Multiparameter Microwave Characterization and Probing of Ultralow Glucose Concentration Using a Microfabricated Biochip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
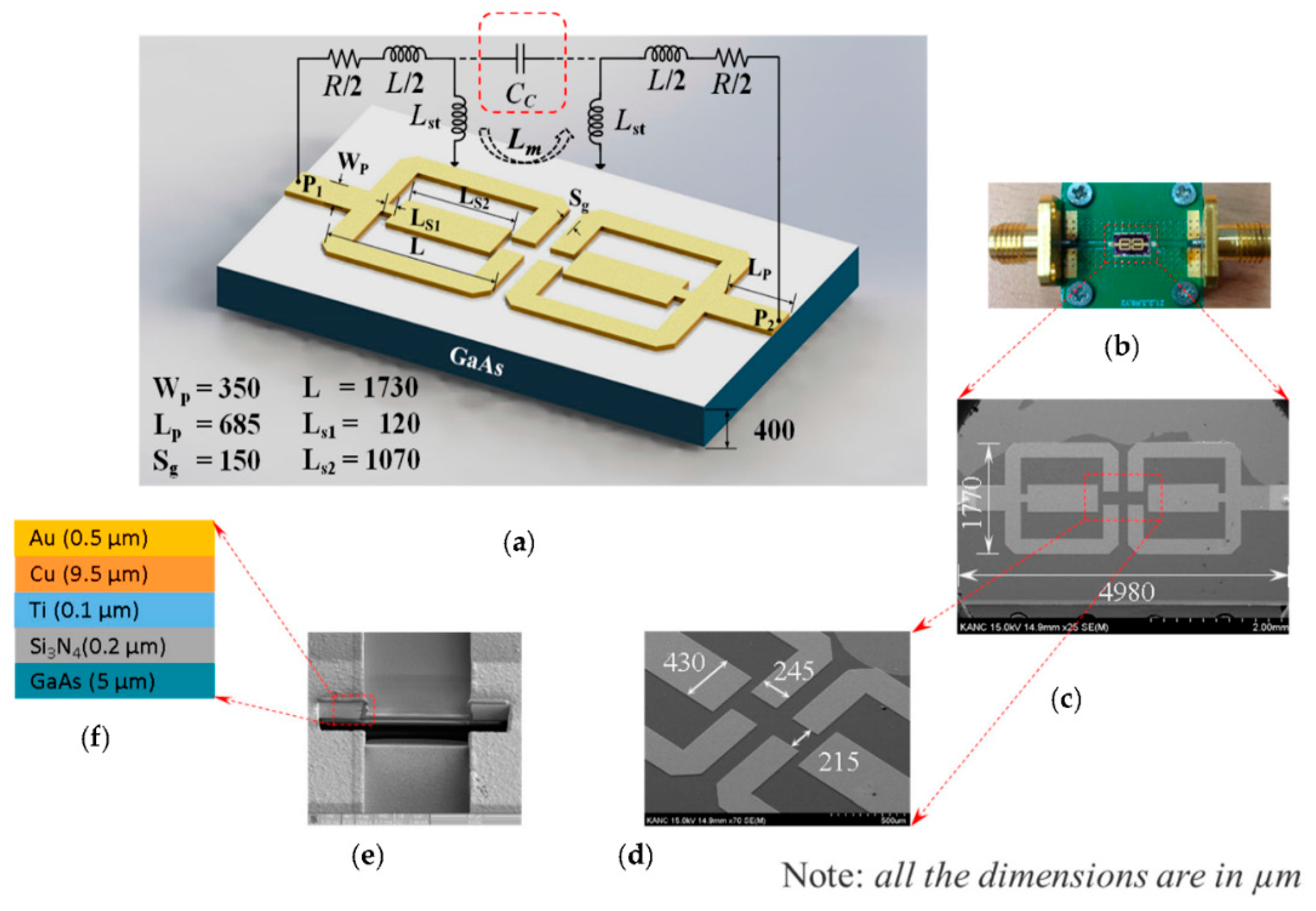
2.1. Biochip Structure, Fabrication, and Sensing Region Modeling
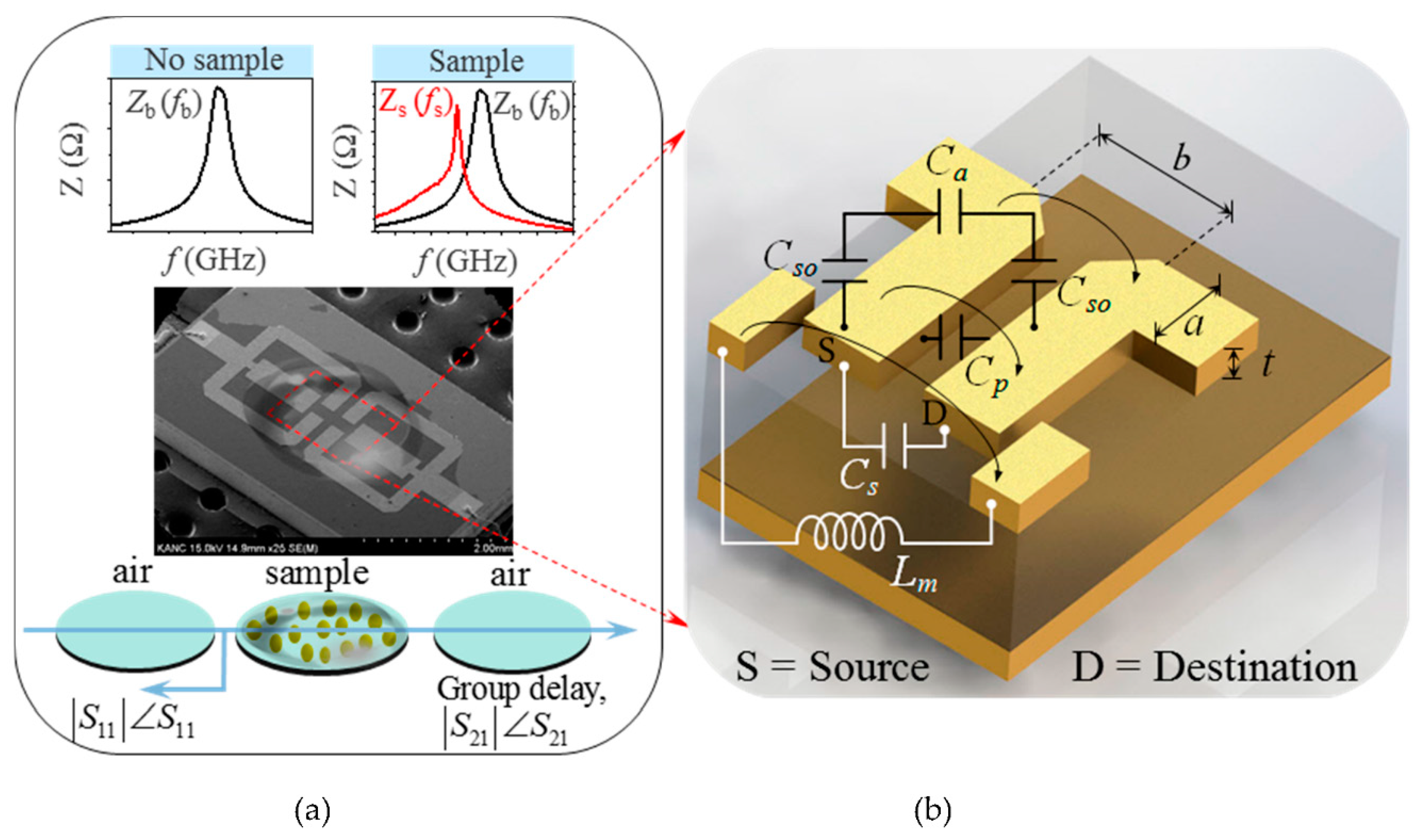
2.2. Modeling of Electromagnetically Coupled Sensing Region
3. Results and Discussion
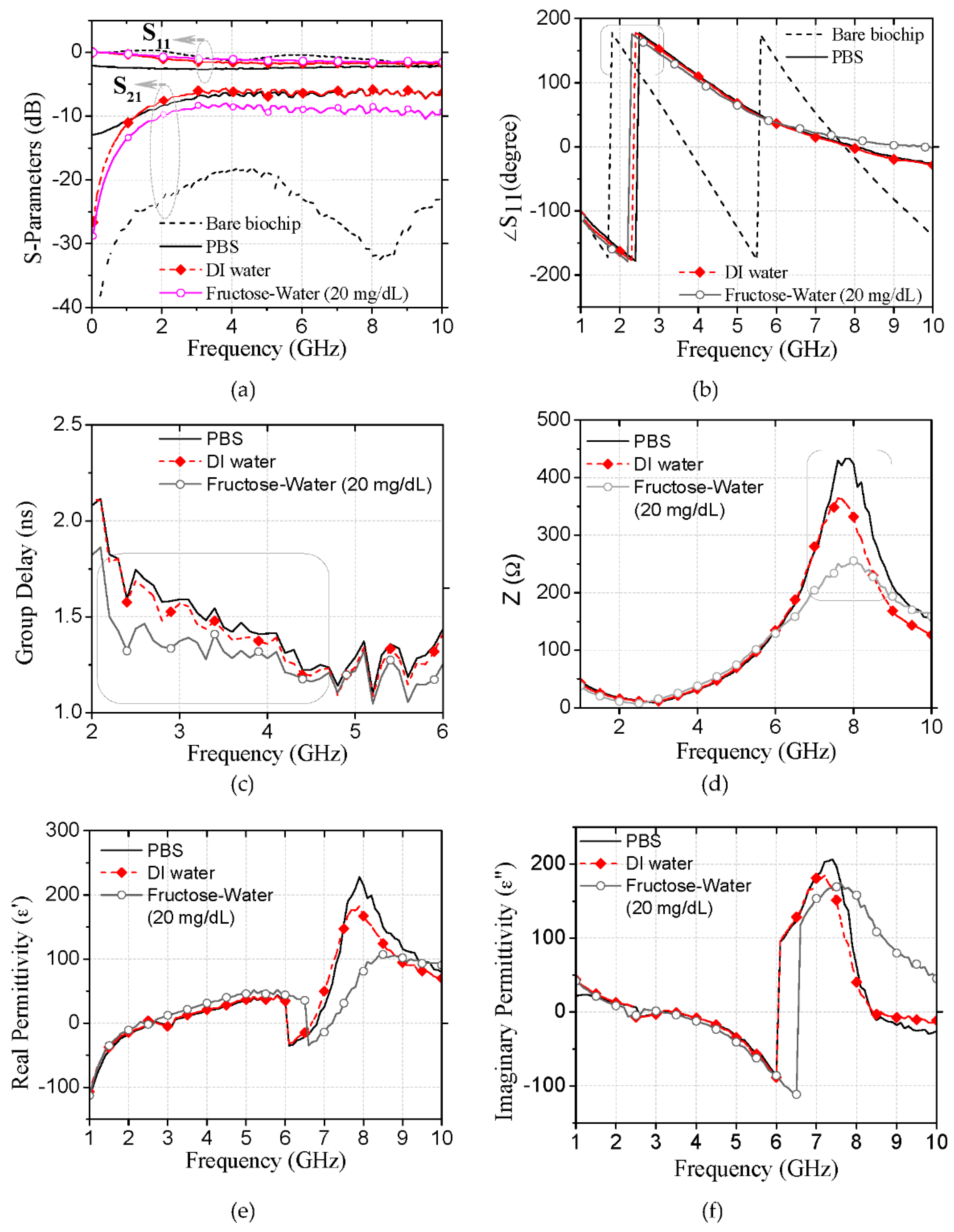
3.1. Biochip Characterization for Aqueous Solutions
3.2. Glucose Probing Using Characteristic Impedance at Its Resonances
3.3. Biochip Detection Accuracy against Interference of Fructose
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.Y.; du Puch, C.B.M.D.; Dalmay, C.; Lacroix, A.; Landoulsi, A.; Leroy, J.; Mélin, C.; Lalloué, F. Discrimination of colorectal cancer cell lines using microwave biosensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 216, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Yoo, K.H.; Yook, J.G. DNA sensing using split-ring resonator alone at microwave regime. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 014908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boybay, M.S.; Ramahi, O.M. Material characterization using complementary split-ring resonators. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmay, C.; Pothier, A.; Cheray, M.; Lalloue, F.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Blondy, P. Label-free RF biosensors for human cell dielectric spectroscopy. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2009, 1, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Adhikari, K.K.; Dhakal, R.; Chuluunbaatar, Z.; Wang, C.; Kim, E.S. Rapid, sensitive, and reusable detection of glucose by a robust radiofrequency integrated passive device biosensor chip. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chretiennot, T.; Dubuc, D.; Grenier, K. A microwave and microfluidic planar resonator for efficient and accurate complex permittivity characterization of aqueous solutions. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2013, 61, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Babajanyan, A.; Hovsepyan, A.; Lee, K.; Friedman, B. Microwave dielectric resonator biosensor for aqueous glucose solution. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 79, 086107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, W.; Schulze, K.D. Zur anwendung der transformations-impedanzspektrometrie. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1975, 65, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.; Kaatze, U. Molecular dynamics of carbohydrate aqueous solutions. Dielectric relaxation as afunction of glucose and fructose concentration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromidis, M.I. Impedimetric biosensors and immunosensors. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2007, 8, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Suni, I.I.; Bever, C.S.; Hammock, B.D. Impedance biosensors applications to sustainability and remaining technical challenges. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Kim, N.Y. A high performance compact Wilkinson power divider using GaAs-based optimized integrated passive device fabrication process for LTE application. Solid State Electron. 2015, 103, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, N.Y. High-performance integrated passive technology by advanced SI-GaAs-based fabrication for RF and microwave applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2009, 52, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakat, S.; Bors, K.A.; Huang, T.Y.; Michel, A.; Zanghi, E.; Gmachl, C.F. In vitro measurements of physiological glucose concentrations in biological fluids using mid-infrared light. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.K.; Kim, N.Y. Ultrahigh-sensitivity mediator-free biosensor based on a microfabricated microwave resonator for the detection of micromolar glucose concentrations. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 2016, 64, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Drewniak, J.L.; Pommerenke, D.J.; Koledintseva, M.Y.; Dubroff, R.E.; Cheng, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Q.B.; Orlandi, A. Causal RLGC(f) models for transmission lines from measured S-parameters. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. C 2010, 52, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.W. Measurement of the diffusion coefficients of fluorescence beads and quantum dots by using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2011, 59, 3177–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Cinar, S.; Steenhuyse, L.V.; Akinc, M. Elucidation of viscosity reduction mechanism of nano alumina suspensions with fructose addition by DSC. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Hsiang, T.Y. Extraction of subterahertz transmission-line parameters of coplanar waveguides. In Proceedings of Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2007 (PIERS 2007), Beijing, China, 26–30 March 2007; pp. 2182–2186.
- Smith, D.R.; Schultz, S.; Marko, P.; Soukoulis, C.M. Determination of effective permittivity and permeability of metamaterials from reflection and transmission coefficients. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 195104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Akbar, Z.; Saeed, M.A.; Alam, S.; Khan, M.J. Double negative metamaterial of copper split ring and graphite materials. Int. J. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Dekker, M. Electroanalytical Chemistry: A Series of Advances; Marcel Dekker Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Mehrjardi, A.H.; Zamiri, N. A novel method for glucose determination based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy using glucose oxidase self-assembled biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2006, 69, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Huang, F.Y.; Chen, J.; Mo, T.; Li, S.X.; Wang, F.; Feng, S.Q.; Li, Y.J. A high performance enzyme-free glucose sensor based on the graphene-CuO nanocomposites. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 6332–6342. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, T.L.; Eusebio, F.A.; Cookb, C.B.; LaBelle, J.T. The promise of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as novel technology for the management of patients with diabetes mellitus. Analyst 2012, 137, 4179–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. A glucose biosensor using methyl viologen redox mediator on carbon film electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 532, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.W.; Li, L.; Wu, L.J.; Gong, J.M.; Zeng, X.P. Glucose biosensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with polythionine and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.X.; Liang, G.H.; Li, H.X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Kong, J.L. A novel nonenzymatic sensor based on CuO nanoneedle/graphene/carbon nanofiber modified electrode for probing glucose in saliva. Talanta 2013, 116, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.C.; Li, P.H.; Xie, Q.J.; Xu, X.H.; Lei, L.H.; Chen, C.; Zou, C.; Deng, W.F.; Yao, S.Z. One-pot preparation of polymer–enzyme–metallic nanoparticle composite films for high-performance biosensing of glucose and galactose. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Roushani, M. Non-enzymatic glucose detection free of ascorbic acid interference using nickel powder and nafion sol–gel dispersed renewable carbon ceramic electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concentration * (mg·dL−1) | Magnitude of Impedance Peak (Ω) | ± RSD # (%) | Frequency of Impedance Peak (GHz) | ± RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare biochip | 562 | 0.00 | 3.72 | 0.00 |
| 100 | 295 | 3.66 | 3.54 | 0.61 |
| 125 | 345 | 4.21 | 3.51 | 0.60 |
| 150 | 391 | 4.35 | 3.46 | 0.14 |
| 175 | 438 | 1.66 | 3.42 | 0.50 |
| 200 | 503 | 4.37 | 3.37 | 0.16 |
| Sample * | Determined by Clinically Established Method (mg/dL) | Determined by Biosensor (mg/dL) ± RSD (%) | Supplemented Fructose (mg/dL) | ± RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 190 | 191.51 ± 1.89 | 0.2 | 191.51 ± 2.40 | 100.79 |
| 2 | 134 | 135.69 ± 3.28 | 0.2 | 135.69 ± 3.79 | 101.26 |
| 3 | 156 | 154.30 ± 2.54 | 0.2 | 154.30 ± 3.09 | 98.91 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adhikari, K.K.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, N.Y. Multiparameter Microwave Characterization and Probing of Ultralow Glucose Concentration Using a Microfabricated Biochip. Micromachines 2016, 7, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060093
Adhikari KK, Kim ES, Kim NY. Multiparameter Microwave Characterization and Probing of Ultralow Glucose Concentration Using a Microfabricated Biochip. Micromachines. 2016; 7(6):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060093
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdhikari, Kishor Kumar, Eun Seong Kim, and Nam Young Kim. 2016. "Multiparameter Microwave Characterization and Probing of Ultralow Glucose Concentration Using a Microfabricated Biochip" Micromachines 7, no. 6: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060093
APA StyleAdhikari, K. K., Kim, E. S., & Kim, N. Y. (2016). Multiparameter Microwave Characterization and Probing of Ultralow Glucose Concentration Using a Microfabricated Biochip. Micromachines, 7(6), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060093







