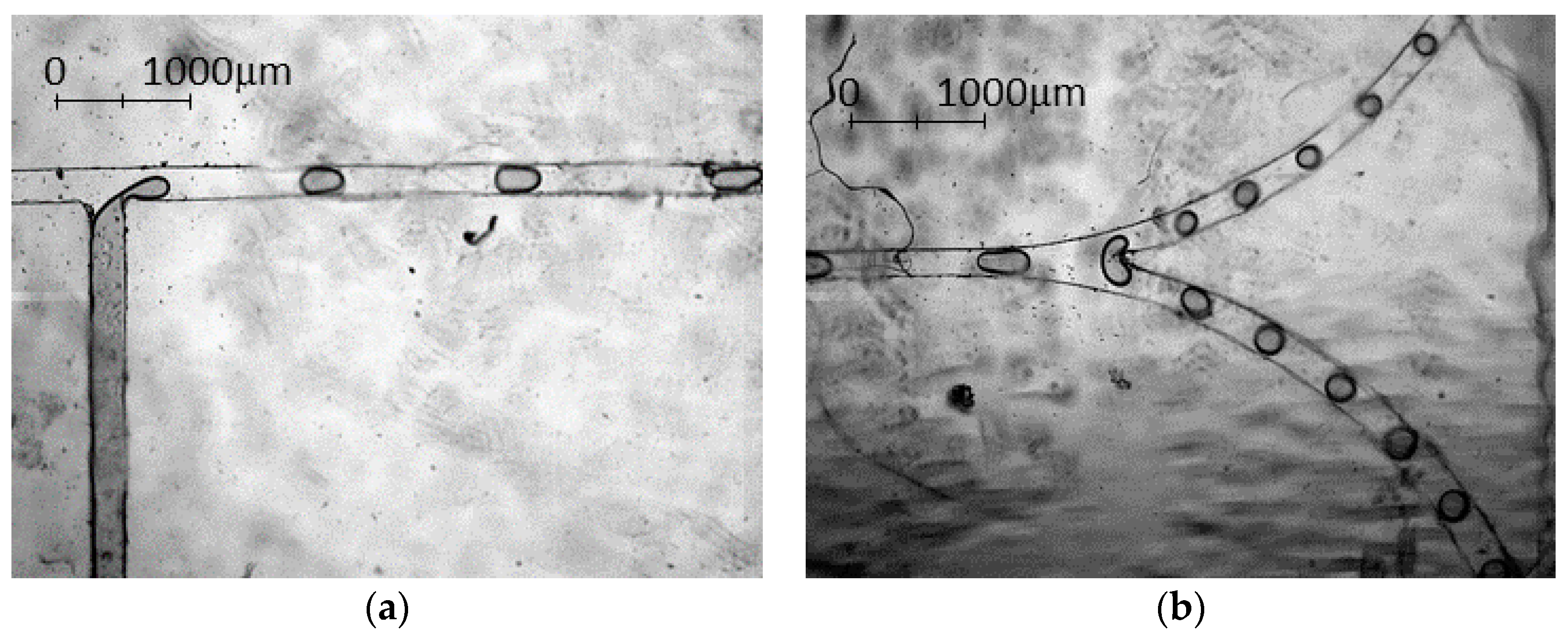
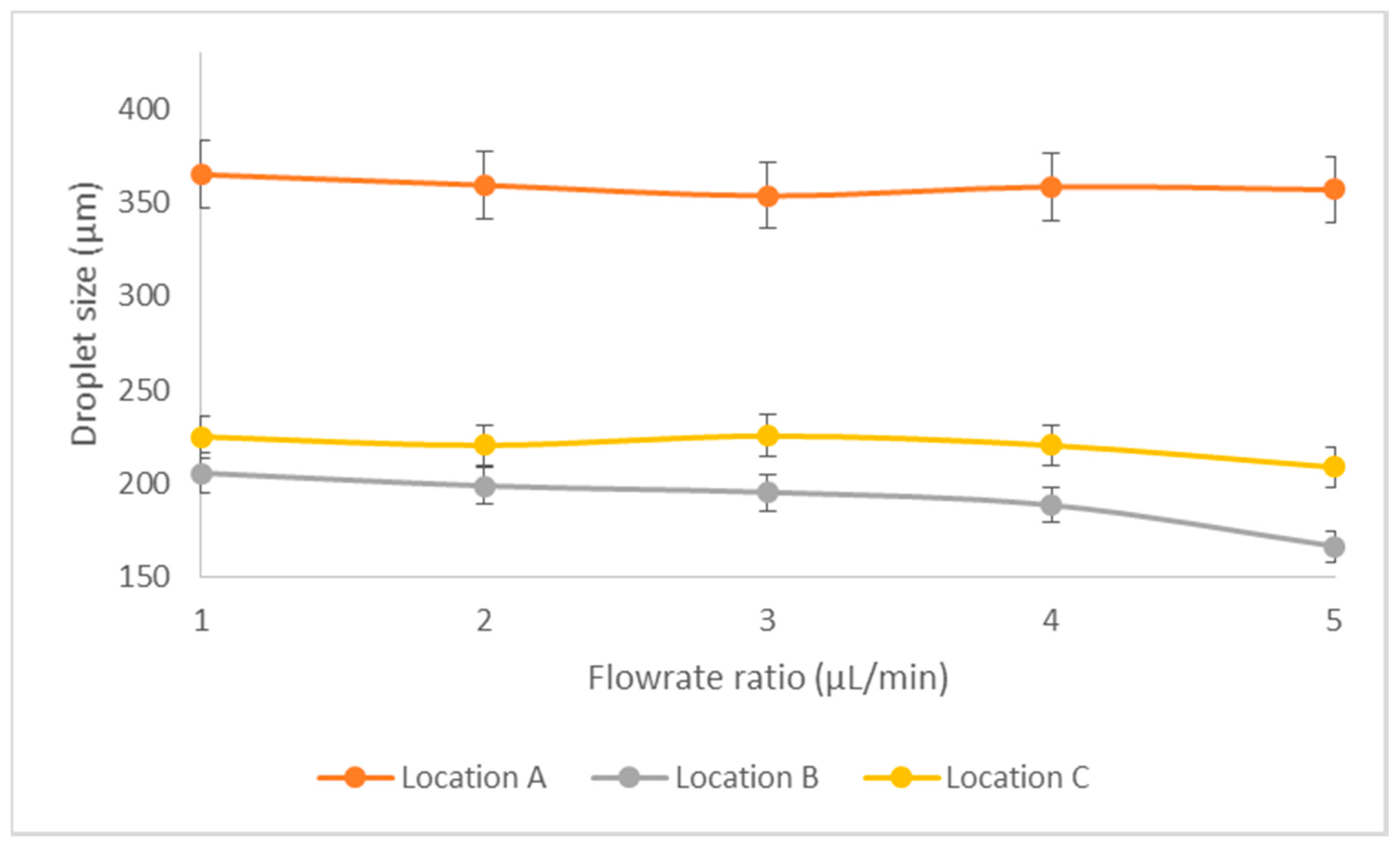
3.3. Experimental Results—Droplet Fission
Effect of Flow Ratio
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chabert, M.; Dorfman, K.D.; Viovy, J.-L. Droplet fusion by alternating current (AC) field electrocoalescence in microchannels. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, D.R.; Anna, S.L.; Weitz, D.A.; Stone, H.A. Geometrically mediated breakup of drops in microfluidic devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 054503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Tice, J.D.; Ismagilov, R.F. A microfluidic system for controlling reaction networks in time. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 42, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazutis, L.; Gilbert, J.; Ung, W.L.; Weitz, D.A.; Griffiths, A.D.; Heyman, J.A. Single-cell analysis and sorting using droplet-based microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 870–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Garstecki, P.; Weibel, D.B.; Whitesides, G.M. An axisymmetric flow-focusing microfluidic device. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.S.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Amstad, E.; Fan, J.; Kim, S.H.; Romanowsky, M.; Shum, H.C.; Sun, B.; Utada, A.S.; Windbergs, M.; et al. 25th anniversary article: Double emulsion templated solid microcapsules: Mechanics and controlled release. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenckhan, W. Generation of superstable, monodisperse microbubbles using a pH-driven assembly of surface-active particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 5245–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, P.; Manz, A.; Zhang, Y. Microdroplet Technology: Principles and Emerging Applications in Biology and Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.T.; Ma, G.H.; Qiu, W.; Su, Z.G. W/O/W double emulsion technique using ethyl acetate as organic solvent: Effects of its diffusion rate on the characteristics of microparticles. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Wu, J.; Yeung, K.W.K.; To, M.K.T.; Shum, H.C.; Wang, L. Microfluidic fabrication of polymeric core-shell microspheres for controlled release applications. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okushima, S.; Nisisako, T.; Torii, T.; Higuchi, T. Controlled production of monodisperse double emulsions by two-step droplet breakup in microfluidic devices. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9905–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, N.-N.; Meng, Z.-J.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Mou, C.-L.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.-Y. Simple and cheap microfluidic devices for the preparation of monodisperse emulsions. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, B. A double emulsion-based, plastic-glass hybrid microfluidic platform for protein crystallization. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utada, A.S.; Lorenceau, E.; Link, D.R.; Kaplan, P.D.; Stone, H.A.; Weitz, D.A. Monodisperse double emulsions generated from a microcapillary device. Science 2005, 308, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.F. Chapter 1 Materials and fabrication techniques for nano- and microfluidic devices. In Microfluidics in Detection Science: Lab-on-a-Chip Technologies; Labeed, F.H., Fatoyinbo, H.O., Eds.; RSC Detection Science, Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Marty, F.; Rousseau, L.; Saadany, B.; Mercier, B.; Français, O.; Mita, Y.; Bourouina, T. Advanced etching of silicon based on deep reactive ion etching for silicon high aspect ratio microstructures and three-dimensional micro- and nanostructures. Microelectron. J. 2005, 36, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goral, V.N.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Petzold, O.N.; Faris, R.A.; Yuen, P.K. Hot embossing of plastic microfluidic devices using poly(dimethylsiloxane) molds. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, Groningen, The Netherlands, 3–7 October 2010; pp. 1214–1216.
- Weigl, B.H.; Bardell, R.; Schulte, T.; Battrell, F.; Hayenga, J. Design and rapid prototyping of thin-film laminate-based microfluidic devices. Biomed. Microdevices 2001, 3, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, U.M.; Marson, S.; Alcock, J.R. Micro-injection moulding of polymer microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeusz, D.A.; Boutté, R.W.; Andrade, J.D. Xurography: Rapid prototyping of microstructures using a cutting plotter. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.P.; de Segato, T.P.; Carrilho, E.; Lima, R.S.; Dossi, N.; Kamogawa, M.Y.; Gobbi, A.L.; Piazzetaf, M.H.; Piccin, E. Fabrication of glass microchannels by xurography for electrophoresis applications. Analyst 2013, 138, 1660–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomeusz, D.A.; Boutté, R.W.; Gale, B.K. Xurography: Microfluidic prototyping with a cutting plotter. In Lab on a Chip Technology: Fabrication and Microfluidics; Caister Academic Press: Poole, UK, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, A.R.; Weitz, D.A. High-order multiple emulsions formed in poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidics. Small 2009, 5, 2030–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shum, H.C. Breakup dynamics and dripping-to-jetting transition in a Newtonian/shear-thinning multiphase microsystem. Lab Chip 2014, 15, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, G.T.; Hlaus, T.; Bass, K.J.; Seelhammer, T.G.; Culbertson, C.T. Sol-gel modified poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices with high electroosmotic mobilities and hydrophilic channel wall characteristics. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Datta, A.; Berg, J.M.; Gangopadhyay, S. Studies on surface wettability of poly(dimethyl) siloxane (PDMS) and glass under oxygen-plasma treatment and correlation with bond strength. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.; Faustino, V.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Pinho, D.; Garcia, V.; Miranda, J.M.; Lima, R. A rapid and low-cost nonlithographic method to fabricate biomedical microdevices for blood flow analysis. Micromachines 2015, 6, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.K.; Tsai, S.S.H.; Wan, J.; Stone, H.A. Dripping and jetting in microfluidic multiphase flows applied to particle and fiber synthesis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garstecki, P.; Fuerstman, M.J.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction-scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Koh, K.S. Droplet fission in non-Newtonian multiphase system using bilayer bifurcated microchannel. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 5th Micro/Nanoscale Heat and Mass Transfer International Conference (MNHMT-16), Singapore, 4–6 January 2016.
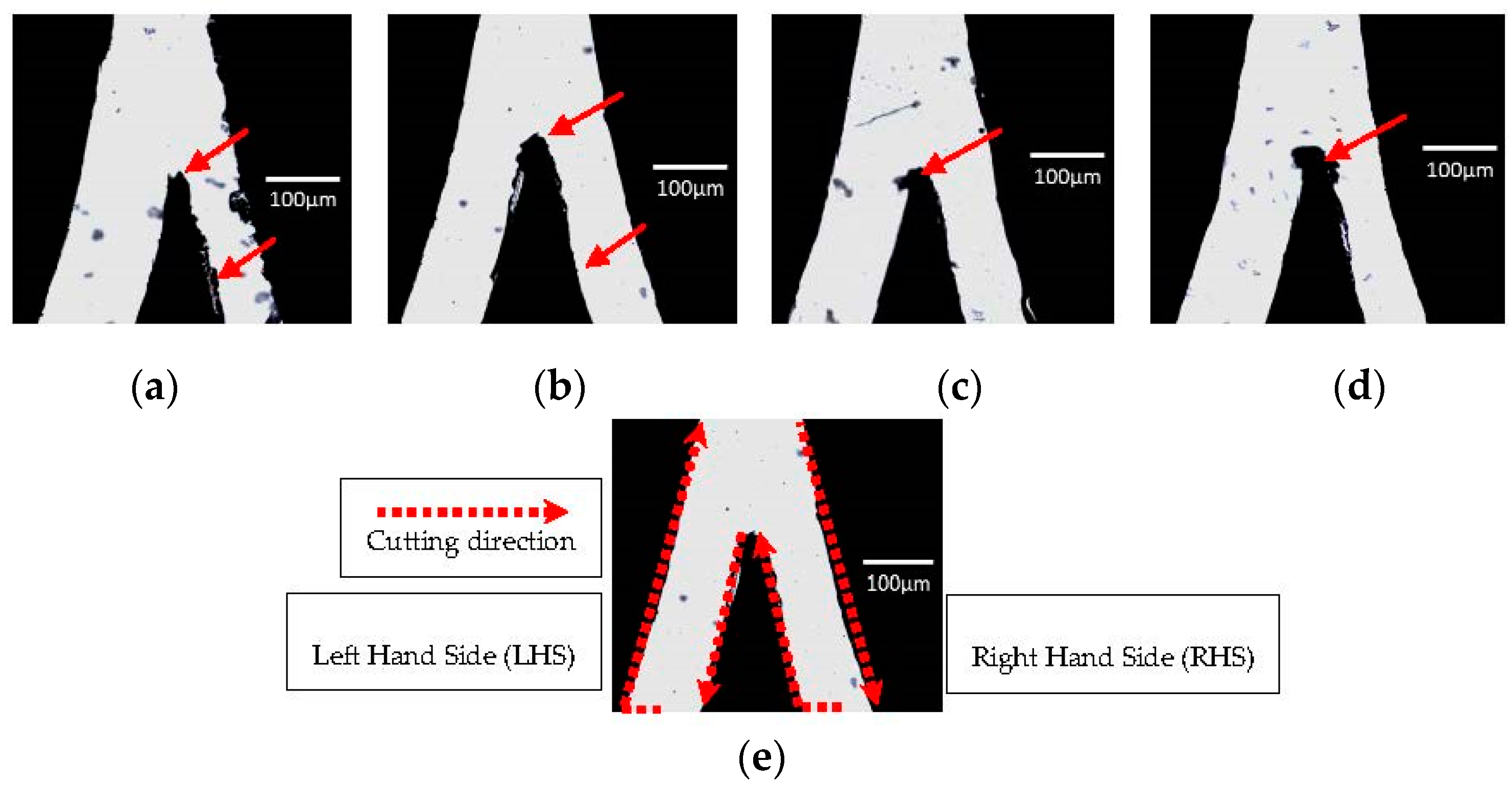
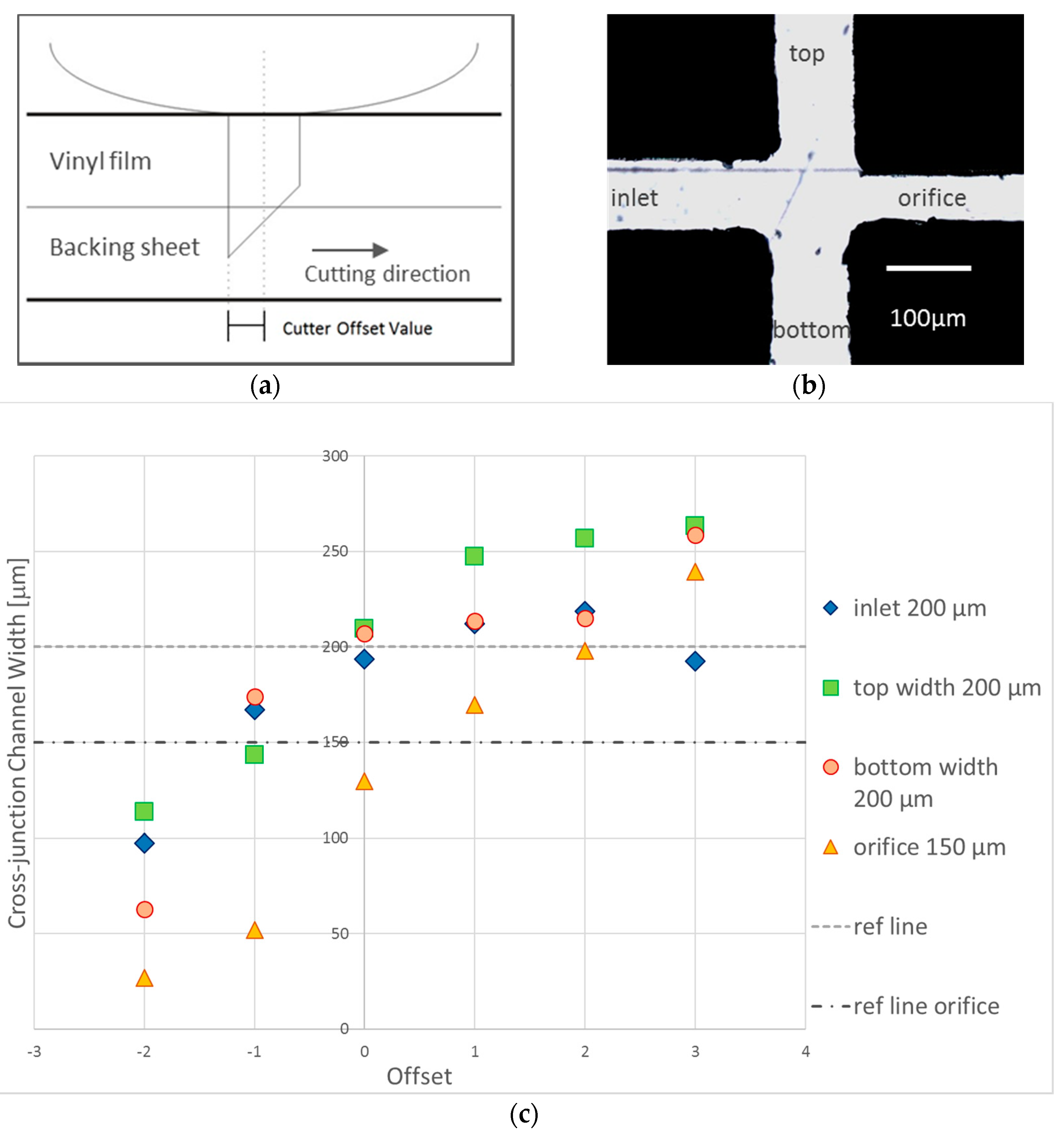
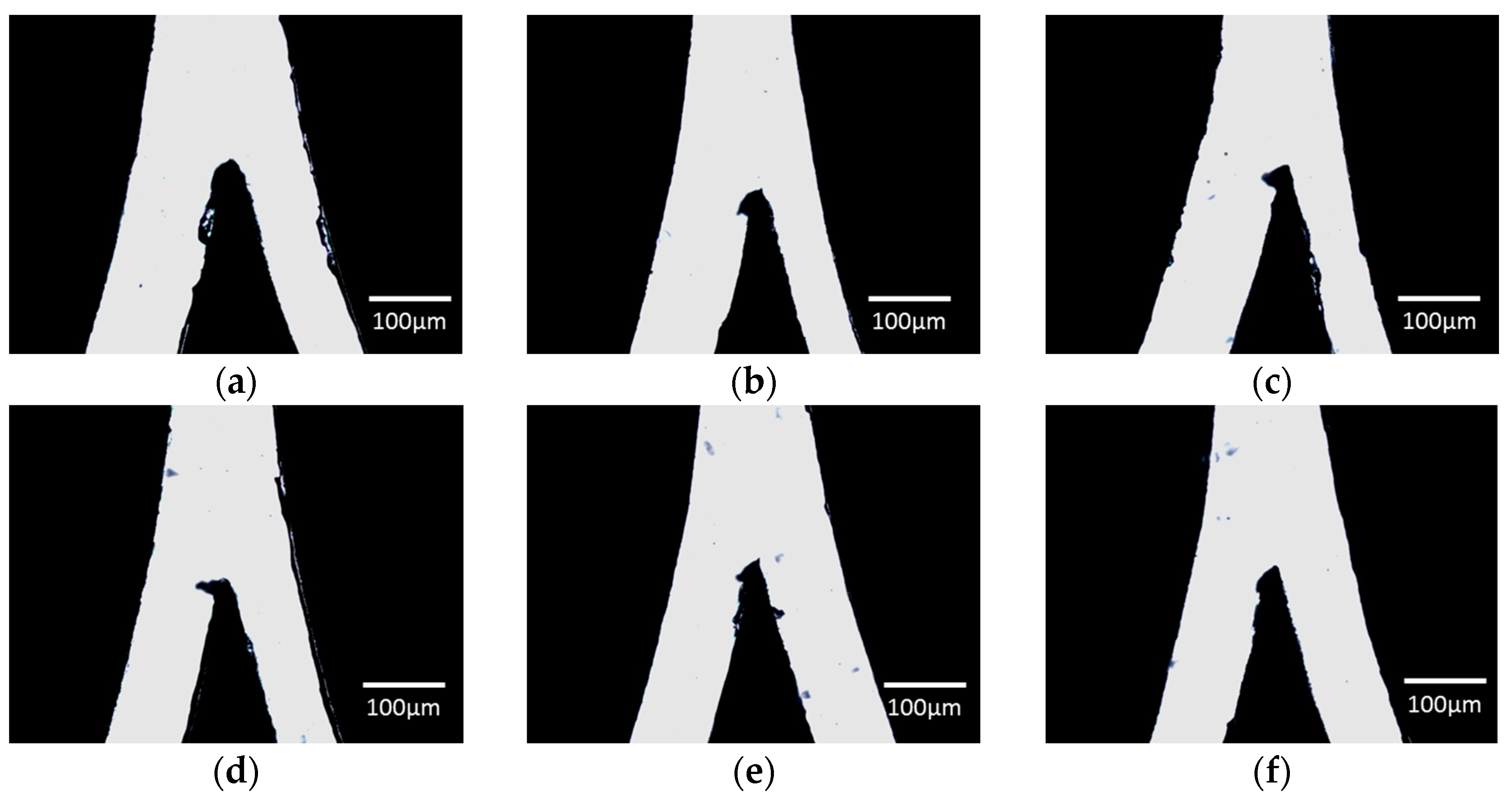
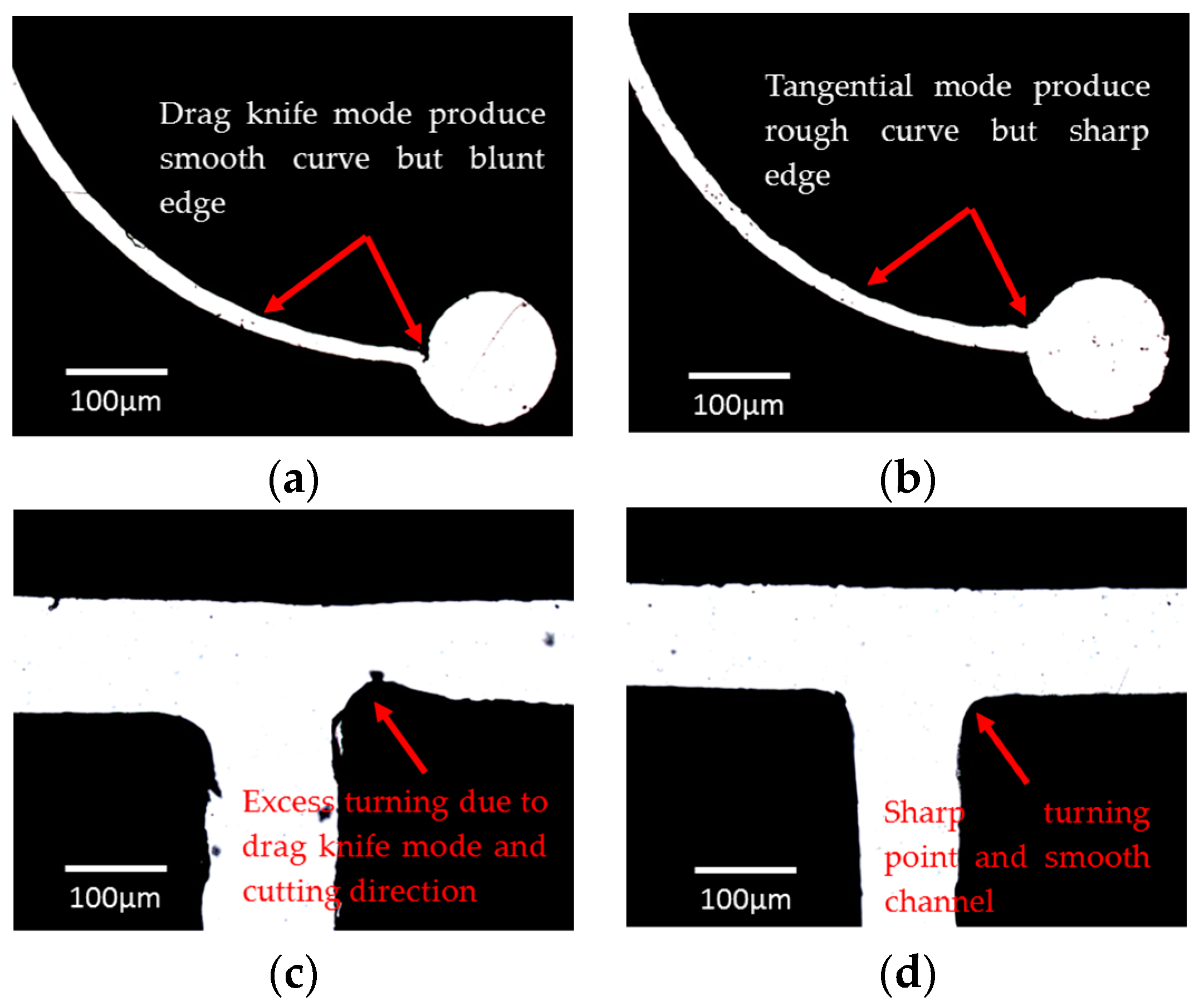

| Cutting Force | LHS Channel Width (μm) 1 | Error (%) | RHS Channel Width (μm) 1 | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 265.01 | 6.0 | 177.79 | 28.9 |
| 15 | 240.97 | 3.6 | 201.16 | 19.5 |
| 14 | 231.10 | 7.6 | 184.69 | 26.1 |
| 13 | 250.60 | 0.2 | 202.07 | 19.1 |
| 12 | 240.52 | 3.8 | 218.70 | 12.5 |
| 11 | 229.59 | 8.2 | 198.30 | 20.7 |
| 10 | 240.15 | 4.0 | 200.71 | 19.7 |
| 5 | 288.45 | 15.4 | 154.01 | 38.4 |
| Position | Default Channel Width (µm) | Channel Width ± Precision (µm, Aligner) | Error Percentage (%, Aligner) | Channel Width (µm, Manual) | Error Percentage (%, Manual) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 151 | 151.13 ± 1.13 | 0.75 | 151.88 ± 1.13 | 0.72 |
| B | 310 | 309.60 ± 3.37 | 1.09 | 302.12 ± 1.63 | 2.34 |
| C | 310 | 310.28 ± 3.00 | 0.97 | 302.68 ± 1.39 | 2.83 |
| Group | Flowrate Ratio (μL/min) | Manipulated Flowrate |
|---|---|---|
| Group A | 1:2:40 | Middle phase—continuous cooking oil |
| 1:4:40 | ||
| 1:6:40 | ||
| Group B | 1:6:40 | Outer aqueous phase—continuous yellow dyed water |
| 1:6:60 |
| Group | Flowrate Ratio (µL/min) | Inner (Red) Droplets CV (%) | Inner (Blue) Droplets CV (%) | Double Emulsion CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 1:2:40 | 17.3 | 20.1 | 10.5 |
| 1:4:40 | 8.0 | 9.7 | 5.6 | |
| 1:6:40 | 9.9 | 13.9 | 6.7 | |
| Group B | 1:6:40 | 9.9 | 13.9 | 6.7 |
| 1:6:60 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 9.8 |
| Group | Flowrate Ratio (µL/min) | Percent of 2 Distinct Droplets Encapsulation (1R1B) | Percent of 2 Similar Droplets Encapsulation (2R or 2B) | Percent of Single Droplet Encapsulation (1R or 1B) | % of Zero Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 1:2:40 | 44.2 | 4.7 | 51.2 | - |
| 1:4:40 | 19.1 | 5.6 | 69.7 | 5.6 | |
| 1:6:40 | 35.0 | 4.0 | 61.0 | - | |
| Group B | 1:6:40 | 35.0 | 4.0 | 61.0 | - |
| 1:6:60 | 49.6 | 11.9 | 38.5 | 0.6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, C.N.; Koh, K.S.; Ren, Y.; Chin, J.K.; Shi, Y.; Yan, Y. Analysis of Liquid–Liquid Droplets Fission and Encapsulation in Single/Two Layer Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by Xurographic Method. Micromachines 2017, 8, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020049
Lim CN, Koh KS, Ren Y, Chin JK, Shi Y, Yan Y. Analysis of Liquid–Liquid Droplets Fission and Encapsulation in Single/Two Layer Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by Xurographic Method. Micromachines. 2017; 8(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Chang Nong, Kai Seng Koh, Yong Ren, Jit Kai Chin, Yong Shi, and Yuying Yan. 2017. "Analysis of Liquid–Liquid Droplets Fission and Encapsulation in Single/Two Layer Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by Xurographic Method" Micromachines 8, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020049
APA StyleLim, C. N., Koh, K. S., Ren, Y., Chin, J. K., Shi, Y., & Yan, Y. (2017). Analysis of Liquid–Liquid Droplets Fission and Encapsulation in Single/Two Layer Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by Xurographic Method. Micromachines, 8(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020049





